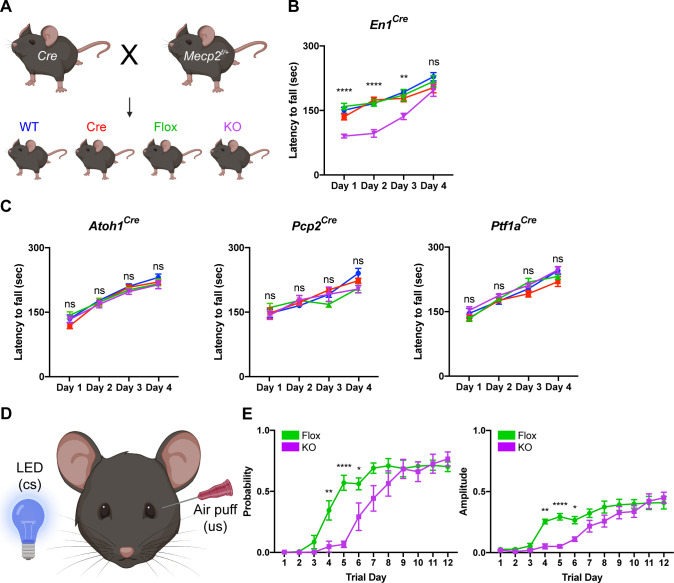
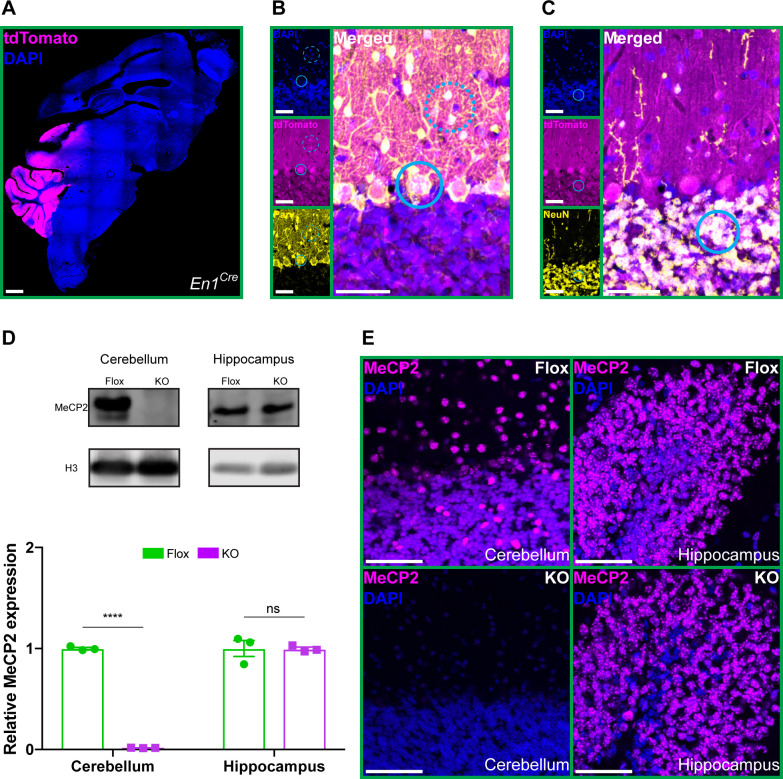
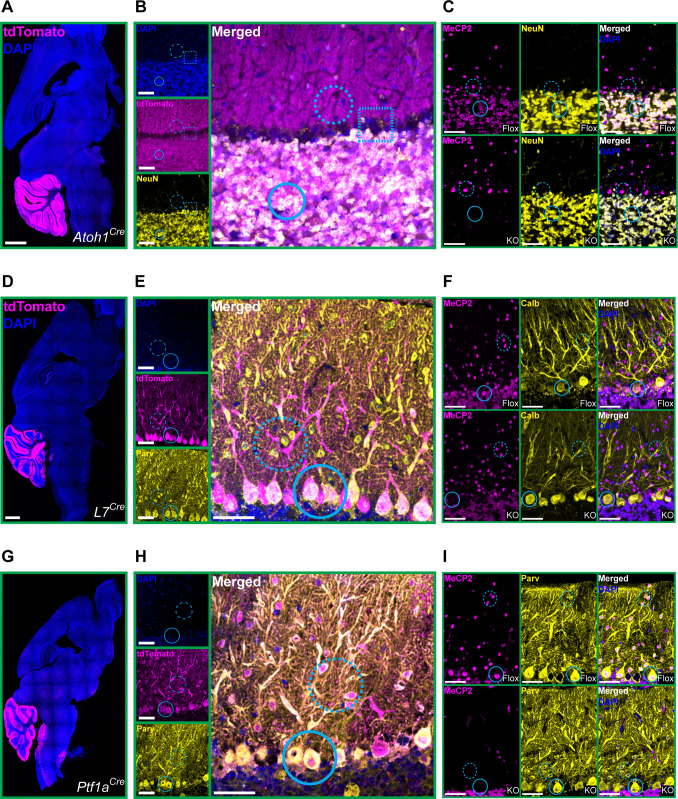
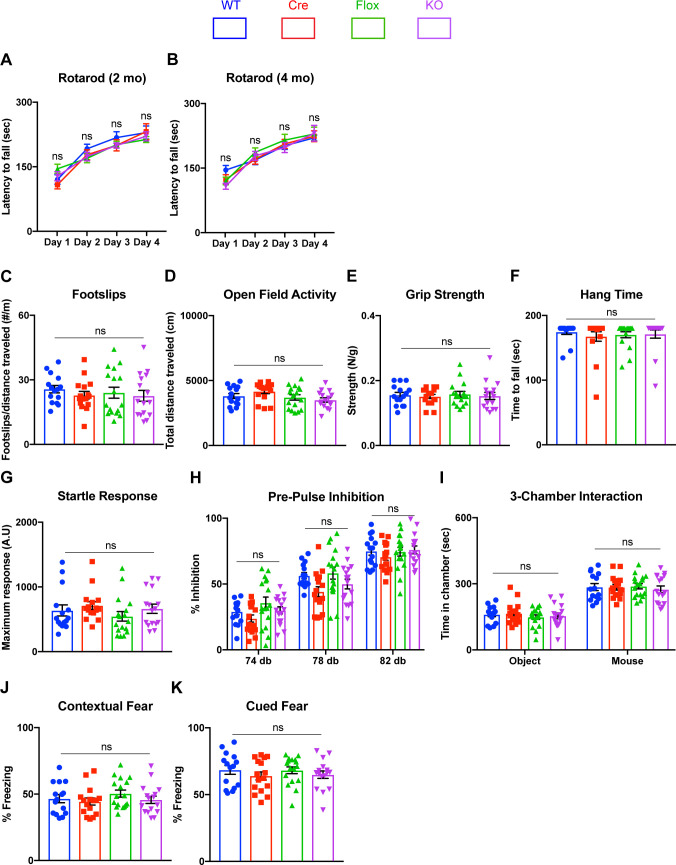
Figure 2. Deleting Mecp2 from the cerebellum, but not its neuronal subtypes, causes motor learning deficits in 6-month-old mice.
(A) Breeding scheme to generate WT, Cre, Flox, and KO mice. (B) Latency to fall on the rotarod over four training days in the En1Cre group. (C) Latency to fall on the rotarod over four training days in mice lacking Mecp2 in the granule cells (Atoh1Cre), Purkinje cells (Pcp2Cre), and Purkinje cells and molecular layer interneurons (Ptf1aCre). (D) Schematic of eyeblink conditioning that pairs an LED light (conditioned stimulus, cs) with an air puff (unconditioned stimulus, us) to generate an anticipatory eyelid closure (conditioned response) before the air puff. (E) Response probability and amplitude of eyelid closure over 12 training days in Flox and KO mice. N = 8–17 biologically independent mice per group. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. Statistical significance was determined by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. ns (p>0.05), *(p<0.05), **(p<0.01), ****(p<0.0001).