In the article titled “Inhibition of uncoupling protein 2 enhances the radiosensitivity of cervical cancer cells by promoting the production of reactive oxygen species” [1], an error was identified in Figure 3 which was introduced by the authors during figure preparation. Figure 3(a) is therefore corrected as below:
Figure 1.
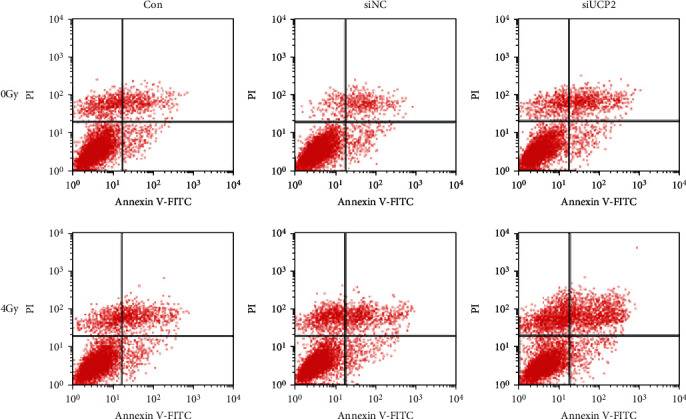
UCP2 knockdown increases apoptosis of irradiated HeLa cells. (a) Flow cytometry analysis of apoptosis after UCP2 knockdown with or without irradiation.
References
- 1.Liu C. H., Huang Z. H., Dong X. Y., et al. Inhibition of uncoupling protein 2 enhances the radiosensitivity of cervical cancer cells by promoting the production of reactive oxygen species. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. 2020;2020:13. doi: 10.1155/2020/5135893.5135893 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


