Abstract
Objectives: Gout is the most common form of inflammatory arthritis and was found to be independently associated with incident dementia in the elderly. However, the associations between anti-gout preparations and dementia were not well-studied.
Methods: Data were collected from Taiwan's National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD). A 2005–2013 retrospective cohort study was conducted, and all investigated subjects were identified by International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 9th Revision, Clinical Modification. Conditional logistic regression was used to evaluate the odds ratio of dementia in relation to different gout preparations (benzbromarone, allopurinol, sulfinpyrazone, probenecid) and number of days of anti-gout preparation use, after adjustment for potential confounding variables.
Results: A total of 3,242 gout patients with and without dementia were selected from the NHIRD and included in the final analysis after 1:1 matching for age, gender, and diagnosis year of gout. In the anti-gout preparations, only use of Benzbromarone decreased the risk of dementia (adjusted OR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.68–0.97). The result of the subgroup analysis revealed a trend toward a lower risk of dementia with longer use of benzbromarone. Use of benzbromarone for ≥180 days showed a significantly lower risk of dementia (adjusted OR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.58–0.89). Moreover, the protective effect was more pronounced in males compared with females.
Conclusion: This cohort study reveals that gout patients taking benzbromarone are at a decreased risk of developing incident dementia, especially with longer use and in male. Further prospective trials are warranted to confirm our findings.
Keywords: gout, uric acid, dementia, benzbromarone, elderly
Introduction
Gout is the most common form of inflammatory arthritis that is caused by the deposition of monosodium urate crystals in and around the joints (1). It is characterized by hyperuricemia, with serum or plasma urate concentrations >6.8 mg/dL, which is the approximate limit of urate solubility (2). Gout may present with different disease manifestations, such as recurrent flares of inflammatory arthritis, chronic arthropathy, accumulation of urate crystals in the form of tophaceous deposits, and uric acid (UA) nephrolithiasis (3). In addition to acute inflammation and chronic UA stone formation, gout has also been associated with various comorbidities, such as diabetes, hypertension, chronic kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease (4). In a recent study, gout was found to be independently associated with a 17–20% higher risk of incident dementia in the elderly (5). The prevalence of gout is estimated to range from 2.5% in Europe to 3.9% in the United States (6, 7).
Dementia is an important public health problem that can be caused by Alzheimer's disease (60–70%), vascular dementia (20%), and other conditions such as Parkinson's disease (8). Moreover, dementia is associated with limited functional ability and decreased quality of life, which can lead to loss of independence and increased morbidity and mortality (9–11). Hence, since gout is associated with an increased risk of dementia, prevention, and treatment are important.
Treatment for gout includes pharmacological urate-lowering therapy (ULT) to prevent gout flare, tophi formation, and related comorbidities (12). Several classes of anti-inflammatory agents are effective for the treatment of gout flares, including systemic and intra-articular glucocorticoids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, colchicine, and biological agents that inhibit the action of interleukin-1β (3, 13). Following an acute flare, ULT usually includes xanthine oxidase inhibitors and uricosuric drugs, to achieve serum urate levels <6 mg/dL (<357 μmol/L), which is substantially below the urate solubility limit (12, 14, 15).
The drugs should be selected according to the cause of disease, comorbidities, and hepatic and renal functions. Xanthine oxidase inhibitor decreases the synthesis of uric acid by inhibiting the activity of xanthine oxidase. Commonly used drugs include allopurinol and febuxostat (2). Allopurinol, in adults, the starting dose is 50–100 mg/d, and the dose can be increased by 50–100 mg increments to a maximum dose of 600 mg/d in patients until the uric acid target is reached. The recommended dose is 50–100 mg/d for chronic kidney disease (CKD), stage 3 to 4, and is contraindicated in patients with CKD, stage 5 (16). Febuxostat is a selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase. The initial dose is 20–40 mg/d, which can be titrated gradually to a maximum of 80 mg/d if the serum uric acid target is not reached. Febuxostat has better safety in patients with renal insufficiency because it is cleared mainly via the liver (17).
The primary uricosuric drugs include probenecid, benzbromarone, and sulfinpyrazone. Benzbromarone increases urinary excretion of uric acid and the starting dose is 25–50 mg/d in adults, which should be adjusted to 75 or 100 mg/d according to the serum UA level (18). Benzbromarone can be used in patients with mild-to-moderate renal dysfunction. The recommended dose is 50 mg/d in patients with an eGFR of 20–60 ml·min−1·1.73 m−2 and is contraindicated in patients with an eGFR <20 ml·min−1·1.73 m−2 or uric acid nephrolithiasis. The most concern adverse reaction of benzbromarone is hepatic toxicity (19). Probenecid can be started by 250 mg twice daily for 1 week and may increase to a maximum of 2 g/day. Moreover, Probenecid is avoided use in patients with eGFR <30 mL/min (20, 21). Sulfinpyrazone is started at a dose of 50 mg twice daily, with increments over several weeks to 100 to 200 mg three or four times daily as needed. The maximum effective dose of sulfinpyrazone is 800 mg/day, and avoid be used in persons with CKD or a history of uric acid kidney stones (22).
Like the description above, gout may be associated with various comorbidities including dementia; however, it is unclear whether anti-gout preparations can reduce the incidence of dementia. Hence, in the present study, we enrolled gout patients (newly diagnosed from 2000 to 2008) from the Taiwan Nation Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD) to investigate the correlations of ULT and further dementia after at least 5 years from gout diagnosis.
Methods
Data Source
In 1995, Taiwan developed a health insurance system based on a single-payer government-run National Health Insurance (NHI) program, which currently includes comprehensive health care data for almost all Taiwanese citizens. The large, computerized databases that became the NHIRD were derived from this system by the Bureau of National Health Insurance and were maintained by the National Health Research Institutes, and include includes information about hospitalization, emergency care, and medical visits. These databases were used for research purposes, with a coverage rate >99% in 2010, and thus contains data for ~23 million beneficiaries (23).
The Longitudinal Health Insurance Research Dataset 2000 contains the clinical information of one million beneficiaries randomly selected from the NHIRD during the period from 2000 to 2013 (24). Moreover, the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 9th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) is used for the diagnosis by physicians. Patients' medical data include drug items, NHI code, dosage, frequency of use, and number of days prescribed. This information can be used to detecting drug interactions and potential duplicate medications when patients visit multiple hospitals. The NHI code corresponds to a code in the five-level Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical classification system recommended by the World Health Organization for studies on drug utilization (25).
