Abstract
Objective
To evaluate whether video visits were being used as substitutes to clinic visits prior to COVID-19 at our institution's outpatient urology centers.
Methods
We reviewed 600 established patient video visits completed by 13 urology providers at a tertiary academic center in southeast Michigan. We compared these visits to a random, stratified sample of established patient clinic visits. We assessed baseline demographics and visit characteristics for both groups. We defined our primary outcome (“revisit rate”) as the proportion of additional healthcare evaluation (ie, office, emergency room, hospitalization) by a urology provider within 30 days of the initial encounter.
Results
Patients seen by video visit tended to be younger (51 vs 61 years, P <.001), would have to travel further for a clinic appointment (82 vs 68 miles, P <.001), and were more likely to be female (36 vs 28%, P = .001). The most common diagnostic groups evaluated through video visits were nephrolithiasis (40%), oncology (18%) and andrology (14.3%). While the 30-day revisit rates were higher for clinic visits (4.3% vs 7.5%, P = .01) primarily due to previously scheduled appointments, revisits due to medical concerns were similar across both groups (0.5% vs 0.67%; P = .60).
Conclusions
Video visits can be used to deliver care across a broad range of urologic diagnoses and can serve as a substitute for clinic visits.
Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, the use of video visits to care for patients from their home has grown exponentially for non-urgent issues.1 Although video visits–live simultaneous audio and visual interactions with patients conducted via videoconferencing platforms–are not new, loosened federal and state regulations have accelerated their expansion during this national emergency.2 For instance, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid removed the originating site requirement, meaning all patients, established and new, are now allowed to engage in telehealth from their homes regardless of geographic location.3 , 4 Complementing these national policies, many state-specific changes are permitting Medicaid patients to receive more care from home and providers to practice across state lines.5 Both federal and state regulatory and reimbursement policies previously cited as barriers to wide-spread telehealth use have been relaxed in an effort to sustain social distancing and mitigate the spread of COVID-19 while continuing to deliver care.6, 7, 8
Prior studies have shown that video visits are safe, cost-effective, and appealing to patients in primary and specialty care settings.9 Within urology, previous research has demonstrated the benefits of telehealth for patients, namely decreased travel time, lower costs, and increased convenience.10, 11, 12, 13, 14 However, it is largely unknown whether video visits in urology can serve as a substitute for clinic evaluations. This critical knowledge gap amplifies uncertainty for policymakers, providers, and healthcare administrators who must understand the downstream impact of widespread video visit adoption. For example, it is plausible that the use of video visits increases overall healthcare utilization, particularly if the visits set the stage for inadequate evaluations of the patient, or if the patient perceives the visit as insufficient and requires a second in-person encounter. Ashwood et al found that virtual visits, including video, were less costly for health systems based on claims data but increased overall healthcare utilization—leading to increased healthcare spending.15 Conversely, urologic video visits may make healthcare delivery more efficient by directly substituting for clinic visits for patients where the physical examination will not impact decision making. In a prospective observational study of on-demand video visits in an academic center emergency room, nearly three-quarters of patients felt their concerns were addressed using telehealth without seeking further evaluation in a doctor's office, urgent care, or emergency room.16
We hypothesized that these visits served as substitutes for clinic encounters, without requiring an additional in person evaluation within 30 days. To answer this question, we evaluated our video experience up to February 2020, a month before COVID-19 was declared a national emergency reducing restrictions on which patients can be evaluated and managed using telehealth.17 , 18 We aim to use pre-COVID-19 data to inform providers, payers, and policymakers on video visits were used by urologists prior to the pandemic and inform how they can continue being used in the future.
METHODS
We performed a retrospective study of the video visit program in the Department of Urology at a single institution from July 11, 2016 to February 4, 2020. Study exemption was obtained from the institutional review board (HUM00141665). We included all patients who completed a video visit during the study period. These visits were performed by eleven urologists and two urology physician assistants. Patients were offered video visits if it was determined that an in-person physical examination would not impact clinical management. All video visits were performed using a Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)-compliant, video communication system integrated into the EPIC™ electronic medical record (EMR). Scheduling of telehealth visits varied from provider to provider. Some providers elected to schedule their visits in blocks, whereas some providers had these visits interspersed throughout their schedule. Our control group comprised an equal number of randomly selected established patients who completed a clinic visit. To reduce clinical differences between our study and control group, we only included encounters from the study period and matched our control population by selecting in-person visits at a 1:1 ratio with each provider's video visit volume. To accurately understand baseline characteristics and outcomes of video visit encounters, we only included video visits conducted prior to the COVID-19 pandemic. While we have performed many more video visits during the pandemic, these visits were excluded because the extraordinary nature of the pandemic would confound the assessment of our primary outcome.
