Abstract
Both cerium oxide (CeOx) nanoparticles and mefenamic acid (MFA) are known anti-inflammatory agents with hepatoprotective properties and are therefore prescribed for one of the major diseases in the world, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). To study the potential cytotoxicity and anti-inflammatory effects as well as drug retention of a potential therapeutic CeOx/MFA supramolecular complex, a well-standardized hepatic (HepG2) spheroid model was used. Results showed that the highest cytotoxicity for the CeOx/MFA supramolecular complex was found at 50 μg/mL, while effective doses of 0.1 and 1 μg/mL yielded a significant decrease of TNF-α and IL-8 secretion. Time-resolved analysis of HepG2 spheroids revealed a spatiotemporal distribution of the supramolecular complex and limited clearance from the internal microtissue over a period of 8 days in cultivation. In summary, our results point at rapid uptake, distribution, and biostability of the supramolecular complex within the HepG2 liver spheroid model as well as a significant anti-inflammatory response at noncytotoxic levels.
Keywords: supramolecular complexes, 3D spheroid models, NAFDL, drug delivery
In the past decade, nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems have become increasingly popular in therapeutic and pharmaceutical applications due to their increased bioavailability, lower drug consumption rates, reduced side effects, and the ability to deliver drugs to a targeted region in the body.1,2 A more recent development trend involves the engineering of functional nanomaterials based on supramolecular principles to create modular platforms with tunable chemical, mechanical, and biological properties.3 Such supramolecular building blocks may combine inorganic nanomaterials with therapeutic agents to take advantage of their combinatorial effect for the treatment of severe diseases.4−6 For instance, a supramolecular system based on cerium dioxide nanoparticles (CeO2NPs) known for its antioxidant and hepatoprotective properties and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as mefenamic acid (MFA) can serve as promising nanodrug candidates for liver-related diseases.7 Among liver diseases, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) represents a major degenerative liver disorder with a global prevalence of 24%.8,9 In fact, despite recent progress in the understanding of the pathogenesis of this common disease, there is still no approved medication for treating NAFLD.10 In the current study, we investigate in detail the effects of a supramolecular hybrid nanocarrier consisting of a CeO2NP core modified with MFA and a hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβ-cyclodextrin) polymer shell on cellular viability, microtissue distribution and retention, as well as cytokine secretion using a three-dimensional (3D) HepG2 human liver spheroid model. The development and application of human 3D tissue models such as the generation of pathophysiological liver systems for drug pharmacokinetics and toxicity follow the international trend to overcome limitations of current animal models that do not represent, e.g., the human pathology of NAFLD.11 Additionally, these in vitro 3D models are in line with recent efforts to promote alternatives to animal experiments according to the “3Rs” concept due to the ability to reproduce a cellular phenotype in vivo.12,13
Primary experiments set out to verify the feasibility and reproducibility of our 3D liver cell culture model for the evaluation of the cytotoxicity, retention, and anti-inflammatory effects of the supramolecular complex. In particular, the quality of HepG2 spheroids was initially evaluated in terms of spheroid size, intracellular ATP concentration, and cellular viability over a defined cultivation time of 6 days. It is important to note that spheroid diameter and cellular aging are known factors to influence the outcome of drug testing results, thus highlighting the need for the reliable generation of identical spheroids.14 Reproducibility results shown in Figure 1 demonstrate similar spheroid diameters for 6 days exhibiting respective RSDs of 2.1, 4.1, and 4.2% using an initial seeding density of 15 000 cells/mL. Additionally, intracellular ATP concentration as an indicator of viability increased significantly between day 1 and day 3 and remained constant for the remaining cultivation period, thus pointing at a highly metabolic active cell model. These results were further confirmed by live/dead viability assays based on calcein-AM and ethidium bromide staining.
Figure 1.