Data Collection
We identified one million people from the database. We selected patients aged ≥50 years with newly diagnosed gout based on the ICD-9-CM code 274 and use of anti-gout preparations, allopurinol (NHI code: M04AA01), benzbromarone (NHI code: M04AB03), sulfinpyrazone (NHI code: M04AB02), or probenecid (NHI code: M04AB01), within 6 months from 2000 to 2008. Dementia was defined as a diagnosis with one or more of the following ICD-9-CM codes: 290.0–290.4, 294.1, and 331.0–331.2. Moreover, the diagnosis of dementia before the first gout diagnosis date was excluded.
Individuals were divided into two groups. The dementia group comprised individuals newly diagnosed with dementia at following ≥2 outpatient assessments or a single inpatient admission after diagnosis of gout and 5 years apart. The non-dementia (control) group comprised of individuals who had never been diagnosed with dementia after being diagnosed with gout. The index date was set at 5 years after taking anti-gout preparations. The ratio of patients in dementia to non-dementia groups was 1:1, with individual matching for age, gender, and gout diagnosis year.
Patient Subgroups
The age of the patients was defined on the index date. For the sex variable, zero represented female and one represented male. Baseline disease was diagnosed from two outpatient or one inpatient assessment 5 years before dementia diagnosis and included hypertension (ICD-9-CM = 401–405), hyperlipidemia (ICD-9-CM = 272.0–272.4), chronic liver disease (CLD; ICD-9-CM = 571), chronic kidney disease (CKD; ICD-9-CM = 585), diabetes (DM) (ICD-9-CM = 250), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD; ICD-9-CM = 491, 492, and 496), autoimmune disease (AD; ICD-9-CM =710, 714, and 720), cardiovascular disease (CVD; ICD-9-CM = 410–414), stroke (ICD-9-CM = 430–438), depression (ICD-9-CM = 296.2–3, 300.4, 311), and Parkinson's disease (PD; ICD-9-CM = 332). Patients with no comorbidities were represented by 0, and those who developed comorbidity were represented by 1. Moreover, use of warfarin (NHI code: B01AA03) or statins (NHI codes: C10AA01–05, 07–08) 5 years before dementia diagnosis were also included in the baseline characteristics.
Statistical Analysis
All analyses were performed using SAS version 9.1.3 for Windows (SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC). P-values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Kaplan–Meier analysis was applied to evaluate the cumulative incidence of dementia in the subgroups and log-rank test was to test for significance. Conditional logistic regression was used to evaluate the odds ratio (OR) of dementia in relation to different gout preparations, and number of days of anti-gout preparation use, after adjustment for potential confounding variables (allopurinol, benzbromarone, sulfinpyrazone, probenecid, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, CLD, CKD, DM, COPD, AD, CVD, stroke, warfarin, and statin). Subgroup analyses were performed by age (50–64 and ≥65 years) and gender.
Results
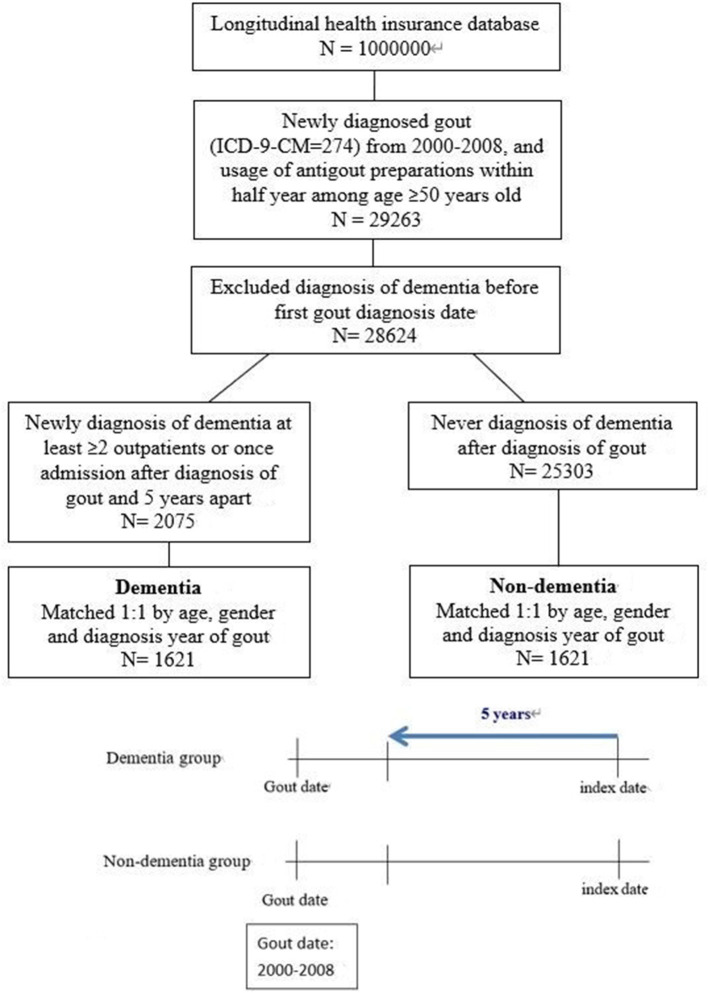
A total of 3,242 gout patients with and without dementia were selected from the NHIRD and included in the final analysis after 1:1 matching for age, gender, and diagnosis year of gout. A flowchart of the study population selection protocol is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
The study population selection protocol. Antigout preparations: use any one of Allopurinol, Benzbromarone, Sulfinpyrazone, and Probenecid.
Table 1 shows the demographic characteristics of the dementia and non-dementia group. The dementia group had higher prevalence of underlying disease include hypertension, DM, COPD, CVD, stroke, depression, and PD. Moreover, the dementia group had a higher prevalence of warfarin use and a similar prevalence of statin use compared with the non-dementia group. The most common anti-gout preparation used was benzbromarone (73.7% in the dementia group, 77.5% in the non-dementia group), followed by allopurinol (29.4% in the dementia group, 27% in the non-dementia group), sulfinpyrazone, and probenecid. Use of benzbromarone was significantly higher in the non-dementia group.
Table 1.
