Abstract
The genomic region (~4 Mb) of the human major histocompatibility complex (MHC) on chromosome 6p21 is a prime model for the study and understanding of conserved polymorphic sequences (CPSs) and structural diversity of ancestral haplotypes (AHs)/conserved extended haplotypes (CEHs). The aim of this study was to use a set of 95 MHC genomic sequences downloaded from a publicly available BioProject database at NCBI to identify and characterise polymorphic human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I genes and pseudogenes, MICA and MICB, and retroelement indels as haplotypic lineage markers, and single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) crossover loci in DNA sequence alignments of different haplotypes across the Olfactory Receptor (OR) gene region (~1.2 Mb) and the MHC class I region (~1.8 Mb) from the GPX5 to the MICB gene. Our comparative sequence analyses confirmed the identity of 12 haplotypic retroelement markers and revealed that they partitioned the HLA-A/B/C haplotypes into distinct evolutionary lineages. Crossovers between SNP-poor and SNP-rich regions defined the sequence range of haplotype blocks, and many of these crossover junctions occurred within particular transposable elements, lncRNA, OR12D2, MUC21, MUC22, PSORS1A3, HLA-C, HLA-B, and MICA. In a comparison of more than 250 paired sequence alignments, at least 38 SNP-density crossover sites were mapped across various regions from GPX5 to MICB. In a homology comparison of 16 different haplotypes, seven CEH/AH (7.1, 8.1, 18.2, 51.x, 57.1, 62.x, and 62.1) had no detectable SNP-density crossover junctions and were SNP poor across the entire ~2.8 Mb of sequence alignments. Of the analyses between different recombinant haplotypes, more than half of them had SNP crossovers within 10 kb of LTR16B/ERV3-16A3_I, MLT1, Charlie, and/or THE1 sequences and were in close vicinity to structurally polymorphic Alu and SVA insertion sites. These studies demonstrate that (1) SNP-density crossovers are associated with putative ancestral recombination sites that are widely spread across the MHC class I genomic region from at least the telomeric OR12D2 gene to the centromeric MICB gene and (2) the genomic sequences of MHC homozygous cell lines are useful for analysing haplotype blocks, ancestral haplotypic landscapes and markers, CPSs, and SNP-density crossover junctions.
Keywords: MHC, haplotypes, snps, retroelements, crossovers, polymorphisms, indels
Introduction
The human major histocompatibility complex (MHC), also referred to as human leukocyte antigen (HLA), is investigated continuously because of its importance in the regulation of the innate and adaptive immune system, autoimmunity, and transplantation (Dawkins et al., 1999; Vandiedonck and Knight, 2009; Lokki and Paakkanen, 2019). The genomic region of the human MHC encompasses approximately 160 coding genes including three distinct structural regions: class I with the classical and non-classical HLA class I genes (HLA-A, -B, -C, -F, -G, and -E) and ~39 non-HLA genes, class II with the classical and non-classical HLA class II genes (HLA-DRB1, -DRA, -DQA1, -DQB1, -DQA2, -DQB2, -DPA1, and -DPB1) and class III that harbours more than 60 genes including the complement genes, TNF, NFKBIL2, and many other genes that code for cytokines, transcription factors, structural and developmental proteins (Shiina et al., 2004, 2009). The MHC class I and class II gene clusters contain numerous sequence duplications, insertions and deletions and considerable sequence diversity or polymorphisms (Trowsdale and Knight, 2013) that have accumulated into distinct multilocus haplotypes with relatively high population frequencies (>1%) (Awdeh et al., 1983; Degli-Esposti et al., 1992; Dawkins et al., 1999; Yunis et al., 2003; Goodin et al., 2018). These date from at least the beginning of human expansion and dispersal out of Africa, 50,000–100,000 years ago (Henn et al., 2012; López et al., 2015). The MHC multilocus haplotypes have been associated strongly with many diseases (Lokki and Paakkanen, 2019). On the basis of the large number of known HLA-B alleles, more than 20,000 different MHC multilocus haplotypes might be distributed worldwide in human populations, with less than a hundred in certain localised populations such as the Europeans (Steele and Lloyd, 2015; Jensen et al., 2017; Goodin et al., 2018). The common Northern European HLA haplotype HLA-A1-B8-C7-DRB3-DQ2 (8.1AH) is estimated to have diverged from a single common ancestor about 23,500 years ago (Smith et al., 2006).
Although the MHC is highly polymorphic for single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), the degree of polymorphism (SNP density per 100 kb) depends on which haplotypes (haploid genotypes) are compared. There are at least two main types of genomic haplotype blocks that are studied for SNP variations: (1) those that are constructed on the basis of linkage disequilibrium (LD) statistical tests of a contiguous set of SNP markers (Ahmad et al., 2003; Walsh et al., 2003; Miretti et al., 2005; Blomhoff et al., 2006) and (2) those constructed from alignments of SNP density maps or genotyped alleles that identify well-defined haplotype blocks or segmental structures without using LD tests (Alper et al., 1983, 2006; Degli-Esposti et al., 1992; Dawkins et al., 1999; Aly et al., 2006; Smith et al., 2006; Lam et al., 2015; Alper and Larsen, 2017). If employed independently of each other, the two methods can result in unrelated single and/or multilocus haplotype block patterns (Yunis et al., 2003; Alper et al., 2006; Jensen et al., 2017). Homologous haplotype sequences have only a few detectable SNPs extended over a long-range of multilocus regions (Smith et al., 2006), whereas a large number of SNPs of varying density are detected in comparisons between different MHC class I haplotypes (Gaudieri et al., 1999, 2000; Miretti et al., 2005; Shiina et al., 2006, 2009; Jensen et al., 2017; Norman et al., 2017). The absence of SNPs over megabases of continuous sequence within the same MHC haplotypes is described as conserved sequence polymorphisms (CSPs) within conserved extended haplotypes (CEHs) (Yunis et al., 2003; Alper et al., 2006) and/or ancestral haplotypes (AHs) (Degli-Esposti et al., 1992; Dawkins et al., 1999), such as 8.1CEH/AH (Price et al., 1999; Aly et al., 2006; Smith et al., 2006; Gambino et al., 2018), 7.1CEH/AH (Gaudieri et al., 1997; Dunn et al., 2005), 57.1CEH/AH (Dunn et al., 2005), 38.1CEH/AH (Romero et al., 2007) and the Sardinian haplotype 18.2CEH/AH (Contu et al., 1989; Bilbao et al., 2006). The non-LD, SNP-poor, long-range haplotypic sequences are mainly contained within polymorphic frozen blocks (PFBs) (Gaudieri et al., 1997; Dawkins et al., 1999) or fixed (conserved) haplospecific blocks (Alper et al., 2006; Barquera et al., 2020).
SNPs within many different recombinant haplotypes are absent for relatively much shorter distances ranging between 10 and 1,000 kb such as those found within PFBs of 60–300 kb (Gaudieri et al., 1997; Dawkins et al., 1999) and/or SNP-LD-blocks of ~18–50 kb (Daly et al., 2001; Jeffreys et al., 2004; Miretti et al., 2005; Blomhoff et al., 2006). The SNP-LD-block based on statistical associations between the frequencies of two or more genotyped loci in population studies cannot map the classical CEH/AH or PFB architectural structures directly or reliably (Schaid et al., 2002; Alper et al., 2006; Slatkin, 2008), whereas reliable linkage mapping is usually dependent on pedigree studies of particular genotyped markers to evaluate their linkage or segregation in meiosis or on phased genomic sequences (Alper and Larsen, 2017) such as those that have been sequenced or genotyped using multilocus HLA-captured haplotype phasing (Guo et al., 2006), de novo assembled trios (Jensen et al., 2017), MHC homozygous cell lines (Dorak et al., 2006; Horton et al., 2008; Norman et al., 2017), sperm (Cullen et al., 2002; Kirkness et al., 2013) or single chromosomes (Murphy et al., 2016). SNP-LD analyses often fail to detect linkage of multiple loci within the conserved haplotype structure as effectively as the genes that may be involved in disease susceptibility or resistance because of the use of non-haplotypic SNP markers (Alper et al., 2006; Slatkin, 2008; Alper and Larsen, 2017). Nevertheless, the SNP-LD-blocks that were identified by LD or long-range haplotype (LRH) and extended haplotype homozygosity (EHH) tests (Traherne, 2008) of the MHC genomic regions include a variety of genotyped haplotypic microsatellites (Karell et al., 2000; Doxiadis et al., 2007), SNPs (Ahmad et al., 2003; de Bakker et al., 2006; Shiina et al., 2006; Smith et al., 2006; Romero et al., 2007; Lam et al., 2013), and indels (WGS500 Consortium et al., 2014; Jensen et al., 2017; Huang et al., 2019) as well as structural dimorphic retroelements (REs), such as Alu, SVA, LTR, and HERVs (Kulski and Dunn, 2005; Kulski et al., 2011).
Segmental shuffling is a meiotic recombination or crossing over process between different haplotypes (Gaudieri et al., 1997; Traherne et al., 2006) that often occurs within nucleotide sequences in regions between the alpha, beta, epsilon and delta frozen polymorphic blocks (Dawkins et al., 1999; Traherne et al., 2006; Romero et al., 2007), although breakpoints have been reported also within and between the HLA class I genes within the alpha (Lam et al., 2013) and beta blocks (Nair et al., 2006) and between the HLA class II genes within the delta block (Jeffreys et al., 2004; Larsen et al., 2014). Many MHC recombinant haplotypes appear to have originated in relatively recent times (Smith et al., 2006; Lam et al., 2013) due to the pressures of bottlenecks, migrations and gene flow, inbreeding, and outbreeding in various times of abundance and deprivation (van Oosterhout, 2009; Lobkovsky et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020). With the formation of new human MHC haplotypes during and/or after speciation, many of the high-frequency (>1%) AHs were preserved over numerous generations and migrations; even across different ethnic populations as deduced from the European (Contu et al., 1989; Aly et al., 2006; Bilbao et al., 2006; Smith et al., 2006) and Asian haplotypes (Lam et al., 2013, 2015, 2017).
Much of genomic sequence diversity, including haplotype diversity, is driven by molecular mechanisms such as DNA repair, replication, single point mutations, indels, recombination, duplication, conversion, transposition, and segmental rearrangements (Gu et al., 2008; Brawand et al., 2014; Lin and Gokcumen, 2019). In addition, interspersed repeat sequences that contribute to >50% of the human genomic content (de Koning et al., 2011) have been implicated in a variety of these DNA molecular processes (Moolhuijzen et al., 2010; George and Alani, 2012; Raviram et al., 2018; Lu et al., 2020). The identification of transposable elements (TEs) near the junctions of duplicated genes (Kulski et al., 1997, 1999b, 2004) and at ectopic and meiotic recombination sites (Myers et al., 2010; Altemose et al., 2017; Kent et al., 2017) emphasise their role in driving genomic diversity. Interspersed REs, because of their mobility, hypermutability, and potential role in meiotic recombination, are an integral part of molecular drive (Dover, 1982) that together with point mutations, gene conversion (Madrigal et al., 1993; Adamek et al., 2015) and balancing selection (van Oosterhout, 2009) with a component of multiplicative fitness (Lobkovsky et al., 2019) probably have generated and maintained haplotypic polymorphisms in the MHC class I regions. This multifunctional role for active REs is evidenced in part by the structural biallelic Alu, SVA, LTR, and HERVs located near to or within putative recombination hotspots throughout the MHC class I, II, and III genomic regions (Kulski et al., 2011). In recent years, the proposed broad roles for TE and polymorphisms in the regulation of meiotic recombination (a mechanism that undoubtedly generated the MHC haplotype diversity in humans) has gained increasing attention (Myers et al., 2008; Zamudio et al., 2015; Altemose et al., 2017; Kent et al., 2017; Bourgeois and Boissinot, 2019).
Both first-generation and second-generation sequencing methods have produced phased genomic sequences of representative MHC haplotypes by using MHC homozygous cell lines (Horton et al., 2004, 2008; Stewart et al., 2004; Traherne et al., 2006; Norman et al., 2017). These phased MHC genomic sequences are important reference DNA sequences that provide representative haplotypes for better informed large population studies and for mapping heterozygous sequence reads such as by inference graphs (Dilthey et al., 2016), SNP-LD based haplotype frequencies (Romero et al., 2007) and EEH tests (Lam et al., 2015), especially for disease associations (Alper and Larsen, 2017; Lokki and Paakkanen, 2019). Although Norman et al. (2017) produced an important database for 95 MHC homozygous cell lines of assembled and resolved MHC genomic sequences, they limited their own analysis to the multilocus alleles and haplotypes of the HLA classical class I and class II genes, MUC22 and the structural diversity of C4 duplications. Missing from their analysis are the many REs, repeats and retrotransposable subfamilies, as well as the amplified and duplicated members of the genomic DNA that make up >50% of the human DNA content and that contribute to disease (Ayarpadikannan and Kim, 2014; Payer et al., 2017; Payer and Burns, 2019), gene regulation and recombination (Moolhuijzen et al., 2010; Myers et al., 2010; Altemose et al., 2017; Chuong et al., 2017) and to the duplicated segmental organisation of the human and other primate MHC genomic structures (Kulski et al., 1997, 1999a,b; Anzai et al., 2003; Kulski et al., 2004).
The purpose of the present study was to extend the Norman et al. (2017) analysis by investigating the haplotypic linkages between the MHC class I genic and intergenic regions including HLA-F, HLA-G, MICA, MICB, eight HLA pseudogenes (HLA-V, -P, -H, -T, -K, -U, -W, and -J) and a set of previously published biallelic REs, AluOR (Kulski et al., 2014), AluHF, AluHG, AluHJ, AluTF, AluMICB (Kulski and Dunn, 2005; Kulski et al., 2019), HERVK9 (Kulski et al., 2008), MER9 (Kulski et al., 2009) and four biallelic SVA haplotypic markers, SVA-HA, SVA-HC, SVA-HB, and SVA-HF (Kulski et al., 2010, 2011). A further aim was to identify and characterise the ancestral SNP-density crossover (XO) loci in DNA sequence alignments of different haplotype blocks or segments from the GPX5 gene in the OR gene region telomeric of HLA-F to the centromeric MICB gene within the MHC class I genomic region. The overall results of the study suggest that the SNP XOs are indicators of haplotype XO, which in turn point to putative ancestral recombination sites that are widely distributed across the 2-Mb-MHC class I genomic region from telomeric of HLA-F to centromeric of MICB.
Materials and Methods
The haplotype data of 95 MHC genomic sequences sequenced and assembled from HLA-homozygous cell lines by Norman et al. (2017) at NCBI BioProject with the accession number PRJEB6763 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/) were downloaded as Fasta files and used for the analyses described below. The other MHC genomic sequences used in haplotype analyses were the GRChr38.p13 (GCF_000001405.39) of the chromosome 6 reference NC_000006.12 at the NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/assembly/GCF_000001405.39/), UCSC (https://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgGateway) and eEnsembl (http://asia.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Info/Index) browsers and databases, the eight human reference haplotypes described by Horton et al. (2008), the chimpanzee sequence of Anzai et al. (2003) and the gorilla sequence of Wilming et al. (2013). All of the Fasta sequences downloaded from the public archives were submitted to the RepeatMasker webserver (http://www.repeatmasker.org/cgi-bin/WEBRepeatMasker) for output files of annotated members of the interspersed repetitive DNA families, their locations in the sequence and their relative similarity or identity in comparison to reference sequences of SINEs, LINEs, LTRs, ERVs, DNA elements, small RNA, and simple repeats. For the online analysis, RepeatMasker used the Dfam database (3.0) for the repeat sequence comparisons (Hubley et al., 2016) (http://www.dfam.org) because since 20th May 2019, it no longer had access to the RepBase library of repetitive elements (Bao et al., 2015) previously provided by GIRI (https://www.girinst.org/repbase/). The main difference between the Dfam database and RepBase for our analysis was that Dfam listed many Alu-like short sequences as SVA, whereas we were interested only in the SVA mosaic of 500 to 1,800 bp in RepBase with structures similar to those described by Shen et al. (1994). Thus, we used four dimorphic SVA sequences (SVA-HA, SVA-HC, SVA-HB, and SVA-MIC) previously reported by Kulski et al. (2010) and added three new dimorphic SVA sequence markers to this analysis (Table 1).
Table 1.
Dimorphic retroelements (absent or present) and STR analysed in this study.
| Retroelement or microsat | Nearest flanking (/) genes | Location within genome reference Ch38/hg38, Chr 6 | Popln frequencies caucasian/Japanese (n = 88–260) | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AluOR | OR12D2 intron | 29396132–29396263 | 0.14 | 0.32 | Kulski et al., 2014 |
| AluOR1 | 3′OR12D1 | 29416044 | Present study | ||
| AluHF | ZFP57/HLA-F | ~29710985* | 0.23 | 0.06 | Dunn et al., 2002 |
| AluHG | HLA-G/HLA-H | ~29850749* | 0.30 | Kulski et al., 2001 | |
| 0.30 | 0.21 | Dunn et al., 2002 | |||
| AluHJ | HLA-J/ETF1P1 | ~30030620* | 0.25 | 0.38 | Dunn et al., 2002 |
| AluTF | MUC21/MUC22 | ~31003947* | 0.11 | 0.08 | Dunn et al., 2003 |
| AluP5 | MICA/MICB | ~31470733* | Present study | ||
| AluMICB | MICB intron 1 | ~31498446* | 0.12 | Kulski et al., 2002a | |
| 0.16 | 0.12 | Kulski and Dunn, 2005 | |||
| HERVK9 | HLA-G/HLA-H | 29875649–29881829 | 0.37 | 0.59 | Kulski et al., 2008 |
| sMER9 (1) | HLA-G/HLA-H | ~29881317* | 0.66 | 0.41 | Kulski et al., 2008 |
| LTR13 | HLA-K/HLA-U | 29929971–29930908 | Present study | ||
| sMER9 (2) | HLA-U/HLA-A | 29936175–29936676 | Kulski et al., 2009 | ||
| LTR5L | TRIM26/HLA-L | ~30221451 | Present study | ||
| MER5/LTR33 | HLA-C/HLA-B | ~31313186 | Present study | ||
| HAL1/MER5A | MICA/MICB | 31418238–31418519 | Present study | ||
| LTR9 | MICA/MICB | 31423445–31424086 | Present study | ||
| SVAOR | 3′GPX6 | 28501515–28503131 | Present study | ||
| SVA-HF | LTR16/HLA-F | 29717873–2972077 | 0.14 | 0.00 | Kulski et al., 2010 |
| SVA-16** | HLA-H/HLA-T | 29895386–29896449 | fixed | Present study | |
| SVA-HA | HLA-K/HLA-A | 29932087–29933753 | 0.26 | 0.06 | Kulski et al., 2010 |
| SVA-T26** | TRIM26/HLA-L | 30221503–30222724 | Present study | ||
| SVA-ER** | MICC/HLA-E | 30474489–30475999 | Present study | ||
| SVA-EG** | HLA-E/GNL1 | 30498159–30499333 | Present study | ||
| SVA-M21** | MUC21/MUC22 | 30992538–30993994 | Present study | ||
| SVA-M22** | MUC22/C6orf15 | 31066602–31068056 | Present study | ||
| SVA-HC | HCG27/HLA-C | 31243860–31245322 | 0.10 | 0.03 | Kulski et al., 2010 |
| SVA-CB | HLA-C/HLA-B | ~31310982* | Present study | ||
| SVA-HB | HLA-C/HLA-B | ~31329940* | 0.65 | 0.25 | Kulski et al., 2010 |
| SVA-MIC | MICA/MICB | 31453745–31456553 | Kulski et al., 2010 | ||
| 9.5-kb del | HLA-C/HLA-B | ~31298645* | Present study | ||
| (ATAG)n | HLA-G/MICF | 29838629–29838750 | Present study | ||
| (CAGAGA)n | HLA-G/MICF | 29838997–29839045 | Present study | ||
| (ATAA)n | HLA-A/HLA-W | 29949553–29949592 | Present study | ||
| (ATTT)n | HLA-A/HLA-W | 29949590–29949639 | Present study | ||
| (TTTA)n | TRIM26/HLA-L | 30221462–30221500 | Present study | ||
| (GAGG)n | MUC22/C60rf15 | ~ 31066254 | Present study | ||
| (TTTC)n | HCG27/HLA-C | 31236405–31236481 | Kulski et al., 1997 | ||
| (ACA)n | HCG27/HLA-C | 31239846–31239880 | Kulski et al., 1997 | ||
| (TTCC)n | HCG27/HLA-C | 31241314–31241352 | Kulski et al., 1997 | ||
| (TTAT)n | HLA-C/HLA-B | 31321185–31321227 | Kulski et al., 1997 | ||
| (CTG)n | within MICA | 31412369–31412393 | Mizuki et al., 1997 | ||
| (TGT)n | within MICA | ~31412394* | Present study | ||
Approximate location because these deletions, retroelements or STR are absent from the Ch38/hg38 Genome Reference that has the HLA haplotype of HLA-A*03:01:01:01/ B*07:02:01:01/C*07:02:01:03/.
Norman et al. (2017) provided the alleles of the HLA-A, -B, and -C class I genes for all the 95 cell line sequences shown in Supplementary Table 1. We confirmed the alleles of the HLA class I genes and included the alleles of HLA-E, -F, and -G, and the MICA and MICB genes and eight HLA-A class I pseudogenes (Supplementary Table 2) in the 95 cell line sequences by comparing them to the IMGT HLA allele sequences (IMGTRelease 3.38.0) using the DNA sequence assembly software Sequencher ver.5.0 (Gencode http://www.genecodes.com). The alleles that were not in the IMGT HLA allele databases (Robinson et al., 2019) at https://www.ebi.ac.uk/ipd/imgt/hla/ are reported here as “new” without providing any further information about the novel nucleotide or amino acid differences. We also found that the FTQW01000001.1 sequence provided by Norman et al. (2017) as the chimpanzee “Clint” (Pan troglodytes genome assembly, contig: 1_COX_Oct2016_Scaffold, whole genome shotgun sequence) has strong identity with the COX cell line sequence that harbours the 8.1AH haplotype A*01:01:01:01/ B*08:01:01:01/ C*07:01:01:01 (Horton et al., 2008).
