Fig. 2 |.
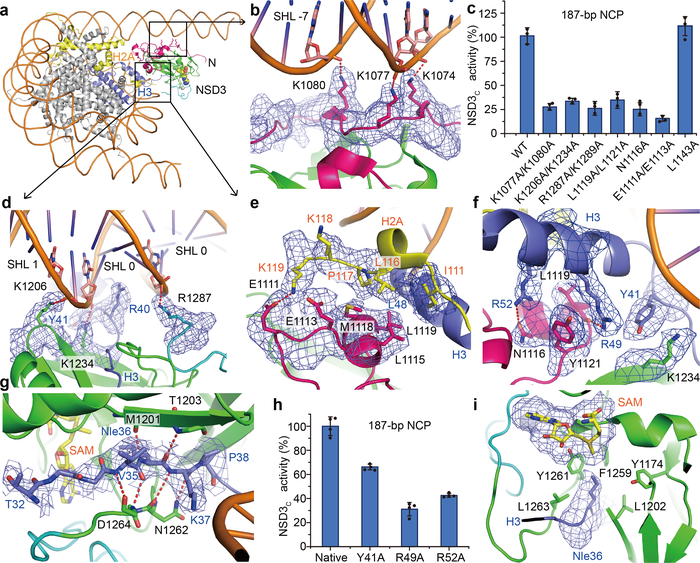
Details of intermolecular contacts between NSD3-E1181K/T1232A and the nucleosome. a, An overview of the contacts between NSD3 and nucleosomal DNA. NSD3 domains are colored as in Fig.1h. Histone H3 and H2A are colored in blue and yellow, respectively. b, The N-terminal loop of NSD3 interacts with the phosphate backbone of the minor groove at SHL −7. c, Relative catalytic activities of the wild-type (WT) and various mutants of NSD3 on 187-bp NCPs. Activity of the WT NSD3 was set to 100%. d, NSD3 SET and post-SET domains interact with the phosphate backbone of the DNA minor groove at SHLs 1 and 0, respectively. e, NSD3 recognizes the C-terminal region of H2A. f, NSD3 recognizes the N-terminal helix of H3. g, NSD3-SET domain recognizes the N-terminal tail of H3. h, NSD3C showed reduced activities on NCPs bearing mutations on NSD3-interacting residues of H3. i, Nle36 binding pocket in NSD3 SET domain. Data are represented as means ± s.d. from n = 3 (panel c) or n = 4 (panel h) independent samples. The cryo-EM density maps of key residues were contoured at 2σ (panels b and g) or 4σ (panels d, e, f and i) level. Red dotted lines in panels b, d, e, f and g indicate salt bridges or hydrogen bonds.