Abstract
Since the Black Lives Matter movement rose to mainstream prominence, the academic enterprise has started recognizing the systematic racism present in science. However, there have been relatively few efforts to make sure that the language used to communicate science is inclusive. Here, I quantify the number of research articles published between 2000 and 2020 that contained non-inclusive terms with racial connotations, such as “blacklist” and “whitelist”, or “master” and “slave”. This reveals that non-inclusive language is being increasingly used in the life sciences literature, and I urge the global academic community to expunge these archaic terms to make science inclusive for everyone.
Research organism: None
Historically, many terms are associated with racial connotations. In the tech world, the words “master” and “slave” are often used to refer to types of storages, circuits, databases or code, in which the slave type is subservient to the master. Other commonly used terms are “blacklist” and “whitelist” — where the blacklists are the problematic entities and whitelists are the good ones (Alter et al., 2016).
These, and several other archaic and non-inclusive terms, are also widely used in scientific manuscripts (Baeckens et al., 2020; Herbers, 2007; Houghton and Houghton, 2018). In publishing, the term “blacklist” is used to filter out predatory journals and publishers from non-predatory and more trustworthy journals that are added to the “whitelist” (Houghton and Houghton, 2018; Silver, 2017). In the life sciences, the term “blacklist” is commonly used to represent problematic genomic regions, variations, genes, or proteins which need to be filtered out as an artifact or noise (Wimberley and Heber, 2019; Maffucci et al., 2019; Collins et al., 2019; Wilfert et al., 2016). For example, the ENCODE blacklist regions are a curated list of non-coding regions in the genome, which is used by the gene regulation community – including myself – as an essential quality filter when analyzing genomic and epigenomic data (Amemiya et al., 2019).
The terms “master” and “slave” are also frequently used in molecular biology to group transcription factors (TFs) or genes based on their function. For example, proteins that are at the top of the regulatory hierarchy and control key biological programs, such as determining a cell’s fate, are commonly named “master regulators” or “master TFs”. While some may argue that it is acceptable to use the term “master”, the problem gets worse when some researchers introduce "slave TFs" (Ocone and Sanguinetti, 2011).
Use of non-inclusive terms in life sciences literature is growing
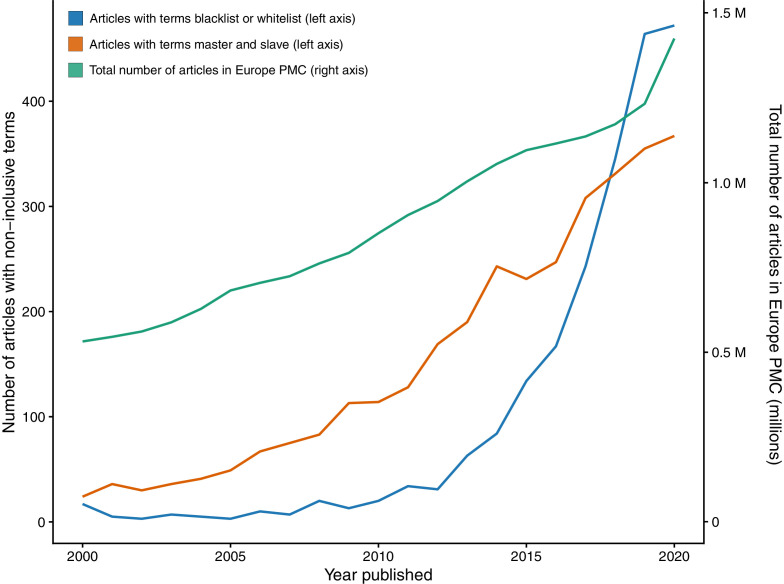
To estimate the use of the terms blacklist/whitelist and master/slave, I performed searches on the open-access repository Europe PMC which contains millions of biomedical research articles. A search for articles containing blacklist/whitelist returned more than 2,000 articles published in more than 600 journals between 2000 and 2020 (Figure 1), with blacklist appearing more often (1,994 articles) than whitelist (439 articles).
Figure 1. The growth of non-inclusive terms in the life sciences literature.
The number of articles on Europe PMC containing the terms blacklist or whitelist (blue; left axis), containing the terms master and slave (orange; left axis), and the total number of articles on Europe PMC (green; right axis) between 2020 and 2000.
