Abstract
Although medically inoperable patients with stage I non-small cell lung cancer cells (NSCLC) are often treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy, its efficacy can be compromised due to poor radiosensitivity of cancer cells. Inhibition of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) using LY364947 and LY2109761 has been demonstrated to radiosensitize cancer cells such as breast cancer, glioblastoma, and lung cancer. Our previous results have demonstrated that another potent and selective inhibitor of TGF-β1 receptor kinases, SB431542, could radiosensitize H460 cells both in vitro and in vivo. In the present study, we investigated whether SB431542 could radiosensitize other NSCLC cell lines, trying to explore the potential implication of this TGF-β1 inhibitor in radiotherapy for NSCLC patients. The results showed that A549 cells were significantly radiosensitized by SB431542, whereas no radiosensitizing effect was observed in H1299 cells. Interestingly, both H460 and A549 cells have wild-type p53, while H1299 cells have deficient p53. To study whether the radiosensitizing effect of SB431542 was associated with p53 status of cancer cells, the p53 of H460 cells was silenced using shRNA transfection. Then it was found that the radiosensitizing effect of SB431542 on H460 cells was not observed in H460 cells with silenced p53. Moreover, X-irradiation caused rapid Smad2 activation in H460 and A549 cells but not in H1299 and H460 cells with silenced p53. The Smad2 activation postirradiation could be abolished by SB431542. This may explain the lack of radiosensitizing effect of SB431542 in H1299 and H460 cells with silenced p53. Thus, we concluded that the radiosensitizing effect of inhibition of TGF-β1 signaling in NSCLC cells by SB431542 was p53 dependent, suggesting that using TGF-β1 inhibitor in radiotherapy may be more complicated than previously thought and may need further investigation.
Key words: Radiosensitization, Non-small cell lung cancer cells (NSCLC), Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), SB431542, p53 status
INTRODUCTION
Medically inoperable patients with stage I non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) can be treated by stereotactic body radiation therapy (RT) (1), but the treatment efficiency is often compromised due to poor radiosensitivity of cancer cells and normal tissue injury (2–6). The radiation doses that normal tissues and organs can tolerate is usually less than those that control tumor growth, resulting in treatment failure (7).
It has been shown that transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), which can be activated by radiation even at low doses (8,9), is one of the most important cytokines that contribute to radiation-induced injury process (10). Radiation-induced lung fibrosis is accompanied by an increase in TGF-β1 expression and activation of TGF-β1 signaling pathways (11,12). Knockout mice lacking Smad3, an important component of TGF-β1 signaling pathways, are resistant to radiation-induced soft tissue fibrosis (13). Moreover, administration of anti-TGF-β1 antibody and TGF-β1 type 1 receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor significantly decreases TGF-β1 expression and activation of its signaling pathways and ameliorates radiation-induced fibrosis (14,15). These studies suggest that targeting TGF-β1 can be useful in lung cancer radiotherapy to ameliorate normal tissue injury.
Moreover, TGF-β1 can also mediate DNA damage response (DDR) and radiosensitivity (16). It has been found that TGF-β1 inhibition using LY364947 and LY2109761 prior to irradiation attenuated DDR through reducing ATM activity, decreasing phosphorylation of Chk1, Rad17, and p53, and reducing the number of radiation-induced γH2AX foci; increased radiosensitivity of breast cancer cells, glioblastoma, and NSCLC in vitro; and delayed tumor growth in vivo (17,20). Our previous results demonstrated that another TGF-β1 receptor inhibitor, SB431542, could radiosensitize H460 NSCLC cells through attenuating DNA damage repair and disturbing cell cycle distribution (21).
In the present study, we investigated whether SB431542 had radiosensitizing effects on other NSCLC cells. We found that although SB431542 did radiosensitize A549 cells, it did not radiosensitize H1299 cells. Unlike previous reports (18,20), we showed that radiosensitization of NSCLC cells by SB431542 was p53 dependent. The results suggest that implication of TGF-β1 receptor inhibitors in NSCLC radiotherapy may be complex.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Chemicals
SB431542, a selective and potent inhibitor of TGF-β1 receptor kinases, and all routine chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
Cell Culture and Irradiation
H460, A549, and H1299 cell lines were obtained from the Cell Bank of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China). H460 and H1299 cells were maintained in high-glucose RPMI-1640 medium (Sigma-Aldrich) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Hyclone, Waltham, MA, USA). A549 cells were cultured in complete high-glucose F12K medium (Sigma-Aldrich). All cell lines were kept at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 95% air and 5% CO2. Cells were irradiated with an RS2000 X-ray machine (Rad Source, Suwanee, GA, USA) at a dose rate of 1.16 Gy/min.