Our tertiary care institution, Michigan Medicine, and satellite clinics are located in Southeastern Michigan and serve urban, suburban, and rural populations across the state of Michigan, as well as neighboring states. We collected demographic information, including gender, age, and insurance coverage through an EMR-based report. We estimated roundtrip distance between each patient's hometown and the clinic their providers are located in using Google Maps and obtained city-based income estimates through Data USA. We also collected data on primary diagnosis code for their follow-up visit which we used to categorize visits into clinical groups including general urology, oncology, andrology, female pelvic medicine and reconstructive surgery; diagnoses such as nephrolithiasis and lower urinary tract symptoms; and symptoms without a final diagnosis such as genitourinary pain, imaging findings, and other (Appendix I).
Our primary outcome was revisit rate defined as an in-person evaluation within 30 days of the patient's initial visit by any urologist or urology advanced practice provider. We included clinic, emergency room, and in-patient hospitalization encounters in our evaluation. We excluded telephone calls because of the inconsistency in documentation and common use of telephone calls for informal updates and sharing of information that is not billed or reimbursed. During data analysis, we identified a secondary outcome of interest when we found that a majority of revisits after video and clinic encounters were due to previously scheduled appointments or clinic procedures. We hypothesized that there would be no difference in revisits that were scheduled due to a medical concern from either a patient or provider.
A secondary outcome was the clinically relevant revisit rate defined as an in-person evaluation within 30 days of the patient's initial visit by any urologist or urology advanced practice provider due to new or persistent medical concern. Through review of EMR documentation, we differentiated previously scheduled appointments from clinically relevant revisits. Chi-Squared (χ2) test or Wilcoxon rank test was used identify differences in demographic characteristics. Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel (CMH) test was used to identify differences in revisit and clinically relevant revisit rates due to the stratification of clinic visits by provider.19 The data analysis for this paper was generated using SAS software, Version 9.4 of the SAS System for Windows. Copyright 2013 SAS Institute Inc.
RESULTS
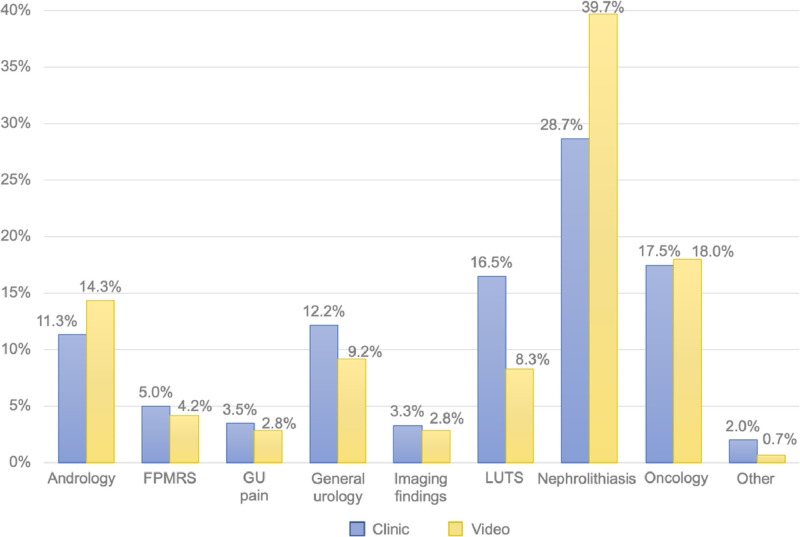
Between July 11, 2016 and February 4, 2020, we identified a total of 600 completed video visits and compared them to 600 clinic visits stratified by provider. The median age of patients using video visits was 51, ranging from 18 to 95 years of age, compared to a median age of 61, ranging from 19 to 95, for clinic visits (P <.0001). Thirty-six percent of video visit patients self-identified as women, compared to 28% of patients participating in clinic encounters (P = .0013). The median roundtrip estimated travel distance for video visit patients was 82 miles and ranged from 0 to 1548 miles. This was greater than the median estimated distance of 68 miles, ranging from 0 to 3686 miles, traveled by patients seen in clinic (P <.0001). Insurance coverage also differed between these 2 groups with higher rates of commercial insurance coverage for patients using video visits (81.2% vs 54.7%, P <.001). There was no difference in the median income of patients’ hometowns (Table 1 ). There were 114 (19%) postoperative video visits compared to 113 (18.8%) postoperative clinic visits (P = .94). A wide variety of urologic conditions were seen across video and clinic visits. The most common diagnostic groups seen through video visits included nephrolithiasis (39.7%), oncology (18%) and andrology (14.3%). For clinic visits, nephrolithiasis (28.7%), oncology (17.5%), and lower urinary tract symptoms (16.5%) made up the largest proportion of encounters (Fig. 1 ).
Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of video and clinic visits
| Video Visit |
Clinic Visit |
P Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | IQR | Median | IQR | Wilcoxon Test | |
| Age, years | 51 | 36-62 | 61 | 45-71 | <.0001 |
| Distance, miles (max) | 82 (1548) | 36-228 | 68 (3686) | 34-128 | <.0001 |
| Median Income | $53,237 | $39,000-$68,403 | $54,722 | $37,037-$63,876 | .53 |
| n (%) | n (%) | P Value (χ2) | |||
| Gender | .0013 | ||||
| Woman | 218 (36%) | 166 (28%) | |||
| Man | 382 (64%) | 434 (72%) | |||
| Insurance | <.0001 | ||||
| Commercial | 487, 81.2% | 328, 54.7% | |||
| Medicare | 81, 13.5% | 166, 27.7% | |||
| Medicare Advantage | 14, 2.3% | 64, 10.7% | |||
| Medicaid | 10, 1.7% | 37, 6.2% | |||
| Self-pay | 7, 1.2% | 0, 0% | |||
| Military | 1, 0.2% | 5, 0.8% | |||
Figure 1.
Categorization of urologic diagnoses managed through video or clinic visits. (Color version available online.)
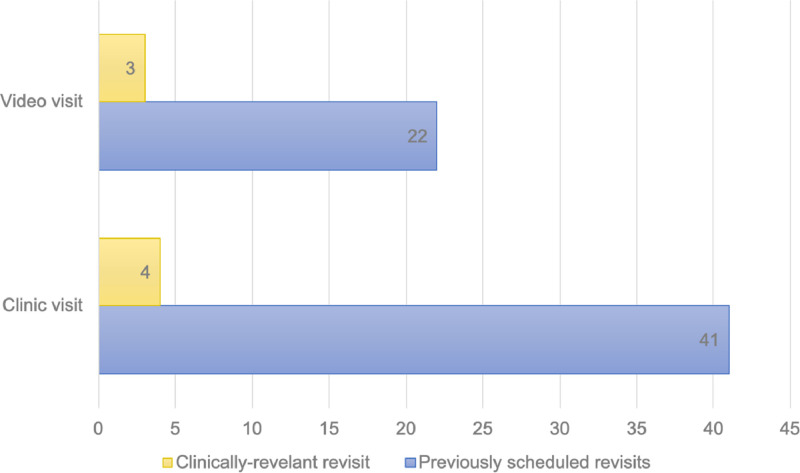
The revisit rate was lower for video visits compared to clinic visits over our study period. Twenty-six patients were seen within 30 days after their video visit (4.3%) compared to 45 patients after a clinic encounter (7.5%, CMH P = .01). There were no ED visits or hospitalizations within 30 days of either video or clinic visits. However, the clinically relevant revisit rate was similar across both groups (0.5% of video visits and 0.67% of clinic visits, CMH P = .60; Fig. 2 ). For video visits, there were 3 repeat evaluations driven by medical concerns. These occurred after post-operative follow-up visits and included a wound check and concerns about post-operative pain. None required further testing or treatment after in-person evaluation. For clinic visits, there were four clinically relevant revisits which included superficial skin infections, flank pain, and peristomal rash. Similarly, these occurred after postoperative clinic visits. None required further testing and one superficial skin infection was treated with oral antibiotics. The remaining revisits that occurred across both groups included scheduled appointments for subspecialist urologic follow-up, clinic procedures, or nursing appointments for clean intermittent catheterization or foley catheter management.
Figure 2.
Number of revisits within 30 days of initial encounter. (Color version available online.)
DISCUSSION
In this study, patients using video visits tended to be younger, would have to travel further for a clinic appointment, and were more likely to be female. As expected, the vast majority of patients using video visits had commercial insurance coverage based on telehealth parity laws that allowed for coverage and reimbursement Providers conducted and completed video visits across a broad range of urologic conditions and there was no difference in the number of post-operative visits across groups. While the 30-day revisit rate was higher after clinic visits, there was no difference in the rate of clinically relevant revisits. Together, these findings suggest that urological video visits can safely substitute in-person visits when providers chose what patients are appropriate for telehealth evaluation and management.