Demographic characteristics.
| Dementia (N = 1,621) | Non-dementia (N = 1,621) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | p-value | |
| Age | 1 | ||||
| 50–64 | 104 | 6.4 | 104 | 6.4 | |
| 65–79 | 920 | 56.8 | 920 | 56.8 | |
| ≥80 | 597 | 36.8 | 597 | 36.8 | |
| Mean ± SD | 76.9 ± 7.1 | 76.9 ± 7.1 | 1 | ||
| Gender | 1 | ||||
| Female | 651 | 40.2 | 651 | 40.2 | |
| Male | 970 | 59.8 | 970 | 59.8 | |
| Hypertension | 1375 | 84.8 | 1272 | 78.5 | <0.001 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 689 | 42.5 | 672 | 41.5 | 0.545 |
| Chronic liver disease | 332 | 20.5 | 302 | 18.6 | 0.184 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 223 | 13.8 | 171 | 10.5 | 0.005 |
| Diabetes | 638 | 39.4 | 538 | 33.2 | <0.001 |
| COPD | 516 | 31.8 | 411 | 25.4 | <0.001 |
| Autoimmune disease | 62 | 3.8 | 50 | 3.1 | 0.248 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 670 | 41.3 | 601 | 37.1 | 0.013 |
| Stroke | 760 | 46.9 | 357 | 22.0 | <0.001 |
| Depression | 285 | 17.6 | 75 | 4.6 | <0.001 |
| Parkinson's disease | 195 | 12.0 | 51 | 3.1 | <0.001 |
| Allopurinol | 476 | 29.4 | 438 | 27.0 | 0.138 |
| Benzbromarone | 1,195 | 73.7 | 1,256 | 77.5 | 0.013 |
| Sulfinpyrazone | 72 | 4.4 | 64 | 3.9 | 0.483 |
| Probenecid | 18 | 1.1 | 10 | 0.6 | 0.129 |
| Warfarin | 96 | 5.9 | 65 | 4.0 | 0.012 |
| Statin | 631 | 38.9 | 591 | 36.5 | 0.147 |
| Gout year | 1 | ||||
| 2000 | 539 | 33.3 | 539 | 33.3 | |
| 2001 | 328 | 20.2 | 328 | 20.2 | |
| 2002 | 247 | 15.2 | 247 | 15.2 | |
| 2003 | 178 | 11.0 | 178 | 11.0 | |
| 2004 | 124 | 7.6 | 124 | 7.6 | |
| 2005 | 90 | 5.6 | 90 | 5.6 | |
| 2006 | 61 | 3.8 | 61 | 3.8 | |
| 2007 | 36 | 2.2 | 36 | 2.2 | |
| 2008 | 18 | 1.1 | 18 | 1.1 | |
| Study period (years) | 7.8 ± 2.4 | 7.8 ± 2.4 | 0.917 | ||
COPD, Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Table 2 shows the conditional logistic regression of risk of dementia. After adjusting for confunding factors, patients with underlying DM (OR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.03–1.43), COPD (OR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.10–1.55), and stroke (OR, 2.76; (95% CI, 2.35–3.24) showed an increased risk of dementia. Moreover, use of benzbromarone decreased the risk of dementia (adjusted OR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.68–0.97).
Table 2.
Conditional logistic regression of risk of dementia.
| Crude OR | 95% C.I. | p-value | Adjusted OR† | 95% C.I. | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allopurinol | 1.13 | 0.97–1.32 | 0.130 | 1.02 | 0.86–1.22 | 0.809 |
| Benzbromarone | 0.82 | 0.70–0.96 | 0.013 | 0.81 | 0.68–0.97 | 0.021 |
| Sulfinpyrazone | 1.13 | 0.80–1.59 | 0.487 | 1.27 | 0.88–1.85 | 0.205 |
| Probenecid | 1.80 | 0.83–3.90 | 0.136 | 1.60 | 0.69–3.7 | 0.273 |
| Hypertension | 1.56 | 1.29–1.87 | <0.001 | 1.20 | 0.97–1.47 | 0.087 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 1.04 | 0.91–1.20 | 0.543 | 0.96 | 0.80–1.16 | 0.704 |
| Chronic liver disease | 1.13 | 0.95–1.34 | 0.183 | 1.05 | 0.87–1.28 | 0.591 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 1.36 | 1.10–1.68 | 0.005 | 1.20 | 0.94–1.51 | 0.137 |
| Diabetes | 1.31 | 1.13–1.52 | <0.001 | 1.21 | 1.03–1.43 | 0.021 |
| COPD | 1.40 | 1.20–1.65 | <0.001 | 1.31 | 1.10–1.55 | 0.003 |
| Autoimmune disease | 1.26 | 0.86–1.84 | 0.245 | 1.27 | 0.84–1.92 | 0.257 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 1.19 | 1.04–1.37 | 0.014 | 1.01 | 0.86–1.19 | 0.879 |
| Stroke | 2.91 | 2.49–3.40 | <0.001 | 2.76 | 2.35–3.24 | <0.001 |
| Depression | 4.44 | 3.37–5.87 | <0.001 | 3.45 | 2.57–4.63 | <0.001 |
| Parkinson's disease | 4.20 | 3.03–5.81 | <0.001 | 2.88 | 2.02–4.10 | <0.001 |
| Warfarin | 1.53 | 1.10–2.12 | 0.012 | 1.17 | 0.82–1.67 | 0.388 |
| Statin | 1.11 | 0.96–1.29 | 0.141 | 0.94 | 0.77–1.14 | 0.515 |
COPD, Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Adjusted for allopurinol, benzbromarone, sulfinpyrazone, probenecid, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, chronic liver disease, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, COPD, autoimmune disease, cardiovascular disease, stroke, depression, parkinson's disease, warfarin, and statin.
The result of the subgroup analysis of anti-gout preparations divided by the number of days of use revealed a trend toward a lower risk of dementia with longer use of benzbromarone. Use of benzbromarone for ≥180 days showed a significantly lower risk of dementia (adjusted OR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.58–0.89) (Table 3). Moreover, the protective effect of benzbromarone on dementia differed among the different age groups (Table 4). In adults aged 50–64 years, benzbromarone use lowered the risk of dementia with use for <90 days (adjusted OR, 0.21; 95% CI, 0.06–0.76), and use for ≥180 days (adjusted OR, 0.21; 95% CI, 0.06–0.76). In the elderly (≥65 years), benzbromarone use for ≥180 days decreased the risk of dementia (adjusted OR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.59–0.92). Table 5 shows the different odd ratios in males and females. Both males and females showed a trend toward a decreased risk of dementia with longer use of benzbromarone. However, only use for ≥180 days showed a significant OR. Moreover, the protective effect was more pronounced in males (adjusted OR, 0.68) compared with females (adjusted OR, 0.72).
