Abstract
Background
Selective serotonin reuptaker inhibitors, including fluoxetine, are widely studied and prescribed antidepressants, while their exact molecular and cellular mechanism are yet to be defined. We investigated the involvement of HDAC1 and eEF2 in the antidepressant mechanisms of fluoxetine using a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced depression-like behavior model.
Methods
For in vivo analysis, mice were treated with LPS (2 mg/kg BW), fluoxetine (20 mg/kg BW), HDAC1 activator (Exifone: 54 mg/kg BW) and NH125 (1 mg/kg BW). Depressive-like behaviors were confirmed via behavior tests including OFT, FST, SPT, and TST. Cytokines were measured by ELISA while Iba-1 and GFAP expression were determined by immunofluorescence. Further, the desired gene expression was measured by immunoblotting. For in vitro analysis, BV2 cell lines were cultured; treated with LPS, exifone, and fluoxetine; collected; and analyzed.
Results
Mice treated with LPS displayed depression-like behaviors, pronounced neuroinflammation, increased HDAC1 expression, and reduced eEF2 activity, as accompanied by altered synaptogenic factors including BDNF, SNAP25, and PSD95. Fluoxetine treatment exhibited antidepressant effects and ameliorated the molecular changes induced by LPS. Exifone, a selective HDAC1 activator, reversed the antidepressant and anti-inflammatory effects of fluoxetine both in vivo and in vitro, supporting a causing role of HDAC1 in neuroinflammation allied depression. Further molecular mechanisms underlying HDAC1 were explored with NH125, an eEF2K inhibitor, whose treatment reduced immobility time, altered pro-inflammatory cytokines, and NLRP3 expression. Moreover, NH125 treatment enhanced eEF2 and GSK3β activities, BDNF, SNAP25, and PSD95 expression, but had no effects on HDAC1.
Conclusions
Our results showed that the antidepressant effects of fluoxetine may involve HDAC1-eEF2 related neuroinflammation and synaptogenesis.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12974-021-02091-5.
Keywords: Fluoxetine, Neuroinflammation, Depression, Synaptogenesis, HDAC1-eEF2
Introduction
Major depressive disorders (MDD) are common but serious mood disorders, affecting millions of people worldwide [1, 2]. Despite the dramatic increase in antidepressants, present treatments are ineffective to one third of patients [3–5], indicating the urgent need for more reliable and effective antidepressants. Among the complex mechanisms, growing shreds of evidence have supported the involvement of neuroinflammation in the pathophysiology of depression [6–9]. Under stresses such as psychological stimuli and physical illness, the release of inflammatory cytokines and glial cell activation can be dramatic, leading to apoptosis, attenuating neuronal differentiation, and suppressing synaptic transmission and maintenance of long-term potentiation, and finally, result in MDD [7–13]. Thus, the questions arose whether neuroinflammation plays a causative role in the pathophysiology of depression [7, 8, 14] and if the current antidepressants may contribute to the suppression of neuroinflammation [6, 15]. In this regard, we recently proved the antidepressive effects of melatonin via attenuating neuroinflammation and as inflammation allied autophagy impairment [15, 16].
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) are the enzymes that induce the deacetylation of histone protein at lysine residues. Class 1 among the 4 classes of HDACs is the most frequently studied histone modifier and transcriptional repressor [17, 18]. Dysregulation of HDACs leads to deacetylation and acetylation impairment which may be involved in the pathological process of diseases including depression [19–21]. HDACs control chromatin architecture around the genes, which are involved in the pathophysiology of depression and the action mechanism of antidepressants [22, 23]. Likely, HDAC2-mediated H3 acetylation in the nucleus accumbent is involved in depression through long-lasting positive neuronal adaptations [24]. Furthermore, accumulating evidence supports the role of HDACs in innate immunity, which acts both as a positive and negative regulator of Toll-like receptors (TLR) signaling [25, 26]. HDAC deacetylates LPS-acetylated mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase (MKP)-1, which then sustains p38 activation and promotes TLR-inducible inflammatory response [27, 28]. However, although preclinical tests show the potential of HDACs inhibitors as antidepressants [21, 24, 29], none of them has been applied in clinical treatment due to the lack of selectivity and risk of serious adverse events [19]. Thus, delineating the etiological role of specific HDAC isoforms would facilitate the application of novel and highly selective HDAC modulators in depression.
Recent evidence indicates that dysregulation of key synaptic protein synthesis and related dendritic and spine complexity underlies the core pathology of depression [30]. Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (eEF2) is known to be at least partially involved in the peptide-chain elongation process of protein synthesis upon stimulation of diverse stimuli [31]. Also, ketamine failed to induced its antidepressant effects in animals pre-treated with protein synthesis inhibitors, suggesting that eEF2-induced translation possibly driven by BDNF (Brain-derived neurotrophic factor) is important to the antidepressant action of ketamine [32]. Interestingly, in response to stresses including mTORC1 (mammalian target of rapamycin) inhibition, eEF2K can be activated, followed by eEF2 phosphorylation and inhibition, eventually leading to reduced protein translation [33–35]. Thus, enhancing eEF2 activity by antidepressants might be a crucial strategy against depression.
Fluoxetine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRIs) and has been clinically widely used for depression [36–38]. It is postulated that fluoxetine and other SSRIs modulate serotonin levels at the central nervous system’s synaptic level to regulate mood disorders [39, 40]. Later studies reveal that fluoxetine also exerts neuroprotective [41], anti-cancer [42, 43], and anti-inflammatory effects [41, 44]. Additional mechanistic results demonstrate that independent of serotonin level adjustment, and fluoxetine treatment promotes neuroplasticity via tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB)/BDNF [45] and neurogenesis via glycogen synthase kinases (GSK-3β)/β-catenin signaling pathway [46], which may also contribute to its antidepressant effects. Although previous studies demonstrate HDAC activity involvement in anti-depression [29, 47], and HDAC inhibition can re-boost the antidepressant effect of fluoxetine [48, 49], the detailed link between specific HDAC subtypes and how it contributes to the antidepressant effects of fluoxetine are yet unknown. Here, we demonstrated that HDAC1-eEF2 activation led to increased synaptogenesis, which may underlie the antidepressant effects of fluoxetine. These results may shed further insights into the molecular mechanism of fluoxetine and may provide alternative strategic clues for the HDAC1 inhibitors as novel antidepressants.
Materials and methods
Animal and drug treatment
Adult C57BL/6J male mice weighing 25–30 g (12–14 weeks) were purchased from Guangdong Medical Laboratory Animal Center, China. The experimental animals were housed at Laboratory Animal Research Center, Peking University Shenzhen Graduate School, under 12-h light/12 h dark cycle at 18–22 °C and had free access to diet and tap water throughout the study. The experimental procedures were set in such a way to minimize mice suffering. All experimental procedures were carried out according to the protocols approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Peking University Shenzhen Graduate School.
The study was conducted into three experiments.
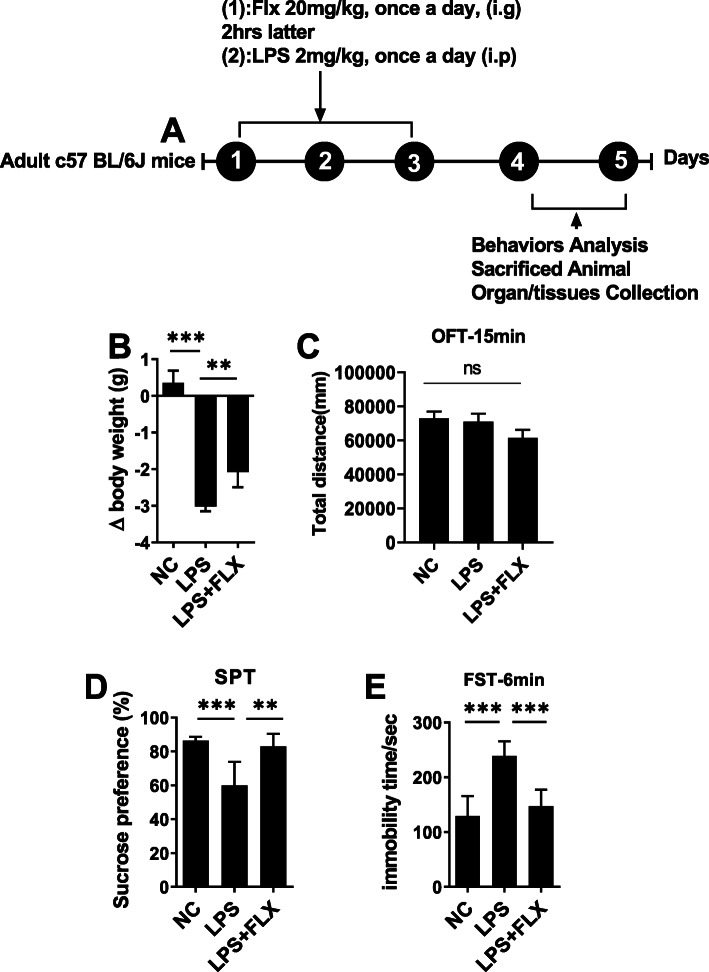
In the first experiment, animals were divided into three groups (8–10 each group): saline-treated, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (2 mg/kg/day, intraperitoneally), and LPS+ fluoxetine (20 mg/kg/day, orally). The drug treatment schedule has been shown in Fig. 1a. The LPS and fluoxetine dose were based on the previous study. After 24 h of the last LPS injection, mice were sacrificed after behaviors analysis (described in detail below). Serum and brain tissues were collected and stored at freezing temperatures (− 80 °C) until further investigation.
Fig. 1.