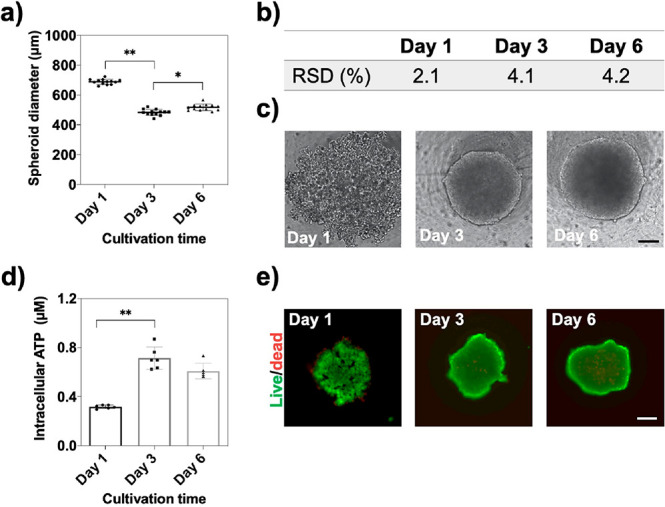
(a) HepG2 spheroid diameter (μm) over a cultivation period of 6 days postseeding, n = 12, ±SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (b) Table of relative standard deviations (RSDs%) of respective HepG2 spheroid cultivation times of 1, 3, and 6 days. (c) Phase-contrast micrographs of HepG2 spheroids at day 1, day 3, and day 6 of cultivation. Scale bar, 100 μm. (d) Time-resolved intracellular ATP concentration of HepG2 spheroids over a cultivation time of 6 days postseeding, n = 6, ±SD, **p < 0.01. (e) Corresponding live (green)/dead (red) fluorescent micrographs. Scale bar, 200 μm.
In a next step, the composition, morphology, thermal properties, and size distribution of the supramolecular complex were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), UV–vis spectroscopy, and dynamic light scattering (DLS) to verify the successful formation of a stable hybrid nanostructure. The supramolecular complex (SMC) consists of the zinc salt of mefenamic acid (ZnMFA), hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβ-CD), and cerium dioxide nanoparticles (see Figure S-1) in a ratio of 1:6:1 (ZnMFA/HPβ-CD/CeO2NP). The morphology and size of the CeO2NP-based supramolecular complex were characterized in water by TEM and DLS, respectively. Electron microscopy (TEM) analysis of CeO2NPs shown in Figure S-1c revealed that the particles exhibit a spherical morphology in the size range of 2–3 nm. DLS measurements were performed to measure the average size distribution of the assembled SMC of ZnMFA, HPβ-CD, and CeO2NP indicated by hydrodynamic diameters in a size range of 5–9 nm as shown in Figure S-1d. Absorption spectra of MFA, ZnMFA, and SMC in methanol revealed two characteristic bands in the UV spectral range (see Figure S-1e). The first band maxima undergo a bathochromic shift at 279.3–283.1–289.5 nm, while a hypsochromic shift at 350.7–344.9–336.8 nm was observed for the second band maxima, for MFA–ZnMFA–SMC, respectively. Similarly, a band maxima in aqueous solution revealed a shift at 285.5 and 335 nm (see Figure S-1f), thus pointing at the presence of ZnMFA within the supramolecular complex. Another important parameter to consider is the degradation characteristics of the supramolecular complex, which describe the connection between temperature and complex stability. Figure S-1g shows differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) curves for SMC and its components ZnMFA and HPβ-CD. The ZnMFA curve reveals two endothermic peaks at 106 and 120 °C, which point at a two-stage degradation process. The observed strong exothermic peak at 162°C can be associated with the thermal destruction of ZnMFA to MFA, while the endothermic peak at 250 °C is typical for MFA exhibiting a polymorph transition from form 1 to form 2.15 In turn, temperatures above 250 °C resulted in MFA destruction. Importantly, DSC patterns for HPβ-CD and SMC revealed similar features, while DSC curves for pure SMC did not show any characteristic peaks for ZnMFA, which indicates the absence of unbound HPβ-CD and ZnMFA. In other words, DSC results confirmed that the individual components are strongly associated with each other, thus resulting in the formation of a stable supramolecular complex.