We added a laboratory identifier number (ID_1 to ID_95) to each of the Norman et al. (2017) sequences (Supplementary Table 2) for ease of identification in comparative sequence analysis. A shorthand identifier for the MHC CEH/AH haplotypes based on the HLA-B allele such as 7.1CEH/AH, 8.1CEH/AH, 13.1CEH/AH was used as previously described (Degli-Esposti et al., 1992, Dawkins et al., 1999, Dorak et al., 2006). The alleles of the HLA class I genes, MIC genes, HLA class I pseudogenes and HLA class II genes were determined also for the GRChr38p13 genomic reference sequence, which corresponds to the 7.1AH of the PGF homozygous cell line (Horton et al., 2008), shown in Supplementary Table 3. The dimorphic RE and microsatellite markers that were searched for and identified by RepeatMasker in the 95 MHC genomic sequences are shown in Table 1. The RE dimorphisms (absence or presence) were easily recognised in each of the RepeatMasker outputs because of their positions within or close proximity to other TE elements and short tandem repeats (STRs). For example, the MER9/HERVK9-int/MER9 insertion at nucleotide positions (nts) 160655 to 166834 in Supplementary Table 4 is flanked by a string of telomeric LTR16B2/MLT1F1/ STR/AluY/STR/L1ME3 elements and a string of centromeric Charlie9 (nts, 89–303)/Charlie9 (nts, 1283–1803)/L1PA10/LMLT1F1/THE1C elements that are easily identified in the RepeatMasker outputs with the solitary MER5 and HERVK9-int deletion at their corresponding locations.
Comparative sequence alignments between two or more sequences to evaluate SNP densities and determine XO regions between SNP-poor regions (SPR) of <20 SNPs per 100 kb and SNP-rich regions (SRR) of >100 SNPs per 100 kb were performed with the web-based MultiPipMaker alignment program (http://pipmaker.bx.psu.edu/cgi-bin/multipipmaker) by uploading the Fasta sequence files, a RepeatMasker output file and using the MultiPipMaker setting for single coverage as described by Schwartz et al. (2000) to generate the optimal sequence alignment. SNPs in the alignments were counted twice manually, and an average number was presented in the results. Obvious assembly errors, polynucleotides, simple microsatellite repeats and indels were not counted as SNPs. Also, a series of many adjoining SNPs (e.g., >5 SNPs in a string of 50 nucleotides) or SNPs within 50 bp of obvious sequencing errors with runs of unspecified nucleotides (Ns) and/or inconsistent long strings of deletions were not counted. The length of sequence alignments usually ranged between 50 and 500 kb depending on (1) the segments targeted for the analysis and the ease of SNP manual counting in the pdf outputs of the nucleotide alignments and/or (2) the length of the Percentage Identity Plot (PIP) output for reproduction as a convenient and readable image. The targeted sequences were selected and trimmed from the Fasta files that had been previous downloaded from the NCBI BioProject, accession number PRJEB6763. The software program Genetyx ver.20 (GENETYX Co., Tokyo, Japan) was used with the Selector function set to select and trim to obtain the required Fasta file sequences with the genomic sequence target positions taken from those listed in the RepeatMasker output text file (Supplementary Table 3). The T-Coffee multiple sequence alignment tool at EMBL-EBI (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/tcoffee/) was used to construct multiple sequences of ERV3-16A3-int in the Fasta format and the CLUSTALW (1.83) format.
Results
MHC Haplotype Sequences
Of the 95 human MHC haplotypes sequenced by Norman et al. (2017), 82 differed at least at one of the 9 loci, HLA-A, -C, -B, -DRB1, -DRB345, -DQA1, -DQB1, -DPA1, and -DPB1. However, there were 46 sequences representing 18 haplotypes that had the same combination of HLA-A, -C, and -B alleles for at least one haplotype pair. Furthermore, 70 sequences represented 19 different HLA-C/-B haplotypes and 67 sequences represented 23 different HLA-A/-C haplotypes (Supplementary Table 1) with a homologous alignment for at least one haplotype pair.
In this study, the haplotypic alleles of 56 loci were analysed, ranging between the OR gene region and the MHC class I region including the classical HLA-A, -B, and -C loci, the non-classical HLA-F, -G, and -E loci, 8 HLA pseudogenes, MICA and MICB, 8 Alu loci, 13 SVA loci, 2 MER9 loci, the HERVK9 locus, 5 LTR or MER5 loci, and 12 STR loci (Tables 1–3, Supplementary Table 2). The 9.5-kb MER5/LTR33 indel between the HLA-C and HLA-B loci also contained within its sequence a string of different L1 fragments, ERVL-E-int fragments, MER3, MIR, AluJ, MLT1B, LTR84b, MLT1G3, AluSx, and MLT2C1 beside the MER5 and LTR33 elements (Supplementary Figure 1). There were numerous other indels ranging between 1 and 40 kb within the beta block sequences (Supplementary Figures 2–4) that were not included as allelic markers in this study. To assess the MHC class I haplotypic integrity of the 95 cell lines, the additional allelic haplotype combinations that we typed were sorted and grouped according to alpha block haplotypes (Table 2, Supplementary Table 5) and beta block haplotypes (Table 3, Supplementary Table 6) and then used for SNP XO studies across ~3 Mb of sequence between GPX5 and MICB (Tables 4–8).
Table 3.
Beta block haplotypes.
| Hap ID | No. Haps | SVA-HC | HLA-C | SVA-BC | 9.5 kb indel | SVA-HB | HLA-B | SVA-MIC | MICA | MICB | CEH/AH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 01:02:01 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 46:01:01 | 2 | 010:01 | 005:02 | 46 | |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 01:02:01 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 51:01:01 | 2 | 010:01 | 005:02 | 51 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 01:02:01 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 54:01:01 | 1 | 012:01 | 005:02 | 54 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 01:02:01 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 56:01:01 | 1 | 012:01 | 005:02 | 56 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 01:02:01 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 15:01:01:01 | 2 | 010:01 | 006 | 15 |
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 03:04:01:01 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 40:01:02 | 2 | 008:04 | 002:01 | 40 |
| 7 | 5 | 1 | 05:01:01:01 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 18:01:01:01 | 1/2 | 001 | 005:02 | 18.2 |
| 8 | 5 | 1 | 05:01:01:02 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 44:02:01:01 | 1 | 008:01 | 005:02 | 44.1 |
| 9 | 2 | 1 | 07:01:01:01 | 1/2 | 2 | 1 | 18:01:01:02 | 1/2 | 018:01 | 002:01 | 18. |
| 10 | 1 | 1 | 07:01:01:01 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 49:01:01 | 1 | 004 | 005:02 | 49.x |
| 11 | 1 | 1 | 07:01:01:01 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 57:01:01 | 2 | 017 | 003 | 57.1 |
| 12 | 8 | 2 | 07:02:01:03 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 07:02:01 | 2 | 008:04 | 004:01 | 7.1 |
| 13 | 1 | 1 | 08:02:01:01 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 14:01:01 | 2 | 019:01 | 005:02 | 14.x |
| 14 | 2 | 1 | 08:02:01:01 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 14:02:01 | 1 | 011 | 005:02 | 14.y |
| 15 | 1 | 1 | 12:02:02 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 52:01:01 | 2 | 009:01 | 002:01 | 52.1 |
| 16 | 1 | 1 | 14:02:01 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 51:01:01 | 2 | 049 | 005:02 | 51 |
| 17 | 1 | 1 | 14:03 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 44:03:01 | 2 | 004 | 005:02 | 44 |
| 18 | 1 | 1 | 15:02:01 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 51:01:01 | 2 | 009:01 | 002:01 | 51.y |
| 19 | 2 | 1 | 15:02:01 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 51:01:01 | 2 | 009:01 | 005:02 | 51.x |
| 20 | 2 | 1 | 01:02:01 | 1 | 2 | 2* | 27:05:02 | 1 | 007:01 | 005:02 | 27.1 |
| 21 | 1 | 1 | 02:02:02:01 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 27:05:02 | 1 | 007:01 | 005:02 | 27.x |
| 22 | 2 | 1 | 02:02:02:01 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 40:02:01 | 2 | 027 | 005:02 | 40.x |
| 23 | 1 | 1 | 02:02:02:01 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 40:02:01 | 2 | 027 | 013 | 40.y |
| 24 | 2 | 1 | 03:03:01 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 15:01:01:01 | 1/2 | 010:01 | 002:01 | 15.x |
| 25 | 1 | 1 | 03:03:01 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 15:01:01:01 | 2 | 010:01 | 005:02 | 15.y |
| 26 | 3 | 1 | 03:04:01:01 | 1 | 2 | 2* | 15:01:01:01 | 2 | 010:01 | 002:01 | 62.1 |
| 27 | 1 | 1 | 03:04:01:01 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 40:01:02 | 2 | 008:04 | 002:01 | 60.x |
| 28 | 1 | 1 | 03:04:01:01 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 40:01:02 | 2 | 008:04 | 004:01 | 60.y |
| 29 | 1 | 1 | 03:04:01:01 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 40:01:02 | 2 | 008:04 | 014 | 60.z |
| 30 | 1 | 1 | C*04:01:01:01 | 1 | 2 | 2* | 15:26N | 2 | 010:01 | 005:02 | 15.n |
| 31 | 1 | 1 | C*04:01:01:01 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 35:01:01:01 | 0 | 002:01 | 005:02 | 35.x |
| 32 | 1 | 1 | C*04:01:01:01 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 35:01:01:01 | 2 | 017 | 003 | 35.y |
| 33 | 1 | 1 | C*04:01:01:01 | 0 | 2 | 2* | 35:01:01:02 | 1 | 002:01 | 002:01 | 35.2 |
| 34 | 2 | 1 | C*04:01:01:01 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 35:02:01 | 2 | 016 | 005:01 | 35.z |
| 35 | 1 | 1 | C*04:01:01:01 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 35:03:01 | 1 | 002:01 | 005:02 | 35.w |
| 36 | 1 | 1 | C*04:01:01:01 | 1 | 2 | 2* | 35:08:01 | 2 | 016 | 002:01 | 35.v |
| 37 | 1 | 1 | C*04:01:01:01 | 1 | 2 | 2* | 53:01:01 | 1 | 002:01 | 006 | 53.x |
| 38 | 3 | 1 | 06:02:01:01 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 13:02:01 | 2 | 008:01 | 005:02 | 13.1 |
| 39 | 1 | 1 | 06:02:01:01 | 1 | 0 | 2* | 37:01:01 | 2 | 010:01 | 002:01 | 37.x |
| 40 | 1 | 1 | 06:02:01:01 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 40:01:02 | 2 | 008:04 | 004:01 | 40.x |
| 41 | 1 | 1 | 06:02:01:01 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 47:01:01: | 2 | 008:01 | 004:01 | 47.1 |
| 42 | 4 | 1 | 06:02:01:01 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 57:01:01 | 2 | 017 | 003 | 57.1 |
| 43 | 1 | 1 | 06:02:01:02 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 50:01:01 | 1 | 009:02 | 005:06 | 50.1 |
| 44 | 5 | 1 | 07:01:01:01 | 1 | 2 | 2/2* | 08:01:01 | 1 | 008:01 | 008 | 8.1 |
| 45 | 1 | 1 | 07:01:01:01 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 08:01:01 | 2 | 008:04 | 004:01 | 8.x |
| 46 | 1 | 1 | 07:18 | 1 | 2 | 2* | 58:01:01 | 1 | 002:01 | 008 | 58.1 |
| 47 | 3 | 1 | 12:02:02 | 1 | 2 | 2/2* | 52:01:01 | 2 | 009:01 | 005:03 | 52.1 |
| 48 | 1 | 1 | 12:03:01:01 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 35:03:01 | 1 | 002:01 | 005:02 | 35.2 |
| 49 | 3 | 1 | 12:03:01:01 | 1 | 0 | 2/2* | 38:01:01 | 1 | 002:01 | 002:01 | 38.x |
| 50 | 1 | 1 | 12:03:01:01 | 1 | 0 | 2* | 51:01:01 | 2 | 006 | 005:02 | 51.x |
| 51 | 3 | 1 | 16:01:01 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 44:03:01 | 1 | 004 | 005:02 | 44.2 |
| 52 | 1 | 1 | 16:01:01 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 45:01:01 | 2 | 015 | 002:01 | 45.x |
| 53 | 1 | 1 | 17:01:01:02 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 41:01:01 | 1 | 004 | 005:02 | 41.x |
| 54 | 1 | 1 | 17:01:01:02 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 42:01:01 | 1 | 004 | 002:01 | 42.1 |
SVA-HB allele 2* is a SVA-HB duplicated sequence within LTR10/HERVI/LTR10 rearrangements that do not correlate with any particular HLA-C lineage and therefore may be sequence assembly errors. For SVA, Alu, and the indel, allele 1 is the absence of the element and allele 2 is the presence of the element.
Table 2.
Alpha block haplotypes and alleles from AluHF to AluHJ including HLA-F, -G, -H, -A, and -J alleles.
| Hap ID | No. Hap | AluHF | HLA-F | HLA-G | AluHG | ERVK9 | HLA-H | HLA-A | HLA-J | AluHJ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 1 | 01:01:01:09 | 01:01:02 | 1 | 1 | 02:01 | 01:01:01 | 01:01:01:02 | 2 |
| 2 | 9 | 1 | 01:01:01:09 | 01:06 | 1 | 1 | 02:01 | 01:01:01 | 01:01:01:02 | 2 |
| 3 | 13 | 1 | 01:01:01:01 | 01:01:01 | 2 | 1 | 01:01 | 02:01:01 | 01:01:01:05 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 01:01:01:01 | 01:01:01 | 2 | 1 | 01:01 | 02:01:01 | 01:01:01:04 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 01:01:01:01 | 01:01:01 | 2 | 1 | 01:01 | 02:01:01 | 01:01:01:05 | 1 |
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 01:01:01:04 | 01:01:01 | 2 | 1 | 01:01 | 02:01:01 | 01:01:01:05 | 1 |
| 7 | 3 | 1/2 | 01:01:01:08 | 01:01:01 | 2 | 1 | 01:01 | 02:01:01 | 01:01:01:05 | 1 |
| 8 | 2 | 1/2 | 01:01:01:08 | 01:01:01 | 2 | 1 | 01:01 | 02:01:01 | 01:01:01:02 | 1 |
| 9 | 1 | 1 | 01:01:01:09 | 01:01:01 | 2 | 1 | 01:01 | 02:01:01 | 01:01:01:05 | 1 |
| 10 | 1 | 1 | 01:04:01:02 | 01:01:01 | 2 | 1 | 01:01 | 02:01:01 | 01:01:01:05 | 1 |
| 11 | 1 | 1 | 01:01:02:07 | 01:03:01 | 1 | 1 | New | 02:05:01 | New | 1 |
| 12 | 1 | 1 | 01:01:01:09 | 01:01:01 | 2 | 1 | 01:01 | 02:01:01 | 01:01:01:05 | 1 |
| 13 | 1 | 1 | 01:04:01:02 | 01:01:01 | 2 | 1 | 01:01 | 02:01:01 | 01:01:01:05 | 1 |
| 14 | 1 | 1 | 01:01:02:07 | 01:03:01 | 1 | 1 | New | 02:05:01 | New | 1 |
| 15 | 1 | 1 | 01:01:01:18/19 | 01:01:22 | 1 | 1 | 02:04 | 03:01:01 | 01:01:01:02 | 2 |
| 16 | 6 | 1 | 01:03:01:01/04 | 01:01:01 | 1 | 2 | 02:04 | 03:01:01 | 01:01:01:04 | 1 |
| 17 | 2 | 1 | 01:01:02:09/12 | 01:01:03 | 1 | 2 | New | 11:01:01 | 01:01:01:04 | 1 |
| 18 | 1 | 1 | 01:03:01:03 | 01:04:04 | 1 | 2 | Deletion | 23:01:01 | 01:01:01:04 | 1 |
| 19 | 1 | 1 | 01:01:01:08 | 01:04:01 | 1 | 2 | Deletion | 24:02:01 | 01:01:01:02 | 2 |
| 20 | 3 | 1 | 01:01:01:09 | 01:04:01 | 1 | 2 | Deletion | 24:02:01 | 01:01:01:02 | 2 |
| 21 | 1 | 1 | 01:01:01:09 | 01:04:01 | 1 | 2 | Deletion | 24:02:01 | 01:01:01:04 | 1 |
| 22 | 1 | 1 | 01:01:02:10 | 01:04:01 | 1 | 2 | Deletion | 24:02:01 | 01:01:01:02 | 2 |
| 23 | 3 | 1 | 01:01:01:18/19 | 01:01:02 | 1 | 2 | Deletion | 24:02:01 | 01:01:01:02 | 2 |
| 24 | 3 | 1/2 | 01:01:01:08 | 01:01:02 | 1 | 1 | 01:02 | 26:01:01 | 01:01:01:08 | 1 |
| 25 | 4 | 2 | 01:01:01:08 | 01:01:01 | 1 | 1 | 02:02 | 29:02:01 | 01:01:01:01 | 1 |
| 26 | 1 | 1 | 01:01:01:09 | 01:01:02 | 1 | 1 | New | 30:01/A68 | New | 1 |
| 30 | 1 | 1 | 01:01:01:09 | 01:05N | 1 | 1 | New | 30:01:01 | New | 1 |
| 31 | 2 | 1 | 01:01:01:01/17 | 01:01:01 | 2 | 1 | New | 30:02:01 | 01:01:01:04 | 1 |
| 32 | 1 | 1 | 01:01:01 | 01:03:01 | 2 | 1 | 01:01 | 31:01:02 | 01:01:01:05 | 1 |
| 33 | 3 | 1 | 01:01:01:11 | 01:03:01 | 1 | 2 | New | 31:01:02 | New | 1 |
| 34 | 2 | 1 | 01:01:02:06/10 | 01:01:22 | 1 | 1 | 02:03 | 32:01:01 | 01:01:01:06 | 2 |
| 35 | 1 | 1 | 01:01:02:06 | 01:01:12 | 1 | 1 | 02:03 | 32:01:01 | 01:01:01:06 | 2 |
| 36 | 2 | 1 | 01:01:02:07 | 01:03:01 | 1 | 2 | New | 33:01:01 | New | 1 |
| 37 | 1 | 1 | 01:01:02:10 | 01:04:01 | 1 | 2 | New | 33:01:01 | New | 1 |
| 38 | 1 | 1 | 01:01:01:08 | 01:01:02 | 1 | 1 | 01:02 | 66:01:01 | New | 1 |
| 39 | 1 | 2 | 01:01:01:18/19 | 01:01:02 | 1 | 1 | New | 68:02:01 | New | 1 |
For AluHF, AluHG, AluHJ, and ERVK9, allele 1 is the absence of the element and allele 2 is the presence of the element. This nine-marker table is a summary of the more detailed Supplementary Table 4 with 21 markers.
Table 4.
SNP-poor (SP) and SNP-rich (SR) haplotypes in the MHC class I region from GPX5 to MICB.
| Lab ID | CEH | Haplotype | SP region | SNPs/100 kb | Sequence length kb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 7.1 | A*03:01/C*07:02/B*07:02 | 2,939 | ||
| 6 | 7.1 | A*03:01/C*07:02/B*07:02 | SP across whole region | 0.816 | 1,962 |
| 51 | 7.1 | A*03:01/C*07:02/B*07:02 | SP across whole region | 0.749 | 2,938 |
| 75 | 7.1 | A*03:01/C*07:02/B*07:02 | SP across whole region | 1.124 | 2,937 |
| 90 | 7.1 | A*03:01/C*07:02/B*07:02 | SP across whole region | 1.054 | 2,942 |
| 27 | 8.1 | A*01:01/C*07:01/B*08:01 | 2,996 | ||
| 11 | 8.1 | A*01:01/C*07:01/ B*08:01 | SP across whole region | 0.716 | 2,933 |
| 12 | 8.1 | A*01:01/C*07:01/B*08:01 | SP across whole region | 0.86 | 3,023 |
| 16 | 8.1 | A*01:01/C*07:01/B*08:01 | SP across whole region | 1.662 | 2,948 |
| 19 | 8.1 | A*01:01/C*07:01/B*08:01 | SP across whole region | 1.181 | 2,963 |
| 25 | 18.2 | A*30:02/C*05:01/B*18:01 | 2,988 | ||
| 26 | 18.2 | A*30:02/C*05:01/B*18:01 | SP across whole region | 0.68 | 2,940 |
| 67 | 51.x | A*02:04/C*15:02/B*51:01 | 2,952 | ||
| 76 | 51.x | A*02:04/C*15:02/B*51:01 | SP across whole region | 0.443 | 2,937 |
| 37 | 57.1 | A*02:01/C*06:02/B*57:01 | 2,984 | ||
| 58 | 57.1 | A*02:01/C*06:02/B*57:01 | SP across whole region | 0.546 | 2,932 |
| 17 | 62.x | A*02:01/C*03:03/B*15:01 | 2,944 | ||
| 32 | 62.x | A*02:01/C*03:03/B*15:01 | SP across whole region | 0.24 | 2,921 |
| 40 | 62.1 | A*02:01/C*03:04/B*15:01 | 2,941 | ||
| 85 | 62.1 | A*02:01/C*03:04/B*15:01 | SP across whole region | 0.769 | 2,990 |
| 41 | 62.1 | A*02:01/C*03:04/B*15:01 | SR/SP at LINC00243 | SR & SP | 2,922 |
| 49 | 65.1 | A*33:01/C*08:02/B*14:02 | 2,940 | ||
| 87 | 65.1 | A*33:01/C*08:02/B*14:02 | SP from MASIF to MICA | 9.1 | 1,923 |
| 78 | 44.2 | A*29:02/C*16:01/B*44:03 | 2,920 | ||
| 79 | 44.2 | A*29:02/C*16:01/B*44:03 | SP from MASIF to MICB | 0.847 | 1,772 |
| 83 | 44.2 | A*29:02/C*16:01/B*44:03 | SP from HLA-F to MICB | SR & SP | 2,975 |
| 23 | 35.5 | A*01:01/C*04:01/B*35:02 | 2,938 | ||
| 45 | 35.5 | A*01:01/C*04:01/B*35:02 | SP from HLA-F to MICB | SR & SP | 2,938 |
| 39 | 27.1 | A*02:01/C*01:02/B*27:05:02 | 2,943 | ||
| 47 | 27.1 | A*02:01/C*01:02/B*27:05:02 | SP from MUC21 to MICB | SR & SP | 2,944 |
| 24 | 44.1 | A*02:01/C*05:01/B*44:02 | 2,921 | ||
| 60 | 44.1 | A*02:01/C*05:01/B*44:02 | SP from HLA-C to MICB | SR & SP | 1,792 |
| 74 | 44.1 | A*02:01/C*05:01/B*44:02 | SP from HLA-F to MICB | SR & SP | 2,937 |
| 30 | 18.x | A*02:01/C*07:01/B*18:01 | 1,912 | ||
| 33 | 18.x | A*02:01/C*07:01/B*18:01 | SP from HLA-E to MICB | SR & SP | 2,929 |
| 62 | 52.1 | A*24:02/C*12:02/B*52:01 | 2,893 | ||
| 93 | 52.1 | A*24:02/C*12:02/B*52:01 | SP from HLA-L to MICB | SR & SP | 2,887 |
| 13 | 60.1 | A*02:01/C*03:04/B*40:01:02 | 2,749 | ||
| 86 | 60.1 | A*02:01/C*03:04/B*40:01:02 | 4 SNP crossover regions | SR & SP | 2,947 |
| 9 | 44.x | A*32:01/C*05:01/B*44:02 | 2,937 | ||
| 72 | 44.x | A*32:01/C*05:01/B*44:02 | 4 SNP crossover regions | SR & SP | 2,976 |
For details of sequence alignments between Lab ID and CEH, see Supplementary Table 8.