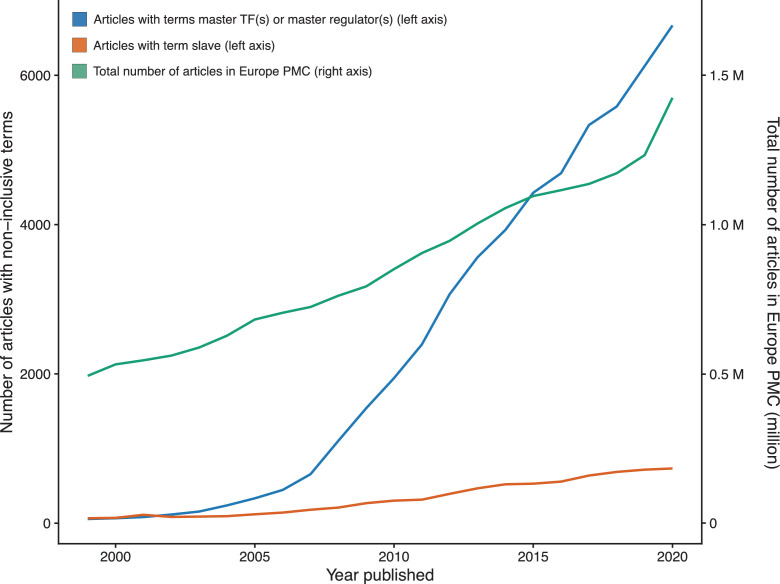
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. The number articles in the life sciences literature that just contain the term "master" or "slave".
The first use of the term “blacklist” dates back to the seventeenth century and has a long history of being used in the labor market (Weir, 2013). However, these terms started appearing in the biomedical literature around the mid-nineteenth century. In 1899, an article in the journal The Hospital suggested maintaining a “whitelist” of firms that treat their employees fairly instead of a “blacklist" of firms with a bad reputation (The Hospital, 1899). Since then, the use of these non-inclusive terms has continued to grow (Figure 1).
The terms “master” and “slave” are also widely used in the scientific literature. A search for articles with both these terms found over 3,500 research articles published in more than 900 journals between 2000 and 2020 (Figure 1). Similar to blacklist and whitelist, the use of master and slave is growing with time. Furthermore, a search for “master TFs” or “master regulators” found more than 50,000 articles from 2000 to 2020, with their use increasing each year (Figure 1—figure supplement 1). This suggests that non-inclusive terms are becoming increasingly pervasive, and possibly the norm in the life sciences literature.
Most of the papers with non-inclusive terms were published in well-known journals, including multidisciplinary journals (such as Nature, Nature Communications, PLOS One, PNAS and Scientific Reports) and journals with broad scopes within the life sciences and medicine (such as BMJ, Cell, Cell Reports and eLife). In addition to these multidisciplinary and broad-scope journals, the journals that used the terms "blacklist" or "whitelist" most often were BMC Bioinformatics, Nature Genetics and Genome Research, and the journals that used the terms "master" and "slave" most often were Sensors, Optics Express, Scientific World Journal and BMC Bioinformatics. Inevitably, larger journals (such as Nature Communications, PLOS One, PNAS, Scientific Reports and Sensors) tended to use these terms more often than small journals with fewer publications.
Let’s expunge non-inclusive terms to make science inclusive for all
Following the Black Lives Matter protests the scientific community has spoken against the systematic racism in science and called for action to make science more diverse and inclusive (Barber et al., 2020; Cell Editorial Team, 2020; Eisen, 2020; Nature, 2020; Sanford, 2020; Stevens et al., 2021; Taffe and Gilpin, 2021). Yet, the growing use of such non-inclusive terms in scientific literature potentially reflects a racist research space that endorses and sustains the use of these terms. The more we use this language, the more it becomes a habit, and we need to act now to avoid passing this behavior on to future generations of scientists.
Some tech and governmental organizations, such as Google, GitHub, the UK National Cyber Security Center, among others Seele, 2020, are already replacing such terms that reflect a racist culture (Google, 2020; GitHub, 2020; Emma, 2020; Seele, 2020; Im, 2020). I urge the scientific community (including institutions, researchers, funders, learned societies, journals and others) to follow suit, and replace the terms blacklist/whitelist with excluded/included or deny/allow lists, and to use the terms primary and secondary instead of master and slave.
There are several other examples of non-inclusive terminologies that are used in the life sciences and beyond. For example, there are growing concerns over terms with racial etymology, such as “slave-making ants” — a slavery metaphor to describe ant behavior (Herbers, 2020; Herbers, 2007), or the word “noosing” to describe catching lizards, which reminds people of the racial lynchings of Black people in the United States (Cahan, 2020). A number of plant and animal species also have non-inclusive names or are named after people who were known for their racist rhetoric (Shiffman, 2019).
Recently, the racially loaded term “quantum supremacy” was introduced to represent the power of quantum computers, which is now getting replaced by “quantum advantage” (Palacios-Berraquero et al., 2019; Wiesner, 2017). Additionally, in response to recent social unrest, the academic enterprise has started renaming academic buildings, programs and prizes, and removing monuments named after people who were known for their racist comments and ideology (Cahan, 2020). Now, it is time for us to also rethink the language we use to communicate science.