Crystal Violet Assay
The toxicity of SB431542 on NSCLC cells was determined using crystal violet assay as described previously (22). In brief, 5,000 cells per well were seeded in 96-well plates. The medium was replaced with fresh medium containing SB431542 at different concentrations 24 h later; the cells were cultured for different times (24, 48, or 72 h). Then the medium was carefully discarded, and the cells were washed, stained with crystal violet solution (0.5%) in methanol, and then destained with tap water and allowed to air dry. The dye was dissolved in 100 µl of 0.1 M sodium citrate (pH 4.2)/50% ethanol for 30 min at room temperature. A plate reader (BioTec PowerWave XS; BioTek, Winooski, VT, USA) was used to measure the absorbance at 540 nm. All data were normalized with the untreated cells at relative time points.
Colony Formation Assay
Cells were seeded in 60-mm Petri dishes at different densities depending on radiation dose. After 24 h, the cells were treated with SB431542 (10 µM) for 1 h followed by irradiation and 14 days of culture. Formed colonies were then fixed with methanol and stained with methylene blue. The number of colonies containing more than 50 cells was counted, and the percentage of cell survival was calculated. Dose enhancement ratio (DER) was calculated as the ratio of the radiation dose in the absence of SB431542 to the radiation dose in the presence of SB431542 at a survival fraction (SF) of 0.3.
Western Blotting
Briefly, proteins were extracted from whole cell lysates, then separated on a SDS-polyacrylamide gel (10%), and transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). The interested proteins were identified using rabbit anti-phospho-Smad2 (Ser465/467) mAb (1:1,000; Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., Danvers, MA, USA), rabbit anti-Smad2 mAb (1:10,000; Abcam, Cambridge, UK), or mouse anti-p53 mAb (1:1,000; Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, Haimen, Jiangsu, China) followed by secondary antibodies [e.g., goat anti-rabbit or goat anti-mouse IgG-horse radish peroxidase-conjugated (HRP) antibodies (1:1,000; Beyotime)]. β-Actin [mouse anti-β-actin mAb (1:1,000; Beotime)] was used as loading control. Chemiluminescent visualization of proteins was achieved using FluorChem M system (Protein Simple, San Jose, CA, USA) after treatment of PVDF membrane with ECL kit (Bio-Rad).
