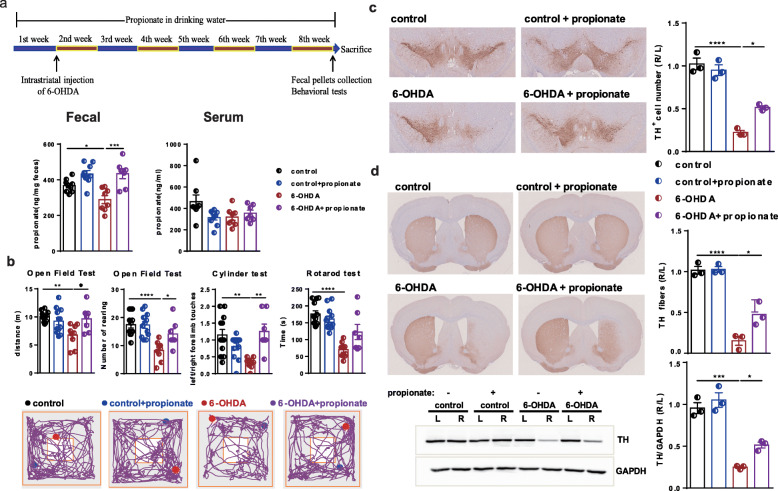
Fig. 6.
Oral administration of propionate prevented motor impairments and dopaminergic neuronal loss in 6-OHDA-induced PD mice. a (Upper panel) The experimental design for propionate intervention in PD mice. (Lower panel) Quantitative measurement by GC/MS showing the fecal and serum levels of propionate. n = 7–12 per group. b (Upper panel) Bar plots of performance in the behavioral tests, including the open field test, cylinder test, and rotarod test. n = 7–12 per group. (Lower panel) Representative traces in the open field test. Blue point: starting position; red point: ending position. c (Left panel) Representative immunostaining showing TH-positive neurons in the SN. (Right panel) The average number of TH-positive neurons in the ST. n = 3 per group, 3 sections per mouse. d (Left panel) Representative immunostaining (upper) and western blotting (lower) showing TH-positive fibers and TH protein levels in the striatum. (Right panel) The quantification of TH-positive fibers (upper) and TH protein levels (lower) in the striatum. Immunostaining: n = 3 per group, 3 sections per mouse; western blotting: n = 3 per group. The data represent the mean ± SEM, p < 0.05 was set as the threshold for significance by one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc comparisons using Tukey’s test for multiple groups’ comparisons, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001