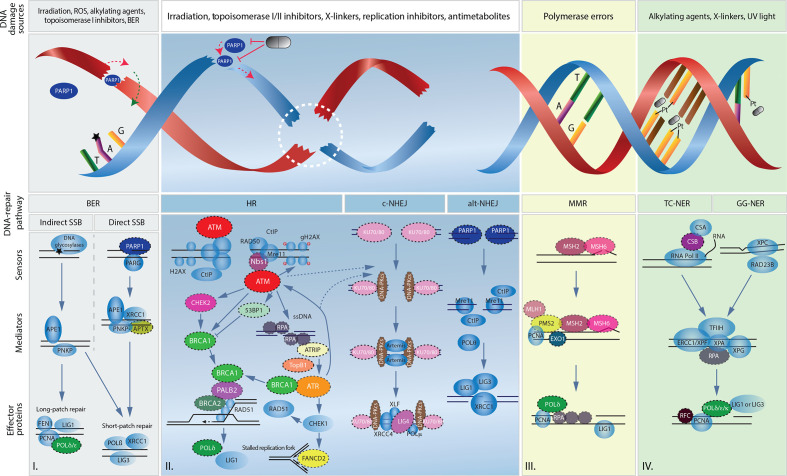
Figure 1.
Overview of main DNA lesions and their related DNA damage repair pathways. Schematic representation of I. single-strand break repair by direct and indirect base excision repair, II. double-strand break repair by homologous recombination and non-homologous end joining, III. replication error repair by mismatch repair and IV. DNA adducts repair by either transcription-coupled nucleotide excision repair (TC-NER) or global genomic nucleotide excision repair (GG-NER). Symbolic pills show potential targeted therapeutic interventions by PARP inhibition and platinum agents (Pt). Black stars represent an indirect single-strand break. Dashed circles emphasize proteins found to be mutated in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Dashed lines represent the regulatory role of ATM and ATR on non-homologous end joining. alt-NHEJ, alternative non-homologous end joining; BER, base excision repair; c-NHEJ, canonical non-homologous end joining; MMR, mismatch repair; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SSB, single-strand break.