Table 3.
Conditional logistic regression of risk of dementia divided by anti-gout preparations use days.
| N | No. of dementia | Crude OR | 95% C.I. | p-value | Adjusted OR† | 95% C.I. | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allopurinol (days) | ||||||||
| None | 2,328 | 1,145 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| <90 | 383 | 191 | 1.03 | 0.83–1.28 | 0.790 | 0.95 | 0.74–1.21 | 0.663 |
| 90–179 | 118 | 68 | 1.40 | 0.97–2.03 | 0.076 | 1.48 | 0.97–2.25 | 0.067 |
| ≥180 | 413 | 217 | 1.15 | 0.93–1.42 | 0.200 | 1.06 | 0.82–1.36 | 0.659 |
| Benzbromarone (days) | ||||||||
| None | 791 | 426 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| <90 | 959 | 487 | 0.89 | 0.74–1.07 | 0.215 | 0.95 | 0.77–1.17 | 0.602 |
| 90–179 | 392 | 200 | 0.89 | 0.70–1.14 | 0.368 | 0.85 | 0.64–1.12 | 0.238 |
| ≥180 | 1,100 | 508 | 0.73 | 0.61–0.88 | 0.001 | 0.72 | 0.58–0.89 | 0.002 |
| Sulfinpyrazone (days) | ||||||||
| None | 3,106 | 1,549 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| <90 | 57 | 30 | 1.11 | 0.66–1.87 | 0.691 | 1.34 | 0.74–2.43 | 0.335 |
| ≥90 | 79 | 42 | 1.14 | 0.73–1.80 | 0.564 | 1.41 | 0.84–2.35 | 0.194 |
| Probenecid | ||||||||
| None | 3,214 | 1,603 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 28 | 18 | 1.80 | 0.83–3.90 | 0.136 | 1.68 | 0.73–3.89 | 0.224 |
Adjusted for allopurinol, benzbromarone, sulfinpyrazone, probenecid, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, chronic liver disease, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, COPD, autoimmune disease, cardiovascular disease, stroke, depression, parkinson's disease, warfarin, and statin.
Table 4.
Conditional logistic regression of risk of dementia divided by anti-gout preparations use days in different age group.
| N | No. of dementia | Crude OR | 95% C.I. | p-value | Adjusted OR† | 95% C.I. | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Age
=
50–64 (years) Allopurinol (days) |
||||||||
| None | 160 | 76 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| <90 | 23 | 14 | 1.76 | 0.69–4.5 | 0.235 | 4.51 | 1.05–19.4 | 0.043 |
| 90–179 | 10 | 5 | 1.05 | 0.3–3.67 | 0.936 | 5.15 | 0.47–56.74 | 0.181 |
| ≥180 | 15 | 9 | 1.68 | 0.54–5.19 | 0.367 | 1.72 | 0.28–10.41 | 0.557 |
| Benzbromarone (days) | ||||||||
| None | 51 | 32 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| <90 | 59 | 27 | 0.51 | 0.23–1.13 | 0.099 | 0.21 | 0.06–0.76 | 0.018 |
| 90–179 | 27 | 14 | 0.62 | 0.24–1.59 | 0.318 | 0.90 | 0.24–3.33 | 0.878 |
| ≥180 | 71 | 31 | 0.45 | 0.21–0.98 | 0.045 | 0.23 | 0.07–0.79 | 0.019 |
| Sulfinpyrazone | ||||||||
| None | 200 | 100 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 8 | 4 | 1.00 | 0.25–4.00 | 1.000 | 0.48 | 0.07–3.48 | 0.469 |
| Probenecid | ||||||||
| None | 207 | 104 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 1 | 0 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
|
Age
≥65 (years) Allopurinol (days) |
||||||||
| None | 2,168 | 1,069 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| <90 | 360 | 177 | 1.00 | 0.79–1.25 | 0.977 | 0.91 | 0.71–1.18 | 0.475 |
| 90–179 | 108 | 63 | 1.43 | 0.97–2.11 | 0.070 | 1.41 | 0.91–2.18 | 0.122 |
| ≥180 | 398 | 208 | 1.13 | 0.91–1.40 | 0.274 | 1.03 | 0.80–1.34 | 0.796 |
| Benzbromarone (days) | ||||||||
| None | 740 | 394 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| <90 | 900 | 460 | 0.92 | 0.76–1.12 | 0.400 | 0.98 | 0.79–1.22 | 0.850 |
| 90–179 | 365 | 186 | 0.92 | 0.71–1.18 | 0.496 | 0.86 | 0.64–1.15 | 0.300 |
| ≥180 | 1,029 | 477 | 0.75 | 0.62–0.91 | 0.004 | 0.73 | 0.59–0.92 | 0.006 |
| Sulfinpyrazone (days) | ||||||||
| None | 2,906 | 1,449 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| <90 | 53 | 26 | 0.96 | 0.56–1.65 | 0.891 | 1.13 | 0.61–2.09 | 0.708 |
| ≥90 | 75 | 42 | 1.29 | 0.81–2.06 | 0.287 | 1.59 | 0.94–2.71 | 0.086 |
| Probenecid | ||||||||
| None | 3,007 | 1,499 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 27 | 18 | 2.00 | 0.90–4.45 | 0.090 | 1.84 | 0.78–4.37 | 0.165 |
Adjusted for allopurinol, benzbromarone, sulfinpyrazone, probenecid, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, chronic liver disease, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, COPD, autoimmune disease, cardiovascular disease, stroke, depression, parkinson's disease, warfarin, and statin.
Table 5.
