In the article titled “Hydrogen Gas Attenuates Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury via Regulation of the MAPK/HO-1/PGC-1a Pathway in Neonatal Rats” [1], the authors identified that there was an error in the western blot images of Figure 5(c) where the incorrect images were presented for the second β-actin bands. The authors confirm that this does not affect the conclusions of the article, and the corrected Figure 5 is as follows:
Figure 1.
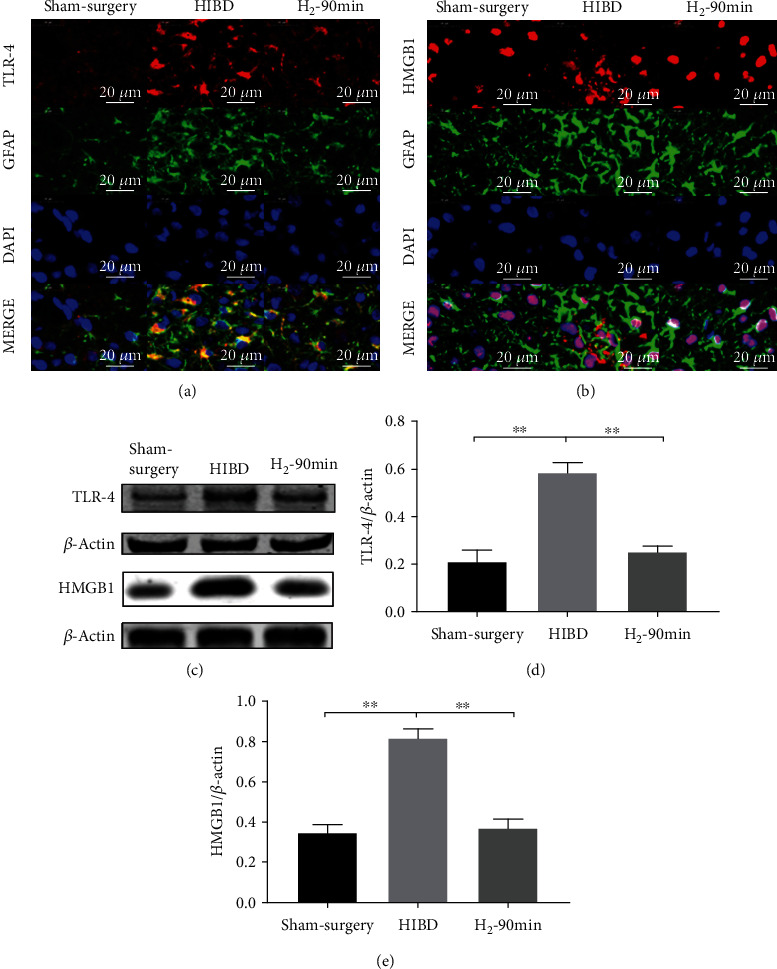
H2 inhibited HMGB1/TLR-4 expression in the hippocampal CA3 region of neonatal HIBI rats. (a) The representative images of TLR-4 (red) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP, green) and 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, blue) immunofluorescence staining as well as merged immunofluorescent signals of all markers in the hippocampal CA3 region of the sham surgery, HIBI, and H2-90 min groups (scale bar: 50 μm). (b) Representative images of HMGB1 (red) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP, green) and 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, blue) immunofluorescence staining as well as merged immunofluorescent signals of all markers in the hippocampal CA3 region of the sham surgery, HIBI, and H2-90 min groups (scale bar: 50 μm). (c) Western blot analysis of TLR-4, HMGB1, and β-actin proteins in the hippocampus of each group. (d, e) Bar graphs of the relative expression of TLR-4, HMGB1 in the hippocampus of each group (n = 3/group; ∗∗p < 0.01).
Contributor Information
Xiao-Kang Li, Email: ri-k@ncchd.go.jp.
Lingling Zhao, Email: llzhao2011@qq.com.
References
- 1.Wang P., Zhao M., Chen Z., et al. Hydrogen gas attenuates hypoxic-ischemic brain injury via regulation of the MAPK/HO-1/PGC-1a pathway in neonatal rats. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. 2020;2020:16. doi: 10.1155/2020/6978784.6978784 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


