A 40-year-old woman with a history of two episodes of epilepsy ten years before presentation was transported to our emergency department (ED) by ambulance on account of generalized seizure. She had been born and raised in Nepal and had never traveled internationally before this visit to Japan. On admission, Computed Tomography (CT) imaging of the brain showed multifocal punctate calcifications throughout the brain (Fig. 1). Two of the lesions adjacent to the trigone of the left lateral ventricle were accompanied by marked parenchymal edema and ring enhancement in Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), which were indicative of neurocysticercosis (Figs. 2 and 3 ). The patient also complained of continuous myalgia of the extremities that had been occurring for several years, and several calcified lesions of the extremities were also identified on X-ray (Black arrow, Fig. 4). Antibodies for Taenia solium were positive. She was started on combination therapy of albendazole 15 mg/kg/day, praziquantel 50 mg/kg/day, along with antiepileptics and corticosteroids. Her symptoms gradually improved. She completed a 14-day-course of antiparasitic therapy and received antiepileptics for more than 6 months after radiographic resolution.
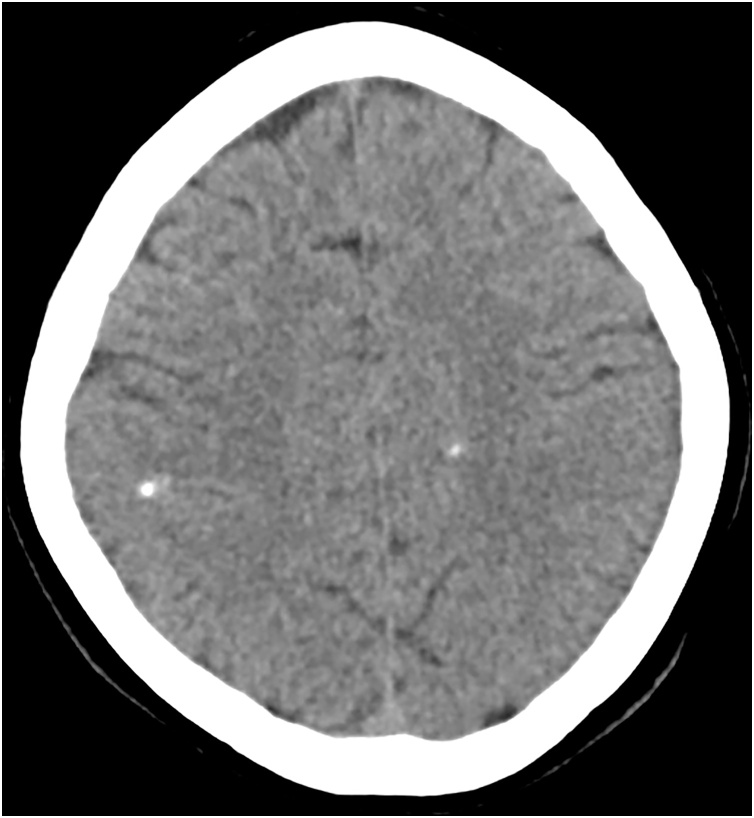
Fig. 1.
CT brain imaging shows multifocal punctate calcifications throughout the brain.
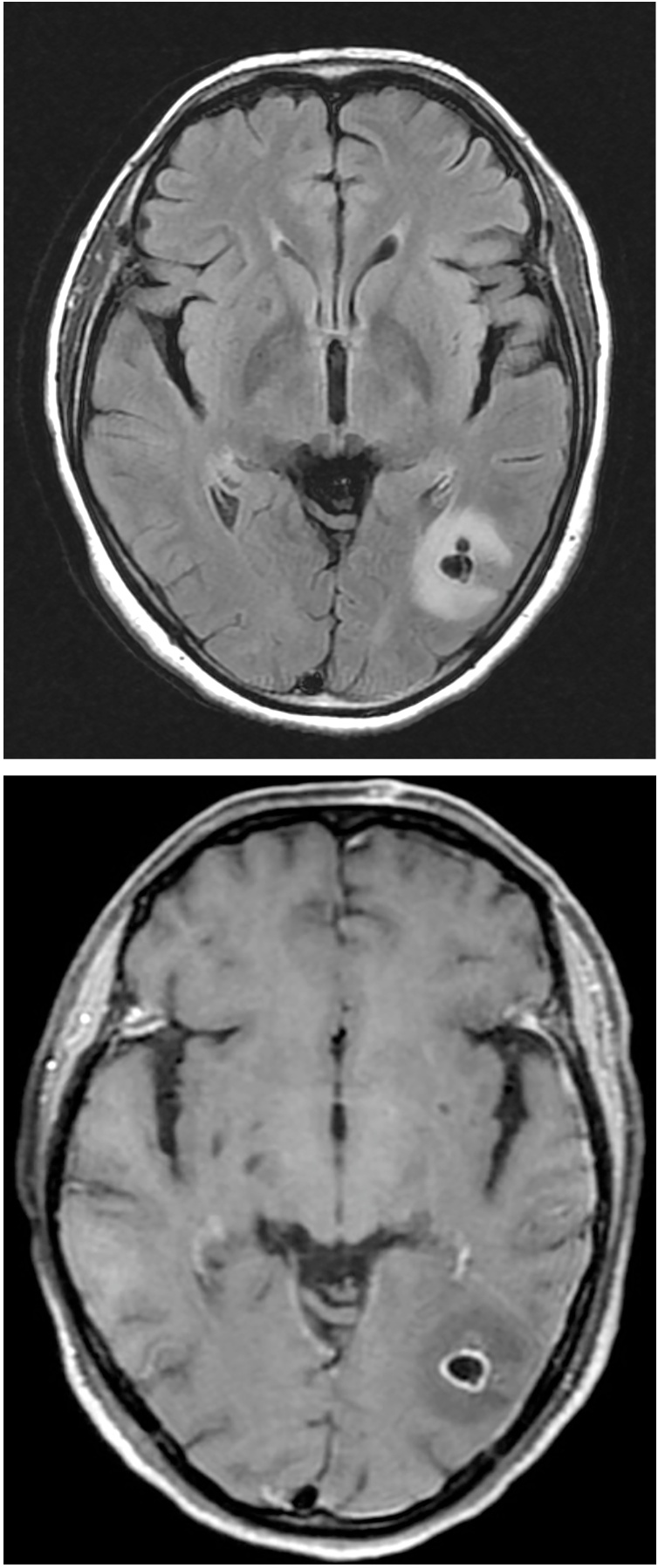
Figs. 2 and 3.