Conditional logistic regression of risk of dementia divided by anti-gout preparations use days in different sex.
| N | No. of dementia | Crude OR | 95% C.I. | p-value | Adjusted OR† | 95% C.I. | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Female Allopurinol (days) |
||||||||
| None | 1,016 | 505 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| <90 | 125 | 65 | 1.09 | 0.75–1.60 | 0.644 | 1.02 | 0.66–1.56 | 0.935 |
| 90–179 | 41 | 24 | 1.41 | 0.76–2.64 | 0.280 | 1.32 | 0.67–2.61 | 0.423 |
| ≥180 | 120 | 57 | 0.93 | 0.63–1.35 | 0.690 | 0.89 | 0.57–1.40 | 0.623 |
| Benzbromarone (days) | ||||||||
| None | 348 | 181 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| <90 | 425 | 219 | 1.01 | 0.77–1.32 | 0.957 | 0.99 | 0.73–1.36 | 0.964 |
| 90–179 | 166 | 89 | 1.09 | 0.75–1.59 | 0.640 | 0.90 | 0.58–1.39 | 0.643 |
| ≥180 | 363 | 162 | 0.74 | 0.55–0.99 | 0.045 | 0.72 | 0.51–1.02 | 0.065 |
| Sulfinpyrazone (days) | ||||||||
| None | 1,253 | 626 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| <90 | 19 | 9 | 0.90 | 0.37–2.21 | 0.819 | 1.10 | 0.41–2.98 | 0.847 |
| ≥90 | 30 | 16 | 1.14 | 0.56–2.34 | 0.715 | 1.49 | 0.64–3.44 | 0.353 |
| Probenecid | ||||||||
| None | 1,289 | 644 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 13 | 7 | 1.17 | 0.39–3.47 | 0.782 | 1.34 | 0.40–4.48 | 0.631 |
|
Male Allopurinol (days) |
||||||||
| None | 1,312 | 640 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| <90 | 258 | 126 | 1.00 | 0.76–1.31 | 0.996 | 0.91 | 0.67–1.25 | 0.573 |
| 90–179 | 77 | 44 | 1.39 | 0.88–2.21 | 0.159 | 1.66 | 0.96–2.86 | 0.068 |
| ≥180 | 293 | 160 | 1.27 | 0.98–1.65 | 0.069 | 1.14 | 0.83–1.57 | 0.404 |
| Benzbromarone (days) | ||||||||
| None | 443 | 245 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| <90 | 534 | 268 | 0.81 | 0.63–1.04 | 0.099 | 0.87 | 0.65–1.17 | 0.348 |
| 90–179 | 226 | 111 | 0.78 | 0.57–1.07 | 0.122 | 0.80 | 0.55–1.17 | 0.252 |
| ≥180 | 737 | 346 | 0.71 | 0.55–0.90 | 0.005 | 0.68 | 0.51–0.91 | 0.010 |
| Sulfinpyrazone (days) | ||||||||
| None | 1,853 | 923 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| <90 | 38 | 21 | 1.24 | 0.65–2.34 | 0.517 | 1.56 | 0.74–3.31 | 0.246 |
| ≥90 | 49 | 26 | 1.14 | 0.64–2.05 | 0.655 | 1.36 | 0.70–2.64 | 0.364 |
| Probenecid | ||||||||
| None | 1,925 | 959 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 15 | 11 | 2.75 | 0.88–8.64 | 0.083 | 1.75 | 0.51–6.02 | 0.372 |
Adjusted for allopurinol, benzbromarone, sulfinpyrazone, probenecid, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, chronic liver disease, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, COPD, autoimmune disease, cardiovascular disease, stroke, depression, parkinson's disease, warfarin, and statin.
Discussion
The present study was a large population real-world study investigating the risk of dementia in gout patients using anti-gout preparations. Our findings indicated that use of benzbromarone to treat hyperuricemia and prevent recurrent gout flares in gout patients decreased the risk of incident dementia. Moreover, the protective effect was more pronounced in younger patients.
The ULT for gout patients may not be the same in different countries. In the United States and Europe, gout patients were treated with allopurinol as the preferred first-line agent and are strongly recommended for all patients with normal renal function (26, 27). However, allopurinol can cause skin allergic reactions and fatal exfoliative dermatitis and other hypersensitivity syndromes might develop in severe cases. Human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-B*5801 allele positivity, which is significantly higher in Han Chinese than in Caucasians, is a risk factor for the development of adverse reactions to allopurinol, and screening for this gene before initiating allopurinol treatment is important (28, 29). Since Allopurinol is contraindicated in HLA-B*5801 allele-positive patients, in Asian areas, allopurinol is usually not the most commonly used ULT (30–32).
Moreover, febuxostat, which can be used in patients with mild-to-moderate CKD, is approved for the treatment of gout in the United States in doses of 40 or 80 mg; by contrast, European approval of febuxostat is for doses of 80 or 120 mg (26, 27). For the choice of uricosuric drugs, probenecid is the only available drug in the United States, but it is neither as efficacious as benzbromarone, which is available in several other countries but not in the United States (26, 33). Benzbromarone, a potent uricosuric drug, was introduced in the 1970s and was registered in about 20 countries throughout Asia, South America, and Europe. In 2003, the drug was withdrawn by Sanofi-Synthélabo, after reports of serious hepatotoxicity and had been not used in American. However, it is still marketed in several countries by other drug companies (33). For example, In Asia (including China and Japan) and Europe, benzbromarone is still the most use uricosuric drugs in gout patients, which is the same as in Taiwan (31, 32, 34). Hence, the use of benzbromarone associated with a reduced risk of future dementia can be a reference in most areas of the world.
In Taiwan, a nationwide population study conducted from 2005 to 2010 reported that the prevalence of gout may be as high as 6.24%, with only 22.93% of patients with gout being prescribed urate-lowering treatment (allopurinol, benzbromarone, probenecid, or sulfinpyrazone) (35). Moreover, among patients who received treatment, 60.08% received uricosuric agents alone (benzbromarone, probenecid, or sulfinpyrazone), 28.54% received xanthine oxidase inhibitor (allopurinol), and 11.38% received combined therapy. In this study, we enrolled gout patients from 2000 to 2008 and is like the epidemiology investigation, most patients use uricosuric drugs than xanthine oxidase (Allopurinol). However, the febuxostat is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2009 and not listed until 2012 in Taiwan. Hence, in the study period, few patients have taken the drug and cannot be enrolled in the analysis.
