Abstract
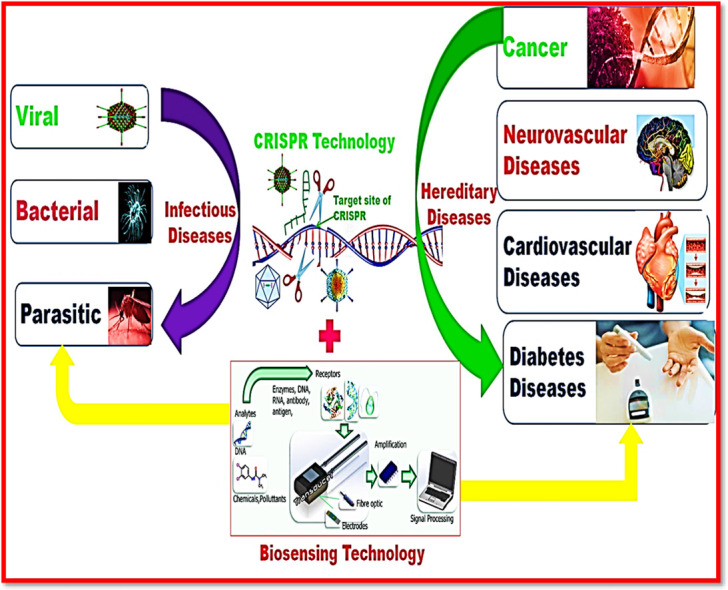
Infectious and hereditary diseases are the primary cause of human mortality globally. Applications of conventional techniques require significant improvement in sensitivity and specificity in therapeutics. However, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPRs) is an innovative genome editing technology which has provided a significant therapeutic tool exhibiting high sensitivity, fast and precise investigation of distinct pathogens in an epidemic. CRISPR technology has also facilitated the understanding of the biology and therapeutic mechanism of cancer and several other hereditary diseases. Researchers have used the CRISPR technology as a theranostic approach for a wide range of diseases causing pathogens including distinct bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites and genetic mutations as well. In this review article, besides various therapeutic applications of infectious and hereditary diseases we have also explained the structure and mechanism of CRISPR tools and role of CRISPR integrated biosensing technology in provoking diagnostic applications.
Abbreviations: CRISPRs, Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic Repeats; WHO, World Health Organization; MERSCoV, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus; SNPs, Single nucleotide polymorphisms; Cas, CRISPR-associated; crRNAs, CRISPR RNAs; IHF, Integrated host factor; sgRNAs, Single-guide RNAs; gRNAs, Guide RNAs; TALENs, Transcription activator-like effector nucleases; NHEJ, Nonhomologous end joining; HDR, Homology-directed repair; dCas9, Deactivated Cas9; NDM-1, New Delhi metallo β-lactamase 1; FISH, Fluorescent in situ hybridization; RPA, Recombinase polymerase amplification; RT, Reverse transcription; DETECTR, DNA endonuclease-targeted CRISPR trans reporter; HPV16, Human papillomavirus 16; HUDSON, Heating unextracted diagnostic samples to obliterate nucleases; HIV, Human immunodeficiency virus; HBV, Hepatitis B virus; EHEC, Enterohemorrhagic E. coli; PCRs, Polymerase chain reactions; LbCas12a, Lachnospiraceae bacterium ND2006 Cas12a; FnCas12a, Francisella tularensis Cas12a; AAV, Adeno-associated virus; HCV, Hepatitis C virus; CAD, Coronary artery disease; PAD, Peripheral artery disease; iPSC, Pluripotent stem cell; ApoE, Apolipoprotein E; LDLR, Low-density lipoprotein receptor; DM, Diabetes mellitus; PAX4, Paired-homeodomain transcription factor 4; IAPP, Islet amyloid polypeptide; iPSCs, Integration-free induced pluripotent stem cells; RDT, Rapid diagnostic testing; SMR, Silicon microring resonator; ST, Scrub typhus; SFTS, Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome; gFET, graphene-based field-effect transistor; YNP, Yellowstone National Park; slmapk3, Mitogen-activated protein kinases 3; SAPK2, Stress/ABA-activated protein kinase 2; TEs, Transposable elements; MITEs, Miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements; RNAi, RNA interference; siRNA, Small interfering RNA
Key words: CRISPR technology, Biosensing technology, Infectious diseases, Cancer, Cardiovascular diseases
Graphical Abstract
CRISPR is an innovative genome editing technology for the diagnosis of several infectious diseases caused by distinct bacteria, fungi, parasitic and viruses. This genome manipulating technology has also provided tremendous therapeutics to various hereditary disorders including cardiac, diabetic, and neurological and cancer. Consequently, these diseases have caused serious threat to human life, necessitating their timely diagnosis and treatment. The issues of conventional techniques have been overcome by CRISPR technology as this technology has revolutionized the distinct therapeutic applications in diverse organisms by performing genome engineering by either loss or gain of functional genes.
Infectious diseases have remained a universal concern of the researchers due to annual high risk of diseases and increased death rate, with the persistent plausibility of threatening epidemics. There are several types of pathogens that have been classified under bacteria, fungi, viruses and parasites. These pathogens have caused severe illness to mankind. Therefore, it is essential to develop an effective therapeutic platform that must be rapid, sensitive, specific, and economic diagnosis of different types of diseases. In addition, the developed platform should be user friendly and instrument independent and show fast detection of pathogen in the initial stage of a disease.1 This desperate need has been reported in 2014-2016 at the time of pandemics caused by Ebola virus.2 In the year 2018, World Health Organization (WHO) has emphasized the urgent development of superior diagnostic technology for the pathogen transmission during outbreaks1. The detection priorities of viruses for pandemics have been found as Ebola, Zika, Marburg virus, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERSCoV) and several others.3
In addition to these infectious diseases, hereditary diseases are congenital and show peculiar phenotypic characters4. These diseases are consequent of genome alteration by inducing mutations by chemical, physical or biological agents such as viruses, bacteria or fungi5. Persons with hereditary diseases are not healthy physically/mentally or both.4 Conventionally, viral mediated transgene expression and RNA interference approaches have been employed for the treatment of these hereditary diseases.5 However, these approaches have shown drawbacks as viral mediated transgene expression increases the risk of inducing mutations while RNA interference cannot repress the gene expression completely. Therefore, CRISPR based therapeutics have aroused the interest of researchers as this technology facilitates the analysis of pathogenic DNA/RNA sequences of any microbes including viruses. The key feature of CRISPR technology in disease diagnosis and therapeutics is based on requirement of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).6 Moreover, this technology has also been used for the treatment of a number of genetic disorders like cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, sickle cell anemia (Knott and Doudna, 2018),7 β-Thalassemia, Huntington diseases, Parkinson’s diseases, phenylketonuria etc.4 Hence, in this review we have explained the various therapeutic applications of infectious and hereditary diseases along with structure and mechanism of CRISPR system and their impact on therapeutics.
Genesis of CRISPR based diagnosis
Japanese researchers have recognized a unique segment of recurring DNA sequences in the bacteria namely Escherichia coli genome7. Later these repeating DNA sequences were known as clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPRs).8 In the early stage of CRISPR technology invention only repeat sequences were the prime focus; however in the successive phases, the intervening sequences called “spacer” were significant constituent of CRISPR-Cas systems. These spacer sequences have been reported for defense mechanism of bacterial and phases because they were similar to nucleotide sequences of alien plasmid and bacteriophage.9 , 10 These spacer sequences have gained defensive significance in the 2007 outbreak. This outbreak was reported due to the retaining of bacteriophage-resistant strains that have spacer nucleic acid sequences which resemble the bacteriophage genetic material.11 Consequently, the integrated spacer segments and the adjoining CRISPR-associated (Cas) genes have been found significant in enhancing the immunity against bacteriophage. Hence, this pivotal study has established a new invention of distinct adaptive defense mechanism known as CRISPR-Cas systems in both bacteria and archaea.
What is the CRISPR-Cas system?
The basic principle of technology integrated with CRISPR-Cas system involves the genome editing and their regulation of physiological phenomenon of several different types of organisms and cells. CRISPR-Cas system exists in bacterial system as an adaptive immune strategy by which bacterial cell is capable of either eradicating the foreign genetic material or showing resistance to phage infection. As it is part of an adaptive immune system, it has memories so that if any newly or previously entered pathogen invades, bacterial cell can recognize to adapt or lyse their genetic sequences.12 , 13 During interference event of CRISPR-Cas system, endonuclease proteins such as spCas9 and Cpf1 are automated by functional cr-RNA that acts as guide RNA and reveals the detection of specific sequence of invading pathogen inside the cell.14 , 15 Thus, genome editing by CRISPR-Cas system has exhibited various benefits like being convenient, fast, facile, and not expensive, and having minimum risk of targeting than other tools like zinc finger nucleases and transcription activator-like effector nucleases.1 , 16 CRISPR technology has played a significant application in cancer therapeutics. Like cancer, a spectrum of genetic diseases including phenylketonuria, Huntington disease, Cockayne syndrome etc. has also been treated by CRISPR technology.17 This CRISPR system has also been employed for the detection of various pathogens. Herein we have discussed the detailed structure of CRISPR-Cas system.
Structure of CRISPR
Main constituents of CRISPR-Cas systems include CRISPR RNAs (crRNAs) and Cas proteins. The crRNAs show complementarity with the corresponding nucleic acid sequence. Therefore, binding of crRNA to specific genome sequence of invading pathogen results in degradation of target DNA/RNA sequence by Cas proteins.18 Moreover, base pairing of crRNA to complementary sequence helps the scientific community in predicting and designing of sequences that can bind and cleave desired sequences. In the CRISPR-Cas system Cas9 protein acts as a catalyst which is involved in binding of site-specific DNA and cleavage of pathogenic genetic material.19 , 12 Therefore, CRISPR-Cas technology has been found useful in demonstrations ranging from nucleic acid editing to molecular imaging. The CRISPR-Cas technology has also provided a platform for eukaryotes by providing effective knowledge of bacterial engineering.18
Components of CRISPR-Cas system
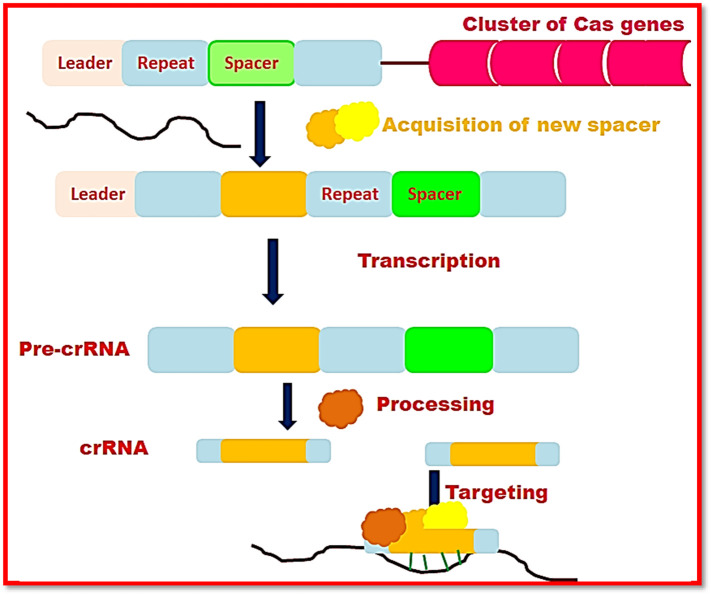
CRISPR-Cas system possesses two classes with six types and several subtypes. In Class 1 CRISPR-Cas systems three different types exist viz. I, III and IV. These types are involved in interference machinery in combination with multiple Cas proteins. On the other hand, chief components of class 2 include types II, V, and VI along with solitary Cas protein that participates in process of interference.18 Figure 1 shows the mechanism of structural components of CRISPR-Cas system. In the below section we have discussed the mechanism of CRISPR-Cas system:
Figure 1.
Diagrammatic illustration of mechanism of structural components of CRISPR-Cas system.
Mechanism of CRISPR-Cas system
CRISPR technology provides defense to bacteria and archaea against foreign genomes like plasmids or bacteriophages. The adaptive immune response imparted by CRISPR-Cas system involves three main steps including acquisition, expression, and interference.
-
(i)
Acquisition or adaptation
Acquisition reveals the formation of spacer from oligo sequence of foreign DNA that is found at the leading stretch of CRISPR locus. The remarkable defense property of CRISPR-Cas system is that it does not impart autoimmunity with bacterial own genome; however, its own CRISPR array degradation has been mediated by using protospacer-adjacent motif (PAM). PAM helps to distinguish bacterial nucleotide sequence from external invaded genomic sequence. Combination of subtype I-E of CRISPR system with Cas1–Cas2 composite helps in recognition of well-matched PAM sequence, cleavage of invaded genomic material, and then incorporation into array of CRISPR system by altering the length of protospacer. Integration of new spacer occurs in proximity with AT-rich leader segment of CRISPR-Cas genes. Subtype I-E system of CRISPR includes a free protein known as integrated host factor (IHF) that twists genomic sequence for binding of Cas1–Cas2 composite. Binding of this entire assembly acting as an integrase complex to the targeted genomic sequence that helps in identification of leader segment from array of CRISPR-Cas genes by correctly locating the spacer sequence. Subtype II-A system of CRISPR-Cas system has been involved in spacer acquisition that requires Csn2, proteins in conjugation with Cas1–Cas2 complex.20 In this sub-type, identification of leader sequence is independent of IHF; however, Cas1–Cas2 conjugate distinguishes the leader segment for the proper orientation of spacer.
