Abstract
COVID-19 seems as global emergency, by infectious virus, caused respiratory illness like having symptoms of flue, sickness, headache, and difficulty in breathing. Within months the world has been transformed into new order, thousands of people died and many more are fallen ill due to COVID-19 outbreak. China was the first country to see the outbreak and the first country to control it. However, the disease has broken out in Europe, the Middle East, the United States and other places. The United States has the highest number of cases in the world.
Keywords: COVID-19, Environmental pollution, Transportation, Oil price
Graphical abstract
COVID-19 seems as global emergency, by infectious virus, caused respiratory illness like having symptoms of flu, sickness, headache, and difficulty in breathing. Within months the world has been transformed into new order, thousands of people died and many more are fallen ill due to COVID-19 outbreak. China was the first country to see the outbreak and the first country to control it. However, the disease has broken out in Europe, the Middle East, the United States and other places. The United States has the highest number of cases in the world (Acter et al., 2020). There are certain precautionary measures introduced by the WHO to reduce the spread of COVID-19 (Wang et al., 2020). Correspondingly, covering the face, use of sanitizers containing appropriate concentration of alcohol, avoiding close contact by maintaining at least 3 ft distance, social distancing, and staying home or quarantining own self by the safety of yourself and for humanity.
Globally there is health emergency, and vast shutdown that is necessary to fight with COVID-19, global trade is disrupted by the shutdown of flights and all types of transportation and closed industries has profound effects on environments. Global pandemic converts into global financial recession, shuttering industries, and financial market reeling in developing as well as developed countries. According to IMF reports, global economy is expected to shrink up to 3% during the second half quarter of 2020 and predicted to rebound in 2021. The World Bank foresees global economy by concluding will be losing $9 trillion in the output of COVID-19. Considering global lockdown, streets of China are deserted, in Italy most extensive travelling restriction are in place since World War II. Worldwide aviation industry buckles and local transportations are being canceled. It seems too difficult to obey all these orders but all these changes have led some unexpected consequences. Several environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, play an important role in the sustainability of global health. Since December 2019, the world has been faced severe acute respiratory infectious diseases like COVID-19, human CoVs shown seasonal patterns (Kroumpouzos et al., 2020). According to an estimation around 4.2 million people are killed by outdoor pollution worldwide (Piqueras and Vizenor, 2016). Moreover, pollution particulates PM2.5 comprises many greenhouse gasses, water vapors weaken the human immunity against health diseases. This was an alarming situation before the outbreak of COVID-19, but now ozone layer and environment healing itself. Some geographical locations have shown less exposure rate in COVID-19 especially in South Asian countries. There are four hypotheses suggested by social scientist listed below;
-
•
Environmental influence theory
-
•
Greater general immunity
-
•
Immunological vulnerability
-
•
Governmental policies for public health during pandemic situation
According to social scientists these factors actively predict the vulnerability of pandemics, among all of them environmental factors contribute mainly.
As we know that industry, business and transportation are locked down so there is considerable emission in greenhouse gases especially in CO2. Just in New York, 50% reduction in pollution just because of the measures to contain the corona virus. In China the world industrious city, CO2 emission fell up to 25% and reduction of 40% coal fuel from China's sixth largest power plants; reports published by the Ministry of Environment and Ecology (Piqueras and Vizenor, 2016). Images captured by satellites over European region shows that there is considerable reduction in emission of NO2.