Risk factors for Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia are similar to those for CVD (36, 37). Hyperuricemia and gout are also positively associated with CVD (38, 39); therefore, it is rational to postulate with common causality reasoning that gout and hyperuricemia are positively correlated with dementia and that anti-gout preparations have a protective effect. However, previous studies have shown these associations to be controversial.
In 2008, Euser et al. conducted a prospective cohort study investigating the association between serum UA and cognitive function and dementia in patients aged ≥55 years. The data showed higher serum UA levels were associated with a decreased risk of dementia and better cognitive function (40). Previous cohort studies have shown that patients with gout have a lower risk of developing dementia and that this phenomenon exists for both Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia (41, 42). These studies indicate that the protective effect may be due to the antioxidative effects of UA, which can reduce biological oxidants such as peroxynitrite radicals and protect from neurodegenerative diseases (43). However, this hypothesis remains controversial, as Hershfield et al. did not observe any changes in oxidative stress markers in patients receiving pegloticase, which greatly lowers serum UA levels (44). Furthermore, Desideri et al. reported that UA increased oxidative stress and potentiated the neurotoxic effects of amyloid-β in neuronal cells (45). In contrast, Singh et al. revealed that gout was independently associated with a 15% higher risk of incident dementia (5), and Latourte et al. found that high serum UA levels may increase the risk of incident dementia in the elderly, particularly vascular or mixed type (46). However, while anti-gout preparations are known to lower serum UA levels and prevent gout flare, few studies have focused on the association between anti-gout preparations and dementia.
A recent case-control study showed a slight reduction in the risk of dementia in patients with hyperuricemia, both with and without anti-hyperuricemic treatment (47). In this study, allopurinol was the most frequently prescribed drug (98.4%), followed by benzbromarone (1.8%) and febuxostat (0.2%). Hence, the association between anti-gout preparations and dementia was mostly affected by allopurinol. However, In the present study, the most used drug was benzbromarone, followed by allopurinol. Use of allopurinol was not associated with incident dementia. However, the use of benzbromarone in patients with gout was associated with a lower risk of incident dementia (OR, 0.81).
Benzbromarone is a uricosuric drug that has been widely used since the 1970s as a therapeutic agent for hyperuricemia. Its mechanism of action was identified as suppression of UA resorption via inhibition of urate transporter 1 (18). At standard doses (100 mg/day), the hypouricaemic activity of benzbromarone is more efficacious than that of allopurinol (300 mg/day) and probenecid (1,000 mg/day) and leads to a mean reduction in plasma urate between 25 and 50% (48–51). Moreover, benzbromarone is more effective than probenecid and sulfinpyrazone in lowering UA and can be used in patients with moderate renal insufficiency (52). As expected from any marked reduction in plasma urate concentrations, long-term treatment with benzbromarone is more effective in reducing the frequency of acute gout attacks by 35–100% after 2 years of treatment (53, 54). Besides, patients taking benzbromarone alone achieved a faster reduction of tophi than patients taking allopurinol alone (55). Hence, since hyperuricemia and gout may be risk factors for dementia (5, 46), the more potent effects of benzbromarone in reducing serum UA level and preventing acute gout attacks may explain the protective effect from incident dementia. A recent study by Muraya et al. suggested that benzbromarone had direct antioxidant effects in vivo (56), and long-term use of antioxidant supplements can reduce the risk of dementia (57, 58). Hence, this antioxidant effect can also explain why the use of benzbromarone was more effective in reducing incident dementia than other anti-gout preparations.
The present study had some limitations. First, all diagnoses in the NHIRD were made by physicians using ICD-9-CM codes and were mainly registered by general practitioners rather than rheumatologists. Therefore, the definition of gout may have resulted in non-differential misclassification. However, patients were diagnosed with gout following at least two outpatient visits or one admission with the use of anti-gout preparations to ensure that only patients with an accurate diagnosis were selected. Second, information about lifestyles, such as smoking habits and alcohol consumption, was not collected in the insurance database. To reduce this bias, we adjusted for COPD to gauge smoking habits, CLD to reflect alcohol consumption, and other comorbidities. Third, as our data were limited to insurance claims and did not provide further information on treatment and test results of serum UA levels or gout flare, we could not attribute the results to the effect of the drugs. However, previous studies showed that gout patients treated with benzbromarone may have relatively lower serum UA compared with those using other agents.
Conclusions
The present study investigated patients with gout who were treated with ULT and showed that the use of benzbromarone was associated with a reduced risk of dementia. This effect may be due to the potent UA-lowering and antioxidant effects of benzbromarone. Further prospective trials are warranted to confirm our findings.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary materials, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Ethics Statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required for this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Glossary
Abbreviations
- NHIRD
National Health Insurance Research Database
- NHI
National Health Insurance
- ICD-9-CM
International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 9th Revision, Clinical Modification
- UA
Uric acid
- ULT
Urate-lowering therapy
- CLD
Chronic liver disease
- CKD
Chronic kidney disease
- DM
Diabetes
- COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- AD
Autoimmune disease
- CVD
Cardiovascular disease
- PD
Parkinson's disease.
Footnotes
Funding. This study was supported by the Taichung Armed Forces General Hospital (Grant No. 107A09) and received assistance of the Department of Medical Education and Research, Taichung Armed Forces General Hospital.
