Abstract
Capsule
This expert opinion summarizes current knowledge on risk factors for infertility and identifies a practical clinical and diagnostic approach for the male and female partners of an infertile couple aimed to improve the investigation and management of fertility problems.
Background
Infertility represents an important and growing health problem affecting up to 16% of couples worldwide. In most cases, male, female, or combined factor can be identified, and different causes or risk factors have been related to this condition. However, there are no standardized guidelines on the clinical-diagnostic approach of infertile couples and the recommendations concerning infertility are sometimes lacking, incomplete, or problematic to apply.
Objective
The aim of this work is to provide an appropriate clinical and diagnostic pathway for infertile couples designed by a multidisciplinary-team of experts. The rationale is based on the history and physical examination and then oriented on the basis of initial investigations. This approach could be applied in order to reduce variation in practice and to improve the investigation and management of fertility problems.
Methods
Prominent Italian experts of the main specialties committed in the ART procedures, including gynecologists, andrologists, embryologists, biologists, geneticists, oncologists, and microbiologists, called “InfertilItaly group”, used available evidence to develop this expert position.
Outcomes
Starting from the individuation of the principal risk factors that may influence the fertility of females and males and both genders, the work group identified most appropriate procedures using a gradual approach to both partners aimed to obtain a precise diagnosis and the most effective therapeutic option, reducing invasive and occasionally redundant procedures.
Conclusions
This expert position provides current knowledge on risk factors and suggests a diagnostic workflow of infertile couples. By using this step-by-step approach, health care workers involved in ART, may individuate a practical clinical management of infertile couples shared by experts.
Keywords: infertility diagnosis, female infertility, couple infertility, male infertility, reproduction, diagnosis, management, assisted reproductive technlogy
Introduction
WHO sets the clinical definition for infertility as a disease of the reproductive system defined by the failure to achieve a clinical pregnancy after 12 months or more of regular unprotected sexual intercourse (1). Although it is difficult to estimate the accurate global burden of infertility and sub fertility, they affect a significant proportion of humanity with an estimated prevalence of 72.4 million infertile people and of these 40.5 million seeking infertility medical care (2). Infertility not only is related to the reproductive health but has psychological, economic, and medical implications resulting in trauma, stress, especially in societies and cultures addressing strong emphasis on child-bearing (1). As a logical result, and attempting to find a solution, assisted reproductive technologies (ARTs) spread globally, constituting a treatment of choice for complicated fertility disorders (3). The term ART denominates all interventions, including the in vitro handling of human oocytes, spermatozoa and embryos, for the purpose of reproduction (3). Owing to the increasing complexity of treatment options, ART procedures are delivered via highly specialized health care workers including: gynecologists, andrologists, embryologists, geneticists, oncologists, urologists, psychologists, obstetricians, and others (4). Nevertheless, there are no international standardized rules and laws regulating these procedures, resulting in the worldwide spread of ART clinics having variable quality standards (4). It is estimated that more than five million infants have been born from ART and, interestingly, Europe has been the most active continent (5).
In order to reduce variation in practice and improve the way fertility problems are investigated and managed, different guidelines have been developed both at national and international levels.
The National Institute of Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guidelines make evidence-based recommendations on a wide range of topics including fertility impairment. They are probably one of the most important international clinical guidelines concerning infertility assessment and treatment. Their development follows rigorous methods and criteria to ensure reliable recommendations for good clinical practice.
The NICE guidelines on fertility examine all aspects related to fertility, from principles of care and initial advice for people concerned about delays in conception, to investigation and management of fertility problems, proper diagnosis work-up and appropriate treatment approach (https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg156). However, some conditions related to age of patients, general health, risk factors, economic situation etc., can raise critical issues making NICE guidelines difficult to apply. One issue is linked to the advanced age. According to European statistical institutes (Eurostat), in 2017 the average age of women who gave birth to their first child is 31.1 years, the highest in Europe where the average is 29.1 years. This determines the need to speed up the diagnostic process of infertile women, who often come to the observation of reproductive medicine specialists at an advanced maternal age and with a compromised ovarian reserve. In addition, some countries do not comply with the NICE guidelines because they have not the possibility to perform invasive procedures within their own center or within reasonable time. Most centers, especially private ones, do not have surgery rooms capable of performing specific techniques, such as laparoscopy. Surgical procedures are often performed by surgeons who are not involved in reproductive medicine, and who therefore are not familiar with techniques such as ovarian drilling or conservative tubal surgery, which should be entrusted to teams with sufficient experience in these procedures. The aforementioned reasons limit access to the invasive diagnostic and therapeutic procedures suggested by the NICE guidelines, which should be reserved for a strictly selected group of patients in a such different context.
Another issue that limits the use of the NICE guidelines is linked to the different legislation in force, compared to most European countries. In Italy, for example, drugs such as metformin for polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are still off-label, the cryopreservation of embryos is theoretically prohibited (although made possible by way of derogation from the law and with well-defined limits) and the donation of gametes is still severely limited as donors are not allowed to receive an economic fee.
The NICE guidelines also deal with male factor infertility and its medical and surgical management. On this topic, there is a great difference with the detailed analysis of female factor infertility. For instance, some important risk factors for male infertility are not mentioned (e.g. cryptorchidism, orchitis and epididymitis, testicular hypotrophy, seminal tract infections, testicular trauma or torsion, testicular neoplasia, systemic diseases, hormonal derangement due to anabolic steroid use, etc.). Moreover, minimal diagnostic work-up is not defined, other than seminal analysis. Recommendations about physical examination, hormonal tests, microbiological analysis, and imaging diagnostics are lacking.
The present expert opinion, describes a practical clinical and diagnostic pathway for infertile couples designed by a multidisciplinary team of experts in the ART procedures, named “InfertilItaly group”, including gynecologists, andrologists, embryologists, biologists, geneticists oncologists, and microbiologists. The objective of this work is to provide clear indications for the management of the infertile couple, completing the diagnostic process as accurately and quickly as possible, taking into account the Italian health, legislative, and social context.
Methods
At the beginning of 2020, a final meeting of Italian experts in couple infertility was held in Rome to discuss risk factors and diagnostic workflow of infertile couples. This document is the result of several meetings, drafts, data discussions, and covered guidance for the care of infertile couples. The proceedings journal is published in Italian (6) and it is downloadable at https://www.ccgm.it website. The final meeting in February 2020 was organized to provide a forum for interdisciplinary discussion involving as many interested parties as possible. More than 100 participants from all Italian Regions took part in the meeting. They included all the professionals involved in the management of the infertile couple. The objectives of the meeting were a) to review literature about causes and risk factors of infertility, b) to identify unresolved issues in the field, and c) to provide standard recommendations tailored for couples seeking fertility in the Italian context.
To permit in-depth analysis and discussion, the meeting did not cover the whole field of ART. Instead, it focused on a selected number of topics including infertility risk factors, national and international surveillance of ART, diagnostic tools and procedures, psychosocial issues, ethical and law aspects in relation to the individual, to the couple and to the offspring, as well as issues of equitable access, the role of consumers.
Background papers were commissioned from invited speakers and peer-reviewed prior to the meeting. The papers were briefly presented with emphasis being given to discussion and the delineation of recommendations for practice and future research. All of the meeting sessions were plenary to allow full interaction among the different disciplines. A wide variety of views and approaches was presented in an intense, dynamic, and rich debate.
This document comprises five sections, consisting of the main specific areas discussed and the recommendations agreed to by the meeting participants: i) risk factors, ii) assessment of infertile couples, iii) infertile couple pathway, iv) gynecological specific flow charts, and v) andrological specific flow charts. The sections are grouped by expertise area in an order similar to that of the final meeting program but also in a way that the different views are juxtaposed or complementary. Despite the diverse opinions on ART voiced at the meeting, there were many points upon which a final consensus was reached.
Risk Factors
Despite general perception that causes of infertility predominantly affect female, the causes of infertility are in fact equally distributed between the sexes. Indeed, according to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine, in 40% of couples with infertility, the female partner is either the single or a contributing cause of infertility, in 40% it is the male partner and in the remaining 20% there are no identifiable reasons termed unexplained infertility (7). Male factor infertility is defined as one or more abnormal parameters detected on semen analysis or the presence of inadequate sexual or ejaculatory function (8). The main fertility risk factors affecting males, females and both sexes are listed in Table 1 .
Table 1.
Female and male infertility risk factors.
| Both genders | Female | Male |
|---|---|---|
| Family history of infertility | Age >35 years | Cryptorchidism |
| Recurrent abortions | Reduced ovarian reserve (AMH and/or AFC count) | Testicular hypotrophy |
| Obesity | Ovulation Disorders | Testicular cancer |
| Using of anabolic steroids | Infertility >3 years | Known genetic factors |
| Lifestyles | Menstrual disorders | Varicocele |
| Environmental/occupational factors | Endometriosis | Testicular trauma |
| Systemic and/or endocrine diseases | Family history of POF | Testicular torsion |
| Iatrogenic factors | PID (consequent to infectious diseases) | Puberty disorders |
| Infertility with previous partners | Aging | |
| Cystic fibrosis | Testicular microlithiasis | |
| Infection | Unhealthy diet and obesity Pollution Cigarette smoking |
AFC, antral follicle count; AMH, anti-müllerian hormone; BMI, body max index; PID, pelvic inflammatory disease; POF, primary ovarian insufficiency.