Fluoxetine reduced LPS-induced depressive-like behaviors. a Drug treatment schedule, b relative body weights, c open field test OFT, d forced swimming test, and e sucrose preference test. All the values are expressed as mean ± SEM: ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001
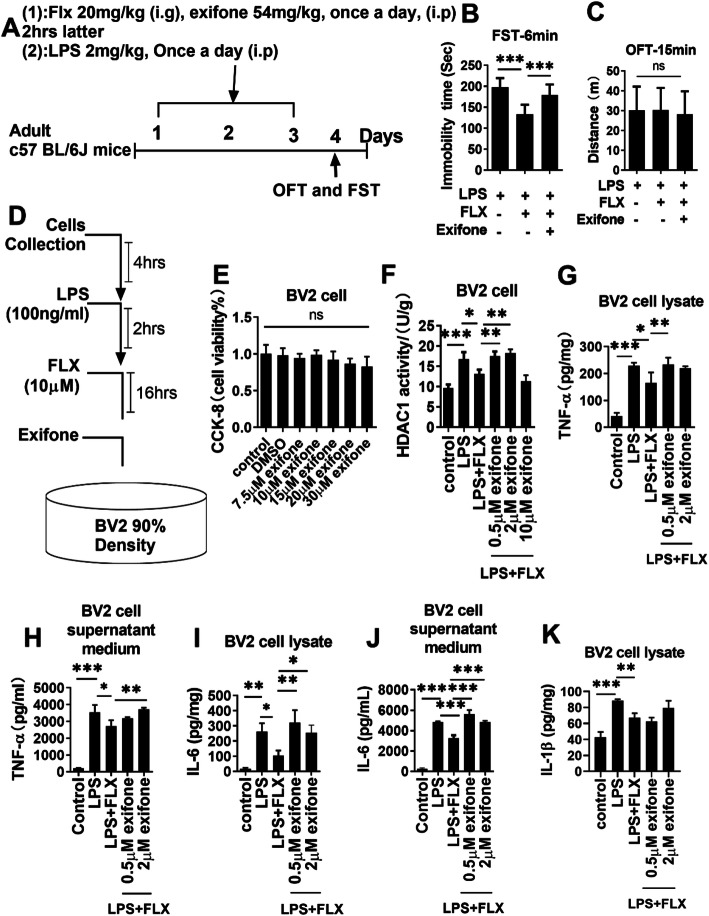
To explore the HDAC1 role in LPS-induced depression, a new experiment was planned, and mice were treated with an HDAC1 activator (exifone). The animal groups were saline-treated, LPS-treated, LPS+ fluoxetine+ exifone (54 mg/kg/day, i.p). The drug treatment schedule (Fig. 6a) was the same as above.
Fig. 6.
Exifone treatment reversed the neuroprotective effect of fluoxetine. a Drug treatment schedule, b FST, c OFT, d BV-2 cell drug treatment schedule, e BV-2 cell viability assay, f HDAC1 activity in exifone, LPS, and fluoxetine-treated BV-2 cells, g TNF-α level in cell lysate, h TNF-α in cell supernatant, i IL-6 level in cell lysate, j IL-6 in cell supernatant, k IL-1β level in exifone, LPS, and fluoxetine-treated BV-2 cell lysates. Data were expressed as ± SEM, one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis. p = < 0.05 were considered significant. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01), ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001
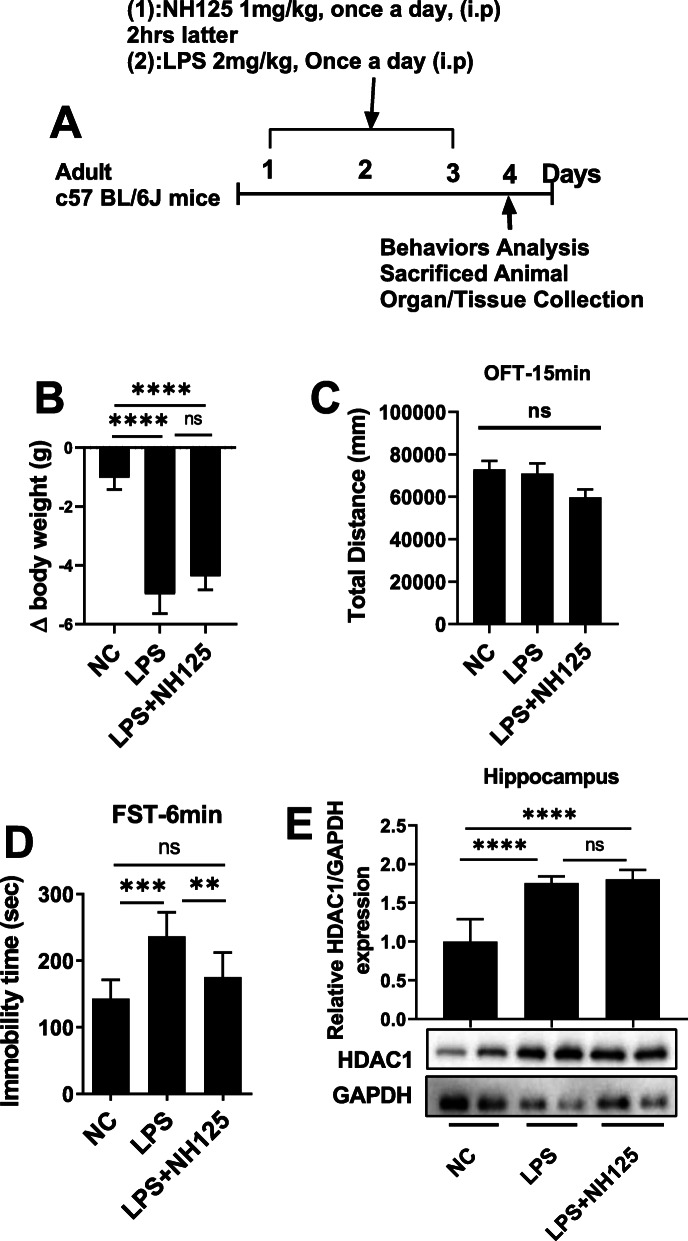
Further, to examine the association of HDAC1 and eERF2, a new experiment was designed, and mice were grouped: saline-treated, LPS-treated, LPS+ NH125 (1 mg/kg/day, i.p). The further drug treatment schedule (Fig. 8a) and behavior, as well as the organ collection process, were the same as above.
Fig. 8.
NH125 reduced LPS-induced changes. a Drug treatment schedule, b relative body weights, c OFT, d FST, e average protein level of HDAC1, and western blot image, normalized by GAPDH. Image Lab Software was used for blot quantitative analysis and was analyzed via GraphPad prism. Data were expressed as ± SEM, one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis. p = < 0.05 were considered significant. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01), ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001
Open field test (OFT)
To eliminate the animal sickness factors and avoid the biases due to sickness and blunted behaviors induced by LPS, OFT was performed according to the previously developed protocols [50]. Briefly, mice were adapted to the experimental room for 1 h and were placed in the chamber of 45× 45 × 30 cm. A total of a 15-min video was recorded to observed the mice locomotor activity. The total distance covered by mice was measured, analyzed, and expressed in meters.
Sucrose preference test
A sucrose preference test was performed while using a two-bottle free-choice paradigm. Mice were habituated with a 1% sucrose solution for 3 days and finally grouped randomly. To assess the individual sucrose intake, mice were deprived of water and food for 24 h on the 3 days of drug administration. On the next day, each mouse had free access to two bottles containing sucrose and water, respectively. The position of water and sucrose-containing bottles were changed after 12 h. Finally, the volume of consumed water and sucrose solution were recorded and calculated by the following formula:
Forced swimming test (FST)
The forced swimming test (FST) was performed according to previously developed protocols [51]. The experimental animals were trained for swimming and pre-experiment FST was performed to select healthy and normal mice. To perform the FST, the animals were placed in a Plexiglas cylinder (height: 70 cm, diameter: 30 cm) filled with water over the 30 cm level at a temperature of 23 ± 1 °C. The video was taped for 6 min and the last 5 min were blindly analyzed. Mice were considered immobile when they remained floating motionless in the water and just making a move to keep their nose above the water surface. The horizontal movement of the animals throughout the cylinder was defined as swimming while vertical movement against the wall of the cylinder was defined as climbing. EthoVision XT was used to record the video and analysis.
Tail suspension test (TST)
The tail suspension test was performed as described previously as [50, 52]. Briefly, the mice the upside down about 40 cm above the floor by placing adhesive tape 1 cm from the tail tip. The immobility time was scored for the first 2 min of the total 4-min video. EthoVision XT software was used for TST recording and analysis.
BV2 cell line culture protocol and stimulation
Mouse microglial BV2 cell lines were grown in high glucose Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Gibco, Waltham, MA). The cells were maintained in a humidified incubator with 95% air and a 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37 °C. Medium containing the appropriate agents was replaced every other day. When the cells grew to a density of about 90%, exifone was added to the cell medium, fluoxetine was added to the cell culture after 16 h, lipopolysaccharide was added after 2 h, and cells were harvested after 4 h.
Cell viability
Cell viability using cell counting kit-8 of MedChemExpress (Monmouth Junction, NJ, USA). Briefly, inoculate cell suspension (100 μL/well) in a 96-well plate. Add different concentration exifone to cell medium, pre-incubated the plate in a humidified incubator at 37 °C, 5% CO2. After 20 h, add 10 μL of the CCK-8 solution to each well of the plate. Then incubate the plate for 1–4 h in the incubator, measure the absorbance at 450 nm using a microplate reader.
Short hairpin (sh)RNA expression constructs and treatment
shRNA plasmid coding for HDAC 1 was purchased from Haixing Biosciences (88 keling Road, Huqiu District, Suzhou, Jiangsu, China. The shRNA targeting HDAC1 had the sequence 5′-GCTGGAAAGGCAAGTATTATCGAGATAATACTTGCCTTTGCCAGC-3′. The scrambled RNA sequence, used as a control, had the sequence 5′-CCTAAGGTTAAGTCGCCCTCGCTCGAGCGAGGGCGACTTAACCTTAGG-3. The plasmid (2.5 μg/well) containing shRNA was transfected to BV2 cells. After 30 h, the BV2 cells were treated with LPS (100 ng/ml). Finally, after 4 h of LPS treatment, cells were collected and proceeded for further analysis.
Nitric oxides and H2O2 measurement
The level of NO and H2O2 was analyzed by a commercially available kit (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, China, CAT# S0021M, and CAT# S0038, respectively) [53, 54] and measured the absorbance at 540 nm using a microplate reader (Biorad-Benchmark, USA).
TBAR assay
TBARS level was estimated [55] to determine the damage to lipids caused by reactive oxygen species in various experimental groups. Briefly, 0.1 ml of sample, 0.1 ml FeSO4, 0.1 ml Tris-HCl, 0.6 ml distilled water, and 0.1 ml ascorbic acid were incubated at 37 °C in a test tube 15 min, and then 1 ml TCA and 2 ml TBA were added. These plugged test tubes were incubated for 15 min at 100 °C followed by centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 10 min. The supernatant O.D. was determined at 532 nm, and the following formula was applied to estimate TBARS as nM/mg protein: TBARS (nM/mg protein) = O.D × total volume × sample volume × 1.56 × 105 × mg protein/ml (1.56 × 105 = molar extinction coefficient).