-
(ii)
Expression into mature crRNA
Acquisition step is followed by expression where alternative repeating sequences and intervening sequences (spacers) are expressed into crRNAs. Now these crRNAs undergo further processing by Cas proteins and auxiliary factors. Production of mature crRNA starts at the time of transcription of precrRNA in the leader segment that exists before the array of CRISPR-Cas system. As a result, multiple segments with multiple repeat spacer units are produced. After that, these segments are sliced to form separate mature crRNAs and monitor Cas proteins to their alien nucleic acid sequence.18
Cas6 proteins exist in class 1, type I and III CRISP-Cas systems. These proteins are enzymatic in nature and cleave the repeat sections of pre-crRNA. This cleavage helps in production of mature functional crRNA. On the other hand, Cas5d plays similar function to Cas6 enzymes in subtype I-C system and subtype III-C and III-D CRISPR-Cas systems.18 It has been found that Cas6 attached with crRNA to form interference complex. Furthermore, in subtypes I-A and I-B systems, detachment of Cas6 led to separation of repeated sequence. Cas6 is found in the dimeric structure in type III systems that also detached in successive maturation stage. In type IV, the process of crRNA maturation is not clear.18
In class 2 systems, crRNA maturation has been accompanied by Cas proteins that participate in interference. However, use of non-Cas proteins has also been reported in few cases. Subtypes II-A and B of CRISPR-Cas systems involve attachment of Cas9 protein with crRNA–tracrRNA that gives signal to host protein i.e. RNase III for the cleavage of repeat sequence in pre-crRNA.21 Maturation of crRNA of type II and subtype V-B CRISPR systems has been accomplished by tracrRNA. Furthermore, Cas12 and Cas13 proteins are the chief components of type V and VI CRISPR-Cas systems. It has been found that Cas12 protein is involved in crRNA processing while Cas 13 protein is involved in the process of interference.18
-
(iii)
Interference
Interference machinery of CRISPR-Cas involves DNA versus RNA targeting and specific versus nonspecific nucleic acid cleavage. Consequently, CRISPR-Cas system has imparted several emerging applications. A ribonucleoprotein complex is composed of Cas proteins and specific crRNA attachment after that cleavage of genomic segments corresponding to spacer sequence of the crRNA.18 The mechanism of cleavage of targeted invaded sequence has been described in the given section below:
-
(i)
Mechanism of class 1 interference machinery
This class is also known as CRISPR-associated complex for antiviral defense (Cascade).22 It involves conjugated protein complexes and Cascade components including subtypes I-A to I-F and I-U of type, PAM to recognize targeted invaded sequence followed by binding of crRNA to Cas6 or Cas5, a Cas7 backbone. Furthermore, R-loop provides the consistency to entire assembly and then Cas3 cleave the target nucleic acid sequence. In subtype I-E the inference machinery is composed of Cas5 and Cas6 that bind to crRNA repeats, a complex involving 6 proteins of Cas7 to form backbone and Cas8 protein helps to identify PAM. This entire assembly starts the unwinding of invaded nucleic acid sequence; followed by binding of two Cas11 subunits to provide stability and forms R loop23. Furthermore, interference complexes of type III include subtype III A and III B that are also known as Csm and Cmr respectively. This complex also contains Cas5, a protein from Cas7 family to form the backbone, large subunit of Cas10 and small subunit of Cas11. In type III interference does not necessarily require PAM identification by all systems. However, this system contains tools for discriminating the self from non-self. Recruitment of entire interference protein complexes including Cas7 cut the ssRNA followed by cleavage of targeted invaded genome sequence by Cas10.24 , 25 Moreover, cleavage with Cas10 in subtype III A Csm conjugate generates the production of cyclic adenylates a 2° messenger that facilitates the random cleavage by Csm6. The mechanism of interference by subtype III-C and III-D and type IV is not well understood.18
-
(ii)
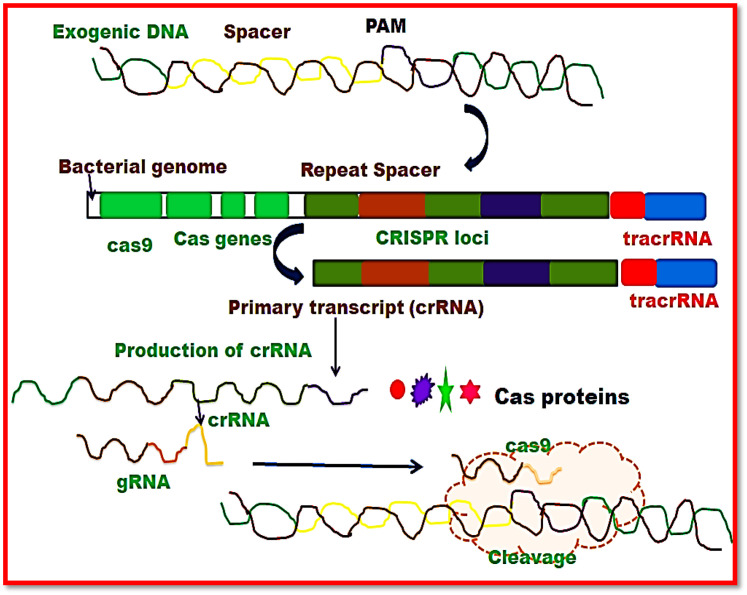
Mechanism of class 2 interference machinery
In contrast to Class 1, Class 2 interference system contains single nuclease instead of protein complex. Type II system of interference mechanism includes bilobed Cas9 nuclease, tracrRNA and crRNA.26 Binding of tracrRNA to corresponding nucleic acid sequence of pre-crRNA repeating segment recruits the attachment of Cas9 protein.27 PAM segment is recognized by Cas9 and then crRNA-tracrRNA conjugate interacts with cDNA to generate double stranded cleaved targeted nucleic acid sequence with blunt ends.28 Interference machinery of class 2 system also composed of subtypes i.e. subtypes II-A, II-B, and II-C. These subtypes have been categorized on the basis of size and variation in sequence of Cas9 gene. In type V of CRISPR system, Cas12 is the chief protein that further includes subtypes V-A, B and C. These subtypes contain cleavage proteins viz. 12a, 12b, and 12c, respectively.29 This system also contains trace RNA that activates 12b protein but not 12a while 12c protein helps to promote further characterization.29 crRNA-Cas12 conjugate binds at PAM site followed by cleavage of targeted dsDNA with sticky ends30. On the other hand, type VI of CRISPR system has Cas13 protein but does not need tracrRNA. Like type III CRISPR system, this system also targets ssRNA. The protospacer flanking sequence (PFS) is recognized by crRNA-Cas13 complex31 followed by cleavage of both target and nonspecific RNA by Cas13.32
Recombinant DNA technology integrated with CRISPR-Cas9 system
Researchers have revealed the application of CRISPR-Cas9 system in multiple sectors of biotechnology in elementary sciences like agriculture, energy production, pharmaceutics, and genetic engineering33. Intrinsic crRNA-tracrRNA conjugates of type II CRISPR systems have been manipulated in the form of chimeric single-guide RNAs (sgRNAs) that include combination of fusing components.12 The application of CRISPR-Cas9 system in gene editing and high throughput screening of genotype and phenotype associations in several cell lines is based on the development of guide RNAs (gRNAs) that requires use of a unit fusion molecule i.e. sgRNA or specific crRNA and tracrRNA constituents.
In the inventory phase CRISPR-Cas9 system was extensively used for genome editing. Gene modification using transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs) and zinc finger nucleases is based on protein engineering. On the other hand, cleavage of targeted dsDNA sequence using CRISPR-Cas9 depends on sgRNAs mediated Cas proteins complex formation.34 After cleavage, dsDNA can be repaired by host-mediated repair processes including nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) or homology-directed repair (HDR). The use of NHEJ is limited because it is less reliable and responsible for causing frameshift mutations and consequently damaging of protein function34. Hence, genome modification by CRISPR technology uses HDR mechanism because it does not cause mutations and produces reliable results of genetic alteration.34
Impact of libraries constructed with sgRNA in the evaluation of genetic and phenotypic interactions
Researchers have understood the function of any gene by inducing genetic alterations induced by CRISPR technology. Researchers have constructed CRISPR libraries that are composed of large number of plasmids with many sgRNAs targeting genes of interest. Mutant cells can be produced in large numbers using CRISPR libraries35 which can be screened by +ve and –ve selection for a particular genotype and phenotype. Thus, aforesaid technology has been used for several distinct human and nonhuman cell lines.36 , 37
Impact of deactivated Cas9 for the regulation of gene transcription
It has been reported that deactivated Cas9 (dCas9) has also been used for the regulation of transcription. On the basis of gene expression, CRISPR can be classified into CRISPR activation and CRISPR interference. In activation state, expression of a gene is enhanced by binding of dCas9 and VP6 transcription activator complex at the promoter site and in interference gene expression is repressed due to itself binding of dCas9 with Krueppel-associated box domain, acting as a transcriptional repressor in the promoter region. This binding causes steric hindrance in the promoter region.35
Impact of CRISPR technology for infectious diseases
Advancement of CRISPR-Cas systems has opened wide applications for the treatment of several infectious ailments. The technology has provided effective diagnostic tools that help in understanding the interaction between host and pathogen. As a result, CRISPR based technology has been proven in accurate detection, prevention and efficient cure of infectious disorders. In the section below we have discussed the interaction between host and pathogen which facilitates the development of improved diagnostic tools:
CRISPR technology in revealing host–pathogen interactions
For the development of better medical caution and coherent approaches for efficient therapeutics, it is a requisite to know the diseases progression to human beings by distinct pathogenic microbes like bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasite. Genome manipulation of pathogenic microorganisms by CRISPR-Cas9 system has provided the basis to understand the molecular mechanism of pathogenesis by identifying specific relationship between gene and proteins.38 Winter and co-workers (2016) deciphered the mechanism of α-hemolysin a virulence factor secreted by Staphylococcus aureus for causing cell toxicity.39 They reported three genes namely SYS1, ARFRP1, and TSPAN14 that are involved in regulation of post transcription processing of a disintegrin and metalloproteinase ADAM-10.
Ma et al (2015) by using CRISPR sgRNA library, investigated seven genes viz. EMC2, EMC3, SEL1L, DERL2, UBE2G2, UBE2J1, and HRD1 of host cells that are responsible for neuronal cell death40 because these genes are target for West Nile Virus. They found that inactivation of these genes led to prevention of neuronal cell death because these genes participate in endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation process. This study helped to understand the mechanism of pathogenicity caused by WNV. Nodvig and co-workers (2015) have reported the genome manipulation of Streptococcus pyogenes using Cas9 system by inserting nuclear localization sequence of 3’ Simian virus41. Consequently, they transformed the promoter of sgRNA that was more efficient for fungi41. Researchers have induced the RNA-directed mutations in the alleles of Aspergillus species using CRISPR-Cas9 system to investigate the fungal physiology. Furthermore, genomes of two parasites such as Toxoplasma gondii and Trypanosoma cruzi known for causing toxoplasmosis and Chagas have also been modified by CRISPR-Cas9 technology.42 , 43
Diagnostic approaches integrated with CRISPR technology for infectious diseases
It is advantageous to develop fast and accurate diagnostic tests that assist in detection of pathogens in primary stage. Consequently, treatment of infectious diseases has offered several benefits including better clinical caution, timely control of infection and prevention of disease spread. An ideal rapid diagnostic test has exhibited several unique characteristics like they are more sensitive, precise, simple, transportable and economic. Owing to these characteristics they will be employed not only in different medical strategies but also in areas where resources are limited. Therefore, CRISPR-Cas technology has been proven significant in quick and specific diagnosis of infective diseases.
Applications of CRISPR-Cas9 system in diagnostics
Scientific community has shown interest in CRISPR-Cas9 technology in development of diagnostics for several infections. Pardee and co-workers (2016) employed the CRISPR-Cas9 system in combination with nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (NASBA), an isothermal amplification technique for accurate distinction of strains of Zika virus in a macaque model.44 Bacterial antibiotic resistance genes have been identified by Muller and co-workers (2016) by integrating CRISPR-Cas9 system with optical DNA.45 This was achieved by binding of guide RNA (gRNA)-Cas9 complex which cuts precise DNA sequences of plasmids composed of resistance genes and a fluorescent dye. It was found that netropsin, an antibiotic, binds at AT-rich site of DNA that causes fluorescence. This demonstration revealed a distinction between plasmids with β-lactamases, cefotaxime 15 (CTX-M-15) and CTX-M-14 and carbapenemases with Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC) and New Delhi metallo β-lactamase 1 (NDM-1). Therefore incorporation of several crRNAs has facilitated the investigation of various antibiotic resistant genes in a given assay.
Moreover, Guk et al (2017) have investigated the methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) by combining CRISPR-Cas9 system and DNA fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) technique46. In this approach sgRNA-dCas9 conjugate integrated with SYBR green I fluorescence emitting probe that helps in identification of mecA nucleotide sequence of MRSA.
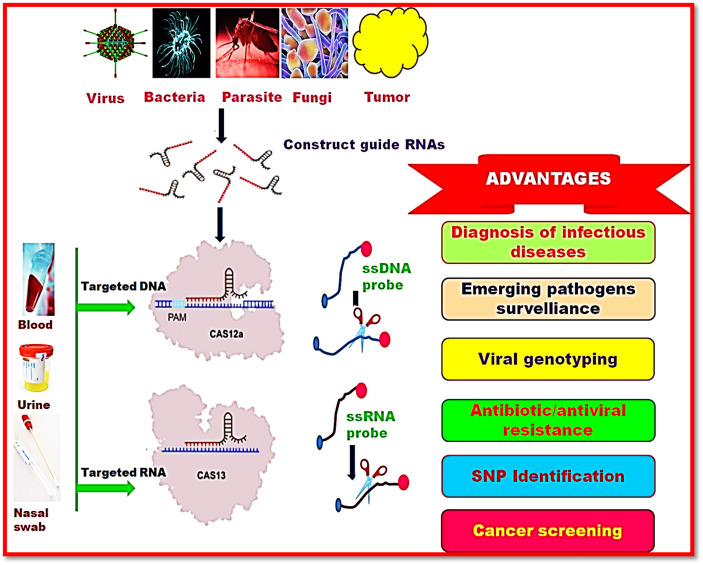
Diagnostic applications of CRISPR-Cas12 and CRISPR-Cas13 system
Moreover, disease diagnostic applications based on CRISPR technology have also been linked with collateral cleavage using Cas12 and Cas13 nucleases. This novel technology has exhibited unique sensitivity, specificity, enzymatic reporter unlocking (SHERLOCK), coupling with isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) or reverse transcription (RT)-RPA with Cas13a cleavage.6 In this technology, a crRNA-Cas13a complex attached with target DNA sequence followed by precise cleavage in the targeted nucleotide sequence. Binding of crRNA-Cas13a complex at the target site leads to cleavage of fluorescent reporter which was attached with non-target RNA. Thus, emission of fluorescence gives the signal of pathogen detection.
