Abstract
Purpose:
To present a patient with giant cell tumor (GCT) of the orbit by changing behavior from an intraorbital mass to an intraosseous tumor.
Methods:
A 16-year-old boy presented with pain, swelling, erythematous of the left upper and lower eyelids, proptosis, and diplopia. Ophthalmic examination revealed chemosis, conjunctival injection, limited elevation, depression as well as abduction in the left eye.
Results:
Multislice computed tomography scan (CT scan) of the orbit and paranasal sinuses showed a hyperdense, oval, extraconal mass with bone erosion. Magnetic resonance imaging of the orbit showed an inferior lateral isointense, oval, extraconal mass that had indented the globe. The patient underwent superior lateral orbitotomy, and the orbital mass was excised. Two months later, the patient developed proptosis, severe chemosis, and eyelid erythema in the same eye. CT scan showed an intraosseous mass in the lateral wall of the orbit that had pushed the globe anteromedially. Intraosseous tumor was resected, and the lateral orbital wall was drilled during the second surgery. GCT was diagnosed based on pathological survey.
Conclusion:
Following the resection of the orbital GCT, the tumor behavior may change to an intraosseous lesion.
Keywords: Diamond burr, Giant cell tumor, Intraosseous, Orbit
INTRODUCTION
Giant cell tumors (GCTs) are rare, aggressive osteoclastogenic tumors.1,2 These tumors are more prevalent between 20 and 40 years of age and occur more in women.3,4,5,6 GCTs comprise 3–7% of all primary bony tumors. GCTs mainly involve epiphysis of long bones, and small bones of the hands, feet, sacrum, and vertebral body are less likely to be involved. Accordingly, the most common sites of tumor are distal of the femur and proximal of the tibia,7 and <3% of cases occur in the skull. Sphenoid and temporal bones are the most common sites of skull involvement.8 Orbital tumors are very rare.2,9,10
The first case of orbital GCT was presented by Vernet in 1993, and due to its rarity, there is no well-established treatment regimen for its management. In this study, we present a case of orbital GCT with interesting features.
CASE REPORT
A 16-year-old boypresented with pain, swelling, erythematic left upper and lower lids, proptosis, and diplopia. Ophthalmic examination revealed chemosis, conjunctival injection, limited elevation, depression, and abduction in the left eye. Best corrected visual acuity was 7/10 in the left eye. Hertel ophthalmometry showed 6 mm proptosis with anterior and medial displacement of the globe. Funduscopy showed choroidal fold with no evidence of optic disc edema. Relative afferent pupillary defect was negative. Multislice computed tomography scan (CT scan) of the orbit and paranasal sinuses was performed and showed a hyperdense oval extraconal mass with bone erosion. Magnetic resonance imaging of the orbit showed an inferior lateral isointense oval extraconal mass on T1-weighted images that had indented the globe. The mass was hyperintense on T2-weighted images and showed enhancement with contrast injection [Figure 1]. The patient underwent superior lateral orbitotomy following general anesthesia, and a 2.5 cm × 2.5 cm × 0.5 cm gray-to-brown mass was completely excised. Pathology evaluation of the mass revealed proliferated stromal cells and round-to-ovoid hyperchromatic nuclei arranged interlacing bundles with intervening scattered numerous multinucleated giant cell osteoclastic type. Osteoid and woven formations were also present at the vicinity blood-filled cavernous spaces lined by stromal and giant cells. There was an area of fibroblastic proliferation. Focal area of necrosis was present as well as occasional mitotic figure. The lesion had destroyed cortical bone and extended into the surrounding soft tissue. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining for Ki67 and CD68 was positive and negative for CD1a in stromal and giant cells. Proliferative index was 15–20% in the more active area. Conventional type giant cell tumor was diagnosed based on pathological survey [Figure 2].
Figure 1.
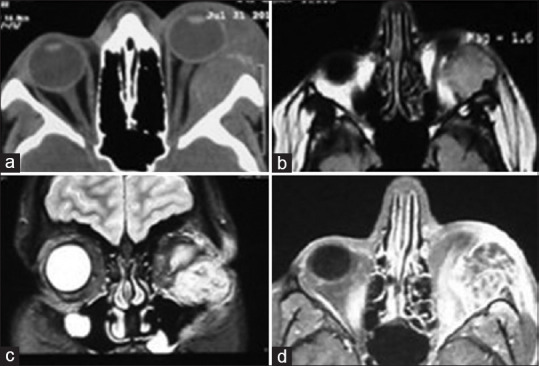
(a) Axial computed tomography scan shows left intraorbital mass with bone erosion (b-d). Magnetic resonance imaging shows isointense oval extraconal mass on T1-weighted images and hyperintense on T2-weighted images and enhancement with contrast, respectively
Figure 2.
