Abstract
Cancer immunotherapy is exhibiting great promise as a new therapeutic modality for cancer treatment. However, immunotherapies are limited by the inability of some tumors to provoke an immune response. These tumors with a ‘cold’ immunological phenotype are characterized by low numbers of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, high numbers of immunosuppressive leukocytes (e.g. regulatory T cells, tumor-associated macrophages), and high production of immune-dampening signals (e.g. IL-10, TGF-β, IDO-1). Strategies to boost the aptitude of tumors to initiate an immune response (i.e. boost tumor immunogenicity) will turn ‘cold’ tumors ‘hot’ and augment the anti-tumor efficacy of current immunotherapies. Approaches to boost tumor immunogenicity already show promise; however, multifaceted delivery and immunobiology challenges exist. For instance, systemic delivery of many immune-stimulating agents causes off-target toxicity and/or the development of autoimmunity, limiting the administrable dose below the threshold needed to achieve efficacy. Moreover, once administered in vivo, molecules such as the nucleic acid-based agonists for many pattern recognition receptors are either rapidly cleared or degraded, and don’t efficiently traffic to the intracellular compartments where the receptors are located. Thus, these nucleic acid-based drugs are ineffective without a delivery system. Biomaterials-based approaches aim to enhance current strategies to boost tumor immunogenicity, enable novel strategies, and spare dose-limiting toxicities. Here, we review recent progress to improve cancer immunotherapies by boosting immunogenicity within tumors using immunostimulatory biomaterials.
Graphical Abstract
This review highlights recent progress to develop biomaterials that boost tumor immunogenicity and improve the response rate to cancer immunotherapies.
1. Introduction
1.1. Cancer Immunotherapy
Cancer immunotherapy harnesses the innate capabilities of the body’s immune system to abate growth and metastasis of tumors. Immunotherapies have shown tremendous potential as a means of treating a broad range of malignancies and over the past decade there has been a significant proliferation in the amount of research conducted using immunotherapies to treat cancers.1 Approaches that harness the immune system to treat cancer include cancer vaccines, adoptive T cell therapy (ACT), immune checkpoint blockade (ICB), and others.
Breakthroughs in ICB therapy have revolutionized cancer treatment, particularly difficult-to-treat and metastatic malignancies.2 Indeed, new food and drug administration (FDA) approvals to expand the usage of ICBs are announced regularly. ICB therapy targets T cells that possess co-inhibitory molecules, or “checkpoints”. Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) and programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) are the most widely studied checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy.3 In normal physiology, these checkpoints prevent overstimulation of the immune system, maintain peripheral self-tolerance, and facilitate resolution of immune responses. Unfortunately, tumors can exploit the immune checkpoints to suppress immunity inside the tumor microenvironment and evade elimination by the immune system (i.e. immunoediting). For instance, tumor cells can upregulate checkpoint molecules, e.g. PD-L1 (programmed death ligand-1), the ligand for PD-1, to promote peripheral T cell exhaustion.4 Antagonistic antibodies blocking immune checkpoints promote anti-tumor immune responses.3 Ipilimumab (CTLA-4 antagonist) was the first FDA-approved drug in this category.5 Pembrolizumab and nivolumab (both PD-1 antagonists) are currently approved for several different indications,6 including second-line therapy for renal cell cancer (nivolumab) and metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (pembrolizumab).6
Cancer vaccines support presentation of tumor antigens to T cells for the prevention and treatment of cancer. Cancer vaccines are used in two ways: as a preventative medicine (prophylactically) or as a treatment for existing malignancy (therapeutically).7 Cancer vaccines such as those containing viral antigens have been developed for prophylactic administration to prevent tumorigenesis. For example, human papilloma virus (HPV) vaccines reduce the risk of cervical cancer8 and hepatitis B virus vaccines help to prevent hepatocellular carcinoma in high risk populations.9 There are currently three types of therapeutic vaccines being investigated: dendritic cell vaccines (DC vaccines), peptide vaccines, and genetic vaccines.7 Dendritic cells perform their function as antigen-presenting cells (APCs) by engulfing protein antigens, degrading the antigens, and presenting peptides to T cells via either major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class-I or class-II.10 Peptides show promise for rapid development of personalized vaccines at reduced cost compared to DC therapy, and multiple peptides can be combined to produce a more effective vaccine than single peptides, as a single tumor-associated antigen might be edited or presented in different stages of cancer progression.11 Genetic vaccines use DNA plasmids or other gene constructs such as mRNA to directly transfer the coding segment of antigens or antigen fragments to APCs.7 For instance, a self-adjuvanted RNA vaccine for prostate cancer CAV9103 is currently in phase IIb clinical trials.12
ACT is an immunotherapy approach that uses an expanded pool of natural or genetically-modified T cells with improved ability to recognize and infiltrate tumors.13 Presently, three types of ACTs are being developed as cancer therapeutics: tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), T cell receptor (TCR) T cells, and CAR (chimeric antigen receptor) T cells.14 TILs are in vitro expanded T cells which upon infusion into patients’ blood induce overall response rates (ORRs) of >50% in melanoma patients.15 TCR therapy is a redirected therapy where T cells are engineered to recognize a specific HLA-peptide complex.16 For this purpose, tumor-specific antigen NY-ESO-1 or MART-1 have been used and shown to achieve durable responses in sarcoma and metastatic melanoma patients.15 Another redirected T cell therapy is CAR T cell therapy. These engineered T cells are transduced with a chimera construct containing an extracellular domain, a single-chain variable fragment of light and heavy chain (scFv) antibody against specific extracellular receptors on tumor cells, and an intracellular domain to activate T cells via CD3 and co-stimulatory receptors CD-28 and 4–1BB.16
Critical for the success of all immunotherapies is the inherent immunogenicity of a tumor, or otherwise, the ability to ‘artificially’ stimulate immunogenicity within the tumor microenvironment.
1.2. Tumor Immunogenicity
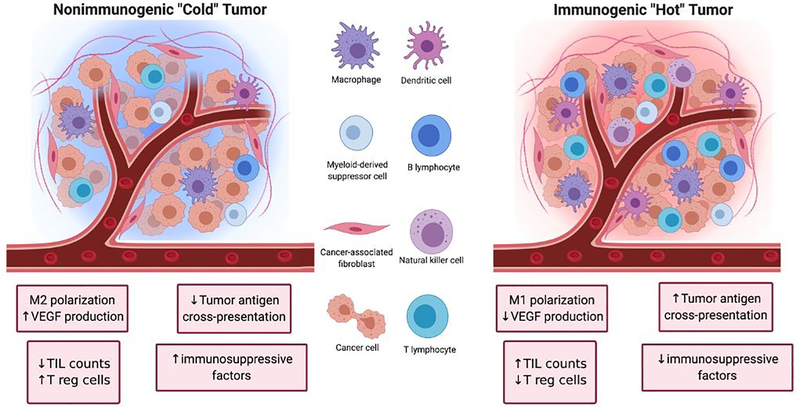
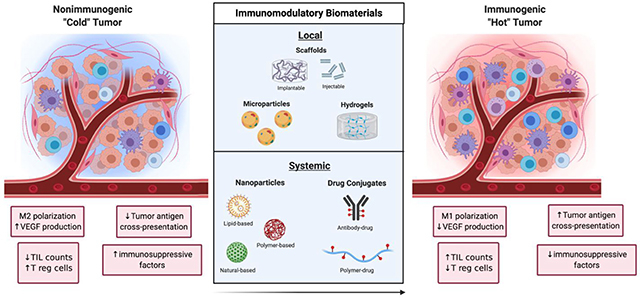
Tumors can be broadly classified into two major categories depending on their ability to initiate an immune response (Figure 1). The first category of tumors is characterized by high TIL counts, high antigen cross-presentation, low immune checkpoint expression, and low presence of immunosuppressive factors. These tumors are referred to as ‘hot’ because of their inherent immunogenicity and high amounts of immune activity. The other category of tumors is characterized by the opposite features (low TIL counts, low antigen cross-presentation, high immune checkpoint expression, and high amounts of immunosuppressive factors). These tumors are referred to as ‘cold’ tumors because of their low immune activity. The nature of the tumor plays a significant role in determining the efficacy of cancer immunotherapies as ‘hot’ tumors tend to correlate with better clinical responses to treatment than ‘cold’ tumors.17
Figure 1.
Left: Non-immunogenic “cold” tumor characterized by M2 macrophage polarization, upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), regulatory T cell (Tregs), downregulation of tumor antigen cross-presentation and tumor infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) count. Right: Immunogenic “Hot” tumor characterized by M1 macrophage polarization, upregulation of tumor antigen presentation and TIL count, and downregulation of VEGF, Tregs and other immunosuppressive factors.
The tumor microenvironment has many immunosuppressive pathways that hinder the efficacy of immune cells to mediate anti-tumor immunity. For instance, Bonaventura et al. identified four factors that determine the level of T cell infiltration in tumors: presence of tumor antigens, presence of and antigen presentation by innate immune cells such as dendritic cells (DCs), the down regulation of chemokines that attract DCs and T cells, and the secretion of immunosuppressive factors in the tumor microenvironment.18 These, and other pathways presented below, provide a number of actionable molecular targets that could be modulated to reverse immunosuppression and boost tumor immunogenicity. These efforts aim to shift tumors from a ‘cold’, immunosuppressive phenotype to ‘hot’, immune-active phenotype and increase the rate of response to immunotherapies such as immune checkpoint blockade and adoptive T cell transfer. Improved immunotherapies of the future will likely include more thorough consideration of immunogenicity in the tumor microenvironment and employ multiple strategies to prime the microenvironment prior to and in combination with immunotherapy.
1.2.1. Immunosuppressive leukocyte populations in the tumor microenvironment
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) are a subset of the T cell population that dampen immune responses by suppressing the activities of other immune cells. These cells play a crucial role in mediating peripheral tolerance by suppressing self-reactive cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). They also work to prevent autoimmune diseases like type 1 diabetes and chronic inflammatory disease. Most Tregs express the transcription factor forkhead (FoxP3) which serves as both an intracellular marker and as an important factor in Treg development and immunosuppressive function. However, a subset of Tregs exist which do not express FoxP3 and are still able to exhibit immunosuppressive activity.19–22 Tregs are recruited to the tumor microenvironment from circulation through the secretion of chemokines from tumor cell or tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). These chemokines include chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 22 (CCL22), CCL28, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 9 (CXCL9), CXCL10, and CXCL11. 20
Tregs can induce an immunosuppressive microenvironment within the tumor by releasing anti-inflammatory cytokines such as transformative growth factor-beta (TGF-β) and IL-1019,21. These cytokines are known to inhibit several APC and CTL functions such as proliferation, differentiation, inflammatory cytokine production, expression of co-stimulatory molecules, and cytotoxicity.23–26 For example, Larmonier et al.26 showed that Tregs obtained from tumor-bearing mice hamper the activity of DCs by releasing TGF-β and IL-10. Also, Chen et al.27 showed that antigen-specific CTLs that have a dominant-negative TGF-β receptor maintained similar ability to reject tumors in CT44 murine colon cancer models in the presence or absence of Tregs while CTLs without the dominant-negative TGF-β receptor could not reject tumors. Another mechanism by which Tregs suppress the immune system is through the expression of CTLA-4. CTLA-4 and the T cell co-stimulatory molecule CD28 share the same ligands (CD80 and CD86), and CTLA-4 can block binding of CD28 to these ligands, resulting in impaired co-stimulation of T cells.28,29 Other immunosuppressive mechanisms such as the secretion of granzyme B,30–32 cytokine deprivation,19,21,33 and the inhibition of the phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) pathway34,35 are also attributed to Tregs.
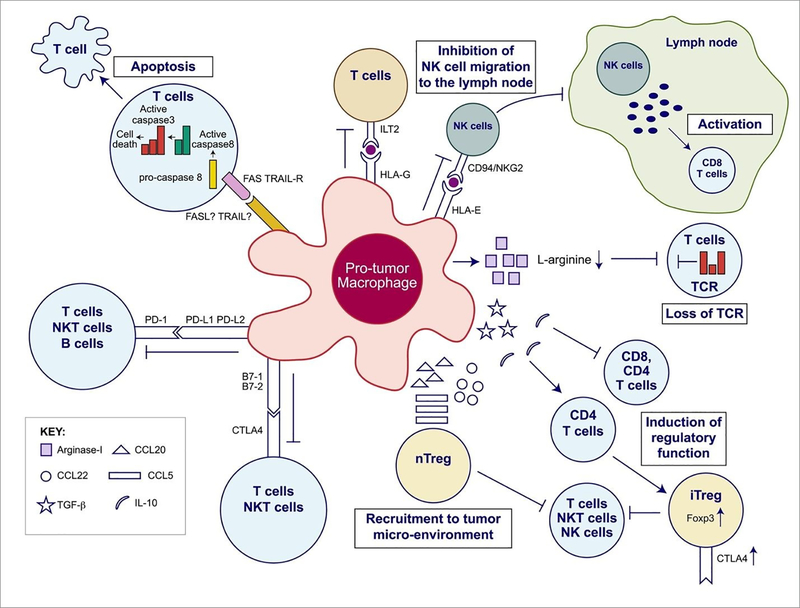
Like Tregs, tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and other myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) support immunosuppression via multifaceted roles within the tumor microenvironment and are broadly considered pro-tumorogenic (Figure 2). TAMs are some of the most prevalent cells within many tumors and are known to support growth and metastasis of advanced malignancies. TAMs secrete pro-angiogenic factors like vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and promote the “angiogenic switch,” a process which provides tumors with growth advantages and aides in the transition to malignancy.36,37 They also release matrix metalloproteinases and chemokines like CCL18 which promote tumor invasion and metastasis.38,39 Furthermore, they release anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10 and express PD-L1 which can suppress CTL-specific anti-tumor immunity.40
Figure 2.