Gootenberg et al (2017) have reported the distinction of similar strains of Zika and dengue viruses, E. coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and K. pneumonia cells containing diverse resistance genes including KPC and NDM through SHERLOCK system. Moreover, DNA endonuclease-targeted CRISPR trans reporter (DETECTR) technique has been used for indiscriminate cleavage of ssDNA that can be identified by emitting fluorescence.6 DETECTR exhibited both isothermal RPA and Cas12a enzymatic activity.47 Chen et al (2018) have also differentiated the human papillomavirus 16 (HPV16) and HPV18 in crude DNA extracts from cultured human cells and from clinical samples by using DETECTR.47
Gootenberg et al (2018) have developed SHERLOCKv2 and this system has benefits as it was composed of a single assay multiplexing with orthogonal CRISPR enzymes, quantitative and sensitive investigation of targeted pathogenic nucleic acid sequence.48 This system can detect 1-4 targets by coupling several pre-screened Cas13 nucleases and a Cas12 nuclease with nucleic acid-fluorescent reporter complexes. These complexes give fluorescence at distinct wavelengths. Quantitative investigation of pathogen was carried out by concentration of optimized RPA primers while sensitivity was accessed by inserting Csm6 that elevates the cleavage of -target ssRNA combined with a fluorescent reporter. On the other hand, portability of the assay can be improved by using streptavidin coated paper test strip in place of fluorescence readouts. One more advanced technique based on CRISPR was developed by Myhrvold and co-workers.49 They use SHERLOCK and heating unextracted diagnostic samples to obliterate nucleases (HUDSON). This technique avoids the necessity of DNA/RNA extraction and detects the pathogen directly from bodily fluids. This approach involves the chemicals reduction at elevated temperature which inactivates chief nucleases of body fluids. Consequently, due to lysis of viral entities nucleic acid released into body fluids.
Emerging therapeutic applications of CRISPR technology
In United States approximately, two million infections and about 23,000 mortality have been reported due to antibiotic-resistant bacteria.50 Furthermore, global human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) epidemic can take about 35 million lives in its inceptive period and the number of infected people is increasing day to day.3 Therefore, the main emphasis of CRISPR technology is on diagnosis and timely treatment of drug-resistant bacteria and persistent viral infections, including HIV and hepatitis B virus (HBV). In the given section we have explored the possible therapeutic applications of CRISPR-system:
Therapeutic applications of CRISPR technology in bacterial diseases
-
(i)
Application of CRISPR-Cas systems in targeting bacterial resistance
All bacteria are not necessary to exhibit CRISPR-Cas systems. Though there are proofs to reveal CRISPR-Cas systems inhibit the adaptation of genetic sequences which provide antibiotic resistance. So it shows, due to therapeutic defense provided by bacteria itself against antibiotic. For instance, Aydin et al (2017) have demonstrated that E. coli has shown susceptibility antibiotic resistance due to existence of type I-F CRISPR system.51 On the other hand, Price et al (2016) have shown that Enterococcus faecalis strains have acquired resistance by conjugation due to deletion of Cas9 gene52. It has been reported that in an in vivo model, transfer of plasmid was found to be more efficient in E. faecalis strains comprised of mutated CRISPR-Cas system than wild strains.52 Figure 2 depicts the bacterial therapeutic applications of CRISPR-Cas system.
Figure 2.
Bacterial therapeutic applications of CRISPR-Cas system.
Recently, researchers have been facing serious issues of resistance due to frequent use of broad-spectrum antibiotic for the treatment of human bacterial infection because it has been documented that increased use of broad-spectrum antibiotics can inhibit the function of CRISPR-Cas system, thereby raising the prevalence of antibiotic resistance in vitro. For example, Lin et al (2016) have demonstrated that K. pneumonia have shown resistance against broad-spectrum antibiotic imipenem because of inactivation of CRISPR-Cas system.53 Therefore, these apprehensions reveal the proper physiology of bacteria on external stimuli and complicated relationship between clinical interferences and subsequent microbial reactions. Hence, improved knowledge of mechanism of CRISPR-Cas systems from inceptive stage in varied environments will help in rational use of aforesaid technology.
-
(ii)
CRISPR technology in targeting pathogenic and drug-resistant bacteria
CRISPR technology can be employed for developing selective and titrable antimicrobials for the elimination of pathogenic bacteria. Gomaa and co-workers (2014) have demonstrated the multiplication of E. coli and Salmonella enterica in pure and mixed culture tests by using subtype I-E of CRISPR-Cas system.54 Citorik and co-workers (2014) have used the application of phagemid mediated delivery of RNA-guided Cas9 for the destruction of eae gene of enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) that synthesizes pathogenic component to facilitate pathogen attachment with the epithelial cells of host organism.55 Yosef et al (2015) have reported the elimination of resistant element without harming the host bacteria by inserting subtype I-E CRISPR-Cas system using temperate phages.56 Using this approach, plasmids containing NDM-1 and CTM-X-15 were eliminated and provided defense against lytic phases. Therefore, drug-resistant bacteria can be eliminated and number of antibiotic-sensitive bacteria increased using lytic phages.
Bikard et al (2014) have also demonstrated the elimination of only virulent S. aureus strains carrying the mecA methicillin resistance gene by inserting RNA-guided Cas9 using phagemid.57 These aforesaid reports reveal that CRISPR-Cas systems could be employed therapeutically to cure acute infections by destroying precise bacteria, segregating patients having resistant microbes, or reforming the human microbiome which is useful for mankind.
-
(iii)
CRISPR technology coupled with conventional techniques for the diagnosis of bacterial diseases
Fabre et al (2014) have employed conventional multiplexed PCR for the investigation and differentiation of Salmonella enterica serotype typhi and paratyphi A using CRISPR technology in a mixed culture isolates.58 They also used EVA Green based real time-PCR for the identification and differentiation of above said Salmonella serotypes. They also reported that these CRISPR integrated PCRs were specific, stable and sensitive. Koskela and co-workers have investigated CRISPR locus sequences of 335 Yersinia pseudotuberculosis for the designing of spacer sequences database.59 By using this database they analyzed the spacer sequences of related strain of Yersinia i.e. Y. pestis.
Li and co-workers (2018) have revealed the diagnostic application of CRISPR based SHERLOCK for the sensitive and specific detection of a number of bacteria namely Lachnospiraceae bacterium ND2006 Cas12a (LbCas12a), Oribacterium sp. NK2B42 Cas12a (OsCas12a), Lachnospiraceae bacterium NC2008 Cas12a (Lb5Cas12a) and Francisella tularensis Cas12a (FnCas12a).60 Transcriptional suppression of Mycobacterium tuberculosis has been achieved by CRISPR interference.61 , 62 The repression of bacterial transcription was due to inhibition of vital gene expression which inactivates Cas9 protein with RNAs CRISPR. As a result, researchers have reported this system for treating the bacteria in multidrug resistant conditions.63
Therapeutic applications of CRISPR technology for targeting persistent viral infection
The novel applications of CRISPR-Cas system have also been employed for the genetic editing of viral genome including Zika, Ebola and several other viruses also. Viruses cause infection either incorporating their genetic material into human chromosomal DNA or in the form episomes inside host body. However, CRISPR technology has provided a therapeutic platform for the cure of viral chronic infections in vitro as well as in vivo. Strich and Chertow (2019) have reported that HIV can be eliminated in vitro by using CRISPR based applications.18 Hu et al (2014) have reported the prevention of de novo HIV-1 infection in TZM-bI cells containing a gRNA-Cas construct which targets long terminal repeat (LTR) sequences of HIV.64 Similarly, scientists have targeted the HIV gag and env genes for destroying HIV proviral DNA from mixture of cell lines using CRISPR technology.65 Yin et al (2017) have investigated the neural progenitor cells for the removal of HIV proviral DNA by incorporating several sgRNAs and S. aureus Cas9 through adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector.66 Bella and co-workers (2018) have applied CRISPR technology using lentivirus vector for the elimination of HIV provirus DNA of diseased human peripheral blood mononuclear cells.67 Similar approach of CRISPR technology has been employed for the prevention of herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) infections. Moreover, van Diemen and co-workers (2016) have investigated the Vero cells for preventing the HSV-1 replication using gRNAs.68
Hou et al (2020) have edited the genome of novel coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) using CRISPR-Cas technology.69 They compared this technology with existing metagenomic sequencing and RT-PCR techniques and reported the sensitive, quick detection of COVID-19 with minimum use of instrumentation by CRISPR-Cas system. One more report related to COVID-19 which causes pneumonia has been documented by Ai et al.70 They also reported the detection of DNA sequence of COVID-19 by coupling CRISPR technology with real-time RT-PCR and metagenomic next-generation sequencing. The detection of COVID-19 was found to be selective and rapid.
Myhrvold and co-workers (2018) documented the diagnosis of viruses from body fluids using CRISPR technology.49 Doudna et al have reported the diagnostic application of enzyme Cas12a to cleave targeted DNA of HPV. They found improved signal generation capacity of Cas12a that helps in quick and accurate point-of-care DNA analysis.50 The applications of CRISPR/Cas 9 system have been employed in hepatitis B virus (HBV) investigation62 , 71, 72, 73 as this system inhibits the process of HBV replication by suppressing the gene expression of the viral multiplication. Furthermore, it has also found that it also disrupts the circularization of viral DNA. It has been documented that approximately 110-180 million people were infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV).74 Among them about 80% were having chronic infection of HCV75. A group of researchers has evaluated the therapeutic significance of CRISPR/Cas9 system for the analysis of chronic infection caused by HCV.77 Ven Diemen and co-workers (2016) reported the CRISPR/Cas9 system as an efficient prophylactic and diagnostic tool for the suppressing herpes simplex virus (HSV) replication.68
Therapeutic applications of CRISPR technology for the diagnosis of parasitic diseases
Sollelis co-workers (2015) have manipulated the genome of Leishmania by using CRISPR/Cas9 system and reported that Cas9 act as an effective therapeutic tool for the Leishmania parasite.76 Zamanian and Andersen, (2016) have reported genome manipulation of Caenorhabditis elegans by using CRISPR/Cas9.77 They have also revealed that CRISPR/Cas9 system can be used for the engineering of gene drives which target the infection caused by mosquito-borne parasites like Plasmodium falciparum and Anopheles Gambiae and filarial nematodes such as Strongyloides spp., Ascaris suum, Brugia malayi, and Haemonchus contortus. Costa and co-workers (2018) have demonstrated the therapeutic application of CRISPR/Cas9 system by editing genome of Trypanosoma cruzi a causal organism of Chagas disease.78 Previously, there was no conventional therapeutics for the efficient treatment of this disease. Therefore, CRISPR-Cas system provided a platform for the diagnosis of T. cruzi. Using this technology, researchers firstly generated the T. cruzi strain which expressed a fusion protein containing red-shifted luciferase and green fluorescent protein domain. Now, this strain was further combined with a T7 RNA polymerase/CRISPR/Cas9 system to understand the mechanism of pathogenesis by editing genome of T. cruzi.
Apicomplexan parasites have been reported for causing malaria in human and toxoplasmosis in livestock. Sidik et al (2016) have screened the genetic and chemical manipulation of Toxoplasma gondii by using CRISPR/Cas9 system integrated with other tools.79 This approach was found to be effective for identifying typical conserved apicomplexan mechanisms in T. gondii. They also revealed the identification of some novel proteins required for causing malaria by P. falciparum parasite. Thus integrated CRISPR/Cas system has provided a basis for the efficient investigation of chromosomal interactions of T. gondii. Knuepfer et al (2017) have reported the efficient genome editing of Plasmodium falciparum, a causal organism of malaria by designing a toolkit based on CRISPR/Cas9 system.80 They achieved the genome editing by using dimerizable Cre-recombinase (DiCre) to remove the loxP-flanked DNA sequences. Medeiros et al (2017) have also manipulated the genome of Trypanosoma cruzi, Trypanosoma brucei and Leishmania which cause Chagas disease, African sleeping sickness and leishmaniasis, respectively.81 Manipulation of genomes of these above parasites was carried out by CRISPR/Cas9 system. They reported that therapeutic approach used for these parasites was easy, quick and independent of cloning and markers. Lander et al (2015) have silenced the expression of GP72, PFR 1 and PFR 2 genes which are required for the motility of Trypanosoma cruzi by using CRISPR/Cas9 system.82 Figure 3 depicts the diagnosis of infectious diseases using CRISPR-Cas system.
Figure 3.
CRISPR based diagnostic significance for infectious diseases.