shRNA and Stable Transfection
shRNA plasmids were purchased from Genechem Co. (Shanghai, China). The shRNA sequence targeting TP53 (GenBank: Accession No. NM_000546) 5′-GCGCACAGAGGAAGAGAAT-3′ corresponded to the coding regions 1095–1115 after the start codon, and the negative control shRNA sequence was 5′-TTCTCCGAACGTGTCACGT-3′. At about 60% confluency 24 h after plating, H460 cells were transfected with shRNA plasmids using Lipofectamine® 2000 (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Forty-eight hours after transfection, the medium was replaced with selective medium containing 6 µg/ml puromycin (Haoran Bio, Shanghai, China). Surviving colonies were picked 2 weeks later and amplified. Stable transfectants were examined for p53 expression and used in relevant experiments.
Statistical Analysis
All data presented are representative of at least three independent experiments, and the results are shown as means ± SE. Cell survival data were analyzed via two-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey post hoc test for multiple comparisons using OriginPro Software (v8.0). Other comparisons between treatment groups and the respective controls were performed using pair-sample Student’s t-test. A value of p < 0.05 between groups was considered significant.
RESULTS
The Toxicity of SB431542 on A549 and H1299 Cells
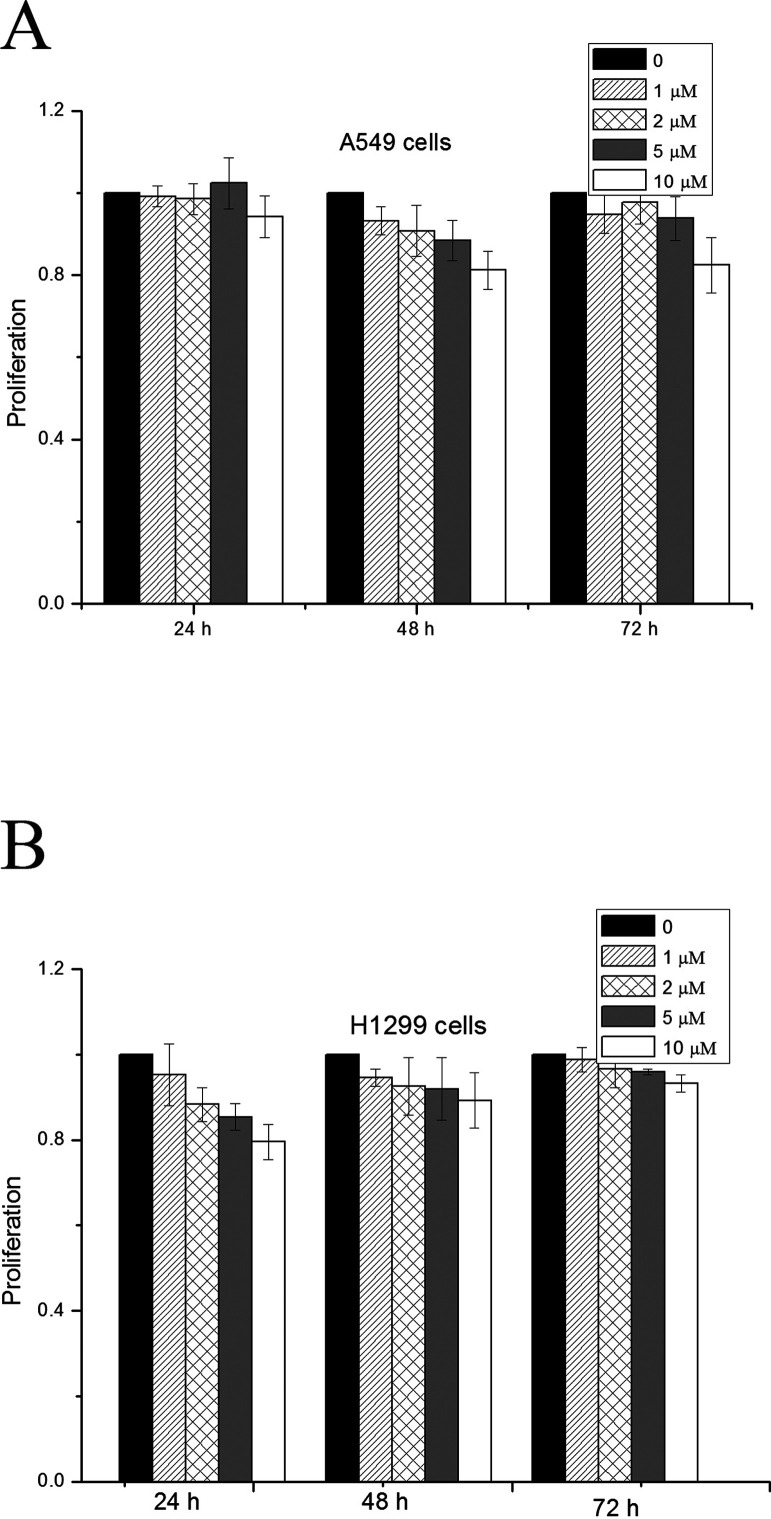
We have previously determined the toxicity of SB431542 on H460 cells and found that the treatment with SB431542 at 10 µM for at least 48 h did not significantly inhibit the proliferation of H460 cells (21). To determine the working concentration of SB431542 for A549 and H1299 cells, we first measured the effect of SB431542 on the proliferation of these two cell lines. As shown in Figure 1, SB431542 up to 10 µM did not show significant inhibition on cell proliferation up to 72 h of treatment in both cell lines. Therefore, 10 µM was chosen as the working concentration for SB431542 for the following experiments. The cells were pretreated with SB43152 for 1 h prior to irradiation.
Figure 1.