Allelic Lineages Within Alpha Block Haplotypes
Supplementary Table 5 shows the 46 alpha block haplotypes and HLA-A and RE allelic lineages of 95 homozygous cell lines (Norman et al., 2017) and the MHC sequence on chromosome 6 of the reference human genome (NC_000006.12, NCBI) using 21 genic and non-genic allelic markers from the telomeric locus of AluHF to the centromeric locus of AluHJ including HLA-F, HLA-G, eight HLA pseudogenes and 14 HLA-A allelic lineages. Of the HLA-A allelic lineages, only seven represented more than three sequence samples: HLA-A*01 (n, 14), -A*02 (n, 29), -A*03 (n, 8), -A*24 (n, 9), -A*29 (n, 4), -A*30 (n, 4), and -A*31 (n, 4). All seven HLA-A haplotype lineages were differentiated by haplotypic and/or haplospecific markers: most of the Alu, SVA, HERVK9, and MER9 within the alpha block (Table 1) were haplotypic and linked to particular HLA-A allelic lineages as well as to those of HLA-F, HLA-G and the HLA pseudogenes (HLA-V, -P, -H, -T, -K, -U, -W, and -J). Table 2 presents a summary of Supplementary Table 5 and shows the linkages of AluHF, AluHG, AluHJ, and HERVK9 with the HLA-F, -G, -H, -A and -J alleles in 39 alpha block haplotypes.
(1) All 14 HLA-A*01:01:01:01 alleles were linked to the haplospecific AluHJ insertion, HLA-J*01:01:01:02, HLA-H*02:01:01:01, HLA-F*01:01:01:09, and the ERV3-16/(ATAA)42/(ATTT)34 microsatellite.
(2) Twenty-seven of 28 HLA-A*02 haplotype lineages were linked to the haplotypic AluHG insertion, the (CAGAGA)n microsatellite deletion, the ERV3-16/(ATAA)46/(ATTT)35 microsatellite, HLA-G*01:01:01:01 and HLA- H*01:01:01:01.
(3) A single sequence sample with the HLA-A allele A*02:05:01 had no AluHG insertion, but had a variant (CAGAGA)n microsatellite number, and different alleles for all the alpha block HLA pseudogenes except for HLA-U*01:03.
(4) The AluHG insertion linked to the (CAGAGA)n microsatellite deletion was haplospecific for HLA-A*02/ G*01:01:01:01/H*01:01:01:01, whereas the AluHJ insertion was haplotypic for HLA-A*01/ G*01:01:02:01 or HLA-A*24/ G*01:01:02:01/G*01:04:01:01, respectively.
(5) The AluHG insertion with the (CAGAGA)n microsatellite deletion was linked also to HLA-A*30 in one haplotype and to HLA*A31 with the HERVK9 deletion in another haplotype, but not to the other three with the HERVK9 insertion, probably as a result of past recombinations or conversions.
(6) The AluHJ insertion in the HLA-A*01, HLA*24 haplotypes and the occasional HLA-A*02 or HLA-A*03 haplotypes was linked to all of the J*01:01:01:02 alleles (25 samples) and to J*01:01:01:06 in three samples of the A*32:01:01 haplotype.
(7) The AluHF was linked to 8 of 14 HLA-F*01:01:01:08 alleles, in 2 of 29 HLA-A*02 haplotypes, 2 of 3 HLA-A*26 haplotypes, all 4 HLA-A*29 haplotypes and 1 HLA-A*68:02 haplotype.
(8) The HERVK9 insertion was present in 25 cell lines, whereas the other 70 cell lines had the signatory deletion marker, a solitary MER9 that is the deletion product of a recombination between the 5′MER9 and 3′MER9 flanking the 6-kb HERVK9 internal sequence.
(9) The HERVK9 insertion was haplotypic for seven of eight HLA-A*03/G*01:01:01:05/H*02:04 samples, all nine HLA-A*24 samples, three of four HLA-A*31, both HLA-A*11 and HLA-A*33 samples, and the single HLA-A*23 sample.
(10) Both HLA-A*11 sequence lineages from the cell lines WT100BIS (Lab ID1) and KGU (Lab ID21) were linked to the HERVK9 insertion, and to C*04:01 and B*35:03:01 as extended haplotypes.
(11) All nine HLA-A*24:02:01:01 lineages and the single A*23:01:01 lineage had a ~55-kb deletion of HLA-H, SVA-16, HLA-T, HLA-K, LTR13A, HLA-U, and sMER9, ranging from centromeric of the HERVK9 in the HLA-H segment to the Charlie9 element at the telomeric end of the MER9 sequence of the HLA-A segment (Supplementary Figure 5).
(12) Eight of the nine HLA-A*24 haplotypes acquired HLA-J*01:01:01:02 with the AluHJ insertion, while the other acquired J*01:01:01:04 without the AluHJ insertion that is similar to the two HLA-A*11 haplotypes and the one HLA-A*23 haplotype.
Allelic Lineages Within Beta Block Haplotypes
Supplementary Table 6 shows the genic and non-genic allelic markers for the beta block haplotype sequences of 95 homozygous cell lines from the telomeric locus of HERVK9/MER9 microsatellite (TTTC)n known as M13 (Kulski et al., 1997) to the centromeric locus of MICB including five other microsatellite loci (M11, M9, Msx, MSa, and Msb), six dimorphic indels (SVA-HC, SVA-BC, 9.5-kb indel, SVA-HC, and AluP5) and four SNP loci (HLA-C and -B alleles and MICA and MICB alleles). There are 12 HLA-C, 21 HLA-B, 16 MICA, and 7 MICB allelic lineages that are linked together to form at least 54 HLA-C/HLA-B/MIC haplotype lineages. These haplotype lineages were sorted in the sequential order for the absence (allele 1) and presence (allele 2) of the SVA-HB insertion, and the alleles of HLA-C, HLA-B, MICA, and MICB, respectively (Table 3). The SVA-HB insertion (allele 2) is missing from the chimpanzee and gorilla MHC (data not shown), and its absence is assumed to be the ancestral allele.
Fifty-six of the 95 sequenced cell lines had the SVA-HB insertion. The HLA-C haplotypic lineages with no SVA-HB insertion were 6 C*01:02:01, 1 C*03:04:01 linked to HLA-B*40:01:02, 10 C*05, 2 C*07:01, 8 C*07:02, 3 C*08, 1 C*12:02 linked to HLA-B*52, 2 C*14 and 3 C*15. The HLA-C lineages with the SVA-HB insertion were 2 C*01:02:01 linked to HLA-B*27, 3 C*02, 9 C*03, 9 C*09, 11 C*06, 6 C*07:01 and 1 C*07:18, 9 C*12, 4 C*16, and 2 C*17. Only C*01, C*03 and C*07 had crossed over to be represented by both the absence and presence of the SVA-HB. Eighteen of 56 SVA-HB positive sequences contained SVA-HB duplications and LTR10/HERVI/LTR10 rearrangements that did not correlate with any particular HLA-C lineage or haplotype, suggesting that these variants were likely sequencing assembly errors. Nevertheless, there are two distinct haplotype evolutionary histories for the beta block that are based on the absence or presence of the SVA-HB insertion.
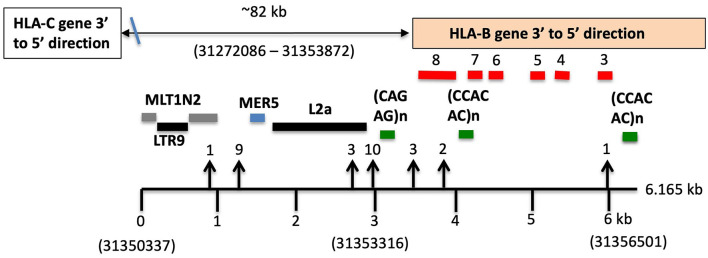
The SVA-HC insertion was specific for the eight HLA-C*07:02:01/B*07:02:01/MICA*008:04/ MICB*008:04 haplotypes, whereas the SVA-BC insertion was linked to six C*01:02 samples with various HLA-B alleles, three of four C*07:01 alleles and both C*14 alleles (Table 3, Supplementary Table 1). The SVA-BC and the SVA-HC insertions were present only in samples without the SVA-HB insertion. In comparison, the SVA-MIC insertion was linked to various HLA-B alleles both with and without linkage to the SVA-HB insertion. The (ACACAT)101 and the (ACACAT)161 simple repeats located between HLA-C and HLA-B further subdivide these HLA-B haplotypic lineages (data not shown). Three different haplotype families with (ACACAT)101 had no SVA-HB insertion, three HLA-B*14, seven HLA-B*18 and five of nine HLA-B*44 (Supplementary Table 6). The five lineage haplotypes with the microsatellite (ACACAT)161, but without the SVA-HB insertion, were B*07, B*46, B*51, B*54 and B*56. Single examples of B*15, B*40, B*44, B*52 and B*57 with (ACACAT)161 were either with or without SVA-HB (Supplementary Table 6). The different HLA-B lineage haplotypes with the SVA-HB insertion were partitioned further into another two lineages: those with the 9-kb deletion between AluY-(AT)n and AluJb-(TTAT)n and those without the 9-kb deletion (Table 3, Supplementary Figure 1). The 18 HLA-B haplotypes with the 9-kb deletion were all linked to either HLA-C*06:02:01 or -C*12:03:01 (Table 3).
Segmental Exchanges and SNP XO Within the MHC Class I Region
Supplementary Table 7 shows 39 examples of segmental shuffling between HLA class I genes A, B, C and E, pseudogene HLA-J and the MICA and MICB genes of 59 different representative AH and subtypes using HLA-B alleles as AH anchor points. Most of the MHC haplotypes within the homozygous cell lines are Caucasoids from Europe, North America, South Africa and Australia. The exceptions are one cell line from a North American Hispanic (MGAR), five Oriental cell lines (SA, ISH3, HOR, AKIBA, and KAWASAKI) and five South American Indian cell lines (LZL, AMALA, SPL, RML, and KRC005). The four RE dimorphic structural markers AluHG, AluHJ, and HERK9 within the alpha block and SVA-HB within the beta block further subdivided some of these AH. It is noteworthy that the Sardinian 18.2AH, HLA-A*30:C*05:B*18 (Contu et al., 1989, Bilbao et al., 2006) in the cell lines EJ32B and DUCAF has two specific dimorphic Alu insertions, AluOR and AluOR1 (Supplementary Table 2), located ~300 kb from the HLA-F gene (Figure 1). This finding confirms that the CPS of some MHC class I haplotypes and AH like the 18.2AH extend well into the OR gene cluster telomeric of the HLA-F gene and the MHC alpha block by at least 1,185 kb. The AluOR insertion was found also in one of two HLA-A*29 sequenced samples (cell lines PITOUT and MOU, respectively), the HLA-A*02:05:01 cell line WT49, the HLA-A*11:01 cell line WT100BIS and the HLA-A*23:01 cell line WT51 (Supplementary Table 2).
Figure 1.
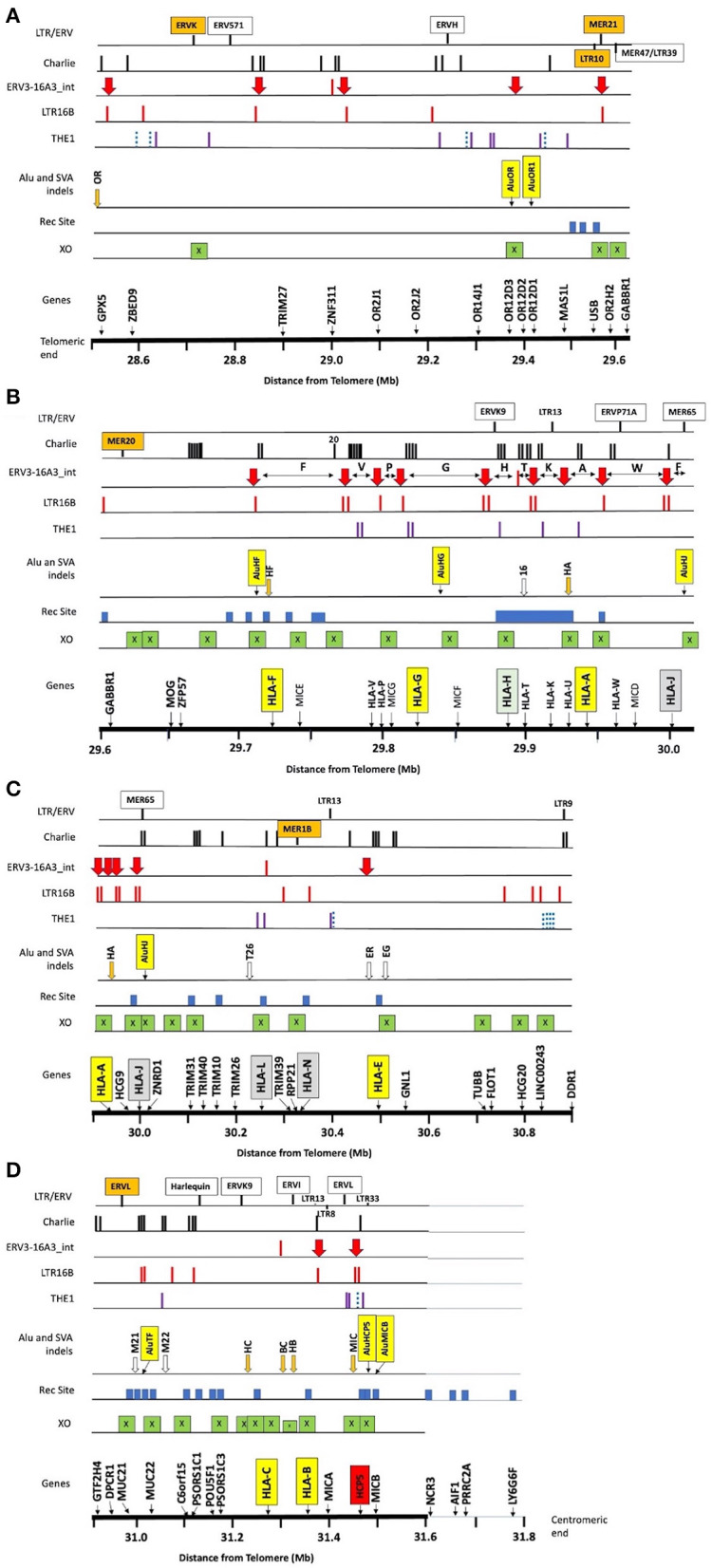
Summary of the locations of gene markers (Genes), 38 crossover sites (XO), 31 recombination sites (Rec Site), 8 Alu and 13 SVA indels, and the repeat elements THE1, LTR16, ERV3-16A3_int (aka HERV16), Charlie, and other labelled LTR/ERV elements within ~3 Mb of OR/MHC class I genomic sequence from GPX5 to MICB and the nucleotide position 28.5–31.6 (Mb distance from telomere on chromosome 6, GRCh38.p12 Primary Assembly NC_000006.12; NCBI, UCSC or ENSEMBL browsers on the Web). (A) The OR genomic region from 28.5 to 29.6 Mb, (B) the OR and MHC alpha block region from 29.6 to 30 Mb with the location of the 10 HLA segmental duplications segment F to segment J indicated by the horizontal double arrows between the ERV3-16A3_int insertions (solid red vertical arrow), (C) the TRIM gene cluster, HLA-L and HLA-N pseudogenes, non-classical HLA-E gene, and structural and regulatory gene marker (TUBB to DDR1) from 29.9 to 30.9 Mb, (D) the regulatory gene region (GTF2H4 to PSORS1C3) and the beta block of HLA-C to MICB from 29.9 to 31.6 Mb. The NCR3 to LY6G6F gene markers from 31.6 to 31.8 Mb are near the putative recombination sites identified by Lam et al. (2013) at the start of the MHC class III region. The X within green boxes indicate crossover sites, the blue solid blocks are the recombination sites reported by Lam et al. (2013), and the vertical orange (indels) and open arrows (fixed) are the SVA listed in Table 1. The Alu indels such as AluOR and AluOR1 in Table 1 are indicated as labelled yellow vertical boxes in the Alu or SVA indel row. The location of the THE1, LTR16B, and Charlie are indicated by the vertical bars in their respective rows. The blue dotted bars represent the THE1B subfamily and the purple vertical bars represent the other subfamilies, THE1A, THE1C, and THE1D.
The four Warao South American Indian cell lines LZL, AMALA, SPL and RML (Supplementary Tables 1, 2) present an interesting ethnic contrast to the Caucasoid cell lines (Supplementary Table 7). The Warao people who inhabit the rainforests of Orinoco Delta of northeastern Venezuela and western Guyana are an ancient ethnic minority with an extant population of ~50,000 people. The Warao 62.xAH and 51.xAH have the HLA-A alleles A*2:17:02, A*02:04, and A*02:12 rather than the common Caucasoid A*02:01:01, but they also carry the AluHG insertion that is linked to most of the Caucasoid A*02 lineages (Table 2). One of the Warao cell lines (SPL, ID73) has the HLA-A*31:02:02 allele linked to the HERVK9 insertion and SVA-HB deletion, which is markedly different to the Caucasoid and Oriental 62.xAHs, but with an alpha block haplotypic structure similar to two Caucasoid HLA-A*31:02 lineages represented by the English cell line JHAF (ID46) and the Australian cell line MT14B (ID82) (Supplementary Tables 1, 2). The other HLA-A*31:02 haplotype represented by the European Caucasoid cell line DEU (ID35) is with an AluHG insertion, a HERVK9 deletion (Table 2) and an SVA-HB insertion (Table 3), suggesting that a more modern HLA-A*31 AH was subsequently generated by segmental shuffling exchanges.
Since the exact SNP XO regions between different MHC haplotypes are poorly defined in regard to the intergenic and genic distribution of repeat elements, a detailed comparative examination of DNA sequence alignments of similar and different haplotypes was undertaken using the PIP method of Schwartz et al. (2000). We started with an examination of ~3 Mb of genomic sequence of the same haplotypes that included the class I region from HLA-F to MICB and the OR gene cluster that included the GPX5, ZNF311, OR2H2, GABBR1, and MOG genes (Table 4, Supplementary Table 8). We then performed a more detailed examination of SNP densities and XOs within the 1.2-Mb OR gene region (Table 5), the 310-kb alpha block (Table 6), the 1,172-kb inter alpha and beta blocks (Supplementary Tables 9, 10) and the 307-kb beta block (Tables 7, 8) of the same and/or different HLA-A, -C and -B haplotypes. The alignments and SNP counts were analysed manually across the entire 3 Mb and in 50-kb to 500-kb segments connecting the various segments as a sliding window. Figure 1 summarises the findings of our analysis of more than 250 sequence alignments between different and the same haplotypes with the identification of at least 38 ancestral SNP XO sites between SNP-poor and SNP-rich regions within ~2.8 Mb from GPX5 to MICB.
Table 5.