Risk Factors for Both Sexes
Several common factors may affect fertility in both sexes with different impact (9). It is well known that fertility declines with age in males and females, but the decline is much faster in women. Female age is not a modifiable risk factor, this is linked both to the progressive depletion of the number of oocytes contained within the ovary (ovarian reserve), and to the progressive deterioration of their chromosomal and structural integrity (10). The increasingly advanced age at which women begin to desire a pregnancy has progressively increased the time window in which numerous lifestyle factors can exert their negative influence on the reproductive system, gametes, and general health. These lifestyle risk factors include: not achieving dietary recommendations and excessive physical activity participation (11–13); overweight (both BMI >25 and BMI >30 are related to a reduction in fertility) (14–17); physical, social or psychological stress (18–20); smoking tobacco (21–23); alcohol consumption; a high caffeine consumption; taking illicit drugs (24, 25); and a wrong timing of sexual intercourse at reproductive aim (26).
Growing evidence exists regarding the role of infectious agents on fertility impairment. In women, they can cause pelvic inflammatory disease and tubal obstruction (27) and in men they can lead to organ damage, create an obstruction or induce cell damage via mediators of inflammation or binding to spermatozoa (28). Interestingly, from 1993 WHO established the role of genital tract infections in human infertility and further studies reported that 15%–20% of infertile subjects are affected by semen infection (29).
Female Risk Factors
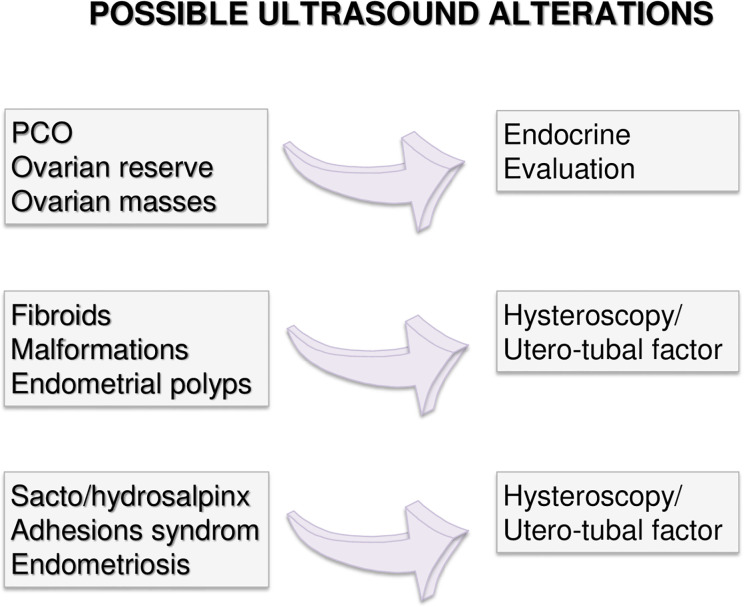
Female infertility may have different causes, like alterations of the reproductive system, congenital malformations, infections and hormonal dysfunctions. Particular attention should be paid to women with reduced ovarian reserve, linked to iatrogenic causes (for example previous cytotoxic treatments), or linked to a reduced follicular heritage from birth (POF family history) (10). In addition to a reduced ovarian reserve, several risk factors can affect the female fertility, and the main ones are summarized in Table 1 . Alongside lifestyle risk factors, an important determinant of female infertility is linked to the reduction in the number of ovulatory and, therefore, potentially fertile cycles. PCOS is the most common endocrine disorder and is the leading cause of anovulatory infertility in women. It is found in 5%–10% of the female population of reproductive age (30). According to ESHRE guidelines, PCOS has to be investigated in cases of clinical or biochemical hyperandrogenism, ovulatory dysfunction, or polycystic ovaries (31). While ESHRE guidelines suggest that where irregular menstrual cycles and hyperandrogenism are present ultrasound is not necessary for diagnosis, in infertile couples it should be mandatory in order to exclude other possible causes of female infertility.
Together with PCOS, all causes of amenorrhea may be a risk factor for female infertility since they are associated with ovulatory disorders. The term amenorrhea defines the absence of spontaneous menstruation for a period of at least 90 days or, according to some classifications, at least 180 days. It is necessary to differentiate physiological amenorrhea (present in some phases of a woman’s life, such as pre-pubertal age, pregnancy, and post-menopause) from pathological amenorrhea. The prevalence of the latter is around 3%–4%. Among the various classifications, the distinction between primary amenorrhea (absence of menarche from the age of 15 in the presence of secondary sexual characteristics or, in the absence of the latter, the absence of menarche from the age of 13) and secondary (absence of menstrual cycles for a period of at least 6 months in a woman who has had previous regular menstrual cycles or at least 12 months in a woman with oligomenorrheic cycles) is considered particularly useful. Indeed, in the presence of secondary amenorrhea, there is a previous evidence of anatomical activity functional of the reproductive axis and of the internal and external genital apparatus, which on the contrary is to be proved in the case of primary amenorrhea. For a list of possible causes of amenorrhea, see the position statement of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (32).
Endometriosis is another known factor of female infertility. Epidemiological data available in the literature, estimate that 6%–10% of the general female population suffers from endometriosis. In infertile women, the prevalence is estimated to be between 25% and 30% while 30%–50% of patients with endometriosis, independently from its stage, are infertile. Hughes et al. reported a monthly fertility rate for patients with endometriosis between 2% and 10%, considerably lower than that of the general population estimated to be between 15% and 20% (33).
Together with the above, other risk factors have been associated with female infertility, although their prevalence is lower than the previous ones.
Male Risk Factors
Male infertility is usually related to a reduced number of spermatozoa or to abnormalities in their quality. Two main conditions of male infertility are recognized: primary infertility, defined when the man has never induced a pregnancy and secondary infertility, when the man has previously fathered. An important risk factor is cryptorchidism. In fact, in congenital cryptorchid testes germ cell loss and the deterioration of the testicular structure can be observed. Importantly, these detrimental changes are observed to a higher level when testes remain undescended (34). Although orchiopexy corrects the inappropriate temperature exposure of the testis, surgery may not reverse the dysgenetic damage that underlies cryptorchidism in the first place (34). Another debated but recognized risk factor is varicocele that, on one side is associated with negative effects on semen quality, sperm function, testicular histology, and reproductive hormones and, on the other side it is present in men able to father children (35). Besides, patients with testicular cancer may have infertility both before cancer treatments due to systemic effects, endocrine changes, possible autoimmune effects, intrinsic testicular damage, possible congenital abnormalities in testicular maturation and after gonadotoxic effects related to orchiectomy, radiation, and chemotherapy (36). Growing evidence is also focusing on genetic factors and it is indeed well established that genetic causes account for 10%–15% of infertility cases, including chromosomal abnormalities and single-gene mutations (37). In addition to these well-known factors, growing evidence suggests that obesity, unhealthy diet, cigarette smoking and pollution may seriously affect sperm parameters and reduce male fertility (38–41). Again, besides bacterial semen infections, the presence of HPV on the male partner is now considered a risk factor both for natural and assisted reproduction outcome (42, 43). In fact, it seems that when infection is present on sperm there is a negative effect on the ongoing pregnancy rate and live birth rate as well as an increase in the rate of miscarriage (44). Finally, anti-sperm antibodies (ASA) have been shown to reduce sperm motility, natural fertilization, and conception thus inducing couple fertility (45). They are frequently associated with semen infections and recently it has been demonstrated that ASA-positive men had lower rates of pregnancy and live births following IVF (46). Therefore, their presence should be considered in infertile couples. Finally, many other factors with more limited evidence are included, such as testicular torsion and microlithiasis.
Assessment of Infertile Couples
The pathway to pregnancy in infertile couples is usually long and requires a high level of resilience owing to several factors including medical procedures, economic costs and psychological stress. In order to minimize the impact and to maximize the results, a well-integrated and multidisciplinary approach including all the different specialists of reproduction is necessary. In fact, it is mandatory to identify the most appropriate procedure with a gradual approach to both partners to obtain a precise diagnosis and the most effective therapeutic option, reducing invasive procedures that are not necessary.
For this reason, the first step should be a preliminary evaluation of both the male and female partner, drawing up the medical history and performing a clinical examination, taking into account the main issues listed in Tables 2 and 3 for male and female respectively. In addition to the medical history and clinical examination, semen analysis, endocrine assessment, and ultrasound scanning should be performed in order to have a more comprehensive picture.
Table 2.
First gynecological approach.
| Medical history | Physical examination | Ultrasound |
|---|---|---|
| Iatrogenic causes Ovulation Ovaria reserve Age Metabolic factors Poliabortivity Lifestyle |
BMI Hirsutism-hyperandrogenism Galactorreha Pelvic masses Cervical-vaginal disorders |
PCO Ovarian Reserve Ovarian masses |
| Metrorrhagia VIP IUD Poliabortivity Malformations Previous surgery |
Fibroids Malformations |
Fibroids Malformations Endometrial polyps Endometrial thickness abnormalities |
| PID Dysmenorrhea/Dyspareunia Recurrent cystitis/vaginitis IUD Previous surgery |
Sacto/hydrosalpinx Adhesions syndrom Endometriosis |
Sacto/hydrosalpinx Adhesions syndrom Endometriosis |
BMI, Body mass index; IUD, intrauterine contraceptive device; PCO, Polycystic ovary; PID, pelvic inflammatory disease; VIP, voluntary interruption of pregnancy.