Overview of the immunosuppressive mechanisms of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). TAMs express an array of effector molecules that inhibit antitumor immune responses; this includes cell surface receptors, cytokines, chemokines, and enzymes. Inhibition of immune responses by direct cell-to cell-contact is based on the interaction of TAM receptor ligands with their counterpart death and/or inhibitory receptors expressed by the target effector cells. TAMs express the ligand receptors for PD-1 and CTLA-4 that upon activation suppress cytotoxic functions of T cell, natural killer (NK) T cells, and NK cells. TAMs also express the ligand for the death receptors FAS and TRAIL that triggers caspase-dependent cell death (apoptosis) in target cells. TAMs also express the nonclassical HLA-G that inhibits T cell function through interaction with the costimulatory signal of T cells ILT2 and HLA-E that inhibit NK cells through CD94 (also known as NKG2). TAMs secrete the cytokines IL-10 and TGF-β that inhibit T cell effector functions and induce regulatory functions and chemokines CCL5, CCL20, and CCL22 that recruit nTreg cells. TAMs secrete Arginase I that inhibit TCR ζ chain re-expression inactivated T cells by the depletion of L-arginine. (Adapted from Noy and Pollard (2014).36 Copyright 2014 Elsevier.)
To properly understand therapeutic approaches that target TAMs, it is important to know how the phenotype of macrophages impacts their function. According to the macrophages balance hypothesis, macrophages phenotype can be classified into two main categories: the classically-activated M1 phenotype and the alternatively-activated M2 phenotype.41 The phenotype exhibited by a macrophage is determined by environmental cues that dictate the type of functions it performs. The M1 phenotype is induced by Th1 cytokines (e.g. interferon-gamma, (IFN-γ)), toll-like receptor (TLR) agonism, and bacterial moieties (lipopolysaccharide). Macrophages expressing this phenotype perform pro-inflammatory activities such as microbe clearance and tumor eradication, antigen presentation, and IL-12 secretion. On the other hand, the M2 phenotype is induced by Th2 cytokines (IL-4, IL-13) and leads to anti-inflammatory functions such as wound healing, angiogenesis, and the secretion of IL-10.41–43 TAMs are generally skewed toward the immunosuppressive M2 phenotype and support tumor progression (i.e. are pro-tumor).
Recently, we and others discovered that the role of immunosuppressive myeloid cells can be expanded further in the aftermath of cytotoxic cancer therapy 44–46. In this setting, wide scale apoptosis of cancer cells in response to cytotoxic drugs initiates a process known as efferocytosis – or apoptotic cell clearance by neighboring phagocytes.44 Efferocytosis prevents secondary necrosis of apoptotic cell debris, limiting pro-inflammatory damage associated molecular pattern (DAMP) release. At the same time, efferocytic macrophages polarize to an M2-like phenotype, secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10, IL-13, and TGF-β), and recruit FoxP3+ Treg cells.44,47 Blockade of efferocytosis after cytotoxic therapy can reverse immunosuppression and significantly reduce the growth and metastasis of tumor residual disease.
1.2.2. Molecular pathways impacting immunity in the tumor microenvironment
Molecular pathways activated by immunosuppressive proteins such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), indoleamine-2,3-dioygenase (IDO1), and others mediate the inhibition of T cell effector functions. The expression of IDO1 on APCs in particular, promotes T cell tolerance.48,49 VEGF hinders APC maturation, promotes tumor metastasis through neovascularization, and enhances the accumulation of pro-tumoral cells such as M2-like macrophages and Tregs in the tumor microenvironment.48,50 It has been reported that the inhibition of VEGF using bevacizumab normalizes the tumor vasculature and improves immune checkpoint blockade in unresectable hepatic carcinoma, a highly immunosuppressive tumor type.50 IDO1 hinders T cell function by two main pathways. The first regulatory pathway involves T cell co-regulatory receptors that induce IDO1 expression in APCs and drive T cell tolerance.49 The second is the effector pathway involving tryptophan abatement in the tumor microenvironment, production of kynurenine, and kynurenine binding to aryl hydrocarbon receptor. The reduction of local tryptophan concentration activates stress kinase GCN2 in CTLs, triggering apoptosis. The IDO1 inhibitor indoximod reverses the effects of IDO1 expression by restoring the activity of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) in T cells in regions that experience tryptophan depletion. Though results with IDO1 have been mixed, IDO1 inhibition shows promise to improve the efficacy of PD-1 in patients with melanoma.49
Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) recognize and alert the immune system when an organism is invaded by harmful, foreign pathogens. They recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) on pathogens and activate pathways that stimulate an immune response.51 Common PRRs include, among others, the stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway, retinoic acid-inducible gene I- (RIG-I)-like receptors (RLRs), and Toll-like receptors (TLRs). PRRs like STING, RLRs, and TLRs are present in many cell types, including cancer cells, macrophages, DCs, and others,52–56 where their intracellular location varies. STING and RLRs reside in the cytosol, whereas nucleic acid sensing TLRs are located primarily within endosomal vesicles.
The STING pathway is activated by cyclic dinucleotides (CDN) such as cyclic-di-AMP. This activation initiates a cascade resulting in the production of pro-inflammatory type 1 IFNs, inducing CD8α+ DCs to cross-present antigen to T cells and prime T cell-mediated antitumor immunity.57–59 STING plays an important role in mediating adaptive immune responses. Thus, STING-deficient mice show greater susceptibility to tumor formation and have impaired antitumor immunity.57 Moreover, STING is important for immune checkpoint blockade-mediated T cell responses as immune checkpoint administration in STING-deficient mice has abrogated T cell responses.56 Thus, the expression of STING in many cancer cells makes it a good therapeutic target for treating non-immunogenic tumors, particularly those resistant to checkpoint inhibitors.58
On the other hand, RLRs recognize viral RNA or viral replication intermediates and initiate an innate immune response.51,60 The RLR family comprises of RIG-I, melanoma differentiation association protein 5 (MDA-5), and laboratory of genetics and physiology 2 (LGP2).60 RIG-I is activated by double stranded RNA sequences containing 5’-diphosphate (5’-ppRNA) or triphosphates (5’-ppp RNA) 52–54,61–63 while MDA5 is activated by polyinosine-polycytidylic acid (poly(I:C)).51 Recognition of these viral RNA by RIG-I and MDA5 results in the activation of nuclear factor kappa-light-chain enhancer of B cells (NF-κB) and interferon regulator factor 3 (IRF3) to produce type I and III interferons and other pro-inflammatory cytokines.
TLRs are a broad family of Drosophila toll homologues that are located either on the cell membrane or in the endosome of the cell. They contain an extracellular leucine-rich-repeat (LRR), a transmembrane domain and an intracellular domain called TIR (Toll/IL-1 receptor).64,65 TLRs can recognize a wide variety of PAMPs from lipopolysaccharides (LPS) on the bacterial cell wall to viral RNA.64 Recognition of nucleic acid-based agonists is however restricted to the endosomal TLRs (TLR 3, 7/8, and 9). Specifically, TLR 3, 7/8, and 9 are activated by dsRNAs, ssRNAs, and CpG-ODN, respectively.64 Just like RLRs, the activation of TLRs leads to NF-κB-mediated release of pro-inflammatory cytokines66,67 and APC maturation.68
2. Classes of Immunostimulatory Biomaterials
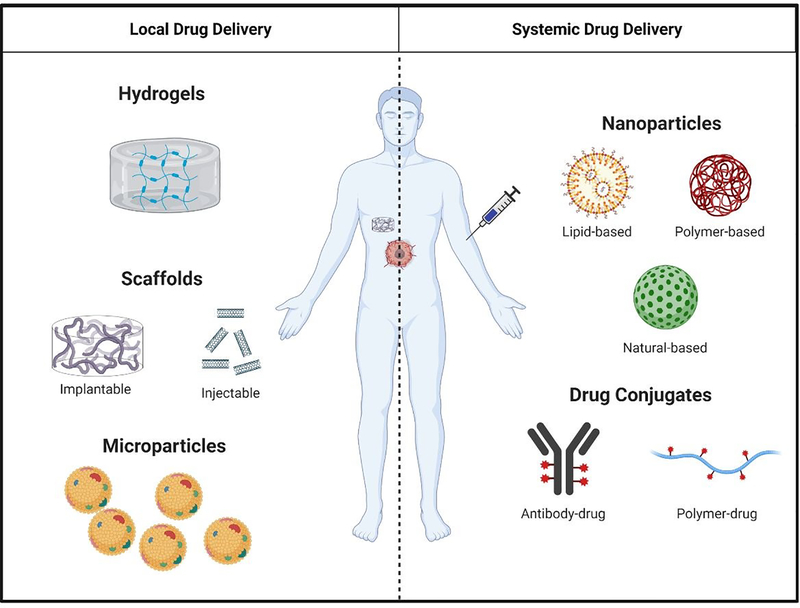
Even though immunostimulatory treatments have proven effective to counteract immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment, shortcomings such as a lack of response in extremely ‘cold’ tumors69 and the toxicity of systemically-administered immunostimulatory drugs limit the effectiveness of existing therapies.70,71 To mitigate these shortcomings of immunostimulatory drugs, biomaterials can be used as a delivery vehicle to alter pharmacokinetics and biodistribution, and control release of therapeutic agents targeting the immune system. This section outlines the general design considerations of biomaterials used for both local and systemic delivery (Figure 3) of immunostimulatory therapies to treat cancer.
Figure 3.
Overview of local and systemic approaches for drug delivery. Local approaches consist of hydrogels, scaffolds (implantable and injectable), and microparticles. Systemic approaches consist of nanoparticles (lipid-, polymer-, and natural-based) and drug conjugates (antibody-drug conjugates and polymer-drug conjugates).
2.1. Biomaterials for the Local Delivery of Immunostimulatory Therapies
In order to combat systemic toxicity and off-target side effects often encountered during the systemic delivery of immunostimulatory drugs, researchers are investigating a more localized approach to immunostimulation leveraging macroscale drug delivery devices and biomaterials. Taking a local approach in immunostimulation of the tumor microenvironment allows for a focused administration of the cancer treatment that directly affects the tumor and immune cells infiltrating the tumor, offering several advantages over systemic immunostimulation.72–75 Local immunostimulatory biomaterials deliver low doses of immunostimulatory agents proximal to the treatment site, circumventing issues of systemic toxicity. Additionally, local drug delivery by biomaterials can be optimized for spatiotemporal control of drug release to optimize the immune response using a variety of properties such as the rate of polymer degradation, diffusion mechanism, and affinity between the biomaterial and drug to tune drug release profile.74
2.1.1. Hydrogels
Hydrogels are injectable biomaterials that can be made from polymers that form cross-links to generate a 3D network. In designing effective hydrogels for local immunostimulation, one must consider multiple parameters that will affect the drug release profile, biocompatibility, and the number of agents that can be loaded into the matrix. These parameters include the polymer volume fraction in the hydrogel, the polymer type, the diffusion coefficient of drug within the matrix, and shear rate.74,76–78 Hydrogels can be used to immobilize numerous immunostimulatory agents; however, the size of the agents that can be stored within the polymer mesh of the hydrogel is controlled by the size of the meshwork and its porosity.76 The porosity of hydrogels is determined by the distance between neighboring cross-links between polymers. As the cross-linking density increases within the hydrogel network, the size of the pores decreases, limiting the size of biological agents that can be loaded into the hydrogel and impacting immune cell infiltration. Additionally, cross-linking density dictates the shear rate and directly affects the injectability of the biomaterial. The chemical properties of hydrogels also impact clinical application and effectiveness.78 The charge and the hydrophilicity of the polymeric chains in the hydrogel affect the swelling of the hydrogel in aqueous solutions such as water and biological interstitial fluid and influence drug compatibility with the hydrogel.
Hydrogels can be created using natural polymers, synthetic polymers, or a combination of the two.75,79–82 Natural polymers have intrinsic bioreactive and biocompatible properties that closely mimic the extracellular matrix (ECM). These polymers often have a high degree of biodegradability and degrade into natural byproducts that are easily cleared by the body. Synthetic polymers offer the ability to tune the hydrogel properties based on the chemical functionality of the polymer, are often nonimmunogenic, and do not interact with the cellular environment. To encourage biological interactions, synthetic polymers can be conjugated to biological ligands and proteins recognizable by host cells. While some synthetic polymers pose a risk of toxicity, many synthetic polymers used in hydrogel development have been tested widely and are FDA-approved. To overcome limitations of hydrogels composed of purely natural or synthetic polymers, hybrid polymers are being studied to combine the best features of both material classes. The customizability of hydrogels allows for hydrogels to be designed to respond to various environmental stimuli, including pH, temperature, oxidative stress, and enzymatic activity.82 Stimuli-responsive hydrogels offer “smart” systems capable of responding to environmental cues and tightly regulating material response based on biological processes occurring within the microenvironment of the hydrogel.
2.1.2. Scaffolds
Scaffolds are 3D polymeric networks with applications in host cell recruitment and spatiotemporal drug release and can be classified as implantable or injectable. Implantable scaffolds are often placed either at the tumor resection site to lower the chances of relapse or placed subcutaneously near a lymph node to recruit and reprogram immune cells. Many implantable scaffolds in development are composed of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) due to its long-standing FDA approval, biocompatibility, and material tunability. To avoid the limitations of surgically-implanted materials, injectable scaffolds are being developed and studied to create local immunogenic treatments on par with implantable scaffolds. Injectable scaffolds offer many advantages over implantable scaffolds, particularly the ability to access hard-to-reach tumors that implantable scaffolds cannot reach. Some tumors are inoperable, so implanting a scaffold to aid in an immunotherapy cancer treatment would be hindered. However, injectable scaffolds could be placed close to inoperable tumor sites to enhance cancer treatment. Injectable scaffolds have been developed using a host of materials including alginate, gelatin,84 and mesoporous silica rods (MSRs).85,86 Injectable scaffold materials are administered as a solution before rapidly assembling into a 3D matrix in vivo that can recruit and activate immune cells or act as an immunostimulatory drug reservoir.