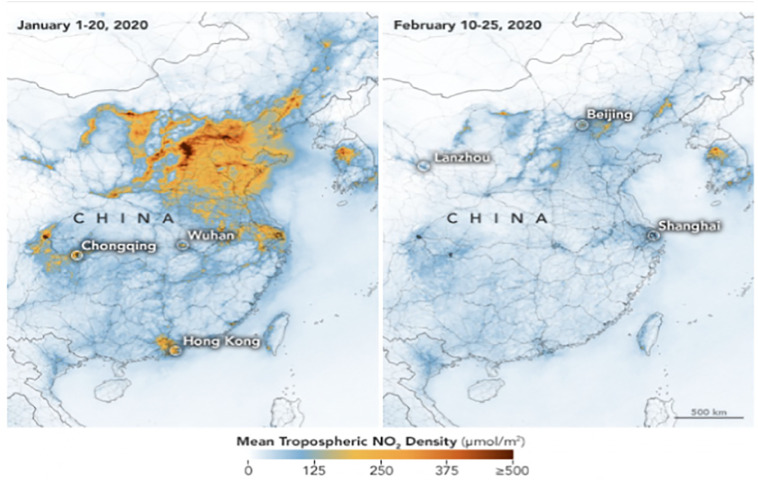
There are many reasons behind the drop of emission level of greenhouse gas. We have to think about when will this pandemic subsides, will all these pollutants bounce back or changes that we have seen today are more persistent and lasting. Many countries are easing lockdown and following smart lockdown policies to sustain the economies. Only 23% of global carbon emission took place by the transportation, driving and aviation contributes almost 72% and 11% in greenhouse gas emissions, respectively (Sohrabi et al., 2020). Some NASA images show that there is significant pollution drop due to COVID-19, especially in China as shown in Fig. 1 .
Fig. 1.
NASA image showing dramatic decline in pollution level over China amid COVID-19 lockdown (Photograph: Nasa Handout/EPA-copyright- Nasa’s Goddard space flight centre/The Guardian).
More interestingly, once again waters of Venice are clean in Italy, because the tourist number is culled. Researchers have found that there is significant reduction in the emission of methane and air quality of New York City is improved by 5–10%. Moreover, in some of the region there is 50% reduction in the emission of CO2 has been measured (Sohrabi et al., 2020). Although domestic energy consumption increases because more of people are staying at home, especially in the demand of internet quality. Surprisingly, some environment analyst and climate experts are predicting, COVID-19 affected countries soon will be able to meet 2015 Paris climate Accord. Huseyin Toros from Istanbul Technical University said that; “COVID-19 driving us towards the reduction of greenhouse gasses emission targeted by the Paris Agreement of International Climate Agreements”.
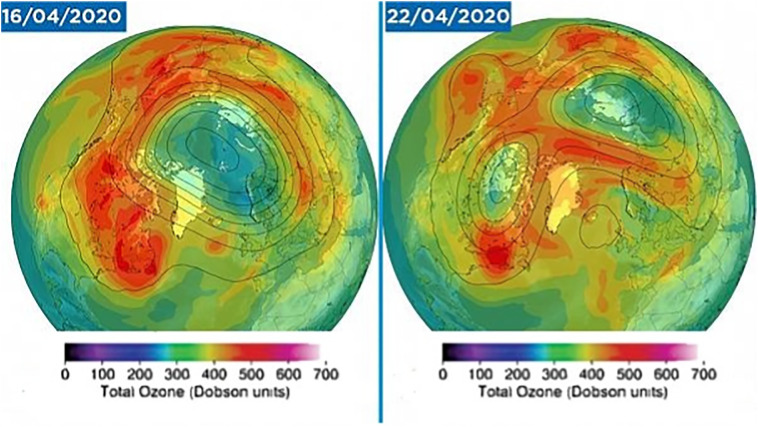
Moreover, quality of air improved over Istanbul, a heavily populated city of Turkey, by the reduction of particulate matter PM2.5 by 36% in the late of March. Similarly, ozone layer is healing after 33 years because of coronavirus outbreak. Recently, statistic revealed by UN world meteorological organization (WMO) shown that the biggest ozone hole over Arctic of an area of 20 million km2 has now closed as shown in Fig. 2 . The scientist and researchers dotted signs in the late March 2020 of the forming of rare hole, being resulted due to low temperature at North Pole. We are well aware that ozone layer protects the Earth from ultraviolet radiation (UV), which seems to be a main cause of the skin cancer. The hole had become a direct threat to the humans if it had of moved, further south towards populated-areas. On Thursday April 23, 2020, it was announced by Copernicus — the EU's earth monitoring programme that the hole had now closed. However, the closing has not played significant role with the reduction in the pollution due to lockdown during this pandemic of COVID-19.
Fig. 2.
Largest hole in the ozone layer over Arctic is finally closed as announced by the EU's earth monitoring programme (Copyright Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service ECMWF).