Table 3.
First andrological approach.
| Medical history | Physical examination | Ultrasound | Sperm parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Family history of infertility Testicular trauma Previous infectious diseases Iatrogenic factors Endocrine diseases Using of anabolic steroids Puberty disorders Infertility with previous partner Occupational factors Lifestyle |
Anthropometric measures Androgenization BMI/WC Testicular evaluation (morphology, size, position, masses presence) Varicocele/hydrocele Penis evaluation Gynecomastia |
Testicular evaluation (morphology, size, masses presence) Varicocele/hydrocele Microlithiasis |
Volume Total number pH Morphology Motility Vitality Swelling Antibody Viscosity |
BMI, Body mass index; WC, waist circumference.
Infertile Couple Pathway
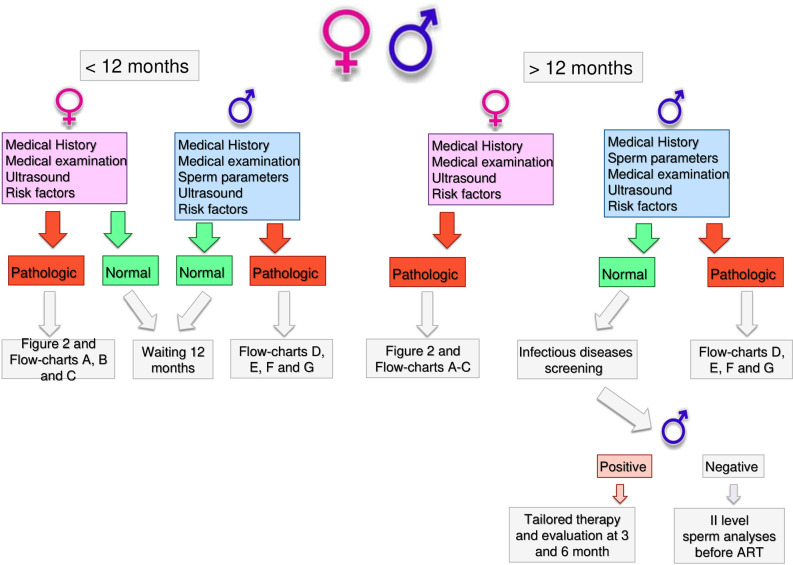
Health workers dealing with infertility should be able to guide couples through a clear, standardized and operative flow, reducing unnecessary burden on couples and optimizing the output of the diagnostic and treatment pathway. In Figure 1 , we reported the results of an Italian consensus recommending a comprehensive approach to infertile couples. Based on WHO definition, couples should firstly be divided based on the time of offspring search (< or >12 months). The threshold chosen for the duration of pregnancy seeking is crucial and can impact on the prevalence of the disease, avoiding couples to undergo unnecessary diagnostic tests or to the risk of overdiagnosis (47). The WHO recommends preconception care between 3 and 6 months before trying for a baby because of its positive impact on maternal and child health outcomes (https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/78067). As medical history, physical examination and ultrasound for women are part of routine pre-conception counselling, the gynecologic and whole health evaluation of the woman seeking pregnancy can be started independently of the diagnosis of infertility (http://www.undp.org/content/undp/en/home/librarypage/mdg/the-millennium-development-goals-report-2015.html). Possible factors involved in determining female infertility can be investigated as early as this stage ( Table 2 ). For males, medical history, physical examination, sperm analysis, and ultrasound should be performed as shown in Table 3 (48).
Figure 1.
Infertile couple flow chart.
If no alteration or risk factors are highlighted by this first level examination, couples are recommended to have free intercourse waiting till 12 months. If any alteration or risk factor emerges, the affected partner should undergo further analyses as described below.
Couples with more than 12 months infertility, should undergo the same preliminary approach. If no alteration is highlighted in both partners, expectant management is acceptable. Indeed, no significant differences in live birth rates between expectant management and other interventions for unexplained infertility have been recently reported, at least excluding patients at poor prognosis of natural conception (49). However, alongside a waiting strategy, further diagnostic investigations are advisable: males should perform a comprehensive microbiological screening (see Andrological Specific Flow-Charts). If any infection is detected, it should be treated and checked after the end of treatment. On the other hand, if any alteration or risk factor emerges from the preliminary examination, the affected partner should undergo further analyses. In particular, targeted examination should be performed for women based on specific risk factors as alterations observed at trans-vaginal ultrasound ( Figure 2 ) or clinical conditions ( Figures 3 – 5 explained below). For men, microbiology tests ( Figure 6 ) or targeted flow charts ( Figures 7– 9 explained below) should be followed based on sperm parameters.
Figure 2.
Possible alteration observable during trans-vaginal ultrasound.
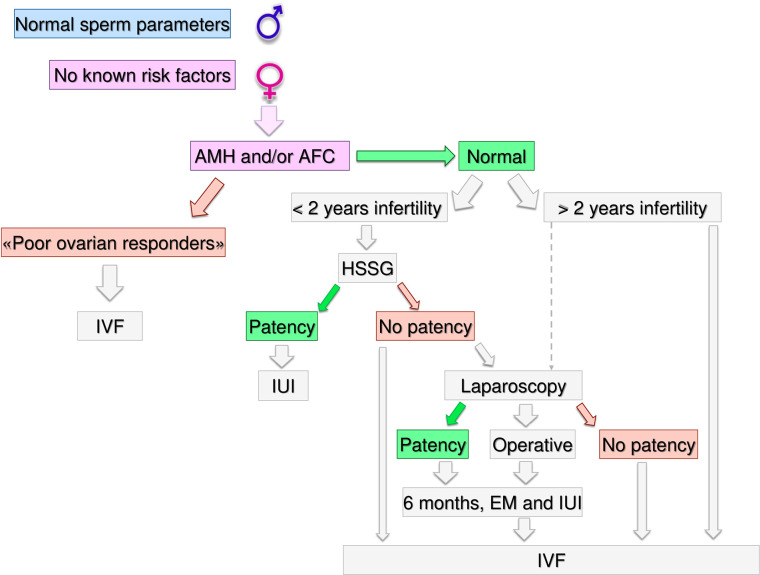
Figure 3.
Gynecological specific flow chart: second level diagnostic investigation and possible therapeutic approach for woman with no known risk factors.
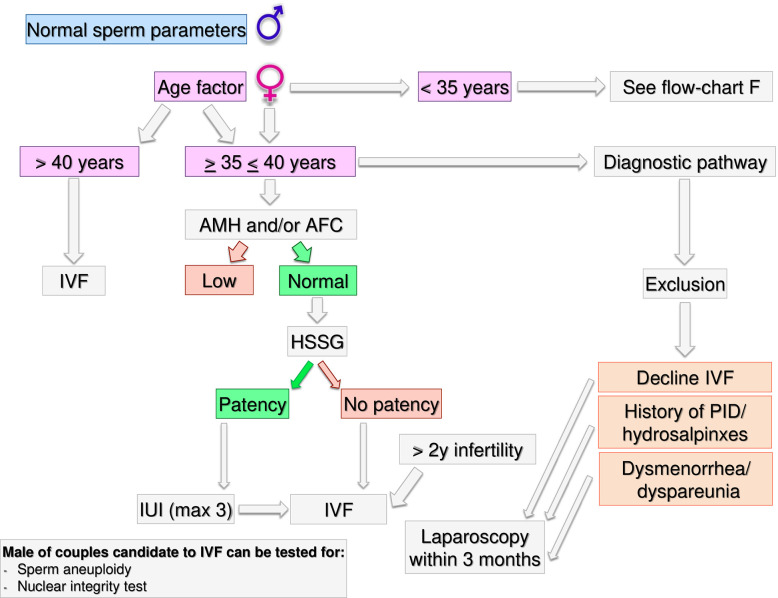
Figure 5.
Gynecological specific flow chart: second level diagnostic investigation and possible therapeutic approach for woman with >35 years.
Figure 6.
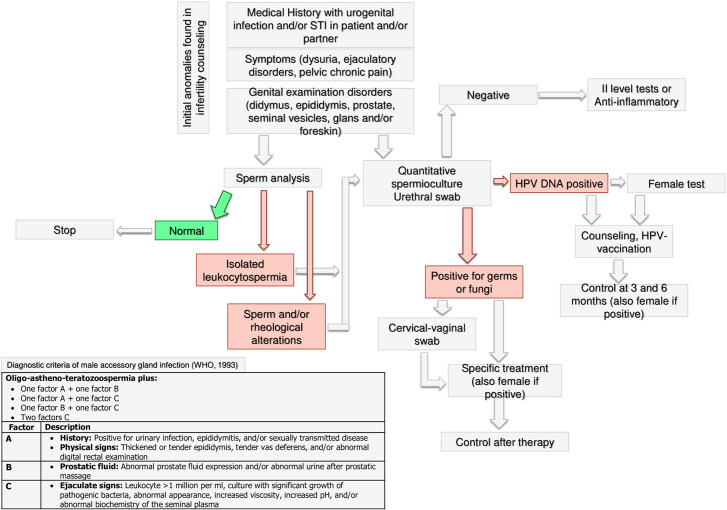
Andrological specific flow chart: microbiological assessment in male with anomalies found in infertility counseling.