Like hydrogels, modifying design parameters of scaffolds can change the physical properties of the matrix, impact diffusivity of immunostimulatory factors to surrounding tissue, and bioreactivity. Diffusion is an important factor for scaffolds in aiding immune cell recruitment and survival as well as controlled drug release. The diffusion coefficient, as well as the drug loading capability, of the scaffold is dependent on the porosity of the matrix. Pores in scaffolds can be introduced by sparging air or carbon dioxide as the 3D matrix sets, through the generation of a gas by the cross-linking process,87 particulate or salt leaching,87 or the use of 3D printing to create scaffolds with controlled degrees of porosity to tune the drug release profile.88 Additionally, the efficacy of scaffolds can be enhanced through surface modification. Some synthetic polymers have poor bioreactivity which can hinder cell recruitment and activation. However, this can be altered through surface modification such as in the MSR scaffolds modified with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG), PEG-RGD (PEG-integrin-binding ligand Arg-Gly-Asp), and PEG-RDG (Arg-Asp-Gly) groups by Li et al.89
2.1.3. Microparticles
Microparticles are substantially smaller than hydrogels and scaffolds and are normally used to encapsulate various immunostimulatory agents including immunotherapy drugs and cancer vaccines. Microparticles can serve both as local and systemic immunostimulatory biomaterials, but systemic applications are limited due to the large relative size of microparticles (~1 μm to 50 μm in diameter) impacting their ability to circulate. The application of the microparticle greatly influences which design parameters to consider during fabrication. After injection, microparticles will either interact with immune cells, specifically phagocytes and APCs, or act as an immunostimulatory agent reservoir, providing controlled and sustained drug release. Microparticles that act as cancer vaccines or tumor antigen reservoirs should be taken in by APCs through phagocytosis. Once inside the APC, the microparticle is broken down in an endosome and freed antigen can bind MHC I or II to start the maturation process for an antitumor response. Foged et al. investigated the role of particle size and surface charge in microparticle uptake by human DCs.90 The authors founds that as particle size decreased, the number of polystyrene spheres bound to DCs, thus potentially endocytosed, increased. Additionally, they found that negatively charged particles interacted less with DCs compared to the particles with a positive surface charge. Based on their results, the researchers concluded that surface charge played a greater role in DC interaction for large particles, suggesting that modifying large particles with positive surface charge could enhance DC uptake. Moon et al. provides an in-depth review of the impact of particle shape and mechanical properties on phagocyte interactions.91
2.2. Biomaterials for the Systemic Delivery of Immunostimulatory Therapies
Systemic administration of immunostimulatory drugs is a promising approach for the treatment of metastatic cancers that have spread to distant sites throughout the body as well as the treatment of primary tumors. Even though many immunotherapies have gained FDA approval,71,92–94 systemic administration of the drugs have multiple drawbacks.93,94 The dose of immunostimulatory drugs given systemically is limited by concerns over toxicity.95 Large portions of the systemically administered drug fails to reach the target site, instead biodistributing to other organs, limiting on-target efficacy and increasing off-target toxicity.82,96 To address the poor natural pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of many immunotherapeutic drugs, numerous immunostimulatory biomaterials have been developed for systemic delivery. Here, we focus our attention on two major classes of systemic delivery materials, nanoparticles and drug conjugates.
2.2.1. Nanoparticles
Due to the systemic administration of nanoparticles, they are able to interact with a wide range of targets and elicit multifaceted immune responses.74,97,98 That said, nanoparticles face a myriad of systemic and cellular trafficking barriers, particularly depending upon the type of drug (e.g. small molecule, antibody, nucleic acid) and final destination. Nanoparticles can be created from a range of polymers and biological agents including synthetic polymers like PEG, lipids and lipid-like materials, natural polymers such as hyaluronic acid (HA), and inorganic metals such as gold.98 Moreover, hybrid materials can be produced by combining different material classes into composites to leverage positive characteristics of each material.
While therapeutic nanoparticles can be fabricated using a variety of methods, there are key design parameters that must be considered in order to create an effective delivery system. The size of nanoparticles plays a key role in nanoparticle accumulation at tumor sites and clearance by phagocytes. Though the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect is variable and mechanisms to better understand nanoparticle accumulation in tumors are being elucidated, tumors that do contain leaky vasculature and impaired lymphatic drainage allow circulating nanoparticles to preferentially infiltrate the tumor and avoid clearance from the tumor interstitium. Moreover, It is now appreciated that nanoparticles can enter tumors by a variety of mechanisms, including passively via EPR99,100, dynamically via vascular vents101, actively via endothelial transport102, and via hitchhiking on-board phagocytes.103 One study of note was conducted by Perrault et. al. to systematically study how particle size (10–100 nm) influenced the pharmacokinetics of nanoparticles.104 The authors showed that 60–100 nm diameter particles had the highest tumor accumulation but smaller particles like the 20 nm diameter nanoparticles tested have improved tumor penetration. Researchers must determine the acceptable size range for nanoparticles to optimize accumulation and permeation within their particular application – though for most cases, nanoparticles in smaller size ranges (~20–50 nm) appear most suitable in order to balance tumor uptake and penetration within the tissue.
Other key design considerations include the material of the particle, surface charge, and degradation mechanism.105,106 Nanoparticles with a positively charged surface have a higher rate of cellular uptake while neutral and slightly negatively charged surfaces reduce cellular uptake. Due to the increased cellular uptake of positively charged nanoparticles, in addition to rapid protein adsorption and aggregation, these particles generally have very short circulation times. For this reason, charged materials are often coated with materials like PEG to shield surface charge, increase biocompatibility, and stealth the particles from the mononuclear phagocyte system (MPS). The degradation mechanism and drug release trigger can be modified to suit a wide range of applications. Some of these triggers include tumor hypoxia, low pH of endosomes and tumor microenvironment, tumor-specific enzymes, and oxidative stress. These triggers cause biodegradation of the nanoparticle material while also enabling a mechanism for drug release from the particles. For further analysis, see the extensive review on linker chemistry design and nanoparticle drug release by Wong and Choi.106
Importantly, recent studies revealing the role of immune cells in nanoparticle transport and antitumor efficacy generate excitement about the potential of nanomedicines specifically in the area of cancer immunotherapy. A series of elegant studies from the Weissleder group indicate that large portions of nanoparticles reaching tumors enter TAMs rather than tumor cells 107–111. Marios Sofias et al. showed that αvβ3-targeted particles accumulate in tumors via phagocyte hitchhiking rather than by canonical receptor-ligand binding within the tumor 103. In this study, both targeted and non-targeted nanoparticles were engulfed by circulating phagocytes (e.g. neutrophils and monocytes) and shuttled to tumors. Korangath et al. recently studied the impact of antibody-functionalization of nanoparticles on tumor accumulation in models of breast cancer.112 Rather than finding that Trastuzumab- (anti-HER2 antibody) functionalized nanoparticles colocalized with HER2+ tumor cells, they found the particles largely colocalized with immune cells in tumors. Further, differences in tumor accumulation of Trastuzumab-functionalized and control IgG-functionalized nanoparticles were not significant, even in HER2+ models of breast cancer. Rather, tumor accumulation changed significantly between immune-competent and immune-compromised models, suggesting that nanoparticle biodistribution was not dictated primarily by active targeting to the HER2 receptor but by immune status. These studies, and others, indicate that nanoparticles target immune cells efficiently in vivo, motivating further studies to probe immunobiology-nanomaterial interactions and signifying the potential promise of nanotechnology to improve cancer immunotherapy.
2.2.2. Drug conjugates
Drug conjugation is a simple and effective modification strategy to improve the pharmacokinetics of systemically administered immunostimulatory drugs. In drug conjugation strategies, immunostimulatory agents are conjugated to targeting ligands such as monoclonal antibodies or synthetic polymers to modify pharmacokinetics of the agents/drugs and minimize their side effects.[59] The two categories of drug conjugates reviewed here are antibody-drug conjugates and polymer-drug conjugates.
In cancer therapy, monoclonal antibody-based drugs recognize specific antigens on or near the tumor site to elicit a cytotoxic response, but therapeutic effects can be augmented through conjugation.113 Antibody-drug conjugates utilize the targeting capabilities of monoclonal antibodies and the cytotoxic/immunotherapeutic effects of the conjugated drug.113,114 The basic design of these conjugates consists of the antibody, a linker, and the drug. Any of these three components can be modified to engineer the system toward the application of choice.115 Once an antibody is chosen that will provide specific binding, other properties must be considered such as antibody stability after conjugation, in systemic transit, and at the site of tumors or immune organs. The linker plays an important role in the stability and drug release of antibody-drug conjugates. These linker components can be sensitive to lysosomal enzymes, pH-responsive, or responsive to glutathione (an intracellular reducing agent). Some antibody-drug conjugates utilized non-cleavable linkers. In these cases, the payload can only be released once the conjugate is taken into the cell and the antibody is degraded. After determining the best antibody and linker to suit the application, the site of conjugation onto the antibody is another important consideration as the conjugation site greatly impacts the activity of the drug conjugate. Most researchers use alkylation of reduced interchain disulfides, acylation of lysine residues, or alkylation of genetically engineered cysteine residues to conjugate the drug and linker to the antibody.116
Polymer-drug conjugation allows researchers to modify the pharmacokinetics of immunotherapy drugs, protect the drug from harsh in vivo environments, and incorporate targeting moieties, all within a single molecule.117 Conjugating immunotherapeutic or cytotoxic drugs to a synthetic polymer such as PEG protects the drugs from enzymatic degradation and rapid clearance via the liver and kidneys.118,119 As a result, polymer-drug conjugates generally increase circulation time compared to the parent drug. Polymer-drug conjugates depend on passive accumulation at tumor sites and can be further modified with targeting ligands in order to bind specific immune cell targets or cancer cells.117 Conjugating small-molecule drugs to polymer chains offers several advantages such as improved solubility, increased drug stability, prolonged circulation half-life, and altered biodistribution.118 Today, many drug conjugates have been approved by the FDA or are being tested in clinical trials.114,117 Current advances in oncology research have primarily used antibody- and polymer-drug conjugation to deliver cytotoxic drugs; however, it is theoretically possible to replace the drug component with common immunotherapies in future iterations.115,117 By conjugating drugs to polymers and/or antibodies, researchers achieve a slower clearance rate, prolonged drug circulation, targeted, delivery and can alleviate toxic, dose-limiting side effects of systemic immunotherapy.
In summary, local and systemic biomaterials-based delivery systems overcome the limitations that attend the use of immunostimulatory drugs by favorably altering their pharmacokinetics and biodistribution to enhance efficacy in vivo. Local biomaterial delivery systems can be fixed close to the target site allowing for low doses of immunostimulatory drugs to achieve efficacious concentrations in the target area while minimizing systemic toxicity. Injectable hydrogels and scaffolds possess greater flexibility than implantable scaffolds and can be used to locally deliver immunostimulatory drugs in hard-to-reach or inoperable tumors which are inaccessible to implantable scaffolds (usually utilized at tumor resection sites120). They also avoid unnecessary tissue damage that accompanies surgical implantation and require less expertise to be administered.120 Moreover, they more uniformly interact with the local tissue microenvironment because they conform to natural cavities and other available spaces before forming a rigid structure. However, injectable scaffolds are limited by the type of materials available for use in their fabrication as few materials possess mechanical properties that allow needle injection followed by hardening in vivo.120
Systemic delivery systems can deliver immunostimulatory drugs to multiple target sites at sufficient doses throughout the body while minimizing toxic side effects. This makes them particularly advantageous when treating metastatic cancers which have disseminated beyond a single point of origin. Nanoparticles make use of both active and targeting mechanisms to preferentially deliver cargo to tumors. However, the physical and biological barriers encountered by nanoparticles in circulation significantly impacts the number of nanoparticles that reach their intended destination.72,121 A recent review by Wilhelm et al analyzes probable phenomena that affect the efficiency of nanoparticle delivery and proffers strategies to overcome these limitations.121
3. Biomaterials that turn ‘Cold’ Tumors ‘Hot’
Today, researchers are applying materials such as hydrogels, scaffolds, microparticles, nanoparticles, and drug conjugates to overcome a myriad of drug delivery challenges in immunoengineering. Lessons learned from the past few decades of interdisciplinary materials science, drug delivery, biomaterials, cancer biology, and immunology research are being leveraged for the rapid development and translation of immunostimulatory biomaterials that can improve clinical outcomes in cancer immunotherapy. Recent advances in the use of biomaterials to boost tumor immunogenicity and improve cancer immunotherapy are reviewed below and summarized in Table 1.
Table 1.
Summary of biomaterials-based approaches to boost tumor immunogenicity.
| Immunotherapy | Approach | Material | Cargo | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cytokine Therapy | Hydrogels | mPEG-PLGA | GM-CSF | 122 |
| Dextran, L-lactide, D-lactide | IL-2 | 123 | ||
| Hyaluronic acid | IFN-α2a | 124 | ||
| PMNT-PEG-PMNT | IL-12 | 125 | ||
| PEGylated poly(L-valine) | Tumor cell lysate, Poly(I:C) | 126 | ||
| Scaffolds | Polyglyconate and porcine gelatin drug-eluting scaffold | CCL17 | 127 | |
| Antibody-cytokine conjugates | scFV diabody specific to EDA of fibronectin (F8) | IL-4 (F8-IL-4) and IL-12 | 128 | |
| F8 | IL-13 (F8-IL-13) and IL-12 | 129 | ||
| Lipid Nanoparticles | Phosphatidylcholine | TRAIL-conjugated ssDNA; two types of ssDNA, DNA-FD and DNA-RD, encapsulated in separate liposomes. | 130 | |
| Polymeric nanoparticles | PBAEs | IL-12 | 131 | |
| Pathogen Recogniztion Receptor agonist | Hydrogels | K2(SL)6K2 multidomain peptide | Cyclic dinucleotide STING agonist | 132 |
| Scaffolds | Hyaluronic acid | 2’3’-cGAMP (STING agonist) or R848 (TLR7/8 agonist) | 133 | |
| Alginate | STING agonist, CAR T cells | 134 | ||
| Lipid nanoparticles | Phosphatidylcholine, DOTAP | cGAMP (STING agonist) | 135 | |
| DOTAP, cholesterol, DSPE-PEG | cGAMP | 136 | ||
| POPE, DMG-PEG, YSK05 | STING agonist | 137 | ||
| Microparticles | PLGA | Poly(I:C) | 138 | |
| Polymeric nanoparticles | PBAEs | cGAMP | 139 | |
| PEG, DEAEMA, BMA, PDSMA (Polymersome) | STING agonist | 57 | ||
| DMAEMA, BMA, PAA | STING agonist | 55 | ||
| Co-delivery of immune stimulating signals | Hydrogels | Hyaluronic acid | Ovalbumin expressing plasmid, GM-CSF | 140 |
| mPEG-b-poly(L-alanine) | GM-CSF, melanoma tumor cell lysates, anti-PD-1, anti-CTLA-4 | 141 | ||
| Microparticles | PLGA | Ovalbuimin and CpG-ODN | 142 | |
| PLGA-PEI | CpG-ODN, IL-10 siRNA, pDNA | 143 | ||
| Lipid nanoparticles | DSPE-PEG | IL-2, TGF-β inhibitor | 144 | |
| DOPC, cholesterol, DSPE-PEG, and DSPE-PEG-maleimide | Anti-CD137 and IL-2-Fc | 145 | ||
| Egg POPC, cholesterol, DSPE-PEG-maleimide, and iRGD coating | PI-3065 (P110δ inhibitor), 7DW8-5 (invariant natural killer T cell agonist, iNKT) | 146 | ||
| Infection mimicking | Scaffold | PLGA | GM-CSF, CpG-ODN, melanoma tumor lysates | 147 |
| PLGA | GM-CSF, CCL20, or Flt3L in combination with CpG-ODN and melanoma tumor lysates. | 148 | ||
| Mesoporous silica rods | GM-CSF, CpG-ODN, ovalbumin | 85 | ||
| Macrophage reprogramming | Lipid nanoparticle | Phosphatidylcholine | CSF1R inhibitor, SHP1 inhibtor | 149 |
| Polymeric nanoparticle | PBAEs | mRNA | 150 | |
| β-cyclodextrin | R848 | 107 | ||
| Modulating antigen trafficking | Polymeric nanoparticle | PAA, DMAEMA | Ovalbumin | 151 |
| PAA | Ovalbumin | 152 | ||
| Microparticle | PLGA | Ovalbumin | 153 | |
| Artificial antigen presenting cells | PLGA | Melanoma antigen | 154 | |
| PEG, PLGA, | H-2Kb TRP2 Ig dimers, anti-CD28, CD47-Fc | 155 | ||
| PLGA | Ovalbumin SIINFEKL peptide, anti-CD28, rhIL-2 | 156 |
Abbreviations: monomethoxypoly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (mPEG-PLGA), granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF), poly[4-(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl piperidine-N-oxyl)aminoethylstyrene] (PMNT), cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate (cGAMP) Fms-related tyrosine kinase 3 ligand (Flt3L), Extra domain A (EDA), 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (DSPE), 1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethyl-ammonium-propane (DOTAP), poly(β-amino esters) (PBAEs), triple negative breast cancer (TNBC), 1-Palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (POPE), 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycerol, (DMG), 2-(diethylamino) ethyl methacrylate (DEAEMA), butyl methacrylate (BMA), pyridyl disulfide ethyl methacrylate (PDSMA), dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate (DMAEMA), propyl acrylic acid (PAA), Tyrosine-related protein 2 (TRP2).