SNP crossover (XO) loci in the extended MHC class I OR gene region.
| Haplotype sequence alignment | OR GENE CLUSTER REGION/GABBR1/MOG | Total SNPs | XO point in haplotype sequence ID_HAP1 | Within or between (/) RE | XO between (/) genes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPX5 to OR2H1 | MAS1L & LINC01015 | USB & OR2H2 | GABBR1 | MOG & ZFP57 | ||||||
| AA | A | B | C | D | A-D | |||||
| ID_HAP1 | ID-HAP2 | 960 kb | SNP/50 kb | SNP/50 kb | SNP/50 kb | SNP/60 kb | SNP/210 kb | |||
| 49_A*33-C*08:02 | 50_A*33-C*14:03 | SRR | 87 | 56 | 17 | 216 (XO) | 376 | 208524 A/G | ERV3-16A3 | F segment |
| 15_A*26-C*05 | 64_A*26-C*12:03 | SRR | 39 | 44 | 21 | 214 (XO) | 318 | 211345 A/G | ERV3-16A3 | F segment |
| 15_A*26-C*05 | 69_A*66-C*12:03 | SRR | 45 | 34 | 11 | 19 (XO) | 109 | 210115 G/A | LTR43/ERV3 | F segment |
| 2_A*01-C*06 | 11_A*01-C*07 | SRR | 105 | 68 | 26 | 2 (XO) 1 | 202 | 165747 T/C | Charlie4/L3b | ZFP57/HLA-F |
| 2_A*01-C*06 | 16_A*01-C*07 | SRR | 93 | 64 | 21 | 2 (XO) 1 | 181 | 165747 T/C | Charlie4/L3b | ZFP57/HLA-F |
| 4_A*03-C*07:02 | 7_A*03-C*06:02 | SRR | 97 | 43 | 4 (XO) | 3 | 147 | 121130 A/C | L3b/MER5 | GABBR1/MOG |
| 9_A*32-C*05 | 22_A*32-C*12:03 | SRR | 90 | 51 | 17(XO) 0 | 2 | 160 | 143183 T/C | AluY/L2 | GABBR1/MOG |
| 9_A*32-C*05 | 72_A*32-C*05 | SRR | 91 | 49 | 15 (XO) 0 | 2 | 157 | 143183 T/C | AluY/L2 | GABBR1/MOG |
| 10_A*02-C*12:03 | 17_A*02:17-C*03 | SRR | 93 | 30 (XO) 0 | 2 | 5 | 130 | 92214 G/A | AluY(Sc8) | OR2H2/GABBR1 |
| 10_A*02-C*12:03 | 92_A*02:12-C*01 | SRR | 91 | 30 (XO) 0 | 2 | 3 | 126 | 92214 G/A | AluY(Sc8) | OR2H2/GABBR1 |
| 5_A*02-C*05 | 10_A*02-C*12:03 | SRR | 77 | 32 (XO) 0 | 0 | 2 | 111 | 75758 T/C | MER21C | USB/OR2H2 |
| 10_A*02-C*12:03 | 5_A*02-C*05 | SRR | 77 | 32 (XO) 0 | 0 | 2 | 111 | 75792 C/T | MER21C | USB/OR2H2 |
| 34_A*24-C*03:04 | 68_A*24-C*04 | SRR | 97 | 15 (XO) 0 | 1 | 0 | 113 | 59547 C/T | LTR10A | USB/OR2H2 |
| 46_A*31-C*15:02 | 73_A*31-C*01:02 | SRR | 58 | 9 (XO) 2 | 2 | 6 | 75 | 59532 T/C | LTR10A | USB/OR2H2 |
| 15_A*26-C*05 | 84_A*26-C*07 | SRR | 37 | 20 (XO) 1 | 2 | 0 | 59 | 66738 A/T | Tigger2b-Pri | USB/OR2H2 |
| 22_A*32-C*12:03 | 72_A*32-C*05 | (XO) | 2 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 7 | 136748 T/C | L2/L1 | OR12D3/OR12D2 |
| 4_A*03-C*07:02 | 6_A*03-C*07:02 | 6_missing seq | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | Undetected | SPR from block AA to block D | ||
| 78_A*29-C*16 | 79_A*29-C*16 | 79_missing seq | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | Undetected | SPR from block AA to block D | ||
| 11_A*01-C*07 | 16_A*01-C*07 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | Undetected | SPR from block AA to block D | |
| 4_A*03-C*07:02 | 51_A*03-C*07:02 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | undetected | SPR from block AA to block D | |
| 34_A*24-C*03:04 | 94_A*24-C*03:04 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 3 | Undetected | SPR from block AA to block D | |
| 25_A*30-C*05 | 26_A*30-C*05 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Undetected | SPR from block AA to block D | |
| 46_A*31-C*15:02 | 82_A*31-C*03:04 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 7 | Undetected | SPR from block AA to block D | |
| 15_A*26-C*05 | 78_A*29-C*16 | SRR | 45 | 37 (XOa) 0 | 3 | 4 (XOb) | 89 | 91066 G/A | L2/MS | OR2H2/GABBR1 |
| 2_A*01-C*06 | 17_A*02:17-C*03 | SRR | 11 | 58 | 48 | 197 | 314 | |||
| 25_A*30-C*05 | 34_A*24-C*03:04 | SRR | 49 | 40 | 85 | 191 | 365 | |||
| 25_A*30-C*05 | 46_A*31-C*15:02 | SRR | 49 | 35 | 27 | 287 | 398 | |||
| 25_A*30-C*05 | 22_A*32-C*12:03 | SRR | 83 | 42 | 13 | 51 | 189 | |||
SRR is SNP-rich region, SPR is SNP-poor region, XO is crossing over, and numbers in the block columns AA to A–D are SNP counts per block.
Table 6.
SNP counts and crossovers (XO) within alpha block segments 1 to 10 between different haplotype sequence alignments (ID_Hap1 and ID_Hap 2).
| Segment number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 1 to 10 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Segment name | OR end | F | V | P | G | H | T | K | A | W | J | F to J | Position and XO SNP | XO within or between (/) RE | |
| Segment size | 2.2 kb | 57 kb | 25 kb | 23 kb | 53 kb | 23.4 kb | 20.4 kb | 19 kb | 15 kb | 51 kb | 34 kb | 320.8 | |||
| Hap sequence comparisons | |||||||||||||||
| ID_Hap 1 | ID_Hap 2 | ||||||||||||||
| 11_A*01:01 | 4_A*03:01 | 12 | 284 | 134 | 198 | 382 | 340 | 330 | 245 | 107 | 180 | 40 | 2,240 | ||
| 2_A*01:01 | 4_A*03:01 | 11 | 280 | 144 | 200 | 388 | 367 | 374 | 248 | 110 | 187 | 38 | 2,336 | ||
| 10_A*02:01 | 4_A*03:01 | 12 | 262 | 32 | 35 | 133 | 328 | 321 | 248 | 343 | 380 | 30 | 2,112 | ||
| 2_A*01:01 | 10_A*02:01 | 9 | 340 | 135 | 194 | 371 | 103 | 55 | 164 | 346 | 380 | 35 | 2,123 | ||
| 5_A*02:01 | 1_A*11:01 | 15 | 280 | 35 | 30 | 517 | 356 | 259 | 80 | 240 | 211 | 27 | 2,035 | ||
| 15_A*26:01 | 78_A*29 | 0 | 4 XO 30 | 137 | 182 | 208 | 69 | 203 | 232 | 148 | 727 | 217 | 2,157 | [F] 56590 G/C | Charlie20a |
| 25_A*30 | 46_A*31 | 13 | 206 | 111 | 152 | 264 | 355 | 260 | 297 | 335 | 491 | 173 | 2,644 | ||
| SNP density | average: SNPs/kb | 4.7 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 6.2 | 6.1 | 11.7 | 12.6 | 11.4 | 15.5 | 7.2 | 2.4 | 7.0 | ||
| 4_A*03:01 | 46_A*31 | 13 | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | ||
| 4_A*03:01 | 49_A*33 | 2 | 279 | 191 | 166 | 236 | 65 | 106 | 268 | 331 | 476 | 169 | 2287 | ||
| 46_A*31 | 49_A*33 | 15 | 245 | 196 | 164 XO 0 | 16 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 11 | 33 | 15 | 707 | [P] 97693 C/T | MICG |
| 4_A*03:01 | 48_A*24/B*15:26N | 11 | 255 | 18 | 27 | 502 | 92/XO/del | del | del | del/XO/175 | 171 | 22 | 1262 | [H] 168684 del | L1/AAAGA/MLT1F1 |
| 4_A*03:01 | 94_A*24 | 10 | 279 | 135 | 194 | 440 | 91/XO/del | del | del | del/XO/175 | 219 | 38 | 1571 | [H] 168684 del | L1/AAAGA/MLT1F1 |
| 5_A*02:01 | 8_A*02:05 | 11 | 268 | 106 | 156 | 371 | 27 XO | 14 | 9 | Assembly errors | 28 | 952 | [H] 168492 G/C | L2/HLA-H/L2 | |
| 10_A*02:01 | 8_A*02:05 | 11 | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR XO | 5 | 7 | 13 | XO 199 | 24 | SRR/SPR | [H] 168959 G/C | L2/HLA-H/L2 |
| 10_A*02:01 | 8_A*02:05 | 13 | XO 199 | 24 | SPR/SRR | [W] 224700 C/T | ERV3-16A3 | ||||||||
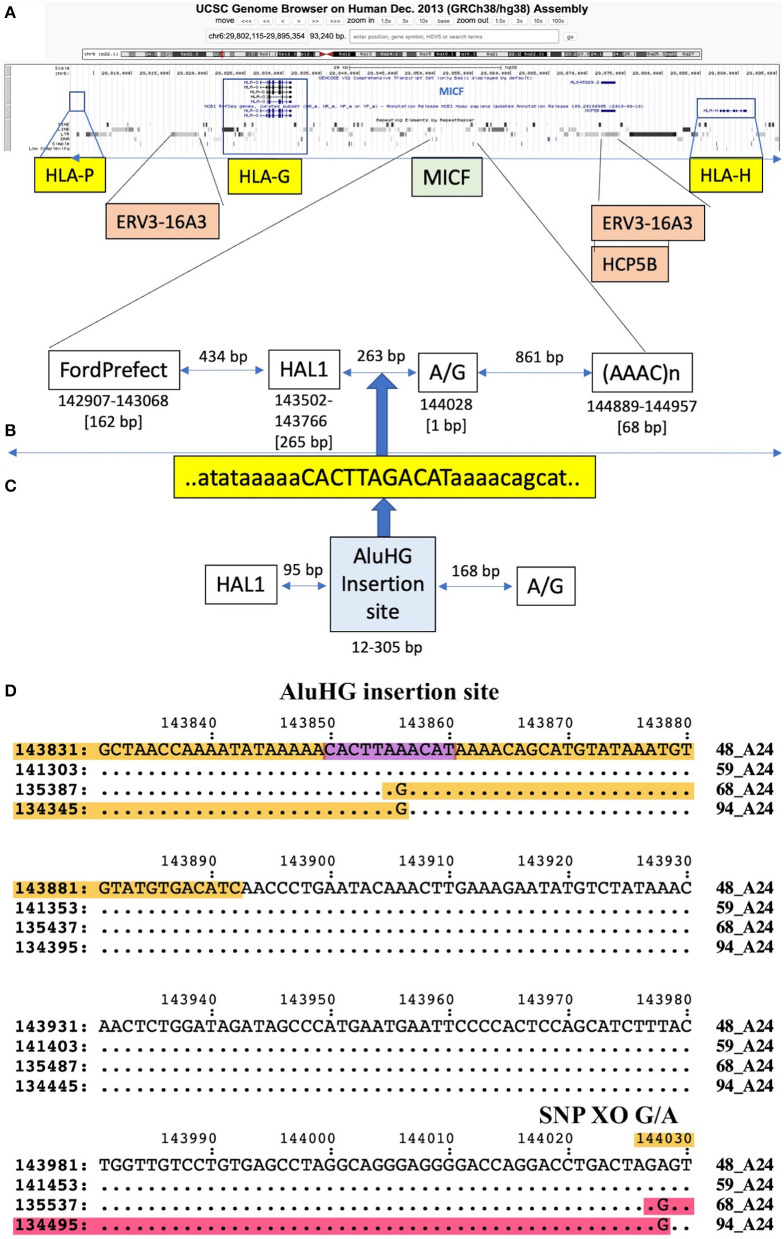
| 34_A*24 | 48_A*24 | 9 | 73 | 139 | 200 | 229/XO/0 | 1/XO/del | del | del | del/XO/2 | 82 | 39 | 763 | [G] 141380 A/G | HAL1/MICF |
| 34_A*24 | 59_A*24 | 2 | 132 | 141 | 199 | 229/XO/1 | 0/XO/del | del | del | del/XO/2 | 5 | 1 | 710 | [G] 141380 A/G | HAL1/MICF |
| 48_A*24 | 68_A*24 | 9 | 86 | 132 | 199 | 331/XO/1 | 0/XO/del | del | del | del/XO | 89 | 41 | 879 | [G] 144028 G/A | HAL1/MICF |
| 48_A*24 | 94_A*24 | 9 | 88 | 132 | 199 | 334/XO/1 | 0/XO/del | del | del | del/XO | 88 | 42 | 884 | [G] 144028 G/A | HAL1/MICF |
| 59_A*24 | 94_A*24 | 2 | 132 | 136 | 197 | 284/XO/1 | 3/XO/del | del | del | del/XO | 4 | 1 | 760 | [G] 141500 G/A | HAL1/MICF |
| 10_A*02:01 | 13_A*02:01 | 10 | 171+XO | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 178 | [F] 53540 G/T | Charlie20a |
| 10_A*02:01 | 67_A*02:04 | 10 | 155+XO | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 152 | [F] 53540 G/T | Charlie20a |
| 10_A*02:01 | 76_A*02:04 | 10 | 155+XO | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 152 | [F] 53540 G/T | Charlie20a |
| 5_A*02:01 | 13_A*02:01 | 11 | 166+XO | 0 | 0 | 6 | 1 | 3 | 3 | Assembly errors | 3 | 7 | [F] 53275 G/T | Charlie20a | |
| 4_A*03:01 | 18_A*03/A*24 | 5 | 137 | 78 | 126 | 179+XO | 0 | 0 | 2 | 7/XO | 131 | 37 | 692 | [G} 150337 C/T | Tigger1/Charlie20a |
| [A] 229198 G/T | L2/HLA-A/L2 | ||||||||||||||
| 48_A*24 | 59_A*24 | 11 | 139 XO 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0/XO/del | del | del | del/XO | 87 | 42 | 269 | [F} 53185 T/C | Tigger1/Charlie20a |
| 34_A*24 | 68_A*24 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | XO/del | del | del | del/XO | 1 | 0 | 2 | [H] del [A] | |
| 34_A*24 | 94_A*24 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | XO/del | del | del | del/XO | 0 | 0 | 1 | [H] del [A] | |
| 10_A*02:01 | 32_A*02:17 | Seq missing | 0 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 9 | OR cluster | ||
| 5_A*02:01 | 10_A*02:01 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 2 | Assembly errors | 3 | 18 | OR cluster | ||
| 11_A*01:01 | 16_A*01:01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 21.5 kb del | 1 | OR cluster | |
| 2_A*01:01 | 16_A*01:01 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 32 | 3 | 21.5 kb del | 47 | OR cluster | |
| 2_A*01:01 | 11_A*01:01 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 18 | OR cluster | |
| 10_A*02:01 | 17_A*02:17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 7 | OR cluster | |
| 10_A*02:01 | 92_A*02:12 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 6 | OR cluster | |
| 4_A*03:01 | 6_A*03:01 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | OR cluster | |
| 4_A*03:01 | 7_A*03:01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 6 | OR cluster | |
| 15_A*26 | 64_A*26 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 13 | OR cluster | |
| 15_A*26 | 84_A*26 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 7 | OR cluster | |
| 15_A*26 | 69_A*66 | 2 | 10 | 3 | 1 | 15 | 7 | 6 | 1 | 3 | 9 | 8 | 63 | OR cluster | |
| 78_A29 | 79_A29 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | OR cluster | |
| 25_A*30 | 26_A*30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | OR cluster | |
| 46_A*31 | 73_A*31 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | OR cluster | |
| 46_A*31 | 82_A*31 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | OR cluster | |
| 9_A*32 | 22_A*32 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | OR cluster | |
| 9_A*32 | 72_A*32 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 8 | OR cluster | |
| 49_A*33 | 50_A*33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | OR cluster | |
The SRR to SPR XO in Seg G (4) at A/G 141380 HAL1 and (ATAAT)n is near the AluHG insertion locus and the MICF pseudogene. XO is the abbreviation for crossover; SRR, SNP-rich region; SPR, SNP-poor region. The numbers before and/or after XO are the number of counted SNPs before and/or after the observed XO. There are XO points outside the alpha block in the telomeric OR gene region and the centromeric non-HLA region between HLA-J and HLA-E. The bold values here show the SNP density and the average number of SNPs/kb for the top 7 haplotype sequence comparisons in the table.
Table 7.
SNP counts and crossover (XO) loci between linked HLA-C and HLA-B alleles using different combinations of haplotype pairs.
| Alignments between haplotypes | Number of SNPs per section | XO | SNP or | closest | XO nt distance | XO in or | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lab ID numbers precede haplotypes | 0–7 k | 7–10 kb HLA-C | 10–20 k | 20–40 k | 40–60 k | 60–80 k | 80–93 k HLA-B | 0–93 k | Location bp | Indel at XO | Repeat | To end of HLA-B exon 8 | Between (/) HLA-C and -B | |
| Haplotype 1 | Haplotype 2 | |||||||||||||
| (A) Different HLA-C/HLA-B haplotypes | ||||||||||||||
| 66_C*02/B*27:05 | 49_C*08:02/B*14:02 | 33 | 32 | 85 | 114 | 455 | 805 + MI | 269 | 1,811 | none | 0 | nd | 0 | SRR |
| 55_C*06:02/B*13:02 | 95_C*07/B*57 | 15 | 88 | 85 | 112 | 247 + MI | 768 | 185 | 1,500 | none | 0 | nd | 0 | SRR |
| (B) Same HLA-C/ HLA-B haplotypes | ||||||||||||||
| 28_C*03:03/B*15 | 17_C*03:03/B*15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 0 | nd | 0 | SPR |
| 54_C*04/B*35 | 23_C*04/B*35 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | nd | 0 | SPR |
| 55_C*06:02/B*13:02 | 91_C*06:02/B*13 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 + indels | 1 | 0 | 0 | nd | 0 | SPR |
| 6_C*07/B*07:02 | 4_C*07/B*07:02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | nd | 0 | SPR |
| 11_C*07/B*08 | 12_C*07/B*08 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | nd | 0 | SPR |
| 65_C*08:02/B*14:01 | 49_C*08:02/B*14:02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 77 | 77 | 0 | 0 | nd | 0 | SPR |
| (C) Same HLA-C allele–different HLA-B allele | ||||||||||||||
| 6_C*07/B*07:02 | 30_C*07/B*18 | 12 | 9 + XO | 68 | 89 | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | HLA-C*7 | 0 | nd | nd | HLA-C |
| 30_C*07/B*18 | 6_C*07/B*07:02 | 12 | 9 + XO | 68 | 89 | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | HLA-C*7 | 0 | nd | nd | HLA-C |
| 6_C*07/B*07:02 | 8_C*07:18/B*58 | 19 | 9 + XO | 122 | 163 | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | HLA-C*7 | 0 | nd | nd | HLA-C |
| 8_C*07:18/B*58 | 6_C*07/B*07:02 | 19 | 9 + XO | 122 | 163 | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | HLA-C*7 | 0 | nd | nd | HLA-C |
| 94_C*12:03/B*51 | 56_C*12:02/B*52 | 41 | XO + 24 | 76 | 195 | SRR + MI | SRR | 41 | SRR | HLA-C*12 | 0 | nd | nd | HLA-C |
| 94_C*12:03/B*51 | 53__C*12:02/B*52 | 41 | 2 + XO | 70 | 217 | SRR | SRR | 41 | SRR | HLA-C*12 | 0 | nd | nd | HLA-C |
| 11_C*07/B*08 | 8_C*07:18/B*58 | 169 | 4 | 2+XO+2 | 163 | 32 | 277 + MI | 387 | 1036 | 19961 | A/G | L1PA13 | 72,286 | HLA-C/HLA-B |
| 11_C*07/B*08 | 30_C*07/B*18 | 159 | 0 | 0+XO+2 | 91 | 327 + MI | 348 + MI | 341 | 1268 | 19961 | A/G | L1PA13 | 72,286 | HLA-C/HLA-B |
| 11_C*07/B*08 | 42_C*07/B*49 | 159 | 0 | 0+XO+2 | 89 | 329 + MI | 348 + MI | 376 | 1303 | 19961 | A/G | L1PA13 | 72,286 | HLA-C/HLA-B |
| 11_C*07/B*08 | 95_C*07/B*57 | 1 | 0 | 0+XO+1 | 91 | 327 + MI | 348 + MI | 373 | 1141 | 19961 | A/G | L1PA13 | 72,286 | HLA-C/HLA-B |
| 92_C*01/B*51 | 39_C*01/B*27:05 | 0 | 0 | 1 | XO+30 | 367 | 578 + 5k MI | 240 | 1216 | 33326 | C/T | MIR/L1MB8 | 55,903 | HLA-C/HLA-B |
| 39_C*01/B*27:05 | 92_C*01/B*51 | 0 | 0 | 1 | XO+SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | 32511 | C/T | MIR/L1MB8 | 60,958 | HLA-C/HLA-B |
| 39_C*01/B*27:05 | 70_C*01/B*46 | 2 | 1 | 2 | XO+SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | 35360 | T/A | AluY/MLT1D | 58,109 | HLA-C/HLA-B |
| 39_C*01/B*27:05 | 89_C*01/B*54 | 26 | 0 | 2 | XO+SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | 35360 | T/A | AluY/MLT1D | 58,109 | HLA-C/HLA-B |
| 39_C*01/B*27:05 | 59_C*01/B*56 | 2 | 0 | 2 | XO+SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | 35360 | T/A | AluY/MLT1D | 58,109 | HLA-C/HLA-B |
| 39_C*01/B*27:05 | 73_C*01/B*15 | 1 | 1 | 2 | XO+SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR | 35360 | T/A | AluY/MLT1D | 58,109 | HLA-C/HLA-B |
| 11_C*07/B*08 | 4_C*07/B*07:02 | 158 | 7 | 67 | 0 | 0 + XO +217 | SRR + MI | SRR | SRR | 47841 | C/T | MIR | 44,406 | HLA-C/HLA-B |
| 11_C*07/B*08 | 6_C*07/B*07:02 | 158 | 7 | 67 | 0 | 0 + XO + 217 | SRR + MI | SRR | SRR | 47841 | C/T | MIR | 44,406 | HLA-C/HLA-B |
| 55_C*06:02/B*13:02 | 31_C*06:02/B*40 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | XO+529 | 210 | 739 | 60351 | G/T | HERVI | 21,449 | HLA-C/HLA-B |
| 5_C*05/B*18 | 9_C*05/B*44:02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | XO+87 | 88 | 89798 | T/C | MLT1N2 | 3,827 | 3′HLA-B |
| 95_C*07/B*57 | 30_C*07/B*18 | 160 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | XO+147 | 319 | 87226 | A/C | MLT1N2/MER5 | 2,767 | 3′HLA-B |
| 28_C*03:03/B*15 | 13_C*03:04/B*40:01 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 3 | XO+184 | 204 | 88616 | indel 36bp | MLT1N2/MER5 | 2,478 | 3′HLA-B |
| 28_C*03:03/B*15 | 34_C*03:04/B*40:01 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 5 | MI + 3 | XO+185 | 205 | 88616 | indel 36bp | MLT1N2/MER5 | 2,478 | 3′HLA-B |
| 54_C*04/B*35 | 48_C*04/B*15:26N | 0 | 0 | MI + 0 | 1 | 0 | 17 | XO+152 | 170 | 88190 | C/T | MLT1N2/MER5 | 2,440 | 3′HLA-B |
| 54_C*04/B*35 | 61_C*04/B*53 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | XO+7 | 10 | 88194 | T/C | MLT1N2/MER5 | 2,436 | 3′HLA-B |
| 50_C*14:03/B*44:03 | 88_C*14:02/B*51 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 5+XO+158 | 174 | 99804 | C/A | MLT1N2/MER5 | 2,273 | 3′HLA-B |
| 30_C*07/B*18 | 95_C*07/B*57 | 160 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | XO+147 | 319 | 93101 | A/C | MLT1N2/MER5 | 2,268 | 3′HLA-B |
| 94_C*12:03/B*51 | 22__C*12:03/B*38 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | XO+182 | 182 | 80294 | G/A | MLT1N2/MER5 | 2,226 | 3′HLA-B |
| 66_C*02:02/B*27:05 | 38_C*02/B*40:02 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | XO+33 | 34 | 88896 | indel 5bp | MLT1N2/MER5 | 2,165 | 3′HLA-B |
| 55_C*06:02/B*13:02 | 77_C*06:02/B*47 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | XO+119 | 120 | 80217 | G/C | L2 | 1,583 | 3′HLA-B |
| 55_C*06:02/B*13:02 | 36_C*06:02/B*57 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | XO+187 | 189 | 81180 | G/A | L2 | 620 | 3′HLA-B |
| 55_C*06:02/B*13:02 | 2_C*06:02/B*57 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | XO+187 | 190 | 81180 | G/A | L2/HLA-B | 620 | 3′HLA-B |
| 55_C*06:02/B*13:02 | 43_C*06:02/B*37 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | XO+190 | 193 | 81180 | G/A | L2/HLA-B | 620 | 3′HLA-B |
| 92_C*01/B*51 | 73_C*01/B*15 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | XO+125 | 126 | 88668 | G/A | L2/HLA-B | 560 | 3′HLA-B |
| 92_C*01/B*51 | 59_C*01/B*56 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | XO+241 | 242 | 88668 | G/A | L2/HLA-B | 560 | 3′HLA-B |
| 92_C*01/B*51 | 70_C*01/B*46 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | XO+127 | 129 | 88668 | G/A | L2/HLA-B | 560 | 3′HLA-B |
| 92_C*01/B*51 | 89_C*01/B*54 | 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | XO+168 | 207 | 88787 | indel 22bp | L2/HLA-B | 441 | 3′HLA-B |
| 83_C*16/B*44:03 | 80_C*16/B*45 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | XO+133 | 137 | 91097 | indel | L2/HLA-B | 503 | 3′HLA-B |
| 29_C*17/B*41 | 14_C*17/B*42 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | XO+205 | 208 | 86647 | G/A | HLA-B exon 3 | −2,542 | HLA-B (ex 3) |
| (D) Different HLA-C allele/same HLA-B allele | ||||||||||||||
| 92_C*01/B*51 | 94_C*12/B*51 | 176 | 132 | 79 + MI | 791 + MI | 190 + XO | 1368 | 89594 | G/A | HLA-B exon 8 | −186 | HLA-B exon 8 | ||
| 5_C*05/B*18 | 30_C*07/B*18 | SRR | SRR | SSR + MI (5.2kb) | SRR | SRR +XO | SRR + MI | 93767 | G/A | HLA-B exon 8 | −142 | HLA-B exon 8 | ||
| 9_C*05/B*4402 | 83_C*16/B*4403 | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR + MI | SRR +XO | SRR + MI | 92080 | C/A | L2/HLA-B | 139 | 3′HLA-B | ||
| 92_C*01/B*51 | 46_C*15/B*51 | 141 | 295 | 222 | 149 | 140 + XO | 947 | 89065 | A/T | L2/HLA-B | 163 | 3′HLA-B | ||
| 9_C*05/B*4402 | 50_C*14/B*4403 | SRR | SRR | SRR + MI | SRR + MI | SRR +XO | SRR + MI | 91971 | T/C | L2/HLA-B | 248 | 3′HLA-B | ||
| 73_C*01/B*15 | 28_C*03/B*15 | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR + MI | SRR + XO | SRR + MI | 87246 | A/G | L2/HLA-B | 640 | 3′HLA-B | ||
| 73_C*01/B*15 | 48_C*04/B*1525N | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR + MI | SRR + XO | SRR + MI | 87246 | A/G | L2/HLA-B | 640 | 3′HLA-B | ||
| 2_C*06/B*57 | 95_C*07/B*57 | SRR | SRR | SRR + MI | SRR | SRR +XO | SRR + MI | 83390 | A/G | L2/HLA-B | 650 | 3′HLA-B | ||
| 54_C*04/B*35 | 20_C*12/B*35 | SRR + MI | SRR + MI | SRR + MI | SRR | SRR +XO | SRR + MI | 89662 | C/A | L2 | 968 | 3′HLA-B | ||
| 39_C*01/B*27:05 | 66_C*02/B*27:05 | 175 | 79+XO+0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 254 | 35005 | T/A | L1MB8/MLT1D | 58523 | HLA-C/HLA-B | ||
| 38_C*02/B*40:02 | 34_C*03/B*40:02 | SRR | SRR | SRR | SRR + MI | SRR | SRR | nd | 0 | nd | nd | SRR | ||
| 38_C*02/B*40:02 | 77_C*06/B*40:01 | SRR | SRR | SRR + MI | SRR | SRR | SRR | nd | 0 | nd | nd | SRR | ||
SRR is SNP-rich region that is estimated to be >100 SNP without manual counts, SPR is SNP-poor region (<10 SNP), and MI is major indel (>1 kb usually <6 kb). XO in columns is crossover and XO + number presents the number of SNPs before or after the crossover in each of the 20-kb genomic sections. nd, not determined.