The effect of SB431542 at different concentrations on cell proliferation. (A) A549 cells and (B) H1299 cells.
SB431542 Radiosensitized A549 but not H1299 Cells
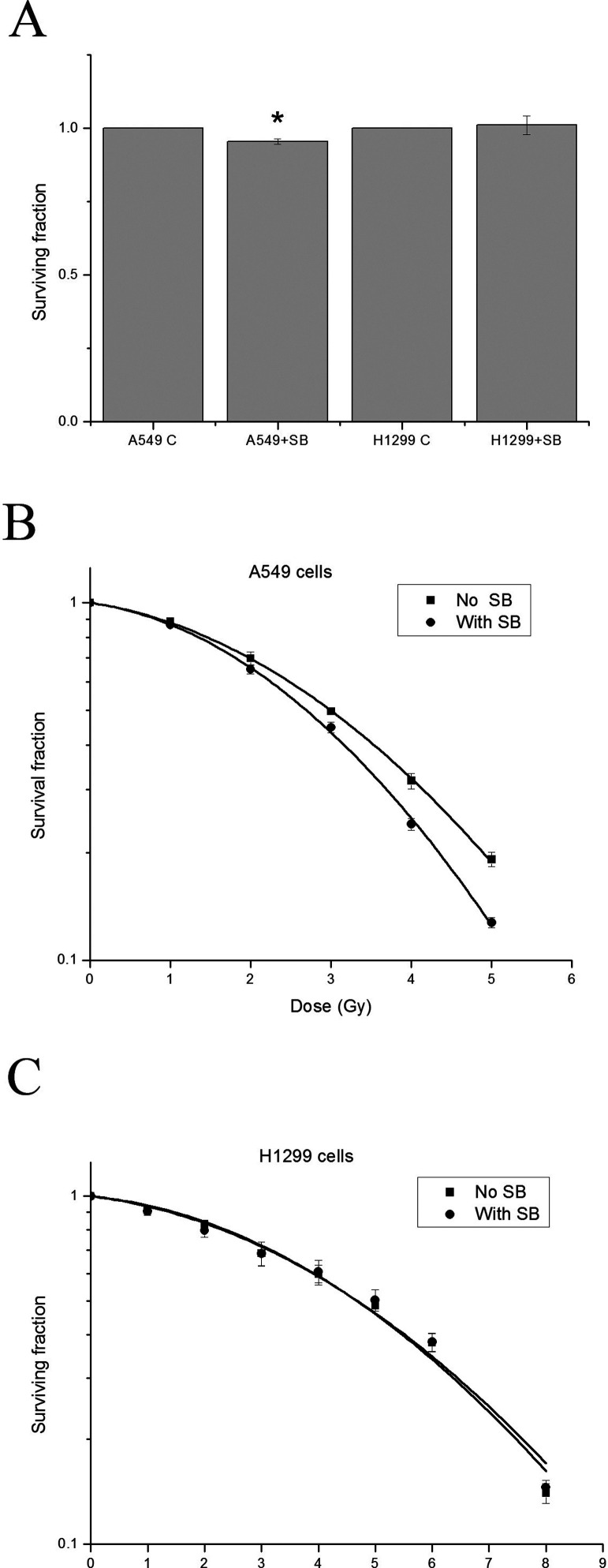
The data from clonogenic assay showed that SB431542 at 10 µM alone decreased the surviving fraction of A549 cells by 5%, but did not have any effect on H1299 cells (Fig. 2A). We then determined whether SB431542 pretreatment prior to irradiation could radiosensitize the two NSCLC cell lines. Surprisingly, after correction of its own toxicity, while SB431542 at 10 µM significantly radiosensitized A549 cells (p < 0.01), it had no radiosensitizing effect on H1299 cells (Fig. 2B, C). The DER at the SF of 0.3 for A549 cells was 1.12 ± 0.01, which was comparable to H460 cells (DER = 1.21 ± 0.04) (21), while that for H1299 cells was 1.00 ± 0.01, indicating a significant increase in radiosensitivity of A549 cells but not in that of H1299 cells after TGF-β1 inhibition.
Figure 2.
SB431542 radiosensitized A549 cells but not H1299 cells. Clonogenic survival of NSCLC cells after irradiation with/without SB431542 pretreatment. (A) The effect of SB431542 at 10 µM on clonogenic survival of NSCLC cells (*p < 0.05 compared with the corresponding control). (B) Survival curves of A549 cells after irradiation with/without SB431542 pretreatment, which fit with linear-quadratic model (ANOVA interaction, p < 0.001). (C) Survival curves of H1299 cells after irradiation with/without SB431542 pretreatment, which fit with linear-quadratic model (p = 0.997).
X-Rays Induced Smad2 Activation in H460 and A549 Cells but not in H1299 Cells
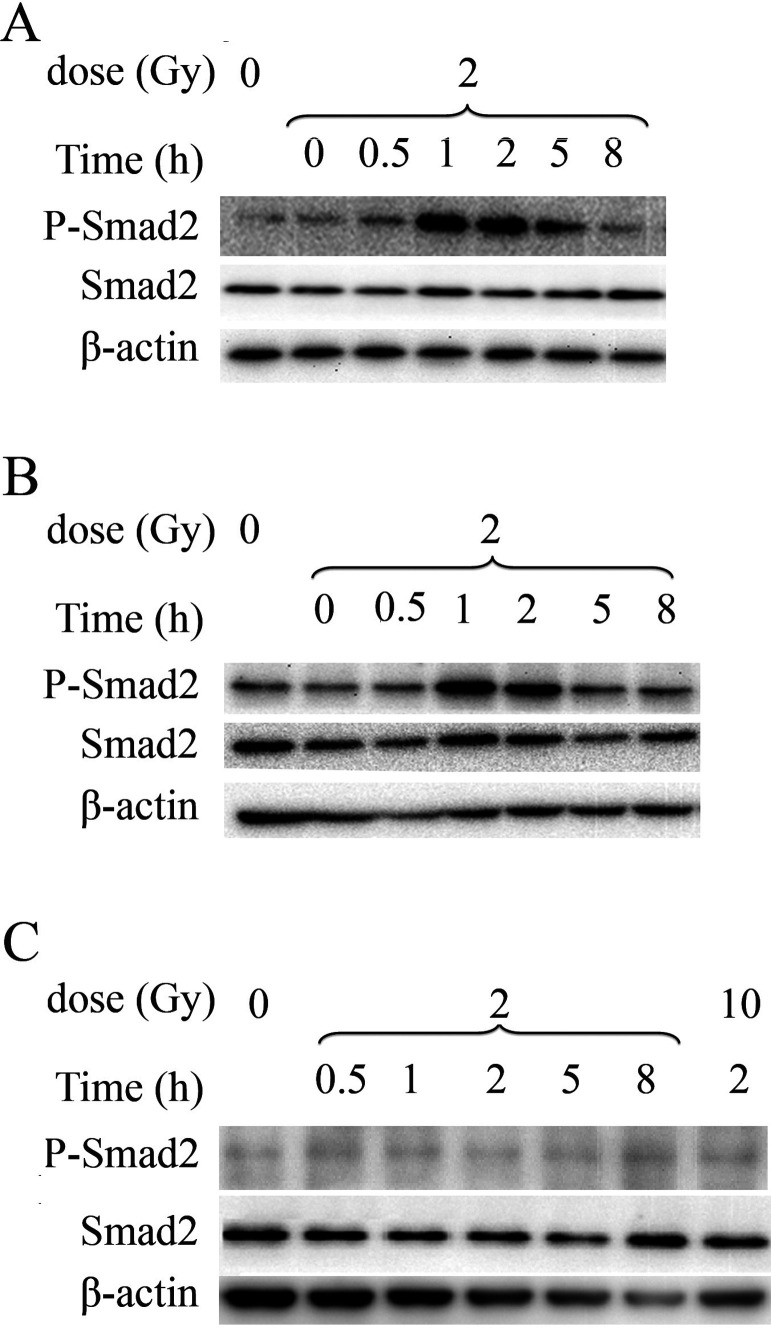
To investigate why the TGF-β1 receptor inhibitor SB431542 radiosensitized H460 and A549 cells but not H1299 cells, we measured Smad2 phosphorylation of the three cell lines irradiated by X-rays. The results show that Smad2 was activated in H460 cells immediately after 2 Gy of X-irradiation, and the activation last for at least 8 h (Fig. 3A). Similar Smad2 phosphorylation was observed in irradiated A549 cells (Fig. 3B). However, when H1299 cells were irradiated, no Smad2 activation was detected even at 8 h postirradiation or with 10 Gy of X-rays (Fig. 3C). These data indicated that X-irradiation could cause Smad2 activation in H460 and A549 cells but not in H1299 cells. This may explain why the TGF-β1 inhibitor SB431542 could radiosensitize H460 and A549 cells, but had no effect on H1299 cells.