3.1. Biomaterials that improve Cytokine Delivery to Tumors
Cytokines play an essential immunostimulatory role in the tumor microenvironment. Some cytokines serve to activate T and NK cells that attack cancer cells144 while others aid tumor growth, survival, and metastasis157–159. Cytokines work in an autocrine or paracrine fashion and short half-lives ensure their effects in normal physiology are usually localized.160 In therapy however, cytokines are often administered systemically and at high doses (to ensure sufficient doses reach the target site to achieve therapeutic effects).161 The systemic administration of high doses of soluble cytokines, however, leads to dose-dependent toxicities159 such as vascular leak syndrome,162,163 hypotension,164 and thrombocytopenia.164 The attempt to limit these toxic side effects can prevent the administration of curative doses.165 Several local and systemic drug delivery approaches can be leveraged to improve the biodistribution of cytokines to tumors in vivo.
3.1.1. Local approaches for cytokine delivery
Macroscale biomaterial delivery systems can release cytokines in therapeutic doses in a controlled and localized manner to enhance therapy. Multiple studies using injectable hydrogels have reported improvements in the efficacy of administered cytokines compared to soluble application. Bos et al.123 used injectable hydrogels composed of dextran modified with lactic acid oligomers (L-lactide and D-lactide) to deliver recombinant human IL-2 in SL2 lymphosarcoma murine tumor models. The in vitro release profile showed that the hydrogels released 65% of IL-2 in 3 days. However, the hydrogel had a slower degradation rate in vivo with about 50% of the hydrogel remaining at day 8. The results showed that mice given IL-2-loaded hydrogels had a 100% survival rate compared to 60% survival in mice given free IL-2. Similarly, Ishii et al.125 made redox-active, injectable gels to deliver IL-12 in murine colon adenocarcinoma tumor models. The gels consisted of poly(acrylic acid) and an ABA triblock copolymer with blocks of poly[4-(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl piperidine-N-oxyl)aminoethylstyrene] (PMNT) flanking a PEG polymer block. PMNT has cationic amine groups as side chains which, when combined with poly(acrylic acid), forms flower-like micelles that turn to a gel under physiological conditions. The IL-12 loaded gels reduced the average tumor size by about 2.1-fold compared to free IL-12 on day 16 while loaded with half the concentration of free IL-12. Importantly, increased tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) concentration in liver homogenates after IL-12 administration can contribute to hepatoxicity. IL-12-loaded gels generated 1.9-fold lower concentration of TNF-α in liver homogenates compared to free IL-12, thus suppressing TNF-α-mediated hepatoxicity.
Implantable scaffolds have also been used to improve cytokine delivery. In one example, drug-eluting scaffolds grafted with pancreatic cancer tissue were implanted in mice for local delivery of CCL17.127 These scaffolds were made of polyglyconate and porcine gelatin. Their release profile showed sustained release of CCL17 for 7 days with a cumulative release of 72%. These scaffolds recruited 5.7-fold and 6.6-fold more CTLs to the cancer tissue than non-eluting scaffolds and the control group, respectively. Additionally, these CCL17-loaded scaffolds reduced the weight of the tumor by 1.6-fold and 1.4-fold compared to non-eluting scaffold and the control group, respectively. In sum, using local delivery systems to dispatch cytokines offers the advantage of boosting the local immune response against cancers at doses that are safe for in vivo administration.
3.1.2. Systemic approaches
3.1.2.1. Antibody-cytokine conjugates
Antibody-cytokine conjugates can be used to achieve targeted delivery of cytokines to tumors, reducing off-target accumulation and systemic toxicity. 128,160,161,165 Here, the antibody has a strong affinity for targets highly abundant in the tumor microenvironment.160,166 These targets include antigens such as extra domain A (EDA) and B (EDB) of fibronectin which are strongly expressed in a majority solid tumors and lymphomas; cellular targets such as integrins (αvβ3), annexin A1, and others 166; and ligands whose expression is largely confined to the tumor microenvironment.160 Antibody-cytokines conjugates can be divided into three categories: (1) whole antibody-cytokines conjugates, (2) Fc fragment-cytokine conjugates, (3) and cytokines fused to antigen binding fragments such as scFv, Fab fragment, and others.167
Antibody-cytokine conjugates have been used for targeted delivery of cytokines such as IL-2, GM-CSF, IL-12, IL-4, TNF, and the chemokine CXCL-10 and represent a promising biomaterials-based approach to improve the pharmacokinetics and tumor delivery of cytokines in vivo.128,161,168,169 As an example, a study in F9 teratocarinoma murine tumor models, showed that antibody-cytokine conjugates facilitate higher cytokine accumulation in tumors compared to untargeted cytokines and completely eradicate tumors when co-administered.128 An antibody named F8, an scFV diabody fragment specific for EDA of fibronectin, was used to deliver IL-4 (F8-IL-4) in combination with IL-12. In the F9 tumor model, F8-IL4 had a higher accumulation in the tumor with a 6-fold increase in the percent injected dose per gram of F8-IL4 in the tumor compared to IL-4 conjugated to non-targeted antibody. Also, there was about 6-fold reduction in tumor volume of F8-IL-4 treated-mice compared to non-targeted IL-4.
3.1.2.2. Nanoparticles for cytokine delivery
Multiple nanoparticle approaches with controlled release mechanisms have been designed to improve cytokine delivery to the tumor microenvironment in therapeutic doses while simultaneously minimizing toxicities associated with systemic delivery. One approach by Wang et al. incorporated a pH-responsive monomer (2-(4-imidazolyl)ethylamine) into nanoparticles made of poly (β-amino esters) (PBAE) copolymers to deliver IL-12 to TAMs in B16F10 murine melanoma models.131 The nanoparticles were tailored to dissociate at the pH of the tumor microenvironment, releasing IL-12 in tumors to repolarize TAMs. Measurement of the concentration of IL-12 in the tumor microenvironment 48 h post injection showed a about 2.5-fold and over 6-fold increase in the concentration IL-12 compared to intratumoral and intravenous injection, respectively. Furthermore, there was a 2-fold increase in the number of TAMs with an M1 phenotype compared to free IL-12 as quantified by the expression of induced nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), a common marker of the M1 phenotype.
In another approach, nanoparticles were designed to release cytokines in response to stimuli in the tumor microenvironment.130 Here, the nanoparticles comprised of complementary DNA nanostructures encapsulated in a phosphatidylcholine liposome shell to deliver TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) to receptors on the cell membrane of human colorectal carcinoma cells. The DNA nanostructures where made through rolling circle amplification of ssDNA templates. Two types of DNA nanostructures were made; the first was made from ssDNA templates with an encoding sequence in the forward direction (DNA-FD) while the second encoding sequence was in the reverse direction (DNA-RD). The phosphatidylcholine liposomes contained an sn-2 acyl ester bond which is cleaved by phospholipase A2, an enzyme overexpressed in the microenvironment of various tumors. Analysis of the ability to deliver TRAIL to the cell membrane showed co-administration of nanoparticles containing DNA-FD and DNA-RD increased the percentage of membrane bound TRAIL from 42% to 76%, confirming that hybridization of both DNA nanostructures facilitates the interaction of TRAIL with the cell membrane receptors. In vitro cytotoxicity analysis showed that co-administration of nanoparticles containing DNA-FD and DNA-RD had an apoptosis ratio of 43.7% after 12h compared to 31.7% and 29.6% when nanoparticles containing DNA-FD or DNA-RD where administered alone.
3.2. Biomaterials for Improving Delivery of Nucleic Acid-Based PRR Agonists
The use of nucleic acid-based agonists to induce signaling pathways stimulating innate and adaptive immunity has emerged as a promising therapeutic approach for boosting tumor immunogenicity. However, the administration of soluble agonists is attended with several difficulties. Many nucleic acid-based PRR agonists have low bioavailability because of their negative charge, small size, and highly hydrophilic nature.170 CDNs also suffer from rapid clearance before they reach the tumor and do not preferentially accumulate in tumors which can lead to off-target inflammation and autoimmunity.57,136 The lack of proper therapeutic responses following the soluble administration of these agonists motivates novel strategies to improve delivery and achieve safe, efficacious therapeutic responses.57,136 Several local and systemic delivery strategies have been used to improve delivery of these agonists.
3.2.1. Local approaches for PRR delivery
The use of macroscale biomaterial delivery systems to achieve higher and more localized concentrations of PRR agonists in the tumor microenvironment results in enhanced adaptive immune responses and higher survival rates compared to free PRR agonists. A couple of prominent studies in this area feature peptide-based hydrogels. Leach et al.132 fabricated hydrogels made of K2(SL)6K2 multidomain peptide to deliver a CDN STING agonist. These peptides contained positive lysine termini which enabled favorable electrostatic interactions with the negative thiophosphate linkages of CDNs resulting in the prolonged release of the CDN.120,132 These hydrogels displayed 14–15 hours of continuous CDN release. Additionally, the delivery of CDN by these hydrogels in MOC2_E6E7 head and neck squamous cell carcinoma murine tumor models resulted in a 6-fold higher survival rate compared to CDN alone or CDN delivered from collagen gels.132 Similarly, Song et al.126 developed PEGylated poly(L-valine) hydrogels to deliver poly(I:C) in a sustained manner with complete release occurring after 8 days. The use of these hydrogels to deliver poly(I:C) with tumor cell lysates resulted in a 1.2-fold higher percentage of tumor-specific CTLs in the draining lymph node (about 27 %) compared to lysates and soluble poly(I:C) (about 22%). These results correlated with a 1.6-fold decrease in tumor volume compared to soluble tumor cell lysates and poly(I:C).
Scaffolds have also exhibited promising efficacy when loaded with PRR agonists. For example, Park et al.133 fabricated hyaluronic acid-based scaffolds to deliver either 2’3’-cGAMP or R848 (TLR7/8 agonist) to mice with resected 4T1 breast tumors. The use of R848-loaded scaffolds to extend the delivery of R848 enabled over 1.5-fold increase in the survival rate of mice compared to R848 and empty scaffolds after 90 days. A survival rate over 1.5-fold higher was also seen in mice treated with 2’3’-cGAMP-loaded scaffolds compared to mice treated when 2’3’-cGAMP and empty scaffolds after 90 days. This study showed that the controlled and localized release of R848 and 2’3’-cGAMP was crucial to survival. Other biomaterials used as implantable scaffolds with promising outcomes include alginate134 and mesoporous silica rods85. In summary, macroscale delivery strategies achieve sustained and localized release of PRR agonists and have the potential to significantly enhance therapeutic efficacy in local settings.134
3.2.2. Systemic approaches for PRR delivery
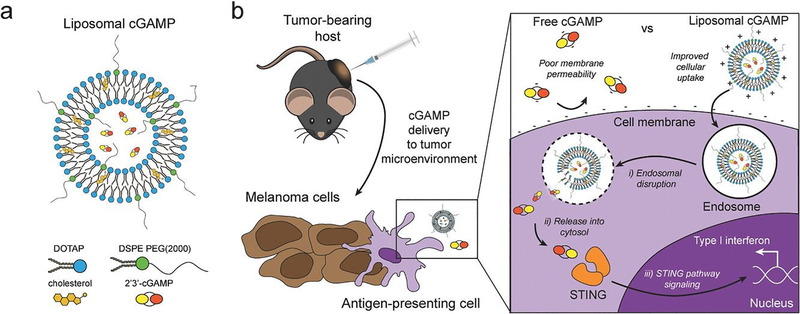
Nanoparticles used for the delivery of PRR agonists are canonically designed with cationic or charge stabilizing properties which enable packaging and delivery of highly negative PRR agonists.135–137 In a study by Cheng et al., a 3-fold increase in the number of CTLs that infiltrated the tumor compared to soluble cGAMP was reported in the orthotopic C3(1) tag model for basal-like triple negative breast cancer.135 Figure 4 highlights one approach taken by Koshy et al.143 PEGylated, cationic cGAMP-loaded nanoparticles induced more potent immunological memory of tumor antigen than free cGAMP resulting in 100% survival, compared to 50% survival in mice administered free cGAMP upon rechallenge with an orthotopic melanoma model. It is important to note here however, that the most cationic nanoparticle, the non-PEGylated liposomes, failed to completely regress the orthotopic melanoma. The authors suggest this meager performance was likely due to the poor distribution of non-PEGylated liposomes observed in tumors.136 In a related study, Nakamura et al. delivered cyclic di-GMP in liposomes and reported over 1.5-fold increase in activated NK cells in the spleen compared to control.137 These NK cells showed enhanced anti-tumor immunity resulting in over 3-fold decrease in B16F10 melanoma lung metastasis compared to control.137
Figure 4.