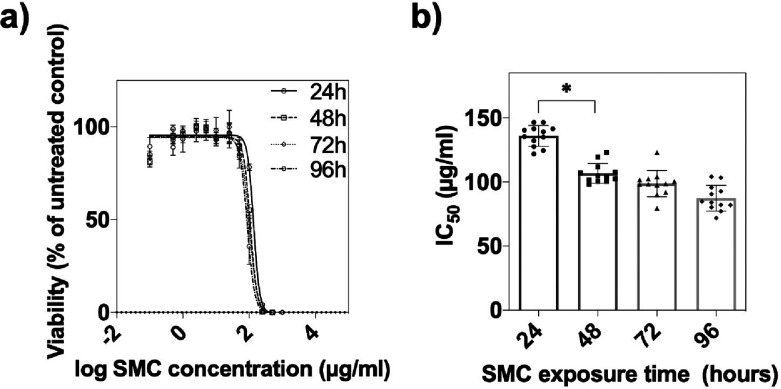
Following the physical and chemical characterization of the supramolecular complex, potential cytotoxicity was evaluated using a HepG2 3D spheroid model in subsequent experiments. The results in Figure 2a illustrate the time dose–response relationship of the nanodrug indicating half-maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50s) of the supramolecular complex of 136.4 ± 7.8, 108.3 ± 6.1, 101.1 ± 7.0, and and 87.5 ± 10.3 μg/mL after effective exposure times of 24, 48, 72, and 96 h, respectively. These results were additionally substantiated using cell viability staining (see also Figure S-2). Interestingly, IC50 values did not change significantly after 48 h of treatment in our 3D HepG2 spheroid model and remained stable, as shown in Figure 2b. As a result of this time–dose relationship study, a maximal exposure period of 48 h in the presence of the supramolecular complex was defined for all subsequent experiments.
Figure 2.
(a) SMC dose–response curves of HepG2 spheroids after drug exposure times of 24, 48, 72 and 96 h at day 6 postseeding. Error bars represent ±SEM (n = 12). (b) Corresponding IC50 values at respective exposure times. Error bars represent ±SD (n = 12), *p < 0.05.
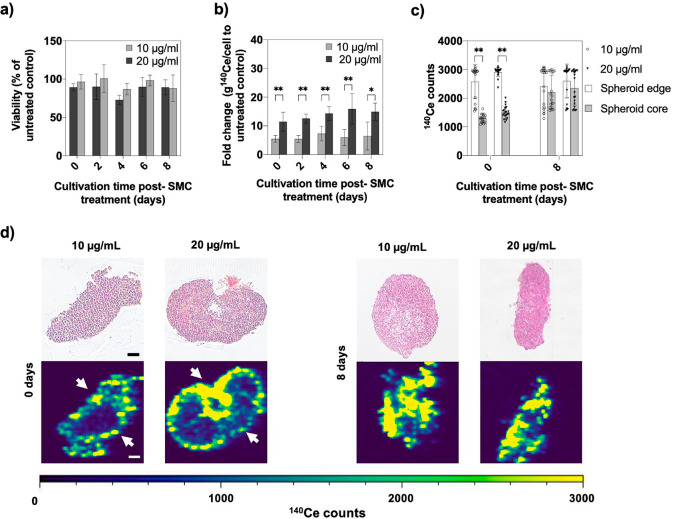
An important aspect of any nanodrug study is concerned with bioavailability including accumulation, retention, and clearance from the tissue of interest. Consequently, tissue retention was analyzed using 3D HepG2 microtissues to evaluate the cellular internalization capacity of the supramolecular complex. Time-resolved retention of SMC in the HepG2 spheroid model was assessed following a 48 h treatment regime at reduced predetermined IC50 concentrations of 10 and 20 μg/mL. Microtissues were subsequently analyzed after each medium exchange step (e.g., every second day) over a cultivation period of 8 days postexposure (see also Scheme S-1). Initial viability studies shown in Figure 3a indicated no significant cytotoxic effects on the HepG2 spheroids as a result of 48 h of exposure during the 8 day post-treatment period. Next, entire 3D cell constructs were quantified and double-normalized to the spheroid cell number and untreated control after each media change to assess nanoparticle retention in the HepG2 microtissues (see Figure 3b). Over 8 days, apparent dose-dependent differences between 10 and 20 μg/mL were observed, resulting in an approximately 7-fold higher internal amount of 140Ce ions present after 48 h of exposure of 10 μg/mL of SMC to an untreated control. In turn, a 20 μg/mL concentration resulted in an approximately 3-times higher amount of 140Ce ions within treated spheroids. Interestingly, despite periodic medium replacement and washing steps, the concentration profile of CeO2NPs inside the microtissues remained stable for both nanodrug concentrations, thus indicating