ELISA
The frozen hippocampal and cortical tissue was lysed with RIPA buffer and homogenized on ice. Supernatants were collected after centrifugation and stored at freezing temperature for further analysis. The expression of cytokines was quantified using ELISA kits (ABclonal) according to the manufacturer’s protocols. Briefly, after washing the wells of 96-well plate, 100 μL standard/sample was added and incubated for 2 h at 37 °C. The plate was then washed, and a biotin-conjugated antibody (1:30) was added to each well. The plate was incubated for 1 h at 37 °C. streptavidin-HRP was added for 30 min at 37 °C. Finally, the reaction was stopped and the optical density was measured accordingly.
Immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence staining was performed according to previously reported protocols [56]. Briefly, brain tissue sections (20-μm thick) were washed with PBS for 15 min (5 min × 3). After washing, the sections were treated with blocking buffer (10% goat serum in 0.3% Triton X-100 in PBS) for 1 h at room temperature. After blocking, the tissue was treated with primary antibodies (Iba1, GFAP) for overnight at 4̊ °C. The next day, secondary antibodies (Alexa Flour secondary antibodies, ThermoFisher) were applied at room temperature for 1 h. The sections were washed with PBS for 5 min three times. After washing, the sections were transferred to slides, and glass coverslips were mounted using the mounting medium. The images were taken under inverted fluorescence microscope I X73 Olympus.
Golgi staining
The FD Rapid GolgiStain Kit (FD NeuroTechnologies, Ellicott City, MD) was used to perform Golgi staining. Briefly, after removing, the animal brain was rinse quickly in double distilled water, immersed impregnation solutions (A/B) (5 ml solution for each tissue), and store at room temperature for 2 weeks. The brain tissues were transferred to solution C and store for 72 h (the solution was replaced after 24 h), followed by freezing. After that, 100- to 200-μm sections were prepared using a sliding microtome and mount to gelatin-coated microscope slides. Then, the brain tissue was placed in staining solution for 10 min and rinsed with double distilled water, followed by dehydration (sequential rinse 50%, 75%, and 95% ethanol) and xylene treatment. Finally, examined under inverted fluorescence microscope IX73 Olympus.
Western blotting
According to the developed protocols, western blotting was performed. Briefly, denatured samples (boiled at 100 °C for 10 min) were separated on SDS-PAGE and then transferred to the nitrocellulose membrane. The membrane was blocked in with non-fat milk in TBST (tris-buffered saline, 0.1% Tween 20), then incubated in primary antibody (1: 500; 1:1,000) (list of antibodies with dilution used, Suplementraty data), overnight at 4 °C. The next day, the membrane was treated with a secondary antibody (1:1000) for 1 h at 4 °C. For detection, the ECL super signal chemiluminescence kit was used according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Blots were developed using Chemidoc mp Bio-red. The densitometry analysis of the bands was performed using Image Lab Software.
Statistical analysis
Western blot bands and morphological data were analyzed using ImageJ and Image Lab Software (Image J 1.30) and analyzed by SPSS Statistics 21 (IBM, US) and GraphPad Prism 8 software. Data were presented as mean ± SEM. Before analysis, data normality tests were performed for all behavior tests (Fig. S4). One-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey’s multiple comparison tests were performed to compare different groups. P < 0.05 was regarded as significant. *p< 0.05, **p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001, and ****p < 0.00001.
Results
Fluoxetine reduced LPS-induced depressive-like behavior
LPS is a well-established inflammatory agent and widely employed to induce depressive-like behavior [51, 57]. Herein, to study the antidepressant role of fluoxetine, we examined LPS-treated animals in validated paradigms, including body weight (Fig. 1b), open field test (Fig. 1c), immobility (Fig. 1d), and sucrose preference (Fig. 1e) for depression-like behaviors. As shown in Fig. 1, LPS-treated mice showed decreased body weight and sucrose preference of less than 65% for a 1% sucrose solution; however, after fluoxetine treatment, body weights, and sucrose preference were significantly recovered. In the forced swimming test, the immobility time was increased in LPS-treated mice, which was reversed by fluoxetine treatment.
Fluoxetine abolished LPS-induced neuroinflammation
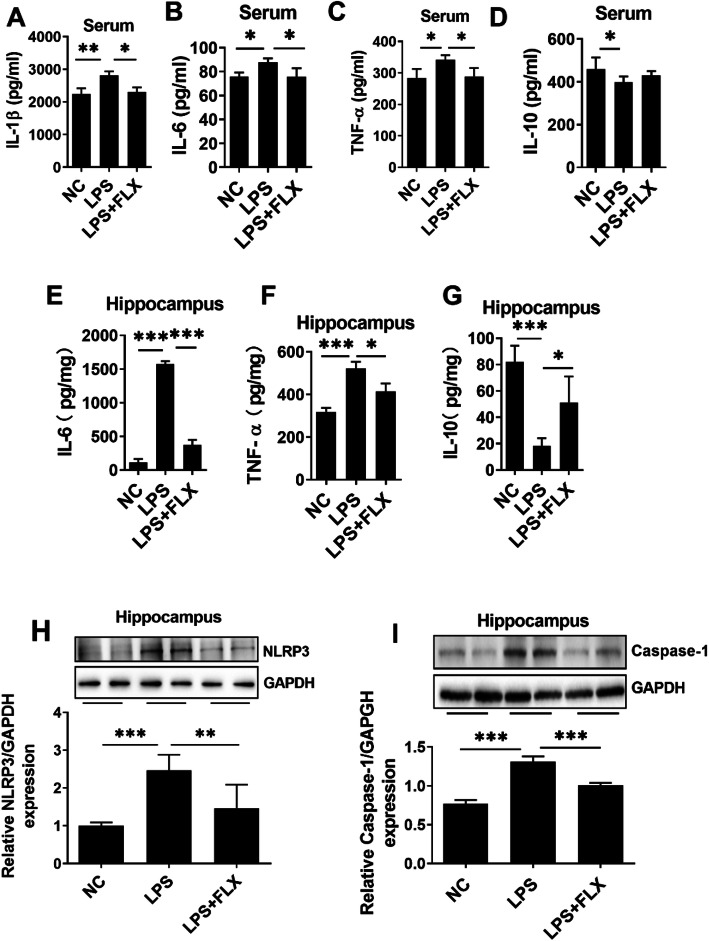
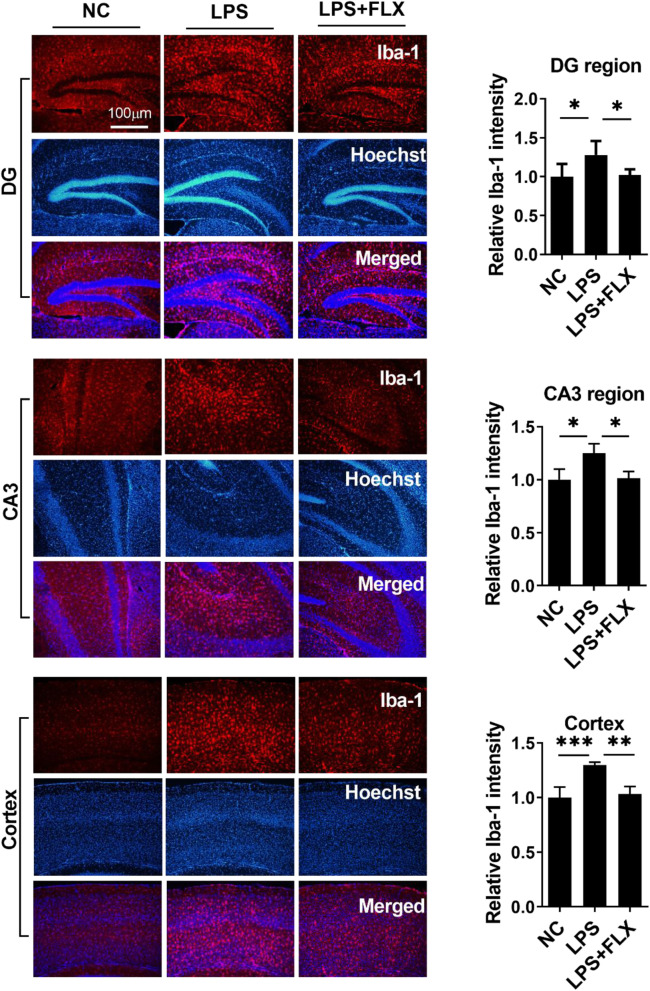
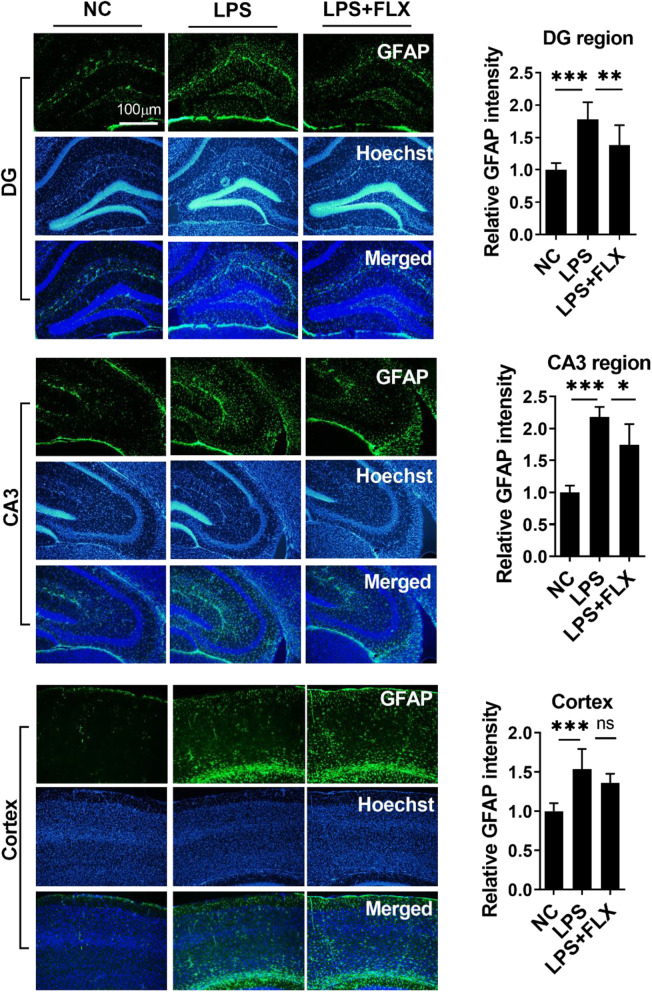
We then evaluated the anti-inflammatory effects of fluoxetine. LPS administration enhanced the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines including tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α), interleukin 1β (IL-1β), interleukin 6 (IL-6), and oxidative stress (Fig. S1) and reduced anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 level in the serum and hippocampus of the experimental animals (Fig. 2a–g). Further, NLR family pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3)-mediated neuroinflammation plays a key role in neurological disorders including MDD [58]. LPS treatment significantly enhanced NLRP3 and caspase-1 expression in the hippocampus (Fig. 2h and i), which is responsible for the maturation of cytokine such as IL-β and finally leads to pyroptosis [59]. To further corroborate LPS-induced neuroinflammation, we measured ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1 (Iba-1) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) expression in the hippocampus and the prefrontal cortex regions (Figs. 3 and Fig. 4). Our immunofluorescence results indicated that LPS-treatment significantly enhanced Iba-1 and GFAP expression in DG and CA3 regions of the hippocampus, as well as in the prefrontal cortex region. Interestingly, fluoxetine treatment reversed the above LPS-induced changes including increased pro-inflammatory cytokines, decreased anti-inflammatory cytokine, increased NRLP3, caspase-1, Iba-1, and GFAP expression, suggesting the strong anti-inflammatory effects of fluoxetine.
