Mondal L, Mukherjee B, Das K, et al. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:8073–8094.
The authors have advised due to an error at the time of figure assembly, Figure 5 on page 8085 is incorrect. The correct Figure 5 is shown below.
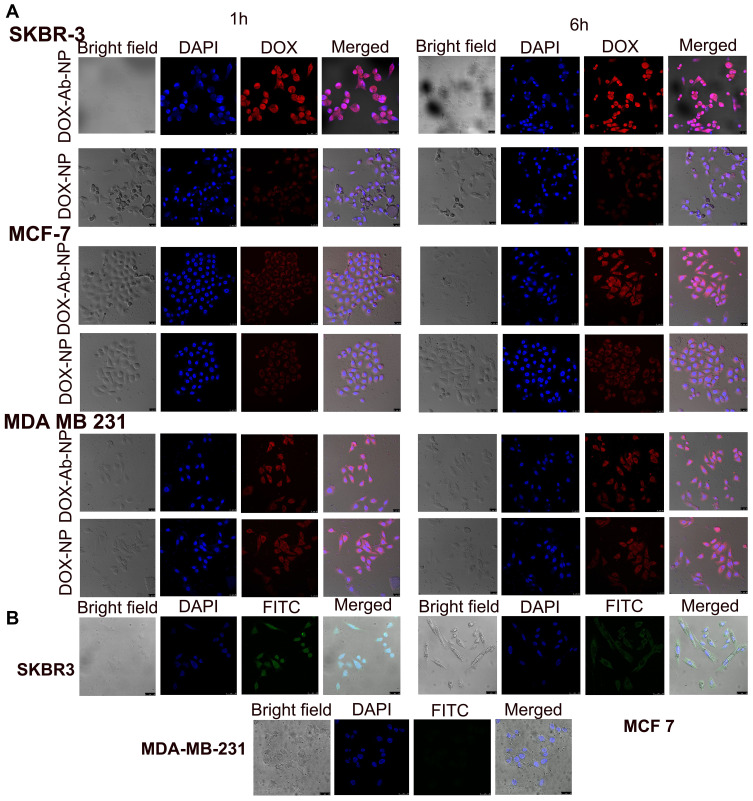
Figure 5.
Cellular uptake of antibody conjugated and unconjugated nanoparticles in various cell lines.
Notes: (A) Cellular uptake of DOX-NP and DOX-Ab-NP in SKBR-3, MCF-7, and MDA-MB-231 cells observed by confocal microscopy at 1 and 6 hrs, respectively. (B) Cellular uptake of antibody-conjugated blank nanoparticles in SKBR-3, MCF-7, and MDA-MB-231 cells observed by confocal microscopy at 6 hrs.
Abbreviations: DOX, doxorubicin; Ab, antibody; NP, nanoparticle.
The authors apologize for this error and advise it does not affect the results of the paper.