Abstract
The Arabidopsis thaliana genome encodes several genes that are known or predicted to participate in the formation of stress granules (SG). One family of genes encodes for Ras GTPase-activating protein–binding protein (G3BP)-like proteins. Seven genes were identified, of which one of the members was already shown to interact with plant virus proteins in a previous study. A phylogenetic and tissue-specific expression analysis, including laser-dissected phloem, by qRT-PCRs was performed and the sub-cellular localization of individual AtG3BP::EYFP fluorescent fusion proteins expressed in Nicotiana benthamiana epidermal cells was observed. Individual AtG3BP-protein interactions in planta were studied using the bimolecular fluorescence complementation approach in combination with confocal imaging in living cells. In addition, the early and late induction of G3BP-like expression upon Turnip mosaic virus infection was investigated by RNAseq and qRT-PCR. The results showed a high divergence of transcription frequency in the different plant tissues, promiscuous protein–protein interaction within the G3BP-like gene family, and a general induction by a viral infection with TuMV in A. thaliana. The information gained from these studies leads to a better understanding of stress granules, in particular their molecular mode of action in the plant and their role in plant virus infection.
Subject terms: Plant sciences, Plant stress responses, Abiotic, Biotic
Introduction
The Ras GTPase-activating protein-binding protein (G3BP), well investigated in humans and animals, is a member of the heterogeneous nuclear RNA-binding proteins and an element of the Ras signal transduction pathway. It was originally reported to bind to the Ras-GTPase-activating protein by associating with its SH3 domain, which was name-giving, but recent findings showed a central role of G3BP in translational control and RNA stability1. In humans, the G3BP protein family is comprised of G3BP-1, G3BP-2a, and its splice variant G3BP-2b. All G3BPs share four distinct motifs: (1) a nuclear transport factor 2 (NTF2)-like domain at the N-terminus, (2) an acidic and proline-rich region in the central part of the protein, (3) an RNA recognition motif (RRM) followed by (4) an arginine and glycine-rich region (RGG domains) at the C-terminus. The NTF2-like domain is involved in nuclear transport of G3BP-1 and, most likely, also G3BP-21. Moreover, the NTF2-like domain has been shown to facilitate protein–protein interactions; thus, G3BP interacts with several proteins but also forms homodimers2 or oligomers3. G3BP interacts with several proteins4–6, most interestingly with CAPRIN1 via its NTF2-like domain7 or with USP108. For CAPRIN1 no plant homolog protein has been identified yet, but the ubiquitin-specific protease 24 from Arabidopsis thaliana (AT4G30890) has striking sequence similarity with HsUSP10. Indeed, a AtG3BP-like protein interacts with AtUBP24 in bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) experiments9. Taken together, G3BP is a multifunctional protein, which interacts with several other cellular proteins at different developmental stages in different cell types, either in human or animal cells. However, the precise biological function(s) of G3BP has not been elucidated yet, but it is suggested that G3BP is involved in neurological diseases10,11. More recently, the overexpression of G3BP-1 has been implicated in cancer, suggesting a functional role of G3BP-1 in tumorigenesis12–14. In addition, G3BP is an important component of the host antiviral defense15,16. The general opinion is that G3BP executes its role by stress granule (SG) formation to regulate cellular homeostasis, RNA metabolism, and gene expression at the posttranscriptional level17,18. For example, human G3BP-1 can initiate SG formation2, which causes clustering of mRNA molecules derived from polysomes into SGs via a mechanism that involves G3BP and other proteins to halt translation. This makes SGs a primary target of virus infection. Viruses can employ different strategies to interfere with SG assembly16,19–21. For example, the non-structural protein 3 (nsP3) of Semliki Forest virus (SFV) can bind to the NTF2-like domain of G3BP-1 via an ‘FGDF’ motif and thereby preventing SG assembly and promoting viral RNA translation22–24 or multiple poliovirus proteins affect RNA granules to varying extents, G3BP-1, for example, is cleaved by 3Cpro25.
The general pathway of SG formation and function seems to be conserved, but only a few studies about plant stress granules are available18,19 compared to mammalian stress granules. For example, the G3BP-like family in A. thaliana has not yet been fully characterized. Abulfaraj and colleagues26 describe eight family members, generated and analyzed AtG3BP-7 (AT5G48650) OEX lines and KO lines, which showed no phenotype compared to control plants. This might be due to the fact that G3BPs in A. thaliana are redundant in their function, and a KO of one AtG3BP could be compensated by one of the others. Nevertheless, G3BP in plants and its interactions with plant viruses are poorly understood, although 'FGDF'-like binding motifs can be found in some plant viruses22, for example, it has been shown that the helper component proteinase (HC-pro) of potato virus A (PVA) induces the formation of RNA granules27. Only a few studies are investigating the interaction between plant viruses and the host's G3BP homologue, only recently, it was shown that A. thaliana G3BP-2 interacts with the nuclear shuttle protein (NSP) of the plant virus Abutilon mosaic virus9, but the purpose of this interaction is still unknown.
Turnip mosaic virus (TuMV), a member of the family Potyviridae, belonging to genus Potyvirus, has a single-stranded RNA genome. In general the size of the genomic RNA is < 10 kb and encodes a polyprotein, including the P1 protease28. At the N-terminal end of the P1 of Turnip mosaic virus (P1-TuMV) two FGDF-like motifs are located. This motif has been shown to bind the host protein G3BP22. This suggests that also P1-TuMV interacts with G3BP in plants in a similar matter. Aim of this study was therefore to gain more information about all putative members of G3BP-like proteins in A. thaliana, i.e. in terms of tissue expression, cellular localization and protein–protein interaction, and to investigate the response of the AtG3BPs to a viral infection, i.e. TuMV. Special emphasis here was also to monitor AtG3BPs expression to an early time point of infection.