Fig. 2.
Fluoxetine reduced LPS-induced neuroinflammation. a Serum IL-1β, b serum IL-6, c serum TNF-α, d serum IL-10 level, e hippocampal IL-6, f hippocampal TNF-α, g hippocampal IL-10, h NLRP3 level column graph, and representative western blots for mice treated with LPS and fluoxetine. i Total level of caspase-1 and representative western blots. All the values were normalized with GAPDH. Image Lab Software was used for blots quantitative analysis and was analyzed via GraphPad prism. Data were expressed as ± SEM, one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis. p = < 0.05 were considered significant. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001
Fig. 3.
Fluoxetine reduced LPS effect on Iba-1 expression. Microscopy results of Iba-1 expression in the different experimental groups of brain tissues, with respective bar graphs (n = 6), x10 magnification. The image data were collected from three independent experiments and were analyzed by ImageJ software. The differences have been shown in the graphs. Data were expressed as ± SEM, one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis. p = < 0.05 were considered significant. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01), ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001
Fig. 4.
Fluoxetine reduced LPS effect on GFAP. Microscopy results of GFAP expression in the different experimental groups of brain tissues, with respective bar graphs (n = 7), x10 magnification. The image data were collected from three independent experiments and were analyzed by ImageJ software. The differences have been shown in the graphs. Data were expressed as ± SEM, one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis. p = < 0.05 were considered significant. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001
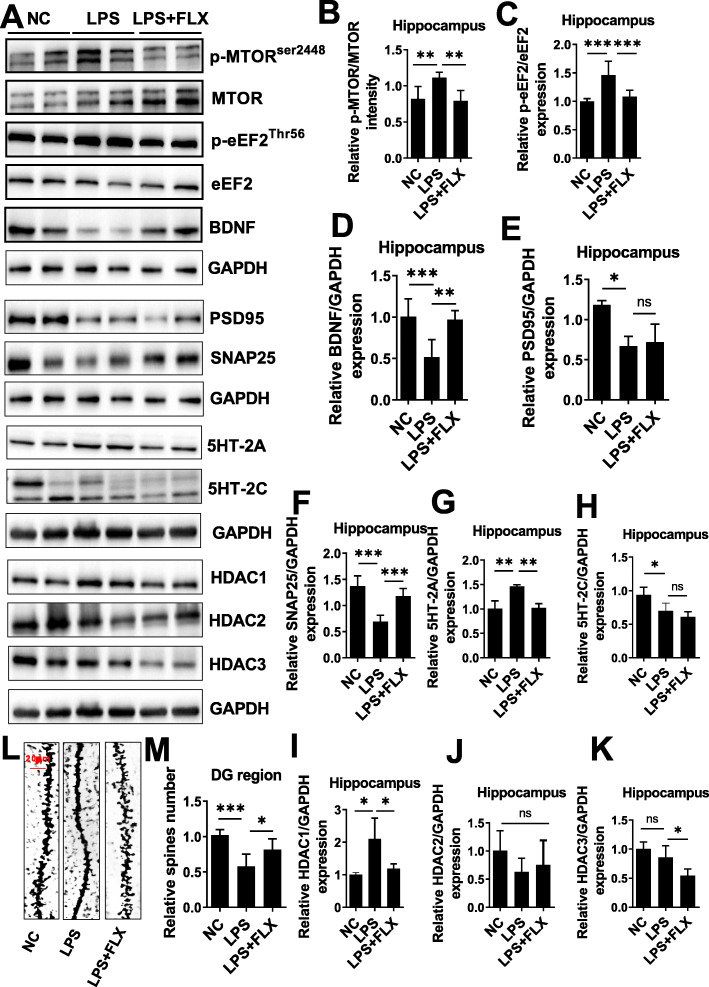
Fluoxetine improved LPS-dysregulated synaptogenic defects via HDAC1 and eEF2 regulation
Dysregulated neurogenesis and synaptogenesis have been reported in the brain of patients with major depressive disorders and multiple molecular pathways are believed to be disrupted in these processes, including BDNF, TrkB, PSD95, and SNAP25 [30, 33, 39], [60]. Destabilized synaptogenesis has been detected during MDD along with declined BDNF and TrkB expression [61, 62]. Our results showed decreased BDNF, PSD95, and SNAP25 expression in LPS-treated mice hippocampus, while fluoxetine treatment markedly reversed these changes (Fig. 5a and d–f). Synaptogenesis-related signaling molecules such as Akt/mTOR were then examined as their activities are involved in various neurological disorders including MDD [63]. As shown in Fig. 5a, b, LPS-treatment increased mTOR phosphorylation that could be attenuated by fluoxetine administration. Similarly, as a key player in protein synthesis and possibly the core of depression, eEF2 activity and expression were then examined [30] [32, 33]. Enhanced eEF2 phosphorylation could be detected in LPS-treated mice hippocampus, which was diminished upon fluoxetine treatment (Fig. 5a, c).
Fig. 5.
Fluoxetine attenuated LPS effect on mTOR/eEF2/BDNF/SNAP25/PSD95 and HDACs. a Representative immune blot images and average protein levels of b p-mTOR, c p-eEF2, d BDNF, e PSD95, f SNAP25, g 5HT2A, and h 5HT-2C. i–k Average level of HDAC1, HDAC2, and HDAC3 levels, respectively. l, m Golgi staining showing spine density and column graph showing spin numbers. Image Lab Software was used for blot quantitative analysis and was analyzed via GraphPad prism. Data were expressed as ± SEM, one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis. p = < 0.05 were considered significant. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01), ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001
To validate the dysregulated protein synthesis and eventually the synaptic morphological changes, spine numbers were measured and analyzed with Golgi staining. Significantly reduced spines numbers (Fig. 5l, m) were found in LPS-administrated mice as compared to fluoxetine-treated animals. Furthermore, serotonin receptor changes were investigated through which fluoxetine act as an antidepressant [64, 65]. Fluoxetine treatment significantly decreased LPS-mediated 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor (5HT-2A) and 5HT-2C expression in the mice hippocampus (Fig. a, g, and h). Besides, accumulating studies show dysregulated HDACs consequently lead to impaired acetylation and deacetylation in translational control [66], which could play a key role in the pathophysiological development of MDD [67]. We then measured HDAC1, 2, and 3 expressions in the hippocampal tissues of the experimental animals. LPS administration significantly enhanced HDAC1 expression but not HDAC2 and HDAC3 expression, which could be substantially attenuated by fluoxetine (Fig. 5a, i–k).
Fluoxetine prevented neuroinflammation via HDAC1 inhibition
To further delineate the role of HDAC1 in LPS-induced neuroinflammation allied depression and the antidepressive effects of fluoxetine, exifone (Fig. 6a), a potent HDAC1 activator [68], was employed. As shown in Fig. 6b, the antidepressive effect of fluoxetine was blocked by exifone as compared to LPS-treated mice, indicating the necessity of HDAC1 in fluoxetine’s antidepressant action.
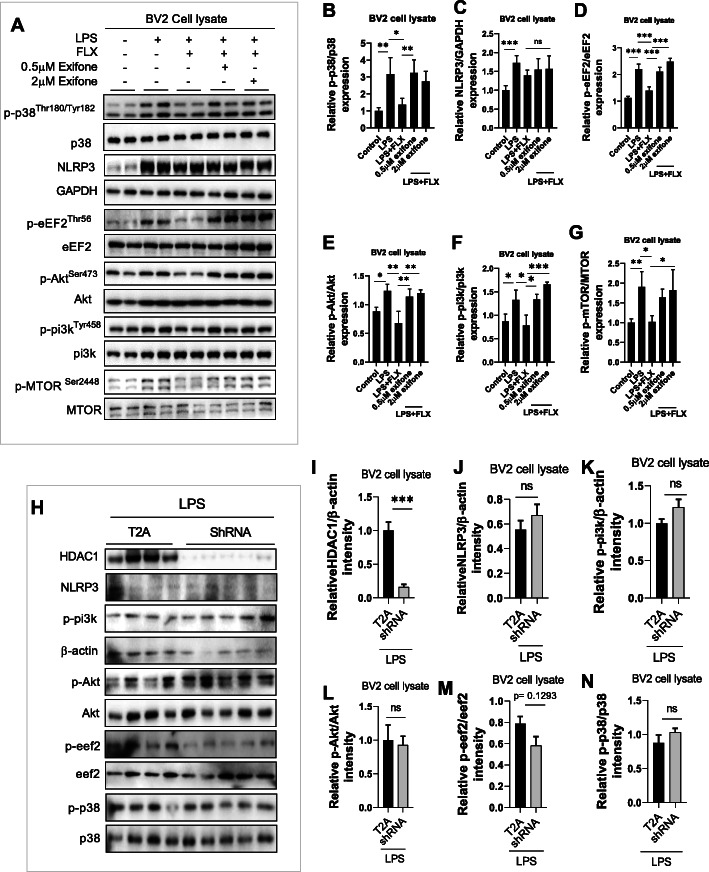
In vitro analysis was performed to further explore the roles of HDAC1 in an inflammatory response and eEF2-related protein synthesis. BV-2 murine microglial cells [69] were treated with different concentrations of exifone (0.5, 2, and 10 μM) for 16 h and then with fluoxetine (100 ng) for 2 h, followed by LPS treatment (100 ng/ml) for 4 h (Fig. 6d). After confirming cell viability (Fig. 6e), HDAC1 expression was measured in collected BV-2 cells. Interestingly, exifone reversed the suppressed HDAC1 level by fluoxetine, with the most significant effects observed at 0.5 and 2 μM.