Figure 7.
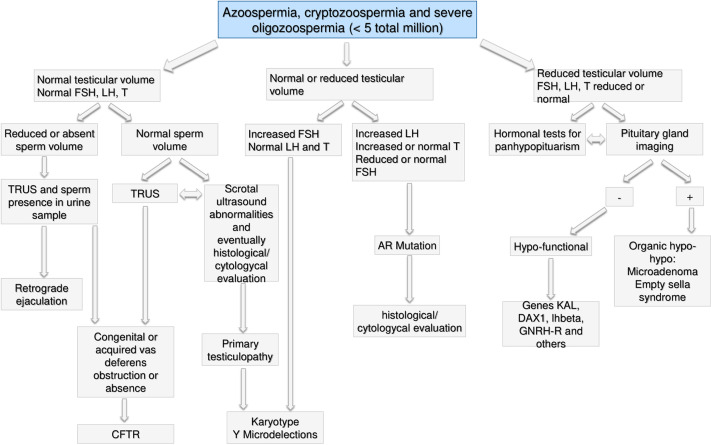
Andrological specific flow chart: diagnostic investigation for man with azoospermia, cryptozoospermia, and severe oligozoospermia (<5 total million).
Figure 9.
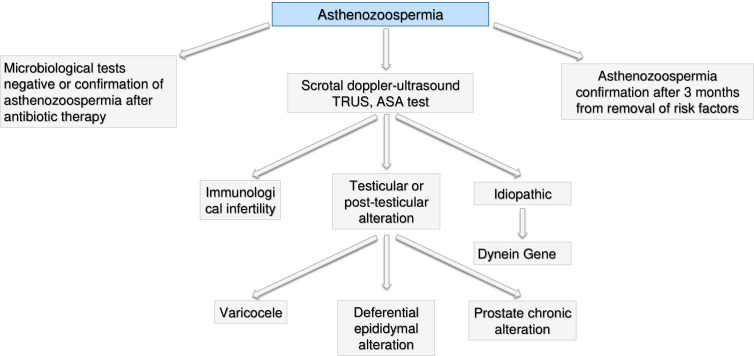
Andrological specific flow chart: diagnostic investigation for man with asthenozoospermia.
Figure 8.
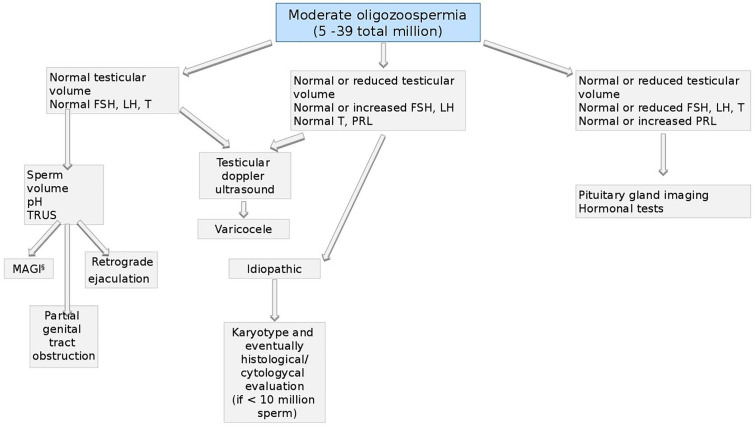
Andrological specific flow chart: diagnostic investigation for man with moderate oligozoospermia (5–39 total million).
Gynecological Specific Flow Charts
Second Level Diagnostic Investigation
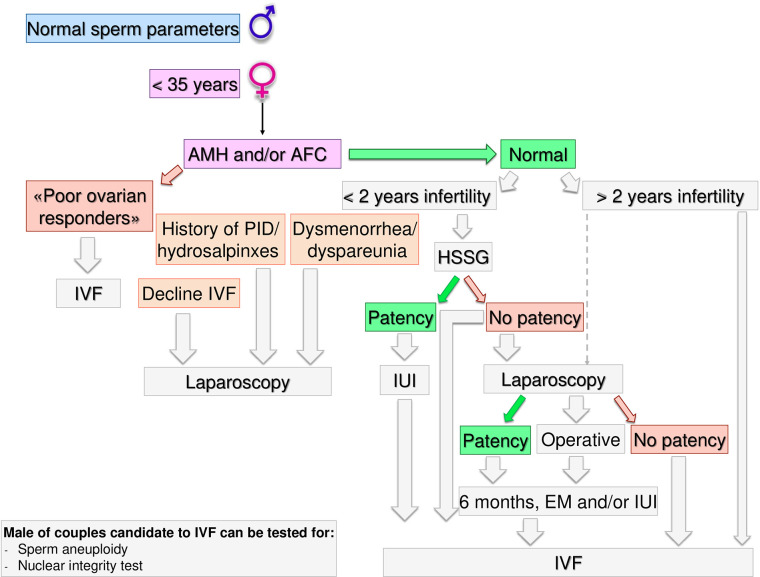
In a couple with > 12 months infertility, where the male partner has normal sperm parameters and woman has no known risk factors, second level investigations should start with the antral follicle count (AFC) and anti-mullerian hormone (AMH) dosage. If the woman was diagnosed as “poor responder”, the couple should be recommended to undergo in-vitro fertilization (IVF) independent of age ( Figure 3 ). As the number and the quality of oocytes are directly related to the probability of obtaining a live birth through IVF, a waiting policy in these couples could be excessively penalizing if spontaneous conception was not obtained (50, 51). Indeed, the age-related decline in ovarian reserve has been shown greater in infertility patients than fertile women (52).
Likewise, women older than 40 years old should be directed to IVF independently from the ovarian reserve because in older women with no other risk factors the immediate access to IVF demonstrated superior pregnancy rates compared to other ART treatments (53). However, several key issues in reproductive physiology cannot be accurately investigated by means of the ordinary diagnostic work up. Thus, in women older than 40 years, unexplained infertility cannot be diagnosed easily and women encountering a physiological “age-related infertility” could be treated without a true indication (54). Although an immediate IVF strategy in these couples has theoretical advantages, there is no strong evidence in support of treatment versus a waiting policy (55).
If AFC and AMH are normal (i.e. patients cannot be defined as poor responders) further steps depend on the time of infertility (< or >2 years) and on female age. If the time of infertility is < 2 years, the management depends on the age: in women with less than 35 years ( Figure 4 ), an hysterosalpingosonography (HSSG) should be performed. In case of tubal patency, it can be suggested intra-uterine injection (IUI) as first approach, as the chance of achieving a live birth are higher than expectant management (56). VF should be recommended after 3 IUI attempts (57), as the same chance to have a pregnancy by IVF (about 30% per attempt) are achieve at the seventh cycle of IUI (58). We do not consider all these attempts acceptable, as time to pregnancy and the couples’ compliance could be compromised after such numbers of failures. Furthermore, previous evidence suggests that the number of IUI attempts should be limited up to four (59–61).
Figure 4.
Gynecological specific flow chart: second level diagnostic investigation and possible therapeutic approach for woman with <35 years.
If the HSSG highlights no tubal patency, a diagnostic and/or operative laparoscopy could be proposed, as laparoscopy in women with unexplained infertility may reveal previously undiagnosed pathologies that could require ART, and in those without abnormal surgical finding, ART does not improve pregnancy rate (62). If laparoscopy show tubal patency or it is possible to perform an operative laparoscopy, 6 months of free intercourses or IUI, can be suggested. If laparoscopy confirms tubal occlusions, the couple should be directed to IVF.
If a female age is between 35–40 years ( Figure 5 ) HSSG could be performed. In case of tubal patency, IUI can be suggested as first approach. IVF should be recommended after 3 IUI attempts. If the HSSG highlights no tubal patency, IVF should be recommended. Independently from the ovarian reserve, in presence of hydrosalpinxes (often related to a PID history) a diagnostic and operative laparoscopy should be proposed before IVF (63–66). In case of dysmenorrhea/dyspareunia or others signs suggesting for mild endometriosis or IVF refusal (67, 68), a diagnostic laparoscopy within 3 months could be proposed, because undiagnosed or subtle pelvic abnormalities may be a significant cause of IVF failure (69).
If the time of infertility is >2 years and women age is <40 years, IVF should be proposed. Laparoscopy must be limited to few selected cases (IVF refusal, history of PID/hydrosalpinxes, dysmenorrhea/dyspareunia) after a careful risk benefit assessment. Male partner of couples candidate to IVF could be tested for sperm aneuploidy and nuclear integrity tests.
Andrological Specific Flow Charts
Microbiological Assessment
The WHO guidelines for the management of male infertility include microbiological investigation and the diagnostic examinations of male accessory gland infection (MAGI) (70). MAGI comprise orchitis, epididymitis, vesiculitis, prostatitis, and urethritis, which are potentially reversible causes of male infertility (71). Following the WHO’s recommendations (70), medical history, physical examination and sperm analysis play a crucial role to suggest a microbiological assessment to the male partner of an infertile couple. In particular, leukocytospermia (leukocytes >1 million/ml), more frequently occurring in infertile patients compared to fertile men (72), deserves microbiological investigation, as suggested by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) Practice Committee (73).