Table 8.
SNP crossover (XO) loci within intergenic regions between HLA-B and MICA or MICB in alignments of different haplotype pairs.
| Alignments between paired haplotype sequences | XO distance from HLA-B | XO | XO within gene or within and between (/) repeat elements | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lab ID numbers precede haplotypes | SNP | |||
| Haplotype 1 | Haplotype 2 | SPR/SRR | ||
| 65_B*14:01/MICA*019/MICB*502 | 49_B*14:02/MICA*011/MICB*502 | 8796 | T/C | L1 |
| 65_B*14:01/MICA*019/MICB*502 | 87_B*14:01/MICA*11/MICB*005:02 | 8822 | G/A | L1 |
| 72_B*44/MICA*008/MICB*005 | 83_B*44:03/MICA*004/MICB*005 | 14436 | A/G | L1M5/L1ME3 |
| 72_B*44/MICA*008/MICB*005 | 50_B*44:03/MICA*004/MICB*005 | 14436 | A/G | L1M5/L1ME3 |
| 25_B*18/MICA*001MICB*5002 | 30_B*18/MICA*018/MICB*201 | 16711 | G/T | L1 |
| 19_B*08/MICA*008/MICB*008 | 84_B*08/MICA*008/MICB*004 | 30243 | C/T | MLT2C1/Charlie9 |
| 94_B*51/MICA*006/MICB*005 | 92_B*51/MICA*010/MICB*005 | 44271 | A/G | LTR8A |
| 94_B*51/MICA*006/MICB*005 | 46_B*51/MICA*009/MICB*002 | 44618 | C/T | LTR8A/AluJb |
| 94_B*51/MICA*006/MICB*005 | 67_B*51/MICA*009/MICB*005 | 52042 | G/A | (CTC)n/L1M3 |
| 88_B*51/MICA*049/MICB*005 | 92_B*51/MICA*010/MICB*005 | 54075 | A/G | LTR8A |
| 54_B*35/MICA*002/MICB*005 | 68_B*35/MICA*016/MICB*002 | 66656/MICA | C/T | L1MB2/MIR in MICA |
| 46_B*51/MICA*009/MICB*002 | 67_B*51/MICA*009/MICB*005 | 95787 | C/T | L1PA3/Tigger3b |
| 86_B*40/MICA*008/MICB*002 | 82_B*40/MICA*008/MICB*004 | 96012 | C/T | L1PA3/Tigger3b |
| 88_B*51/MICA*049/MICB*005 | 94_B*51/MICA*006/MICB*005 | 100093 | G/A | THE1D/ L1M2 |
| 32_B*15/MICA*010/MICB*002 | 28_B*15/MICA*010/MICB*005 | 101267 | A/C | MER2 |
| 32_B*15/MICA*010/MICB*002 | 73_B*15/MICA*010/MICB*006 | 101267 | A/C | MER2 |
| 86_B*40/MICA*008/MICB*002 | 13_B*40/MICA*008/MICB*014 | 102370 | C/T | SVA-MIC indel |
| 21_B*35/MICA*002/MICB*005 | 1_B*35/MICA*002/MICB*002 | 105577 | G/C | MER21C/MER4 |
| 54_B*35/MICA*002/MICB*005 | 21_B*35/MICA*002/MICB*005 | 113437 | C/G | MER21C/MER4 |
| 68_B*35/MICA*016/MICB*002 | 23_B*35/MICA*16/MICB*005 | 116829 | G/A | 5′-ERV3-16A3_I (HCP5) |
| 54_B*35/MICA*002/MICB*005 | 1_B*35/MICA*002/MICB*002 | 119556 | A/G | 5′-ERV3-16A3_I |
| 88_B*51/MICA*049/MICB*005 | 46_B*51/MICA*009/MICB*002 | 123534 | G/C | 5′-ERV3-16A3_I |
| 88_B*51/MICA*049/MICB*005 | 67_B*51/MICA*009/MICB*005 | 123570 | C/T | 5′-ERV3-16A3_I |
| 38_B*40/MICA*027/MICB*005 | 71_B*40/MICA*027/MICB*013 | 124806 | A/G | THE1A/LTR33 |
| 28_B*15/MICA*010/MICB*005 | 73_B*15/MICA*010/MICB*006 | undetected | SPR | SPR HLA-B to MICB gene |
| 19_B*08/MICA*008/MICB*008 | 27_B*08/MICA*008/MICB*008 | no XO | SPR | SPR from HLA-B to MICB |
| 65_B*1401/MICA*019/MICB*502 | 49_B*1402/MICA*011/MICB*502 | SRR/112318/SPR | A/G | 5′-ERV3-16A3 (HCP5) |
| 65_B*1401/MICA*019/MICB*502 | 87_B*14:01/MICA*11/MICB*005:02 | SRR/146518/SPR | C/T | L1 |
| 38_B*40/MICA*027/MICB*005 | 86_B*40/MICA*008/MICB*002 | undetected | SRR | SRR from HLA-B to MICB |
| 38_B*40/MICA*027/MICB*005 | 82_B*40/MICA*008/MICB*004 | undetected | SRR | SRR from HLA-B to MICB |
| 54_B*35/MICA*002/MICB*005 | 35_B*35/MICA*017/MICB*003 | undetected | SRR | SRR from HLA-B to MICB |
SRR is SNP-rich region, SPR is SNP-poor region, and XO is crossover.
SNP Densities Within MHC Class I Homologous Haplotypes
We grouped and aligned 41 sequences to evaluate the variations of SNP density and the degree of homology within the same CEHs/AHs (Table 4 and Supplementary Table 8). The homologous sequence alignments for 12 of 16 different CEHs/AHs revealed a scarcity of SNPs ranging over ~1.8 Mb from HLA-F to MICB with <150 SNPs over the entire region at an average of 20 SNPs for 17 sequence alignments. Seven of the 16 different CEHs/AHs were SNP poor (<150 SNPs over ~3 Mb) from the GPX5 locus in the OR gene region to the MICB gene in the beta block region. These highly homologous sequence runs represented the seven sequences of 8.1AH, five sequences of 7.1AH, two sequences each of 18.2AH, 51.1AH, 57.xAH and 62.xAH, and two of three sequences classified as 62.1AHs. The SNP counts over the same range for the alignment of different haplotypes such as between the 7.1 CEH/AH and 8.1 CEH/AH were >2,000 for ~3 Mb.
Six CEHs/AHs had regions of substantial diversity that were SNP-rich between the alpha and beta blocks and/or in the OR gene region at the telomeric end of the alpha block. These haplotypes consisted of different-sized, SNP-poor recombinant blocks interspersed between SNP-rich recombinant blocks. The most surprising results were for the comparison between the three sequences of the 62.1 CEH/AH and the three sequences of the 44.1 CEH/AH. The sequence of LAB ID_41 had varying regions of SNP density with three SNP XOs, whereas ID_40 and ID_85 had few detectable SNPs (0.77 SNPs per 100 kb) and no XO SNPs in their alignment from GPX5 to MICB. Similarly, the ID_60 sequence with the 44.1 CEH/AH had at least two SNP XO events, one in the region between HLA-J and HLA-E and another in the region between MUC21 and HLA-C. In comparison, the ID_74 sequence of 44.1 CEH/AH had few SNPs and no detectable SNP XO in the 1.8-Mb sequence block from HLA-F to MICB.
Crossing Over Within the OR Extended Gene Region
The SNP XOs for some CEHs/AHs were detected in the OR gene regions hundreds of kilobases telomeric of the HLA-F gene (Table 5). For the sequence comparison between haplotype pairs, the OR genomic region was divided into four segmental blocks of 210–300 kb each, ranging from the telomeric GPX5 gene to the ZFP57 gene that are 1,118.4 kb and 42.1 kb telomeric of the HLA-F locus, respectively. The average SNP/210 kb for four different haplotype pairs was 317 SNPs within the genomic region between MAS1L and the start of the alpha block F segment. In paired sequence comparisons of 23 similar haplotypes, a SNP XO was found in 15 pairs within 237 kb between MAS1L and HLA-F. A SNP XO was found near to or within ERV3-16A3, an ancient HERV-16 element at the junction of the F segment in five haplotype pairs, within LTR10A of two haplotype pairs, within MER21C of two haplotype pairs, within AluY/Sc8 of two haplotype pairs and within Tigger2b of one haplotype pair. Most SNP XO were found in loci between ZFP57 and HLA-F (five haplotype pairs), USB and OR2H2 (five haplotype pairs), GABBR1 and MOG (three haplotype pairs) and OR2H2 and GABBR1 (two haplotype pairs), revealing the variability of the SNP XO junctions that were involved with ancestral recombinations.
The SNP XO in a region between the OR12D3 and ORD12D2 genes in the sequence alignment of 22_A*32-B*38 and 72_A*32-B*44:02 is ~332.2 kb from the HLA-F gene. Moreover, this SNP XO site is in close proximity to the young Alu indel, AluOR, that was detected in Japanese and Caucasians at a frequency of 0.32 and 0.14, respectively (Table 1). This SNP XO and active Alu insertion site appear to mark a hotspot for meiotic and insertion recombinations. Of the seven other sequence comparisons, no SNP XO was detected in two pairs (ID4 v ID6 and ID78 v ID79) of sequences that ended at the MA1L/LINC01015 segmental block and in five pairs (ID11 v ID16, ID4 v ID51, ID34 v ID94, ID25 v ID26, and ID46 v ID82) that ended near the GPX5 locus because of the absence of sequence for further analysis. The comparisons between two 7.1AH (ID4 v ID51) and two 8.1AH (ID11 v ID16) were striking because the SNP-poor region extended from the alpha block to at least the GPX5 gene that is ~1118 kb from the HLA-F gene. Both of the extended A*30-B*18 haplotypes (ID25 v ID26) carried the haplospecific AluOR insertion and the novel AluOR1 insertion (Table 1).
SNP Density XOs Within the Alpha Block of Different HLA-A Haplotypes
The alpha block was divided into 10 segments containing the duplicated HLA genes and pseudogenes from segment F with the HLA-F gene to segment J with the HLA-J pseudogene (Dawkins et al., 1999; Kulski et al., 1999a,b) for SNP counts and XO analysis (Table 6) as shown in Supplementary Figure 6 and Supplementary Table 3. The SNP counts were zero to less than 20 SNPs over 320.3 kb of sequence for 20 of 35 similar alpha block haplotype pairs (Table 6). In contrast, the SNP counts were much greater in the sequence alignments of seven different haplotype pairs ranging between 2,035 and 2,644 SNPs per 320.3 kb at an average of 7 SNPs/kb. The highest average SNP density was 16 SNPs/kb in the A segment and the lowest density was 2 SNPs/kb in the J segment. Because of deletions or XO within the alpha block, some recombinant haplotypes had intermediate SNP numbers such as 692 to 884 SNPs per 320.8 kb for six of the HLA-A*24 haplotypes, 269 SNPs for the 48_A*24 vs. 59_A*24 haplotypes and 707 SNPs for the 46_A*31 vs. 49_A*33 haplotypes. The smallest amount of SNP diversity within the alpha blocks of different HLA-A allelic lineages was between the HLA-A*26 and the HLA-A*66 haplotypes with only 66 SNP differences across the 320.8 kb alpha block (one SNP per 4.9 kb compared to an average of one SNP per 0.14 kb for an average of seven haplotype pairs). The biggest SNP difference among the different haplotypes was in the 53-kb G-segment and the smallest was within the 15-kb A segment that had only a total of three SNP differences. A previous analysis of the HLA-A*26/A*66 loci indicated that the HLA-A*66 was a product of a gene conversion (Madrigal et al., 1993). Alternatively, the relatively small number of SNP differences across the entire alpha block of the HLA-A*26/A*66 haplotypes suggests that they might have evolved from the same AH and diverged slightly by gene conversions and mutagenesis over time because of their age.
An intermediate amount of SNP diversity was detected between HLA-A*31 and HLA-A*33 with 707 SNPs within the 320.8-kb alpha block. However, the first 100 kb of the alpha block including the F, V and P duplicated segments was 605 SNPs and the remaining 220 kb of the alpha block from the G segment to the J segment was only 102 SNPs including 11 SNPs in the A segment. This segmental division with sequence homogeneity at the centromeric end of the HLA-A*31 and HLA-A*33 haplotype sequences and large diversity at the telomeric end of their alpha blocks has an ancestral SNP XO at the centromeric end of the P segment within the MICG pseudogene (C/T). In comparison to the 707 SNPs across the alpha block of the HLA-A*31 and -A*33 haplotypes, there were 2,287 SNPs across the alpha block of the HLA-A*03 and -A*33 haplotypes. Coincidently, the HLA-A*03, -A*31, and -A*33 haplotypes all have an HERVK9 insertion. Thus, two thirds of the HLA-A*31/*33 alpha blocks have the same haplotype lineage whereas the other third are evidently from different haplotype lineages.
The largest difference among different HLA-A haplotypes was between HLA-A*30 and HLA-A*31 with 2,644 SNPs in the alpha block, whereas on average there were 2,235 SNPs in the alpha block for seven different sequence pairs. The biggest differences between the same HLA-A haplotypes were obtained for the HLA-A*24 pairs, suggesting that their alpha blocks may have undergone numerous shuffling and exchanges with various other HLA-A haplotypes. No SNPs were detected in the alpha blocks of the HLA-A*32 haplotype pair and only one SNP was detected in the alpha blocks of an HLA-A*24 haplotype pair and the HLA-A*29, -A*30, and -A*31 haplotype pairs.
The SNP XOs for the same haplotypes at the telomeric end of the alpha block were variable depending on which haplotypes were compared (Table 6), but mostly involved the F segment with the HLA-F gene and sites within or between the Tigger1 and Charlie20 DNA elements. In genomic sequence comparisons between seven similar HLA-A*24 haplotype pairs, all of them had the 54-kb deletion of the T and K segments between the H and A segments (Supplementary Figure 5). Also, some XOs occurred in the G segment at A/G 141380 between HAL1 and (ATAAT)n, which is near the AluHG insertion locus and the MICF pseudogene (ID34 v ID48, ID34 v ID59, ID48 v ID68, and ID48 v ID94) (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Putative recombination site in the MICF pseudogene region with a SNP rich to SNP poor crossover in segment G at 144028 G/A, which is 168 bp from the site of an AluHG insertion site in the sequence alignment of ID48_A24, ID59_A24, ID68_A24, and ID94_A24 (Table 6). (A) Location of the MICF pseudogene in segment G relative to the HLA-P, HLA-G, and HLA-H genes as depicted in the UCSC browser. (B) Magnification of the MICF pseudogene region showing the positions of the flanking TE, FordPrefect and HAL1, and the A/G SNP crossover located between HAL1 and the (AAAC)n microsatellite. (C) The AluHG insertion site and sequence CACTTAGACAT located between HAL1 and the A/G SNP position. (D) A 200-bp nucleotide sequence showing the location of the AluHG insertion site and the SNP G/A crossover (XO) site in a comparison between four different haplotypes (48, 59, 68, and 94) with the same HLA-A*24 allelic lineage. The structural biallelic AluHG insertion is linked to HLA-A*02, but is absent in HLA-A*24 (Table 2). The AluHG TD insertion site CACTTAAACAT (Kulski et al., 2001) is outlined in purple.
The sequence comparison between the HLA-A*02:01:01 and HLA-A*02:05:01 haplotypes revealed large SNP differences within five segments from F to H of the alpha block (ID5 v ID8 and ID10 v ID8). This difference indicates that an exchange of segments T, K and A had occurred in the HLA-A*02:05:01 haplotype (Italian cell line WT49) that lacks the haplospecific A*02 lineage marker AluHG within the G segment (Supplementary Table 2). The sequence comparison between 4_A*03:01:01:01 and 18_A*03:01:01:01/A*24:02:01 with a low SNP density within the segments H to A is noteworthy because it reveals that the 18_A*03:01:01:01/A*24, if assembled correctly from the heterozygous Australian Caucasoid cell line LO081785, is an atypical and highly divergent A*03 haplotype with a HERVK9 deletion (Hap ID19.A*03.2 in Supplementary Table 6 and ID_18 in Supplementary Table 2). The SNP XO was within the G segment at nucleotide position 150337 C/T located between the Tigger1 and Charlie20a DNA elements (Table 6).
XO in Regions Between HLA-J and HLA-C
(a) SNP XOs within HLA-A haplotypes. The analysis of XO junctions in the genomic sequences between HLA-J and HLA-C outside the alpha and beta blocks using the same HLA-A and different HLA-C alleles was limited to only 15 comparisons (Supplementary Table 9). Of these, the XO was between HLA-A and HLA-J in two comparisons, between HLA-J and HLA-E in six pairs, and between HLA-E and MUC21 in six pairs. In the sequence comparison between 11_A*01-C*07-B*08 and 2_A*01-C*06-B*57 (example 6* in Supplementary Table 9), at least five different XO junctions were detected in different regions of segments B to E, including the transition from SPR to SRR in block B, two separate XO transitions in block C, a SRR to SPR XO in block D and a SPR to SRR XO in block E. Multiple XOs were observed also for analyses numbered 5 to 8 in Supplementary Table 9. The entire SNP-poor region (20 SNPs) was extended from HLA-J to HLA-C in the sequence alignment of cell lines with the same haplotype, A*01-C*06.
