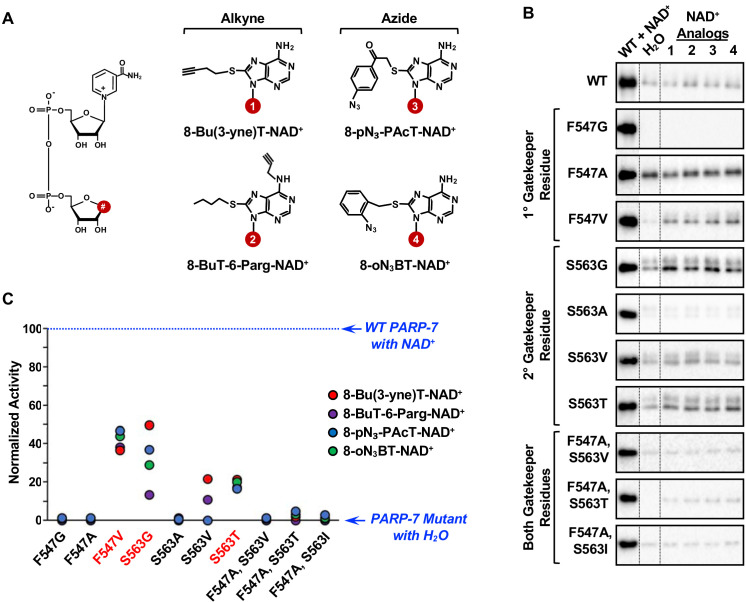
Figure 4. Screening the activity of potential analog-sensitive PARP-7 mutants with clickable NAD+ analogs.
(A) Chemical structures of four clickable NAD+ analogs used for the asPARP-7 screen. (Left) The R groups are linked at position 8 (#) of the adenine ring of NAD+. (Right) 8-BuT-6-Parg-NAD+ and 8-Bu(3-yne)T-NAD+ are clickable through their alkyne groups, whereas 8-oN₃-BT-NAD+ and 8-pN3-PAcT-NAD+ are clickable through their azide groups. (B) Western blots showing the wild-type and mutant PARP-7 automodification reactions performed with NAD+ or the clickable NAD+ analogs shown in (A). The MAR signals were detected using a MAR binding reagent. (C) Normalized automodification activity of wild-type and mutant PARP-7 proteins with NAD+ or the clickable NAD+ analogs shown in (A). PARP-7 automodification assays like those shown in (B) were used to determine the activity of the mutants with the NAD+ analogs. This screen was performed twice and yielded similar results each time; the results from one replicate are shown.