There is a lack of consensus about the specific microbiological analysis that should be requested in infertile patients with MAGI. Although the WHO guidelines (70) indicate sperm culture, more recent research suggests that the urethral swab, which could more accurately detect intracellular microorganisms such as mycoplasmas (71, 74), may be useful. Accordingly, a systematic review with meta-analysis carried out on cohort and case-control studies found an association between Mycoplasma hominis and Ureaplasma urealyticum and male infertility, underlining the importance of their identification (75). If the culture is negative, the specialist could decide, case by case, both to treat the male with anti-inflammatory or to request second level tests. In the case of positive culture, the female partner should also be tested and tailored treatment should be prescribed to patients with infection. A microbiological re-evaluation at the end of the treatment may be useful because of the relatively high persistence rate at the end of the antibiotic treatment (71).
The microbiological assessment of infertile couples should include the search for Papillomavirus (HPV) DNA, especially in case of current or anamnestic presence of condylomatosis, or in recurrent pregnancy loss. Accordingly, HPV infection shows a significantly higher prevalence in infertile patients compared to fertile men (20.4% vs. 11.4%), as indicated by a meta-analysis (76). Also, results from 5203 men revealed significantly worse conventional sperm parameters in HPV-positive than HPV-negative patients, with the motility being the parameter more strongly associated with HPV-infection. Importantly, a significantly higher miscarriage rate has been reported in HPV-positive patients compared to controls (77). Finally, if the HPV DNA test is positive, both male and female should be counseled for possible HPV vaccination and followed-up at 3 and 6 months after counseling.
Azoospermia, Cryptozoospermia, and Severe Oligozoospermia (< 5 Total Million)
The first step for men with azoospermia, cryptozoospermia and severe oligozoospermia (<5 total million sperm), should be the assessment of testicular volume and sex hormones levels (48, 73, 78).
If both, testicular volume and FSH, LH, and total testosterone (T) are normal, further analyses are performed based on semen volume: on one hand, if it is reduced or absent, a trans-rectal ultrasound (TRUS) and the search of sperm in the urine sample should be performed to evaluate the possibility of retrograde ejaculation (79–82) or vas deferens obstruction. In the latter case, the CFTR gene mutations should be investigated (83). On the other hand, if the semen volume is normal, TRUS could highlight genital tract obstruction and vas deferens pathologies and should be investigated as above described (84). At the same time scrotal ultrasound should exclude epididymal abnormalities (85, 86). If no alteration is found, histological/cytological evaluation may be performed to highlight spermatogenic function, distinguishing obstructive forms from primary testiculopathy (87, 88). In case of spermatogenic impairment, it makes sense to perform genetic screening for karyotype and Y microdeletions (89–91).
If the testicular volume is normal or reduced, hormonal levels lead to further investigation: in case of increased FSH and normal LH and testosterone levels, genetic screening for karyotype and Y microdeletions should be performed (92) and histological/cytological evaluation procedure could be performed aimed to clarify the tubular status. When LH is increased, testosterone normal or increased and FSH normal or reduced, the genetic screening for androgen receptor (AR) mutations should be performed (93) and also in this case, histological/cytological evaluation option may be considered.
Lastly, if the testicular volume is reduced, FSH and LH and testosterone are normal or reduced, pituitary-testicular axis should be assessed by both, hormonal tests for hypopituitarism and pituitary imaging to assess the abnormalities (94). In addition, if pituitary imaging doesn’t reveal any alteration, genetic screening for KAL, DAX1, LHbeta, and GNRH-R gene mutations should be performed (95–97).
Moderate Oligozoospermia (5–39 Total Million)
Also for men with moderate oligozoospermia (from 5 to 39 total million sperm), the first approach should be the assessment of testicular volume and hormonal asset (48, 73, 78).
If both, volume and hormones are normal, testicular doppler ultrasound should be performed aimed to exclude the presence of varicocele (98–100). Also based on semen volume, pH, and TRUS, four conditions should be considered: MAGI (see the section Microbiological Assessment— Figure 6 ), partial genital tract obstruction (101), retrograde ejaculation, and idiopathic oligozoospermia (102).
In the last scenario, a genetic screening for karyotype should be performed (92) and, in case of sperm count below 10 million, histological/cytological evaluation, could highlight the cause of oligozoospermia (88, 103).
In presence of normal or reduced testicular volume, normal or increased FSH and LH and normal T and PRL, the presence of varicocele or idiopathic infertility should be investigated as described above (99, 100).
Finally, if testicular volume, FSH, LH and T are normal or reduced and PRL is normal or increased, pituitary-testicular axis should be assessed by both, imaging and further hormonal test for hypopituitarism as previously described (94) (see Figure 7 ).
Asthenozoospermia
In presence of isolate asthenozoospermia, first of all genital tract infections should be excluded (see the section Microbiological Assessment— Figure 6 ) and a further semen analysis should be performed after 3 months from the end of treatment to re-evaluate such condition. If confirmed, a scrotal doppler-ultrasound, a TRUS and test for anti-sperm antibodies (ASA) test should be performed (104). Based on the results, we could face three scenarios: i) immunological infertility (105); ii) testicular or post-testicular infertility, including epididymal-deferential alterations, prostate chronic abnormalities or varicocele (106, 107) and iii) idiopathic infertility. In the case of idiopathic infertility, mutation of dynein gene should be investigated (108, 109). In case of presence of possible environmental or lifestyle causes of semen alteration, asthenozoospermia should be confirmed after 3 months from removal of risk factors (frequent saunas, smoking, work activities, tight sportswear) (108, 110, 111).
Conclusions
This expert opinion is an attempt to create a comprehensive, clear, standardized and personalized approach to infertile couples considering their health and wellness of offspring conceived. It contains practical recommendations useful for health workers dealing with reproductive health and to the research community. Considering the dynamism and the continuous evolution in the setup of diagnostic tools, this expert opinion provides just a general informed debate intending to stimulate further discussions among all those interested in the scientific, social, and ethical aspects of ART and to provide some guidance and clarification for ongoing discussion.
The Infertilitaly Group
Andrologists: Angela Alamo, Aldo Eugenio Calogero, Rossella Cannarella, Nicola Caretta, Francesco Cargnelutti, Mario Ciletti, Laura Cimino, Stefano Colangelo, Michele Compagnone, Rosita A. Condorelli, Christian Corsini, Alessandro Dal Lago, Giuseppe Defeudis, Antonella Di Mambro, Alberto Ferlin, Carlo Foresta, Giorgio Franco, Mariagrazia Gallo, Andrea Garolla, Marco Ghezzi, Daniele Gianfrilli, Giuseppe Grande, Michele Guidotti, Sandro La Vignera, Maria Agnese Latino, Andrea Lenzi, Emanuele Licata, Francesco Lombardo, Francesco Lotti, Giovanni Luca, Massimo Manno, Marco Marasco, Fernando Mazzilli, Rossella Mazzilli, Maurizio Merico, Domenico Milardi, Laura M. Mongioì, Pierfrancesco Palego, Alessandra Petrozzi, Damiano Pizzol, Rocco Rago, Francesco Romanelli, Riccardo Selice, Lee Smith, Umberto Valente.
Gynecologists: Anna Biasioli, Andrea Borini, Andrea Roberto Carosso, Claudio Castello, Maria Elisabetta Coccia, Cristofaro De Stefano, Lino Del Pup, Stefano Facchin, Andrea Gallinelli, Gianluca Gennarelli, Maurizio Guido, Assunta Iuliano, Giovanni Battista La Sala, Irene Ladisa, Antonio Lanzone, Stefano Palomba, Fedro Alessandro Peccatori, Fabio Perricone, Stefania Piccolo, Alberto Revelli, Francesca Rizzello, Chiara Romanelli, Francesca Salvagno, Sergio Schettini, Paolo Scollo, Francesco Tomei, Filippo Maria Ubaldi, Francesca Vasoin, Alessandra Vucetich.
Oncologist: Giovanni Codacci-Pisanelli.
Biologists and Embryologists: Attilio Anastasi, Elisabetta Baldi, Alberto Bottacin, Francesco Capodanno, Tania Carlini, Sara Corrò, Ilaria Cosci, Giovanni Coticchio, Lucia De Santis, Fabiana Faja, Elena Marcazzan, Massimo Menegazzo, Alessio Paffoni, Donatella Paoli, Nicola Passerin, Alessandra Patimo, Marianna Pelloni, Adriano Presciutti, Laura Rienzi, Jessica Sebellin, Riccardo Talevi, Chiara Tempio.
Geneticists: Ivana Antonucci, Savina Dipresa, Valentina Gatta, Antonio Novelli, Liborio Stuppia.
Microbiologists: Valeria Meroni, Guido Scalia, Alessandra Sensini.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge all components of the InfertilItaly group and their collaborators for the generous and huge job.
References
- 1. WHO Sexual and Reproductive health. Available at: https://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/topics/infertility/multiple-definitions/en/ (Accessed October 2019).