Results
Phylogenetic analysis
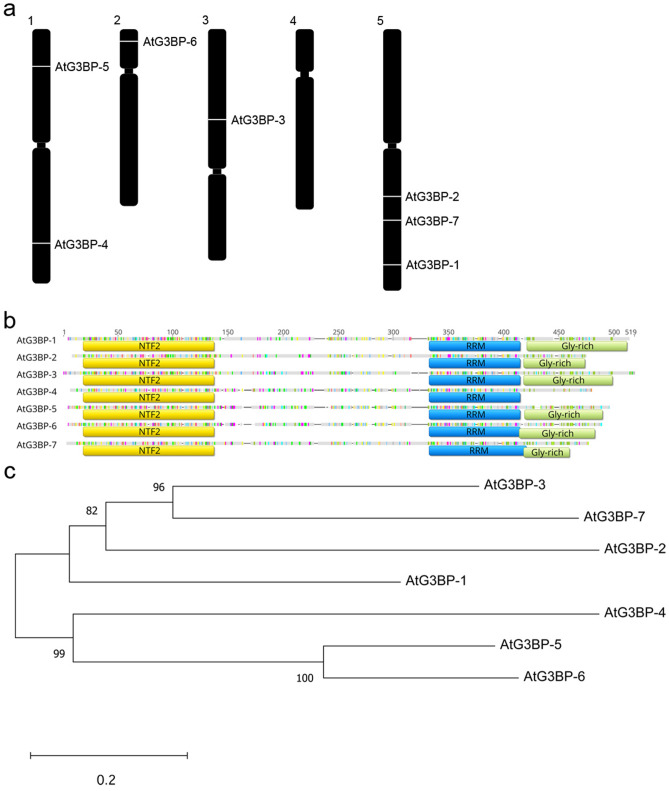
Bioinformatic analysis of the A. thaliana genome (TAIR10) revealed seven possible members of an A. thaliana G3BP-like gene family. These candidates are distributed on different chromosomes of the A. thaliana genome (Fig. 1a). AtG3BP-1, -2, and -7 are located on chromosome 5, AtG3BP-3 on chromosome 3, AtG3BP-4, and -5 on chromosome 1 and AtG3BP-6 on chromosome 2. They all have been identified by and thus share an N-terminal NTF2-like domain and a C-terminal RRM domain. Furthermore, all of them harbor the Gly-rich region and RG(G) motifs at the C-terminus, except AtG3BP-4 (Fig. 1b). Additionally, they contain several conserved amino acids whose functional relevance has been demonstrated in the human homolog, such as phenylalanine at position 41 of the consensus sequence (equivalent to position 33 in HsG3BP-1), which all AtG3BPs, again with the exception of AtG3BP-4, share with their mammalian homolog. A protein sequence alignment was performed to show the intra-family relatedness between the postulated members (Fig. 1c). They cluster into two main groups, the first one consisting of AtG3BP-1, -2, -3, and -7, the second one consisting of AtG3BP-4, -5, and -6.
Figure 1.
Relationship of the G3BP-like gene family in A. thaliana. (a) Genomic location of the different G3BP-like gene family in A. thaliana. The image was drawn using Adobe Photoshop CS4 (https://www.adobe.com/de/products/photoshop.html). (b) Schematic alignment of the seven G3BPs from A. thaliana generated with Geneious Prime® 2020 software. Nuclear transport factor 2 (NTF2), RNA-binding (RRM), and Gly-rich domains are annotated and highlighted with yellow, blue and green boxes, respectively. (c) The evolutionary history was inferred as described in the methods section. The optimal tree with the sum of branch length = 3.69183953 is shown. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. This analysis involved 7 amino acid sequences. All ambiguous positions were removed for each sequence pair (pairwise deletion option). There were a total of 524 positions in the final dataset.
Sequence comparison of each of the three different AtG3BP domains showed no significant alteration to the phylogenetic analysis based on the full amino acid sequences comparison. AtG3BP-1, -2, -3, and -7, and AtG3BP-4, -5, and -6 still cluster together if only the NTF2 domain is analyzed (Supplementary Fig. S1a) and with minor changes if the RRM domain is compared (Supplementary Fig. S1b). Strikingly, AtG3BP-1 and -7, and -2 and -3 cluster together, when comparing only the Gly-rich regions (Supplementary Fig. S1c), because AtG3BP-4 lacks this region. The cluster AtG3BP-5 and -6 remains unchanged. Table 1 summarizes the protein sequence similarity and the nucleotide sequence identity of the coding sequences based on the ClustalW sequence alignment. Here, AtG3BP-5 and AtG3BP-6 show the highest amino acid sequence identity, 67%, whereas AtG3BP-2 and -5 the lowest with 36.2%.
Table 1.
Sequence similarity of the different AtG3BPs in %.
The protein sequence similarity (shaded in grey) and the nucleotide sequence identity (white boxes) of the coding sequences were calculated based on the ClustalW alignment with the BLOSUM62 matrix and a threshold of 0.
Subcellular localization of AtG3BP::EYFP fusion proteins in N. benthamiana
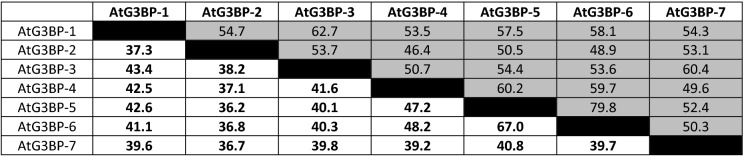
To study the subcellular localization, the AtG3BPs were each transiently overexpressed in functional fusion with enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (EYFP) under the control of the CaMV 35S promoter in N. benthamiana epidermis cells (Fig. 2). All possible members of the AtG3BP family showed a cytoplasmic signal under ambient condition, with AtG3BP-6 also a nuclear EYFP signal in addition. Furthermore, AtG3BP-3, -5, and -7 form granule-like structures already under ambient condition. After heat shock treatment, these structures can be observed also for the other AtG3BPs (Fig. 2). The nuclear EYFP signal of AtG3BP-6 can still be observed after stress application (Supplementary Fig. S2). The expression of the fusion proteins was verified by western blot analysis (Supplementary Fig. S3).
Figure 2.
Subcellular localization of AtG3BP proteins and free EYFP in transient expressing N. benthamiana leaves under ambient conditions and after heat shock. Pictures are maximum projections of z-stacks obtained by confocal laser scanning microscopy and were taken 2 dpai. The individual pictures correspond to a size of 145 × 145 µm.
