Abstract
Some coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients develop rapidly progressive acute respiratory distress syndrome and require veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (V-V ECMO). A previous study recommended the transfer of ECMO patients to ECMO centers. However, because of the pandemic, a limited number of ECMO centers are available for patient transfer. The safe long-distance interhospital transport of these patients is a concern. To minimize transportation time, helicopter use is a suitable choice. We report the first case of a COVID-19 patient on V-V ECMO, transferred to our ECMO center by helicopter.
A 45-year-old man with rheumatoid arthritis history, treated with immunosuppressants, presented with fever and sore throat. He was diagnosed with COVID-19 following a positive severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 polymerase chain reaction test result and was subsequently prescribed favipiravir. However, his respiratory failure progressively worsened. On day 10 of hospitalization at the previous hospital, he was intubated, and we received a request for ECMO transport on the next day. The ECMO team, who wore personal protective equipment (N95 respirators, gloves, gowns, and face shields), initiated V-V ECMO in the referring hospital and safely transported the patient by helicopter. The flight time was 7 min. He was admitted to the intensive care unit of our hospital and received tocilizumab. He was discharged on hospital day 31 with no significant sequelae.
In this case report, we discuss important factors for the safe and appropriate interhospital transportation of COVID-19 patients on ECMO as well as staff and patient safety during helicopter transportation.
Abbreviations: COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; ECMO, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; PPE, personal protective equipment; ICU, intensive care unit
Keywords: Coronavirus, Mobile ECMO, Primary transport, Favipiravir, Tocilizumab
1. Background
The most severe cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) that present with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) require extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) [1]. It has been previously indicated that patients should be transported to ECMO centers with a well-established protocol to improve outcomes [2] because mortality is associated with the number of cases in ECMO centers [3]. However, a transport program for COVID-19 patients undergoing ECMO has not yet been established [4].
Here, we report a case of COVID-19 wherein the patient required multidisciplinary critical care following successful interhospital transportation by helicopter by the ECMO transport team.
2. Case presentation
A 45-year-old man with a medical history of rheumatoid arthritis requiring immunosuppressants developed a fever of 39 °C and was diagnosed with COVID-19 following a positive polymerase chain reaction (PCR) result for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
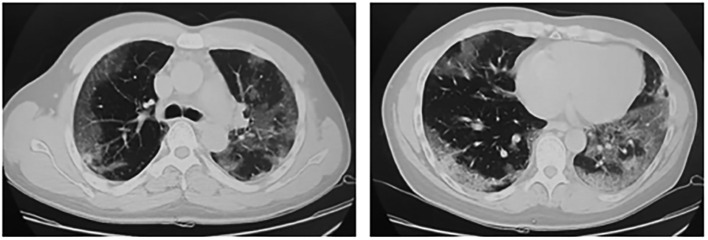
He was admitted to a hospital approximately 40 km away from our hospital (Supplemental Table 1). Chest x-ray revealed consolidation with air bronchograms in the left and right lower lobes, indicating multifocal pneumonia (Fig. 1, Fig. 2 ). After admission, the patient complained of shortness of breath, and his oxygen saturation gradually decreased. On day 10 of hospitalization, invasive mechanical ventilation was initiated owing to low blood oxygen saturation with a PO2/FIO2 ratio of 60 (mechanical ventilator settings: BIPAP, FIO2, 1.0; PEEP, 12 cmH2O; inspiratory pressure, 22 cmH2O; ventilation rate, 28/min) (Fig. 3 ).
Fig. 1.
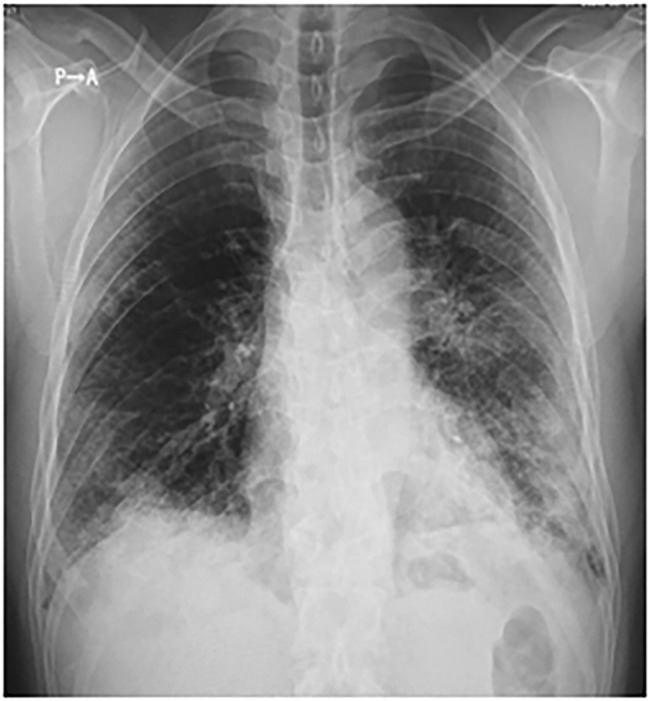
Chest X-ray on emergency department admission at the referring hospital.