Next, the contribution of HDAC1 in LPS-induced inflammatory response was evaluated in exifone treated BV-2 cells in the presence of LPS and/or fluoxetine. LPS treatment significantly increased pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 expression, which could be markedly reversed by fluoxetine treatment. Interestingly, the anti-inflammatory effects of fluoxetine were tremendously abolished by exifone (Fig. 6h–k), suggesting the requirement of HDAC1 in fluoxetine’s anti-inflammatory response. Interestingly, the signaling specificity of exifone was further identified with NLRP3 and p38, two distinct yet integrated molecules contributing to inflammatory responses [58, 70, 71]. Our results showed the effects of exifone were selective in that it could reverse phosphorated p38 changes (Fig. 7a, b) but not NLRP3 expression affected by fluoxetine (Fig. 7a, c), demonstrating HDAC1 was not general anti-inflammatory signaling involved in fluoxetine.
Fig. 7.
Exifone attenuated fluoxetine effects during in vitro analysis. a Representative immune blot images and average protein levels of b p-p38, c NLRP3, d p-eEF2, e p-Akt, f p-pi3k, and g p-mTOR.h Representative immune blot images and average protein levels of i HDAC1, j NLRP3, k p-pi3k, l p-Akt, m p-eeF2, and n p-p38. Image Lab Software was used for blot quantitative analysis and was analyzed via GraphPad prism. Data were expressed as ± SEM, one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis. p = < 0.05 were considered significant. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01), ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001
To validate further the role of HAC1, the proteins, including NLRP3, p-p38, p-pi3k, p-Akt, and p-eEF2 level, were measured using immunoblot in BV2 cells transfected with HDAC1 shRNA in the presence of LPS (Fig. 7h). Surprisingly, we did not find any significant changes in the expression of these proteins (Fig. 7h-n); however, decrease levels of TNF-α and IL-6 were detected in shRNA-treated BV2 cells compared to control subjects (Fig. 2i, j). It indicates that HDAC1 could play a positive role in the progression of neuroinflammation and its associated pathologies.
HDAC1-induced depressive-like behaviors were mediated by eEF2 inhibition
Previous studies suggest an association between neuroinflammation and dysregulated protein synthesis, leading to depressive-like behaviors [72]. Herein, protein synthesis regulatory factor eEF2 was measured in BV-2 cells. Exifone treatment abolished the reducing effects of fluoxetine on LPS-enhanced eEF2 phosphorylation (Fig. 7a, d). Similarly, it also diminished the reversing effects of fluoxetine on LPS-increased p-Akt/p-PI3k/p-mTOR expression (Fig. 7a, e–g), strongly supporting a pivotal role of HDAC1 in protein synthesis possibly via regulating mTOR/Akt/PI3k signaling and eEF2 activity, which may contribute to augmented synaptogenesis underlying the therapeutic mechanisms of fluoxetine.
To further evaluate whether eEF2 is a downstream target of HDAC1, animals were treated with eEF2 kinase inhibitor NH125 (Fig. 8a) [73], which may reduce eEF2 phosphorylation. NH125 treatment reduced LPS-induced immobility (Fig. 8d). At the same time, it enhanced LPS-decreased sucrose preference (Fig. S2A). However, it did not significantly alter body weights (Fig. 8b), locomotor activity (Fig. 8c), and immobility time during TST (Fig. S2B). Further results indicated that NH125-treatment did not affect HDAC1 expression (Fig. 8d), confirming that eEF2 maybe the downstream target of HDAC1.
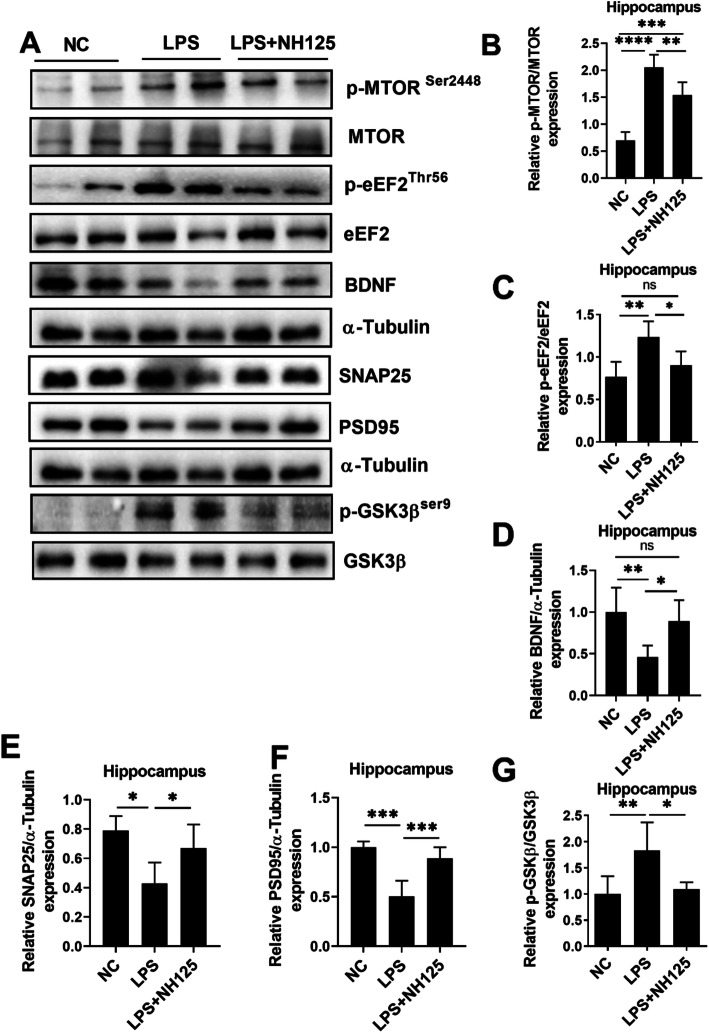
Activating mTOR rescues eEF2 from eEF2 kinase over-activating, which in turn upregulates BDNF [74, 75]. Next, we extend our investigation line to examine mTOR, BDNF, SNAP25, PSD95, and GSK3β changes after NH125 treatment. As shown in Fig. 9, NH125 treatment reduced the phosphorylation levels of eEF2 (Fig. 9a, c) and mTOR (Fig. 9a, b), while enhanced BDNF and eventually SNAP25 and PSD95 expression (Fig. 9a, d–f), suggesting an etiological role of eEF2 in LPS-induced synaptogenetic dysfunction and depression. GSK3β can activate eEF2 by reducing its phosphorylation, whereas inhibition of GSK3β can induce opposing effects [76]. Interestingly, our results also revealed that LPS treatment increased GSK3β phosphorylation and NH125 reversed the changes, indicating the possible involvement of GSK3β in eEF2 activation (Fig. 9a, g). Finally, the effects of NH125 on LPS-induced inflammation were examined to exclude its antidepressant effects via indirect anti-inflammation. Interestingly, NH125 treatment did not significantly affect LPS-altered Iba-1, IL-1β increase, GFAP, serum IL-1 β, IL-10, and IL-10 expression (Fig. S2; Fig. S3), suggesting the direct targeting of eEF2 on synaptogenesis processes.
Fig. 9.
NH125 treatment attenuated LPS-induced changes in the brain of mice. a Representative immune blot images and average protein levels of b p-mTOR, c p-eEF2, d BDNF, e SNAP25, f PSD95, and g p-GSK3β. Image Lab Software was used for blot quantitative analysis and was analyzed via GraphPad prism. Data were expressed as ± SEM, one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis. p = < 0.05 were considered significant. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01), (***) p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001
Discussion
Fluoxetine is one of the new generation antidepressants and the most commonly prescribed medicine for treating depression [77]. However, its efficacy and tolerability are controversial. Studies demonstrate variable and incomplete efficacy of fluoxetine, as 30–40% of depression patients do not show a significant response while 60–70% of patients do not experience remission [77–80]. Furthermore, previous results studying the molecular and cellular mechanisms of fluoxetine show ambiguous results of BDNF level and neurogenesis [78, 79], [80], [81–85], demanding further investigations to delineate the pharmacological basis of fluoxetine. Here, we demonstrated that apart from inhibiting neuroinflammation, fluoxetine could restore HDAC1-eEF2 activity (phosphorylation), which eventually reversed synaptogenic loss and depression-like phenotypes. These results not only for the first time, presented a novel antidepressant mechanism of fluoxetine but also offered an alternative choice to explore further therapeutic targets in depression.
Previous preclinical and clinical data support a strong association between neuroinflammation and depression [7, 9, 15, 74, 86]. Elevated cytokines are first recorded in patients with mood disorders, including MDD [87, 88]. Besides, the therapeutic effects of antidepressant and anti-inflammatory treatments against infection-induced sicknesses allied depressive-like symptoms further support the causal relation between neuroinflammation and depression [89–91]. HDACs play a critical role in immunity and regulate pleural TLR-targeted gene expressions [25, 92]. Although HDACs inhibition reduces inflammatory responses evoked by inflammatory agents like LPS [93], and altered HDACs including HDAC1 expression has been reported in the brain of patients with MDD [94, 95], the exact roles of HDACs in neuroinflammation and depression are still largely unknown. Elucidation of the etiological contribution of specific HDACs is essential for the development of novel therapeutic targets. Our findings of the anti-inflammatory activity of fluoxetine and its blockade by HDAC1 activator exifone strongly suggested HDAC1 in LPS-induced neuroinflammation. Additionally, exifone-induced alterations in mTOR/Akt/PI3k signaling and eEF2 activity further supported HDAC1 in the synaptogenesis associated with neuroinflammation-induced depression. It is yet unknown how HDAC1 modulated the transcription and translation processes. Previous studies examining the antidepressant effects of HDAC inhibitors suggest molecular adaptation in the brain, which might be due to chromatin remodeling by HDACs [29, 48, 49, 96]. Indeed, HDAC-induced acetylation is long proposed as a promising target for the novel treatment of psychiatric disorders, including MDD [24, 97]. Our findings supported a significant role of HDAC1 signaling in the pathophysiology of neuroinflammation-related depression. Further, a substantial role of HDAC1 has also been reported, as HDAC1 inhibitor treatment removes acetyl groups from histone, resulting in improved symptoms in different inflammatory diseases [98–100]. Herein, after blocking HDAC1 via shRNA, we did not detect any significant changes in the expression of genes, including NLPR3, p-p38, p-pi3k, and eEF2 involved in the molecular mechanism of neuroinflammation and its associated pathologies. Thus, it indicates that HDAC1 could play a positive role in accelerating neuroinflammation under LPS-induced stress conditions.