AtG3BP protein interaction profiling in vivo
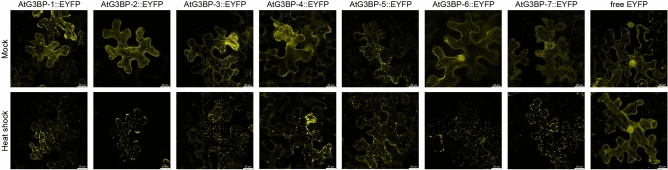
Previous studies have shown that the NTF2-domain plays a key role in the oligomerization of HsG3BP-12. Since all predicted A. thaliana G3BP homologs share this domain, we analyzed their ability to form homo- and heterooligomers by BiFC. All 49 pair-wise combinations were co-expressed in N. benthamiana leaves and monitored for a reconstituted fluorescent YFP signal under ambient conditions and after heat shock treatment. The data for homooligomerization is shown in Fig. 3a and b, and for heterooligomerization summarized in Fig. 3c and d, pictures in the Figs. S4–S7. Figure 3a shows the reconstituted YFP signals for the different AtG3BPs C-terminally fused to the respective YFP fragment before and after heat shock. All AtG3BPs but AtG3BP-6 showed cytoplasmatic YFP signal under ambient conditions, with AtG3BP-1, -4, -5, and -7 already forming granule-like structures under these conditions. After heat shock, the evenly distributed cytoplasmic-localized YFP fluorescence changed almost completely into a granular YFP signals. AtG3BP-6 C-terminally fused to splitYFP did not show any signal after heat shock. When fused N-terminally to the respective YFP fragments, only AtG3BP-1, -2, and -4 showed an exclusively cytoplasmatic reconstituted YFP signal. After heat shock treatment YFP fluorescent, granule-like structures can be observed for AtG3BP-1, -2, -4, -5, and now also for -6. We also tested the ability of the different AtG3BPs to form heterodimers in vivo with each other by co-infiltrating the reciprocal splitYFP fusion proteins and examining for reconstituted YFP signals two days post agroinfiltration (dpai) by laser scanning microscopy (Figs. S4–S7). The results are summarized in Fig. 3c and d. Overall, all AtG3BPs seem to interact with each other under ambient conditions as well as stress conditions (in this case heat shock).
Figure 3.
Visualization of self-interaction of the various AtG3BPs via bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) under ambient conditions and heat shock (45 min at 37 °C). (a) Self-interaction of A. thaliana G3BP homologs fused C-terminally with splitYFP. (b) Self-interaction of the respective AtG3BPs N-terminally fused to splitYFP. All pictures are projections of z-stacks obtained by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Fusion constructs of the protein with the corresponding reporter were transiently expressed in N. benthamiana leaves by co-infiltration via A. tumefaciens at an OD600 = 0.1. The individual pictures correspond to a size of 185 × 185 µm. (c,d) Schematic overview of the protein–protein interactions between the different AtG3BPs. Proteins were fused C-terminally (c) or N-terminally (d) to splitYFP and pairwise co-expressed in N. benthamiana leaves. Cells were checked for re-constituted YFP signal 2 dpai and heat shock was performed to examine changes of interaction under stress conditions. Schematic overviews were created using Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 software.
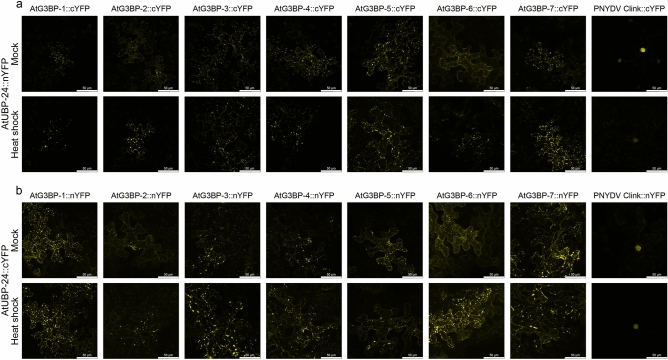
To test whether the observed granule-like structures are indeed stress granules, we performed BiFC experiments with the stress granule protein AtUBP-24 (AT4G30890)9. As a control, we used the Clink protein of the Pea necrotic yellow dwarf virus (Accession JN133280) to show that our predicted AtG3BPs actually promote stress granule formation and not AtUBP-24 alone (Fig. 5). AtUBP-24 harbors an ‘FGSF’-motif at its N-terminal end, similar to the ‘FGDF’-motif of HsUSP-10, the protein’s G3BP binding domain. C-terminal fusion constructs of AtG3BP or Clink with cYFP were co-agroinfiltrated into N. benthamiana leaves with AtUBP-24::nYFP (Fig. 4a), AtG3BP::nYFP and Clink::nYFP with AtUBP-24::cYFP (Fig. 4b), respectively. Epidermal cells were monitored for reconstituted YFP signals at two dpai by confocal microscopy. All combinations of the different AtG3BPs with AtUBP-24 showed granular YFP signal at ambient conditions and after heat shock, whereas co-expression of Clink with AtUBP-24 showed an exclusively nuclear signal for both conditions.
Figure 5.
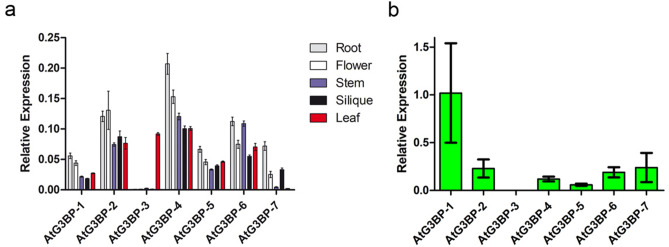
Expression level analyses. (a) qRT-PCR was used to measure the relative gene expression of the different AtG3BPs in roots, stem, flower, silique, and rosette leaves. Transcript levels were calculated using the 2-∆Ct method with AtActin-2 as the endogenous control. The error bar represents the standard error. (b) Expression ratio of AtG3BP genes in phloem tissue compared to non-phloem tissue in A. thaliana leaves extracted by laser dissection of AtSUC2promoter::GFP plants. Gene expression was normalized to AtActin-2 and expression levels were calculated using the 2−∆Ct method.