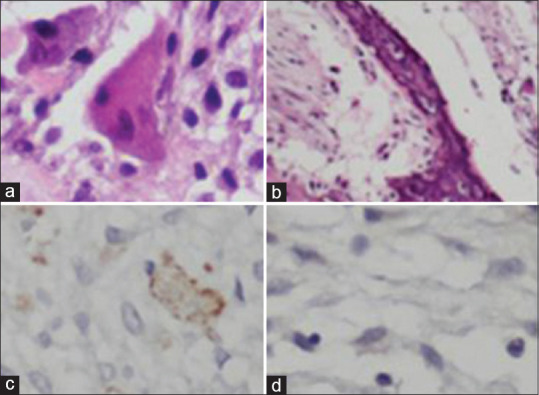
(a and b) Hematoxylin and eosin staining (×400 and × 100 times) shows giant cells and trabeculae of bone, respectively. (c and d) Immunohistochemistry survey shows CD68 positive and CD1a negative, respectively
The patient was under regular follow-up to evaluate any signs of recurrence. Two months following surgery, the patient developed proptosis, severe chemosis, and eyelid erythema in the same eye. Multislice orbital CT scan showed an intraosseous mass in the lateral wall which pushed the globe anteromedially [Figure 3]. The patient underwent a second surgery, and lateral orbitotomy was performed again. In addition to resection of the bone tumor in the second surgery, the involved bone was also drilled (STORZ drill, KARL STORZ Company, Germany). Tumoral tissue was resected, and margins were extended using high-speed burr until normal bony tissue was diagnosed completely. Then, tiny residual debris was irrigated using sterile saline. The patient received oral corticosteroid 1 mg/kg 1 week following surgery. Pathologic examination showed a giant cell lesion composed of osteoclast-like giant cells with numerous nuclei in the background of mononuclear round-to-spindle cells with round-to-oval nuclei, small nucleoli, and eosinophilic cytoplasm. The nuclear features of giant cells and mononuclear cells were almost the same. Giant cells were scattered throughout the lesion. Fibrohistiocytic features were seen in some areas.
Figure 3.
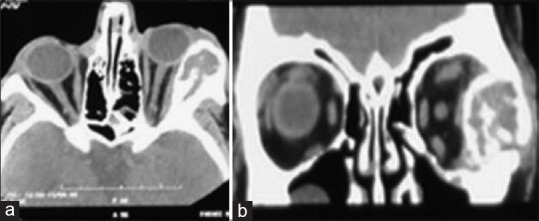
(a and b) Axial and coronal views of computed tomography scan show intraosseous lesion, respectively
Hemosiderin-laden macrophages and aneurismal bone cyst-like areas were also evident. The giant cell lesion was surrounded by woven or lamellar bone trabeculae and dense collagenous tissue in most areas. Scattered mitotic figures were seen. Considering histopathological and IHC findings of the current and previously resected lesions, GCT with aneurismal bone cyst-like features was the most probable diagnosis. In the next 12 months of follow-up, the patient was symptom-free, and no signs of recurrence were seen [Figure 4]. Also patient consent form has been obtained.
Figure 4.
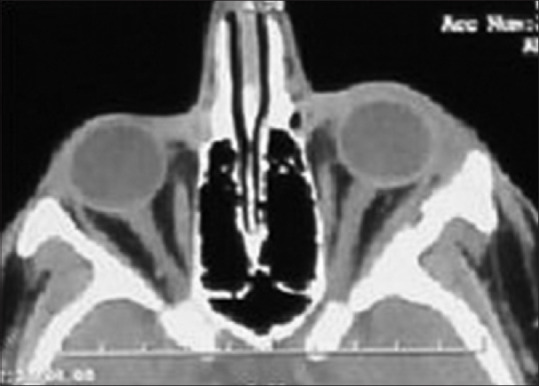
Axial computed tomography scan after the second surgery
DISCUSSION
GCTs are usually benign tumors in the skull but can become locally aggressive and be biologically unpredictable.3,4,11,12,13,14,15 Radiographic findings of GCT are non-specific. These tumors are well-circumscribed, radiolucent, and osteolytic on CT scan. GCTs might have low- to isointensity signal on T1-weighted images, low- to hyperintensity signal on T2-weighted images, and homogenous enhancement following contrast injection.1,10 Radical resection of tumor is not practical; therefore,recurrence rate of GCT is about 40-60% which usually happens in the first two years following the surgery.14 Differential diagnosis included giant cell granuloma, aneurismal bone cyst, brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism, ossifying fibroma, metastasis, multiple myeloma, Paget's disease, plasmacytoma, and Langerhans cell histiocytosis.1,2,8,11 Total resection of GCT is proposed to be the treatment of choice.2,8,9,12 However, in cases with skull base involvement, radical bone resection is not possible.15 The tumors that are not been completely removed or are not suitable for surgery might benefit from chemotherapy.10 There are no standard chemotherapy treatment protocols for GCTs. Since GCTs are radioresistant and radiation might result in malignant transformation of residual tumor, adjuvant radiation is debatable.2,8,10 Tumoral cells of GCTs present receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL) on their surface. Osteoclasts are activated by RANKL and lead to bone resorption.16 Denosumab is a monoclonal antibody that binds RANKL and inhibits osteoclastogenesis by binding to RANKL. This antibody could be used in cases with incomplete resection or those with recurrence tumor.5,9 In recurrence cases, bisphosphonates can be applied with a similar effect as denosumab.11 Bone drilling with high-speed diamond burr following resection of the lesion could reduce the recurrence rate. This effect is proposed to be due to thermal effect and further resection of the tumoral tissue by drilling.17,18 Balke et al. found that burring was the most important factor in reducing the local recurrence of tumor after resection.19 In this study, we presented a patient with intraorbital mass which happened to be GCT. This presentation is unique since these tumors typically are bone tumors. Following the first resection, tumor behavior changed, and it became an intraosseous tumor. This growth pattern and involvement of orbit by GCT has not been reported in the literature yet. Radical tumor removal including burring of surrounding bone could be the reason of no recurrence for 12 months following the second surgery; however, further follow-up is necessary to diagnose tumor recurrence.