- 2. Boivin J, Bunting L, Collins JA, Nygren KG. International estimates of infertility prevalence and treatment-seeking: potential need and demand for infertility medical care. Hum Reprod (2007) Jun;22(6):1506–12. 10.1093/humrep/dem046 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Zegers-Hochschild F, Adamson GD, Dyer S, Racowsky C, de Mouzon J, Sokol R, et al. The International Glossary on Infertility and Fertility Care, 2017. Hum Reprod (2017) Sep 1 32(9):1786–801. 10.1093/humrep/dex234 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. De Geyter C. Assisted reproductive technology: Impact on society and need for surveillance. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab (2019) Feb 33(1):3–8. 10.1016/j.beem.2019.01.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. De Geyter C, Calhaz-Jorge C, Kupka MS, Wyns C, Mocanu E, Motrenko T, et al. ART in Europe, 2014: results generated from European registries by ESHRE: The European IVF-monitoring Consortium (EIM) for the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE). Hum Reprod (2018) Sep 1 33(9):1586–601. 10.1093/humrep/dey242 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Foresta C. La medicina della riproduzione “Il percorso clinico e diagnostico della coppia infertile”. Editeam (2020). [Google Scholar]
- 7. American Society for Reproductive Medicine Infertility: An overview. Available at: https://www.asrm.org/topics/topics-index/infertility/ (Accessed October 2019).
- 8. Rumbold AR, Sevoyan A, Oswald TK, Fernandez RC, Davies MJ, Moore VM. Impact of male factor infertility on offspring health and development. Fertil Steril (2019) Jun;111(6):1047–53. 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2019.05.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Vander Borght M, Wyns C. Fertility and infertility: Definition and epidemiology. Clin Biochem (2018) Dec 62:2–10. 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2018.03.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Leridon H. Can assisted reproduction technology compensate for the natural decline in fertility with age? A model assessment. Hum Reprod (2004) Jul 19(7):1548–53. 10.1093/humrep/deh304 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Freizinger M, Franko DL, Dacey M, Okun B, Domar AD. The prevalence of eating disorders in infertile women. Fertil Steril (2010) Jan 93(1):72–8. 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.09.055 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Gaskins AJ, Rich-Edwards JW, Missmer SA, Rosner B, Chavarro JE. Association of fecundity with changes in adult female weight. Obstet Gynecol (2015) Oct 126(4):850–8. 10.1097/AOG.0000000000001030 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Wise LA, Rothman KJ, Mikkelsen EM, Sørensen HT, Riis AH, Hatch EE. A prospective cohort study of physical activity and time to pregnancy. Fertil Steril (2012) May 97(5):1136–42.e1-4. 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2012.02.025 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Koning AM, Mutsaerts MA, Kuchenbecker WK, Broekmans FJ, Land JA, Mol BW, et al. Complications and outcome of assisted reproduction technologies in overweight and obese women. Hum Reprod (2012) Feb 27(2):457–67. 10.1093/humrep/der416 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Ramlau-Hansen CH, Thulstrup AM, Nohr EA, Bonde JP, Sørensen TI, Olsen J. Subfecundity in overweight and obese couples. Hum Reprod (2007) Jun 22(6):1634–7. 10.1093/humrep/dem035 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Sim KA, Partridge SR, Sainsbury A. Does weight loss in overweight or obese women improve fertility treatment outcomes? A systematic review. Obes Rev (2014) Oct 15(10):839–50. 10.1111/obr.12217 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Goldman KN, Hodes-Wertz B, McCulloh DH, Flom JD, Grifo JA. Association of body mass index with embryonic aneuploidy. Fertil Steril (2015) Mar 103(3):744–8. 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2014.11.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Domar AD, Clapp D, Slawsby EA, Dusek J, Kessel B, Freizinger M. Impact of group psychological interventions on pregnancy rates in infertile women. Fertil Steril (2000) Apr 73(4):805–11. 10.1016/S0015-0282(99)00493-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Louis GM, Lum KJ, Sundaram R, Chen Z, Kim S, Lynch CD, et al. Stress reduces conception probabilities across the fertile window: evidence in support of relaxation. Fertil Steril (2011) Jun 95(7):2184–9. 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2010.06.078 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Frederiksen Y, Farver-Vestergaard I, Skovgård NG, Ingerslev HJ, Zachariae R. Efficacy of psychosocial interventions for psychological and pregnancy outcomes in infertile women and men: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open (2015) Jan 28 5(1):e006592. 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-006592 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Vanhoutte L, De Sutter P, Van der Elst J, Dhont M. Clinical benefit of metaphase I oocytes. Reprod Biol Endocrinol (2005) Dec 15 3:71. 10.1186/1477-7827-3-71 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Freour T, Masson D, Mirallie S, Jean M, Bach K, Dejoie T, et al. Active smoking compromises IVF outcome and affects ovarian reserve. Reprod BioMed Online (2008) Jan 16(1):96–102. 10.1016/S1472-6483(10)60561-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Waylen AL, Metwally M, Jones GL, Wilkinson AJ, Ledger WL. Effects of cigarette smoking upon clinical outcomes of assisted reproduction: a meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update (2009) Jan-Feb 15(1):31–44. 10.1093/humupd/dmn046 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Revonta M, Raitanen J, Sihvo S, Koponen P, Klemetti R, Männistö S, et al. Health and life style among infertile men and women. Sex Reprod Healthc (2010) Aug;1(3):91–8. 10.1016/j.srhc.2010.06.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Gore AC, Chappell VA, Fenton SE, Flaws JA, Nadal A, Prins GS, et al. EDC-2: The Endocrine Society’s Second Scientific Statement on Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals. Endocr Rev (2015) Dec 36(6):E1–E150. 10.1210/er.2015-1010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Wilcox AJ, Weinberg CR, Baird DD. Timing of sexual intercourse in relation to ovulation. Effects on the probability of conception, survival of the pregnancy, and sex of the baby. N Engl J Med (1995) Dec 7 333(23):1517–21. 10.1056/NEJM199512073332301 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Hart RJ. Physiological Aspects of Female Fertility: Role of the Environment, Modern Lifestyle, and Genetics. Physiol Rev (2016) Jul;96(3):873–909. 10.1152/physrev.00023.2015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Ochsendorf FR. Sexually transmitted infections: impact on male fertility. Andrologia (2008) Apr 40(2):72–5. 10.1111/j.1439-0272.2007.00825.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Garolla A, Pizzol D, Bertoldo A, Menegazzo M, Barzon L, Foresta C. Sperm viral infection and male infertility: focus on HBV, HCV, HIV, HPV, HSV, HCMV, and AAV. J Reprod Immunol (2013) Nov;100(1):20–9. 10.1016/j.jri.2013.03.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Polson DW, Adams J, Wadsworth J, Franks S. Polycystic ovaries–a common finding in normal women. Lancet (1988) Apr 16 1(8590):870–2. 10.1016/S0140-6736(88)91612-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Costello MF, Misso ML, Balen A, Boyle J, Devoto L, Garad RM, et al. Evidence summaries and recommendations from the international evidence-based guideline for the assessment and management of polycystic ovary syndrome: assessment and treatment of infertility. Hum Reprod Open (2019) Jan:hoy021. 10.1093/hropen/hoy021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Practice Committee of American Society for Reproductive Medicine Current evaluation of amenorrhea. Fertil Steril (2008) Nov;90(5 Suppl):S219–25. 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.08.038 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Hughes EG, Fedorkow DM, Collins JA. A quantitative overview of controlled trials in endometriosis-associated infertility. Fertil Steril (1993) May 59(5):963–70. 10.1016/S0015-0282(16)55911-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Virtanen HE, Toppari J. Cryptorchidism and Fertility. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am (2015) Dec;44(4):751–60. 10.1016/j.ecl.2015.07.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Jensen CFS, Østergren P, Dupree JM, Ohl DA, Sønksen J, Fode M. Varicocele and male infertility. Nat Rev Urol (2017) Sep 14(9):523–33. 10.1038/nrurol.2017.98 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Ostrowski KA, Walsh TJ. Infertility with Testicular Cancer. Urol Clin North Am (2015) Aug 42(3):409–20. 10.1016/j.ucl.2015.05.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Pizzol D, Ferlin A, Garolla A, Lenzi A, Bertoldo A, Foresta C. Genetic and molecular diagnostics of male infertility in the clinical practice. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) (2014) Jan 1 19:291–303. 10.2741/4208 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Salas-Huetos A, Maghsoumi-Norouzabad L, James ER, Carrell DT, Aston KI, Jenkins TG, et al. Male adiposity, sperm parameters and reproductive hormones: An updated systematic review and collaborative meta-analysis. Obes Rev (2021) 22(1):e13082. 10.1111/obr.13082 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Salas-Huetos A, Bulló M, Salas-Salvadó J. Dietary patterns, foods and nutrients in male fertility parameters and fecundability: a systematic review of observational studies. Hum Reprod Update (2017) Jul 1 23(4):371–89. 10.1093/humupd/dmx006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Sharma R, Harlev A, Agarwal A, Esteves SC. cigarette smoking and semen quality: a new meta-analysis examining the effect of the 2010 world health organization laboratory methods for the examination of human semen. Eur Urol (2016) Oct 70(4):635–45. 