Figure 4.
Visualization of protein–protein interaction of the AtUBP-24 with the various AtG3BPs and PNYDV Clink via bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) under ambient conditions and heat shock (45 min at 37 °C). (a) Interaction of AtUBP-24 with the corresponding partners fused C-terminally with splitYFP. (b) Interaction of AtUBP-24 and the respective AtG3BPs and PNYDV Clink N-terminally fused to splitYFP. All pictures are projections of z-stacks obtained by confocal laser scanning microscopy. The individual pictures correspond to a size of 185 × 185 µm.
qRT-PCR analysis of AtG3BP gene transcript abundance
The presence of seven A. thaliana G3BP-like homologs raises the question of their distinct function(s), the possibility of redundancy in function(s) in either the same or in different tissues and their possible role in virus infection9. To investigate the expression levels a qRT-PCR analysis of transcript abundance has been performed for G3BP-like gene family members in different plant tissue, namely root, stem, flower, silique, leaf, and phloem under ambient conditions. Except for AtG3BP-3 and AtG3BP-7, the different G3BP genes show a ubiquitous expression throughout all tested tissues. While AtG3BP-3 shows expression only in leaf tissue, AtG3BP-7 is nearly not detectable in leaves, but primarily in root tissue. Overall expression levels between the different AtG3BPs were comparable, with AtG3BP-4 showing the highest constitutive expression level (Fig. 5a).
Phloem tissue from a transgenic GFP driven under the AtSUC2 promoter A. thaliana plant was sampled utilizing a laser dissection microscope (Supplementary Video S1) to monitor AtG3BPs transcripts abundance in this specialized tissue. With the exception of AtG3BP-3, all AtG3BPs were detectable in the phloem. AtG3BP-1 shows the highest relative expression, followed by AtG3BP-2, -6, and -7. AtG3BP-4 and -5 are the lowest expressed in the phloem compared to the other AtG3BPs (Fig. 5b). A direct comparison between the relative expression values in the phloem tissue and the other tissues might be incorrect, due to the differences in the RNA extraction procedure. Petioles were cut, fixed, sectioned, and laser-dissected to gain phloem tissue. Nevertheless, an expression level analyses of the different AtG3BPs transcripts in roots, stem, flower, silique, and rosette leaves, which includes the data from phloem tissue, is shown in Supplementary Fig. S8.
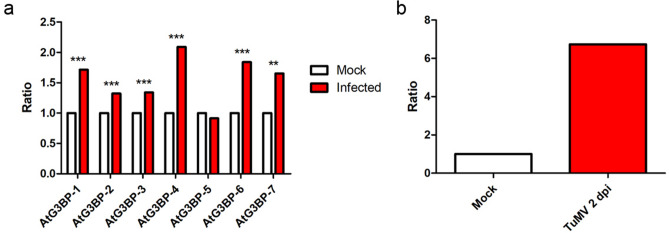
AtG3BP-2 was shown to interact with the nuclear shuttle protein of a plant virus9, which raised the question if the expression levels of the different A. thaliana G3BP-like homologs are affected by a plant virus in A. thaliana, for example TuMV. TuMV, which also expressed a RFP fused with a nuclear localization signal (TuMV-RFP29) was used in further studies. Microscopic analysis confirmed systemic infection of A. thaliana plants and RFP expression (Supplementary Fig. S9). TuMV-RFP infection generally induced AtG3BPs expression in the leaf (Fig. 6a) at 14 dpi, significantly, except AtG3BP-5.
Figure 6.
Expression level analyses. (a) Transcript abundance in TuMV-infected leaf tissue was measured and compared to non-infected tissue to determine the regulation of the expression level of the different AtG3BPs, AtActin-2 served as the internal control. The asterisks indicate significance measured by two-tailed t-test (** = p < 0.01; *** = p < 0.005) (b) qRT-PCR analysis for verification of RNAseq data. AtG3BP-4 expression level in TuMV infection sites 2 dpi was measured and compared to mock-inoculated tissue.
The success or failure to establish an infection of a plant by a pathogen depends on an early cascade of molecular interactions between the plant and the pathogen in the initially infected cells. To study the early events of virus infection in plants, avoid dilution effects and thus to obtain the most meaningful information, micro-dissected tissue at 2 dpi was collected and subsequently analyzed in a transcriptomic approach (RNAseq) (Table 2) and subsequently by qRT-PCR (Fig. 6b).
Table 2.
RNAseq data for the different AtG3BPs and AtUBP-24 in TuMV-RFP infection sites at 2 dpi compared to the mock-treated tissue.
| Gene ID | Gene name | log2 FC | p value | P-adj |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT5G60980 | AtG3BP-1 | 0.483 | 0.496 | NA |
| AT5G43960 | AtG3BP-2 | 1.022 | 0.269 | NA |
| AT3G25150 | AtG3BP-3 | − 0.022 | 0.983 | NA |
| AT1G69250 | AtG3BP-4 | 1.711 | 0.009 | 0.060 |
| AT1G13730 | AtG3BP-5 | − 0.174 | 0.867 | NA |
| AT2G03640 | AtG3BP-6 | 0.063 | 0.951 | NA |
| AT5G48650 | AtG3BP-7 | − 0.387 | 0.694 | NA |
| AT4G30890 | AtUBP-24 | 0.175 | 0.849 | NA |
The different AtG3BPs were unevenly expressed, either up- or down-regulated, with the striking feature that AtG3BP-4 most probably significantly upregulated (1.7fold), which was then confirmed by qRT-PCR analysis (Fig. 6b). AtG3BP-4 was induced sixfold by TuMV infection at 2 dpi.