Fig. 2.
Computed tomography of the chest on emergency department admission at the referring hospital.
Fig. 3.
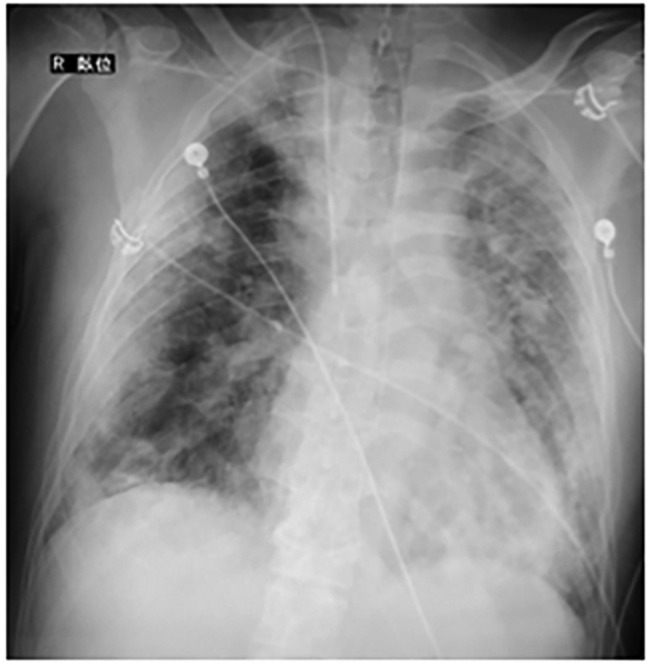
Chest X-ray at V–V ECMO initiation.
As we received a request for ECMO transport 11 days after the patient was admitted, we decided to send the ECMO team to initiate ECMO at the referring hospital and transport the patient back to our hospital by helicopter. Three doctors and one clinical engineer (ECMO perfusionist) arrived at the referring hospital within 90 min and initiated V-V ECMO in a negative pressure room (Supplemental Table 2). As soon as the patient was prepared for transportation, using a dedicated equipment for ECMO transportation attached to a backboard (Backboard Tree®: BBT®) (supplemental Fig. 1), interhospital transportation was executed by two medical crew from our ECMO team and five flight crew belonging to the fire department. The helicopter (Eurocopter AS365N3) also belonged to the fire department. The entire cabin was protected by a plastic sheet and was also separated from the cockpit (Supplemental Fig. 2a, 2b). All of the flight crew wore full personal protective equipment (PPE), including Tyvek® and N95 respirator equipment, except the pilot who wore a surgical mask owing to the microphone's technical capability. Within 6 h of the ECMO team leaving our facility, the patient was safely transported to our intensive care unit (ICU) following a 7-min flight (supplemental Fig. 3). The transport route and vehicles were disinfected by a multi-purpose disinfectant cleaner (RUBYSTA® KYORIN Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) as quickly as possible. No individual from the transport team or helicopter crew developed COVID-19 thereafter.
After admission to the ICU (Supplemental Table 3), the patient was again treated with favipiravir for 2 weeks. Tocilizumab was administered for 2 days. Prone positioning was applied for 16 h daily, with careful attention to V-V ECMO. Consequently, the patient's respiratory condition gradually improved, followed by successful weaning from V-V ECMO after 12 days of ECMO treatment. He was extubated 16 days after being admitted to ICU and was discharged from the hospital 31 days after admission without sequelae.
3. Discussion
Since 15%–30% of COVID-19 patients develop ARDS [5], V-V ECMO may have the potential to improve patient outcomes. Because ECMO is not available in all hospitals, interhospital transportation of COVID-19 patients is a possibility that should be considered [6]. Although it is reported that a well-trained transport team is essential to safely transport patients on ECMO, transportation of COVID-19 patients is challenging, especially in cases of primary transport (i.e., the transport team performs cannulation for ECMO at the referring hospital and then transports the patient to the ECMO center [7]).