Schematic of liposomal cGAMP structure and therapeutic strategy. a) 2’3’-cGAMP is encapsulated in cationic liposomes created from 1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane (DOTAP) and cholesterol using thin film rehydration, freeze thawing, and membrane extrusion. A polyethylene glycol(PEG)-containing lipid (1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[methoxy(polyethylene glycol)-2000]; DSPE-PEG(2000)) is optionally included in the liposome preparation to create a PEG coating that improves liposome stability. b) In a therapeutic setting, melanoma tumor-bearing hosts are injected with free or liposomal cGAMP, where cells, for example antigen-presenting cells (APCs), in the tumor microenvironment take up liposomal cGAMP concurrent with melanoma cell antigens. (Inset) Free cGAMP has limited transport into the cytosol due to the presence of two negative charges that limit its permeability through the negatively charged cell membrane. cGAMP encapsulated in cationic liposomes shows improved cell membrane binding and uptake. Once internalized into the endosomal compartment, cationic liposomes facilitate the release of cGAMP into the cytosol, where cGAMP binds to the stimulator of interferon genes (STING) adaptor molecule, leading to type I interferon production by the APC (Adapted from Koshy et al. (2017).136 Copyright 2017 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.)
Biodegradable polymer-based nanoparticle delivery platforms that contain cationic materials have also been used to enable the delivery of negatively charged nucleic acid-based PRR agonists. PBAEs are one class of cationic polymers used in these type of nanoparticles and has been used to deliver STING agonists.139 In this study by Wilson et al., cCAMP-loaded nanoparticles were co-administered with anti-PD-1 to boost immunity against B16F10 murine melanoma tumor models. After 18 days, there was a 3-fold decrease in tumor volume compared to soluble cGAMP combined with anti-PD-1 immunotherapy.
In addition, delivery of PRR agonists mediated by polymersomes has shown increased CTL infiltration and enhanced anti-tumor activity of checkpoint inhibitors.57,58 For example, polymersomes designed by Shae et al.57 were composed of a cationic block which imparts electrostatic complexation and cargo protection along with an endosome-destabilizing terpolymer block that mediates efficient cytosolic delivery. These nanoparticles were used to deliver cGAMP to B16F10 murine melanoma tumor models. The intratumoral administration of cGAMP-loaded nanoparticles showed an 11-fold decrease in tumor growth compared to soluble cGAMP. Also, delivery mediated by cGAMP-loaded nanoparticles resulted in one-third of mice completely rejecting tumors compared to 100% tumor penetrance for mice given free cGAMP.
Furthermore, polymeric micelles featuring a similar design strategy were used to deliver RLR agonists to tumors to mediate immunogenic cell death52,55. Jacobson et al.55 used endosomolytic polymeric micelles to deliver 5’-ppp-RNA to CT26 murine tumor models and measured the amount of Annexin V and 7-AAD double positive cells indicating cell apoptosis and necrosis, respectively. The results showed that the 5’-ppp-RNA loaded micelles increased the percent of cells double positive for Annexin V and 7-AAD 5-fold compared to empty micelles. In vivo results showed the combination of anti-PD-1 and the 5’-ppp-RNA-loaded micelles resulted in about 30% survival rate compared to no survival in the mice given PBS and anti-PD-1 therapy.
3.3. Biomaterials for the Co-Delivery of Immune Agonists
Adjuvants are regularly co-administered with subunit antigens to boost immunogenicity of the antigen. For this combination to be maximally effective, both antigen and adjuvant should be present within the same APC.171 However, the soluble administration of antigen and adjuvant cannot guarantee that they are presented to the same APC on similar timescales. To ensure antigen and adjuvant co-delivery, biomaterial-based dual delivery systems have been developed that can co-encapsulate and deliver multiple molecules simultaneously. Several studies have reported improved immune response when co-delivering antigen and adjuvant using biomaterial-based delivery systems.126,172–174 In one study, Wilson et al. investigated the use of pH-responsive polymeric micelles to co-deliver ovalbumin and CpG ODN, incorporating both within sub-100 nm particles.175 In vitro studies showed a 5.5-fold and 2.5-fold increase in uptake of ovalbumin and CpG ODN when the micelles were used compared to soluble ovalbumin and CpG ODN. In vivo studies showed an 18-fold increase in the amount of IFN-γ-positive CTLs compared to the soluble administration of both antigen and adjuvant.
In addition, dual delivery systems can be used to deliver signals that initiate multiple pathways that synergistically boost anti-tumor immunity 17,144. The rationale behind this concept is that tumors use multiple immunosuppressive avenues to escape eradication by the immune system. Often, this results in diminished efficacy of single immunotherapies. For instance, the secretion of immunosuppressive cytokines can downregulate NK and T cell activity when pro-inflammatory cytokine therapy is being administered, resulting in reduced therapeutic efficacy of the pro-inflammatory cytokine.144 Inhibiting the effects of immunosuppressive signals produced by tumor cells while concomitantly administering pro-inflammatory molecules can significantly boost anti-tumor immunity.144 Combination therapies can, however, be toxic if administered in soluble form. Therefore, delivery systems that can deliver multiple immune stimulating molecules while minimizing toxicity could significantly improve treatment outcomes.176
In a seminal study, Park et al. developed biodegradable core-shell nanogels to co-deliver IL-2 and a TGF-β inhibitor to aggressive melanomas.144 These nanoscale liposomal and polymeric gels were composed of phosphatidylcholine and the lipid-polymer conjugate 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[amino(polyethylene glycol)-2000] (DSPE-PEG) forming an external lipid bilayer around a polymeric nanogel core (hydrophilic for encapsulation of IL-2). Methacrylate-conjugated-β-cyclodextrins (β-CD) were included to enable hydrophobic drug loading into inclusion complexes of the β-CD. The nanoparticles showed sustained delivery of IL-2 and the TGF-β inhibitor, SB505124, over 7 days. Co-delivery of IL-2 and SB505214 in the nanoparticles resulted in a 5-fold increase in survival rate compared to soluble administration of the combination therapy. Also, analysis of CTL infiltration into tumors showed approximately 3-fold increase in the number of activated CTLs in the tumors compared to the control. Finally, the nanoparticles helped to avoid the toxicities associated with high-dose administrations of IL-2 which tends to abate its therapeutic benefits.
Another example that epitomizes the improvements of combination therapies delivered by biomaterials is that of Zhang et al.145 Here, IL-2 Fc or anti-CD137 were conjugated to the surface of PEGylated liposomes and pharmacokinetics were measured and compared to that of the soluble forms of IL-2-Fc or anti-CD137. The authors discovered that combined delivery of both agonists (encapsulated within liposomes) to B16F10-Trp2KO tumor xenografts increased tumor accumulation markedly. Liposomal anti-CD137 showed a 5-fold increase in tumor accumulation compared to free anti-CD137 at 4h and 24 h while Liposomal IL-2-Fc showed 50% greater accumulation at 4h than free IL-2F-Fc. The use of PEGylated liposomes to co-deliver IL-2 and anti-CD137 mediated similar anti-tumor activity to soluble agents while reducing the systemic toxicities associated with free administration of the agonists.
3.4. Infection-Mimicking Biomaterials
The creation of vaccines has proven to be one of the most important breakthroughs in medicine and has enabled the successful prevention and treatment of various diseases.177 Vaccines usually incorporate antigens against an infectious disease and adjuvants which serve as “danger signals” to enhance innate immune response against an antigen.178 The goal of using vaccines is to replicate the immune response generated by pathogens without inducing the negative effects associated with infection.179 Current cancer vaccines are therefore unable to provide entirely protective responses due to a lack of strong, long-lasting humoral and cellular immune responses that resemble those generated by pathogens.177,179. Novel biomaterial-based approaches that can mimic pathogen behavior to bring about prolonged immune activation and continued APC stimulation could be a solution to bring about more robust treatment responses.147,177,179
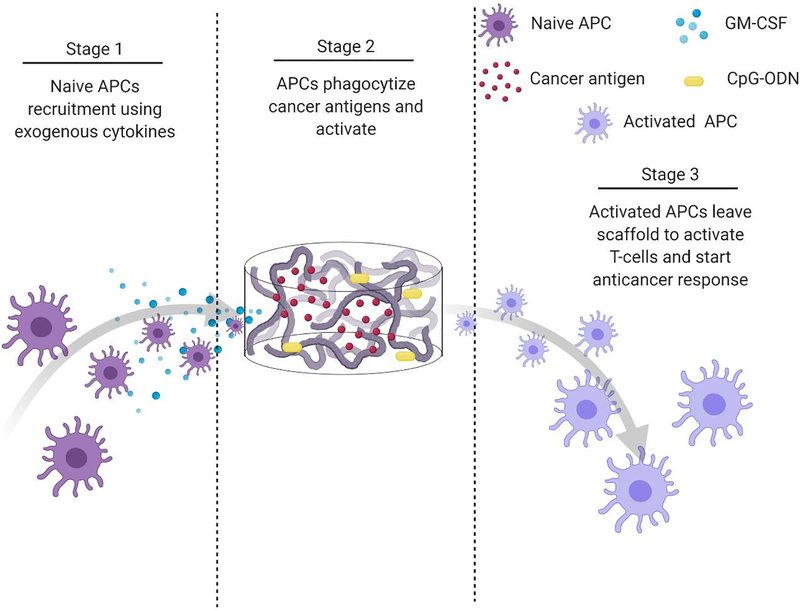
Polymeric scaffolds can be used to create an infection-mimicking microenvironment in which exogenous cytokines, PRR agonists, and a cancer antigen are combined to enable precise control over the magnitude and kinetics of DC activation (Figure 5).147,148 Cytokines are used to recruit DCs to the site of the scaffold where they are loaded with antigen and activated by adjuvants, both of which are immobilized within the scaffold.147 The polymeric scaffolds act as an antigen/adjuvant depot and delivery system to enhance recruitment and activation of DCs. They would mediate spatiotemporal control over delivery of immune stimulants to control cell activation. This approach mimics bacterial infections where cells are recruited by pro-inflammatory cytokines and are activated at the site of infection by PRR agonists. This approach was used by Ali et al.147 where they synthesized PLGA scaffolds to deliver granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF), CpG-ODN, and melanoma tumor lysates for improved priming of DCs. At high concentrations, GM-CSF gradients can entrap DCs at the site of the scaffold and preclude homing to the lymph nodes. However, the combination of CpG-ODN with GM-CSF enables DCs to leave the site of the scaffold and traffic to the lymph node. The authors showed the importance of using PLGA scaffolds as a residence for the DCs during activation by comparing to bolus injections of melanoma tumor lysates with CpG-ODN and GM-CSF. In a model of melanoma, the administration of tumor lysate, CpG ODN, and GM-CSF within PLGA scaffolds resulted in about 50% survival after 90 days compared to 0% (at day 40) for the bolus injections of the three molecules. After increasing the CpG-ODN concentration 10 times within the scaffolds, 90% survival was achieved after 90 days.147 Since this seminal work, multiple infection-mimicking systems have been developed to recruit and activate DCs.85,141
Figure 5.
Process schematic of Ali et al. infection-mimicking scaffold design. Stage 1: Recruit naïve APCs using released GM-CSF. Stage 2: The recruited APCs reside in the matrix of the scaffold to be programmed using preloaded cancer antigens and adjuvants. Stage 3: The newly programmed APCs leave the scaffold to activate T-cells and initiate an anticancer immune response.147
Additionally, particulate delivery systems can be designed to mimic infection and boost the efficacy of antigens.177,180 Pathogen-mimicking nanoparticles are divided into three broad categories: synthetic particulate systems, virus-like particles, and bacterial outer membrane vesicles.181 Pathogen-mimicking delivery systems have been shown to enhance antigen delivery compared to nanoparticles made from the canonical polymeric materials. For example, inulin-acetate, a bioactive polymer, which activates TLR4 on DCs increased antigen concentration in DCs by 6.2-fold compared to PLGA nanoparticles with similar physical properties in vitro.177 Moreover, these inulin-acetate delivery systems show enhanced ability to induce humoral response.177 The ovalbumin-loaded inulin-acetate particles increased the total amount of ovalbumin-specific IgGs almost 30 times compared to ovalbumin delivered with the adjuvant alum. The potent adaptive immune responses generated by infection-mimicking systems indicate great potential for improving the response to cancer immunotherapy and warrant continued attention.
3.5. Macrophage Reprogramming
TAMs are some of the most prevalent cells within many tumors and are known to support the growth and metastasis of advanced malignancies.36 TAMs can express a range of phenotypes, but most TAMs tend toward an M2, wound healing phenotype. The M2 macrophage phenotype mediates immunosuppressive activities in the tumor microenvironment and can provide tumors with resistance to immunotherapy.40,182 In contrast, the M1 phenotype is anti-tumoral and mediates important pro-inflammatory events that boost tumor immunogenicity.150 The plasticity of TAMs can be harnessed to program their phenotype toward anti-tumoral activities that enhance the response to immunotherapy.149
Targeting pathways responsible for differentiating TAMs is a viable strategy to repolarize TAMs from an M2 phenotype to M1.149 Colony stimulating factor 1 (CSF1) is one important pathway linked to the recruitment and differentiation of TAMs to an M2 phenotype, and inhibition of this pathway has been shown to correlate with the downregulation of M2-associated genes and the upregulation of M1-associated genes.183 Accordingly, Ramesh et al. sought to reprogram TAMs to exhibit an M1 phenotype by delivering a CSF1R inhibitor in lipid nanoaprticles.149 They designed self-assembling lipid nanoparticles comprised of phosphatidylcholine and DSPE-PEG to deliver a CSF1R inhibitor and Src homology region 2 (SH2) domain phosphatase 2 (SHP2) inhibitor. The SHP2 inhibitor promotes phagocytosis by M1 TAMs and its combination with the CSF1R inhibitor enhances the anti-tumoral activity of M1 TAMs. In a 4T1 murine breast tumor model, the CSF1R-SHP2-nanoparticles decreased the percentage of M2 macrophages 5-fold and increased the percentage of M1 macrophages 3-fold compared to control. Also, CSF1R-SHP2-nanoparticles reduced tumor volume by about 3-fold compared to control. Another suitable target is the interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) pathway. Zhang et al. designed hydrolytically-degradable nanoparticles comprised of cationic PBAEs to deliver in vitro-transcribed mRNA encoding IRF 5 and IKKβ to mice bearing ID8 ovarian tumors.150 The IRF5-IKKβ-nanoparticles resulted in a 17-fold decrease in the percentage of M2 macrophages and 20-fold increase in the percentage of M1 macrophages compared to control. Also, IRF5-IKKβ-nanoparticles increased median survival by over 2-fold compared to control and resulted in a 40% survival rate.