Discussion
Human G3BP, first reported by Parker and colleagues30, binds to the SH3 domain of RasGAP. Responsible for the binding was the N-terminal nuclear transfer factor 2 (NTF2)-like domain31. The C-terminal portion of HsG3BP-1 contains an RRM motif, indicating that HsG3BP-1 has RNA-binding capacities. Indeed, HsG3BP-1 was reported to co-immunoprecipitated with mRNAs and to bind to and cleave, for example, the 3′ untranslated region of the c-myc mRNA in vitro9. Database searching has allowed the identification of members of the A. thaliana G3BP-like gene family. Seven G3BP-like proteins, within the group of NTF2 and RRM domain family proteins, in A. thaliana were identified and further investigated in this study. Abulfaraj and colleagues26 described additionally an RNA-binding (RRM-RBD-RNP motif) domain nuclear transport factor 2 family protein (AT3G07250), but in contrast to the other seven, AT3G07250 has a different domain structure, i.e., three RRM domains instead of one and the Gly-rich region and the RG(G) motifs are missing. In addition, the A. thaliana Information Resource (TAIR) database32 and Klepikova eFP RNAseq data revealed that AT3G07250 is only expressed in flowers 12–1433. Attempts to amplify the ORF of AT3G07250 by RT-PCR from leaf tissue consequently failed (data not shown), whereas transcriptional analysis showed that AtG3BP-1 to -7 were expressed, mostly throughout the plant, with the exception of AtG3BP-3. AtG3BP-3 amplification was negative in phloem tissue but exclusively expressed in leaf tissue, which might be a hint for guard cell-specific expression. Guard cells form stomata and are highly specialized cells, in which gene expression is often regulated by specific promoter activity34. Promoter studies will provide insight into plant cell-specific gene expression of the AtG3BP gene family in the future. In summary, it is a reasonable assumption that the different G3BP-like proteins within the G3BP gene family in A. thaliana have redundant function in different tissues at different developmental stages. It is therefore suggested that the AtG3BPs, like their animal counterparts, are likely to be involved in a wide variety of cellular processes, most importantly in stress granules formation. This suggestion is strongly supported by the fact that the two G3BP family members in mammals,, G3BP-1 and G3BP-2, and both proteins co-localize in SGs, when cells are subjected to stress35,36. Sub-cellular localization studies showed that the different AtG3BPs are also localized in SG upon heat stress. In addition, AtG3BP-2 localizes into SGs, if the plant cell is treated with KCN9. Kedersha and colleagues37 concluded that G3BP binds 40S ribosomes through its RGG region and is essential for stress granule condensation, but distinct from polysome disassembly, and the condensation process is regulated by competitive Caprin1/USP10 binding to G3BP. The A. thaliana UBP-24 protein is the plant homolog of human USP109. Consequently, all putative members of the AtG3BP family studied interact in planta with AtUBP-24. In addition, homo- and heterodimerization, as described for the human G3BPs2, was also confirmed in this study. The analyzed AtG3BP family members may, therefore, fulfill a similar role in SG assembly and disassembly as their well investigated mammalian counterpart and thus may also play a pivotal role in viral infection15,16, as previously suggested by interaction studies of AtG3BP-2 and the nuclear shuttle proteins of ssDNA plant viruses9. Therefore, it was necessary to investigate if the other identified members of the AtG3BP family were also affected by a virus infection. First, tissue tropism and expression level of the AtG3BPs was determined, and then the question was addressed if the expression level alters upon virus infection. Not surprisingly, six of seven AtG3BP members were significantly upregulated in infected leaf tissue, but most interestingly only AtG3BP-4 was significantly induced in early infection, as shown by transcriptomic data obtain from dissected tissue and confirmed by qRT-PCR analysis. The complete analysis of the TuMV differentially induced expressed genes in A. thaliana tissue at 2 dpi will be described elsewhere and further analyses on the role of AtG3BP-4 in early and systemic virus infection, in general, must and will be performed in the future. It is reasonable to assume that G3BP plays a role at an early stage of infection; for example, members of the Picornaviridae family also modulate SGs accumulation during replication. Poliovirus regulates SGs in a time-dependent manner; at early times the 2A proteinase induces assembly of SGs that are later disassembled by the 3C proteinase through G3BP-1 cleavage38. Similar temporal control of SG assembly is exhibited by Coxsackievirus B3 assembly as early as 3 h post-infection.
Given that SGs are generally associated with regulation of gene expression, viruses have evolved different mechanisms to counteract their assembly or to use them in their favor to replicate within the host environment successfully. In this study, data is presented about a SG key factor, namely G3BP. As their mammalian equivalents, the AtG3BPs behave similarly and their expression in early response to a virus infection was investigated and confirmed. Particular focus must, therefore, be on AtG3BP-4, which we show is highly upregulated upon TuMV infection. Analysis of KO and OEX plant lines in the future will shed more light on the G3BP family's role in virus infection in particular and other stresses in general.
Methods
Plant material and growth conditions
Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype Columbia (Col-0; NASC ID N1092) and AtSUC2promoter::GFP plants (as described in39) were used throughout the study. A. thaliana plants were grown on soil in a growth chamber at 24 °C under short-day conditions (8 h light/16 h dark). Nicotiana benthamiana plants were grown in an insect-free greenhouse under long-day conditions (16 h supplementary light) at 22 °C.
Expression plasmid construction
The coding regions of AtG3BP-1 (AT5G60980), AtG3BP-2 (AT5G43960), AtG3BP-3 (AT3G25150), AtG3BP-4 (AT1G69250), AtG3BP-5 (AT1G13730), AtG3BP-6 (AT2G03640), AtG3BP-7 (AT5G48650), AtUBP-24 (AT4G30890) and PNYDV Clink (Accession JN133280) were amplified by PCR and inserted into the vector pENTR™/D-TOPO™ (Invitrogen). For C-terminal fusion constructs the translational stop codon was removed by PCR. The inserts were then transferred into the expression vectors pGWB44140, pB4nYGW, pB4cYGW, pB4GWnY, pB4GWcy41, pRB-C-VenusN173 and pRB-C-VenusC15542 using L/R-Clonase™ II enzyme mix (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The resulting plasmids are expressing the corresponding genes in fusion with the reporter gene under the control of the CaMV 35S promoter. All destination vectors and the used primers are listed in Supplementary Table S1. All plasmids were confirmed by Sanger sequencing (Eurofins, Ebersberg, Germany).