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services originating site requirement was in place and a major barrier to the use of video visits with Medicare beneficiaries, who are 65 and older.20 Furthermore, in the state of Michigan, commercial payers cover and reimburse video visits at similar rates to clinic visits. This combination of state and federal policies in part explains why video visit users tended to be younger and the vast majority had commercial insurance coverage.21 In addition, patients had the option to use a hospital-based, flat fee schedule when video visits were not covered by their insurance. Prior researchers have demonstrated the value of urologic video visits in an outpatient setting and studies have confirmed that telehealth is not only a safe alternative to urologic clinic visits but also cost-effective, more efficient for patients, and with high patient satisfaction.10 , 22, 23, 24 While the overall revisit rate for clinic encounters was higher than video visits in our study, this difference was primarily driven by previously scheduled appointments. When we compared the clinically relevant revisit rate, we found no difference between video and clinic visits. These findings suggest that at least for 30 days after their initial encounter, video visits provide equal level of care as clinic visits when clinicians account for the impact of the physical examination on decision making.
Our study does have several limitations. First, this was a single institution and single specialty study in an outpatient setting. These results are therefore not generalizable to inpatient care, emergency urological care, or other outpatient specialty clinics, especially in scenarios where physical examination findings will inform decision-making. Second, we evaluated whether patients returned for a urologic visit within 30 days at our institution. This may not capture urologic issues addressed by primary care physicians, healthcare providers outside of our institution, or medical issues that arise more than 30 days after a visit. Third, the case-control design has inherent selection bias. While we attempted to reduce clinical differences by matching controls by provider, a randomized control trial is the optimal study design for this research question.
These limitations notwithstanding, our finding that video visits can serve as substitutes for clinic visits across a spectrum of urologic conditions should help mitigate provider concerns about using video visits during and after the COVID-19 pandemic. Relevant to payers, these results demonstrate that video visits are safe ways for patients to be managed by their providers without increasing overall healthcare utilization. For policymakers, this data should be used to advocate for upholding the current changes in health policy that allow for equal reimbursement of video visits while allowing new patients to access providers virtually. The use of telehealth has expanded exponentially and will continue to do so during the COVID-19 pandemic.1 Future research should evaluate whether the low proportion of patients requiring in-person evaluation extends beyond 30 days, which conditions are more or less suited for telehealth, and how this medium can mitigate or perpetuate health disparities. Patient-specific barriers to telehealth use such as computer or smartphone access, internet coverage, and digital literacy disproportionately impact low socioeconomic groups, people of color, and the elderly.25 If not all patients are able to participate in video visits, different strategies such as reimbursing for phone visits may need to be explored. Furthermore, with the expansion of telehealth services to new patients during COVID-19, researchers must evaluate the impact on access to urologic care especially given existing concerns about workforce shortage issues and impact of rurality on access to specialty care.26 , 27
CONCLUSION
Video visits can be used to deliver care across a broad range of urologic diagnoses and can serve as a substitute for clinic visits.
Footnotes
Financial Disclosure:The authors declare that they have no relevant financial interests.
Support:Dr. Ellimoottil's research is supported by the Telehealth Research Incubator project grant (MPrOVE Research Challenge Grant) but these funds were not required for completion of this project.
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found in the online version at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2020.05.080.
Appendix. SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
References
- 1.Mehrotra A, Ray K, Brockmeyer DM, Barnett ML, Bender JA. Rapidly converting to “virtual practices”: outpatient care in the era of COVID 19. NEJM Catal. 2020 doi: 10.1056/CAT.20.0091. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gadzinski AJ, Ellimoottil C, Odisho AY, Watts KL, Gore JL. Telemedicine in urology: a crash course during the COVID-19 pandemic. https://www.urologytimes.com/coronavirus/telemedicine-urology-crash-course-during-covid-19-pandemic. Published 2020. Accessed March 31, 2020.
- 3.CMS. Physicians and Other Clinicians : CMS Flexibilities to Fight COVID-19; 2020. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/covid-19-physicians-and-practitioners.pdf.
- 4.The White House. Proclamation on Declaring a National Emergency Concerning the Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Outbreak. White House Proclamations.https://www.whitehouse.gov/presidential-actions/proclamation-declaring-national-emergency-concerning-novel-coronavirus-disease-covid-19-outbreak/. Published 2020. Accessed 5 April 2020.