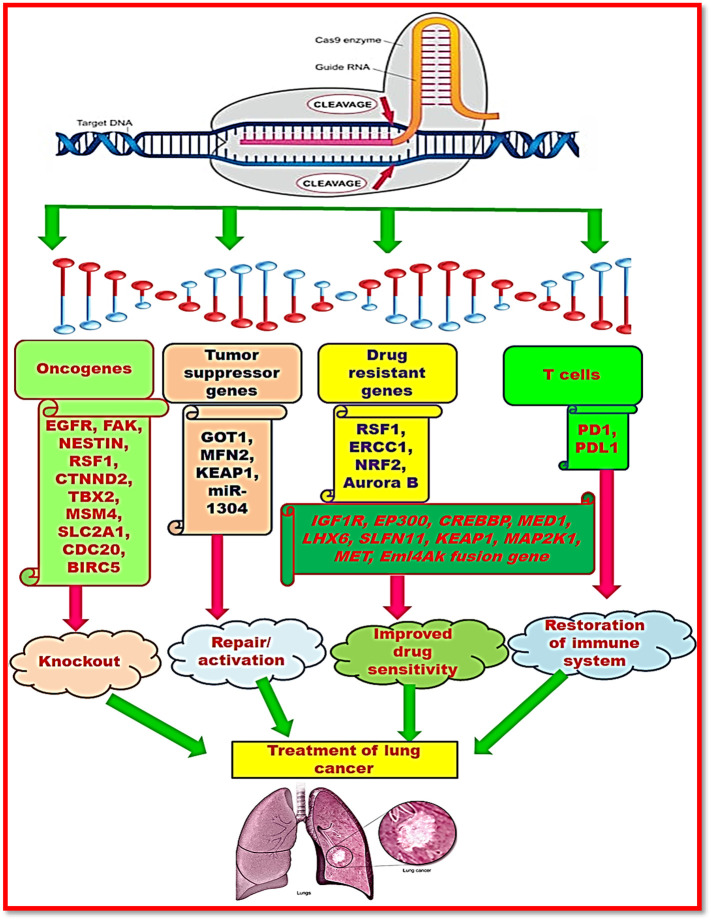
Therapeutic applications of CRISPR technology in cancer treatment
Though, researchers have gained progress to some extent in the cancer treatment, mortality caused by cancer is still high. Therefore, it is urgent need to develop some efficient therapeutics for cancer. Presently, recent developments are focusing on gene editing by CRISPR/Cas9 system that exhibited vast prospective in production of cancer therapeutics.83 CRISPR/Cas9 system has been employed for cancer therapeutics by regulating gene expression. Hart and co-workers (2015) have constructed a CRISPR/Cas9 gRNA library. This library was found to be significant in evaluation of fitness of human cell lines.84 They also studied the genome complexity by oncogenes mediated genetic alterations. Cancer is the resultant of continuous accumulation of genetic alteration in the somatic cells. Drost and co-workers (2018) reported the application of CRISPR/Cas9 system to demonstrate origin of mutational signatures in human stem cell organoids. Organoid is the technique for in vitro growth of man epithelial tissues starting from a single adult stem cell.85 In this study they deleted the mismatch repair MLH1 genes in colon organoids of man through CRISPR/Cas9 system. Mei et al (2020) have demonstrated the evolutionary relationships in breast cancer subtypes by developing a multiplexing CRISPR/dCas9 system.86 Various applications of CRISPR-Cas system in cancer treatment have been shown in Figure 4 .
Figure 4.
Therapeutic applications of CRISPR-Cas system in cancer.
Researchers have documented that gRNAs recruit the binding of catalytically inactive dCas9 at the target nucleotide sequence.87 Binding of dCas9 at transcriptional activation or inhibition region either enhances or suppresses the expression of targeted genes.88 Moreover, dCas9 is also significant in targeted epigenome editing by binding itself to histone modifiers and proteins regulating DNA methylation.89 It has been reported that a number of epigenetic factors have been found significant in distinct types of cancers including acute lymphoblastic leukemia and Ewing sarcoma for targeting epigenetic process that prevents cancer.90 Furthermore, it has also been documented that dCas9 targets the specific tumor markers in cancerous cells.91 Therefore, it necessitates the identification of specific genome altering factors that regulate the viability of cancer cells. Furthermore, better outcomes can be made possible by efficient transport of CRISPR tools into all cancer cells. Table 1 depicts the significant cancer therapeutic applications rendered by CRISPR/Cas9 system.
Table 1.
Application of CRISPR-Cas9 system in cancer therapeutics.
| Sr. no. | Name of cancer | Target cell/tissue/organ | Target gene | Application/advantage | Name of cell line | Strategy used | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Breast | - | BRCA1m and PARP1m | Screening of doxorubicin, gemcitabine and docetaxel chemotherapeutic drugs | MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-436 | Deletion of genes | 92 |
| 2. | Refractory | Mouse T cells | TRAC, TRBC and PDCD1 | Increased stability of T cells | HLA-A*0201 and | Gene editing by chromosomal translocation | 93 |
| 3. | Leukemia | Murine acute myeloid leukemia cells, U6-sgRNA-EFS-GFP or the U6-sgRNA-EFS-mCherry plasmids | Brd4, Smarca4, Eed, Suz12, and Rnf20 | Discovering therapeutic targets in cancer | HEK293T cells, MLL-AF9/NrasG12D acute myeloid leukemia , MSCV-hCas9-PGK-Puro and RPMI1640 | Genome editing | 94 |
| 4. | Colorectal adenocarcinoma | Chondrocytes of mice | MMP3 and CCN2/CTGF | Inhibition of metastatic tumor in vitro and in vivo | Chondrosarcoma-derived chondrocytic cell line HCS-2/8, MDA-MB-231 | Genome editing | 95 |
| 5. | Breast cancer | Breast cancer cells |
OCT4, KLF, MYC, SOX2 |
Study the phylogenetic relationships among breast cancer subtypes as stratified by cancer stemness | MCF7, SKBR3 and MDAMB231 | Genome editing by overexpressing of OCT4, KLF, MYC, SOX2 | 85 |
| 6. | Colon organoids | Human colonic stem cells | mismatch repair gene MLH1 | Explore the origin of cancer-associated mutational signatures | MLH1KO and NTHL1KO | Delete key DNA repair genes followed by delayed subcloning and whole-genome sequencing | 86 |
Therapeutic applications of CRISPR technology in cardiac disease treatment
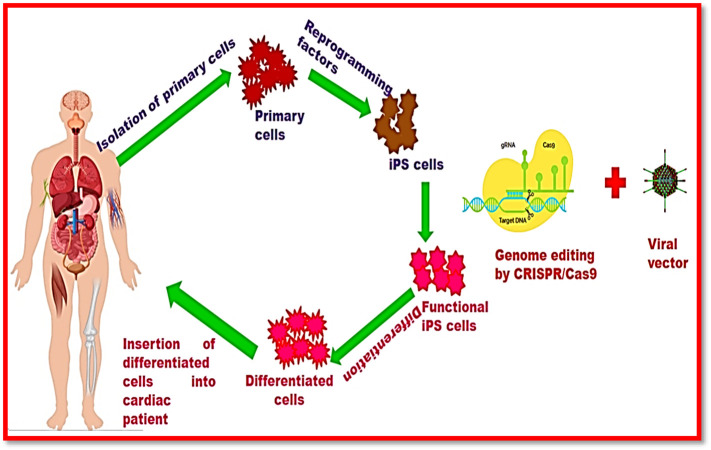
The prevalence of cardiovascular diseases is increasing.96 , 97 Therefore, it requires understanding mechanisms for causing mortality and morbidity due to cardiovascular diseases. Therapeutic approaches for cardiovascular diseases comprise blood vessels and heart. Various cardiovascular disorders include coronary artery disease (CAD), cerebrovascular disease (stroke), peripheral artery disease (PAD), cardiomyopathies, rheumatic heart disease, arrhythmias, hypertensive heart disease, and congenital heart diseases98. These cardiac ailments have been diagnosed by using genetic testing and bioinformatics analyses.99 However, these diagnostics have faced some issues of; extraction and culture of primary human cardiomyocytes for cardiovascular research are very challenging.100 Recently, CRISPR/Cas9 system provided a wide horizon for the cardiac therapeutics.99 Researchers have developed the mouse models suffering from cardiomyopathy to understand the mechanism of disease.101 , 102 Furthermore, the investigation of cardiac diseases has been carried out by introducing CRISPR/Cas9 into embryonic cells of rats, rabbits, and primates.103 , 104 The molecular phenomena of cardiac diseases and effect of mutations can be demonstrated by using induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) technology coupled with CRISPR/Cas9 system.105 , 106 Therefore, CRISPR/Cas9 system offered tremendous applications for cardiovascular diagnostics.99 Figure 5 shows the mechanism of treatment of cardiac diseases using CRISPR technology.
Figure 5.
Therapeutic applications of CRISPR-Cas system in cardiovascular diseases.
Researchers have employed therapeutic applications of CRISPR/Cas9 system for cardiac diseases (Table 2 ).
Table 2.
Applications of CRISPR-Cas9 system in cardiovascular diseases.
| Sr. no. | Name of cardiovascular diseases | Target cell/tissue/organ | Target gene | Application | Name model organism | Vector used | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cardiomyopathy | Cardiomyocytes | Myh6 | Demonstrated the role of Myh6 in heart function | Mice | Adeno-associated virus | 102 |
| 2. | Atherosclerosis | Embryo | Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) and low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) | To study human cardiovascular disease by accessing the level of biochemical constituents | Pigs | Genome editing | 107 |
| Fibroblast and myoblast | Mef2d and Klf15 loci | Controlling transcription in cardiomyocytes of the postnatal heart | Mice | Genome editing | 108 | ||
| 3. | Cardiac dysfunction | Lineage-negative bone marrow cells | TET2 and Dnmt3a | Role of targeted genes in cardiac dysfunction and renal fibrosis | Mice | Lentivirus | 109 |
| 4. | Duchenne muscular dystrophy | C2C12 mouse myoblasts | Dmd exon 44 | Restoration of dystrophin protein expression | Mice | Adeno-associated virus | 110 |
| 5. | Atherosclerosis | Hepatocytes | Low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) | Effective therapeutic approach for the treatment of familial hypercholesterolemia | Mice | Adeno-associated virus | 111 |
Therapeutic applications of CRISPR technology in diabetes treatment
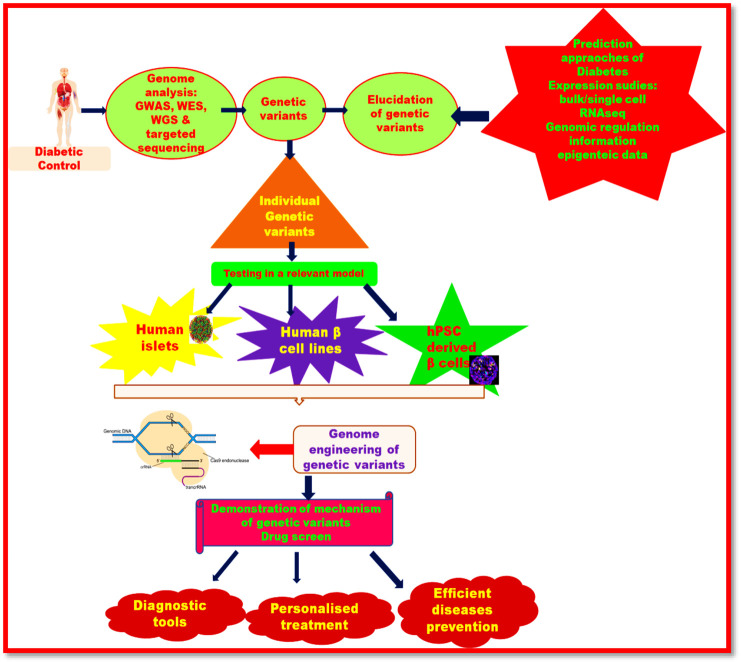
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disorder in which abnormal level of insulin hormone is secreted by β-cells of pancreatic cells. Person suffering from diabetes passes out more urine and experiences dehydration, appetite and loss of body weight.112 The prevalence of diabetes is increasing worldwide. In the year 2017, it has been reported that about 425 million people aged 20-79 years are suffering from diabetes.113 Furthermore, according to a report by the International Diabetes Federation (2017), the count of diabetic person will rise to 629 million people in the year 2045.114 Children and young people are also more susceptible to obesity and various chronic complications.115 , 116 Acute hyperglycemia causes ketoacidosis while chronic hyperglycemia has increased the risk of myocardial infarction and stroke and thereby diabetic nephropathy, retinopathy and neuropathy.117 Though existing diabetic therapeutics have been used for the treatment of diabetes, still there are some issues which have not been resolved such as improper stratification of people for their risk to convert from a prediabetic to a clinical diabetic state.118 Therefore, genome engineering by CRISPR/Cas9 system has been employed for diabetes therapeutics. Researchers have developed the animal models for the study of molecular mechanism of diabetes.
For example, Xu et al (2018) have developed rabbit model for diabetes therapeutics by editing genome using CRISPR/Cas9 system.119 They targeted the paired-homeodomain transcription factor 4 (PAX4) gene into zygote and concluded that rabbit model based on CRISPR/Cas9 technology was effective for the study of pathogenic mechanisms associated with diabetes mellitus. Cho et al (2018) have produced piglets which were deficient of insulin by inactivating INS gene by CRISPR/Cas9 system.118
Song et al (2019) have developed pathogenicity in rabbit model. They mutated the genome of rabbit by deleting small segment of glucokinase (GCK) gene which led to development of maturity onset diabetes of the young 2 (MODY-2) in humans.120 Zou and co-workers (2019) have designed type II diabetic miniature pig model based on CRISPR/Cas9 system.112 Using CRISPR/Cas9 system they targeted gene for islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) protein in human. Deposition of IAPP protein causes diabetic complications. Therefore engineered pigs based on CRISPR/Cas9 have provided efficient means to study the diabetic pathogenicity. Figure 6 illustrates the therapeutic applications of diabetes.
Figure 6.
Therapeutic applications of CRISPR-Cas system in diabetes.