Transient expression of fusion proteins in N. benthamiana
All expression plasmids were transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain LBA4404 or GV3101 by electroporation. Agrobacterium cultures were grown in selective media and infiltrated at a final OD600 = 0.1. For bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) experiments cultures were mixed and then co-infiltrated at a 1:1 ratio into the abaxial surface of 3–5 week-old N. benthamiana leaves.
Heat treatment of plant samples and microscopy
Heat stress was applied by incubating the samples for 45 min at 37 °C in a humidified box. Fluorescence was visualized in epidermal cell layers of the leaves after 2–3 days of infiltration using confocal microscopy. A Leica TCS SP8 confocal laser-scanning microscope was utilized for visualization of EYFP and BiFC signals. Enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (EYFP) and VENUS were excited by using a 488 and 514 nm laser. A Leica HC PL APO CS2 63×/1.20 (NA = 0.75) water objective was employed. BiFC images were acquired with a resolution of 1024 × 1024 pixels. Images for the analyses of the cellular localization were acquired with a resolution of 2632 × 2632 pixels for deconvolution with the SVI Huygens Essential software (Scientific Volume Imaging B.V., Hilversum, Netherlands) embedded in the Leica LAS X program (Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany) using the standard strategy. Images were processed and compiled using Photoshop CS4 (Adobe, San Jose, CA).
Western blot analysis
Proteins were extracted from 100 mg infiltrated leaf material with 250 µl SDS-sample buffer (4% SDS, 20% glycerol, 5% β-Mercaptoethanol, 100 mM Tris–HCl pH 6.8, 0.005% bromophenol blue) after grinding in liquid nitrogen. The extracts were then centrifuged at 13.000 rpm for 10 min and the supernatants were collected. Samples were resolved in a 4–20% Mini-PROTEAN® TGX™ Precast Protein Gel (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA) and transferred to an Amersham™ Hybond™ P 0.45 PVDF membrane (GE Healthcare, Germany). PVDF membranes were blocked using 5% skim milk powder in TBS-T (0.05% Tween 20) and incubated with primary antibody (Mouse anti-GFP; Invitrogen, GF28R, 1:2000) for 16 h at 4 °C followed by incubation with HRP-linked secondary antibody (Goat anti-Mouse HRP-conjugated; Invitrogen, 32,430, 1:500) (1 h at room temperature) in TBS-T. Chemiluminescence was detected using SuperSignal West Pico substrate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Germany) and a ChemiDoc XRS + Imaging system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA).
Sap inoculation of experimental plants
The mechanical inoculation of A. thaliana Col-0 plants was performed by grinding TuMV-RFP29 infected leaf material in homogenization buffer (0.05 M K/Na-phosphate, 1 mM EDTA, 5 mM Na-DIECA, 5 mM thioglycolic acid; pH 7.0) and rubbing onto the Celite-covered abaxial surface of healthy 4-week-old A. thaliana plants. As a control, mock inoculations with buffer only were performed. Since we were also interested in sampling early infection sites such as two dpi, we used eight-weeks-old A. thaliana plants with fully developed leaves to avoid tissue damage during rub inoculation in small seedlings.
Laser dissection microscopy
Samples of AtSUC2promoter::GFP plant petioles or TuMV-RFP29 infection sites, respectively, were fixed in 10% formalin under vacuum for 15 min and left shaking in fixative at 4 °C overnight. Fixed samples were then washed twice in PBS for 15 min at 4 °C before being vacuum infiltrated with ice-cold 10% sucrose followed by 20% sucrose. The cryo-protected leaves are then embedded in OCT compound within molds and immediately frozen in isopentane cooled with liquid nitrogen. Cryosections were carried out in a Cryostar NX50 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA). 10 µm thick sections were mounted onto membrane slides (Molecular Machines and Industries, Eching, Germany) and washed with distilled water and dehydrated in pre-chilled ethanol grades (70%, 95%, and 100%) and air-dried. Fluorescent cells were then collected with a CellCut laser microdissection microscope (MMI, Eching, Germany). The slides were observed using a CFI S Plan Fluor ELWD 20x (NA = 0.45) objective with UV light excitation. Extraction was performed employing the following laser settings: Cut velocity 15 µm/s; Laser focus 158 µm; Laser power 85%. For phloem analysis, approximately 1 mm2 of GFP-labelled phloem cells were pooled in a 0.2 ml Isolation cap microcentrifuge tube (MMI, Eching, Germany).
RNA was extracted from plant material with the GenElute FFPE RNA Purification Kit (Sigma, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s protocol with modifications. The Deparaffinization step was omitted since samples were embedded in OCT. 30 μl Digestion Buffer A and 1 μl of the reconstituted Proteinase K were added to the cap and incubated for 30 min at 55 °C with vortexing each 10 min. The tubes were inverted. After a spin down, samples were transferred to a new 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube, and another 270 μl of Digestion Buffer A and 9 μl of Proteinase K were added. The tube was incubated for 15 min at 55 °C with vortexing each 5 min.
We used laser microdissection to collect only infection sites with minimum non-infected surrounding tissue (CellCut laser microdissection microscope, MMI, Eching, Germany). Small pieces (~ 0.25 mm2) of infected and mock leaves were mounted onto membrane slides (Molecular Machines and Industries, Eching, Germany) and covered with 70% ethanol for 10 min for a quick fixation and then with 100% ethanol until the ethanol evaporated from the slide. This step will reduce the water content of the leaves and facilitate the sectioning. RFP-labeled infection sites were precisely dissected, and the similar dissected area was obtained from mock-inoculated plants using the fluorescence module of the CellCut laser microdissection microscope. Three infection sites per plant were collected and pooled in the same 0.2 ml cap, and five replicates were obtained.
