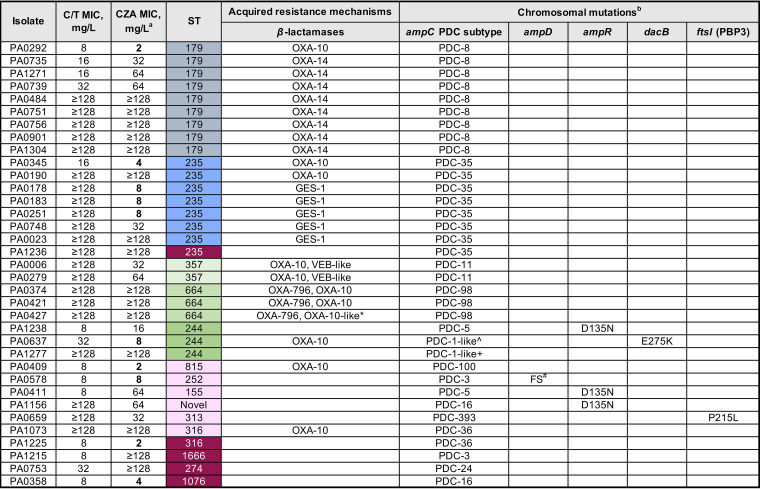
FIG 2.
Mechanisms of C/T resistance in 35 non-carbapenemase-producing CNSPA isolates. a, Bold values indicate CZA susceptibility. b, The main chromosomal mutations (ampC, ampR, dacB, and ftsI) leading to amino acid substitutions compared to the reference wild-type comparator amino acid sequences from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 are shown. The list of nonsynonymous variations was refined to include only those more likely to be involved in the C/T-resistant phenotype, i.e., (i) mutations with known effect on resistance according to published evidence and (ii) mutations with predicted functional impact (i.e., deleterious) and not identified in wild-type/susceptible isolates. *, G439C amino acid substitution in OXA-10; ^, A163T amino acid substitution in AmpC; +, ΔK74-E75 in AmpC; #, frameshift (FS) at position 149.