References
- 1.Miao Z, Li C, Chen Y, Zhao S, Wang Y, Wang Z, et al. Dietary and lifestyle changes associated with high prevalence of hyperuricemia and gout in the Shandong coastal cities of Eastern China. J Rheumatol. (2008) 35:1859–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Loeb JN. The influence of temperature on the solubility of monosodium urate. Arthritis Rheum. (1972) 15:189–92. 10.1002/art.1780150209 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Richette P, Bardin T. Gout. Lancet. (2010) 375:318–28. 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60883-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Robinson PC, Merriman TR, Herbison P, Highton J. Hospital admissions associated with gout and their comorbidities in New Zealand and England 1999-2009. Rheumatology. (2013) 52:118–26. 10.1093/rheumatology/kes253 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Singh JA, Cleveland JD. Gout and dementia in the elderly: a cohort study of medicare claims. BMC Geriatr. (2018) 18:281. 10.1186/s12877-018-0975-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhu Y, Pandya BJ, Choi HK. Prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia in the US general population: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2008. Arthritis Rheum. (2011) 63:3136–41. 10.1002/art.30520 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wijnands JMA, Viechtbauer W, Thevissen K, Arts ICW, Dagnelie PC, Stehouwer CDA, et al. Determinants of the prevalence of gout in the general population: a systematic review and meta-regression. Eur J Epidemiol. (2015) 30:19–33. 10.1007/s10654-014-9927-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dubois B, Picard G, Sarazin M. Early detection of Alzheimer's disease: new diagnostic criteria. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. (2009) 11:135–9. 10.31887/DCNS.2009.11.2/bdubois [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Banerjee S, Smith SC, Lamping DL, Harwood RH, Foley B, Smith P, et al. Quality of life in dementia: more than just cognition an analysis of associations with quality of life in dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (2006) 77:146–8. 10.1136/jnnp.2005.072983 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bunn F, Burn AM, Goodman C, Rait G, Norton S, Robinson L, et al. Comorbidity and dementia: a scoping review of the literature. BMC Med. (2014) 12:192. 10.1186/s12916-014-0192-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Johnson NB, Hayes LD, Brown K, Hoo EC, Ethier KA. CDC National Health Report: leading causes of morbidity and mortality and associated behavioral risk and protective factors–United States, 2005-2013. MMWR Suppl. (2014) 63:3–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Qaseem A, Harris RP, Forciea MA. Management of acute and recurrent gout: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of physicians. Ann Intern Med. (2017) 166:58–68. 10.7326/M16-0570 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sundy JS. Progress in the pharmacotherapy of gout. Curr Opin Rheumatol. (2010) 22:188–93. 10.1097/BOR.0b013e3283369014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wallace SL, Singer JZ. Therapy in gout. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. (1988) 14:441–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zhang W, Doherty M, Bardin T, Pascual E, Barskova V, Conaghan P, et al. EULAR evidence based recommendations for gout part II: management. Report of a task force of the EULAR Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics (ESCISIT). Ann Rheumatic Dis. (2006) 65:1312–24. 10.1136/ard.2006.055269 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Stamp LK, Taylor WJ, Jones PB, Dockerty JL, Drake J, Frampton C, et al. Starting dose is a risk factor for allopurinol hypersensitivity syndrome: a proposed safe starting dose of allopurinol. Arthritis Rheum. (2012) 64:2529–36. 10.1002/art.34488 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Schumacher HR, Jr, Becker MA, Wortmann RL, Macdonald PA, Hunt B, Streit J, et al. Effects of febuxostat versus allopurinol and placebo in reducing serum urate in subjects with hyperuricemia and gout: a 28-week, phase III, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group trial. Arthritis Rheum. (2008) 59:1540–8. 10.1002/art.24209 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fujimori S, Ooyama K, Ooyama H, Moromizato H. Efficacy of benzbromarone in hyperuricemic patients associated with chronic kidney disease. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. (2011) 30:1035–8. 10.1080/15257770.2011.622732 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.van Echteld IA, van Durme C, Falzon L, Landewé RB, van der Heijde DM, Aletaha D. Treatment of gout patients with impairment of renal function: a systematic literature review. J Rheumatol Suppl. (2014) 92:48–54. 10.3899/jrheum.140462 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Khanna D, Fitzgerald JD, Khanna PP, Bae S, Singh MK, Neogi T, et al. 2012 American College of Rheumatology guidelines for management of gout part 1: systematic nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic therapeutic approaches to hyperuricemia. Arthritis Care Res. (2012) 64:1431–46. 10.1002/acr.21772 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mason RM. Studies on the effect of probenecid (‘Benemid') in gout. Ann Rheum Dis. (1954) 13:120–30. 10.1136/ard.13.2.120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Underwood M. Diagnosis and management of gout. BMJ. (2006) 332:1315–9. 10.1136/bmj.332.7553.1315 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hsing AW, Ioannidis JPA. Nationwide population science: lessons from the Taiwan national health insurance research database. JAMA Intern Med. (2015) 175:1527–9. 10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.3540 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Chen HH, Perng WT, Chiou JY, Wang YH, Huang JY, Wei JCC. Risk of dementia among patients with Sjogren's syndrome: a nationwide population-based cohort study in Taiwan. Semin Arthritis Rheum. (2019) 48:895–9. 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2018.06.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hsu MH, Yeh YT, Chen CY, Liu CH, Liu CT. Online detection of potential duplicate medications and changes of physician behavior for outpatients visiting multiple hospitals using national health insurance smart cards in Taiwan. Int J Med Inform. (2011) 80:181–9. 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2010.11.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.FitzGerald JD, Dalbeth N, Mikuls T, Brignardello-Petersen R, Guyatt G, Abeles AM, et al. 2020 American college of rheumatology guideline for the management of Gout. Arthritis Care Res. (2020) 72:744–60. 10.1002/acr.24375 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Richette P, Doherty M, Pascual E, Barskova V, Becce F, Castañeda-Sanabria J, et al. 2016 updated EULAR evidence-based recommendations for the management of gout. Ann Rheumatic Dis. (2017) 76:29–42. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209707 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Khanna D, Khanna PP, Fitzgerald JD, Singh MK, Bae S, Neogi T, et al. 2012 American College of Rheumatology guidelines for management of gout part 2: therapy and antiinflammatory prophylaxis of acute gouty arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. (2012) 64:1447–61. 10.1002/acr.21773 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hande KR, Noone RM, Stone WJ. Severe allopurinol toxicity description and guidelines for prevention in patients with renal insufficiency. Am J Med. (1984) 76:47–56. 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90743-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Multidisciplinary Expert Task Force on Hyperuricemia and Related Diseases Chinese multidisciplinary expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of hyperuricemia and related diseases. Chin Med J. (2017) 130:2473–88. 