Figure 3.
X-irradiation induced Smad2 activation in H460 and A549 cells but not in H1299 cells. Smad2 phosphorylation in NSCLC cells after irradiation was determined by Western blotting. (A) H460 cells, (B) A549 cells, and (C) H1299 cells.
Radiosensitization Effect of SB431542 in NSCLC Cells Was p53 Dependent
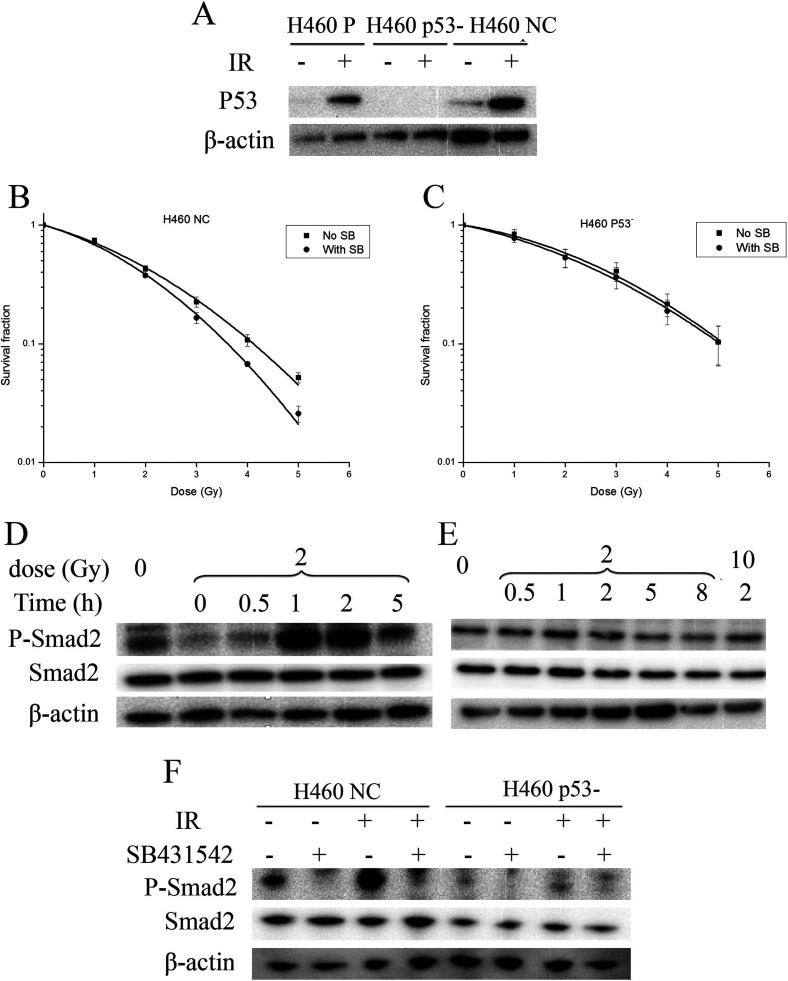
Coincidently, both H460 and A549 cells that were radiosensitized by SB431542 had wild-type p53, but H1299 cells that were not radiosensitized had deficient p53. To investigate whether p53 status played a role in the radiosensitization effect of SB431542, we silenced p53 in H460 cells and determined the DER and X-irradiation-induced Smad2 activation in the H460 cells with silenced p53. The results in Figure 4A show a successful silence of p53 in H460 cells after shRNA transfection. We then found that while SB431542 could radiosensitize the H460 cells transfected with negative control plasmids (H460 NC) (the DER was 1.14 ± 0.02), it had little effect on the H460 cells with silenced p53 (H460 p53−) (the DER was 1.04 ± 0.03) (Fig. 4B, C). Moreover, whereas Smad2 was phosphorylated in H460 NC after X-irradiation (Fig. 4D), we did not observe obvious Smad2 activation in H460 p53− after X-irradiation (Fig. 4E). Additionally, SB431542 pretreatment abolished Smad2 activation in irradiated H460 NC (Fig. 4F). These data suggested that wild-type p53 was indeed essential for the radiosensitizing effect of SB431542 in NSCLC cells.
Figure 4.
p53 silencing in H460 cells abolished radiosensitization effect of SB431542 and inhibited Smad2 activation upon irradiation. (A) Silence effect of p53 shRNA. H460 P represents H460 parental cells, H460 NC represents H460 cells transfected with negative control plasmids, H460 p53− represents H460 cells with silenced p53. (B) Survival curves of H460 NC after irradiation with/without SB431542 pretreatment, which fit with linear-quadratic model (p = 0.00687). (C) Survival curves of H460 p53− after irradiation with/without SB431542 pretreatment, which fit with linear-quadratic model (p = 0.520). (D) Smad2 activation in H460 NC upon irradiation. (E) No Smad2 activation in H460 p53− upon irradiation. (F) Inhibition effect of SB431542 on Smad2 activation in H460 NC induced by irradiation.