Language matters — it shapes the way we think, see and behave. The list of non-inclusive terms in science is long and widespread across multiple disciplines. As scientists, we have a responsibility to fix the problem and to use language that is inclusive to everyone.
Methods
The research articles with specific terms were queried through Europe PMC using the europepmc R package v0.4 (Ferguson et al., 2021). The search query was restricted to publication year between January 01, 2000, to December 31, 2020. Preprints were excluded from the search.
The query used to search articles with terms blacklist and whitelist is as follows: ((blacklist OR blacklisted OR “black-listed” OR “black-list” OR blacklisting) OR (whitelist OR whitelisted OR “white-listed” OR “white-list” OR whitelisting)) AND (FIRST_PDATE:[2000-01-01 TO 2020-12-31]) NOT (SRC:PPR).
The query used to search articles with terms master and slave is as follows: (“master” AND “slave”) AND (FIRST_PDATE:[2000-01-01 TO 2020-12-31]) NOT (SRC:PPR).
The query used to search articles with master TF(s) or master regulator(s) is as follows: ("master TFs" OR "Master transcription factor" OR "master regulator" OR "master TF") AND (FIRST_PDATE:[2000-01-01 TO 2020-12-31]) NOT (SRC:PPR).
All the figures were created using ggplot2 v3.3.2 Wickham, 2016 with R v3.6.1. The figures can be reproduced using the available code in the code and data availability section (Wickham, 2016).
Code and data availability
The source code and data used to generate figures are available on GitHub (https://github.com/asntech/inclusive-science) and also on Zenodo (Khan, 2021).
Acknowledgements
The author thanks Drs. Roza Berhanu Lemma, Sarvenaz Sarabipour, Anthony Mathelier and Jaime Abraham Castro-Mondragon for their useful comments and suggestions.
Biography
Aziz Khan is a computational biologist in the Stanford Cancer Institute, School of Medicine, Stanford University, Stanford, California, United States. He is an ambassador for ASAPbio and eLife ambassador for 2018-2020. He often tweets about research practices, preprints, reproducibility in research and EDI in science from @khanaziz84
Funding Statement
No external funding was received for this work.
Contributor Information
Aziz Khan, Email: azizk@stanford.edu.
Julia Deathridge, eLife, United Kingdom.
Peter Rodgers, eLife, United Kingdom.
Additional information
Competing interests
No competing interests declared.
Author contributions
Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing - original draft, Writing - review and editing.
Additional files
Data availability
The source code and data used to generate figures are available on GitHub (https://github.com/asntech/inclusive-science; copy archived at https://github.com/asntech/inclusive-science/releases/tag/v1.1) and also on Zenodo (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4458453).
The following dataset was generated:
Aziz K. 2021. A call to eradicate non-inclusive terms from science. Zenodo.
References
- Alter AL, Stern C, Granot Y, Balcetis E. The "bad is Black" effect: why people believe evildoers have darker skin than do-gooders. Personality & Social Psychology Bulletin. 2016;42:1653–1665. doi: 10.1177/0146167216669123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amemiya HM, Kundaje A, Boyle AP. The ENCODE blacklist: identification of problematic regions of the genome. Scientific Reports. 2019;9:1–5. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45839-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeckens S, Blomberg SP, Shine R. Inclusive science: ditch insensitive terminology. Nature. 2020;580:185. doi: 10.1038/d41586-020-01034-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber PH, Hayes TB, Johnson TL, Márquez-Magaña L, 10,234 signatories Systemic racism in higher education. Science. 2020;369:1440–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.abd7140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahan E. Amid protests against racism, scientists move to strip offensive names from journals, prizes, and more. Science. 2020;1:abd6441. doi: 10.1126/science.abd6441. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Cell Editorial Team Science has a racism problem. Cell. 2020;181:1443–1444. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins JE, White RJ, Staudt N, Sealy IM, Packham I, Wali N, Tudor C, Mazzeo C, Green A, Siragher E, Ryder E, White JK, Papatheodoru I, Tang A, Füllgrabe A, Billis K, Geyer SH, Weninger WJ, Galli A, Hemberger M, Stemple DL, Robertson E, Smith JC, Mohun T, Adams DJ, Busch-Nentwich EM. Common and distinct transcriptional signatures of mammalian embryonic lethality. Nature Communications. 2019;10:2792. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10642-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen MB. We need to act now. eLife. 2020;9:e59636. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emma W. Terminology: it’s not black and white. [January 19, 2020];National Cyber Security Center. 2020 https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/blog-post/terminology-its-not-black-and-white