RNA isolation and qRT-PCR analysis
Total RNA from A. thaliana rosette leaves, stem, siliques, flowers, and roots was extracted using the RNeasy Plant Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. RNA extracts were treated with RNase-free DNase I and quantified with a NanoDrop2000 spectrophotometer. For cDNA synthesis, 1.5 µg of total RNA were transcribed with 300 U M-MLV Reverse Transcriptase using oligo (dT)12–18 primer (0.5 µM). For each 20 µl qRT-PCR reaction 1 µL of cDNA, 10 µl of KAPA SYBR® FAST qPCR Master Mix (2X), and primers (0.2 µM) specific for AtActin-2 (AT3G18780), AtG3BP-1 (AT5G60980), AtG3BP-2 (AT5G43960), AtG3BP-3 (AT3G25150), AtG3BP-4 (AT1G69250), AtG3BP-5 (AT1G13730), AtG3BP-6 (AT2G03640), and AtG3BP-7 (AT5G48650) were used. Reactions were run on a qTOWER3 G (Analytik Jena, Jena, Germany) and a Mastercycler® realplex (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany). Between 6 and 12 biological replicates, with 3 technical replicates each, were used in every experiment. Transcript levels and ratios were then calculated using the 2−∆Ct or the 2−∆∆Ct method, respectively, with AtActin-2 as the endogenous control. Statistical significance was measured by two-tailed t-test. The primers utilized for the detection of specific transcripts are listed in Supplementary Table S2.
Library preparation, characterization and sequencing
Individual libraries from mock and TuMV-RFP-infected plants were prepared according to the Smart-3SEQ protocol previously described in43. The quality of libraries was checked with Agilent 2200 using the high sensitive DNA chip from Agilent. Libraries were sequenced in the NextSeq 500 using the NextSeq 500/550 high output Kit v2.5, 75 cycles from Illumina (Illumina Inc., San Diego, US).
Data preprocessing
After sequencing, reads were demultiplexed and converted to FASTQ with bcl2fastq (Illumina Inc., San Diego, US) with the adapters trimmed. UMI sequence, G-overhang, and A-tails from FASTQ data were removed with the script umi_homopolymer.py as described by Ref.43. Reads shorter than 18 nt were removed with the tool Filter FASTQ44.
Read alignment, counting and analysis of gene expression
Final reads were mapped to the genome of A. thaliana Col-0 using Bowtie2 tool using the default setting45. Resulting BAM files from Bowties2 were used to count the reads with the tool featureCounts46. Gene differential expression between mock and TuMV-RFP-infected plants was calculated using output files from featureCounts with the DESeq2 tool47.
Phylogenetic analysis
AtG3BP protein and coding sequences were retrieved from the TAIR10 genome annotation data set (http://www.arabidopsis.org/). Multiple sequence alignments were carried out in MEGA X software utilizing the CLUSTAL W algorithm48. A BLOSUM62 matrix was used with a gap opening penalty of 10 and a gap extension penalty of 0.2. All phylogenetic trees were constructed with the Neighbor Joining (NJ) method49 with 1000 bootstrap replicas50 using the Poisson correction method51 and are in the units of the number of amino acid substitutions per site. Protein domains were identified using ExPASy PROSITE (https://prosite.expasy.org/)52. Geneious Prime® 2020.1.2 (https://www.geneious.com) was used to visualize alignments and protein domains.
Supplementary Information
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) – KR4875/3-1. The authors would like to thank Verena Maiberg and the entire team of the DSMZ Plant Virus Department for technical assistance and taking care of the experimental plants.
Author contributions
H.R., K.A. and B.K. conceived and designed the experiments; H.R. prepared the figures and drawings; H.R. and K.A. performed the experiments; K.A. designed and performed transcriptomic analysis of early infection sites; H.R., K.A. and B.K. wrote the paper.
Funding
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41598-021-81276-7.
References
- 1.Alam U, Kennedy D. Rasputin a decade on and more promiscuous than ever? A review of G3BPs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2019;1866:360–370. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.09.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tourrière HH, et al. The RasGAP-associated endoribonuclease G3BP assembles stress granules. J. Cell Biol. 2003;160:823–831. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200212128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 3.Kristensen O, Vognsen T, Runa I. Crystal structures of the human G3BP1 NTF2-Like domain visualize FxFG Nup repeat specificity. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e80947. doi: 10.1371/annotation/b4a49855-87b9-436a-a4bd-bc64b50a6c93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kaehler C, et al. Ataxin-2-like is a regulator of stress granules and processing bodies. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:1–12. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hinton SD, Myers MP, Roggero VR, Allison LA, Tonks NK. The pseudophosphatase MK-STYX interacts with G3BP and decreases stress granule formation. Biochem. J. 2010;427:349–357. doi: 10.1042/BJ20091383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Liu ZS, et al. G3BP1 promotes DNA binding and activation of cGAS. Nat. Immunol. 2019;20:18–28. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0262-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Solomon S, et al. Distinct structural features of caprin-1 mediate its interaction with G3BP-1 and its induction of phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF2α, entry to cytoplasmic stress granules, and selective interaction with a subset of mRNAs. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007;27:2324–2342. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02300-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Soncini C, Berdo I, Draetta G. Ras-GAP SH3 domain binding protein (G3BP) is a modulator of USP10, a novel human ubiquitin specific protease. Oncogene. 2001;20:3869–3879. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Krapp S, Greiner E, Amin B, Sonnewald U, Krenz B. The stress granule component G3BP is a novel interaction partner for the nuclear shuttle proteins of the nanovirus pea necrotic yellow dwarf virus and geminivirus abutilon mosaic virus. Virus Res. 2017;227:6–14. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.09.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Anisimov S, et al. G3BP1 inhibits ubiquitinated protein aggregations induced by p62 and USP10. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:1–16. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46237-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Martin S, et al. Deficiency of G3BP1, the stress granules assembly factor, results in abnormal synaptic plasticity and calcium homeostasis in neurons. J. Neurochem. 2013;125:175–184. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zhang H, et al. Involvement of Ras GTPase-activating protein SH3 domain-binding protein 1 in the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-induced metastasis of breast cancer cells via the Smad signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 2015;6:17039–17053. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wang Y, et al. G3BP1 promotes tumor progression and metastasis through IL-6/G3BP1/STAT3 signaling axis in renal cell carcinomas article. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:1–13. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0012-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dou N, Chen J, Yu S, Gao Y, Li Y. G3BP1 contributes to tumor metastasis via upregulation of Slug expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016;6:2641–2650. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.White JP, Cardenas AM, Marissen WE, Lloyd RE. Inhibition of cytoplasmic mRNA stress granule formation by a viral proteinase. Cell Host Microbe. 2007;2:295–305. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2007.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zhang Q, Sharma NR, Zheng ZM, Chen M. Viral regulation of RNA granules in infected cells. Virol. Sin. 2019;34:175–191. doi: 10.1007/s12250-019-00122-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Anderson P, Kedersha N. RNA granules: post-transcriptional and epigenetic modulators of gene expression. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009;10:430–436. doi: 10.1038/nrm2694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chantarachot T, Bailey-Serres J. Polysomes, stress granules, and processing bodies: a dynamic triumvirate controlling cytoplasmic mRNA fate and function. Plant Physiol. 2018;176:254–269. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.01468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mäkinen K, Lõhmus A, Pollari M. Plant RNA regulatory network and RNA granules in virus infection. Front. Plant Sci. 2017;8:1–15. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.02093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.McCormick C, Khaperskyy DA. Translation inhibition and stress granules in the antiviral immune response. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017;17:647–660. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Xu M, Mazur MJ, Tao X, Kormelink R. Cellular RNA hubs: friends and foes of plant viruses. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2020;33:40–54. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-06-19-0161-FI. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Panas MD, et al. Viral and cellular proteins containing FGDF motifs bind G3BP to block stress granule formation. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11:1–22. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Panas MD, et al. Sequestration of G3BP coupled with efficient translation inhibits stress granules in Semliki Forest virus infection. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2012;23:4701–4712. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e12-08-0619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Panas MD, Ahola T, McInerney GM. The C-terminal repeat domains of nsP3 from the old world alphaviruses bind directly to G3BP. J. Virol. 2014;88:5888–5893. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00439-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Dougherty JD, Tsai WC, Lloyd RE. Multiple poliovirus proteins repress cytoplasmic RNA granules. Viruses. 2015;7:6127–6140. doi: 10.3390/v7122922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Abulfaraj AA, et al. The Arabidopsis homolog of human G3BP1 is a key regulator of stomatal and apoplastic immunity. Life Sci. Alliance. 2018;1:1–13. doi: 10.26508/lsa.201800046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hafrén A, Lõhmus A, Mäkinen K. Formation of potato virus A-induced RNA granules and viral translation are interrelated processes required for optimal virus accumulation. PLOS Pathog. 2015;11:e1005314. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zerbini FM, et al. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: dicistroviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017;98:355–356. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gutiérrez S, et al. Dynamics of the multiplicity of cellular infection in a plant virus. PLOS Pathog. 2010;6:e1001113. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Parker F, et al. A Ras-GTPase-activating protein SH3-domain-binding protein. Mol Cell. Biol. 1996;16:2561–2569. doi: 10.1128/MCB.16.6.2561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kennedy D, et al. Characterization of G3BPs: tissue specific expression, chromosomal localisation and rasGAP120 binding studies. J. Cell. Biochem. 2002;84:173–187. doi: 10.1002/jcb.1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Berardini TZ, et al. The arabidopsis information resource: making and mining the ‘gold standard’ annotated reference plant genome. Genesis. 2015;53:474–485. doi: 10.1002/dvg.22877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Klepikova AV, Kasianov AS, Gerasimov ES, Logacheva MD, Penin AA. A high resolution map of the Arabidopsis thaliana developmental transcriptome based on RNA-seq profiling. Plant J. 2016;88:1058–1070. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hachez C, Ohashi-Ito K, Dong J, Bergmann DC. Differentiation of arabidopsis guard cells: analysis of the networks incorporating the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor, FAMA. Plant Physiol. 2011;155:1458–1472. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.167718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Martin S, Tazi J. Visualization of G3BP stress granules dynamics in live primary cells. J. Vis. Exp. 2014;43:1–8. doi: 10.3791/51197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Guillén-Boixet J, et al. RNA-induced conformational switching and clustering of G3BP drive stress granule assembly by condensation. Cell. 2020;181:346–361.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kedersha N, et al. G3BP-Caprin1-USP10 complexes mediate stress granule condensation and associate with 40S subunits. J. Cell Biol. 2016;212:845–860. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201508028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gaete-Argel A, Márquez CL, Barriga GP, Soto-Rifo R, Valiente-Echeverría F. Strategies for success. Viral infections and membraneless organelles. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019;9:336. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Imlau A, Truernit E, Sauer N. Cell-to-cell and long-distance trafficking of the green fluorescent protein in the phloem and symplastic unloading of the protein into sink tissues. Plant Cell. 1999;11:309–322. doi: 10.1105/tpc.11.3.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Nakagawa T, et al. Improved gateway binary vectors: high-performance vectors for creation of fusion constructs in transgenic analysis of plants. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007;71:2095–2100. doi: 10.1271/bbb.70216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kamigaki A, et al. Gateway vectors for simultaneous detection of multiple protein–protein interactions in plant cells using bimolecular fluorescence complementation. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:1–15. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Nietzsche M, Schießl I, Börnke F. The complex becomes more complex: protein-protein interactions of SnRK1 with DUF581 family proteins provide a framework for cell- and stimulus type-specific SnRK1 signaling in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2014;5:54. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Foley JW, et al. Gene expression profiling of single cells from archival tissue with laser-capture microdissection and Smart-3SEQ. Genome Res. 2019;29:1816–1825. doi: 10.1101/gr.234807.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Blankenberg D, et al. Galaxy: a web-based genome analysis tool for experimentalists. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2010;89:19.10.1–19.10.21. doi: 10.1002/0471142727.mb1910s89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Langmead B, Salzberg SL. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods. 2012;9:357–359. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Liao Y, Smyth GK, Shi W. featureCounts: an efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics. 2014;30:923–930. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Love MI, Huber W, Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014;15:1–21. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K. MEGA X : molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018;35:1547–1549. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msy096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Saitou N, Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987;4:406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Felsenstein J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution (N. Y.) 1985;39:783. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1985.tb00420.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Zuckerkandl E, Pauling L. Molecules as documents of history. J. Theor. Biol. 1965;8:357–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(65)90083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Castro ED, et al. ScanProsite: detection of PROSITE signature matches and ProRule-associated functional and structural residues in proteins. NucleicAcids Res. 2006;34:362–365. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.