Rodell et al.107 synthesized nanoparticles made of β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) to deliver R848 to TAMs for repolarization in MC38 murine colorectal tumor models. Here, the use of nanoparticles with negative zeta potentials prevented undesirable uptake by hepatic cells. The cyclodextrin nanoparticles were made through amide bond formation between succinyl-β-CD and L-lysine. Though β-CD are not normally anionic, the 1:2 L-lysine to succinyl group molar ratio resulted in a negative zeta potential of −9.87±0.59 mV. β-CD was used because the chemical structure mimics dextran molecules and has high avidity for macrophages. Repolarization of TAMs was measured in p40-IRES-eYFP-IL-12 reporter mice which co-express YFP with the M1 prototypical marker IL-12. Results showed approximately 2-fold increase in the average quantified expression of IL-12 compared to mice receiving soluble R848, reducing tumor growth 2–3-fold compared to vehicle control. Several other strategies such as microRNA delivery have also been used to reprogram TAMs with promising early results.184,185
3.6. Modulating Antigen Trafficking
Antigen presentation is a vital process for generating successful tumor-specific immune responses. Tumors generate neoantigens which when recognized by APCs are taken up and processed for presentation to T cells on MHCs. CTLs are particularly effective at mediating robust anti-tumor immunity, but they require that antigen be presented on MHC-I. For presentation on MHC-I, antigens must either be cross-presented or delivered to the cytosolic MHC-I antigen processing pathway. However, the administration of soluble antigen usually leads to destruction in early endosomes before reaching the cytosol.152 Soluble antigens are also preferentially presented on MHC-II which primes T helper cells but not CTLs.186 These challenges limit the efficacy of soluble antigens to generate suitable CTL responses.
Several particulate delivery systems have shown the ability to overcome these delivery challenges and augment antigen presentation on MHC-I.151,152 pH-responsive polymeric nanoparticles are particularly suitable because they drive rapid cellular uptake of antigens and their endosomolytic features enable endosomal escape, providing the antigen access to MHC-I processing machinery in the cytosol.152 To our knowledge, the first work detailing the use of pH-responsive polymeric nanoparticles for protein antigen delivery in vivo was done by Foster et al.151 Here, poly(propylacrylic acid) (pPAA) was conjugated to ovalbumin and used either by itself or in combination with the cationic polymer pDMAEMA. The administration of pPAA-ovalbumin conjugates (with or without pDMAEMA) significantly reduced exocytosis of ovalbumin with 50% exocytosed in 4 h compared to the control which had 75% exocytosed in 30 min. Additionally, pPAA/pDMAEMA-ovalbumin conjugates had an 8-fold increase in ovalbumin-specific CTLs. This work was furthered by forming nanoplexes comprising of a MHC-I-restricted epitope from ovalbumin (SIINFEKL) that incorporated a cationic N-terminal decalysine tail and a three amino acid spacer to aid intracellular peptidase cleavage.152 The nanoplexes provided prolonged antigen presentation at higher magnitudes compared to free antigen. The use of nanoplexes to deliver antigen resulted in robust generation of antigen-specific CTLs whereas antigen alone generated CTL levels that were barely detectable. When combined with an adjuvant, the nanoplexes achieved a 10-fold increase in CTLs compared to the nonadjuvanted nanoplexes. This correlated with a prolonged duration of survival in melanoma tumor models (45 days for 100 percent death) compared to nonadjuvanted nanoplexes and free antigen with adjuvant (approximately 27 and 37 days, respectively). Co-loading of adjuvant inside the nanoplexes could possibly increase the number of CTLs cells even further.152
PLGA microparticles are another particulate delivery system that can modulate antigen trafficking for enhanced antigen presentation. Shen et al.153 studied the efficacy of PLGA microparticles for ovalbumin delivery with regards to antigen cross-presentation and CTL activation. Human DC-like cells co-cultured with ovalbumin-loaded PLGA microparticles generated comparable antigen cross-presentation to soluble ovalbumin at 1000-fold lower concentration. Measurements of the delivery of antigen to the cytosol showed that ovalbumin-loaded PLGA microparticles had a 36-fold increase in cytosolic antigen compared to ovalbumin delivered in soluble form. Though the authors could not highlight the mechanism by which microparticles enabled cytosolic delivery, Koerner et al.187 described two possible ways in which PLGA microparticles escape the endosome. The first involves the slow hydrolysis of the particle which leads to the gradual endosomal acidification making particles more positively charged and encouraging interaction with the endolysosomal membrane. The second mechanism is via the proton-sponge effect where the influx of hydronium and chloride ions during endosomal acidification increases osmotic pressure, leading to lysis of the endosomal membrane and antigen delivery to the cytosol. Other microparticles have been developed for enhanced antigen trafficking to achieve MHC-I antigen presentation and many of them incorporate adjuvants for CTL activation.142,187,188
Artificial antigen presenting cells (aAPCs) serve as another suitable strategy to improve antigen presentation as they can directly present antigen to CTLs, bypassing the challenges of cytosolic delivery.154,155,189 aAPCs are divided into two broad categories: cellular aAPCs which are made by genetically modifying living cells to present antigen and acellular aAPCs which are made from synthetic materials and modified with surface antigen and costimulatory signals to activate antigen-specific CTLs.156 Activation of T cells can be done ex vivo or in vivo. For ex vivo activation, studies showed that microsized-aAPCs are more effective at stimulating T cell response than nanosized aAPCs.156,190 However, for in vivo applications, nanosized-aAPCs tend to be more suitable because their small size enables better biodistribution.155 The shape of aAPCs play an important role in generating adequate T cell responses as well. Generally, ellipsoidal aAPCs generate higher CTL cell expansion than spherical aAPCs.154,155 This is because the aspect ratio of ellipsoidal aAPCs more closely mimics the immunological synapse of natural APCs.154 Furthermore, stealth can be added to aAPCs by PEGylation and the surface conjugation of CD47 which interacts with the signal receptor protein-α of MPS cells to inhibit phagocytosis.155 The use of these modified aAPCs resulted in 17.5-fold and 15.8-fold increases of antigen-specific CTLs in the blood and spleen, respectively, compared to control. Furthermore, CTL infiltration into tumors increased by 25.2-fold compared to control. These studies show that biomaterial-based platforms can modulate the trafficking and presentation of antigen to significantly boost cell-mediated responses against cancer.
Innovations in biomaterials-based delivery design have shown tremendous potential to provide clinically relevant solutions while overcoming several hurdles associated with current cancer immunotherapy technologies. Early implantable polymeric scaffolds that delivered tumor lysates, cytokines and adjuvants pioneered a shift in approach to vaccine administration as it enabled large amounts of DCs to be recruited to and primed for anti-tumor activity in situ. These scaffolds exhibited the potential to circumvent several hurdles faced by ex vivo activation of DC in vaccines such as the death of a significant population of the transplanted DCs or the two-patient procedure requirement which could be burdensome. Here, DCs are recruited and activated in one step, migrating directly to the target site to preserve a significant amount of cells that could be lost during transplantation.147 Since then, new designs have been developed to recruit DCs while bypassing the need for a surgical procedure. For instance, Kim et al. developed mesoporous silica rods with hexagonous mesoporous structures which could be injected through a needle then form macro-porous 3D structures in vivo that recruit and modulate DCs before the DCs traffic to their site of action. This design allows for the in situ assembly of the scaffold structure and has demonstrated the ability to recruit higher number of DCs than its predecessors.85
Smart biomaterial-based technologies that respond to biological or external stimuli such as pH, enzymatic activity, light, and temperature have been developed to improve control over cargo release, enhancing further the specificity of the drug delivered.191,192 pH-responsive nanoparticles are one of the most prominent smart technologies used in cancer immunotherapy. These nanoparticles feature ionic polymers that change ionization state in response to pH in the endosome or tumor microenvironment, triggering either cytosolic release of cargo or selective release of cargo in the tumor microenvironment.193 Lately, multi-stimuli responsive delivery systems have been developed to enable even greater selectivity in drug delivery.192 Delivery platforms that respond to multiple stimuli have yet to be widely utilized for cancer immunotherapies. This serves a suitable opportunity to introduce more innovative drug delivery systems to the field of cancer immunotherapy that can target immunostimulatory drugs based on multiple stimuli relevant to the particular immune delivery challenge under investigation.
Clinical Translation
The enhanced preclinical results achieved by immunostimulatory biomaterials has set the stage for many clinical trials involving these platforms. Biomaterial-based delivery systems have already been established as a viable method for delivering chemotherapy with myriads of clinical trials dedicated to biomaterial-loaded chemotherapies such as doxorubicin, paclitaxel and others. In the relatively newer field of cancer immunotherapy, clinical trials involving biomaterials have begun to emerge. A summary of phase I/II clinical trials for immunostimulatory biomaterials in can be found in Table 2. Most of these clinical trials are still ongoing therefore their results are pending, however some of these trials have exhibited promise. In one study, the polymer-cytokine conjugate PEG-IFN-α−2b achieved a median progression free and overall survival of 2 and 9.7 months respectively in patients with melanoma.194 As innovation continues to drive the wheels of cancer immunotherapy, more clinical trials involving sophisticated biomaterial-based designs are expected.
Table 2.
Summary of Immunostimulatory Biomaterials in Clinical Trials.
| Biomaterial | Cancer type | Phase | Trial ID | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liposome | Ovarian, Breast and Prostate Cancer | I | NCT01095848 | 195 |
| Melanoma | I | NCT01052142 | 196 | |
| Melanoma | I | NCT02410733 | 197 | |
| Leukemia | I | NCT00860522 | 198 | |
| PEG-IFN-alfa (Intron) | Melanoma | II | NCT0049530 | 194 |
| Melanoma | I | NCT00457418 | 199 | |
| Melanoma | II | NCT01959633 | 200 | |
| Sacituzumab govitecan | Metastatic Breast Cancer | II | NCT04039230 | 201 |
| PLGA scaffold | Melanoma | I | NCT01753089 | 202 |
4. Conclusions
Cancer immunotherapy is a breakthrough form of cancer therapy with tremendous potential to generate treatment responses. The efficacy of cancer immunotherapy is however inhibited by immunosuppressive molecular pathways that render the tumor microenvironment poorly immunogenic and unresponsive to treatment. Novel strategies to boost tumor immunogenicity can overcome these suppressive pathways to attain desirable treatment responses. However, these strategies are attended with several adverse side-effects which include short half-life, poor cellular uptake, and off-target accumulation resulting in harmful activity in vivo. Local and systemic strategies that incorporate sophisticated biomaterials engineered to address these challenges show great potential to bring about proper therapeutic outcomes. Local strategies involve the use of scaffolds, hydrogels, and microparticles placed in the vicinity of the tumor or immune organs to locally release immune agonists and/or recruit immune cells in situ. Systemic strategies mediate drug delivery through nanoparticles and drug conjugates, among other technologies, in order to access disseminated sites such as hard-to-access tumors and metastases. Both local and systemic strategies utilize controlled or stimuli-responsive mechanisms to deliver agonists thereby improving the pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, and therapeutic window of the cargo. The biomaterials-based approaches to boost tumor immunogenicity that were reviewed here offer exciting new therapy directions with the potential to increase both the safety and efficacy of future cancer immunotherapies.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank The Ronald E. McNair Program at The University of Mississippi for funding this research project though Grant #P217A170028 from the US Department of Education. Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number 1P20GM130460-01A1. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Footnotes