the ability of SMC to accumulate and remain in the liver microtissue. For instance, a fold change of 5.5 ± 1.2 and 11.5 ± 3.3 g of 140Ce per cell relative to untreated control was found at day 0 post-treatment, while similar values of 6.4 ± 1.9 and 14.9 ± 3.0 of g 140Ce per cell were obtained after 8 days for 10 and 20 μg/mL of SMC, respectively. These results are in good correlation with published in vivo studies using rats, where CeO2NPs accumulated mainly in the liver after administration and were still detectable after 8 weeks and, in some cases, up to 5 months.16,17 In an attempt to assess cerium oxide nanoparticle distribution inside our 3D liver tissue analogues in more detail, laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) was employed to determine the spatiotemporal allocation of 140Ce ions within the liver tissue structure. Results shown in Figure 3c display the amount of 140Ce ions in the spheroid edge and core at day 0 and day 8 following a 48 h administration of two nanodrug concentrations. While 140Ce ion intensities of 2578 ± 595 and 2911 ± 161 counts for both 10 and 20 μg/mL SMC concentrations were similar in the outer cell layers of the spheroid after 48 h of exposure (day 0), significant lower intensities of 1285 ± 139 and 1595 ± 214 counts were found in the core of the spheroid. Moreover, following 8 days post-treatment with SMC, no significant differences of 140Ce ion counts throughout the entire 3D cell constructs (e.g., from the edge to the core of the spheroid) were observed as illustrated in Figure 3d. In comparison, analysis of the two-dimensional (2D) monolayer culture revealed a random distribution of 140Ce across the culture area over the whole cultivation period, as shown in Figure S-3. These results clearly suggest spatiotemporal alterations and stable localization of nanoceria within the 3D HepG2 liver model, since even after repeated washing procedures, only limited clearance took place.
Figure 3.
(a) Cellular viability of HepG2 spheroids after 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 days of exposure at SMC concentrations of 20 and 10 μg/mL, n = 3 ± SD. (b) Quantitative analysis of isotope 140Ce detected by ICP-MS in 3D HepG2 spheroids incubated with 0, 10, and 20 μg/mL of SMC, n = 6 ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (c) Cerium distribution in HepG2 spheroids after 0 and 8 days post-treatment with 10 and 20 μg/mL of SMC. 140Ce counts of the spheroid edge (50 μm from outer spheroid rim) and spheroid core (150 μm from outer rim), n = 20 ± SD, **p < 0.01. (d) Microscopic image of H&E stained HepG2 spheroid thin sections and isotope distribution of 140Ce from edges (arrows) to core after incubation with SMC for 48 h with 10 and 20 μg/mL after 0 days (left) and 8 days (right) post-treatment. Scale bar, 100 μm. LA-ICP-MS images were obtained with a laser spot size of 10 μm.