(b) SNP XOs within HLA-C haplotypes. Supplementary Table 10 shows the XO regions for 44 recombinant sequence pairs with the same HLA-C, but different HLA-A allelic lineages. A control homologous sequence pair (analysis 45) with the same HLA-A and HLA-C allelic lineages, 2_A*01-C*06-B*57 and 31_A*01-C*06-B*40, was SNP poor with only 20 SNPs counted over 1,322.9 kb of sequence. In comparison, the other sequences were heterologous (SNP rich) over most of the genomic region between the HLA-A and HLA-C genes. XOs occurred from SNP rich to SNP poor within the HLA-C gene or the 3′ non-coding region (NCR) of HLA-C in a comparison of 14 haplotype pairs, implying that recombinations occurred within the coding region of the ancestral HLA-C*07:18 and some other ancestral HLA-C*07 allelic lineages. The HLA-C haplotypic alleles that transitioned from SNP-poor to SNP-rich regions within 12 kb of the 3′end of exon 8 of HLA-C included C*01, C*04, C*05, C*07, C*08, C*12, and C*14 depending on their linkage with HLA-A alleles. The C*03/HLA-A*01, -A*02, -A*24, and the C*17/HLA-A*01, -A*30 combinations were SNP poor until the PSORS1C3 gene that is located about 100 kb from the HLA-C gene. Some of the HLA-C*06 and HLA-C*07 alleles within different recombinant haplotypes (analysis numbers 31 to 34) were homologous (SNP-poor) in the region from the HLA-C locus to the HCG22 locus. This long-range, homologous genomic segment of ~215 kb between HLA-C and HCG22 includes the various psoriasis candidate genes HCG27, PSORS1C3, POU5F1, TCF19, CCHCR1, PSORS1C2, PSORS1C1, CDSN, and C6orf15 (Nair et al., 2006). However, in combinatorial analyses of recombinant risk haplotypes and alleles genotyped in 678 families with early-onset psoriasis, Nair et al. (2006) determined that HLA-C*06 was the solitary risk allele that conferred susceptibility to early-onset psoriasis. Other HLA-C/HLA-A recombinant haplotypes were SNP poor over even greater distances ranging between 156 kb from the HLA-C gene to C6orf15 (C*01) and 730 kb from the HLA-C gene to a region between the LINC02569 and GNL1 loci. XO between SPR and flanking SRRs also occurred within or near to the MUC22 and MUC21 genes that are 234 kb and 279 kb from the HLA-C gene locus, respectively.
SNP-density XOs in Regions Between Different HLA-C and HLA-B Alleles
Table 7 shows the results of SNP counts and XO loci for 59 HLA-C and HLA-B haplotype sequence alignments using various combinations of similar and different haplotypes. As controls for comparing the various HLA-C/HLA-B recombinants, two were different HLA-C and HLA-B haplotypes and six were the same HLA-C and HLA-B haplotypes. The different haplotype pairs yielded an average of 1,656 SNP counts for ~93 kb, whereas the same haplotype pairs produced a few or no SNPs over the same distance between HLA-C and HLA-B loci. There were 39 sequence pairs of HLA-C/HLA-B recombinants with the same HLA-C allele and a different HLA-B allele, whereas 12 pairs of HLA-C/HLA-B recombinants had the same HLA-B allele and different HLA-C allele. Most SNP XO occurred near to or within the HLA-B or HLA-C coding region depending on which HLA-C/HLA-B recombinant haplotype sequences were aligned. SNP XOs occurred within the 3′ NCR or coding region of the HLA-B gene and within a 3-kb portion between a MLT1N2 element and the HLA-B gene (Figure 3) for 28 of 51 HLA-C/HLA-B haplotype alignments (Table 7). The SNP XOs in the intermediate loci regions were (1) within the L1PA13 fragment that is ~9 kb from HLA-C and ~72 kb from HLA-B, (2) between the L1MB8 and MLT1D elements ~53 kb from HLA-B, (3) a MIR element ~44 kb from HLA-B, and (4) within the HERVI ~21.5 kb from the HLA-B gene.
Figure 3.
SNP crossover sites within a 3-kb HLA-B extended 3′non-coding region (3′-NCR) of a 6-kb genomic region indicated by the lower horizontal line. Repetitive elements (grey, blue, and black horizontal lines) and STRs (green horizontal lines) are labelled. Numbers in brackets are the Reference Genome positions on chromosome 6 (UCSC = GRCh38/hg38 assembly—https://genome.ucsc.edu). The location of the HLA-B gene is boxed and the relative exons labelled 3 to 8 are indicated above the red bars. The HLA-C gene is ~82 kb telomeric of the HLA-B gene. SNP crossover loci are indicated by vertical arrows and were found within 29 of the 51 HLA-C/HLA-B haplotype alignments shown in (C,D) of Table 7. Numbers above the arrowheads represent the number of different haplotype alignments revealing the SNP crossovers. Although more than half of the crossover sites were found within the 3-kb 3′-NCR of HLA-B, six were found within HLA-C and another 13 were outside the 3-kb 3′-NCR of HLA-B and downstream towards HLA-C.
SNP-density XOs in Regions Between Various HLA-B and MIC Gene Alleles
The SNP XOs in the genomic region between HLA-B and MICA and between MICA and MICB for 31 recombinant haplotypes are listed in Table 8. There are 12 examples of a SNP XO within the genomic region of ~46.4 kb between HLA-B and MICA, and 13 examples of a SNP XO in the 94.5 kb genomic region between MICA and MICB. A SNP XO was detected in the MICA gene for the comparison between 54_B*35/MICA*002/MICB*005 and 68_B*35/MICA*016/MICB*002. The SNP XOs in the genomic region between MICA and MICB were within or near to putative recombinant hotspot REs: Tigger3b, MER2, THE1, MER21, LTR33, and ERV3-16A3_I of the HCP5 lncRNA gene (Figure 4). A SNP XO was found also within the insertion sequence of the SVA-MIC indel (Table 1) for the haplotypes 86_B*40/MICA*008/MICB*002 and 13_B*40/MICA*008/ MICB*014. SNP XO locations were not identified in five sequence comparisons because the genomic region from HLA-B to MICB was either too SNP-rich (comparisons 29 to 31) or too SNP-poor (comparisons 25 and 26).
Figure 4.
Percent Identity Plot and SNP crossover site within the ERV3-16A3 sequence and 3′ of the HCP5 long coding RNA locus of sequence alignment from HLA-B (grey box) to MICB (lowest yellow box) between the haplotypes ID68_B*35-MICA*016-MICB*002 (upper) and ID23_B*35-MICA*16-MICB*005 (lower). The SNP-poor region (green rows) and SNP-rich region (lilac rows) are indicated below the upper sequence that also has the labelled locations of HLA-B*35, MICA*16, MICB*002, and repeat elements L2, ERV3-16A3, HERVL, SVA-MIC, MLT2/Charlie9, LTR8, Tigger3b/L1/Tigger3b, MER2, MER21/MER4, THE1, and LTR33. The other repeats in the upper sequence such as the Alu, MIR, and L1 fragments are unlabelled but are indicated with the symbols used by Schwartz et al. (2000).
Discussion
The comparative sequence analyses of the 95 genomic sequences using RepeatMasker (Hubley et al., 2016) and PIP (Schwartz et al., 2000) confirmed the identity and HLA class I allelic linkages of 12 haplotypic RE markers (Table 1) that had been genotyped previously in population frequency studies and MHC homozygous and heterozygous cell lines (Kulski and Dunn, 2005; Kulski et al., 2011). We identified another four novel REs and indels; three of them were annotated as AluOR1, AluP5, and SVA-BC indels (Table 1, Figure 1). A fourth indel was 9.5 kb in size and composed of the MER5B and LTR33 subfamily members (Supplementary Figure 1). The deletion variant of the 9.5-kb indel that is located between the SVA-BC and SVA-HB loci within the beta block was linked to all 11 HLA-C*06:02 alleles, all 4 HLA-C*12:03 alleles, and 1 of 9 C*04:01 alleles (Table 3). The 9.5-kb indel, SVA-BC and SVA-HB are all located within a relatively strong recombination hotspot of 82 kb between the HLA-B and HLA-C genes (Figures 1, 3). This intergenic recombination hotspot was identified previously in sperm studies (Cullen et al., 2002) and HapMap studies (Lam et al., 2013). Interestingly, a SNP XO was detected within the SVA-MIC insertion between the MICA and MICB loci (Figure 4) of the A*02/C*03:04/B*40 haplotype pair ID13 and ID86 (Table 3), suggesting that this insertion locus is near a recombination site that exchanged the MICB*002:01 allele with MICB*014.
We included eight HLA class I pseudogenes (V, P, H, T, K, U, W, and J) as haplotypic markers in our analysis of the alpha block haplotype diversity even though most of them may have no physiological functions or regulatory roles. However, the HLA-H gene is polymorphic and has transcriptional activity, and the signal peptide of the membrane-bound HLA-H molecule can mobilise HLA-E to the cell surface of mononuclear cells, bronchial epithelial cells and lymphoblastoid cell lines (Jordier et al., 2020). The HLA-H*02:07 allele was found at a frequency of 19.6% in some East Asian populations (Paganini et al., 2019) and encodes a full-length HLA protein that may have tolerogenic activity (Jordier et al., 2020) in comparison to immunosuppressive activity of its neighbouring gene product, HLA-G (Elliott, 2016). Taken together, the alleles of the pseudogenes confirmed that the alpha block haplotypes consist of multilocus alleles and that the recombinant XOs were mostly at the telomeric and centromeric ends of the block often within the telomeric F segment and/or the centromeric W and J segments (Table 2), but also in MICF fragment of the G segment close to the biallelic AluHG insertion site (Figure 2) and in proximity of HERVK9 of the HLA-H segment associated with the 54-kb deletion of the HLA-A*24 lineage (Supplementary Figure 5). Thus, the haplotypic HERVK9, AluHF, AluHG, and AluHJ insertion loci are located within 2 to 15 kb of these SNP XO junctions that might have co-evolved as a consequence of recombination events between AH. In previous population and homologous cell line genotyping studies, the AluHF insertion was associated with HLA-A*26, AluHJ was associated with HLA-A*01, -A*24 and -A*32 (Dunn et al., 2002; Kulski et al., 2019) and AluHG was associated with HLA-A*02 (Kulski et al., 2001) and HLA-G*01:01 (Santos et al., 2013) allelic lineages. The present study not only confirms these Alu haplospecificities and HLA associations but also has linked them to HLA pseudogene alleles and the non-classical HLA-F and HLA-G alleles (Table 2). Thus, the AluHF insertion, which is 12.4 kb telomeric of the HLA-F genes and within an ERV3-16A3_int sequence, is linked to HLA-F*01:01:01:08 and a number of different HLA-A alleles (A*02, A*03, A*26, A*29, and A*67) revealing the occurrence of frequent recombination events in the proximity of the HLA-F gene. The AluHG insertion is linked consistently to the HLA-G*01:01/HLA-H*01:01 haplotypic alleles and mostly to HLA-A*02. However, the occasional linkage of the AluHG/HLA-G*01:01/HLA-H*01:01 haplotype with HLA-A*30 and HLA-A*31 suggests a recombination site within a region somewhere nearer the HLA-A locus and probably within the A segment. Similarly, the AluHJ insertion at the centromeric terminal end of the alpha block is linked mainly to HLA-A*01/HLA-J*01:01:01:02, HLA-A*24/HLA-J*01:01:01:02 and HLA-A*33/HLA-J*01:01:01:06 of the 25 analysed haplotype sequences. The two exceptions were the HLA-J*01:01:01:02/AluHJ linkage in the heterologous A*03/A*24 sample and the linkage of HLA-J*01:01:01:02/AluHJ to the HLA-A*02 that again provides different examples of recombination activity within and at the borders of the alpha block.
The alpha block HERVK9 insertion in chimpanzee (Kulski et al., 2005), gorilla (Wilming et al., 2013) and human (Kulski et al., 2008) heralds its ancient hominid lineage. The loss and replacement of the HERVK9 sequence with a solitary MER9 sequence presumably generated the most recent alpha block haplotypes. In contrast, the absence of the SVA-HB from the beta block is the ancestral lineage for the SVA-HB indel (Kulski et al., 2010). The ancient HERVK9 insertion allele occurs frequently in the Caucasian, African American and Japanese ranging between 34 and 59% (Kulski et al., 2008) as does the SVA-HB insertion that was genotyped at 65% in Caucasians, 64% in African Americans and 25% in Japanese (Kulski et al., 2010). Both the alpha block HERVK9 insertion and the beta block SVA-HB insertion separate the HLA-A/B/C haplotypes into four distinct ancestral lineages, HERVK9+/SVA-B+, HERVK9+/SVA-B-, HERVK9-/SVA-B+ and HERVK9-/SVA-HB-. Other TE alleles and indels could be added to the TE classification system as more data evolve to assess MHC class I segmental exchanges and recombinants (Kulski et al., 2011), but this would require more annotated data on polymorphic TE and indels than presently available. Also, the question arises whether the nine different alpha-beta block haplotypes (Tables 2, 3) with the HERVK9 insertion and no SVA-HB insertion that includes A*03:01/C*07:02/B*07:02 are older than those with the alpha block HERVK9 deletion and the beta block SVA-HB insertion (28 different haplotypes) (Supplementary Table 5). Although the 7.1AH with the HERVK9+/SVA-B- alleles might be older than 8.1AH, 27.1AH, 57.1AH, 60.1AH, and 62.1AH that are HERVK9-/SVA-HB-, classifying the evolutionary age of the haplotypes according to the presence and absence of HERVK9 and SVA-HB is probably unreliable because of segmental conversions and exchanges between genomic sequences. In addition, the 7.1AH and the 8.1AH are among the most common European haplotypes with population frequencies of 8.1AH up to at least 18% (Sanchez-Velasco et al., 2003; Kiszel et al., 2007; Sanchez-Mazas et al., 2013; Robinson et al., 2019). In addition, seven of the other nine HERVK9+/SVA-B- haplotypes (Supplementary Table 5) are common in Europeans (Suslova et al., 2012; Robinson et al., 2019) or Japanese (Ikeda et al., 2015), whereas A*31/C01:02/B*15:01 is from the cell line of a Warao South American Indian, which may be moderately common in some Amerindians (Watkins et al., 1992; Cadavid and Watkins, 1997), but not in others (Barquera et al., 2020). Taken together, these observations suggest that the human MHC ERVK9+/SVA-HB− haplotype might be broadly spread at relatively high frequency within many different worldwide populations.
The most commonly inferred haplotype blocks that are free of genetic recombination are supposedly those that are identified by LD statistical tests of SNP associations (Daly et al., 2001; Ahmad et al., 2003; Miretti et al., 2005; Blomhoff et al., 2006, Traherne, 2008). However, SNP densities vary markedly throughout the human genome (Sachidanandam et al., 2001) and their transition between SNP-rich and SNP-poor regions can be used to identify recombination free haplotypes without the need for LD tests (Myers, 2005; Kauppi et al., 2007; Bairagya et al., 2008). In the present study, we identified the junctions of haplotype blocks on the basis of SNP densities using homozygous haplotype sequences without applying LD statistical tests. We classified the haplotype junctions as XOs between SNP poor and SNP rich regions of haploidentical and haplodiverse genomic sequence comparisons (Tables 5–8). The SNP XOs between rich and poor SNP regions revealed a clear block structure both for haplotype mapping potential ancestral recombination sites and for objective analysis of haplotypes in different populations for disease associations. Since block patterns vary between common haplotypes, it will be important to construct maps for each different haplotype from a variety of populations to assess the degree of haplotype diversity within and between populations (Goodin et al., 2018). Many of the XOs that we identified are in close vicinity of recombination hotspots (Figure 1) that were previously identified in studies of MHC recombination sites using homozygous sperm DNA (Cullen et al., 2002) and HapMap populations (Lam et al., 2013).
SNP densities in our haplotype alignments were counted manually while avoiding obvious assembly errors, polynucleotides, simple microsatellite repeats, and indels by scanning overlapping windows of 50 to 500 kb of sequence. SNP-poor regions were easy to count manually because of small SNP numbers (<5 SNPs/100 kb), but SNP-rich regions were more difficult because of large SNP numbers at an average of 7 SNPs/kb. In comparison to our findings, Lam et al. (2015) reported an average of 7 SNPs/100 kb for the A33-B58-DR3 haplotype for 4136 kb and 8.7 SNPs/100 kb for the A2-B46-DR9 for 2721 kb, which are much higher than our comparative counts. This difference is possibly due to spikes of diversity in their localised regions of sequence. The SNP counts by Lam et al. (2015) within homologous haplotypes represented as nucleotide diversity values were still at least 38× less than that found between 7.1CEH/AH and 8.1CEH/AH, the two different common European MHC heterologous haplotypes of the cell lines PGF and COX, respectively. The count of 2240 SNPs per 320.8 kb (7 SNPs/kb) for PGF (LAB ID_4) and COX (LAB ID_11) in our study when their alpha blocks were aligned (Table 6) further demonstrates the large SNP diversity between them. In comparison, the average SNP density of the human genome is one SNP per 1.9 kb or between 5 and 9 SNPs per 10 kb (Sachidanandam et al., 2001; Zhao et al., 2003).
The two longest MHC haplotypes in the human genome are considered to be the European 7.1AH and 8.1AH (Horton et al., 2004, 2008) with CPS extending into the telomeric OR gene cluster region beyond the GPX5 gene that is 1.2 Mb telomeric of HLA-F (Figure 1). However, the CPS of at least four other MHC class I haplotype pairs also extended beyond the GPX5 gene: 18.2AH, 51.xAH, 57.1AH, 62.xAH, and 62.1AH (Table 5, Supplementary Table 8). The CPS of another three HLA-A haplotype pairs also extend beyond the GPX5 gene: HLA-A*24/C*03:04, HLA-A*31/C*15:02 and HLA-A*32/C*12:03 presented in Supplementary Table 8. The SNP XO junctions could not be determined for these haplotypes because they are telomeric of the GPX5 gene (NCBI ID:2880) and located somewhere beyond the region of the available genomic sequences provided for these cell lines (Norman et al., 2017). In comparison, the SNP XO junctions for two other HLA-A*01/C*06 and HLA-A*01/C*07 pairs and two HLA-A*03/C*07:02 and HLA-A*03/C*06:02 pairs were closer to the MOG and OR2H2 genes (Table 5) that are 51 kb and 134 kb from the HLA-F gene, respectively (Figure 1). It seems that the recombinant breakpoint of different haplotype segments or blocks generates the SNP XO site even if the classical HLA alleles are the same. For example, a number of HLA-A*02 allelic lineages were represented by distinctly different alpha block haplotypes (Table 2) that evolved from various shuffling events as well as segmental conversions (Table 6). Thus, the SNP XO within the alpha block F segment was strongly correlated with different local HLA-F alleles even if the downstream HLA-A allele within the A segment of the alpha block was the same; that is, the XO between HLA-F*01:01:01:01 of 18.xAH or 38.a2AH and F*01:04:01:02 of 60.1AH are both linked to HLA-A*02. The SNP XO defines the junction of the haplotype XO, which in turn points towards a putative ancestral recombination site. Whether this relationship that is based on a small number of comparative examples can be confirmed in the future will depend on the empirical findings of a much greater number of haplotypes with different HLA-A allelic and haplotypic lineages.
During mammalian and primate evolution, the MHC region transitioned through various genomic rearrangements including recombinant XO events of MIC, HERV16 and HLA class I genes, which resulted in the current structural organisation of the human MHC class I genomic region (Kulski et al., 1999a,b; Kulski et al., 2004). The HERV16, now classified as ERV3-16A3 (repeated throughout the MHC class I and class II regions), along with HLA class I coding and non-coding sequences, seems to have been a recombination site for many of the duplication events by way of unequal XOs (Kulski et al., 1999a,b; Kulski et al., 2004). Ancient hominoid haplotypes undoubtedly were the progenitors to the modern human CEH/AH, but when, how and where is unknown. In addition, each AH is a unique integrated genetic module consisting of many immunologically related protein-coding genes with gene copy number variations, segmental duplications and fragmented or relatively intact transposons and REs that contribute to more than 50% of the genomic content. In this regard, the MHC haplotype comprising a cluster of multilocus, monocistronic expression units is analogous to the polycistronic bacterial operon, which is a functional unit of DNA containing a cluster of genes under the control of a single promoter (Lee and Sonnhammer, 2003; Blumenthal, 2004). However, the MHC haplotype structures are far more complex with their regulatory network of cis-acting multilocus expression units known as haplotype-specific expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) (Lamontagne et al., 2016; Lam et al., 2017) that are largely controlled by an array of virus-derived REs and DNA transposons, both as binding sites for transcription factors and as sources of regulatory non-coding RNAs (Kulski, 2019; Sznarkowska et al., 2020). Random mutations, methylations and recombinations can generate considerable haplotype diversity that is part of the MHC immune system's response to highly prevalent infectious (Gao et al., 2019; Sanchez-Mazas, 2020) and chemical agents, including those responsible for drug hypersensitivities (Alfirevic and Pirmohamed, 2010).