Two of the lesions adjacent to the trigone of the left lateral ventricle were accompanied by marked parenchymal edema and ring enhancement in MRI.
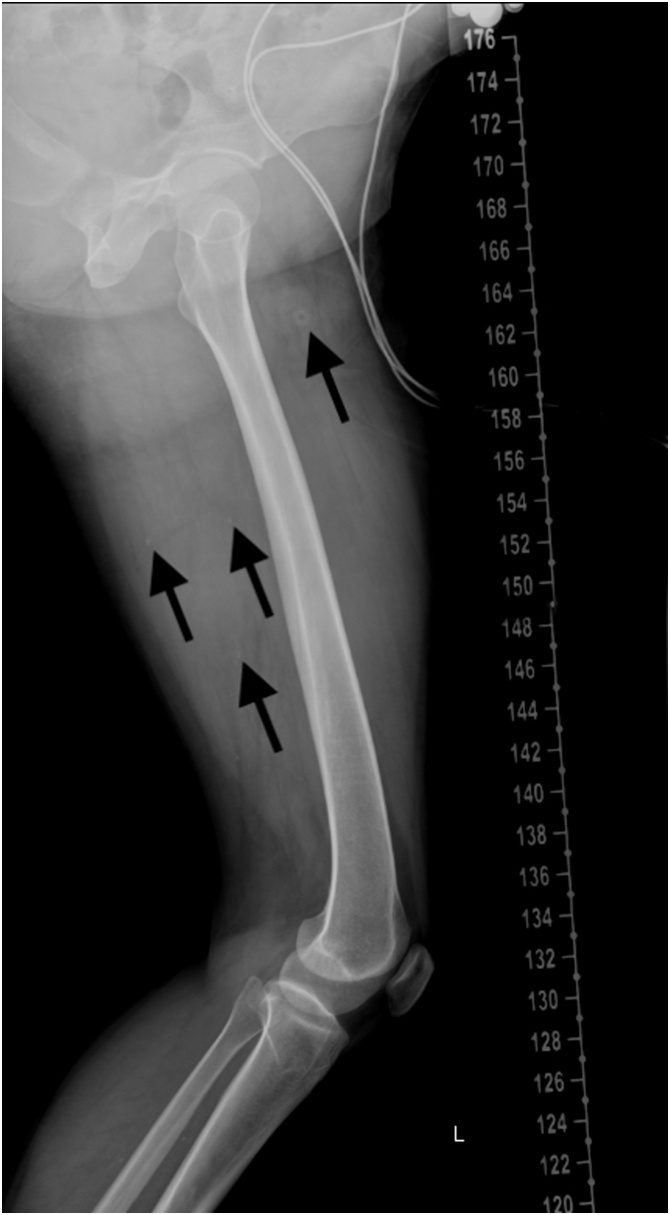
Fig. 4.
Several calcified lesions of the extremities were identified on X-ray.
Neurocysticercosis (NCC) is an important parasitic infection worldwide. It remains a common cause of epilepsy and seizures in developing countries, representing about 30 % of patients with seizures in endemic countries. Nevertheless, NCC is extremely rare in Japan and other developed countries, with sporadic cases imported from developing countries. Interestingly, even in the United States, approximately 2 % of patients with seizures in EDs have been attributed to NCC. Diagnosis is based on neuroimaging and confirmed by serology. Because of increased international travel and the upcoming Tokyo Olympics, clinicians should be aware of NCC as a common cause of epilepsy in patients from endemic regions.
Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal on request.
Contributors
All authors are equally responsible for the treatment of the patient and contributed to the writing of this clinical picture.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors report no declarations of interest.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Masumi Suzuki Shimizu: Writing - original draft. Takahiro Matsuo: Writing - review & editing. Nobuyoshi Mori: Writing - review & editing, Supervision. Aki Sakurai: Writing - review & editing. Keiichi Furukawa: Writing - review & editing, Supervision.