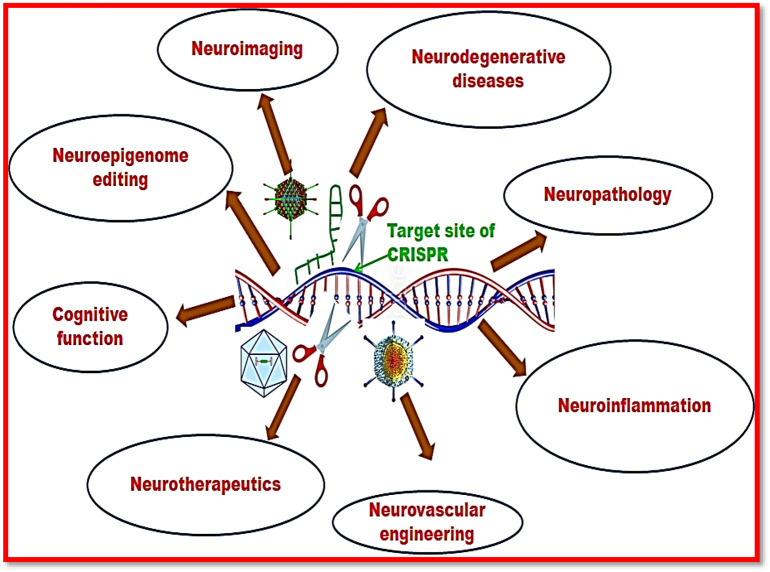
Therapeutic applications of CRISPR technology in treatment of neurovascular diseases
Researchers have focused their interest to cure several neurological disorders due to bona fide uses of CRISPR/Cas9 system. Richard and co-workers (2020) have revealed the therapeutic significance of CRISPR/Cas9 technology for phenylketonuria treatment.121 This disease is caused by the deficiency of phenylalanine hydroxylase due to which level of phenylalanine is raised, thus impairing the function of central nervous system. They used the adeno associated virus vector for the transmission of CRISPR/Cas9 machinery. They targeted the Pahenu2 allele by homologous recombination and vanillin, a non-homologous end joining inhibitor along with viral drug was injected into hepatocytes of mouse. They reported that therapeutic approach using CRISPR/Cas9 system has permanently cured the phenylketonuria. Furthermore, Shannon (2020) has demonstrated the therapeutic approach for Huntington disease which is a neurodegenerative disorder due to repetition of unstable trinucleotide.122 Using CRISPR/Cas9 system they targeted the HTT gene by synthesizing one sgRNA specific for translational start region of HTT gene and other sgRNA targeted the Cas9 gene. Due to this approach, the repletion of trinucleotide was decreased and provided the basis of Huntington disease therapeutics.
Wang et al (2020) have also demonstrated the therapeutic application of CRISPR/Cas9 system for the treatment of Cockayne syndrome.123 This syndrome has been reported as an autosomal recessive disorder which shows cachectic dwarfism, clinical photosensitivity, continuous neurological disintegration, and early aging. They used the integration-free induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and neural stem cells which can bear the effect of mutation caused by two deficient genes namely Cockayne syndrome, CSA/ERCC8 (ERCC excision repair 8, CSA ubiquitin ligase complex subunit) and CSB/ERCC6 (ERCC excision repair 6, chromatin remodeling factor). CRISPR/Cas9 system has suppressed the effect of deficient genes and thus can be used for the Cockayne syndrome therapeutics. Paschon et al (2019) have also reported the therapeutic significance of CRISPR/Cas9 system in the cure of spinal cord injury.124 A number of therapeutic neurological applications have been described in Figure 7 .
Figure 7.
Therapeutic neurological applications of CRISPR-Cas system.
Miscellaneous therapeutic applications of CRISPR technology
CRISPR integrated biosensors for diagnostic purpose: An innovative therapeutics
Rapid diagnostic testing (RDT) for the diagnosis of infectious diseases involves detection of pathogen specific immunoglobulins. However, these testing procedures are less sensitive and take too much time for reproducing the results.125 , 126 Though sensitivity of PCR and other sequence based techniques is better than RDT, they also exhibited several drawbacks including delayed response, being complicated and expensive, and requirement of highly trained personnel.127 , 128 Therefore, biosensing technology integrated electrical, electrochemical, and optical techniques and can overcome the limitations of RDT and nucleic acid amplification based approaches.129 Scientists have further improved the applications of biosensing technology by combining isothermal solid-phase DNA amplification and detection of DNA/RNA sequences of several infectious diseases on silicon microring resonator (SMR). The SMR biosensor has exhibited various merits like generating fast response, marker independent, simple, sensitive and real-time multiplexed detection of biomolecules in proximate of sensor surface by altering refractive index.130 , 131
Kaoo and co-workers (2018) developed a biosensing device coupled with CRISPR technology for the diagnosis of tick-borne like scrub typhus (ST) and severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS).132 The aforesaid biosensor was fabricated by using an inactivated nuclease Cas9 (dCas9) and single microring resonator. The developed biosensor was based on an isothermal diagnostic approach which was used for synchronized nucleic acid amplification and detection. The developed biosensor has provided a novel diagnostic tool that exhibited a number of unique advantages in terms of simplicity, speed, sensitivity, specificity, reliability, cost-effectiveness and better analytical performance. The response time of this SMR biosensor was 20 min, 100 times more sensitive than RT-PCR and detection limits for ST and SFTS were 0.54 aM and 0.63 aM, respectively.132
Moreover, Hajian et al (2019) have digitally detected a target DNA sequence within the intact genome by designing a CRISPR-enhanced graphene-based field-effect transistor (gFET) known as CRISPR-Chip.133 This CRISPR-Chip was used for the analysis of HEK293T cell lines marked with blue fluorescent protein, and clinical samples of DNA with two distinct mutations at exons usually not found in patients of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. They reported that detection of mutation by CRISPR-Chip was easy, rapid and sensitive. The limit of detection of CRIPSR-Chip grapheme transistor was 2.3 fM, response time 15 min and sensitivity 1.7 fM.133 Pardee and co-workers (2016) have documented the fabrication of freeze-dried, paper-based sensors known as toehold switch sensors combined with isothermal RNA amplification and CRISPR/Cas9 system.44 The aforesaid sensor was employed to investigate Zika virus RNA genome from plasma of vero cells and rhesus macaque. The aforesaid sensor exhibited merits like being economical, rapid, easy to perform, and highly sensitive as it can detect single nucleotide change and resolve the issues of molecular diagnostics. Hu et al (2020) have reported the designing of DNA-AuNPs bioprobes using freezing based method which were salt free and had no thiol modification.134 These AuNPs bioprobes were used for the detection of RNA by coupling CRISPR/Cas13a system. The above said bioprobes were used for the investigation of Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella typhimurium, Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Programmable materials are the encapsulated cells and have been used significantly for diagnostic applications as they release soluble components in controlled manner.135, 136, 137 English and co-workers (2019) have designed the hydrogels encapsulated with DNA using programmability application based on nucleases of CRISPR/Cas system.138 The encapsulated DNA is acting as either a structural component or an anchor for overhanging groups. They reported the programmability applications by designing smart materials called as of activated hydrogels. These hydrogels have exhibited distinct applications including (i) branched poly (ethylene glycol) hydrogels for the release of DNA-anchored compounds, (ii) polyacrylamide-DNA hydrogels encapsulated with nanoparticles and living cells can be easily recycled, (iii) conductive carbon-black-DNA hydrogels used as electrical fuses can also be recycled and (iv) a polyacrylamide-DNA hydrogel that worked as fluidic regulator generated an electrical display for remote gesturing. Moreover, these smart tools employing CRISPR/Cas12a system were used for the investigation of antibiotic resistant genes in Staphyloccocus aureus. These smart hydrogels have been used in tissue engineering, bioelectronics, and diagnostics.
Environmental applications based on CRISPR technology
Due to global industrialization, the world is facing many environmental problems such as increased risk of global warming due to increased emissions of greenhouse gases, attack of microbial pathogens including viruses on crops, vulnerability of crops to various abiotic stresses like drought and salinity, deliberate release of distinct types of pollutants in the surroundings, expensive and complicated pollutants detection and recyclable procedures. Though the aforesaid challenges are being resolved by existing conventional and genetic engineering techniques. These techniques could not achieve the goal of environmental sustainability. Therefore, genome editing using CRISPR technology has contributed significantly to resolve the existing challenges of environment. Though research in the field of CRISPR technology based on environmental applications is in very infancy stage, still this technology has offered a number of remarkable applications for sustainable environment. Phelps (2019) has documented the significance of CRISPR technology in monitoring of ecosystem biodiversity using dynamic environmental DNA (eDNA)139. Williams et al (2019) have demonstrated the on-site application of CRISPR technology combined with molecular ecology for the identification of eDNA of Salmo salar 140. In the given below sections we have explained the applications of genome editing using CRISPR technology for sustainable environment:
CRISPR technology in biofuel production
Extensive use of oils, petroleum and its related products has increased the environmental problems.141 To minimize the emission of greenhouse gases in the environment, there is increasing demand of utilization of biofuels. However, conventional methods used for production of biofuels are tedious and could not produce the enough quantity to meet the global requirement. Therefore, researchers have shown their interest in the production of biofuels using CRISPR technology. Shin et al (2016) have reported the production of biofuel by editing the genome of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii microalgae using CRISPR-Cas 9 system142. In this demonstration they knock out three genes loci i.e. MAA7, CpSRP43 and ChlM of C. reinhardtii. Consequently, mutagenic microalgae exhibited high efficiency for the production of biofuels. Moreover, Shanmugam et al (2019) have also reported the tremendous application of CRISPR-Cas systems in production of biofuels using microbial sources143. They documented that CRISPR technology can be helpful in development of biorefineries for the production of biofuels in large amount.
CRISPR technology in toxicity assessment
Researchers have revealed the significance of genome editing using CRISPR technology in various environmental based applications. For instance, Snyder et al (2010) have demonstrated that bacteria and archaea containing CRISPR loci can help in identification of unknown viruses in the environment144. They reported that spacer sequences that exist between the direct repeats of CRISPR systems are obtained from viruses. These spacer sequences are acting as guide sequences to protect bacterial and archaeal cell from infecting virus. They obtained the spacer sequences of CRISPR from metagenomic data from hot spring environments located in Yellowstone National Park (YNP). The storing conditions of these genomic data involve >80 °C temperature and pH < 4. For the detection of viruses from such environmental conditions, they used DNA microarray approach in combination with CRISPR system.
CRISPR technology in remediation of toxic compounds
CRISPR technology in conjugation with existing bioremediation approaches has been used for the degradation/remediation of pollutants. Li et al (2020) have demonstrated that tuning electron flux approach linked with CRISPR technology was employed to enhance the degradation efficiency of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 by increasing the extracellular electron transfer of bacteria145. This approach was used for degradation of pollutants like methyl orange and chromium. CRISPR-Cas 9 system has also been used to modify the genome of plants growing in the paddy fields to lower the intake of cadmium heavy metallic ions by removing the OsNramp5 gene.146 Stein et al (2018) have documented that CRISPR-Cas 9 system can be used for altering the genome of fungi for the metabolism of xenobiotic compounds147. Wu et al (2020) have also revealed the significance of types II CRISPR system in remediation process of environmental pollutants148. In this demonstration they edited the genome sequences of Aeromonas hydrophila and identified the genes essential for regulating the biochemical pathway for transformation of hazardous compounds such as methyl orange.
CRISPR technology in abiotic stress
Effect of environment on gene expression has been revealed in plants. CRISPR-Cas 9 system increased the drought tolerance in tomato plant by deleting the mitogen-activated protein kinases 3 (slmapk3) gene.149 Similarly, CRISPR-Cas 9 system has modified the genome of rice plant by inactivating the stress/ABA-activated protein kinase 2 (SAPK2) gene, responsible for regulating abscisic acid signaling pathway.150 Removal of this SAPK2 gene results in more sensitivity to drought and elevated oxidative stress in modified rice plants than wild rice plants. One more study reveals the application of CRISPR-Cas9 system in protection of plants growing at low temperature. Researchers using CRISPR-Cas9 system knock out the annexin (Osann3) gene to produce mutants of japonica rice plants.149 , 151 This gene is responsible for formation of Ca2+-dependent phospholipid binding protein. These proteins elevate the electron kinetics and decrease the survival of rice plants. However due to genome modification of mutant rice plants, they showed better survival capability at low temperature.151 Shi et al (2017) have also revealed the application of CRISPR-Cas9 system by overexpressing auxin regulated gene involved in organ size (ARGOS8), in Zea mays 152 . Overexpression of ARGOS8 has replaced the actual position of promoter with the GOS2 promoter. Consequently, it increases the productivity of maize in drought conditions. Furthermore, CRISPR-Cas 9 system was used to create point mutations in rice for the production of herbicide resistant rice plants.153
Environmental applications based on transposons integrated CRISPR technology
Genomes of most eukaryotic organisms are composed of transposable elements (TEs) or mobile genes. These TEs have shown profound impact on genome phylogenetic. It has been reported that insertion of TEs under the influence of changing environmental conditions has shown beneficial effects to host organisms.154 Furthermore TEs have been considered as efficient tools for genes allocations and epigenetic process. Under specific environmental conditions transposons alter the gene expression of regulatory pathway of host machinery to survive in changed environment.155 TEs are efficient tools for the generation of desired mutations in the genomic DNA.156 However, conventional genome editing practices use large nucleotide sequences that increase the risk of production of pseudo mutants. Thus, CRISPR-Cas9 system has played a significant role in the designing of highly efficient and targeted TEs integrated genome editing systems.156 Insertion of these systems in response to environmental conditions, like drought, cold, salinity etc., has augmented the host organism adaptability.156 Furthermore, the functional integrity of transposons in aforesaid TE based system after genome editing has shown similar effect in the regulation of host system.156
Miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements (MITEs) are generated by the insertion of Class II TEs into direct repeats of CRISPR system.157 During infection of bacteriophage, MITEs have shown functional similarity with the CRISPR systems, as they are also involved in the process of RNA interference (RNAi) mediated gene silencing by producing single stranded RNA in response to environmental hormonal signaling or stress conditions.158 Mai et al (2016) have documented presence of MITEs generated from direct repeat sequences of CRISPR systems reveals the targeted integration of TEs that leads to production of CRISPR arrays157. In plants, insertion of TEs has been observed in two signature nucleotides sequences i.e. AT dinucleotide and ATT trinucleotide.159 , 160 TEs provide adaptive defense to host from hereditary and nonhereditary genomic alterations. In specific environmental conditions, transposition mediated by transposase enzyme starts the expression of those genes that are essential for proper physiological processes.156 Singer et al (2010) have reported that in humans, during neuronal differentiation activation of Class I retrotransposons has triggered the arrangement of chromosomes to attain somatic plasticity161. MITEs have been used in modification of TE integrated systems.156 During cancer modeling, Molyneux et al (2014) have revealed that DNA Sleeping Beauty TE integrated systems were employed for the targeted mutations in somatic cells162. They concluded from this study that these TE integrated systems can be used for the recognition of genes that are responsible for causing tumor. Moreover, Vaschetto (2017) has reported the significance of TE integrated systems in regulation of plant development process156. Researchers have also developed the transgenic soybean using mPing MITEs.163 Moreover, MITEs have been acknowledged for RNA mediated gene regulation by producing either miRNA precursors or small interfering RNA (siRNA). Thus, genome editing using MITEs has altered the expression of genes either by up-regulating or down regulating their expression to enhance the susceptibility of crops in varying environmental conditions.156
Engineering of CRISPR/Cas9-targeted loci for targeted insertion of TE has also regulated expression of targeted genes by using natural potential of TE.156 Furthermore it has been documented that TEs have played a crucial role in regulation of several physiological phenomena of host such as telomere maintenance, reorganization of chromosomes, duplication of genes, and epigenetic process.156 Thus this CRISPR technology combined with transposons has provided a remarkable platform to understand the mechanisms to identify essential genes and their function for gene regulation in diverse environments and evolution of wide arrays of genes.156
Future prospects of CRISPR technology
By seeing the ample reports, CRISPR based technology has been acknowledged in the field of diagnostics and therapeutics due to its effectiveness and potent defense system. Recent progress on CRISPR/Cas9 technology is providing a horizon for the discovery of novel therapeutic genes and their mechanism of action. For instance, using CRISPR/Cas9 system, ample gRNAs have been constructed to target possible coding genes for screening gain and loss of function mutations.33 This rapid scanning of genetic material will help in identification of genes responsible for drug resistance to neurodisintegration. Consequently, researchers can develop effective therapeutics to combat the genetic as well as infectious diseases. Thus, the inclusive genetic screening helps to recognize suppressive mutations like loss-of-function mutations in CCR5 and PCSK9 which provided defense against the HIV infection and hypercholesterolemia respectively.164 In the future, CRISPR/Cas9 system will provide direct therapy to genetic diseases by reversing the symptoms associated with them.165 Furthermore, efficient CRISPR based therapeutics must have an appropriate vector, specificity and capable repair system.166 A number of animal models containing CRISPR system have been used for the treatment of eye and hearing disorders.167 Researchers are also trying to condense the CRISPR/Cas9 system so that a compact system can be delivered as a single unit. Therefore, novel techniques have promise by exhibiting various advantages such as robustness, point-of-care use, unique sensitivity, specificity, rapidness and cost-effectiveness.