Dysregulated protein synthesis can play a crucial role in reduced synaptogenesis in the response of diverse stimuli, leading to depression. eEF2 contributes a significant part to the translational control of protein synthesis. Our results showed that LPS reduced eEF2 activity in the hippocampus and cortex, which could be reversed by fluoxetine through HDAC1. eEF2 is one of the downstream signaling molecules of mTOR and can be activated by eEF2K suppression [101]. Besides, mTOR serves as a kinase hub that can be activated by neurotransmitters and growth factors via PI3K/Akt signaling [102] and regulates post-synaptic protein translation to influence synaptogenesis [103].
Furthermore, eEF2 signaling regulates BDNF/TrkB protein synthesis, leading to BNDF suppression followed by depressive-like behaviors [61, 75, 104]. Accordingly, in our study, LPS-administration enhanced mTOR phosphorylation and altered synaptogenesis as demonstrated by reduced BDNF, PSD95, SNAP25, and spine numbers, which can also be abolished by fluoxetine treatment. In agreement with our findings, HDAC1 activity can be inhibited via PI3K/Akt signaling activation which might be dependent on GSK3β activity [105–108].
Disturbed protein synthesis and dysregulated synaptogenesis contribute to the pathogenesis of depression, as chronic stress can lead to synaptogenesis disruption [75, 89, 104, 109, 110], and fewer synapses and decreased synaptic protein have been reported in the brain of a patient with MDD [111, 112]. Antidepressants including SSRI (fluoxetine) trigger protein synthesis to increase dendritic growth and branching along with synaptic markers of PSD95 and synaptophysin in mTOR independent manner [102, 111]. Besides, disrupted BDNF/TrkB signaling under stress conditions causes a reduction of ERK/Akt signaling [109], which then influences synaptic maturation and stability via protein synthesis regulation [109, 113]. Our findings showed that NH125 disinhibited eEF2 (reduced phosphorylation) via suppression of eEF2 kinases increased BDNF, SNAP25, and PSD95 expression, as well as GSK3β activity in the hippocampus of the brain. These results suggested that disturbed signalings may cause synapse shrank and underline the pathological basis of depression, while strategies augmenting new spine formation would attenuate MDD-associated symptoms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, our results demonstrated that increased HDAC1 expression contributed to neuroinflammation associated with MDD via inhibition of eEF2 activity and associated synaptogenesis. Fluoxetine could reverse these effects via increasing HDAC1-eEF2 activity and synaptogenesis, which ultimately abolished depressive-like symptoms besides its anti-inflammatory effects.
Supplementary Information
Acknowledgements
Shenzhen-Hong Kong Institute of the Brain Science-Shenzhen Fundamental Research Institutions, Shenzhen, 518055, China
Abbreviations
- HDACs
Histone deacetylases
- LPS
Lipopolysaccharides
- CNS
Central nervous system
- MDD
Major depressive disorder
- ROS
Reactive oxygen species
- AKT
Serine-threonine protein kinase
- GSK3
Glycogen synthase kinase 3
- PIK3
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- NF-κB
Nuclear Factor Kappa B Subunit
- BDNF
Brain-derived neurotrophic factors
- TrkB
Tropomyosin receptor kinase B
- mTOR
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- MAPK
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase
- TLR4
Toll-like receptor 4
- IL-1β
Interleukin 1 beta
- IL-6
Interleukin 6
- TNF-α
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha
- FST
Force swimming test
- TBARs
Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substance
- ELISA
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- GFAP
Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein
- IBA1
Allograft inflammatory factor 1
- SNAP25
Synaptosome Associated Protein 25
- PSD-95
Post-synaptic density protein 95
- NLRP3
NLR family pyrin domain containing 3
- EEF2
Eukaryotic elongation factor 2
- DG
Dentate gyrus
- CA3
Cornu Ammonis
- ERK
Signal-regulated kinase
- 5HT
5-Hydroxytryptamine
- NH125
1-Benzyl-3-cetyl-2-methylimidazolium Iodide
- ANOVA
Analysis of variance
Authors’ contributions
WL designed and performed the experiments. TA analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. ZL, FAS, KH, CZ, and SUR helped in the experiment. QR, NL, and ZY helped in writing the manuscript and experimental tools and support the study. SL supported the study, corresponding authors, reviewed and approved the manuscript, and held all the responsibilities related to this manuscript. The authors reviewed and approved the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Grants Science and Technology Innovation Committee of Shenzhen No: JCYJ20170810163329510; Shenzhen-Hong Kong Institute of Brain Science No: 2019SHIBS0004; Sanming Project of Medicine in Shenzhen (No. SZSM201911003) Shenzhen Key Medical Discipline Construction Fund (No. SZXK06162)
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experimental procedures were carried out according to the protocols approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Peking University Shenzhen Graduate School.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Weifen Li, Email: 2001112065@pku.edu.cn.
Tahir Ali, Email: tali@bs.qau.edu.pk.
Chengyou Zheng, Email: zhengchengyou@pku.edu.cn.
Zizhen Liu, Email: ZzLiu@pku.edu.cn.
Kaiwu He, Email: 1701111197@pku.edu.cn.
Fawad Ali Shah, Email: fawad.shah@riphah.edu.pk.
Qingguo Ren, Email: renqingguo1976@163.com.
Shafiq Ur Rahman, Email: Shafiq@sbbu.edu.pk.
Ningning Li, Email: ningning.li@mail.com.
Zhi-Jian Yu, Email: yuzhijiansmu@163.com.
Shupeng Li, Email: lisp@pku.edu.cn.
References
- 1.Liu Q, He H, Yang J, Feng X, Zhao F, Lyu J. Changes in the global burden of depression from 1990 to 2017: findings from the Global Burden of Disease study. Journal of Psychiatric Research. 2020;126:134–140. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2019.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wang J, Wu X, Lai W, Long E, Zhang X, Li W, Zhu Y, Chen C, Zhong X, Liu Z, et al. Prevalence of depression and depressive symptoms among outpatients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2017;7:e017173. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-017173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ruberto VL, Jha MK, Murrough JW. Pharmacological treatments for patients with treatment-resistant depression. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020;13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 4.Driessen E, Dekker JJM, Peen J, Van HL, Maina G, Rosso G, Rigardetto S, Cuniberti F, Vitriol VG, Florenzano RU, et al. The efficacy of adding short-term psychodynamic psychotherapy to antidepressants in the treatment of depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. Clin Psychol Rev. 2020;80:101886. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2020.101886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ionescu DF, Rosenbaum JF, Alpert JE. Pharmacological approaches to the challenge of treatment-resistant depression. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2015;17:111–126. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2015.17.2/dionescu. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Xu X, Zeng XY, Cui YX, Li YB, Cheng JH, Zhao XD, Xu GH, Ma J, Piao HN, Jin X, Piao LX. Anti-depressive effect of arctiin by attenuating neuroinflammation via HMGB1/TLR4- and TNF-α/TNFR1-mediated NF-κB activation. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 7.Tohidpour A, Morgun AV, Boitsova EB, Malinovskaya NA, Martynova GP, Khilazheva ED, Kopylevich NV, Gertsog GE, Salmina AB. Neuroinflammation and Infection: molecular mechanisms associated with dysfunction of neurovascular unit. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017;7:276. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jeon SW, Kim YK. Neuroinflammation and cytokine abnormality in major depression: cause or consequence in that illness? World J Psychiatry. 2016;6:283–293. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v6.i3.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Singhal G, Jaehne EJ, Corrigan F, Toben C, Baune BT. Inflammasomes in neuroinflammation and changes in brain function: a focused review. Front Neurosci. 2014;8:315. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nettis MA, Pariante CM. Is there neuroinflammation in depression? Understanding the link between the brain and the peripheral immune system in depression. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2020;152:23–40. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2019.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ignácio ZM, da Silva RS, Plissari ME, Quevedo J, Réus GZ. Physical exercise and neuroinflammation in major depressive disorder. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56:8323–8335. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01670-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Guijarro-Muñoz I, Compte M, Álvarez-Cienfuegos A, Álvarez-Vallina L, Sanz L. Lipopolysaccharide activates Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway and proinflammatory response in human pericytes. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:2457–2468. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.521161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Song C, Wang H. Cytokines mediated inflammation and decreased neurogenesis in animal models of depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2011;35:760–768. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.06.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Goldwirt L, Beccaria K, Ple A, Sauvageon H, Mourah S. Ibrutinib brain distribution: a preclinical study. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018;81:783–789. doi: 10.1007/s00280-018-3546-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ali T, Hao Q, Ullah N, Rahman SU, Shah FA, He K, Zheng C, Li W, Murtaza I, Li Y, et al. Melatonin act as an antidepressant via attenuation of neuroinflammation by targeting Sirt1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020;13:96. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.00096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ali T, Rahman SU, Hao Q, Li W, Liu Z, Ali Shah F, Murtaza I, Zhang Z, Yang X, Liu G, Li S. Melatonin prevents neuroinflammation and relieves depression by attenuating autophagy impairment through FOXO3a regulation. J Pineal Res. 2020. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 17.Haberland M, Montgomery RL, Olson EN. The many roles of histone deacetylases in development and physiology: implications for disease and therapy. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10:32–42. doi: 10.1038/nrg2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Choudhary C, Kumar C, Gnad F, Nielsen ML, Rehman M, Walther TC, Olsen JV, Mann M. Lysine acetylation targets protein complexes and co-regulates major cellular functions. Science. 2009;325:834–840. doi: 10.1126/science.1175371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Misztak P, Pańczyszyn-Trzewik P, Sowa-Kućma M. Histone deacetylases (HDACs) as therapeutic target for depressive disorders. Pharmacol Rep. 2018;70:398–408. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2017.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Deussing JM, Jakovcevski M. Histone modifications in major depressive disorder and related rodent models. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;978:169–183. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-53889-1_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fuchikami M, Yamamoto S, Morinobu S, Okada S, Yamawaki Y, Yamawaki S. The potential use of histone deacetylase inhibitors in the treatment of depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2016;64:320–324. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2015.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bagot RC, Labonté B, Peña CJ, Nestler EJ. Epigenetic signaling in psychiatric disorders: stress and depression. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2014;16:281–295. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2014.16.3/rbagot. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sun H, Kennedy PJ, Nestler EJ. Epigenetics of the depressed brain: role of histone acetylation and methylation. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013;38:124–137. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Covington HE, 3rd, Maze I, LaPlant QC, Vialou VF, Ohnishi YN, Berton O, Fass DM, Renthal W, Rush AJ, 3rd, Wu EY, et al. Antidepressant actions of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Neurosci. 2009;29:11451–11460. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1758-09.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Shakespear MR, Halili MA, Irvine KM, Fairlie DP, Sweet MJ. Histone deacetylases as regulators of inflammation and immunity. Trends Immunol. 2011;32:335–343. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2011.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Aung HT, Schroder K, Himes SR, Brion K, van Zuylen W, Trieu A, Suzuki H, Hayashizaki Y, Hume DA, Sweet MJ, Ravasi T. LPS regulates proinflammatory gene expression in macrophages by altering histone deacetylase expression. Faseb j. 2006;20:1315–1327. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-5360com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Halili MA, Andrews MR, Labzin LI, Schroder K, Matthias G, Cao C, Lovelace E, Reid RC, Le GT, Hume DA, et al. Differential effects of selective HDAC inhibitors on macrophage inflammatory responses to the Toll-like receptor 4 agonist LPS. J Leukoc Biol. 2010;87:1103–1114. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0509363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cao W, Bao C, Padalko E, Lowenstein CJ. Acetylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 inhibits Toll-like receptor signaling. J Exp Med. 2008;205:1491–1503. doi: 10.1084/jem.20071728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Covington HE, 3rd, Maze I, Vialou V, Nestler EJ. Antidepressant action of HDAC inhibition in the prefrontal cortex. Neuroscience. 2015;298:329–335. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.04.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sossin WS, Heaney CF, Raab-Graham KF. Dysregulated protein synthesis in major depressive disorder. Oxford University Press. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Xie J, de Souza AV, von der Haar T, O'Keefe L, Lenchine RV, Jensen KB, Liu R, Coldwell MJ, Wang X, Proud CG. Regulation of the elongation phase of protein synthesis enhances translation accuracy and modulates lifespan. Curr Biol. 2019;29:737–749. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.01.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Suzuki K, Monteggia LM. The role of eEF2 kinase in the rapid antidepressant actions of ketamine. Adv Pharmacol. 2020;89:79–99. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2020.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sossin WS, Costa-Mattioli M. Translational control in the brain in health and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019;11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 34.Bevilaqua LRM, Cammarota M. PERK, mTORC1 and eEF2 interplay during long term potentiation: an editorial for 'Genetic removal of eIF2a kinase PERK in mice enables hippocampal L-LTP independent of mTORC1 activity' on page 133. J Neurochem. 2018;146:119–121. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hizli AA, Chi Y, Swanger J, Carter JH, Liao Y, Welcker M, Ryazanov AG, Clurman BE. Phosphorylation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (eEF2) by cyclin A-cyclin-dependent kinase 2 regulates its inhibition by eEF2 kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 2013;33:596–604. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01270-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Rebai R, Jasmin L, Boudah A. The antidepressant effect of melatonin and fluoxetine in diabetic rats is associated with a reduction of the oxidative stress in the prefrontal and hippocampal cortices. Brain Res Bull. 2017;134:142–150. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.07.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Micheli L, Ceccarelli M, D'Andrea G, Tirone F. Depression and adult neurogenesis: positive effects of the antidepressant fluoxetine and of physical exercise. Brain Res Bull. 2018;143:181–193. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Buga AM, Ciobanu O, Bădescu GM, Bogdan C, Weston R, Slevin M, Di Napoli M, Popa-Wagner A. Up-regulation of serotonin receptor 2B mRNA and protein in the peri-infarcted area of aged rats and stroke patients. Oncotarget. 2016;7:17415–17430. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Micheli L, Ceccarelli M, D’Andrea G, Tirone F. Depression and adult neurogenesis: Positive effects of the antidepressant fluoxetine and of physical exercise. Brain Research Bulletin. 2018;143:181–193. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kraus C, Castrén E, Kasper S, Lanzenberger R. Serotonin and neuroplasticity – links between molecular, functional and structural pathophysiology in depression. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews. 2017;77:317–326. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Liu FY, Cai J, Wang C, Ruan W, Guan GP, Pan HZ, Li JR, Qian C, Chen JS, Wang L, Chen G. Fluoxetine attenuates neuroinflammation in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a possible role for the regulation of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15:347. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1388-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hsu L-C, Tu H-F, Hsu F-T, Yueh P-F, Chiang IT. Beneficial effect of fluoxetine on anti-tumor progression on hepatocellular carcinoma and non-small cell lung cancer bearing animal model. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2020;126:110054. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bowie M, Pilie P, Wulfkuhle J, Lem S, Hoffman A, Desai S, Petricoin E, Carter A, Ambrose A, Seewaldt V, et al. Fluoxetine induces cytotoxic endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in triple negative breast cancer. World J Clin Oncol. 2015;6:299–311. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v6.i6.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ghosh S, Choudhury S, Chowdhury O, Mukherjee S, Das A, Sain A, Gupta P, Adhikary A, Chattopadhyay S. Inflammation-induced behavioral changes is driven by alterations in Nrf2-dependent apoptosis and autophagy in mouse hippocampus: role of fluoxetine. Cell Signal. 2020;68:109521. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2019.109521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Levy MJF, Boulle F, Emerit MB, Poilbout C, Steinbusch HWM, Van den Hove DLA, Kenis G, Lanfumey L. 5-HTT independent effects of fluoxetine on neuroplasticity. Sci Rep. 2019;9:6311. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42775-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Hui J, Zhang J, Kim H, Tong C, Ying Q, Li Z, Mao X, Shi G, Yan J, Zhang Z, Xi G. Fluoxetine regulates neurogenesis in vitro through modulation of GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014;18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 47.Muñoz-Cobo I, Erburu MM, Zwergel C, Cirilli R, Mai A, Valente S, Puerta E, Tordera RM. Nucleocytoplasmic export of HDAC5 and SIRT2 downregulation: two epigenetic mechanisms by which antidepressants enhance synaptic plasticity markers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2018;235:2831–2846. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-4975-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Schmauss C. An HDAC-dependent epigenetic mechanism that enhances the efficacy of the antidepressant drug fluoxetine. Sci Rep. 2015;5:8171. doi: 10.1038/srep08171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sarkar A, Chachra P, Kennedy P, Pena CJ, Desouza LA, Nestler EJ, Vaidya VA. Hippocampal HDAC4 contributes to postnatal fluoxetine-evoked depression-like behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014;39:2221–2232. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Zhao X, Cao F, Liu Q, Li X, Xu G, Liu G, Zhang Y, Yang X, Yi S, Xu F, et al. Behavioral, inflammatory and neurochemical disturbances in LPS and UCMS-induced mouse models of depression. Behavioural Brain Research. 2019;364:494–502. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2017.05.064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Sekio M, Seki K. Lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior is associated with α1-adrenoceptor dependent downregulation of the membrane GluR1 subunit in the mouse medial prefrontal cortex and ventral tegmental area. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015;18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 52.Steru L, Chermat R, Thierry B, Simon P. The tail suspension test: a new method for screening antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1985;85:367–370. doi: 10.1007/BF00428203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Dai X, Sun Y, Jiang Z. Protective effects of vitamin E against oxidative damage induced by Abeta1-40Cu(II) complexes. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 2007;39:123–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7270.2007.00261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Li YH, Yan ZQ, Jensen JS, Tullus K, Brauner A. Activation of nuclear factor kappaB and induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase by Ureaplasma urealyticum in macrophages. Infect Immun. 2000;68:7087–7093. doi: 10.1128/iai.68.12.7087-7093.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ali T, Waheed H, Shaheen F, Mahmud M, Javed Q, Murtaza I. Increased endogenous serotonin level in diabetic conditions may lead to cardiac valvulopathy via reactive oxygen species regulation. Biologia. 2015;70:273–278. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Shah SA, Khan M, Jo MH, Jo MG, Amin FU, Kim MO. Melatonin stimulates the SIRT 1/Nrf2 signaling pathway counteracting lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced oxidative stress to rescue postnatal rat brain. CNS neuroscience & therapeutics. 2017;23:33–44. doi: 10.1111/cns.12588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Jeon SA, Lee E, Hwang I, Han B, Park S, Son S, Yang J, Hong S, Kim CH, Son J, Yu JW. NLRP3 inflammasome contributes to lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behaviors via indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase induction. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017;20:896–906. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyx065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Zhang Y, Liu L, Liu YZ, Shen XL, Wu TY, Zhang T, Wang W, Wang YX, Jiang CL. NLRP3 inflammasome mediates chronic mild stress-induced depression in mice via neuroinflammation. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015;18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 59.Malik A, Kanneganti TD. Inflammasome activation and assembly at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2017;130:3955–3963. doi: 10.1242/jcs.207365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Hill AS, Sahay A, Hen R. Increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sufficient to reduce anxiety and depression-like behaviors. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015;40:2368–2378. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Sonoyama T, Stadler LKJ, Zhu M, Keogh JM, Henning E, Hisama F, Kirwan P, Jura M, Blaszczyk BK, DeWitt DC, et al. Human BDNF/TrkB variants impair hippocampal synaptogenesis and associate with neurobehavioural abnormalities. Sci Rep. 2020;10:9028. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65531-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Li S, Luo X, Hua D, Wang Y, Zhan G, Huang N, Jiang R, Yang L, Zhu B, Yuan X, et al. Ketamine alleviates postoperative depression-like symptoms in susceptible mice: the role of BDNF-TrkB signaling. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:1702. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.LiCausi F, Hartman NW. Role of mTOR complexes in neurogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 64.Castañé A, Kargieman L, Celada P, Bortolozzi A, Artigas F. 5-HT2A receptors are involved in cognitive but not antidepressant effects of fluoxetine. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015;25:1353–1361. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2015.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Ni YG, Miledi R. Blockage of 5HT2C serotonin receptors by fluoxetine (Prozac) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94:2036–2040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.5.2036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Saavedra K, Molina-Márquez AM, Saavedra N, Zambrano T, Salazar LA. Epigenetic modifications of major depressive disorder. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 67.Aguilar-Valles A, Haji N, De Gregorio D, Matta-Camacho E, Eslamizade MJ, Popic J, Sharma V, Cao R, Rummel C, Tanti A, et al. Translational control of depression-like behavior via phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E. Nat Commun. 2018;9:2459. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04883-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Pao P-C, Patnaik D, Watson LA, Gao F, Pan L, Wang J, Adaikkan C, Penney J, Cam HP, Huang W-C, et al. HDAC1 modulates OGG1-initiated oxidative DNA damage repair in the aging brain and Alzheimer’s disease. Nature Communications. 2020;11:2484. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16361-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Stansley B, Post J, Hensley K. A comparative review of cell culture systems for the study of microglial biology in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation. 2012;9:115. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Li D, Ren W, Jiang Z, Zhu L. Regulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and macrophage pyroptosis by the p38 MAPK signaling pathway in a mouse model of acute lung injury. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18:4399–4409. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Gee MS, Kim SW, Kim N, Lee SJ, Oh MS, Jin HK, Bae JS, Inn KS, Kim NJ, Lee JK. A novel and selective p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor attenuates LPS-induced neuroinflammation in BV2 microglia and a mouse model. Neurochem Res. 2018;43:2362–2371. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2661-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Zhao YW, Pan YQ, Tang MM, Lin WJ. Blocking p38 signaling reduces the activation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the phosphorylation of p38 in the habenula and reverses depressive-like behaviors induced by neuroinflammation. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:511. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Liu XY, Zhang L, Wu J, Zhou L, Ren YJ, Yang WQ, Ming ZJ, Chen B, Wang J, Zhang Y, Yang JM. Inhibition of elongation factor-2 kinase augments the antitumor activity of Temozolomide against glioma. PLoS One. 2013;8:e81345. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Sahin C, Dursun S, Cetin M, Aricioglu F. The neuroinflammation perspective of depression: reuniting the outstanding mechanisms of the pathophysiology. Klinik Psikofarmakoloji Bülteni-Bulletin of Clinical Psychopharmacology. 2016;26:196–206. [Google Scholar]