In 1987, a Montreal protocol was signed by 197 countries in which they ensure the reduction of harmful elements such as CFCs for the protection of ozone layer. Healing of ozone layer can also sustain the climatic conditions of environment, such as decrease in global temperature, rain falling patterns, and storms. Rate of natural photosynthesis is increased by the reduction of particulates and improved air quality globally. Leaves are more responsive to solar light without the involvement of particulates, harmful oxides, sulfides, etc. sulfuric acid that is a leading agent as harmful pollutant for the surface of plant leaves. Most probably, now rains drops are purer and cleaner as in pre-industrial era without acidity.
Last year we have seen worst wild forest fire in Australia, Indonesia, South East Asia, Brazilian Amazon, Siberia fires, etc. Due to Australian bush fires we have seen second hottest year 2019, on record. These wild fires also release the CO2 emission level besides greenhouse gasses. And these released gasses from burning biomass will remain in environment over long distance, that will affect the quality of air more drastically. But due to transport lock down climate conditions improved surprisingly, that will lead to less chance of wild fires (Sohrabi et al., 2020).
Due to pandemic COVID-19 outbreak in Middle East and North Africa, there is sudden collapse in oil price. Due to global lock down, worldwide industry and transportation confinement leads towards the negative oil demands shocks the oil industry and prices (Awazu et al., 2020). This reduction in oil demands initially shock the labor community, most of the daily wages are jobless. Especially, in third world countries governments have to fight with COVID-19 besides hunger and poverty. According to an estimate global GDP is reduced by 2% due to COVID-19 measures. Moreover, spread COVID-19 hurt the level of regional investment and oil supply (Baldwin and di Mauro, 2020). On 20th March, a report published by the benchmark West Texas Intermediate shows that oil price reduces to the lowest rate of $22.39 per barrel after America-Iran War would incline towards another innovation drive (Acter et al., 2020). This new oil cycle will lead towards the worst situation for stakeholders, and transporters. Reduction in oil price shocks the world super power economy America, the S&P 500 predicted that the American economy going to face worst situation on Wall Street since after financial crises. Now world is going to see new world order, a bipolar world, like exploiter and exploited. Those countries who will survive from COVID-19 will become world leading power. This is not the cycle that will end after several time period and recover, but we have to adjust ourselves in new reconstruct cycle that is new normal.
In short, we can conclude from all above discussion, we are moving step forward towards green world with 0.3% drop in global emission of CO2 after the crash of 2009 (Baldwin and di Mauro, 2020). All this happen cause of COVID-19 measures including confinement of local transport and aviation sector. According to climate analysts, COVID-19 is just like “blessing in disguise” for postmodern world with the improvement of air quality for next generation. But no one wants to lower the emission of CO2 in this way. Because COVID-19 has taken global grim toll on mental lives, health, lives and jobs. This article is a way forward for the socio-economic researchers to think about sustainable environment by interlinking different parameters in a chain. It's time to educate the people and aware them the global health, sustainability of the green environment by confining the amount of CO2 emission and controlling carbon foot.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Muhammad Bilal Tahir:Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing - original draft, Writing - review & editing.Amber Batool:Methodology, Data curation, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing - review & editing.
Declaration of competing interest
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Editor: Pavlos Kassomenos
References
- Acter T., Uddin N., Das J., Akhter A., Kim S. Evolution of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2(SARS-CoV-2) as coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic:A global health emergency. Sci. Total Environ. 2020;730:138996. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awazu P.B.-M.D.-L., Da Silva P., Svartzman F.S.-R. 2020. The Green Swan. [Google Scholar]
- Kroumpouzos G., Gupta M., Jafferany M., Lotti T., Sadoughifar R., Sitkowska Z., Goldust M. COVID-19: a relationship to climate and environmental conditions? Dermatol. Ther. 2020:e13399. doi: 10.1111/dth.13399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piqueras P., Vizenor A. Policy Brief for GSDR. 2016. The rapidly growing death toll attributed to air pollution: a global responsibility; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Sohrabi C., Alsafi Z., O’Neill N., Khan M., Kerwan A., Al-Jabir A.…Agha R. World Health Organization declares global emergency: A review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) International Journal of Surgery. 2020;76:71–76. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.02.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin R., di Mauro B. Weder. 2020. Mitigating the COVID Economic Crisis: Act Fast and Do Whatever It Takes. [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Horby P.W., Hayden F.G., Gao G.F. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):470–473. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30185-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]