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.04.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Deng Z, Chen F, Zhang M, Lan L, Qiao Z, Cui Y, et al. Association between air pollution and sperm quality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ Pollut (2016) Jan;208(Pt B):663–9. 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.10.044 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Garolla A, Engl B, Pizzol D, Ghezzi M, Bertoldo A, Bottacin A, et al. Spontaneous fertility and in vitro fertilization outcome: new evidence of human papillomavirus sperm infection. Fertil Steril (2016) Jan 105(1):65–72. 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.09.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Depuydt CE, Donders GGG, Verstraete L, Vanden Broeck D, Beert JFA, Salembier G, et al. Infectious human papillomavirus virions in semen reduce clinical pregnancy rates in women undergoing intrauterine insemination. Fertil Steril (2019) Jun 111(6):1135–44. 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2019.02.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Siristatidis C, Vaidakis D, Sertedaki E, Martins WP. Effect of human papilloma virus infection on in-vitro fertilization outcome: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol (2018) Jan 51(1):87–93. 10.1002/uog.17550 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Taiyeb AM, Ridha-Albarzanchi MT, Taiyeb SM, Kanan ZA, Alatrakchi SK, Kjelland ME. Muhsen Alanssari SA Improvement in pregnancy outcomes in couples with immunologically male infertility undergoing prednisolone treatment and conventional in vitro fertilization preceded by sperm penetration assay: a randomized controlled trial. Endocrine (2017) Dec 58(3):448–57. 10.1007/s12020-017-1446-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Lu SM, Li X, Wang SL, Yang XL, Xu YZ, Huang LL, et al. Success rates of in vitro fertilization versus intracytoplasmic sperm injection in men with serum anti-sperm antibodies: a consecutive cohort study. Asian J Androl (2019) Sep-Oct 21(5):473–7. 10.4103/aja.aja_124_18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Capri Workshop Group ESHRE. A prognosis-based approach to infertility: understanding the role of time. Hum Reprod (2017) 32(8):1556–9. 10.1093/humrep/dex214 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Ferlin A, Foresta C. Infertility: Practical Clinical Issues for Routine Investigation of the Male Partner. J Clin Med (2020) 9(6):1644. 10.3390/jcm9061644 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Wang R, Danhof NA, Tjon-Kon-Fat RI, Eijkemans JC, Bossuyt PMM, Mochtar MH, et al. Interventionsfor unexplained infertility: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (2019) 9: (9):CD012692. 10.1002/14651858.CD012692.pub2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. McLernon DJ, Steyerberg EW, Te Velde ER, Lee AJ, Bhattacharya S. Predicting the chances of a live birth after one or more complete cycles of in vitro fertilisation: population based study of linked cycle data from 113 873 women. BMJ (2016) 355:i5735. 10.1136/bmj.i5735 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Sunkara SK, Rittenberg V, Raine-Fenning N, Bhattacharya S, Zamora J, Coomarasamy A. Association between the number of eggs and live birth in IVF treatment: an analysis of 400 135 treatment cycles. Hum Reprod (2011) 26(7):1768–74. 10.1093/humrep/der106 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Iliodromiti S, Iglesias Sanchez C, Messow C-M, Cruz M, Garcia Velasco J, Nelson SM. Excessive Age-Related Decline in Functional Ovarian Reserve in Infertile Women: Prospective Cohort of 15,500 Women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab (2016) 101(9):3548–54. 10.1210/jc.2015-4279 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Goldman MB, Thornton KL, Ryley D, Alper MM, Fung JL, Reindollar RH, et al. A randomized clinical trial to determine optimal infertility treatment in older couples: the Forty and Over Treatment Trial (FORT-T). Fertil Steril (2014) 101(6):1574–81.e1-2. 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2014.03.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Somigliana E, Paffoni A, Busnelli A, Filippi F, Pagliardini L, Vigano P, et al. Age-related infertility and unexplained infertility: an intricate clinical dilemma. Hum Reprod (2016) 31(7):1390–6. 10.1093/humrep/dew066 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Tjon-Kon-Fat RI, Bensdorp AJ, Scholten I, Repping S, van Wely M, Mol BWJ, et al. IUI and IVF for unexplained subfertility: where did we go wrong? Hum Reprod (2016) 31(12):2665–7. 10.1093/humrep/dew241 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Ayeleke RO, Asseler JD, Cohlen BJ, Veltman-Verhulst SM. Intra-uterine insemination for unexplained subfertility. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (2020) 3(3):CD001838. 10.1002/14651858.CD001838.pub6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. De Geyter C, Calhaz-Jorge C, Kupka MS, Wyns C, Mocanu E, Motrenko T, et al. ART in Europe, 2015: results generated from European registries by ESHRE. Hum Reprod Open (2020) 2020(1):hoz038. 10.1093/hropen/hoz044 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Custers IM, Steures P, Hompes P, Flierman P, van Kasteren Y, van Dop PA, et al. Intrauterine insemination: how many cycles should we perform? Hum Reprod (2008) 23(4):885–8. 10.1093/humrep/den008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Aboulghar MA, Mansour RT, Serour GI, Abdrazek A, Amin Y, Rhodes C. Controlled ovarian hyperstimulation and intrauterine insemination for treatment of unexplained infertility should be limited to a maximum of three trials. Fertil Steril (2001) 75:88–91. 10.1016/S0015-0282(00)01641-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Sahakyan M, Harlow BL, Hornstein MD. Influence of age, diagnosis, and cycle number on pregnancy rates with gonadotropin-induced controlled ovarian hyperstimulation and intrauterine insemination. Fertil Steril (1999) 72:500–4. 10.1016/S0015-0282(99)00300-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Aboulghar MA, Mansour RT, Serour GI, Al-Inany HG. Diagnosis and management of unexplained infertility: an update. Arch Gynecol Obstet (2003) 267(4):177–88. 10.1007/s00404-002-0300-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. De Cicco S, Tagliaferri V, Selvaggi L, Romualdi D, Di Florio C, Immediata V, et al. Expectant management may reduce overtreatment in women affected by unexplained infertility confirmed by diagnostic laparoscopy. Arch Gynecol Obstet (2017) 295(2):427–33. 10.1007/s00404-016-4246-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Andersen AN, Yue Z, Meng FJ, Petersen K. Low implantation rate after in-vitro fertilization in patients with hydrosalpinges diagnosed by ultrasonography. Hum Reprod (1994) 9:1935–8. 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a138362 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Shelton KE, Butler L, Toner JP, Oehninger S, Muasher SJ. Salpingectomy improves the pregnancy rate in in-vitro fertilization patients with hydrosalpinx. Hum Reprod (1996) 11:523–5. 10.1093/HUMREP/11.3.523 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Strandell A, Lindhard A, Waldenstrom U, Thorburn J, Janson PO, Hamberger L. Hydrosalpinx and IVF outcome: a prospective, randomized multicentre trial in Scandinavia onsalpingectomy prior to IVF. Hum Reprod (1999) 14:2762–9. 10.1093/humrep/14.11.2762 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Fouda UM, Elshaer HS, Youssef MA, Darweesh FF. Extended doxycycline treatment versus salpingectomy in the management of patients with hydrosalpinx undergoing IVF-ET. J Ovarian Res (2020) 13(1):69. 10.1186/s13048-020-00665-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Littman E, Giudice L, Lathi R, Berker B, Milki A, Nezhat C. Role of laparoscopic treatment of endometriosis in patients with failed in vitro fertilization cycles. Fertil Steril (2005) 84(6):1574–8. 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2005.02.059 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Brichant G, Audebert A, Nisolle M. Minimal and mild endometriosis: which impact on fertility? Rev Med Liege (2016) 71(5):236–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Yu X, Cai H, Guan J, Zheng X, Han H. Laparoscopic surgery: Any role in patients with unexplained infertility and failed in vitro fertilization cycles? Med (Baltimore) (2019) 98(13):e14957. 10.1097/MD.0000000000014957 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. World Health Organization Rowe P, Comhaire F, Hargreave TB, Mellows HJ, editors. WHO manual for the standardized investigation and diagnosis of the infertile couple. Cambridge University Press; (1993). [Google Scholar]