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Khalil DN, Smith EL, Brentjens RJ and Wolchok JD, Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol, 2016, 13, 273–290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Couzin-Frankel J, Science, 2013, 342, 1432–1433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Korman AJ, Peggs KS and Allison JP, 2007, 32. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tumeh PC, Harview CL, Yearley JH, Shintaku IP, Taylor EJM, Robert L, Chmielowski B, Spasic M, Henry G, Ciobanu V, West AN, Carmona M, Kivork C, Seja E, Cherry G, Gutierrez AJ, Grogan TR, Mateus C, Tomasic G, Glaspy JA, Emerson RO, Robins H, Pierce RH, Elashoff DA, Robert C and Ribas A, Nature, 2014, 515, 568–571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wróbel S, Przybyło M and Stępień E, J. Clin. Med, 2019, 8, 368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fessas P, Lee H, Ikemizu S and Janowitz T, Semin. Oncol, 2017, 44, 136–140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Song Q, Zhang C and Wu X, Immunol. Lett, 2018, 196, 11–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wang R, Pan W, Jin L, Huang W, Li Y, Wu D, Gao C, Ma D and Liao S, Cancer Lett, 2020, 471, 88–102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jeanbart L and Swartz MA, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, 2015, 112, 14467–14472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Steinman RM, 28. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Parmiani G, Castelli C, Dalerba P, Mortarini R, Rivoltini L, Marincola FM and Anichini A, JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst, 2002, 94, 805–818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kübler H, Scheel B, Gnad-Vogt U, Miller K, Schultze-Seemann W, vom Dorp F, Parmiani G, Hampel C, Wedel S, Trojan L, Jocham D, Maurer T, Rippin G, Fotin-Mleczek M, von der Mülbe F, Probst J, Hoerr I, Kallen K-J, Lander T and Stenzl A, J. Immunother. Cancer, 2015, 3, 26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chen L, Qiao D, Wang J, Tian G and Wang M, Immunol. Lett, 2019, 216, 51–62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.June CH, O’Connor RS, Kawalekar OU, Ghassemi S and Milone MC, Science, 2018, 359, 1361–1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Karpanen T and Olweus J, Mol. Oncol, 2015, 9, 2019–2042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sathyanarayanan V and Neelapu SS, Mol. Oncol, 2015, 9, 2043–2053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sharma P and Allison JP, Science, 2015, 348, 56–61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bonaventura P, Shekarian T, Alcazer V, Valladeau-Guilemond J, Valsesia-Wittmann S, Amigorena S, Caux C and Depil S, Front. Immunol, 2019, 10, 168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zou W, Nat. Rev. Immunol, 2006, 6, 295–307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nishikawa H and Sakaguchi S, Curr. Opin. Immunol, 2014, 27, 1–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Vignali DAA, Collison LW and Workman CJ, Nat. Rev. Immunol, 2008, 8, 523–532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hossain DMS, Panda AK, Manna A, Mohanty S, Bhattacharjee P, Bhattacharyya S, Saha T, Chakraborty S, Kar RK, Das T, Chatterjee S and Sa G, Immunity, 2013, 39, 1057–1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Dennis KL, Blatner NR, Gounari F and Khazaie K, Curr. Opin. Oncol, 2013, 25, 637–645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jarnicki AG, Lysaght J, Todryk S and Mills KHG, J. Immunol, 2006, 177, 896–904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Li MO, Wan YY, Sanjabi S, Robertson A-KL and Flavell RA, Annu. Rev. Immunol, 2006, 24, 99–146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Larmonier N, Marron M, Zeng Y, Cantrell J, Romanoski A, Sepassi M, Thompson S, Chen X, Andreansky S and Katsanis E, Cancer Immunol. Immunother, 2006, 56, 48–59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chen M-L, Pittet MJ, Gorelik L, Flavell RA, Weissleder R, von Boehmer H and Khazaie K, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, 2005, 102, 419–424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Qureshi OS, Zheng Y, Nakamura K, Attridge K, Manzotti C, Schmidt EM, Baker J, Jeffery LE, Kaur S, Briggs Z, Hou TZ, Futter CE, Anderson G, Walker LSK and Sansom DM, Science, 2011, 332, 600–603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Selby MJ, Engelhardt JJ, Quigley M, Henning KA, Chen T, Srinivasan M and Korman AJ, Cancer Immunol. Res, 2013, 1, 32–42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sun B, Liu M, Cui M and Li T, Immunol. Lett, 2020, 217, 7–14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cao X, Cai SF, Fehniger TA, Song J, Collins LI, Piwnica-Worms DR and Ley TJ, Immunity, 2007, 27, 635–646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Cullen SP, Brunet M and Martin SJ, Cell Death Differ, 2010, 17, 616–623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pandiyan P, Zheng L, Ishihara S, Reed J and Lenardo MJ, Nat. Immunol, 2007, 8, 1353–1362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sharma MD, Shinde R, McGaha TL, Huang L, Holmgaard RB, Wolchok JD, Mautino MR, Celis E, Sharpe AH, Francisco LM, Powell JD, Yagita H, Mellor AL, Blazar BR and Munn DH, Sci. Adv, 2015, 1, e1500845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Munn DH, Sharma MD, Johnson TS and Rodriguez P, Cancer Immunol. Immunother, 2017, 66, 1049–1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Noy R and Pollard JW, Immunity, 2014, 41, 49–61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lin EY, Li J-F, Gnatovskiy L, Deng Y, Zhu L, Grzesik DA, Qian H, Xue X. -n. and Pollard JW, Cancer Res, 2006, 66, 11238–11246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Shih J-Y and Yuan A, 2006, 6. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chen J, Yao Y, Gong C, Yu F, Su S, Chen J, Liu B, Deng H, Wang F, Lin L, Yao H, Su F, Anderson KS, Liu Q, Ewen ME, Yao X and Song E, Cancer Cell, 2011, 19, 541–555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Biswas SK, Allavena P and Mantovani A, Semin. Immunopathol, 2013, 35, 585–600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Quatromoni JG and Eruslanov E, 14. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Gordon S, Nat. Rev. Immunol, 2003, 3, 23–35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jablonski KA, Amici SA, Webb LM, de D. Ruiz-Rosado J, Popovich PG, Partida-Sanchez S and Guerau-de-Arellano M, PLOS ONE, 2015, 10, e0145342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Werfel TA and Cook RS, Semin. Immunopathol, 2018, 40, 545–554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Werfel TA, Elion DL, Rahman B, Hicks DJ, Sanchez V, Gonzales-Ericsson PI, Nixon MJ, James JL, Balko JM, Scherle PA, Koblish HK and Cook RS, Cancer Res, 2019, 79, 171–182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sulciner ML, Serhan CN, Gilligan MM, Mudge DK, Chang J, Gartung A, Lehner KA, Bielenberg DR, Schmidt B, Dalli J, Greene ER, Gus-Brautbar Y, Piwowarski J, Mammoto T, Zurakowski D, Perretti M, Sukhatme VP, Kaipainen A, Kieran MW, Huang S and Panigrahy D, J. Exp. Med, 2018, 215, 115–140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Korns D, Frasch SC, Fernandez-Boyanapalli R, Henson PM and Bratton DL, Front. Immunol,, DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2011.00057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Voron T, Marcheteau E, Pernot S, Colussi O, Tartour E, Taieb J and Terme M, Front. Oncol,, DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Prendergast GC, Mondal A, Dey S, Laury-Kleintop LD and Muller AJ, Trends Cancer, 2018, 4, 38–58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kudo M, Cancers, 2020, 12, 1089. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kato H, Takeuchi O, Sato S, Yoneyama M, Yamamoto M, Matsui K, Uematsu S, Jung A, Kawai T, Ishii KJ, Yamaguchi O, Otsu K, Tsujimura T, Koh C-S, Reis e Sousa C, Matsuura Y, Fujita T and Akira S, Nature, 2006, 441, 101–105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Elion DL, Jacobson ME, Hicks DJ, Rahman B, Sanchez V, Gonzales-Ericsson PI, Fedorova O, Pyle AM, Wilson JT and Cook RS, Cancer Res, 2018, 78, 6183–6195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Elion DL and Cook RS, Oncotarget,, DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.25626. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Palmer CR, Jacobson ME, Fedorova O, Pyle AM and Wilson JT, Bioconjug. Chem, 2018, 29, 742–747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Jacobson ME, Wang-Bishop L, Becker KW and Wilson JT, Biomater. Sci, 2019, 7, 547–559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Barber GN, Nat. Rev. Immunol, 2015, 15, 760–770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Shae D, Becker KW, Christov P, Yun DS, Lytton-Jean AKR, Sevimli S, Ascano M, Kelley M, Johnson DB, Balko JM and Wilson JT, Nat. Nanotechnol, 2019, 14, 269–278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Wang-Bishop L, Wehbe M, Shae D, James J, Hacker BC, Garland K, Chistov PP, Rafat M, Balko JM and Wilson JT, J. Immunother. Cancer, 2020, 8, e000282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Woo S-R, Fuertes MB, Corrales L, Spranger S, Furdyna MJ, Leung MYK, Duggan R, Wang Y, Barber GN, Fitzgerald KA, Alegre M-L and Gajewski TF, Immunity, 2014, 41, 830–842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Kasumba DM and Grandvaux N, Trends Pharmacol. Sci, 2019, 40, 116–127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Daßler-Plenker J, Paschen A, Putschli B, Rattay S, Schmitz S, Goldeck M, Bartok E, Hartmann G and Coch C, Int. J. Cancer, 2019, 144, 1645–1656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Zillinger T and Hartmann G, Mol. Ther, 2019, 27, 491–492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Ranoa DRE, Parekh AD, Pitroda SP, Huang X, Darga T, Wong AC, Huang L, Andrade J, Staley JP, Satoh T, Akira S, Weichselbaum RR and Khodarev NN, Oncotarget,, DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.8420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Sharma S, Garg I and Ashraf MZ, Vascul. Pharmacol, 2016, 87, 30–37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Gupta GK and Agrawal DK, BioDrugs, 2010, 24, 225–235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kim H, Niu L, Larson P, Kucaba TA, Murphy KA, James BR, Ferguson DM, Griffith TS and Panyam J, Biomaterials, 2018, 164, 38–53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Zhang H, Yan T, Xu S, Feng S, Huang D, Fujita M and Gao X-D, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2017, 73, 144–151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Shirota H and Klinman DM, Expert Rev. Vaccines, 2014, 13, 299–312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Kandalaft LE, Singh N, Liao JB, Facciabene A, Berek JS, Powell DJ and Coukos G, Gynecol. Oncol, 2010, 116, 222–233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.D’Errico G, Machado HL and Sainz B, Clin. Transl. Med,, DOI: 10.1186/s40169-016-0130-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Oiseth SJ and Aziz MS, J. Cancer Metastasis Treat, 2017, 3, 250. [Google Scholar]
- 72.Dellacherie MO, Seo BR and Mooney DJ, Nat. Rev. Mater, 2019, 4, 379–397. [Google Scholar]
- 73.Kearney CJ and Mooney DJ, Nat. Mater, 2013, 12, 1004–1017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Huang P, Wang X, Liang X, Yang J, Zhang C, Kong D and Wang W, Acta Biomater, 2019, 85, 1–26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Chai Q, Jiao Y and Yu X, Gels, 2017, 3, 6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Chyzy A, Tomczykowa M and Plonska-Brzezinska ME, Materials, 2020, 13, 188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Peppas NA, Huang Y, Torres-Lugo M, Ward JH and Zhang J, Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng, 2000, 2, 9–29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Kirschner CM and Anseth KS, Acta Mater, 2013, 61, 931–944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Lau HK and Kiick KL, Biomacromolecules, 2015, 16, 28–42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Kharkar PM, Kiick KL and Kloxin AM, Chem Soc Rev, 2013, 42, 7335–7372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Lee KY and Mooney DJ, Chem. Rev, 2001, 101, 1869–1880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Vermonden T, Censi R and Hennink WE, Chem. Rev, 2012, 112, 2853–2888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Yan J, Miao Y, Tan H, Zhou T, Ling Z, Chen Y, Xing X and Hu X, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2016, 63, 274–284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Koshy ST, Ferrante TC, Lewin SA and Mooney DJ, Biomaterials, 2014, 35, 2477–2487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Kim J, Li WA, Choi Y, Lewin SA, Verbeke CS, Dranoff G and Mooney DJ, Nat. Biotechnol, 2015, 33, 64–72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Cheung AS, Zhang DKY, Koshy ST and Mooney DJ, Nat. Biotechnol, 2018, 36, 160–169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Subia B, Kundu J and S. C., in Tissue Engineering, ed. Eberli D, InTech, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 88.Yang Y, Qiao X, Huang R, Chen H, Shi X, Wang J, Tan W and Tan Z, Biomaterials, 2020, 230, 119618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Li WA, Lu BY, Gu L, Choi Y, Kim J and Mooney DJ, Biomaterials, 2016, 83, 249–256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Foged C, Brodin B, Frokjaer S and Sundblad A, Int. J. Pharm, 2005, 298, 315–322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Moon JJ, Huang B and Irvine DJ, Adv. Mater, 2012, 24, 3724–3746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Lee S and Margolin K, Cancers, 2011, 3, 3856–3893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Hamid O, Robert C, Daud A, Hodi FS, Hwu W-J, Kefford R, Wolchok JD, Hersey P, Joseph RW, Weber JS, Dronca R, Gangadhar TC, Patnaik A, Zarour H, Joshua AM, Gergich K, Elassaiss-Schaap J, Algazi A, Mateus C, Boasberg P, Tumeh PC, Chmielowski B, Ebbinghaus SW, Li XN, Kang SP and Ribas A, N. Engl. J. Med, 2013, 369, 134–144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Carvajal RD, Sosman JA, Atkins MB, Leming PD, Spigel DR, Antonia SJ, Horn L, Drake CG, Pardoll DM, Chen L, Sharfman WH, Anders RA, Taube JM, McMiller TL, Xu H, Korman AJ, Jure-Kunkel M, Agrawal S, McDonald D, Kollia GD, Gupta A, Wigginton JM and Sznol M, N. Engl. J. Med, 2012, 366, 2443–2454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Hussein M, Berenson JR, Niesvizky R, Munshi N, Matous J, Sobecks R, Harrop K, Drachman JG and Whiting N, Haematologica, 2010, 95, 845–848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Pisal DS, Kosloski MP and Balu-Iyer SV, J. Pharm. Sci, 2010, 99, 2557–2575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Cheung AS and Mooney DJ, Nano Today, 2015, 10, 511–531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Graciotti M, Berti C, Klok H-A and Kandalaft L, J. Transl. Med, 2017, 15, 142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Torchilin V, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev, 2011, 63, 131–135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Duncan R, Nat. Rev. Drug Discov, 2003, 2, 347–360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Matsumoto Y, Nichols JW, Toh K, Nomoto T, Cabral H, Miura Y, Christie RJ, Yamada N, Ogura T, Kano MR, Matsumura Y, Nishiyama N, Yamasoba T, Bae YH and Kataoka K, Nat. Nanotechnol, 2016, 11, 533–538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Sindhwani S, Syed AM, Ngai J, Kingston BR, Maiorino L, Rothschild J, MacMillan P, Zhang Y, Rajesh NU, Hoang T, Wu JLY, Wilhelm S, Zilman A, Gadde S, Sulaiman A, Ouyang B, Lin Z, Wang L, Egeblad M and Chan WCW, Nat. Mater, 2020, 19, 566–575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Sofias AM, Toner YC, Meerwaldt AE, van Leent MMT, Soultanidis G, Elschot M, Gonai H, Grendstad K, Flobak Å, Neckmann U, Wolowczyk C, Fisher EL, Reiner T, de L. Davies C, Bjørkøy G, Teunissen AJP, Ochando J, Pérez-Medina C, Mulder WJM and Hak S, ACS Nano, 2020, acsnano.9b08693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Perrault SD, Walkey C, Jennings T, Fischer HC and Chan WCW, Nano Lett, 2009, 9, 1909–1915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Alexis F, Pridgen E, Molnar LK and Farokhzad OC, Mol. Pharm, 2008, 5, 505–515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Wong PT and Choi SK, Chem. Rev, 2015, 115, 3388–3432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Rodell CB, Arlauckas SP, Cuccarese MF, Garris CS, Li R, Ahmed MS, Kohler RH, Pittet MJ and Weissleder R, Nat. Biomed. Eng, 2018, 2, 578–588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Miller MA, Chandra R, Cuccarese MF, Pfirschke C, Engblom C, Stapleton S, Adhikary U, Kohler RH, Mohan JF, Pittet MJ and Weissleder R, Sci. Transl. Med, 2017, 9, eaal0225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Miller MA, Gadde S, Pfirschke C, Engblom C, Sprachman MM, Kohler RH, Yang KS, Laughney AM, Wojtkiewicz G, Kamaly N, Bhonagiri S, Pittet MJ, Farokhzad OC and Weissleder R, Sci. Transl. Med, 2015, 7, 314ra183–314ra183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Wang SJ, Li R, Ng TSC, Luthria G, Oudin MJ, Prytyskach M, Kohler RH, Weissleder R, Lauffenburger DA and Miller MA, Sci. Adv, 2020, 6, eaaz8521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Miller MA, Zheng Y-R, Gadde S, Pfirschke C, Zope H, Engblom C, Kohler RH, Iwamoto Y, Yang KS, Askevold B, Kolishetti N, Pittet M, Lippard SJ, Farokhzad OC and Weissleder R, Nat. Commun, 2015, 6, 8692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Korangath P, Barnett JD, Sharma A, Henderson ET, Stewart J, Yu S-H, Kandala SK, Yang C-T, Caserto JS, Hedayati M, Armstrong TD, Jaffee E, Gruettner C, Zhou XC, Fu W, Hu C, Sukumar S, Simons BW and Ivkov R, Sci. Adv, 2020, 6, eaay1601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Senter PD, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol, 2009, 13, 235–244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Teicher BA and Chari RVJ, Clin. Cancer Res, 2011, 17, 6389–6397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Perez HL, Cardarelli PM, Deshpande S, Gangwar S, Schroeder GM, Vite GD and Borzilleri RM, Drug Discov. Today, 2014, 19, 869–881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Sievers EL and Senter PD, Annu. Rev. Med, 2013, 64, 15–29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Ekladious I, Colson YL and Grinstaff MW, Nat. Rev. Drug Discov, 2019, 18, 273–294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Caliceti P, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev, 2003, 55, 1261–1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Turecek PL, Bossard MJ, Schoetens F and Ivens IA, J. Pharm. Sci, 2016, 105, 460–475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Leach DG, Young S and Hartgerink JD, Acta Biomater, 2019, 88, 15–31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Wilhelm S, Tavares AJ, Dai Q, Ohta S, Audet J, Dvorak HF and Chan WCW, Nat. Rev. Mater, 2016, 1, 16014. [Google Scholar]