In our case, primary transport was successfully executed. Based on our experience with this case, we make the following practical recommendations for the safe and appropriate interhospital transportation of COVID-19 patients on ECMO (Supplemental Table 4). First, preparation on a routine basis and effective communication allowed for quick adaptation to the modified protocol for COVID-19 cases [8]. We previously established a bi-annual training program for ECMO patient transport using a helicopter in collaboration with the fire department. Furthermore, problems related to ECMO patient transport are discussed every 2 weeks at an ECMO team meeting and all issues are subsequently addressed. Further training for PPE was compulsory for all medical staff following the initial outbreak of the virus, in addition to regular training programs. In a combination of these programs, a modified protocol for the transport of COVID-19 patients was established immediately after the outbreak and appropriately executed in this case through a careful briefing at each step. Second, it is important that the virus does not disseminate across regions, with regard to not only the public but also the medical staff [4]. According to a previously published suggestions for the development of guidelines for helicopter transportation of COVID-19 patients, a lower threshold for intubation is recommended to prevent aerosolization in the confined setting [9]. Furthermore, to reduce the risk of aerosol generation and contagion by aerosol, a practical recommendation has been published, suggesting that all staff should wear PPE, including N95 respirators, and that high-efficiency particulate air filters should be inserted between the ventilator and patient [10]. Immediate disinfection of the route and vehicles and strict ongoing compliance with infection control policies are also indicated in a practical recommendation by ECMO experts [4]. Finally, it is necessary to consider the vehicle used for transportation to minimize the exposure time of medical staff with regard to temporal and spatial distances and the patient's condition [8]. Because the risk of infection is higher during transport in the confined environment than in a hospital setting [9], we strongly recommend that the fastest means of transportation available is utilized.
The medical treatment for severe COVID-19 requiring ECMO remains unclear. We believe favipiravir worked well with regard to controlling the viral pneumonia as evidenced by the negative SARS-CoV-2 PCR test from the tracheal aspirate on the day of admission to our facility. In our experience, favipiravir in combination with the immuno-modulating agent tocilizumab worked exceptionally well.
4. Conclusions
Here, the patient with COVID-19-associated ARDS was successfully supported by primary transport using a helicopter along with critical care that includes a combination of favipiravir and tocilizumab.
Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report along with all accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Authors' contributions
TI and NH contributed to study conception, acquisition of data, interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript, and critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. RA, SI, DS, KK, WC, TT, and TN contributed to study conception, interpretation of data, and critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. Yoshihisa Tateishi for providing information on the course of treatment at the referring hospital. We also thank Chiba City Fire Department for the photographs of the helicopter.
Footnotes
Supplemental data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2020.09.089.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
Supplementary material
References
- 1.Yang X., Yu Y., Xu J., et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8:475–481. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Peek G.J., Mugford M., Tiruvoipati R., et al. Efficacy and economic assessment of conventional ventilatory support versus extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe adult respiratory failure (CESAR): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2009;374:1351–1363. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61069-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Barbaro R.P., Odetola F.O., Kidwell K.M., et al. Association of hospital-level volume of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation cases and mortality. Analysis of the extracorporeal life support organization registry. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;191:894–901. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201409-1634OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ramanathan K., Antognini D., Combes A., et al. Planning and provision of ECMO services for severe ARDS during the COVID-19 pandemic and other outbreaks of emerging infectious diseases. Lancet Respir Med. 2020 Mar;20 doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30121-1. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Li X., Ma X. Acute respiratory failure in COVID-19: is it “typical” ARDS? Critical Care (London, England) 2020;24:198. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-02911-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.World Health Organization Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection when novel coronavirus (nCoV) infection is suspected. 2020. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/330893 accessed 26 August 2020.
- 7.ELSO Guidance Document Guidelines for ECMO Transport. 2020. https://www.elso.org/Resources/Guidelines.aspx accessed 26 August 2020.
- 8.Brown A.S., Hustey F.M., Reddy A.J. Interhospital transport of patients with COVID-19: Cleveland Clinic approach. Cleve Clin J Med. 2020 Jun;9 doi: 10.3949/ccjm.87a.ccc045. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bredmose P.P., Diczbalis M., Butterfield E., et al. Decision support tool and suggestions for the development of guidelines for the helicopter transport of patients with COVID-19. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2020;28:43. doi: 10.1186/s13049-020-00736-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wax R.S., Christian M.D. Practical recommendations for critical care and anesthesiology teams caring for novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) patients. Can J Anaesth. 2020 doi: 10.1007/s12630-020-01591-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material