- 71. Calogero AE, Duca Y, Condorelli RA, La Vignera S. Male accessory gland inflammation, infertility, and sexual dysfunctions: a practical approach to diagnosis and therapy. Andrology (2017) 5:1064–72. 10.1111/andr.12427 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Jue JS, Ramasamy R. Significance of Positive Semen Culture in Relation to Male Infertility and the Assisted Reproductive Technology Process. Transl Androl Urol (2017) Oct 6(5):916–22. 10.21037/tau.2017.06.23 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine Diagnostic Evaluation of the Infertile Male: A Committee Opinion. Fertil Steril (2015) Mar;103(3):e18–25. 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2014.12.103 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. La Vignera S, Condorelli RA, Vicari E, Salmeri M, Morgia G, Favilla V, et al. Microbiological investigation in male infertility: a practical overview. J Med Microbiol (2014) 63(Pt 1):1–14. 10.1099/jmm.0.062968-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Huang C, Zhu HL, Xu KR, Wang SY, Fan LQ, Zhu WB. Mycoplasma and ureaplasma infection and male infertility: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Andrology (2015) 3:809–16. 10.1111/andr.12078 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Lyu Z, Feng X, Li N, Zhao W, Wei L, Chen Y, et al. Human papillomavirus in semen and the risk for male infertility: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis (2017) 17:714. 10.1186/s12879-017-2812-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Weinberg M, Sar-Shalom Nahshon C, Feferkorn I, Bornstein J. Evaluation of human papilloma virus in semen as a risk factor for low sperm quality and poor in vitro fertilization outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Fertil Steril (2020) 113:955–69. 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2020.01.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Condorelli R, Calogero AE, La Vignera S. Relationship between Testicular Volume and Conventional or Nonconventional Sperm Parameters. Int J Endocrinol Hindawi (2013) 2013:e145792. 10.1155/2013/145792 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Jarow JP. Transrectal ultrasonography of infertile men. Fertil Steril (1993) Dec 1 60(6):1035–9. 10.1016/S0015-0282(16)56406-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. La Vignera SL, Calogero AE, Condorelli RA, Vicari LO, Catanuso M, D’Agata R, et al. Ultrasonographic evaluation of patients with male accessory gland infection. Andrologia (2012) 44(s1):26–31. 10.1111/j.1439-0272.2010.01132.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Parnham A, Serefoglu EC. Retrograde ejaculation, painful ejaculation and hematospermia. Transl Androl Urol (2016) Aug 5(4):592–601. 10.21037/tau.2016.06.05 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Lotti F, Maggi M. Ultrasound of the male genital tract in relation to male reproductive health. Hum Reprod Update (2015) Jan 1 21(1):56–83. 10.1093/humupd/dmu042 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Dörk T, Dworniczak B, Aulehla-Scholz C, Wieczorek D, Böhm I, Mayerova A, et al. Distinct spectrum of CFTR gene mutations in congenital absence of vas deferens. Hum Genet (1997) Aug 1 100(3):365–77. 10.1007/s004390050518 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Colpi GM, Francavilla S, Haidl G, Link K, Behre HM, Goulis DG, et al. European Academy of Andrology guideline Management of oligo-astheno-teratozoospermia. Andrology (2018) 6(4):513–24. 10.1111/andr.12502 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Dogra VS, Gottlieb RH, Oka M, Rubens DJ. Sonography of the scrotum. Radiology (2003) 227(1):18–36. 10.1148/radiol.2271001744 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86. Foresta C, Garolla A, Bettella A, Ferlin A, Rossato M, Candiani F. Doppler ultrasound of the testis in azoospermic subjects as a parameter of testicular function. Hum Reprod (1998) Nov 1 13(11):3090–3. 10.1093/humrep/13.11.3090 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87. Foresta C, Varotto A, Scandellari C. Assessment of testicular cytology by fine needle aspiration as a diagnostic parameter in the evaluation of the azoospermic subject. Fertil Steril (1992) Apr 1 57(4):858–65. 10.1016/S0015-0282(16)54971-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Foresta C, Varotto A. Assessment of testicular cytology by fine needle aspiration as a diagnostic parameter in the evaluation of the oligospermic subject**Supported by grant 326/01/90 from Regione Veneto, Italy. Fertil Steril (1992) Nov 1 58(5):1028–33. 10.1016/S0015-0282(16)55455-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89. Ferlin A, Arredi B, Speltra E, Cazzadore C, Selice R, Garolla A, et al. Molecular and Clinical Characterization of Y Chromosome Microdeletions in Infertile Men: A 10-Year Experience in Italy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab (2007) Mar 1 92(3):762–70. 10.1210/jc.2006-1981 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90. Krausz C, Hoefsloot L, Simoni M, Tuttelmann F. EAA/EMQN best practice guidelines for molecular diagnosis of Y-chromosomal microdeletions: state-of-the-art 2013. Andrology (2014) 2(1):5–19. 10.1111/j.2047-2927.2013.00173.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91. Oud MS, Ramos L, O’Bryan MK, McLachlan RI, Okutman Ö, Viville S, et al. Validation and application of a novel integrated genetic screening method to a cohort of 1,112 men with idiopathic azoospermia or severe oligozoospermia. Hum Mutat (2017) 38(11):1592–605. 10.1002/humu.23312 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92. Foresta C, Ferlin A, Garolla A, Rossato M, Barbaux S, De Bortoli A. Y-Chromosome Deletions in Idiopathic Severe Testiculopathies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab (1997) Apr 1 82(4):1075–80. 10.1210/jcem.82.4.3798 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93. Yong EL, Loy CJ, Sim KS. Androgen receptor gene and male infertility. Hum Reprod Update (2003) Jan 1 9(1):1–7. 10.1093/humupd/dmg003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94. Cheer K, Trainer PJ. Evaluation of pituitary function. In: Fliers E, Korbonits M, Romijn JA, editors. Handbook of Clinical Neurology Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier; (2014). p. 141–9. 10.1016/B978-0-444-59602-4.00010-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95. Pitteloud N, Boepple PA, DeCruz S, Valkenburgh SB, Crowley WF, Hayes FJ. The Fertile Eunuch Variant of Idiopathic Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism: Spontaneous Reversal Associated with a Homozygous Mutation in the Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab (2001) Jun 1 86(6):2470–5. 10.1210/jcem.86.6.7542 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96. Jameson JL. Inherited disorders of the gonadotropin hormones. Mol Cell Endocrinol (1996) Dec 20 125(1):143–9. 10.1016/S0303-7207(96)03950-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97. Vezzoli V, Duminuco P, Bassi I, Guizzardi F, Persani L, Bonomi M. The complex genetic basis of congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Minerva Endocrinol (2016) Jun 41(2):223–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98. Gorelick JI, Goldstein M. Loss of fertility in men with varicocele Presented in part at the 45th Annual Meeting of The American Fertility Society, San Francisco, California, November 13 to 16, 1989. Fertil Steril (1993) Mar 1 59(3):613–6. 10.1016/S0015-0282(16)55809-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99. Zini A, Buckspan M, Berardinucci D, Jarvi K. The influence of clinical and subclinical varicocele on testicular volume. Fertil Steril (1997) Oct 1 68(4):671–4. 10.1016/S0015-0282(97)00311-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100. Damsgaard J, Joensen UN, Carlsen E, Erenpreiss J, Blomberg Jensen M, Matulevicius V, et al. Varicocele is associated with impaired semen quality and reproductive hormone levels: A study of 7035 Healthy Young Men from Six European Countries. Eur Urol (2016) Dec 1 70(6):1019–29. 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.06.044 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101. Mak V, Zielenski J, Tsui L-C, Durie P, Zini A, Martin S, et al. Cystic fibrosis gene mutations and infertile men with primary testicular failure. Hum Reprod (2000) Feb 1 15(2):436–9. 10.1093/humrep/15.2.436 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102. McLachlan RI. Approach to the patient with oligozoospermia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab (2013) Mar 1 98(3):873–80. 10.1210/jc.2012-3650 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103. Bettella A, Ferlin A, Menegazzo M, Ferigo M, Tavolini IM, Bassi PF, et al. Testicular fine needle aspiration as a diagnostic tool in non-obstructive azoospermia. Asian J Androl (2005) Sep 7(3):289–94. 10.1111/j.1745-7262.2005.00043.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104. Barbonetti A, Castellini C, D’Andrea S, Minaldi E, Totaro M, Francavilla S, et al. Relationship between natural and intrauterine insemination-assisted live births and the degree of sperm autoimmunisation. Hum Reprod (2020) Jun 1 35(6):1288–95. 10.1093/humrep/deaa070 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105. Dondero F, Lenzi A, Gandini L, Lombardo F. Immunological infertility in humans. Exp Clin Immunogenet (1993) 10(2):65–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106. La Vignera S, Condorelli R, Vicari E, D’Agata R, Calogero AE. Effects of varicocelectomy on sperm DNA fragmentation, mitochondrial function, chromatin condensation, and apoptosis. J Androl (2012) Jun 33(3):389–96. 10.2164/jandrol.111.013433 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107. Vicari E, Calogero AE, Condorelli RA, Vicari LO, Vignera SL. Male accessory gland infection frequency in infertile patients with chronic microbial prostatitis and irritable bowel syndrome: transrectal ultrasound examination helps to understand the links. J Androl (2012) 33(3):404–11. 10.2164/jandrol.111.014654 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108. Neesen J, Kirschner R, Ochs M, Schmiedl A, Habermann B, Mueller C, et al. Disruption of an inner arm dynein heavy chain gene results in asthenozoospermia and reduced ciliary beat frequency. Hum Mol Genet (2001) May 15 10(11):1117–28. 10.1093/hmg/10.11.1117 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109. Zuccarello D, Ferlin A, Cazzadore C, Pepe A, Garolla A, Moretti A, et al. Mutations in dynein genes in patients affected by isolated non-syndromic asthenozoospermia. Hum Reprod (2008) Aug 1 23(8):1957–62. 10.1093/humrep/den193 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110. Garolla A, Torino M, Sartini B, Cosci I, Patassini C, Carraro U, et al. Seminal and molecular evidence that sauna exposure affects human spermatogenesis. Hum Reprod (2013) Apr 1 28(4):877–85. 10.1093/humrep/det020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111. Jung A, Schill WB. Male infertility. Current life style could be responsible for infertility. MMW Fortschr Med (2000) Sep 1 142(37):31–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]