10.4103/0366-6999.216416 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Engel B, Just J, Bleckwenn M, Weckbecker K. Treatment options for Gout. Dtsch Arztebl Int. (2017) 114:215–22. 10.3238/arztebl.2017.0215 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Koto R, Nakajima A, Horiuchi H, Yamanaka H. Real-world treatment of gout and asymptomatic hyperuricemia: a cross-sectional study of Japanese health insurance claims data. Mod Rheumatol. (2020) 31:261–9. 10.1080/14397595.2020.1784556 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lee MH, Graham GG, Williams KM, Day RO. A benefit-risk assessment of benzbromarone in the treatment of gout was its withdrawal from the market in the best interest of patients? Drug Saf. (2008) 31:643–65. 10.2165/00002018-200831080-00002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Multidisciplinary Expert Task Force on Hyperuricemia and Related Diseases . [Chinese multi-disciplinary consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of hyperuricemia and its related diseases]. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. (2017) 56:235–48. 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2017.03.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kuo C-F, Grainge MJ, See L-C, Yu K-H, Luo S-F, Zhang W, et al. Epidemiology and management of gout in Taiwan: a nationwide population study. Arthritis Res Therapy. (2015) 17:13. 10.1186/s13075-015-0522-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Debette S, Seshadri S, Beiser A, Au R, Himali JJ, Palumbo C, et al. Midlife vascular risk factor exposure accelerates structural brain aging and cognitive decline. Neurology. (2011) 77:461–8. 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318227b227 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.de Bruijn RF, Ikram MA. Cardiovascular risk factors and future risk of Alzheimer's disease. BMC Med. (2014) 12:130. 10.1186/s12916-014-0130-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Fang J, Alderman MH. Serum uric acid and cardiovascular mortality the NHANES I epidemiologic follow-up study, 1971-1992. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. JAMA. (2000) 283:2404–10. 10.1001/jama.283.18.2404 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kuo CF, See LC, Yu KH, Chou IJ, Chiou MJ, Luo SF. Significance of serum uric acid levels on the risk of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Rheumatology. (2013) 52:127–34. 10.1093/rheumatology/kes223 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Euser SM, Hofman A, Westendorp RGJ, Breteler MMB. Serum uric acid and cognitive function and dementia. Brain. (2008) 132:377–82. 10.1093/brain/awn316 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hong JY, Lan TY, Tang GJ, Tang CH, Chen TJ, Lin HY. Gout and the risk of dementia: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Arthritis Res Therapy. (2015) 17:139. 10.1186/s13075-015-0642-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lu N, Dubreuil M, Zhang Y, Neogi T, Rai SK, Ascherio A, et al. Gout and the risk of Alzheimer's disease: a population-based, BMI-matched cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis. (2016) 75:547–51. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206917 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Squadrito GL, Cueto R, Splenser AE, Valavanidis A, Zhang H, Uppu RM, et al. Reaction of uric acid with peroxynitrite and implications for the mechanism of neuroprotection by uric acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. (2000) 376:333–7. 10.1006/abbi.2000.1721 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hershfield MS, Roberts LJ 2nd, Ganson NJ, Kelly SJ, Santisteban I, Scarlett E, et al. Treating gout with pegloticase, a PEGylated urate oxidase, provides insight into the importance of uric acid as an antioxidant in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2010) 107:14351–6. 10.1073/pnas.1001072107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Desideri G, Gentile R, Antonosante A, Benedetti E, Grassi D, Cristiano L, et al. Uric acid amplifies Aβ amyloid effects involved in the cognitive dysfunction/dementia: evidences from an experimental model in vitro. J Cell Physiol. (2017) 232:1069–78. 10.1002/jcp.25509 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Latourte A, Soumaré A, Bardin T, Perez-Ruiz F, Debette S, Richette PJ. Uric acid and incident dementia over 12 years of follow-up: a population-based cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis. (2018) 77:328–35. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210767 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Engel B, Gomm W, Broich K, Maier W, Weckbecker K, Haenisch B. Hyperuricemia and dementia – a case-control study. BMC Neurol. (2018) 18:131. 10.1186/s12883-018-1136-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Schepers GW. Benzbromarone therapy in hyperuricaemia; comparison with allopurinol and probenecid. J Int Med Res. (1981) 9:511–5. 10.1177/030006058100900615 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Perez-Ruiz F, Alonso-Ruiz A, Calabozo M, Herrero-Beites A, Garcia-Erauskin G, Ruiz-Lucea EJ. Efficacy of allopurinol and benzbromarone for the control of hyperuricaemia. a pathogenic approach to the treatment of primary chronic gout. Ann Rheum Dis. (1998) 57:545–9. 10.1136/ard.57.9.545 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Reinders MK, van Roon EN, Jansen TL, Delsing J, Griep EN, Hoekstra M, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of urate-lowering drugs in gout: a randomised controlled trial of benzbromarone versus probenecid after failure of allopurinol. Ann Rheum Dis. (2009) 68:51–6. 10.1136/ard.2007.083071 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Reinders MK, Haagsma C, Jansen TL, van Roon EN, Delsing J, van de Laar MA, et al. A randomised controlled trial on the efficacy and tolerability with dose escalation of allopurinol 300-600 mg/day versus benzbromarone 100-200 mg/day in patients with gout. Ann Rheum Dis. (2009) 68:892–7. 10.1136/ard.2008.091462 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kuzmits R, Bresnik W, Müller MJ. The effect of benzbromaron in gout patients with limited kidney function. Fortschr Med. (1979) 97:2057–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Bluestone R, Klinenberg J, Lee IK. Benzbromarone as a long-term uricosuric agent. Adv Exp Med Biol. (1980) 122A:283–6. 10.1007/978-1-4615-9140-5_46 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kumar S, Ng J, Gow P. Benzbromarone therapy in management of refractory gout. N Z Med J. (2005) 118:U1528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Perez-Ruiz F, Calabozo M, Pijoan JI, Herrero-Beites AM, Ruibal A. Effect of urate-lowering therapy on the velocity of size reduction of tophi in chronic gout. Arthritis Rheum. (2002) 47:356–60. 10.1002/art.10511 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Muraya N, Kadowaki D, Miyamura S, Kitamura K, Uchimura K, Narita Y, et al. Benzbromarone attenuates oxidative stress in angiotensin II- and salt-induced hypertensive model rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2018) 2018:7635274. 10.1155/2018/7635274 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Devore EE, Grodstein F, van Rooij FJA, Hofman A, Stampfer MJ, Witteman JCM, et al. Dietary antioxidants and long-term risk of dementia. Arch Neurol. (2010) 67:819–25. 10.1001/archneurol.2010.144 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kryscio RJ, Abner EL, Caban-Holt A, Lovell M, Goodman P, Darke AK, et al. Association of antioxidant supplement use and dementia in the prevention of Alzheimer's disease by vitamin E and selenium trial (PREADViSE). JAMA Neurol. (2017) 74:567–73. 10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.5778 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary materials, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.