Moreover, CRISPR/dCas9-mediated biosensor should be further improved in terms of being simple to use, cheap, sensitive, specific, eco-friendly, quick, portable, and free of instruments for the investigation of clinical samples. A lab-on-chip platform has also been designed for diagnostic applications which facilitate the facile analysis, not expensive, fast and high through put extraction of DNA/RNA from clinical samples. In our opinion, incorporation of sample preparation and CRISPR/dCas9- integrated biosensors into a single cartridge will provide potential diagnostics for emerging infectious diseases. By seeing the immense applications of therapies based on genome editing, scientific communities are motivated to design therapeutics based on CRISPR technology in reality.
Conclusion
Recently, CRISPR-Cas systems have gained immense significance due to the existence of versatile and efficient defense mechanisms. Integration of CRISPR technology with lateral flow system has been significantly used for the diagnosis of emerging pathogens causing infectious diseases. It has offered several remarkable advantages such as economic, quick, sensitive and precise investigation of target host pathogens and can interfere with the therapeutic cures of several infections. CRISPR technology can be easily used for translating the target DNA sequence to restore the normal function of a defected gene, Thus, due to tremendous applications imparted by CRISPR technology, it has become a demanding therapeutic approach in the present system. Furthermore, biosensors integrated with CRISPR/Cas system have also provided quick and accurate molecular diagnostics with potential clinical applications.
Acknowledgments
Dr. Neelam thankfully acknowledges the UGC granted Dr. D. S. Kothari Post-Doctoral Fellowship (No.F.4-2/2006 (BSR)/BL/18-19/0107) for financial assistance. This funding agency has no conflict on the publishing of article.
Footnotes
Conflict of interest: All the authors of aforesaid review article hereby declare no conflict of interest for its publishing.
Reference
- 1.Khambhati K., Bhattacharjee G., Singh V. Current progress in CRISPR-based diagnostic platforms. J Cell Biochem. 2018;120(3):2721–2725. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pollock N.R., Wonderly B. Evaluating novel diagnostics in an outbreak setting: lessons learned from Ebola. J Clin Microbiol. 2017;55(5):1255–1261. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00053-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.World Health Organization Global Health Observatory (GHO) data: HIV/AIDS. 2018. http://www.who.int/gho/hiv/en
- 4.Pandey V.K., Tripathi A., Bhushan R., Ali A., Dubey P.K. Application of CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing in genetic disorders: a systematic review up to date. J Genetic Syndrom Gene Therap. 2017;8(2) [Google Scholar]
- 5.Parsa N. Environmental factors inducing human cancers. Iranian J Pub Health. 2012;41(11):1. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gootenberg J.S., Abudayyeh O.O., Lee J.W., Essletzbichler P., Dy A.J., Joung J., et al. Nucleic acid detection with CRISPR-Cas13a/C2c2. Science. 2017;356(6336):438–442. doi: 10.1126/science.aam9321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ishino Y., Shinagawa H., Makino K., Amemura M., Nakata A. Nucleotide sequence of the iap gene, responsible for alkaline phosphatase isozyme conversion in Escherichia coli, and identification of the gene product. J Bacteriol. 1987;169(12):5429–5433. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5429-5433.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jansen R., Embden J.D.V., Gaastra W., Schouls L.M. Identification of genes that are associated with DNA repeats in prokaryotes. Mol Microbiol. 2002;43(6):565–1575. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bolotin A., Quinquis B., Sorokin A., Ehrlich S.D. Clustered regularly interspaced short palindrome repeats (CRISPRs) have spacers of extra chromosomal origin. Microbiology. 2005;151(8):2551–2561. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.28048-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mojica F.J., García-Martínez J., Soria E. Intervening sequences of regularly spaced prokaryotic repeats derive from foreign genetic elements. J Mol Evol. 2005;60(2):174–182. doi: 10.1007/s00239-004-0046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Barrangou R., Fremaux C., Deveau H., Richards M., Boyaval P., Moineau S., et al. CRISPR provides acquired resistance against viruses in prokaryotes. Science. 2007;315(5819):1709–1712. doi: 10.1126/science.1138140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jinek M., Chylinski K., Fonfara I., Hauer M., Doudna J.A., Charpentier E. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science. 2012;337(6096):816–821. doi: 10.1126/science.1225829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wright A.V., Nuñez J.K., Doudna J.A. Biology and applications of CRISPR systems: harnessing nature’s toolbox for genome engineering. Cell. 2016;164(1-2):29–44. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.12.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Singh V., Gohil N., Ramirez Garcia R., Braddick D., Fofié C.K. Recent advances in CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing technology for biological and biomedical investigations. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(1):81–94. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zetsche B., Gootenberg J.S., Abudayyeh O.O., Slaymaker I.M., Makarova K.S., Essletzbichler P., et al. Cpf1 is a single RNA-guided endonuclease of a class 2 CRISPR-Cas system. Cell. 2015;163(3):759–771. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.09.038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gupta R.M., Musunuru K. Expanding the genetic editing tool kit: ZFNs, TALENs, and CRISPR-Cas9. J Clin Invest. 2014;124(10):4154–4161. doi: 10.1172/JCI72992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Baliou S., Adamaki M., Kyriakopoulos A.M., Spandidos D.A., Panayiotidis M., Christodoulou I., et al. CRISPR therapeutic tools for complex genetic disorders and cancer. Int J Oncol. 2018;53(2):443–468. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Strich J.R., Chertow D.S. CRISPR-Cas biology and its application to infectious diseases. J Clin Microbiol. 2019;57(4):01307–01318. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01307-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gasiunas G., Barrangou R., Horvath P., Siksnys V. Cas9–crRNA ribonucleoprotein complex mediates specific DNA cleavage for adaptive immunity in bacteria. Proceed Nation Acad Sci. 2012;109(39):2579–E2586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1208507109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Heler R., Samai P., Modell J.W., Weiner C., Goldberg G.W., Bikard D., et al. Cas9 specifies functional viral targets during CRISPR–Cas adaptation. Nature. 2015;519(7542):199–202. doi: 10.1038/nature14245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Deltcheva E., Chylinski K., Sharma C.M., Gonzales K., Chao Y., Pirzada Z.A., et al. CRISPR RNA maturation by trans-encoded small RNA and host factor RNase III. Nature. 2011;471(7340):602–607. doi: 10.1038/nature09886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Brouns S.J., Jore M.M., Lundgren M., Westra E.R., Slijkhuis R.J., Snijders A.P., et al. Small CRISPR RNAs guide antiviral defense in prokaryotes. Science. 2008;321(5891):960–964. doi: 10.1126/science.1159689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Xiao Y., Luo M., Hayes R.P., Kim J., Ng S., Ding F., et al. Structure basis for directional R-loop formation and substrate handover mechanisms in type I CRISPR-Cas system. Cell. 2017;170(1):48–60. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.06.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Staals R.H., Zhu Y., Taylor D.W., Kornfeld J.E., Sharma K., Barendregt A., et al. RNA targeting by the type III-A CRISPR-Cas Csm complex of Thermus thermophilus. Mol Cell. 2014;56(4):518–530. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.10.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fukao T., Fukuda Y., Kiga K., Sharif J., Hino K., Enomoto Y., et al. An evolutionarily conserved mechanism for microRNA-223 expression revealed by microRNA gene profiling. Cell. 2007;129(3):617–631. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hille F., Richter H., Wong S.P., Bratovič M., Ressel S., Charpentier E. The biology of CRISPR-Cas: backward and forward. Cell. 2018;172(6):1239–1259. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Mali P., Yang L. esvelt KM, Aach J., Guell M., Dicarlo Je, et al. Science. 2013;339(6121):823–826. doi: 10.1126/science.1232033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Garneau J.E., Dupuis M.È., Villion M., Romero D.A., Barrangou R., Boyaval P., et al. The CRISPR/Cas bacterial immune system cleaves bacteriophage and plasmid DNA. Nature. 2010;468(7320):67–71. doi: 10.1038/nature09523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Shmakov S., Abudayyeh O.O., Makarova K.S., Wolf Y.I., Gootenberg J.S., Semenova E., et al. (2015). Discovery and functional characterization of diverse class 2 CRISPR-Cas systems. Mol Cell. 2015;60(3):385–397. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.10.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zetsche B., Gootenberg J.S., Abudayyeh O.O., Slaymaker I.M., Makarova K.S., Essletzbichler P. Cpf1 is a single RNA-guided endonuclease of a class 2 CRISPR-Cas system. Cell. 2015;163(3):759–771. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.09.038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Abudayyeh O.O., Gootenberg J.S., Konermann S., Joung J., Slaymaker I.M., Cox D.B. C2c2 is a single-component programmable RNA-guided RNA-targeting CRISPR effector. Science. 2016;353(6299) doi: 10.1126/science.aaf5573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.East-Seletsky A., O’Connell M.R., Knight S.C., Burstein D., Cate J.H., Tjian R., et al. Two distinct RNase activities of CRISPR-C2c2 enable guide-RNA processing and RNA detection. Nature. 2016;538(7624):270–273. doi: 10.1038/nature19802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hsu P.D., Lander E.S., Zhang F. Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering. Cell. 2014;157(6):1262–1278. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Deng L., Luo M., Velikovsky A., Mariuzza R.A. Structural insights into the evolution of the adaptive immune system. Annu Rev Biophys. 2013;42:191–215. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-083012-130422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Shalem O., Sanjana N.E., Zhang F. High-throughput functional genomics using CRISPR–Cas9. Nat Rev Genet. 2015;16(5):299–311. doi: 10.1038/nrg3899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Koike-Yusa H., Li Y., Tan E.P., Velasco-Herrera M.D.C., Yusa K. Genome-wide recessive genetic screening in mammalian cells with a lentiviral CRISPR-guide RNA library. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32(3):267. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zhou Y., Zhu S., Cai C., Yuan P., Li C., Huang Y., et al. High-throughput screening of a CRISPR/Cas9 library for functional genomics in human cells. Nature. 2014;509(7501):487–491. doi: 10.1038/nature13166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Doerflinger M., Forsyth W., Ebert G., Pellegrini M., Herold M.J. CRISPR/Cas9—the ultimate weapon to battle infectious diseases? Cell Microbiol. 2017;19(2):12693. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Winter S.V., Zychlinsky A., Bardoel B.W. Genome-wide CRISPR screen reveals novel host factors required for Staphylococcus aureus α-hemolysin-mediated toxicity. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):1–9. doi: 10.1038/srep24242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ma H., Dang Y., Wu Y., Jia G., Anaya E., Zhang J., et al. A CRISPR-based screen identifies genes essential for West-Nile-virus-induced cell death. Cell Rep. 2015;12(4):673–683. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.06.049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Nødvig C.S., Nielsen J.B., Kogle M.E., Mortensen U.H. A CRISPR-Cas9 system for genetic engineering of filamentous fungi. PLoS One. 2015;10(7) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Sidik S.M., Hackett C.G., Tran F., Westwood N.J., Lourido S. Efficient genome engineering of Toxoplasma gondii using CRISPR/Cas9. PLoS One. 2014;9(6) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lander N., Chiurillo M.A., Vercesi A.E., Docampo R. Endogenous C-terminal tagging by CRISPR/Cas9 in Trypanosoma cruzi. Bio Protoc. 2017;7(10) doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Pardee K., Green A.A., Takahashi M.K., Braff D., Lambert G., Lee J.W., et al. Rapid, low-cost detection of Zika virus using programmable biomolecular components. Cell. 2016;165(5):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.04.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Muller V., Rajer F., Frykholm K., Nyberg L.K., Quaderi S., Fritzsche J., et al. Direct identification of antibiotic resistance genes on single plasmid molecules using CRISPR/Cas9 in combination with optical DNA mapping. Sci Rep. 2016;6:37938. doi: 10.1038/srep37938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Guk K., Keem J.O., Hwang S.G., Kim H., Kang T., Lim E.K., et al. A facile, rapid and sensitive detection of MRSA using a CRISPR-mediated DNA FISH method, antibody-like dCas9/sgRNA complex. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;95:67–71. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Chen J.S., Ma E., Harrington L.B., Da Costa M., Tian X., Palefsky J.M., et al. CRISPR-Cas12a target binding unleashes indiscriminate single-stranded DNase activity. Science. 2018;360:436–439. doi: 10.1126/science.aar6245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Gootenberg J.S., Abudayyeh O.O., Kellner M.J., Joung J., Collins J.J., Zhang F. Multiplexed and portable nucleic acid detection platform with Cas13, Cas12a, and Csm6. Science. 2018;360(6387):439–444. doi: 10.1126/science.aaq0179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Myhrvold C., Freije C.A., Gootenberg J.S., Abudayyeh O.O., Metsky H.C., Durbin A.F., et al. Field-deployable viral diagnostics using CRISPR-Cas13. Science. 2018;360(6387):444–448. doi: 10.1126/science.aas8836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Atlanta, GA: 2013. Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States, 2013.https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/pdf/ar-threats -2013-508.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 51.Aydin S., Personne Y., Newire E., Laverick R., Russell O., Roberts A.P., et al. Presence of Type IF CRISPR/Cas systems is associated with antimicrobial susceptibility in Escherichia coli. J Antimicro Chemotherap. 2017;72(8):2213–2218. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkx137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Price V.J., Huo W., Sharifi A., Palmer K.L. CRISPR-Cas and restriction-modification act additively against conjugative antibiotic resistance plasmid transfer in Enterococcus faecalis. Msphere. 2016;1(3):00064. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00064-16. 16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Lin T.L., Pan Y.J., Hsieh P.F., Hsu C.R., Wu M.C., Wang J.T. Imipenem represses CRISPR-Cas interference of DNA acquisition through H-NS stimulation in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Sci Rep. 2016;6:31644. doi: 10.1038/srep31644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Gomaa A.A., Klumpe H.E., Luo M.L., Selle K., Barrangou R., Beisel C.L. Programmable removal of bacterial strains by use of genome-targeting CRISPR-Cas systems. MBio. 2014;5(1) doi: 10.1128/mBio.00928-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Citorik R.J., Mimee M., Lu T.K. Sequence-specific antimicrobials using efficiently delivered RNA-guided nucleases. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32(11):1141. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Yosef I., Manor M., Kiro R., Qimron U. Temperate and lytic bacteriophages programmed to sensitize and kill antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Proceed Nat Acad Sci. 2015;112(23):7267–7272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1500107112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Bikard D., Euler C.W., Jiang W., Nussenzweig P.M., Goldberg G.W., Duportet X., et al. Exploiting CRISPR-Cas nucleases to produce sequence-specific antimicrobials. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32(11):1146–1150. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Fabre L., Zhang J., Guigon G., Le Hello S., Guibert V., Accou-Demartin M., et al. CRISPR typing and subtyping for improved laboratory surveillance of Salmonella infections. PLoS One. 2012;7(5) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Koskela K.A., Mattinen L., Kalin-Mänttäri L., Vergnaud G., Gorgé O., Nikkari S., et al. Generation of a CRISPR database for Yersinia pseudotuberculosis complex and role of CRISPR-based immunity in conjugation. Environ Microbiol. 2015;17(11):4306–4321. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Li S.Y., Cheng Q.X., Wang J.M., Li X.Y., Zhang Z.L., Gao S., et al. CRISPR-Cas12a-assisted nucleic acid detection. Cell Discov. 2018;4(1):1–4. doi: 10.1038/s41421-018-0028-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Singh A.K., Carette X., Potluri L.P., Sharp J.D., Xu R., Prisic S., et al. Investigating essential gene function in Mycobacterium tuberculosis using an efficient CRISPR interference system. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(18):143–e143. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Choudhary E., Thakur P., Pareek M., Agarwal N. Gene silencing by CRISPR interference in mycobacteria. Nat Commun. 2015;6(1):11. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Bakhrebah M.A., Nassar M.S., Alsuabeyl M.S., Zaher W.A., Meo S.A. CRISPR technology: new paradigm to target the infectious disease pathogens. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(11):3448–3452. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201806_15169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Hu W., Kaminski R., Yang F., Zhang Y., Cosentino L., Li F., et al. RNA-directed gene editing specifically eradicates latent and prevents new HIV-1 infection. Proceed Nat Acad Sci. 2014;111(31):11461–11466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1405186111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Wang G., Zhao N., Berkhout B., Das A.T. CRISPR-Cas based antiviral strategies against HIV-1. Virus Res. 2018;244:321–332. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2017.07.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Yin C., Zhang T., Qu X., Zhang Y., Putatunda R., Xiao X., et al. In vivo excision of HIV-1 provirus by saCas9 and multiplex single-guide RNAs in animal models. Mol Therap. 2017;25(5):1168–1186. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.03.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Bella R., Kaminski R., Mancuso P., Young W.B., Chen C., Sariyer R., et al. Removal of HIV DNA by CRISPR from patient blood engrafts in humanized mice. Mol Therapy-Nucleic Acid. 2018;12:275–282. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.05.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.van Diemen F.R., Kruse E.M., Hooykaas M.J., Bruggeling C.E., Schürch A.C., van Ham P.M., et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing of herpesviruses limits productive and latent infections. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12(6) doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Hou T., Zeng W., Yang M., Chen W., Ren L., Ai J., et al. Development and evaluation of a CRISPR-based diagnostic for 2019-novel coronavirus. medRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.02.22.20025460. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Ai J.W., Zhang Y., Zhang H.C., Xu T., Zhang W.H. Era of molecular diagnosis for pathogen identification of unexplained pneumonia, lessons to be learned. Emerg Microb Infection. 2020;9(1):597–600. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1738905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Zhen S., Hua L., Liu Y.H., Gao L.C., Fu J., Wan D.Y., et al. Harnessing the clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated Cas9 system to disrupt the hepatitis B virus. Gene Therap. 2015;22(5):404–412. doi: 10.1038/gt.2015.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Kennedy E.M., Bassit L.C., Mueller H., Kornepati A.V., Bogerd H.P., Nie T., et al. Suppression of hepatitis B virus DNA accumulation in chronically infected cells using a bacterial CRISPR/Cas RNA-guided DNA endonuclease. Virology. 2015;476:196–205. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.12.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Ramanan V., Shlomai A., Cox D.B., Schwartz R.E., Michailidis E., Bhatta A., et al. CRISPR/Cas9 cleavage of viral DNA efficiently suppresses hepatitis B virus. Sci Rep. 2015;5:10833. doi: 10.1038/srep10833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Kennedy E.M., Kornepati A.V., Goldstein M., Bogerd H.P., Poling B.C., Whisnant A.W., et al. Inactivation of the human papillomavirus E6 or E7 gene in cervical carcinoma cells by using a bacterial CRISPR/Cas RNA-guided endonuclease. J Virol. 2014;88(20):11965–11972. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01879-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Ren Q., Li C., Yuan P., Cai C., Zhang L., Luo G.G., et al. A dual-reporter system for real-time monitoring and high-throughput CRISPR/Cas9 library screening of the hepatitis C virus. Sci Rep. 2015;5:8865. doi: 10.1038/srep08865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Sollelis L., Ghorbal M., MacPherson C.R., Martins R.M., Kuk N., Crobu L., et al. First efficient CRISPR-C as9-mediated genome editing in Leishmania parasites. Cell Microbiol. 2015;17(10):1405–1412. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Zamanian M., Andersen E.C. Prospects and challenges of CRISPR/Cas genome editing for the study and control of neglected vector-borne nematode diseases. The FEBS J. 2016;283(17):3204–3221. doi: 10.1111/febs.13781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Costa F.C., Francisco A.F., Jayawardhana S., Calderano S.G., Lewis M.D., Olmo F., et al. Expanding the toolbox for Trypanosoma cruzi: a parasite line incorporating a bioluminescence-fluorescence dual reporter and streamlined CRISPR/Cas9 functionality for rapid in vivo localisation and phenotyping. PLoS Neglect Trop Dis. 2018;12(4) doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Sidik S.M., Huet D., Ganesan S.M., Huynh M.H., Wang T., Nasamu A.S., et al. A genome-wide CRISPR screen in Toxoplasma identifies essential apicomplexan genes. Cell. 2016;166(6):1423–1435. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.08.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Knuepfer E., Napiorkowska M., van Ooij C., Holder A.A. Generating conditional gene knockouts in Plasmodium—a toolkit to produce stable DiCre recombinase-expressing parasite lines using CRISPR/Cas9. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03984-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Medeiros L.C.S., South L., Peng D., Bustamante J.M., Wang W., Bunkofske M., et al. Rapid, selection-free, high-efficiency genome editing in protozoan parasites using CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoproteins. MBio. 2017;8(6):01788. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01788-17. 17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Lander N., Li Z.H., Niyogi S., Docampo R. CRISPR/Cas9-induced disruption of paraflagellar rod protein 1 and 2 genes in Trypanosoma cruzi reveals their role in flagellar attachment. MBio. 2015;6(4):01012–01015. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01012-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Martinez-Lage M., Puig-Serra P., Menendez P., Torres-Ruiz R., Rodriguez-Perales S. CRISPR/Cas9 for cancer therapy: hopes and challenges. Biomedicine. 2018;6(4):105. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines6040105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Hart T., Chandrashekhar M., Aregger M., Steinhart Z., Brown K.R., MacLeod G., et al. High-resolution CRISPR screens reveal fitness genes and genotype-specific cancer liabilities. Cell. 2015;163(6):1515–1526. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.11.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Drost J., Van Boxtel R., Blokzijl F., Mizutani T., Sasaki N., Sasselli V., et al. Use of CRISPR-modified human stem cell organoids to study the origin of mutational signatures in cancer. Science. 2017;358(6360):234–238. doi: 10.1126/science.aao3130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Mei Y., Cai D., Dai X. Modulating cancer stemness provides luminal a breast cancer cells with HER2 positive-like features. J Cancer. 2020;11(5):1162–1169. doi: 10.7150/jca.37117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Friedland A.E., Tzur Y.B., Esvelt K.M., Colaiácovo M.P., Church G.M., Calarco J.A. Heritable genome editing in C. elegans via a CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nature Method. 2013;10(8):741. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Chen B., Gilbert L.A., Cimini B.A., Schnitzbauer J., Zhang W., Li G.W., et al. Dynamic imaging of genomic loci in living human cells by an optimized CRISPR/Cas system. Cell. 2013;155(7):1479–1491. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Klann T.S., Black J.B., Chellappan M., Safi A., Song L., Hilton I.B., et al. CRISPR–Cas9 epigenome editing enables high-throughput screening for functional regulatory elements in the human genome. Nat Biotechnol. 2017;35(6):561. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Lawlor E.R., Thiele C.J. 2012. Epigenetic changes in pediatric solid tumors: promising new targets. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Shachaf C.M., Kopelman A.M., Arvanitis C., Karlsson Å., Beer S., Mandl S. MYC inactivation uncovers pluripotent differentiation and tumour dormancy in hepatocellular cancer. Nature. 2004;431(7012):1112–1117. doi: 10.1038/nature03043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Mintz R.L., Lao Y.H., Chi C.W., He S., Li M., Quek C.H., et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutagenesis to validate the synergy between PARP1 inhibition and chemotherapy in BRCA1-mutated breast cancer cells. Bioeng Trans Med. 2020;5(1):1–8. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10152. e10152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Stadtmauer E.A., Fraietta J.A., Davis M.M., Cohen A.D., Weber K.L., Lancaster E., et al. CRISPR-engineered T cells in patients with refractory cancer. Science. 2020;367(6481) doi: 10.1126/science.aba7365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Shi J., Wang E., Milazzo J.P., Wang Z., Kinney J.B., Vakoc C.R. Discovery of cancer drug targets by CRISPR-Cas9 screening of protein domains. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33(6):661. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Okusha Y., Eguchi T., Tran M.T., Sogawa C., Yoshida K., Itagaki M., et al. 2020. Extracellular oncosomes rich in moonlighting metalloproteinase (MMP3) are transmissive, pro-tumorigenic, and induces cellular communication network factor 2 (CCN2/CTGF): CRISPR against cancer. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Eckel R.H., Jakicic J.M., Ard J.D. 2013 AHA/ACC guideline on lifestyle management to reduce cardiovascular risk: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Americ Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(25):3027–3028. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.11.003. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013 Nov 12 [E-pub ahead of print. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Wilkins E., Wilson L., Wickramasinghe K., Bhatnagar P., Leal J., Luengo-Fernandez R., et al. 2017. European cardiovascular disease statistics; p. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 98.Moran A.E., Roth G.A., Narula J., Mensah G.A. 1990-2010 global cardiovascular disease atlas. Glob Heart. 2014;9(1):3–16. doi: 10.1016/j.gheart.2014.03.1220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Motta B.M., Pramstaller P.P., Hicks A.A., Rossini A. Stem Cells International; 2017. The impact of CRISPR/Cas9 technology on cardiac research: from disease modelling to therapeutic approaches; p. 2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Louch W.E., Sheehan K.A., Wolska B.M. Methods in cardiomyocyte isolation, culture, and gene transfer. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011;51(3):288–298. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.06.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Hall B., Limaye A., Kulkarni A.B. Overview: generation of gene knockout mice. Curr Protocol Cell Bio. 2009;44(1):19. doi: 10.1002/0471143030.cb1912s44. 12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Carroll K.J., Makarewich C.A., McAnally J., Anderson D.M., Zentilin L., Liu N., et al. A mouse model for adult cardiac-specific gene deletion with CRISPR/Cas9. Proceed Nat Acad Sci. 2016;113(2):338–343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1523918113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Niu Y., Shen B., Cui Y., Chen Y., Wang J., Wang L., et al. Generation of gene-modified cynomolgus monkey via Cas9/RNA-mediated gene targeting in one-cell embryos. Cell. 2014;156(4):836–843. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Shao Y., Guan Y., Wang L., Qiu Z., Liu M., Chen Y., et al. CRISPR/Cas-mediated genome editing in the rat via direct injection of one-cell embryos. Nat Protoc. 2014;9(10):2493. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2014.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Hinson J.T., Chopra A., Nafissi N., Polacheck W.J., Benson C.C., Swist S., et al. Titin mutations in iPS cells define sarcomere insufficiency as a cause of dilated cardiomyopathy. Science. 2015;349(6251):982–986. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa5458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Wang Y., Liang P., Lan F., Wu H., Lisowski L., Gu M., et al. Genome editing of isogenic human induced pluripotent stem cells recapitulates long QT phenotype for drug testing. J Americ Coll Cardio. 2014;64(5):451–459. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.04.057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Huang L., Hua Z., Xiao H., Cheng Y., Xu K., Gao Q., et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated ApoE−/− and LDLR−/− double gene knockout in pigs elevates serum LDL-C and TC levels. Oncotarget. 2017;8(23):37751. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Schoger E., Carroll K.J., Iyer L.M., McAnally J.R., Tan W., et al. CRISPR-mediated activation of endogenous gene expression in the postnatal heart. Circ Res. 2020;26(1):6–24. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.314522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Sano S., Oshima K., Wang Y., Katanasaka Y., Sano M., Walsh K. CRISPR-mediated gene editing to assess the roles of Tet2 and Dnmt3a in clonal hematopoiesis and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 2018;123(3):335–341. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.313225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Zhang Y., Li H., Min Y.L., Sanchez-Ortiz E., Huang J., Mireault A.A., et al. Enhanced CRISPR-Cas9 correction of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in mice by a self-complementary AAV delivery system. Sci Adv. 2020;6(8):6812. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aay6812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Zhao H., Li Y., He L., Pu W., Yu W., Li Y., et al. In vivo AAV-CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing ameliorates atherosclerosis in familial hypercholesterolemia. Circulation. 2020;141(1):67–79. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.042476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Zou X., Ouyang H., Yu T., Chen X., Pang D., Tang X., et al. Preparation of a new type 2 diabetic miniature pig model via the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(11):1–10. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2056-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Renner S., Blutke A., Clauss S., Deeg C.A., Kemter E., Merkus D., et al. Porcine models for studying complications and organ crosstalk in diabetes mellitus. Cell Tissue Res. 2020:1–38. doi: 10.1007/s00441-019-03158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.International Diabetes Federation . International Diabetes Federation (IDF); Brüssel: 2017. IDF diabetes atlas. [Google Scholar]