- 75.Monteggia LM, Gideons E, Kavalali ET. The role of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase in rapid antidepressant action of ketamine. Biol Psychiatry. 2013;73:1199–1203. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.09.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Karyo R, Eskira Y, Pinhasov A, Belmaker R, Agam G, Eldar-Finkelman H. Identification of eukaryotic elongation factor-2 as a novel cellular target of lithium and glycogen synthase kinase-3. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2010;45:449–455. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2010.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Alboni S, van Dijk RM, Poggini S, Milior G, Perrotta M, Drenth T, Brunello N, Wolfer DP, Limatola C, Amrein I, et al. Fluoxetine effects on molecular, cellular and behavioral endophenotypes of depression are driven by the living environment. Molecular Psychiatry. 2017;22:552–561. doi: 10.1038/mp.2015.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Bessa J, Ferreira D, Melo I, Marques F, Cerqueira JJ, Palha JA, Almeida O, Sousa N. The mood-improving actions of antidepressants do not depend on neurogenesis but are associated with neuronal remodeling. Molecular psychiatry. 2009;14:764–773. doi: 10.1038/mp.2008.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Rygula R, Abumaria N, Flügge G, Hiemke C, Fuchs E, Rüther E, Havemann-Reinecke U. Citalopram counteracts depressive-like symptoms evoked by chronic social stress in rats. Behav Pharmacol. 2006;17:19–29. doi: 10.1097/01.fbp.0000186631.53851.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Malberg JE, Eisch AJ, Nestler EJ, Duman RS. Chronic antidepressant treatment increases neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus. Journal of Neuroscience. 2000;20:9104–9110. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-24-09104.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.David DJ, Samuels BA, Rainer Q, Wang J-W, Marsteller D, Mendez I, Drew M, Craig DA, Guiard BP, Guilloux J-P. Neurogenesis-dependent and-independent effects of fluoxetine in an animal model of anxiety/depression. Neuron. 2009;62:479–493. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.04.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Brenes JC, Fornaguera J. The effect of chronic fluoxetine on social isolation-induced changes on sucrose consumption, immobility behavior, and on serotonin and dopamine function in hippocampus and ventral striatum. Behavioural brain research. 2009;198:199–205. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2008.10.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Jacobsen JPR, Mørk A. The effect of escitalopram, desipramine, electroconvulsive seizures and lithium on brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA and protein expression in the rat brain and the correlation to 5-HT and 5-HIAA levels. Brain research. 2004;1024:183–192. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2004.07.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Prendergast MA, Yells DP, Balogh SE, Paige SR, Hendricks SE. Fluoxetine differentially suppresses sucrose solution consumption in free-fed and food-deprived rats--reversal by amantadine. Medical Science Monitor. 2002;8:BR385–BR390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Zetterstrom T, Pei Q, Madhav T, Grahame-Smith D. Manipulation of brain 5-HT levels affects gene expression for BDNF in rat brain. Brit J Pharmacology-Proceedings Supplement. 1998;231P. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 86.Miller AH, Maletic V, Raison CL. Inflammation and its discontents: the role of cytokines in the pathophysiology of major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2009;65:732–741. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.11.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Nanni V, Uher R, Danese A. Childhood maltreatment predicts unfavorable course of illness and treatment outcome in depression: a meta-analysis. Am J Psychiatry. 2012;169:141–151. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11020335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Kreisel T, Frank MG, Licht T, Reshef R, Ben-Menachem-Zidon O, Baratta MV, Maier SF, Yirmiya R. Dynamic microglial alterations underlie stress-induced depressive-like behavior and suppressed neurogenesis. Mol Psychiatry. 2014;19:699–709. doi: 10.1038/mp.2013.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Kappelmann N, Lewis G, Dantzer R, Jones PB, Khandaker GM. Antidepressant activity of anti-cytokine treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials of chronic inflammatory conditions. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23:335–343. doi: 10.1038/mp.2016.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Köhler O, Benros ME, Nordentoft M, Farkouh ME, Iyengar RL, Mors O, Krogh J. Effect of anti-inflammatory treatment on depression, depressive symptoms, and adverse effects: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. JAMA Psychiatry. 2014;71:1381–1391. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.1611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.O'Connor JC, Lawson MA, André C, Moreau M, Lestage J, Castanon N, Kelley KW, Dantzer R. Lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior is mediated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activation in mice. Mol Psychiatry. 2009;14:511–522. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4002148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Adcock IM. HDAC inhibitors as anti-inflammatory agents. Br J Pharmacol. 2007;150:829–831. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Bode KA, Schroder K, Hume DA, Ravasi T, Heeg K, Sweet MJ, Dalpke AH. Histone deacetylase inhibitors decrease Toll-like receptor-mediated activation of proinflammatory gene expression by impairing transcription factor recruitment. Immunology. 2007;122:596–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Schroeder FA, Lewis MC, Fass DM, Wagner FF, Zhang YL, Hennig KM, Gale J, Zhao WN, Reis S, Barker DD, et al. A selective HDAC 1/2 inhibitor modulates chromatin and gene expression in brain and alters mouse behavior in two mood-related tests. PLoS One. 2013;8:e71323. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Hobara T, Uchida S, Otsuki K, Matsubara T, Funato H, Matsuo K, Suetsugi M, Watanabe Y. Altered gene expression of histone deacetylases in mood disorder patients. J Psychiatr Res. 2010;44:263–270. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2009.08.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Meylan EM, Halfon O, Magistretti PJ, Cardinaux JR. The HDAC inhibitor SAHA improves depressive-like behavior of CRTC1-deficient mice: possible relevance for treatment-resistant depression. Neuropharmacology. 2016;107:111–121. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.03.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Faraco G, Pittelli M, Cavone L, Fossati S, Porcu M, Mascagni P, Fossati G, Moroni F, Chiarugi A. Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors reduce the glial inflammatory response in vitro and in vivo. Neurobiol Dis. 2009;36:269–279. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2009.07.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Glauben R, Batra A, Fedke I, Zeitz M, Lehr HA, Leoni F, Mascagni P, Fantuzzi G, Dinarello CA, Siegmund B. Histone hyperacetylation is associated with amelioration of experimental colitis in mice. The Journal of Immunology. 2006;176:5015. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.8.5015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Tsai R-Y, Wang J-C, Chou K-Y, Wong C-S, Cherng C-H. Resveratrol reverses morphine-induced neuroinflammation in morphine-tolerant rats by reversal HDAC1 expression. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association. 2016;115:445–454. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2015.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Chung Y-L, Lee M-Y, Wang A-J, Yao L-F. A therapeutic strategy uses histone deacetylase inhibitors to modulate the expression of genes involved in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Molecular Therapy. 2003;8:707–717. doi: 10.1016/s1525-0016(03)00235-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Liu R, Proud CG. Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase as a drug target in cancer, and in cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 2016;37:285–294. doi: 10.1038/aps.2015.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Takei N, Nawa H. mTOR signaling and its roles in normal and abnormal brain development. Front Mol Neurosci. 2014;7:28. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2014.00028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Laplante M, Sabatini DM. mTOR signaling at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2009;122:3589–3594. doi: 10.1242/jcs.051011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Hoshi O, Sugizaki A, Cho Y, Takei N. BDNF reduces eEF2 phosphorylation and enhances novel protein synthesis in the growth cones of dorsal root ganglia neurons. Neurochem Res. 2018;43:1242–1249. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2541-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Del'Guidice T, Latapy C, Rampino A, Khlghatyan J, Lemasson M, Gelao B, Quarto T, Rizzo G, Barbeau A, Lamarre C, et al. FXR1P is a GSK3β substrate regulating mood and emotion processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112:E4610–E4619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1506491112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Beaulieu JM, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG. Akt/GSK3 signaling in the action of psychotropic drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2009;49:327–347. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.011008.145634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Kaidanovich-Beilin O, Milman A, Weizman A, Pick CG, Eldar-Finkelman H. Rapid antidepressive-like activity of specific glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitor and its effect on beta-catenin in mouse hippocampus. Biol Psychiatry. 2004;55:781–784. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Klein PS, Melton DA. A molecular mechanism for the effect of lithium on development. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 1996;93:8455–8459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.16.8455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Verpelli C, Piccoli G, Zibetti C, Zanchi A, Gardoni F, Huang K, Brambilla D, Di Luca M, Battaglioli E, Sala C. Synaptic activity controls dendritic spine morphology by modulating eEF2-dependent BDNF synthesis. J Neurosci. 2010;30:5830–5842. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0119-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Takei N, Kawamura M, Ishizuka Y, Kakiya N, Inamura N, Namba H, Nawa H. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhances the basal rate of protein synthesis by increasing active eukaryotic elongation factor 2 levels and promoting translation elongation in cortical neurons. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:26340–26348. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.023010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Kang HJ, Voleti B, Hajszan T, Rajkowska G, Stockmeier CA, Licznerski P, Lepack A, Majik MS, Jeong LS, Banasr M, et al. Decreased expression of synapse-related genes and loss of synapses in major depressive disorder. Nat Med. 2012;18:1413–1417. doi: 10.1038/nm.2886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Feyissa AM, Chandran A, Stockmeier CA, Karolewicz B. Reduced levels of NR2A and NR2B subunits of NMDA receptor and PSD-95 in the prefrontal cortex in major depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2009;33:70–75. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2008.10.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Fang ZH, Lee CH, Seo MK, Cho H, Lee JG, Lee BJ, Park SW, Kim YH. Effect of treadmill exercise on the BDNF-mediated pathway in the hippocampus of stressed rats. Neurosci Res. 2013;76:187–194. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2013.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].