Various factors have been hypothesised to elucidate the generation and maintenance of MHC CEHs/AHs including recombination suppression, balancing selection and demographic factors such as population bottlenecks, genetic drift, migration and admixture (Aly et al., 2006; van Oosterhout, 2009; Prohaska et al., 2019). If CEHs/AHs were generated in recent population history, for example, during the last 21,000 to 26,000 years as estimated from the mutation rates of the Caucasian A1-B8-DR3-DQ2 haplotype (Smith et al., 2006) and the Asian A2-B46-DR9 and A33-B58-DR3 haplotypes (Lam et al., 2013), then there may have been insufficient time over a period of a few thousand generations to have disrupted the LRHs by recombination. It seems that there is a time-associated equilibrium between the population amplification of the LRH and its meiotic recombinational breakage over periods of human population coalescent times (Song et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2020). Polymorphism and sequence heterozygosity also might suppress crossing over and recombination (Ohta, 1999; Dluzewska et al., 2018) and it is well-known that an excess of heterozygosity (overdominance) contributes to MHC diversity as one form of balancing selection (van Oosterhout, 2009; Lenz et al., 2016; Lobkovsky et al., 2019). However, in the context of molecular mechanisms and our study, the connection between the silencing of TE/REs and recombination suppression warrants greater consideration (Campos-Sánchez et al., 2016). TEs are known to affect recombination rates by acting as recombination modifiers, activators and suppressors in mice and humans (McVean, 2010; Altemose et al., 2017; Yamada et al., 2017). Although TEs can directly modulate the local recombination environment either through silencing-mediated suppression or the recruitment of recombination hotspots, the silencing of TEs and other repetitive sequences may also contribute directly to recombination suppression. The densities of DNA methylation and repressive chromatin marks associated with the silencing of TEs and other repeats are often negatively correlated with recombination rates (Myers, 2005; Kent et al., 2017). A recombination suppression mechanism discovered and studied in recent years involves the PRDM9-mediated recombination machinery that initiates at specific sequence motifs and alters chromatin structure (Myers et al., 2010; Parvanov et al., 2017). In humans, PRDM9 determines the locations of meiotic recombination hotspots and binds multiple motifs including the ATCCATG/CATGGAT motif of the THE1B repeat for both dependent and independent recombination suppression (Myers et al., 2008; Altemose et al., 2017). The active PRDM9 binding sites are also enriched with other classes of human repeat sequences including L2 LINEs and AluY elements (Myers et al., 2008; McVean, 2010). Recent studies with B6 mice demonstrated that a third of meiotic DNA strand breaks occurred within repetitive sequences of different classes, especially within the DNA transposons like TcMar-Mariner and hAT-Charlie, that resulted in their depletion from the PRDM9 binding sites (Yamada et al., 2017). This finding led the authors to hypothesise that the PRDM9 coevolved with meiotic recombination in order to target active transposons and limit their spread by inactivating or eliminating them by creating mutations or deletions at the PRDM9 binding site. Moreover, a proportion of the duplicated MHC ERV3-16A3_I (HERV16 int) sequences (Kulski and Dawkins, 1999; Kulski et al., 1999a,b) have the PRDM9 binding motif ATCCATG/CATGGAT at one or two of its nucleotide positions (Supplementary Figure 7).
Although TEs, methylations and recombinations can influence each other markedly (Myers et al., 2008; McVean, 2010; Moolhuijzen et al., 2010; Jones, 2012; Zamudio et al., 2015; Altemose et al., 2017; Kent et al., 2017), there is a surprising paucity of such studies in the MHC genomic region of different haplotypes (Rakyan et al., 2004; Jongsma et al., 2019). The genomic PRDM9 binding motif ATCCATG/CATGGAT (Altemose et al., 2017) is spread broadly throughout the MHC class I region and can be found in various fragmented TEs: L1, L2, MER5, HUERS-P3-int (2×), HERVK9-int (2×), HERVK14 (2×), LTR73, MER2, MER8, MER41, MER84, Charlie9, MLT1, MLT2B, Tigger1, ERV3-16A3_I, four of ~1450 Alu elements and various coding regions including the MICB sequence (present study, data not shown). The 38 SNP XOs at the borders of the haplotype blocks that are described in our study appear to reflect regions of historical recombination sites that currently might be involved with recombination suppression and haplotype maintenance (Figure 1). Some TEs are likely to have provided the recombination sequence motifs that Cullen et al. (2002) considered could be due to microsatellites and particularly to those with long tracts of GT repeats. Many of the SNP XO junctions are within 10 kb of TEs that are commonly repeated throughout the MHC genomic region including LTR16B/ERV3-16A3_I, L1, L2, MLT1, THE1, Charlie, Tigger, MST, and MER5 sequences. The presence of the LTR16B/ERV3-16A3_I sequences at the XO and recombination sites is not surprising since this RE was associated with various genomic rearrangements including XO events of MIC, HERV16, and HLA class I genes, which influenced the structural organisation of the MHC locus during primate evolution (Kulski et al., 1997, 1999a,b, 2002b, 2004, 2005). The LTR16B/ERV3-16A3_I and THE1 elements often are located together in close proximity to the XOs. Moreover, there are ATCCATG/CATGGAT motifs in the MER2 and L2 that flank the ERV3-16A3-int extension of the HCP5 gene (Kulski, 2019) that is within a recombination hotspot located between the MICA and MICB genes (Table 8, Figure 4). On the other hand, the THE1 elements in the MHC genomic region are represented by different subfamilies, and most of them lack the ATCCATG motif and therefore might not interact with PRDM9. Some active or young TE insertions are found in regions close to meiotic recombination sites. Therefore, the TE insertions in the MHC class I region that have yet to reach fixation such as the structurally polymorphic Alu and SVA elements (Table 1) are regional markers of insertion bias, and they are in close proximity to SNP XOs that could be active recombination hotspots (Figure 1). This implies that young TE insertion polymorphisms are relatively recent ancestral recombination hotspots; that is, the younger and more haplospecific TE insertions represent the integration and recombination sites of younger haplotype segments (Campos-Sánchez et al., 2016), whereas the fixed TE insertions, such as SVA-16, -T26, -ER, -EG, -M21, and -M22 (Table 1, Figure 1), reveal the older haplotype recombination XO spots of our primate progenitors (Anzai et al., 2003, Wilming et al., 2013). The presence of SNP XOs near to or within the HLA-B and HLA-C genes (Tables 7, 8) suggests that these genes and/or neighbouring TE's L1, Alu, L2, MLT1, MST, MER21, MER41, LTR9, MER1, and MER4 (Kulski et al., 1997) have had a role in recombination (Cullen et al., 2002, Lam et al., 2013) along with the occasional gene conversions (Madrigal et al., 1993, Adamek et al., 2015). Many of these old elements may now contribute to recombination suppression. Further detailed sequence multiple alignment studies at SNP XOs using HLA-B/HLA-C recombinant haplotypes such as previously described by Nair et al. (2006) in their psoriasis association studies may help to resolve this consideration.
The genomic sequences that we analysed in this study have important implications in medical research and treatment (Lokki and Paakkanen, 2019). Genotyping SNPs of the five major HLA class I and class II loci for cross matching provides most of the haplotype information needed for successful transplantation outcomes. However, ignoring SNPs outside the five loci when comparing the same or similar haplotypes may be problematic and misleading and result in choosing the wrong SNP markers for GWAS of disease or phenotypes, although GWAS need to be correlated to the MHC haplotype and not to the SNP per se. Nevertheless, particular haplospecific segments can be used to identify likely “disease” genes or regions (Lokki and Paakkanen, 2019) in comparative haplomics as previously performed for the psoriasis gene (Nair et al., 2006). Haplotypic or haplospecific markers like the well-defined HLA alleles and dimorphic RE markers may assist in narrowing genomic segments and loci towards MHC disease regions. Also, the haplospecific and haplotypic regions of the non-HLA coding regions such as the ~39 non-HLA genes between HLA-A and HLA-C are still poorly defined and need to be better characterised as essential components of haplotype regulatory modules. We found some SNP XO junctions in the non-HLA gene region between HLA-E and HLA-C that might have important implications in affecting disease. The systematic comparison of various recombinant haplotypes (Nair et al., 2006) is a promising approach that has been little utilised in GWAS (Alper and Larsen, 2017; Lokki and Paakkanen, 2019). Imputing haplotypes from 3D genome structures of single diploid human cells (Tan et al., 2018) along with tagging regulatory TEs using chromosome conformation capture techniques (Raviram et al., 2018) might be new and productive technical approaches to investigate haplotype regulatory modules.
Conclusion
Our study confirms that the genomic sequences of MHC homozygous cell lines are useful for analysing MHC haplotypic landscapes and characterising unique CPS, haplotypic markers, and XO zones without a need to use LD or other probabilistic statistical imputations. Comparative sequence analyses confirmed the identity of 12 haplotypic RE markers and revealed that the HERVK9 indel within the alpha block and a SVA indel within the beta block divided the HLA-A/B/C haplotypes into a series of distinctly interrelated historical lineages, and we identified numerous ancestral segmental XOs between different haplotypes within various REs, lncRNA, MUC22, C6orf15, and HLA-C and/or HLA–B genes extending over 2 Mb from the HLA-A to the MICB loci. It is evident from this study and previous studies that there is a vast MHC haplotype and allelic diversity in the human and that we have captured only a fraction of the complexity. Here, we analysed and characterised the polymorphic REs and the duplicated copies of MHC class I genes within genomic sequences of 95 haplotypes that were sequenced and assembled previously by Norman et al. (2017) in order to broaden the framework of the reference sequences so that they can be further improved and utilised to interrogate the human MHC in greater detail. More attention than usual was given to the polymorphic TE and RE at the SNP-density XOs as potential recombination hotspots. A greater emphasis on the commonality and differences of MHC class I recombinants may set the scene for better functional studies involving the described MHC alleles and haplotypes and their role in immunity, transplantation and overall health and well-being.
Data Availability Statement
All datasets generated for this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material.
Ethics Statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required for this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author Contributions
JK carried out the analyses of the repeat elements, SNP-density XOs and interpretation of the data, and wrote the manuscript. SS and TS analyzed and interpreted parts of the data and provided the alleles for the non-classical HLA class I genes, HLA pseudogenes, and the MICA and MICB genes. All authors checked the final version of the paper.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
JK thanks Karen Barfield for her help with word Table formatting and Enrico Rossi for proof-reading.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fgene.2020.594318/full#supplementary-material
References
- Adamek M., Klages C., Bauer M., Kudlek E., Drechsler A., Leuser B., et al. (2015). Seven novel HLA alleles reflect different mechanisms involved in the evolution of HLA diversity: description of the new alleles and review of the literature. Hum. Immunol. 76, 30–35. 10.1016/j.humimm.2014.12.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad T., Neville M., Marshall S. E., Armuzzi A., Mulcahy-Hawes K., Crawshaw J., et al. (2003). Haplotype-specific linkage disequilibrium patterns define the genetic topography of the human MHC. Hum. Mol. Genet. 12, 647–656. 10.1093/hmg/ddg066 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alfirevic A., Pirmohamed M. (2010). Drug induced hypersensitivity and the HLA complex. Pharmaceuticals 4, 69–90. 10.3390/ph4010069 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Larsen C. E. (2017). “Pedigree-defined haplotypes and their applications to genetic studies,” in Haplotyping Methods in Molecular Biology, eds. Tiemann-Boege I., Betancourt A. (New York, NY: Springer New York; ), 113–127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Larsen C. E., Dubey D. P., Awdeh Z. L., Fici D. A., Yunis E. J. (2006). The haplotype structure of the human major histocompatibility complex. Hum. Immunol. 67, 73–84. 10.1016/j.humimm.2005.11.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Raum D., Karp S., Awdeh Z. L., Yunis E. J. (1983). Serum complement ‘supergenes’ of the major histocompatibility complex in man (complotypes). Vox Sang. 45, 62–67. 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1983.tb04124.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altemose N., Noor N., Bitoun E., Tumian A., Imbeault M., Chapman J. R., et al. (2017). A map of human PRDM9 binding provides evidence for novel behaviors of PRDM9 and other zinc-finger proteins in meiosis. eLife 6:e28383. 10.7554/eLife.28383 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aly T. A., Eller E., Ide A., Gowan K., Babu S. R., Erlich H. A., et al. (2006). Multi-SNP analysis of MHC region: remarkable conservation of HLA-A1-B8-DR3 haplotype. Diabetes 55, 1265–1269. 10.2337/db05-1276 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anzai T., Shiina T., Kimura N., Yanagiya K., Kohara S., Shigenari A., et al. (2003). Comparative sequencing of human and chimpanzee MHC class I regions unveils insertions/deletions as the major path to genomic divergence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 7708–7713. 10.1073/pnas.1230533100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awdeh Z. L., Raum D., Yunis E. J., Alper C. A. (1983). Extended HLA/complement allele haplotypes: evidence for T/t-like complex in man. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 259–263. 10.1073/pnas.80.1.259 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayarpadikannan S., Kim H.-S. (2014). The impact of transposable elements in genome evolution and genetic instability and their implications in various diseases. Genomics Inform. 12, 98–104. 10.5808/GI.2014.12.3.98 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bairagya B. B., Bhattacharya P., Bhattacharya S. K., Dey B., Dey U., Ghosh T., et al. (2008). Genetic variation and haplotype structures of innate immunity genes in eastern India. Infect. Genet. Evol. 8, 360–366. 10.1016/j.meegid.2008.02.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bao W., Kojima K. K., Kohany O. (2015). Repbase update, a database of repetitive elements in eukaryotic genomes. Mob. DNA 6:11. 10.1186/s13100-015-0041-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barquera R., Zuniga J., Flores-Rivera J., Corona T., Penman B. S., Hernández-Zaragoza D. I., et al. (2020). Diversity of HLA class I and class II blocks and conserved extended haplotypes in Lacandon Mayans. Sci. Rep. 10:3248. 10.1038/s41598-020-58897-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilbao J. R., Calvo B., Aransay A. M., Martin-Pagola A., Perez de Nanclares G., Aly T. A., et al. (2006). Conserved extended haplotypes discriminate HLA-DR3-homozygous Basque patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and celiac disease. Genes Immun. 7, 550–554. 10.1038/sj.gene.6364328 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomhoff A., Olsson M., Johansson S., Akselsen H. E., Pociot F., Nerup J., et al. (2006). Linkage disequilibrium and haplotype blocks in the MHC vary in an HLA haplotype specific manner assessed mainly by DRB1*03 and DRB1*04 haplotypes. Genes Immun. 7, 130–140. 10.1038/sj.gene.6364272 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal T. (2004). Operons in eukaryotes. Brief. Funct. Genomic. Proteomic. 3, 199–211. 10.1093/bfgp/3.3.199 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeois Y., Boissinot S. (2019). On the population dynamics of junk: a review on the population genomics of transposable elements. Genes 10:419. 10.3390/genes10060419 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawand D., Wagner C. E., Li Y. I., Malinsky M., Keller I., Fan S., et al. (2014). The genomic substrate for adaptive radiation in African cichlid fish. Nature 513, 375–381. 10.1038/nature13726 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadavid L. F., Watkins D. I. (1997). Heirs of the jaguar and the anaconda: HLA, conquest and disease in the indigenous populations of the Americas. Tissue Antigens 50, 702–711. 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1997.tb02940.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos-Sánchez R., Cremona M. A., Pini A., Chiaromonte F., Makova K. D. (2016). Integration and fixation preferences of human and mouse endogenous retroviruses uncovered with functional data analysis. PLOS Comput. Biol. 12:e1004956. 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004956 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuong E. B., Elde N. C., Feschotte C. (2017). Regulatory activities of transposable elements: from conflicts to benefits. Nat. Rev. Genet. 18, 71–86. 10.1038/nrg.2016.139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contu L., Carcassi C., Dausset J. (1989). The “Sardinian” HLA-A30,B18,DR3,DQw2 haplotype constantly lacks the21-OHA andC4B genes. is it an ancestral haplotype without duplication? Immunogenetics 30, 13–17. 10.1007/BF02421464 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen M., Perfetto S. P., Klitz W., Nelson G., Carrington M. (2002). High-resolution patterns of meiotic recombination across the human major histocompatibility complex. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71, 759–776. 10.1086/342973 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly M. J., Rioux J. D., Schaffner S. F., Hudson T. J., Lander E. S. (2001). High-resolution haplotype structure in the human genome. Nat. Genet. 29, 229–232. 10.1038/ng1001-229 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawkins R., Leelayuwat C., Gaudieri S., Tay G., Hui J., Cattley S., et al. (1999). Genomics of the major histocompatibility complex: haplotypes, duplication, retroviruses and disease. Immunol. Rev. 167, 275–304. 10.1111/j.1600-065X.1999.tb01399.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bakker P. I. W., McVean G., Sabeti P. C., Miretti M. M., Green T., Marchini J., et al. (2006). A high-resolution HLA and SNP haplotype map for disease association studies in the extended human MHC. Nat. Genet. 38, 1166–1172. 10.1038/ng1885 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Koning A. P. J., Gu W., Castoe T. A., Batzer M. A., Pollock D. D. (2011). Repetitive elements may comprise over two-thirds of the human genome. PLoS Genet. 7:e1002384. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002384 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degli-Esposti M. A., Leaver A. L., Christiansen F. T., Witt C. S., Abraham L. J., Dawkins R. L. (1992). Ancestral haplotypes: conserved population MHC haplotypes. Hum. Immunol. 34, 242–252. 10.1016/0198-8859(92)90023-G [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilthey A. T., Gourraud P.-A., Mentzer A. J., Cereb N., Iqbal Z., McVean G. (2016). High-accuracy HLA type inference from whole-genome sequencing data using population reference graphs. PLOS Comput. Biol. 12:e1005151. 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005151 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dluzewska J., Szymanska M., Ziolkowski P. A. (2018). Where to cross over? defining crossover sites in plants. Front. Genet. 9:609. 10.3389/fgene.2018.00609 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorak M. T., Shao W., Machulla H. K. G., Lobashevsky E. S., Tang J., Park M. H., et al. (2006). Conserved extended haplotypes of the major histocompatibility complex: further characterization. Genes Immun. 7, 450–467. 10.1038/sj.gene.6364315 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. (1982). Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature 299, 111–117. 10.1038/299111a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxiadis G. G. M., de Groot N., Claas F. H. J., Doxiadis I. I. N., van Rood J. J., Bontrop R. E. (2007). A highly divergent microsatellite facilitating fast and accurate DRB haplotyping in humans and rhesus macaques. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104, 8907–8912. 10.1073/pnas.0702964104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn D. S., Inoko H., Kulski J. K. (2003). Dimorphic Alu element located between the TFIIH and CDSN genes within the major histocompatibility complex. Electrophoresis 24, 2740–2748. 10.1002/elps.200305524 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn D. S., Naruse T., Inoko H., Kulski J. K. (2002). The association between HLA-A alleles and young alu dimorphisms near the HLA-J, -H, and -F genes in workshop cell lines and Japanese and Australian populations. J. Mol. Evol. 55, 718–726. 10.1007/s00239-002-2367-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn D. S., Tait B. D., Kulski J. K. (2005). The distribution of polymorphic Alu insertions within the MHC class I HLA-B7 and HLA-B57 haplotypes. Immunogenetics 56, 765–768. 10.1007/s00251-004-0745-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott R. L. (2016). Cancer immunotherapy “HLA-G an Important Neglected Immunosuppressive Molecule.” SOJ Immunol. 4, 1–3. 10.15226/2372-0948/4/1/0014627774526 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Gambino C. M., Aiello A., Accardi G., Caruso C., Candore G. (2018). Autoimmune diseases and 8.1 ancestral haplotype: an update. HLA 92, 137–143. 10.1111/tan.13305 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao J., Zhu C., Zhu Z., Tang L., Liu L., Wen L., et al. (2019). The human leukocyte antigen and genetic susceptibility in human diseases: J. Bio-X Res. 2, 112–120. 10.1097/JBR.0000000000000044 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudieri S., Dawkins R. L., Habara K., Kulski J. K., Gojobori T. (2000). SNP profile within the human major histocompatibility complex reveals an extreme and interrupted level of nucleotide diversity. Genome Res. 10, 1579–1586. 10.1101/gr.127200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudieri S., Kulski J. K., Dawkins R. L., Gojobori T. (1999). Extensive nucleotide variability within a 370 kb sequence from the central region of the major histocompatibility complex. Gene 238, 157–161. 10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00255-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudieri S., Leelayuwat C., Tay G. K., Townend D. C., Dawkins R. L. (1997). The major histocompatability complex (MHC) contains conserved polymorphic genomic sequences that are shuffled by recombination to form ethnic-specific haplotypes. J. Mol. Evol. 45, 17–23. 10.1007/PL00006194 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George C. M., Alani E. (2012). Multiple cellular mechanisms prevent chromosomal rearrangements involving repetitive DNA. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 47, 297–313. 10.3109/10409238.2012.675644 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodin D. S., Khankhanian P., Gourraud P.-A., Vince N. (2018). Highly conserved extended haplotypes of the major histocompatibility complex and their relationship to multiple sclerosis susceptibility. PLoS ONE 13:e0190043. 10.1371/journal.pone.0190043 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu W., Zhang F., Lupski J. R. (2008). Mechanisms for human genomic rearrangements. PathoGenetics 1:4. 10.1186/1755-8417-1-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo Z., Hood L., Malkki M., Petersdorf E. W. (2006). Long-range multilocus haplotype phasing of the MHC. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 6964–6969. 10.1073/pnas.0602286103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henn B. M., Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Feldman M. W. (2012). The great human expansion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109, 17758–17764. 10.1073/pnas.1212380109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R., Gibson R., Coggill P., Miretti M., Allcock R. J., Almeida J., et al. (2008). Variation analysis and gene annotation of eight MHC haplotypes: the MHC haplotype project. Immunogenetics 60, 1–18. 10.1007/s00251-007-0262-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R., Wilming L., Rand V., Lovering R. C., Bruford E. A., Khodiyar V. K., et al. (2004). Gene map of the extended human MHC. Nat. Rev. Genet. 5, 889–899. 10.1038/nrg1489 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M., Zhu M., Jiang T., Wang Y., Wang C., Jin G., et al. (2019). Fine mapping the MHC region identified rs4997052 as a new variant associated with nonobstructive azoospermia in Han Chinese males. Fertil. Steril. 111, 61–68. 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.08.052 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubley R., Finn R. D., Clements J., Eddy S. R., Jones T. A., Bao W., et al. (2016). The Dfam database of repetitive DNA families. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, D81–D89. 10.1093/nar/gkv1272 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda N., Kojima H., Nishikawa M., Hayashi K., Futagami T., Tsujino T., et al. (2015). Determination of HLA-A, -C, -B, -DRB1 allele and haplotype frequency in Japanese population based on family study: HLA allele and haplotype frequency in Japanese population. Tissue Antigens 85, 252–259. 