- Ferguson C, Araújo D, Faulk L, Gou Y, Hamelers A, Huang Z, Ide-Smith M, Levchenko M, Marinos N, Nambiar R, Nassar M, Parkin M, Pi X, Rahman F, Rogers F, Roochun Y, Saha S, Selim M, Shafique Z, Sharma S, Stephenson D, Talo' F, Thouvenin A, Tirunagari S, Vartak V, Venkatesan A, Yang X, McEntyre J. Europe PMC in 2020. Nucleic Acids Research. 2021;49:D1507–D1514. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GitHub Renaming the default branch from master. 040636eGitHub. 2020 https://github.com/github/renaming
- Google Writing inclusive documentation. [January 19, 2020];Google. 2020 https://developers.google.com/style/inclusive-documentation
- Herbers JM. Watch your language! Racially loaded metaphors in scientific research. BioScience. 2007;57:104–105. doi: 10.1641/B570203. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Herbers JM. Racist words in science. BioScience. 2020;70:946. doi: 10.1093/biosci/biaa113. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton F, Houghton S. "Blacklists" and "whitelists": a salutary warning concerning the prevalence of racist language in discussions of predatory publishing. Journal of the Medical Library Association. 2018;106:527–530. doi: 10.5195/JMLA.2018.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Im S. There’s an industry that talks daily about “masters” and “slaves.” It needs to stop. [January 19, 2020];2020 https://www.washingtonpost.com/opinions/2020/06/12/tech-industry-has-an-ugly-master-slave-problem/
- Khan A. A call to eradicate non-inclusive terms from science. v1.1Zenodo. 2021 doi: 10.5281/zenodo.4458453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Maffucci P, Bigio B, Rapaport F, Cobat A, Borghesi A, Lopez M, Patin E, Bolze A, Shang L, Bendavid M, Scott EM, Stenson PD, Cunningham-Rundles C, Cooper DN, Gleeson JG, Fellay J, Quintana-Murci L, Casanova JL, Abel L, Boisson B, Itan Y. Blacklisting variants common in private cohorts but not in public databases optimizes human exome analysis. PNAS. 2019;116:950–959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1808403116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nature Systemic racism: Science must listen, learn and change. Nature. 2020;582:147. doi: 10.1038/d41586-020-01678-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ocone A, Sanguinetti G. Reconstructing transcription factor activities in hierarchical transcription network motifs. Bioinformatics. 2011;27:2873–2879. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios-Berraquero C, Mueck L, Persaud DM. Instead of ‘supremacy’ use ‘quantum advantage’. Nature. 2019;576:213. doi: 10.1038/d41586-019-03781-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford MS. Equity and inclusion in the chemical sciences requires actions not just words. ACS Central Science. 2020;6:1010–1011. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.0c00784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seele M. Striking out racist terminology in engineering. [February 3, 2021];2020 http://www.bu.edu/articles/2020/striking-out-racist-terminology-in-engineering/
- Shiffman D. Scientists should stop naming species after awful people. [January 19, 2020];Scientific American. 2019 https://blogs.scientificamerican.com/observations/scientists-should-stop-naming-species-after-awful-people/
- Silver A. Pay-to-view blacklist of predatory journals set to launch. Nature. 2017:22090. doi: 10.1038/nature.2017.22090. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens KR, Masters KS, Imoukhuede PI, Haynes KA, Setton LA, Cosgriff-Hernandez E, Lediju Bell MA, Rangamani P, Sakiyama-Elbert SE, Finley SD, Willits RK, Koppes AN, Chesler NC, Christman KL, Allen JB, Wong JY, El-Samad H, Desai TA, Eniola-Adefeso O. Fund black scientists. Cell. 2021 doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taffe MA, Gilpin NW. Racial inequity in grant funding from the US National Institutes of Health. eLife. 2021;10:e65697. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The Hospital Annotations. The Hospital. 1899;25:324–325. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir RE. Workers in America: A Historical Encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. Verlag New York: Springer; 2016. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesner K. The careless use of language in quantum information. arXiv. 2017 https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.06768
- Wilfert AB, Chao KR, Kaushal M, Jain S, Zöllner S, Adams DR, Conrad DF. Genome-wide significance testing of variation from single case exomes. Nature Genetics. 2016;48:1455–1461. doi: 10.1038/ng.3697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimberley CE, Heber S. PeakPass: automating ChIP-Seq blacklist creation. Journal of Computational Biology : A Journal of Computational Molecular Cell Biology. 2019 doi: 10.1089/cmb.2019.0295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Citations
- Aziz K. 2021. A call to eradicate non-inclusive terms from science. Zenodo. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The source code and data used to generate figures are available on GitHub (https://github.com/asntech/inclusive-science) and also on Zenodo (Khan, 2021).
The source code and data used to generate figures are available on GitHub (https://github.com/asntech/inclusive-science; copy archived at https://github.com/asntech/inclusive-science/releases/tag/v1.1) and also on Zenodo (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4458453).
The following dataset was generated:
Aziz K. 2021. A call to eradicate non-inclusive terms from science. Zenodo.