- 115.Afshin A., Reitsma M.B., Murray C.J. Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries. New Eng J Med. 2017;377(15):1496. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1710026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Lascar N., Brown J., Pattison H., Barnett A.H., Bailey C.J., Bellary S. Type 2 diabetes in adolescents and young adults. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6(1):69–80. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30186-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Forbes J.M., Cooper M.E. Mechanisms of diabetic complications. Physiol Rev. 2013;93(1):137–188. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00045.2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Cho B., Kim S.J., Lee E., Ahn S.M., Lee J.S., Ji D.Y., et al. Generation of insulin-deficient piglets by disrupting INS gene using CRISPR/Cas9 system. Transgenic Res. 2018;27(3):289–300. doi: 10.1007/s11248-018-0074-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Xu Y., Wang Y., Song Y., Deng J., Chen M., Ouyang H., et al. Generation and phenotype identification of PAX4 gene knockout rabbit by CRISPR/Cas9 system. G3: Gene Genom Genet. 2018;8(8):2833–2840. doi: 10.1534/g3.118.300448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Song Y., Sui T., Zhang Y., Wang Y., Chen M., Deng J., et al. Genetic deletion of a short fragment of glucokinase in rabbit by CRISPR/Cas9 leading to hyperglycemia and other typical features seen in MODY-2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019:1–13. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03354-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Richards D.Y., Winn S.R., Dudley S., Nygaard S., Mighell T.L., Grompe M., et al. AAV-mediated CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing in murine phenylketonuria. Mol Therapy-Method Clin Develop. 2020;17:234–245. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2019.12.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Shannon K.M. Recent advances in the treatment of Huntington’s disease: targeting DNA and RNA. CNS Drug. 2020:1–10. doi: 10.1007/s40263-019-00695-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Wang S., Min Z., Ji Q., Geng L., Su Y., Liu Z., et al. Rescue of premature aging defects in Cockayne syndrome stem cells by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene correction. Protein cell. 2020;11(1):1–22. doi: 10.1007/s13238-019-0623-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Paschon V., Correia F.F., Morena B.C., da Silva V.A., dos Santos G.B., da Silva M.C.C., et al. CRISPR, prime editing, optogenetics, and DREADDs: new therapeutic approaches provided by emerging technologies in the treatment of spinal cord injury. Mol Neurobiol. 2020:1–16. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01861-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Wilson M.L. Malaria rapid diagnostic tests. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54(11):1637–1641. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Boelaert M., Bhattacharya S., Chappuis F., El Safi S.H., Hailu A., Mondal D., et al. Evaluation of rapid diagnostic tests: visceral leishmaniasis. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007;5(11):S31–S39. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Lanciotti R.S., Kosoy O.L., Laven J.J., Velez J.O., Lambert A.J., Johnson A.J., et al. Genetic and serologic properties of Zika virus associated with an epidemic, Yap State, Micronesia, 2007. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14(8):1232. doi: 10.3201/eid1408.080287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Baker M. New-wave diagnostics. Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24(8):931–938. doi: 10.1038/nbt0806-931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Yoo S.M., Lee S.Y. Optical biosensors for the detection of pathogenic microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol. 2016;34(1):7–25. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2015.09.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Koo B., Jin C.E., Lee T.Y., Lee J.H., Park M.K., Sung H., et al. An isothermal, label-free, and rapid one-step RNA amplification/detection assay for diagnosis of respiratory viral infections. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;90:187–194. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.11.051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Shin Y., Perera A.P., Tang W.Y., Fu D.L., Liu Q., Sheng J.K., et al. A rapid amplification/detection assay for analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis using an isothermal and silicon bio-photonic sensor complex. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;68:390–396. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.01.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Koo B., Kim D.E., Kweon J., Jin C.E., Kim S.H., Kim Y., et al. CRISPR/dCas9-mediated biosensor for detection of tick-borne diseases. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;273:316–321. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2018.06.069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Hajian R., Balderston S., Tran T., DeBoer T., Etienne J., Sandhu M., et al. Detection of unamplified target genes via CRISPR-Cas9 immobilized on a graphene field-effect transistor. Nature Biomed Eng. 2019;3(6):427. doi: 10.1038/s41551-019-0371-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Hu M., Yuan C., Tian T., Wang X., Sun J., Xiong E., et al. Single-step, salt aging-free and thiol-free freezing construction of AuNP-based bioprobes for advancing CRISPR-based diagnostics. J Am Chem Soc. 2020;142(16):7506–7513. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c00217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Li J., Mooney D.J. 2016. Designing hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Nature Rev Mat. 2016;1(12):1–17. doi: 10.1038/natrevmats.2016.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Rosales A.M., Anseth K.S. 2016. The design of reversible hydrogels to capture extracellular matrix dynamics. Nature Rev Mat. 2016;1(2):1–15. doi: 10.1038/natrevmats.2015.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Purcell B.P., Lobb D., Charati M.B., Dorsey S.M., Wade R.J., Zellars K.N., et al. 2014. Injectable and bioresponsive hydrogels for on-demand matrix metalloproteinase inhibition. Nature Mat. 2014;13(6):653–661. doi: 10.1038/nmat3922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.English M.A., Soenksen L.R., Gayet R.V., de Puig H., Angenent-Mari N.M., Mao A.S., et al. Programmable CRISPR-responsive smart materials. Science. 2019;365(6455):780–785. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw5122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Phelps M. Increasing eDNA capabilities with CRISPR technology for real-time monitoring of ecosystem biodiversity. Mol Ecol Resour. 2019;19(5):1103–1105. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Williams M.A., O'Grady J., Ball B., Carlsson J., de Eyto E., McGinnity P., et al. 2019. The application of CRISPR-Cas for single species identification from environmental DNA. Mol Ecol Resour. 2019;19(5):1106–1114. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Ozsoz M., Ibrahim A.U., Coston P.P. Application of Crispr technology for the generation of biofuels: a review. J Fundam Renew Energy Appl 2019. 2019;9(278):2. [Google Scholar]
- 142.Shin S.E., Lim J.M., Koh H.G., Kim E.K., Kang N.K., Jeon S., et al. CRISPR/Cas9-induced knockout and knock-in mutations in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):1–15. doi: 10.1038/srep27810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Shanmugam S., Ngo H.H., Wu Y.R. Advanced CRISPR/Cas-based genome editing tools for microbial biofuels production: a review. Renew Energy. 2020;149:1107–1119. [Google Scholar]
- 144.Snyder J.C., Bateson M.M., Lavin M., Young M.J. Use of cellular CRISPR (clusters of regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) spacer-based microarrays for detection of viruses in environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010;76(21):7251–7258. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01109-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Li J., Tang Q., Li Y., Fan Y.Y., Li F.H., Wu J.H., et al. Rediverting electron flux with an engineered CRISPR-ddAsCpf1 system to enhance the pollutant degradation capacity of Shewanella oneidensis. Environ Sci Technol. 2020;54(6):3599–3608. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b06378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Tang L., Mao B., Li Y., Lv Q., Zhang L., Chen C., et al. Knockout of OsNramp5 using the CRISPR/Cas9 system produces low Cd-accumulating indica rice without compromising yield. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14832-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Stein H.P., Navajas-Pérez R., Aranda E. Approaches in bioremediation. Springer; Cham: 2018. Potential for CRISPR genetic engineering to increase xenobiotic degradation capacities in model fungi; pp. 61–78. [Google Scholar]
- 148.Wu J., Cheng Z.H., Min D., Cheng L., He R.L., Liu D.F., et al. CRISPRi system as an efficient, simple platform for rapid identification of genes involved in pollutant transformation by Aeromonas hydrophila. Environ Sci Technol. 2020;54(6):3306–3315. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b07191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Abdelrahman M., Al-Sadi A.M., Pour-Aboughadareh A., Burritt D.J., Tran L.S.P. Genome editing using CRISPR/Cas9-targeted mutagenesis: an opportunity for yield improvements of crop plants grown under environmental stresses. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2018;131:31–36. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.03.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Lou D., Wang H., Liang G., Yu D. OsSAPK2 confers abscisic acid sensitivity and tolerance to drought stress in rice. Front Plant Sci. 2017;8:993. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Shen C., Que Z., Xia Y., Tang N., Li D., He R., et al. Knock out of the annexin gene OsAnn3 via CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing decreased cold tolerance in rice. J Plant Bio. 2017;60(6):539–547. [Google Scholar]
- 152.Shi J., Gao H., Wang H., Lafitte H.R., Archibald R.L., Yang M., et al. ARGOS 8 variants generated by CRISPR-Cas9 improve maize grain yield under field drought stress conditions. Plant Biotechnol J. 2017;15(2):207–216. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Shimatani Z., Kashojiya S., Takayama M., Terada R., Arazoe T., Ishii H., et al. Targeted base editing in rice and tomato using a CRISPR-Cas9 cytidine deaminase fusion. Nat Biotechnol. 2017;35(5):441–443. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.McClintock B. Nobel lecture. The significance of response of the genome to challenge. Science. 1984;226:792–801. doi: 10.1126/science.15739260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Feschotte C. Transposable elements and the evolution of regulatory networks. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:397–405. doi: 10.1038/nrg2337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Vaschetto L.M. Modulating signaling networks by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated transposable element insertion. Curr Genet. 2018;64(2):405–412. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0765-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Mai G., Ge R., Sun G., Meng Q., Zhou F. A comprehensive curation shows the dynamic evolutionary patterns of prokaryotic CRISPRs. Biomed Res Int. 2016:2016. doi: 10.1155/2016/7237053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Yan Y., Zhang Y., Yang K., Sun Z., Fu Y., Chen X., et al. Small RNAs from MITE-derived stem-loop precursors regulate abscisic acid signaling and abiotic stress responses in rice. Plant J. 2011;65(5):820–828. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04467.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Jiang N., Wessler S.R. Insertion preference of maize and rice miniature inverted repeat transposable elements as revealed by the analysis of nested elements. Plant Cell. 2001;13(11):2553–2564. doi: 10.1105/tpc.010235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Jiang N., Bao Z., Zhang X., Hirochika H., Eddy S.R., McCouch S.R., et al. An active DNA transposon family in rice. Nature. 2003;21(6919):163–167. doi: 10.1038/nature01214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Singer T., McConnell M.J., Marchetto M.C., Coufal N.G., Gage F.H. LINE-1 retrotransposons: mediators of somatic variation in neuronal genomes? Trends Neurosci. 2010;33(8):345–354. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2010.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Molyneux S.D., Waterhouse P.D., Shelton D., Shao Y.W., Watling C.M., Tang Q.L., et al. Human somatic cell mutagenesis creates genetically tractable sarcomas. Nat Genet. 2014;46(9):964. doi: 10.1038/ng.3065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Hancock C.N., Zhang F., Floyd K., Richardson A.O., LaFayette P., Tucker D., et al. The rice miniature inverted repeat transposable element mPing is an effective insertional mutagen in soybean. Plant Physiol. 2011;157(2):552–562. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.181206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Cameron J., Holla Ø.L., Laerdahl J.K., Kulseth M.A., Ranheim T., Rognes T., et al. Characterization of novel mutations in the catalytic domain of the PCSK9 gene. J Intern Med. 2008;263(4):420–431. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2007.01915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Zhang F. CRISPR/Cas9: prospects and challenges. Hum Gene Ther. 2015;26(7):409–410. doi: 10.1089/hum.2015.29002.fzh. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Khan F.A., Pandupuspitasari N.S., Chun-Jie H., Ao Z., Jamal M., Zohaib A., et al. CRISPR/Cas9 therapeutics: a cure for cancer and other genetic diseases. Oncotarget. 2016;7(32):52541. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Wu S.S., Li Q.C., Yin C.Q., Xue W., Song C.Q. Advances in CRISPR/Cas-based gene therapy in human genetic diseases. Theranos. 2020;10(10):4374. doi: 10.7150/thno.43360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]