- 5.Center for Connected Health Policy. COVID-19 Related State Actions. CCHP Telehealth Policy. https://www.cchpca.org/resources/covid-19-related-state-actions. Published 2020. Accessed 5 April 2020.
- 6.Bootsma MCJ, Ferguson NM. The effect of public health measures on the 1918 influenza pandemic in U.S. cities. Chowell G, ed. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2007;104:7588–7593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611071104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gavin K. Flattening the Curve for COVID-19: What Does It Mean and How Can You Help? Michigan Health Lab.https://healthblog.uofmhealth.org/wellness-prevention/flattening-curve-for-covid-19-what-does-it-mean-and-how-can-you-help. Published 2020. Accessed 5 April 2020.
- 8.Badalato GM, Kaag M, Lee R, Vora A, Burnett A, AUA telemedicine workgroup the role of telemedicine in urology: contemporary practice patterns and future directions. 2020. doi:10.1097/UPJ.0000000000000094 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 9.Gettman M, Rhee E, Spitz A. Telemedicine in urology. AUA White Pap. 2016:3081. http://www.auanet.org/guidelines/telemedicine-in-urology [Google Scholar]
- 10.Viers BR, Lightner DJ, Rivera ME. Efficiency, satisfaction, and costs for remote video visits following radical prostatectomy : a randomized controlled trial. Eur Urol. 2015;68:729–735. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Andino JJ, Guduguntla V, Weizer A. Examining the value of video visits to patients in an outpatient urology clinic. Urology. 2017:110. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2017.07.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nikolian VC, Williams AM, Jacobs BN. Pilot study to evaluate the safety, feasibility, and financial implications of a postoperative telemedicine program. Ann Surg. 2018;268:700–707. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Finkelstein JB, Cahill D, Kurtz MP. The use of telemedicine for the postoperative urological care of children: results of a pilot program. J Urol. 2019;202:159–163. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ellimoottil C, Andino JJ, Mukundi S. Telemedicine in urology. AUA Updat Ser Lesson. 2018;37:271–276. doi: 10.1097/UPJ.0000000000000094. 28. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ashwood JS, Mehrotra A, Cowling D, Uscher-Pines L. Direct-to-consumer telehealth may increase access to care but does not decrease spending. Health Aff. 2017;36:485–491. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2016.1130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sterling R, LeRouge C. On-demand telemedicine as a disruptive health technology: qualitative study exploring emerging business models and strategies among early adopter organizations in the United States. J Med Internet Res. 2019;21 doi: 10.2196/14304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Telemedicine Health Care Provider Fact Sheet; 2020.https://www.cms.gov/newsroom/fact-sheets/medicare-telemedicine-health-care-provider-fact-sheet. Accessed 7 April 2020.
- 18.Gadzinski AJ, Ellimoottil C, Odisho AY, Watts KL, Gore JL. Implementing telemedicine in response to the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic. J Urol. 2020;203 doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000001033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sato T. A further look at the Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel risk difference. Control Clin Trials. 1995;16:359–361. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(95)00004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Claims Processing Manual; 2019. https://www.cms.gov/Regulations-and-Guidance/Guidance/Manuals/Downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed 2 September 2019.
- 21.Andino JJ, Castaneda PR, Shah PK, Ellimoottil C. The impact of video visits on measures of clinical efficiency and reimbursement. Urol Pract. 2020 doi: 10.1097/UPJ.0000000000000149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ellimoottil C, Skolarus T, Gettman M. Telemedicine in urology: state of the art. Urology. 2015;94:10–16. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2016.02.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chu S, Boxer R, Madison P. Urologic care to remote clinics. Urology. 2015;86:255–261. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2015.04.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Thelen-Perry S, Ved R, Ellimoottil C. Evaluating the patient experience with urological video visits at an academic medical center. mHealth. 2018;4 doi: 10.21037/mhealth.2018.11.02. 54-54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Velasquez D, Mehrotra A. Ensuring the growth of telehealth during COVID-19 does not exacerbate disparities in care. Health Affairs Blog. doi:10.1377/hblog20200505.591306
- 26.Cohen AJ, Ndoye M, Fergus KB. Forecasting limited access to urology in rural communities: analysis of the American Urological Association Census. J Rural Heal. 2019;0:1–7. doi: 10.1111/jrh.12376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.American Urological Association. Physician workforce planning and graduate medical education. AUA Policy Statements. https://www.auanet.org/guidelines/physician-workforce-planning-and-graduate-medical-education. Published 2018. Accessed 21 April 2020.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.