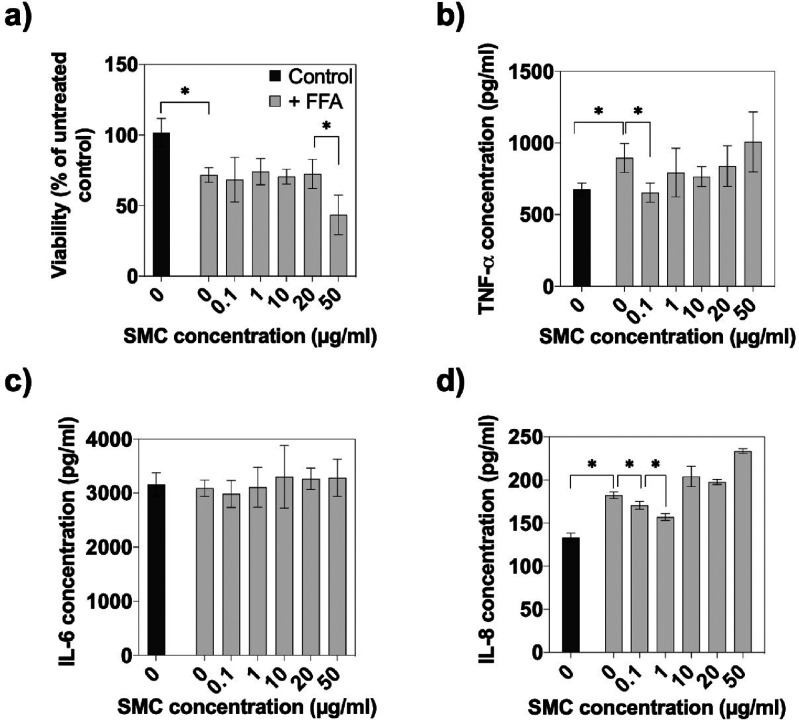
In a final set of experiments, the anti-inflammatory property of the mefenamic-acid-carrying supramolecular nanoceria complex was investigated using ELISA to determine the secretion of relevant cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8. Prior to our nanodrug efficacy study, however, the ability of high concentrations of free fatty acids (FFAs) to induce inflammatory responses that are similar to those observed in patients with NAFLD and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) was investigated in the 3D liver spheroid model.18 Since the main fatty acids are palmitic acid and oleic acid in the human body, our human hepatic HepG2 model was incubated with a mixture of these FFAs to induce an inflammatory response that causes steatosis in vitro.19,20Figure 4a confirmed the hepatoxicity of fat overloading via FFA as indicated by an overall reduction of viability of 33.5 ± 16.9% for FFA-exposed HepG2 spheroids in comparison to healthy controls. Importantly, the cellular viability of SMC treated healthy spheroids remained stable at a concentration range of 0.1 to 20 μg/mL and slightly decreased at 50 μg/mL. Results of the final evaluation of the anti-inflammatory effects of the supramolecular nanoceria complex are shown in Figure 4b–d, where the release of three selected cytokines after 24 h of FFA exposure was monitored. While significantly elevated TNF-α and IL-8 secretion was observed in the presence of FFA, no effect on IL-6 production was detected, thus effectively eliminating IL-6 from the panel of cytokine markers. Also, SMC exposure to spheroids did not produce an additional anti-inflammatory impact at any concentration on IL-6 secretion (see Table S-2). However, notable reductions of the other proinflammatory factors were discovered at 0.1–1 μg/mL SMC concentrations, resulting in a decreased TNF-α release of 31 ± 1.7% at 0.1 μg/mL and a stepwise reduction of IL-8 secretion by 6.4 ± 3.6 and 13.9 ± 0.7% at 0.1 and 1 μg/mL, respectively. In other words, the initial inflammatory response induced by the excess of free fatty acids yielded an increased TNF-α and IL-8 cytokine production, which was significantly reduced by SMC treatment, thus indicating the hepatoprotective function of the nanodrug. These results correlate with the known anti-inflammatory capacities of both, CeO2NPs and MFA, in the literature.16,21−24
Figure 4.
(a) Dose–response effects of the supramolecular complex on the viability of HepG2 spheroids treated with 600 μM FFA, n = 3 ± SD, *p < 0.05. Secretion of (b) TNF-α, (c) IL-6, and (d) IL-8 of healthy and FFA treated HepG2 spheroids to evaluate the anti-inflammatory effect of SMC, n = 3 ± SD, *p < 0.05.