10.1111/tan.12536 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Holloway J. K., Kauppi L., May C. A., Neumann R., Slingsby M. T., et al. (2004). Meiotic recombination hot spots and human DNA diversity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 359, 141–152. 10.1098/rstb.2003.1372 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J. M., Villesen P., Friborg R. M., The Danish Pan-Genome Consortium Mailund, T. Besenbacher S. . (2017). Assembly and analysis of 100 full MHC haplotypes from the Danish population. Genome Res. 27, 1597–1607. 10.1101/gr.218891.116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A. (2012). Functions of DNA methylation: islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet. 13, 484–492. 10.1038/nrg3230 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongsma M. L. M., Guarda G., Spaapen R. M. (2019). The regulatory network behind MHC class I expression. Mol. Immunol. 113, 16–21. 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.12.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordier F., Gras D., De Grandis M., D'Journo X.-B., Thomas P.-A., Chanez P., et al. (2020). HLA-H: transcriptional activity and HLA-E mobilization. Front. Immunol. 10:2986. 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02986 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karell K., Klinger N., Holopainen P., Levo A., Partanen J. (2000). Major histocompatibility complex (MHC)- linked microsatellite markers in a founder population. Tissue Antigens 56, 45–51. 10.1034/j.1399-0039.2000.560106.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauppi L., Jasin M., Keeney S. (2007). Meiotic crossover hotspots contained in haplotype block boundaries of the mouse genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104, 13396–13401. 10.1073/pnas.0701965104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent T. V., Uzunović J., Wright S. I. (2017). Coevolution between transposable elements and recombination. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 372:20160458. 10.1098/rstb.2016.0458 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkness E. F., Grindberg R. V., Yee-Greenbaum J., Marshall C. R., Scherer S. W., Lasken R. S., et al. (2013). Sequencing of isolated sperm cells for direct haplotyping of a human genome. Genome Res. 23, 826–832. 10.1101/gr.144600.112 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiszel P., Kovács M., Szalai C., Yang Y., Pozsonyi É., Blaskó B., et al. (2007). Frequency of carriers of 8.1 ancestral haplotype and its fragments in two caucasian populations. Immunol. Invest. 36, 307–319. 10.1080/08820130701241404 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulski J. K. (2019). Long noncoding RNA HCP5, a hybrid HLA class I endogenous retroviral gene: structure, expression, and disease associations. Cells 8:480. 10.3390/cells8050480 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulski J. K., AlSafar H. S., Mawart A., Henschel A., Tay G. K. (2019). HLA class I allele lineages and haplotype frequencies in Arabs of the United Arab Emirates. Int. J. Immunogenet. 46, 152–159. 10.1111/iji.12418 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulski J. K., Anzai T., Inoko H. (2005). ERVK9, transposons and the evolution of MHC class I duplicons within the alpha-block of the human and chimpanzee. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 110, 181–192. 10.1159/000084951 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulski J. K., Anzai T., Shiina T., Hidetoshi I. (2004). Rhesus macaque class I duplicon structures, organization, and evolution within the alpha block of the major histocompatibility complex. Mol. Biol. Evol. 21, 2079–2091. 10.1093/molbev/msh216 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulski J. K., Dawkins R. L. (1999). The P5 multicopy gene family in the MHC is related in sequence to human endogenous retroviruses HERV-L and HERV-16. Immunogenetics 49, 404–412. 10.1007/s002510050513 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulski J. K., Dunn D. S. (2005). Polymorphic Alu insertions within the major histocompatibility complex class I genomic region: a brief review. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 110, 193–202. 10.1159/000084952 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulski J. K., Dunn D. S., Hui J., Martinez P., Romphruk A. V., Leelayuwat C., et al. (2002a). Alu polymorphism within the MICB gene and association with HLA-B alleles. Immunogenetics 53, 975–979. 10.1007/s00251-001-0409-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulski J. K., Gaudieri S., Bellgard M., Balmer L., Giles K., Inoko H., et al. (1997). The evolution of MHC diversity by segmental duplication and transposition of retroelements. J. Mol. Evol. 45, 599–609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulski J. K., Gaudieri S., Inoko H., Dawkins R. L. (1999a). Comparison between two Human Endogenous Retrovirus (HERV)-rich regions within the major histocompatibility complex. J. Mol. Evol. 48, 675–683. 10.1007/PL00006511 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulski J. K., Gaudieri S., Martin A., Dawkins R. L. (1999b). Coevolution of PERB11 (MIC) and HLA class I genes with HERV-16 and retroelements by extended genomic duplication. J. Mol. Evol. 49, 84–97. 10.1007/PL00006537 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulski J. K., Martinez P., Longman-Jacobsen N., Wang W., Williamson J., Dawkins R. L., et al. (2001). The association between HLA-A alleles and an alu dimorphism near HLA-G. J. Mol. Evol. 53, 114–123. 10.1007/s002390010199 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulski J. K., Shigenari A., Inoko H. (2010). Polymorphic SVA retrotransposons at four loci and their association with classical HLA class I alleles in Japanese, Caucasians and African Americans. Immunogenetics 62, 211–230. 10.1007/s00251-010-0427-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulski J. K., Shigenari A., Inoko H. (2011). Genetic variation and hitchhiking between structurally polymorphic Alu insertions and HLA-A, -B, and -C alleles and other retroelements within the MHC class I region. Tissue Antigens 78, 359–377. 10.1111/j.1399-0039.2011.01776.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulski J. K., Shigenari A., Inoko H. (2014). Variation and linkage disequilibrium between a structurally polymorphic Alu located near the OR12D2 gene of the extended major histocompatibility complex class I region and HLA-A alleles. Int. J. Immunogenet. 41, 250–261. 10.1111/iji.12102 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulski J. K., Shigenari A., Shiina T., Hosomichi K., Yawata M., Inoko H. (2009). HLA-A allele associations with viral MER9-LTR nucleotide sequences at two distinct loci within the MHC alpha block. Immunogenetics 61, 257–270. 10.1007/s00251-009-0364-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulski J. K., Shigenari A., Shiina T., Ota M., Hosomichi K., James I., et al. (2008). Human endogenous retrovirus (HERVK9) structural polymorphism with haplotypic HLA-A allelic associations. Genetics 180, 445–457. 10.1534/genetics.108.090340 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulski J. K., Shiina T., Anzai T., Kohara S., Inoko H. (2002b). Comparative genomic analysis of the MHC: the evolution of class I duplication blocks, diversity and complexity from shark to man. Immunol. Rev. 190, 95–122. 10.1034/j.1600-065X.2002.19008.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam T., Tay M., Wang B., Xiao Z., Ren E. (2015). Intrahaplotypic variants differentiate complex linkage disequilibrium within human MHC haplotypes. Sci. Rep. 5:16972. 10.1038/srep16972 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam T. H., Shen M., Chia J.-M., Chan S. H., Ren E. C. (2013). Population-specific recombination sites within the human MHC region. Heredity 111, 131–138. 10.1038/hdy.2013.27 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam T. H., Shen M., Tay M. Z., Ren E. C. (2017). Unique allelic eQTL clusters in human MHC haplotypes. G3 7, 2595–2604. 10.1534/g3.117.043828 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamontagne M., Joubert P., Timens W., Postma D. S., Hao K., Nickle D., et al. (2016). Susceptibility genes for lung diseases in the major histocompatibility complex revealed by lung expression quantitative trait loci analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 48, 573–576. 10.1183/13993003.00114-2016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen C. E., Alford D. R., Trautwein M. R., Jalloh Y. K., Tarnacki J. L., Kunnenkeri S. K., et al. (2014). Dominant sequences of human major histocompatibility complex conserved extended haplotypes from HLA-DQA2 to DAXX. PLoS Genet. 10:e1004637. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004637 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. M., Sonnhammer E. L. L. (2003). Genomic gene clustering analysis of pathways in eukaryotes. Genome Res. 13, 875–882. 10.1101/gr.737703 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz T. L., Spirin V., Jordan D. M., Sunyaev S. R. (2016). Excess of deleterious mutations around HLA genes reveals evolutionary cost of balancing selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 33, 2555–2564. 10.1093/molbev/msw127 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y.-L., Gokcumen O. (2019). Fine-scale characterization of genomic structural variation in the human genome reveals adaptive and biomedically relevant hotspots. Genome Biol. Evol. 11, 1136–1151. 10.1093/gbe/evz058 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobkovsky A. E., Levi L., Wolf Y. I., Maiers M., Gragert L., Alter I., et al. (2019). Multiplicative fitness, rapid haplotype discovery, and fitness decay explain evolution of human MHC. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 116, 14098–14104. 10.1073/pnas.1714436116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lokki M., Paakkanen R. (2019). The complexity and diversity of major histocompatibility complex challenge disease association studies. HLA 93, 3–15. 10.1111/tan.13429 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López S., Van Dorp L., Hellenthal G. (2015). Human dispersal out of Africa: a lasting debate. Evol. Bioinform. Online 11 (Suppl. 2), 57–68. 10.4137/EBO.S33489 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu J. Y., Shao W., Chang L., Yin Y., Li T., Zhang H., et al. (2020). Genomic repeats categorize genes with distinct functions for orchestrated regulation. Cell Rep. 30, 3296–3311.e5. 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.02.048 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madrigal J. A., Hildebrand W. H., Belich M. P., Benjamin R. J., Little A.-M., Zemmour J., et al. (1993). Structural diversity in the HLA-A10 family of alleles: correlations with serology. Tissue Antigens 41, 72–80. 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1993.tb01982.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McVean G. (2010). What drives recombination hotspots to repeat DNA in humans? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 365, 1213–1218. 10.1098/rstb.2009.0299 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miretti M. M., Walsh E. C., Ke X., Delgado M., Griffiths M., Hunt S., et al. (2005). A high-resolution linkage-disequilibrium map of the human major histocompatibility complex and first generation of tag single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 76, 634–646. 10.1086/429393 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuki N., Ota M., Kimura M., Ohno S., Ando H., Katsuyama Y., et al. (1997). Triplet repeat polymorphism in the transmembrane region of the MICA gene: a strong association of six GCT repetitions with Behcet disease. Proc. Nat Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94, 1298–1303. 10.1073/pnas.94.4.1298 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolhuijzen P., Kulski J. K., Dunn D. S., Schibeci D., Barrero R., Gojobori T., et al. (2010). The transcript repeat element: the human Alu sequence as a component of gene networks influencing cancer. Funct. Integr. Genomics 10, 307–319. 10.1007/s10142-010-0168-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy N. M., Burton M., Powell D. R., Rossello F. J., Cooper D., Chopra A., et al. (2016). Haplotyping the human leukocyte antigen system from single chromosomes. Sci. Rep. 6:30381. 10.1038/srep30381 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers S. (2005). A fine-scale map of recombination rates and hotspots across the human genome. Science 310, 321–324. 10.1126/science.1117196 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers S., Bowden R., Tumian A., Bontrop R. E., Freeman C., MacFie T. S., et al. (2010). Drive against hotspot motifs in primates implicates the PRDM9 gene in meiotic recombination. Science 327, 876–879. 10.1126/science.1182363 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers S., Freeman C., Auton A., Donnelly P., McVean G. (2008). A common sequence motif associated with recombination hot spots and genome instability in humans. Nat. Genet. 40, 1124–1129. 10.1038/ng.213 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair R. P., Stuart P. E., Nistor I., Hiremagalore R., Chia N. V. C., Jenisch S., et al. (2006). Sequence and haplotype analysis supports HLA-C as the psoriasis susceptibility 1 gene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 78, 827–851. 10.1086/503821 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman P. J., Norberg S. J., Guethlein L. A., Nemat-Gorgani N., Royce T., Wroblewski E. E., et al. (2017). Sequences of 95 human MHC haplotypes reveal extreme coding variation in genes other than highly polymorphic HLA class I and II. Genome Res. 27, 813–823. 10.1101/gr.213538.116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T. (1999). A note on the correlation between heterozygosity and recombination rate. Genes Genet. Syst. 74, 209–210. 10.1266/ggs.74.209 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paganini J., Abi-Rached L., Gouret P., Pontarotti P., Chiaroni J., Di Cristofaro J. (2019). HLAIb worldwide genetic diversity: new HLA-H alleles and haplotype structure description. Mol. Immunol. 112, 40–50. 10.1016/j.molimm.2019.04.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvanov E. D., Tian H., Billings T., Saxl R. L., Spruce C., Aithal R., et al. (2017). PRDM9 interactions with other proteins provide a link between recombination hotspots and the chromosomal axis in meiosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 28, 488–499. 10.1091/mbc.e16-09-0686 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payer L. M., Burns K. H. (2019). Transposable elements in human genetic disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 20, 760–772. 10.1038/s41576-019-0165-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payer L. M., Steranka J. P., Yang W. R., Kryatova M., Medabalimi S., Ardeljan D., et al. (2017). Structural variants caused by Alu insertions are associated with risks for many human diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 114, E3984–E3992. 10.1073/pnas.1704117114 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P., Witt C., Allock R., Sayer D., Garlepp M., Kok C. C., et al. (1999). The genetic basis for the association of the 8.1 ancestral haplotype (A1, B8, DR3) with multiple immunopathological diseases. Immunol. Rev. 167, 257–274. 10.1111/j.1600-065X.1999.tb01398.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prohaska A., Racimo F., Schork A. J., Sikora M., Stern A. J., Ilardo M., et al. (2019). Human disease variation in the light of population genomics. Cell 177, 115–131. 10.1016/j.cell.2019.01.052 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakyan V. K., Hildmann T., Novik K. L., Lewin J., Tost J., Cox A. V., et al. (2004). DNA methylation profiling of the human major histocompatibility complex: a pilot study for the human epigenome project. PLoS Biol. 2:e405. 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020405 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raviram R., Rocha P. P., Luo V. M., Swanzey E., Miraldi E. R., Chuong E. B., et al. (2018). Analysis of 3D genomic interactions identifies candidate host genes that transposable elements potentially regulate. Genome Biol. 19:216. 10.1186/s13059-018-1598-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J., Barker D. J., Georgiou X., Cooper M. A., Flicek P., Marsh S. G. E. (2019). IPD-IMGT/HLA Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 48, D948–D955. 10.1093/nar/gkz950 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero V., Larsen C. E., Duke-Cohan J. S., Fox E. A., Romero T., Clavijo O. P., et al. (2007). Genetic fixity in the human major histocompatibility complex and block size diversity in the class I region including HLA-E. BMC Genet. 8:14. 10.1186/1471-2156-8-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachidanandam R., Weissman D., Schmidt S. C., Kakol J. M., Stein L. D., Marth G., et al. (2001). A map of human genome sequence variation containing 1.42 million single nucleotide polymorphisms. Nature 409, 928–933. 10.1038/35057149 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Mazas A. (2020). A review of HLA allele and SNP associations with highly prevalent infectious diseases in human populations. Swiss Med. Wkly. 150:W20214. 10.4414/smw.2020.20214 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Mazas A., Buhler S., Nunes J. M. (2013). A new HLA map of europe: regional genetic variation and its implication for peopling history, disease-association studies and tissue transplantation. Hum. Hered. 76, 162–177. 10.1159/000360855 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Velasco P., Gomez-Casado E., Martinez-Laso J., Moscoso J., Zamora J., Lowy E., et al. (2003). HLA alleles in isolated populations from North Spain: origin of the Basques and the ancient Iberians. Tissue Antigens 61, 384–392. 10.1034/j.1399-0039.2003.00041.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos K. E., Lima T. H. A., Felicio L. P., Massaro J. D., Palomino G. M., Silva A. C. A., et al. (2013). Insights on the HLA-G evolutionary history provided by a nearby alu insertion. Mol. Biol. Evol. 30, 2423–2434. 10.1093/molbev/mst142 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaid D. J., McDonnell S. K., Wang L., Cunningham J. M., Thibodeau S. N. (2002). Caution on pedigree haplotype inference with software that assumes linkage equilibrium. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71, 992–995. 10.1086/342666 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Zhang Z., Frazer K. A., Smit A., Riemer C., Bouck J., et al. (2000). PipMaker-a web server for aligning two genomic DNA sequences. Genome Res. 10, 577–586. 10.1101/gr.10.4.577 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L., Wu L., Sanlioglu S., Chen R., Mendoza A. R., Dangel A. W., et al. (1994). Structure and genetics of the partially duplicated gene RP located immediately upstream of the complement C4A and the C4B genes in the HLA class III region. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 8466–8476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiina T., Hosomichi K., Inoko H., Kulski J. K. (2009). The HLA genomic loci map: expression, interaction, diversity and disease. J. Hum. Genet. 54, 15–39. 10.1038/jhg.2008.5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiina T., Inoko H., Kulski J. K. (2004). An update of the HLA genomic region, locus information and disease associations: 2004. Tissue Antigens 64, 631–649. 10.1111/j.1399-0039.2004.00327.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiina T., Ota M., Shimizu S., Katsuyama Y., Hashimoto N., Takasu M., et al. (2006). Rapid evolution of major histocompatibility complex class I genes in primates generates new disease alleles in humans via hitchhiking diversity. Genetics 173, 1555–1570. 10.1534/genetics.106.057034 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slatkin M. (2008). Linkage disequilibrium — understanding the evolutionary past and mapping the medical future. Nat. Rev. Genet. 9, 477–485. 10.1038/nrg2361 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. P., Vu Q., Li S. S., Hansen J. A., Zhao L. P., Geraghty D. E. (2006). Toward understanding MHC disease associations: partial resequencing of 46 distinct HLA haplotypes. Genomics 87, 561–571. 10.1016/j.ygeno.2005.11.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song S., Sliwerska E., Emery S., Kidd J. M. (2017). Modeling human population separation history using physically phased genomes. Genetics 205, 385–395. 10.1534/genetics.116.192963 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele E. J., Lloyd S. S. (2015). Soma-to-germline feedback is implied by the extreme polymorphism at IGHV relative to MHC: the manifest polymorphism of the MHC appears greatly exceeded at Immunoglobulin loci, suggesting antigen-selected somatic V mutants penetrate Weismann. BioEssays 37, 557–569. 10.1002/bies.201400213 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. A., Horton R., Allcock R. J., Ashurst J. L., Atrazhev A. M., Coggill P., et al. (2004). Complete MHC haplotype sequencing for common disease gene mapping. Genome Res. 14, 1176–1187. 10.1101/gr.2188104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suslova T. A., Burmistrova A. L., Chernova M. S., Khromova E. B., Lupar E. I., Timofeeva S. V., et al. (2012). HLA gene and haplotype frequencies in Russians, Bashkirs and Tatars, living in the chelyabinsk Region (Russian South Urals): HLA gene and haplotype frequencies in Russians, Bashkirs and Tatars. Int. J. Immunogenet. 39, 394–408. 10.1111/j.1744-313X.2012.01117.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sznarkowska A., Mikac S., Pilch M. (2020). MHC class I regulation: the origin perspective. Cancers 12:1155. 10.3390/cancers12051155 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan L., Xing D., Chang C.-H., Li H., Xie X. S. (2018). Three-dimensional genome structures of single diploid human cells. Science 361, 924–928. 10.1126/science.aat5641 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traherne J. A. (2008). Human MHC architecture and evolution: implications for disease association studies. Int. J. Immunogenet. 35, 179–192. 10.1111/j.1744-313X.2008.00765.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traherne J. A., Horton R., Roberts A. N., Miretti M. M., Hurles M. E., Stewart C. A., et al. (2006). Genetic analysis of completely sequenced disease-associated MHC haplotypes identifies shuffling of segments in recent human history. PLoS Genet. 2:e9. 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Knight J. C. (2013). Major histocompatibility complex genomics and human disease. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 14, 301–323. 10.1146/annurev-genom-091212-153455 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oosterhout C. (2009). A new theory of MHC evolution: beyond selection on the immune genes. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 276, 657–665. 10.1098/rspb.2008.1299 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandiedonck C., Knight J. C. (2009). The human major histocompatibility complex as a paradigm in genomics research. Brief. Funct. Genomic. Proteomic. 8, 379–394. 10.1093/bfgp/elp010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh E. C., Mather K. A., Schaffner S. F., Farwell L., Daly M. J., Patterson N., et al. (2003). An integrated haplotype map of the human major histocompatibility complex. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 73, 580–590. 10.1086/378101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., Mathieson I., O'Connell J., Schiffels S. (2020). Tracking human population structure through time from whole genome sequences. PLOS Genet. 16:e1008552. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008552 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins D. I., McAdam S. N., Liu X., Strang C. R., Mitford E. L., Levine C. G., et al. (1992). New recombinant HLA-B alleles in a tribe of South American Amerindians indicate rapid evolution of MHC class I loci. Nature 357, 329–333 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WGS500 Consortium. Rimmer A., Phan H., Mathieson I., Iqbal Z., Twigg S. R. F., Wilkie A. O. M., et al. (2014). Integrating mapping-, assembly- and haplotype-based approaches for calling variants in clinical sequencing applications. Nat. Genet. 46, 912–918. 10.1038/ng.3036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilming L. G., Hart E. A., Coggill P. C., Horton R., Gilbert J. G. R., Clee C., et al. (2013). Sequencing and comparative analysis of the gorilla MHC genomic sequence. Database 2013:bat011. 10.1093/database/bat011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada S., Kim S., Tischfield S. E., Jasin M., Lange J., Keeney S. (2017). Genomic and chromatin features shaping meiotic double-strand break formation and repair in mice. Cell Cycle 16, 1870–1884. 10.1080/15384101.2017.1361065 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis E. J., Larsen C. E., Fernandez-Vina M., Awdeh Z. L., Romero T., Hansen J. A., et al. (2003). Inheritable variable sizes of DNA stretches in the human MHC: conserved extended haplotypes and their fragments or blocks. Tissue Antigens 62, 1–20. 10.1034/j.1399-0039.2003.00098.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamudio N., Barau J., Teissandier A., Walter M., Borsos M., Servant N., et al. (2015). DNA methylation restrains transposons from adopting a chromatin signature permissive for meiotic recombination. Genes Dev. 29, 1256–1270. 10.1101/gad.257840.114 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Z., Fu Y.-X., Hewett-Emmett D., Boerwinkle E. (2003). Investigating single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) density in the human genome and its implications for molecular evolution. Gene 312, 207–213. 10.1016/S0378-1119(03)00670-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All datasets generated for this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material.