- 122.Liu Y, Xiao L, Joo K-I, Hu B, Fang J and Wang P, Biomacromolecules, 2014, 15, 3836–3845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Bos GW, Jacobs JJL, Koten JW, Van Tomme S, Veldhuis T, van Nostrum CF, Den Otter W and Hennink WE, Eur. J. Pharm. Sci, 2004, 21, 561–567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Xu K, Lee F, Gao SJ, Chung JE, Yano H and Kurisawa M, J. Controlled Release, 2013, 166, 203–210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Ishii S, Kaneko J and Nagasaki Y, Biomaterials, 2016, 84, 210–218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Song H, Huang P, Niu J, Shi G, Zhang C, Kong D and Wang W, Biomaterials, 2018, 159, 119–129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Zhan Q, Shen B, Fang Y, Deng X, Chen H, Jin J, Peng C and Li H, Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces, 2017, 158, 469–473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Hemmerle T and Neri D, Int. J. Cancer, 2014, 134, 467–477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Hess C and Neri D, Cancer Immunol. Immunother, 2015, 64, 635–644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Sun W, Ji W, Hu Q, Yu J, Wang C, Qian C, Hochu G and Gu Z, Biomaterials, 2016, 96, 1–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Wang Y, Lin Y-X, Qiao S-L, An H-W, Ma Y, Qiao Z-Y, Rajapaksha RPYJ and Wang H, Biomaterials, 2017, 112, 153–163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Leach DG, Dharmaraj N, Piotrowski SL, Lopez-Silva TL, Lei YL, Sikora AG, Young S and Hartgerink JD, Biomaterials, 2018, 163, 67–75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Park CG, Hartl CA, Schmid D, Carmona EM, Kim H-J and Goldberg MS, Sci. Transl. Med, 2018, 10, eaar1916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Smith TT, Moffett HF, Stephan SB, Opel CF, Dumigan AG, Jiang X, Pillarisetty VG, Pillai SPS, Wittrup KD and Stephan MT, J. Clin. Invest, 2017, 127, 2176–2191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Cheng N, Watkins-Schulz R, Junkins RD, David CN, Johnson BM, Montgomery SA, Peine KJ, Darr DB, Yuan H, McKinnon KP, Liu Q, Miao L, Huang L, Bachelder EM, Ainslie KM and Ting JP-Y, JCI Insight, 2018, 3, e120638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Koshy ST, Cheung AS, Gu L, Graveline AR and Mooney DJ, Adv. Biosyst, 2017, 1, 1600013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Nakamura T, Miyabe H, Hyodo M, Sato Y, Hayakawa Y and Harashima H, J. Controlled Release, 2015, 216, 149–157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Jewell CM, Bustamante Lopez SC and Irvine DJ, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, 2011, 108, 15745–15750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Wilson DR, Sen R, Sunshine JC, Pardoll DM, Green JJ and Kim YJ, Nanomedicine Nanotechnol. Biol. Med, 2018, 14, 237–246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Duong HTT, Thambi T, Yin Y, Kim SH, Nguyen TL, Phan VHG, Kim J, Jeong JH and Lee DS, Biomaterials, 2020, 230, 119599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Song H, Yang P, Huang P, Zhang C, Kong D and Wang W, Theranostics, 2019, 9, 2299–2314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Joshi VB, Geary SM and Salem AK, AAPS J, 2013, 15, 85–94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Pradhan P, Qin H, Leleux JA, Gwak D, Sakamaki I, Kwak LW and Roy K, Biomaterials, 2014, 35, 5491–5504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Park J, Wrzesinski SH, Stern E, Look M, Criscione J, Ragheb R, Jay SM, Demento SL, Agawu A, Licona Limon P, Ferrandino AF, Gonzalez D, Habermann A, Flavell RA and Fahmy TM, Nat. Mater, 2012, 11, 895–905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Zhang Y, Li N, Suh H and Irvine DJ, Nat. Commun, 2018, 9, 6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Zhang F, Stephan SB, Ene CI, Smith TT, Holland EC and Stephan MT, Cancer Res, 2018, canres.0306.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Ali OA, Huebsch N, Cao L, Dranoff G and Mooney DJ, Nat. Mater, 2009, 8, 151–158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Ali OA, Tayalia P, Shvartsman D, Lewin S and Mooney DJ, Adv. Funct. Mater, 2013, 23, 4621–4628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Ramesh A, Kumar S, Nandi D and Kulkarni A, Adv. Mater, 2019, 31, 1904364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Zhang F, Parayath NN, Ene CI, Stephan SB, Koehne AL, Coon ME, Holland EC and Stephan MT, Nat. Commun, 2019, 10, 3974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Foster S, Duvall CL, Crownover EF, Hoffman AS and Stayton PS, Bioconjug. Chem, 2010, 21, 2205–2212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Qiu F, Becker KW, Knight FC, Baljon JJ, Sevimli S, Shae D, Gilchuk P, Joyce S and Wilson JT, Biomaterials, 2018, 182, 82–91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Shen H, Ackerman AL, Cody V, Giodini A, Hinson ER, Cresswell P, Edelson RL, Saltzman WM and Hanlon DJ, Immunology, 2006, 117, 78–88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Sunshine JC, Perica K, Schneck JP and Green JJ, Biomaterials, 2014, 35, 269–277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Song S, Jin X, Zhang L, Zhao C, Ding Y, Ang Q, Khaidav O and Shen C, Int. J. Nanomedicine, 2019, Volume 14, 2465–2483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Steenblock ER and Fahmy TM, Mol. Ther, 2008, 16, 765–772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Nguyen PM and Putoczki TL, Cytokine, 2019, 118, 8–18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Liang S, Chen Z, Jiang G, Zhou Y, Liu Q, Su Q, Wei W, Du J and Wang H, Cancer Lett, 2017, 386, 12–23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Whiteside TL, Oncogene, 2008, 27, 5904–5912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Dougan M, Ingram JR, Jeong H-J, Mosaheb MM, Bruck PT, Ali L, Pishesha N, Blomberg O, Tyler PM, Servos MM, Rashidian M, Nguyen Q-D, von Andrian UH, Ploegh HL and Dougan SK, Cancer Immunol. Res, 2018, 6, 389–401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Ortiz-Sánchez E, Helguera G, Daniels TR and Penichet ML, Expert Opin. Biol. Ther, 2008, 8, 609–632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Hu P, Mizokami M, Ruoff G, Khawli LA and Epstein AL, Blood, 2003, 101, 4853–4861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Létourneau S, van Leeuwen EMM, Krieg C, Martin C, Pantaleo G, Sprent J, Surh CD and Boyman O, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, 2010, 107, 2171–2176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Floros T and Tarhini AA, Semin. Oncol, 2015, 42, 539–548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Halin C, Gafner V, Villani ME, Borsi L, Berndt A, Kosmehl H, Zardi L and Neri D, 10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Hutmacher C and Neri D, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev, 2019, 141, 67–91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Kontermann RE, Arch. Biochem. Biophys, 2012, 526, 194–205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Probst P, Kopp J, Oxenius A, Colombo MP, Ritz D, Fugmann T and Neri D, Cancer Res, 2017, 77, 3644–3654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Hess C and Neri D, Exp. Biol. Med, 2014, 239, 842–852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Shim G, Kim M-G, Park JY and Oh Y-K, Asian J. Pharm. Sci, 2013, 8, 72–80. [Google Scholar]
- 171.Zhang R, Billingsley MM and Mitchell MJ, J. Controlled Release, 2018, 292, 256–276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Morishita M, Takahashi Y, Matsumoto A, Nishikawa M and Takakura Y, Biomaterials, 2016, 111, 55–65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Du G, Hathout RM, Nasr M, Nejadnik MR, Tu J, Koning RI, Koster AJ, Slütter B, Kros A, Jiskoot W, Bouwstra JA and Mönkäre J, J. Controlled Release, 2017, 266, 109–118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Silva JM, Zupancic E, Vandermeulen G, Oliveira VG, Salgado A, Videira M, Gaspar M, Graca L, Préat V and Florindo HF, J. Controlled Release, 2015, 198, 91–103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Wilson JT, Keller S, Manganiello MJ, Cheng C, Lee C-C, Opara C, Convertine A and Stayton PS, ACS Nano, 2013, 7, 3912–3925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Xie Y-Q, Wei L and Tang L, Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol, 2018, 10, e1506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Kumar S, Kesharwani SS, Kuppast B, Bakkari MA and Tummala H, J. Controlled Release, 2017, 261, 263–274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Song W, Musetti SN and Huang L, Biomaterials, 2017, 148, 16–30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Petersen LK, Ramer-Tait AE, Broderick SR, Kong C-S, Ulery BD, Rajan K, Wannemuehler MJ and Narasimhan B, Biomaterials, 2011, 32, 6815–6822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Molino NM, Neek M, Tucker JA, Nelson EL and Wang S-W, Biomaterials, 2016, 86, 83–91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Rosenthal JA, Chen L, Baker JL, Putnam D and DeLisa MP, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol, 2014, 28, 51–58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Lin Y, Xu J and Lan H, J. Hematol. Oncol.J Hematol Oncol, 2019, 12, 76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Zhu Y, Knolhoff BL, Meyer MA, Nywening TM, West BL, Luo J, Wang-Gillam A, Goedegebuure SP, Linehan DC and DeNardo DG, Cancer Res, 2014, 74, 5057–5069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Liu L, Yi H, He H, Pan H, Cai L and Ma Y, Biomaterials, 2017, 134, 166–179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Parayath NN, Parikh A and Amiji MM, Nano Lett, 2018, 18, 3571–3579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.De Temmerman M-L, Rejman J, Demeester J, Irvine DJ, Gander B and De Smedt SC, Drug Discov. Today, 2011, 16, 569–582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Koerner J, Horvath D and Groettrup M, Front. Immunol, 2019, 10, 707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Yang Y-W and Hsu PY-J, Biomaterials, 2008, 29, 2516–2526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Sunshine JC and Green JJ, Nanomed, 2013, 8, 1173–1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Eggermont LJ, Paulis LE, Tel J and Figdor CG, Trends Biotechnol, 2014, 32, 456–465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Lu Y, Aimetti AA, Langer R and Gu Z, Nat. Rev. Mater, 2017, 2, 16075. [Google Scholar]
- 192.Kowalski PS, Bhattacharya C, Afewerki S and Langer R, ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng, 2018, 4, 3809–3817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Kanamala M, Wilson WR, Yang M, Palmer BD and Wu Z, Biomaterials, 2016, 85, 152–167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.U.S. National Library of Medicine, PEG-Interferon Alfa-2b in Treating Patients With Stage IV Melanoma, https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT0049530?term=PEG&cond=MELANOMA&draw=2&rank=7.
- 195.U.S. National Library of Medicine, A Phase I Safety Study of a Cancer Vaccine to Treat HLA-A2 Positive Advanced Stage Ovarian, Breast and Prostate Cancer, clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01095848.
- 196.U.S. National Library of Medicine, Safety Study of a Liposome Vaccine to Treat Malignant Melanoma, clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01052142.
- 197.U.S. National Library of Medicine, Evaluation of the Safety and Tolerability of i.v. Administration of a Cancer Vaccine in Patients with Advanced Melanoma (Lipo-MERIT), https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02410733?cond=NCT02410733&draw=2&rank=1.
- 198.U.S. National Library of Medicine, JVRS-100 for the Treatment of Patients with relapsed or Refractory Leukemia, clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT00860522.
- 199.U.S. National Library of Medicine, High-Dose PEG-intron Pharmacokinetic Study in Patients With Melanoma (Study P04831 AM2), clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT00457418?term=PEG&cond=MELANOMA&draw=2&rank=4.
- 200.U.S. National Library of Medicine, Vemurafenib Plus Cobimetinib Plus PEG-interferon in Advanced Melanoma Patients Harboring the V600BRAF Mutation (VEMUPLINT), clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01959633?term=PEG&cond=MELANOMA&draw=2&rank=3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 201.U.S. National Library of Medicine, Study to Evaluate Sacituzumab Govitecan in Combination With Talazoparib in Patients With Metastatic Breast Cancer, clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT04039230?cond=Breast+Cancer&draw=3&rank=12.
- 202.U.S. National Library of Medicine, Dendritic Cell Activating Scaffold in Melanoma, clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01753089?term=01753089?term&draw=2&rank=1.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.