In conclusion, the investigated mefenamic-acid-carrying nanoceria-based supramolecular complex showed encouraging results leading to a significant reduction of an anti-inflammatory response in the presence of noncytotoxic levels of the nanodrug in our HepG2 liver spheroid model. Although the positive effects of both MFA and nanoceria have long been established in liver-related diseases, their combination and application in the form of a supramolecular complex are still in its infancy. Additionally, our clearance study confirmed stable localization of cerium oxide nanoparticles in the tissue construct lacking an effective clearance mechanism, as demonstrated in several previous in vivo studies. In this respect, the application of LA-ICP-MS has proven to be a valuable bioimaging tool for sample-specific high-resolution visualization in the field of drug delivery and tissue engineering. The presented differences in nanoparticle allocation in 2D and 3D HepG2 cultures support the hypothesis that spheroids’ enhanced dimensionality and complexity can imitate transport processes closer to the in vivo situation than monolayer cultures. These results also mean that spheroidal in vitro 3D tissue models can serve as an alternative to animal testing at earlier stages of drug development. The translation to a more advanced 3D hepatic coculture model, including human primary hepatocytes combined with nonparenchymal cells, may be beneficial to investigate experimentally the intercellular effects of fat accumulation and inflammation in the liver as well as to study the complex phenotype of NAFLD in more detail. Further investigations not covered in our study need to examine the extent to which clearance mechanisms are influenced by particle load and dose rate as well as a broader evaluation of the antilipotoxic role of the supramolecular complex, thus providing a more detailed understanding of their nanobiology interactions.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Lukas Brunnbauer from the Institute of Chemical Technologies and Analytics at the Vienna University of Technology for performing the LA-ICP-MS analysis of the monolayer samples. The authors acknowledge the TU Wien University Library for financial support through its Open Access Funding Program.
Supporting Information Available
The Supporting Information is available free of charge at https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsptsci.0c00170.
Experimental section, supramolecular complex characterization, LIVE/DEAD staining of HepG2 microtissues, LA-ICP-MS analysis, experimental workflow of clearance study and ELISA data analysis (PDF)
Author Contributions
C.E., F.S., Y.L, and B.S. performed experiments and analyzed data with support from M.R., A.L., J.G., V.M., and P.E. N.K., V.K., and Y.M. designed and synthesized the supramolecular complex. The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors.
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): Work in this paper was partially supported by funding from Farmak JSC who also produced the supramolecular complex in cooperation with the Institute for Scintillation Materials. All experiments were performed by the Technical University of Vienna in cooperation with SAICO Biosystems.
Supplementary Material
References
- Fu L.; Chung R.; Shi B. (2019) Upconversion Nanoparticle-Based Strategy for Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier to Treat the Central Nervous System Disease. Methods Mol. Biol. 2054, 263–282. 10.1007/978-1-4939-9769-5_17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Y.; Li Z.; Chen H.; Gao Y. (2020) Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems for controllable photodynamic cancer therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 144, 105213. 10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webber M. J. (2016) Engineering responsive supramolecular biomaterials: Toward smart therapeutics. Bioeng Transl Med. 1, 252–266. 10.1002/btm2.10031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y. L.; Yin H.; Zhao F.; Li J. (2013) Multifunctional hybrid nanocarriers consisting of supramolecular polymers and quantum dots for simultaneous dual therapeutics delivery and cellular imaging. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2, 297–301. 10.1002/adhm.201200183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozou S.; Antoniadou-Vyza E. (1998) An improved HPLC method overcoming Beer’s law deviations arising from supramolecular interactions in tolfenamic acid and cyclodextrins complexes. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 18, 899–905. 10.1016/S0731-7085(98)00227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L.; Li L. L.; Fan Y. S.; Wang H. (2013) Host-guest supramolecular nanosystems for cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. Adv. Mater. 25, 3888–3898. 10.1002/adma.201301202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvajal S.; Perramón M.; Oró D.; Casals E.; Fernández-Varo G.; Casals G.; Parra M.; González de la Presa B.; Ribera J.; Pastor Ó.; Morales-Ruíz M.; Puntes V.; Jiménez W. (2019) Cerium oxide nanoparticles display antilipogenic effect in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep. 9, 12848. 