DISCUSSION
Sensitizing cancer cells to radiation is critical to the efficacy of RT for lung cancer due to variation of radiosensitivity (23). This may be achieved by targeting TGF-β signaling pathways in lung cancer cells, given the radiosensitizing effects of TGF-β inhibitors such as LY364947 and LY2109761 on breast cancer cells, glioblastoma, and NSCLC (18–20). We have previously demonstrated that TGF-β1 inhibition by another selective inhibitor, SB431542, radiosensitized wild-type p53 H460 cells (21).
Second, a higher incidence of metastasis after therapy has been suggested to be associated with the radiotherapy regimens currently used for lung cancer (24). Lung cancer cells surviving radiation may undergo epithelial–mesenchymal transdifferentiation (EMT) characterized by reduced intercellular adhesion and increased cell motility, and contribute to radiation-associated metastasis posttherapy (24). In addition, TGF-β has been found to play a critical role in radiation-induced EMT in cancer cells, and SB431542 could reverse radiation-induced EMT events in A549 cells through TGF-β inhibition (25). This suggests that TGF-β inhibitor may be beneficial for prevention of metastasis associated with radiotherapy.
Third, the maximum radiation dose used for NSCLC is often limited by the radiation toxicity to the surrounding normal lung tissue. Lung injury and pulmonary fibrosis are the most common side effects after radiotherapy for lung cancer patients, in which TGF-β induced by radiation has been found to be involved (26). It has also been found that elevation of circulating TGF-β1 in lung cancer patients’ plasma 4 weeks during radiation therapy was predictive of radiation-induced lung toxicity (RILT) (27). Therefore, TGF-β1 could be a potential target of RILT prevention. For example, rhubarb extract has been found to significantly attenuate RILT and improve pulmonary function by decreasing the levels of TGF-β1 and IL-6 (28).