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form, the legal guardian has given his consent for images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The guardian understands that names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Tang PH, Mettu P, Maltry AC, Harrison AR, Mokhtarzadeh A. Giant cell tumor of the frontal bone presenting as an orbital mass. Ophthalmol Ther. 2017;6:215–20. doi: 10.1007/s40123-017-0081-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Goto Y, Furuno Y, Kawabe T, Ohwada K, Tatsuzawa K, Sasajima H, et al. Treatment of a skull-base giant cell tumor with endoscopic endonasal resection and denosumab: Case report. J Neurosurg. 2017;126:431–4. doi: 10.3171/2016.3.JNS152802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sobti A, Agrawal P, Agarwala S, Agarwal M. Giant cell tumor of bone – An overview. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2016;4:2–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gamboa NT, Ronna B, Gamboa CT, Palmer CA, Park MS, Gurgel RK, et al. Giant cell tumor of the lateral skull base: Diagnostic and management options. J Neurol Surg Rep. 2018;79:e41–54. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1645885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jamshidi K, Gharehdaghi M, Hajialiloo SS, Mirkazemi M, Ghaffarzadehgan K, Izanloo A. Denosumab in patients with giant cell tumor and its recurrence: A systematic review. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2018;6:260–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yamamoto M, Fukushima T, Sakamoto S, Tomonaga M. Giant cell tumor of the sphenoid bone: Long-term follow-up of two cases after chemotherapy. Surg Neurol. 1998;49:547–52. doi: 10.1016/s0090-3019(97)00219-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Puri A, Agarwal MG, Shah M, Jambhekar NA, Anchan C, Behle S. Giant cell tumor of bone in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Orthop. 2007;27:635–9. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0b013e3181425629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Vernet O, Ducrey N, Déruaz JP, de Tribolet N. Giant cell tumor of the orbit. Neurosurgery. 1993;32:848–51. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199305000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bardakhchyan S, Kager L, Danielyan S, Avagyan A, Karamyan N, Vardevanyan H, et al. Denosumab treatment for progressive skull base giant cell tumor of bone in a 14 year old female – A case report and literature review. Ital J Pediatr. 2017;43:32. doi: 10.1186/s13052-017-0353-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kamoshima Y, Sawamura Y, Imai T, Furukawa H, Kubota K, Houkin K. Giant cell tumor of the frontal bone in a girl: Case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2011;51:798–800. doi: 10.2176/nmc.51.798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tamura R, Miwa T, Shimizu K, Mizutani K, Tomita H, Yamane N, et al. Giant cell tumor of the skull: Review of the literature. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2016;77:239–46. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1554808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Harris AE, Beckner ME, Barnes L, Kassam A, Horowitz M. Giant cell tumor of the skull: A case report and review of the literature. Surg Neurol. 2004;61:274–7. doi: 10.1016/S0090-3019(03)00428-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Llavero-Valero P, Hermosilla AM, Ruiz MC, Aldana DG, Álvarez AF, Arjona FE. Giant cell tumour of frontal bone in a patient with bilateral retinoblastoma. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2019;94:200–3. doi: 10.1016/j.oftal.2018.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Campanacci M, Baldini N, Boriani S, Sudanese A. Giant-cell tumor of bone. J Bone Jt Surg Am. 1987;69:106–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yip CM, Lee HP, Hsu SS, Chen YT. Left orbital roof giant cell tumor of bone: A case report. Surg Neurol Int. 2018;9:127. doi: 10.4103/sni.sni_467_17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Thomas DM. RANKL, denosumab, and giant cell tumor of bone. Curr Opin Oncol. 2012;24:397–403. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0b013e328354c129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Malek F, Krueger P, Hatmi ZN, Malayeri AA, Faezipour H, O’Donnell RJ. Local control of long bone giant cell tumour using curettage, burring and bone grafting without adjuvant therapy. Int Orthop. 2006;30:495–8. doi: 10.1007/s00264-006-0146-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Turcotte RE, Wunder JS, Isler MH, Bell RS, Schachar N, Masri BA, et al. Giant cell tumor of long bone: A Canadian sarcoma group study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;397:248–58. doi: 10.1097/00003086-200204000-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Balke M, Schremper L, Gebert C, Ahrens H, Streitbuerger A, Koehler G, et al. Giant cell tumor of bone: Treatment and outcome of 214 cases. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2008;134:969–78. doi: 10.1007/s00432-008-0370-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


