Abstract
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are playing emerging role in the pathogenesis of cancers, but the mechanisms still unknown. In the recent issue of the Nature Communications, Chen and colleagues have demonstrated that YTHDC1 facilitates N6-methyladenosine modified circNSUN2 cytoplasmic export and the circNSUN2/IGF2BP2/HMGA2 complex stabilizes HMGA2 to promote colorectal liver metastasis. These discoveries not only expand our understanding of circRNAs biology in tumor, but also demonstrate that m6A modification plays a key role for circRNAs in RNA metabolism. Therefore, these findings indicate that circRNAs may be a new approach for therapeutic target of cancers.
Keywords: CircRNAs, Colorectal carcinoma, IGF2BP2, Metastasis, N6-methyladenosine
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been identified as a new class of small noncoding RNAs, and accumulating evidence indicates that circular RNAs (circRNAs) are dysregulated and can play a pivotal role in regulation of pathogenesis processes, including cancer.1 N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most abundant modification of RNAs, both mRNAs and noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs).2 It has been demonstrated that ncRNAs present m6A modifications.3,4 However, the effects of m6A modification for circRNAs metabolism require further exploration.
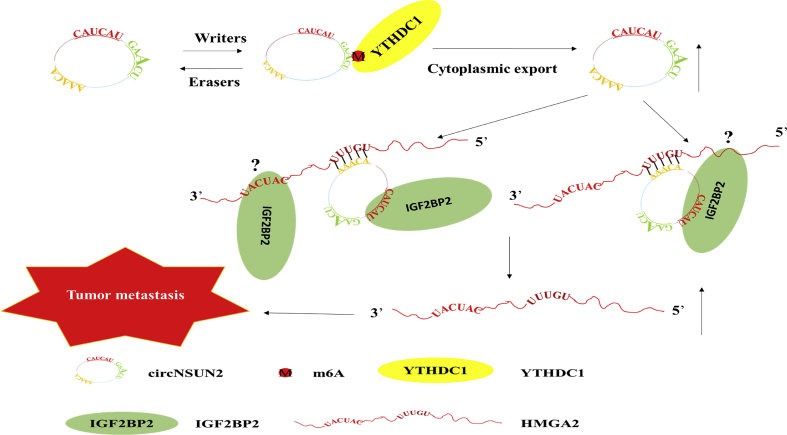
In the recent issue of the Nature Communications, Chen and colleagues demonstrated that YTHDC1 facilitates N6-methyladenosine modified circNSUN2 cytoplasmic export and the circNSUN2/IGF2BP2/HMGA2 complex stabilizes HMGA2 to promote colorectal liver metastasis.5 The authors showed that circNSUN2 promotes liver metastasis in colorectal carcinoma. YTHDC1 mediates nuclear export of circNSUN2 in an m6A methylation-dependent manner with binding the GAACU m6A motif. Moreover, circNSUN2 helps to stabilize HMGA2 mRNA by forming a circNSUN2/IGF2BP2/HMGA2 complex, which leads to the liver metastasis in colorectal carcinoma.
There were one m6A motif (GAACU), one IGF2BP2 binding motif (CAUCAU) and one HMGA2 mRNA binding site (AAACA) in circNSUN2. The authors found that IGF2BP2 interacts with the CAUCAU motif of circNSUN2, but it is yet not clear whether the motif of HMGA2 mRNA binds to IGF2BP2. We analyzed the sequence of circNSUN2 and HMGA2 mRNA, and found no GGAC motif, but there were an IGF2BP2 binding motif (CAUCAU) and a number of GGAC motifs in HMGA2 mRNA. There are two possibilities for the circNSUN2/IGF2BP2/HMGA2 complex (Fig. 1). One possibility is that circNSUN2 binds HMGA2 mRNA with AAACA site, and interacts with IGF2BP2 protein through CAUCAU, and IGF2B2P2 binds HMGA2 mRNA with other motif, such as GGAC motif. IGF2BP2 has been reported to be an m6A reader by interacting with GGAC m6A core motif.6 Interestingly, there are some GGAC motifs in HMGA2 mRNA. Another possibility is that one IGF2BP2 binds HMGA2 mRNA with CAUCAU, and another IGF2BP2 binds the CAUCAU motif of circNSUN2. If one IGF2BP2 simultaneously interacts with HMGA2 mRNA and circNSUN2 by CAUCAU, HMGA2 mRNA and circNSUN2 may competitively bind to IGF2BP2. Additional experiments must be performed to determine which motif of HMGA2 mRNA binds with IGF2BP2.
Figure 1.
Model of circNSUN2/IGF2BP2/HMGA2 axis in metastasis of colorectal carcinoma.
The discoveries of Chen and colleagues have demonstrated that circNSUN2 is a pivotal oncogenic circRNA and the biomarker of colorectal carcinoma. CircNSUN2 acts as a platform to forming a circNSUN2/IGF2BP2/HMGA2 complex and stabilizing HMGA2 mRNA. Then CircNSUN2 promotes colorectal carcinoma metastasis. In conclusion, the authors provide comprehensive evidence of the contributions of m6A modification of circRNAs to cancer therapy.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (81773165), Hunan Province Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (2018JJ1021), the Key R&D Program of Hunan Province (2017SK2172), and the Science and Technique Foundation of Chenzhou (jsyf2017023).
Footnotes
Peer review under responsibility of Chongqing Medical University.
Contributor Information
Rong-Zhang He, Email: rongzhang412@163.com.
Di-Xian Luo, Email: luodixian_2@163.com.
References
- 1.Yin Y., Long J., He Q. Emerging roles of circrna in formation and progression of cancer. J Cancer. 2019;10(21):5015–5021. doi: 10.7150/jca.30828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gilbert W.V., Bell T.A., Schaening C. Messenger rna modifications: form, distribution, and function. Science. 2016;352(6292):1408–1412. doi: 10.1126/science.aad8711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chen Y.G., Chen R., Ahmad S. N6-methyladenosine modification controls circular rna immunity. Mol Cell. 2019;76(1):96–109. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.07.016. e9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Yang Y., Fan X., Mao M. Extensive translation of circular rnas driven by n(6)-methyladenosine. Cell Res. 2017;27(5):626–641. doi: 10.1038/cr.2017.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chen R.X., Chen X., Xia L.P. N(6)-methyladenosine modification of circnsun2 facilitates cytoplasmic export and stabilizes hmga2 to promote colorectal liver metastasis. Nat Commun. 2019;10 doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12651-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Huang H., Weng H., Sun W. Recognition of rna n(6)-methyladenosine by igf2bp proteins enhances mrna stability and translation. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20(3):285–295. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0045-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]