In this study, we aimed to demonstrate the radiosensitizing effects of SB431542 on other NSCLC cells based on our previous results in H460 cells (21). However, we confirmed that SB431542 could radiosensitize wild-type p53 A549 cells but not p53-deficient H1299 cells (Fig. 2). Interestingly, X-irradiation caused Smad2 phosphorylation in both H460 and A549 cells, but not in H1299 cells (Fig. 3), suggesting that the TGF-β1–Smad2 pathway could not be activated in H1299 cells by X-rays. Furthermore, when p53 in H460 cells was silenced, the TGF-β1–Smad2 pathway was no longer activated by X-irradiation, nor were the cells radiosensitized by SB431542 (Fig. 4). These results suggested that radiosensitization of NSCLC cells by SB431542 was p53 dependent, and the activation of the TGF-β1–Smad2 pathway might be a protective mechanism for wild-type p53 NSCLC cells upon X-irradiation; thus, inhibition of TGF-β1 signaling by SB431542 could radiosensitize these cells. On the other hand, the TGF-β1–Smad2 pathway could not be activated in H1299 cells; therefore, SB431542 had no target in p53-deficient NSCLC cells. This appears in contrast to the previous report that regardless of their p53 status, all the breast and NSCLC cell lines used were radiosensitized by TGF-β1 inhibition (18,20). The reason for the discrepancy is not clear yet but is probably related to different TGF-β1 inhibitors. Further studies are needed to verify the p53 dependency of radiosensitization effect of SB431542 in other cancer cells, such as breast cancer cells.
Taken together, our results have demonstrated that the radiosensitizing capability of SB431542 in NSCLC cells was p53 dependent. Therefore, given the additional potential roles in preventing metastasis and normal tissue injury associated with radiotherapy, TGF-β1 inhibition by SB431542 can be an effective adjunct in radiotherapy for certain lung cancer subtypes.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant Nos. 31270898 and 11335011), the Key programs of Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Educational Committee (12KJA310005), Jiangsu Provincial Special Program of Clinical Medical Science (BL2014040), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institution (PARD).
REFERENCES
- 1. Reck M.; Heigener D. F.; Mok T.; Soria J. C.; Rabe K. F. Management of non-small-cell lung cancer: Recent developments. Lancet 382:709–719; 2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Choi N.; Baumann M.; Flentjie M.; Kellokumpu-Lehtinen P.; Senan S.; Zamboglou N.; Kosmidis P. Predictive factors in radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer: Present status. Lung Cancer 31:43–56; 2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Armstrong J.; McGibney C. The impact of three-dimensional radiation on the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 56:157–167; 2000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Kong F. M.; Hayman J. A.; Griffith K. A.; Kalemkerian G. P.; Arenberg D.; Lyons S.; Turrisi A.; Lichter A.; Fraass B.; Eisbruch A.; Lawrence T. S.; Ten Haken R. K. Final toxicity results of a radiation-dose escalation study in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Predictors for radiation pneumonitis and fibrosis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 65:1075–1086; 2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Yorke E. D.; Jackson A.; Rosenzweig K. E.; Braban L.; Leibel S. A.; Ling C. C. Correlation of dosimetric factors and radiation pneumonitis for non-small-cell lung cancer patients in a recently completed dose escalation study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 63:672–682; 2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Milano M. T.; Constine L. S.; Okunieff P. Normal tissue tolerance dose metrics for radiation therapy of major organs. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 17:131–140; 2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Anscher M. S. Targeting the TGF-beta1 pathway to prevent normal tissue injury after cancer therapy. Oncologist 15:350–359; 2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Portess D. I.; Bauer G.; Hill M. A.; O’Neill P. Low-dose irradiation of nontransformed cells stimulates the selective removal of precancerous cells via intercellular induction of apoptosis. Cancer Res. 67:246–253; 2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Ehrhart E. J.; Segarini P.; Tsang M. L.; Carroll A. G.; Barcellos-Hoff M. H. Latent transforming growth factor beta1 activation in situ: Quantitative and functional evidence after low-dose gamma-irradiation. FASEB J. 11:991–1002; 1997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Anscher M. S.; Chen L.; Rabbani Z.; Kang S.; Larrier N.; Huang H.; Samulski T. V.; Dewhirst M. W.; Brizel D. M.; Folz R. J.; Vujaskovic Z. Recent progress in defining mechanisms and potential targets for prevention of normal tissue injury after radiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 62:255–259; 2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Franko A. J.; Sharplin J.; Ghahary A.; Barcellos-Hoff M. H. Immunohistochemical localization of transforming growth factor beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha in the lungs of fibrosis-prone and “non-fibrosing” mice during the latent period and early phase after irradiation. Radiat. Res. 147:245–256; 1997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Chen L.; Brizel D. M.; Rabbani Z. N.; Samulski T. V.; Farrell C. L.; Larrier N.; Anscher M. S.; Vujaskovic Z. The protective effect of recombinant human keratinocyte growth factor on radiation-induced pulmonary toxicity in rats. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 60:1520–1529; 2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Flanders K. C.; Sullivan C. D.; Fujii M.; Sowers A.; Anzano M. A.; Arabshahi A.; Major C.; Deng C.; Russo A.; Mitchell J. B.; Roberts A. B. Mice lacking Smad3 are protected against cutaneous injury induced by ionizing radiation. Am. J. Pathol. 160:1057–1068; 2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Anscher M. S.; Thrasher B.; Rabbani Z.; Teicher B.; Vujaskovic Z. Antitransforming growth factor-beta antibody 1D11 ameliorates normal tissue damage caused by high-dose radiation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 65:876–881; 2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Anscher M. S.; Thrasher B.; Zgonjanin L.; Rabbani Z. N.; Corbley M. J.; Fu K.; Sun L.; Lee W. C.; Ling L. E.; Vujaskovic Z. Small molecular inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta protects against development of radiation-induced lung injury. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 71:829–837; 2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Andarawewa K. L.; Paupert J.; Pal A.; Barcellos-Hoff M. H. New rationales for using TGFbeta inhibitors in radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 83:803–811; 2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Kirshner J.; Jobling M. F.; Pajares M. J.; Ravani S. A.; Glick A. B.; Lavin M. J.; Koslov S.; Shiloh Y.; Barcellos-Hoff M. H. Inhibition of transforming growth factor-beta1 signaling attenuates ataxia telangiectasia mutated activity in response to genotoxic stress. Cancer Res. 66:10861–10869; 2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Bouquet F.; Pal A.; Pilones K. A.; Demaria S.; Hann B.; Akhurst R. J.; Babb J. S.; Lonning S. M.; DeWyngaert J. K.; Formenti S. C.; Barcellos-Hoff M. H. TGF-β1 inhibition increases the radiosensitivity of breast cancer cells in vitro and promotes tumor control by radiation in vivo . Clin. Cancer Res. 17:6754–6765; 2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Zhang M.; Herion T. W.; Timke C.; Han N.; Hauser K.; Weber K. J.; Peschke P.; Wirkner U.; Lahn M.; Huber P. E. Trimodal glioblastoma treatment consisting of concurrent radiotherapy, temozolomide, and the novel TGF-β receptor I kinase inhibitor LY2109761. Neoplasia 13:537–549; 2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Du S.; Bouquet S.; Lo C. H.; Pellicciotta I.; Bolourchi S; Parry R.; Barcellos-Hoff M. H. Attenuation of the DNA damage response by transforming growth factor-beta inhibitors enhances radiation sensitivity of non-small-cell lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo . Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 91:91–99; 2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Huang Q.; Zhao Y.; Jiang Y., Wang J.; Yang H. Inhibition of TGF-β1 radiosensitizes H460 lung cancer cells through interfering DNA damage response. J. Radiat. Res. Radiat. Process. 34:010202; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 22. Jiang Y.; Chen X.; Tian W.; Yin X.; Wang J.; Yang H. The role of TGF-β1-miR-21-ROS pathway in bystander responses induced by irradiated non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer. 111:772–780; 2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Kupelian P. A.; Komaki R.; Allen P. Prognostic factors in the treatment of node-negative non small cell lung carcinoma with radiotherapy alone. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 36:607–613; 1996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Jung J. W.; Hwang S. Y.; Hwang J. S.; Oh E. S.; Park S.; Han I. O. Ionising radiation induces changes associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation and increased cell motility of A549 lung epithelial cells. Eur. J. Cancer 43:1214–1224; 2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Zhou Y.; Liu J.; Zhang J.; Xu Y.; Zhang H.; Qiu L.; Ding G.; Su X.; Shi M.; Guo G. Ionizing radiation promotes migration and invasion of cancer cells through transforming growth factor beta-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 81:1530–1537; 2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Danceal H. C.; Shareef M. M.; Ahmed M. M. Role of Radiation-induced TGF-beta signaling in cancer therapy. Mol. Pharmacol. 1:44–56; 2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Zhao L.; Sheldon K.; Chen M.; Yin M. S.; Hayman J. A.; Kalemkerian G. P.; Arenberg D.; Lyons S. E.; Curtis J. L.; Davis M.; Cease K. B.; Brenner D.; Anscher M. S.; Lawrence T. S.; Kong F. M. The predictive role of plasma TGF-beta1 during radiation therapy for radiation-induced lung toxicity deserves further study in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 59:232–239; 2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Yu H. M.; Liu Y. F.; Cheng Y. F.; Hu L. K.; Hou M. Effects of rhubarb extract on radiation induced lung toxicity via decreasing transforming growth factor-beta-1 and interleukin-6 in lung cancer patients treated with radiotherapy. Lung Cancer 59:219–226; 2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]