10.1038/s41598-019-49262-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanuri G.; Bergheim I. (2013) In vitro and in vivo models of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 14, 11963–11980. 10.3390/ijms140611963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Younossi Z.; Anstee Q. M.; Marietti M.; Hardy T.; Henry L.; Eslam M.; George J.; Bugianesi E. (2018) Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 15, 11–20. 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam B.; Younossi Z. M. (2010) Treatment options for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 3, 121–137. 10.1177/1756283X09359964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y.; Soejima Y.; Fukusato T. (2012) Animal models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol 18, 2300–2308. 10.3748/wjg.v18.i19.2300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannenbaum J.; Bennett B. T. (2015) Russell and Burch’s 3Rs then and now: the need for clarity in definition and purpose. J. Am. Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 54, 120–132. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilenberger C.; Kratz S. R. A.; Rothbauer M.; Ehmoser E. K.; Ertl P.; Küpcü S. (2018) Optimized alamarBlue assay protocol for drug dose-response determination of 3D tumor spheroids. MethodsX 5, 781–787. 10.1016/j.mex.2018.07.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilenberger C.; Rothbauer M.; Ehmoser E.-K.; Ertl P.; Küpcü S. (2019) Effect of Spheroidal Age on Sorafenib Diffusivity and Toxicity in a 3D HepG2 Spheroid Model. Sci. Rep. 9, 4863. 10.1038/s41598-019-41273-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adam A.; Schrimpl L.; Schmidt P. C. (2000) Some physicochemical properties of mefenamic acid. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 26, 477–487. 10.1081/DDC-100101258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oró D.; Yudina T.; Fernández-Varo G.; Casals E.; Reichenbach V.; Casals G.; González de la Presa B.; Sandalinas S.; Carvajal S.; Puntes V.; Jiménez W. (2016) Cerium oxide nanoparticles reduce steatosis, portal hypertension and display anti-inflammatory properties in rats with liver fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 64, 691–698. 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.10.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckman K. L.; DeCoteau W.; Estevez A.; Reed K. J.; Costanzo W.; Sanford D.; Leiter J. C.; Clauss J.; Knapp K.; Gomez C.; Mullen P.; Rathbun E.; Prime K.; Marini J.; Patchefsky J.; Patchefsky A. S.; Hailstone R. K.; Erlichman J. S. (2013) Custom cerium oxide nanoparticles protect against a free radical mediated autoimmune degenerative disease in the brain. ACS Nano 7, 10582–10596. 10.1021/nn403743b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavez-Tapia N. C.; Rosso N.; Tiribelli C. (2012) Effect of intracellular lipid accumulation in a new model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 12, 20. 10.1186/1471-230X-12-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grishko V.; Rachek L.; Musiyenko S.; Ledoux S. P.; Wilson G. L. (2005) Involvement of mtDNA damage in free fatty acid-induced apoptosis. Free Radical Biol. Med. 38, 755–762. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.11.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu H. C.; Kovacs A.; Ford D. A.; Hsu F. F.; Garcia R.; Herrero P.; Saffitz J. E.; Schaffer J. E. (2001) A novel mouse model of lipotoxic cardiomyopathy. J. Clin. Invest. 107, 813–822. 10.1172/JCI10947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainsford K. D. (2007) Anti-inflammatory drugs in the 21st century. Subcell. Biochem. 42, 3–27. 10.1007/1-4020-5688-5_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madrigal-Perez V. M.; García-Rivera A.; Rodriguez-Hernandez A.; Ceja-Espiritu G.; Briseño-Gomez X. G.; Galvan-Salazar H. R.; Soriano-Hernandez A. D.; Guzman-Esquivel J.; Martinez-Fierro M. L.; Newton-Sanchez O. A.; Olmedo Buenrostro B. A.; Rodriguez-Sanchez I. P.; López-Lemus U. A.; Lara-Esqueda A.; Delgado-Enciso I. (2015) Preclinical analysis of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug usefulness for the simultaneous prevention of steatohepatitis, atherosclerosis and hyperlipidemia. Int. J. Clin Exp Med. 8, 22477–22483. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utzeri E.; Usai P. (2017) Role of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on intestinal permeability and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol 23, 3954–3963. 10.3748/wjg.v23.i22.3954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y.; Hou X.; Yang C.; Pang Y.; Li X.; Jiang G.; Liu Y. (2019) Photoprotection of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles against UVA radiation-induced Senescence of Human Skin Fibroblasts due to their Antioxidant Properties. Sci. Rep. 9, 2595. 10.1038/s41598-019-39486-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.