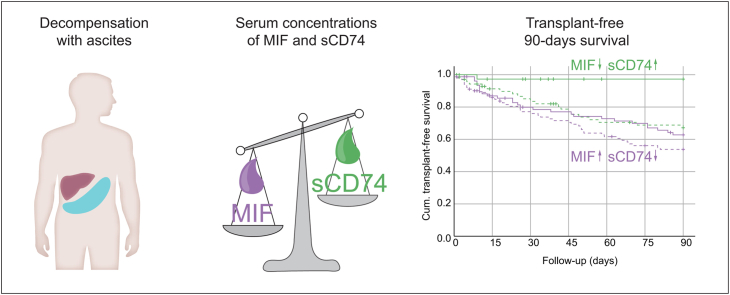
Abstract
Background & Aims
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is an inflammatory cytokine and an important regulator of innate immune responses. We hypothesised that serum concentrations of MIF are associated with disease severity and outcome in patients with decompensated cirrhosis and acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF).
Methods
Circulating concentrations of MIF and its soluble receptor CD74 (sCD74) were determined in sera from 292 patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis defined as new onset or worsening of ascites requiring hospitalisation. Of those, 78 (27%) had ACLF. Short-term mortality was assessed 90 days after inclusion.
Results
Although serum concentrations of MIF and sCD74 did not correlate with liver function parameters or ACLF, higher MIF (optimum cut-off >2.3 ng/ml) and lower concentrations of sCD74 (optimum cut-off <66.5 ng/ml) both indicated poorer 90-day transplant-free survival in univariate analyses (unadjusted hazard ratio [HR] 2.01 [1.26–3.22]; p = 0.004 for MIF; HR 0.59 [0.38–0.92]; p = 0.02 for sCD74) and after adjustment in multivariable models. Higher MIF concentrations correlated with surrogates of systemic inflammation (white blood cells, p = 0.005; C-reactive protein, p = 0.05) and were independent of genetic MIF promoter polymorphisms. Assessment of MIF plasma concentrations in portal venous blood and matched blood samples from the right atrium in a second cohort of patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt insertion revealed a transhepatic MIF gradient with higher concentrations in the right atrial blood.
Conclusions
Serum concentrations of MIF and its soluble receptor CD74 predict 90-day transplant-free survival in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis. This effect was independent of liver function and genetic predispositions, but rather reflected systemic inflammation. Therefore, MIF and sCD74 represent promising prognostic markers beyond classical scoring systems in patients at risk of ACLF.
Lay summary
Inflammatory processes contribute to the increased risk of death in patients with cirrhosis and ascites. We show that patients with high serum levels of the inflammatory cytokine macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) alongside low levels of its binding receptor sCD74 in blood indicate an increased mortality risk in patients with ascites. The cirrhotic liver is a relevant source of elevated circulating MIF levels.
Keywords: Acute-on-chronic liver failure, Inflammation, Liver cirrhosis, Biomarker, Survival
Abbreviations: ACLF, acute-on-chronic liver failure; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; CRP, C-reactive protein; CXCL10, C-X-C motif chemokine; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; MELD, model for end-stage liver disease; MIF, macrophage migration inhibitory factor; SBP, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis; sCD74, soluble receptor CD74; SDC, stable decompensated cirrhosis; SHR, subdistribution hazard ratio; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; TIPS, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt; UDC, unstable decompensated cirrhosis; WBC, white blood cell count
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
MIF serum concentrations do not correlate with hepatic function but with systemic inflammation in decompensated cirrhosis patients.
-
•
MIF serum concentrations are independent of genetic MIF promoter polymorphisms in patients with decompensated cirrhosis.
-
•
MIF and sCD74 serum concentrations predict transplant-free 90-day survival in patients with decompensated cirrhosis.
-
•
Patients with decompensated cirrhosis and both high MIF and low sCD74 serum concentrations have impaired survival.
-
•
Patients with decompensated cirrhosis show a transhepatic gradient with higher MIF concentrations in right atrial blood.
Introduction
Acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) is a syndrome with high mortality in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis.1 Although the pathogenesis of ACLF is multifactorial, systemic inflammation is pivotal for ACLF development and outcome.2 A hallmark of decompensated liver cirrhosis is the upregulation of not only inflammatory, but also anti-inflammatory cytokines.3 Increased blood cell count, macrophage activation markers, and cytokine concentrations have been shown to predict the course of cirrhosis and the risk of future complications such as decompensation and ACLF.[4], [5], [6], [7], [8], [9] Therefore, identifying readily available surrogate markers is desirable to reveal patients at risk for ACLF at an early stage.
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine with chemokine-like functions and is known to be an important regulator of the innate and adaptive immune system.10,11 It is expressed upstream during the inflammatory cascade and modulates various inflammatory and immune responses. This has prompted the characterisation of MIF as a biomarker in several chronic inflammatory diseases.[12], [13], [14] In a murine model of experimental liver fibrosis, MIF was first stated to exert anti-fibrotic effects.15 In human disease, the liver has recently been identified as a significant source of circulating MIF in alcoholic hepatitis, which correlated with disease severity and mortality in this setting.16 Moreover, circulating MIF concentrations correlate with disease severity in autoimmune and cholestatic liver disease17,18 and MIF could be identified as a mediator of chemokine production and immune cell infiltration in alcoholic steatosis.19
In the setting of acute stressors and/or inflammatory stimuli, MIF is secreted by several immune cells, as well as endothelial cells, thrombocytes, and selected parenchymal cells including hepatocytes as well as liver-resident macrophages, Kupffer cells.[20], [21], [22] Within these cells, MIF is constitutively synthesised, stored in pre-formed intracellular pools and is rapidly released in response to different stimuli.23 Among others, the transcriptional activity of MIF is influenced by promoter polymorphisms: rs755622 represents a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) whereas rs5844572 is a microsatellite marker of the tetra nucleotide motive ‘CATT’ with alleles ranging from 5 to 8 repeats (CATT5, CATT6, CATT7, or CATT8). Less frequent genotypes (C/C; CATT7/X) of both polymorphisms show increased basal transcriptional activity of the MIF promoter.12,24,25
MIF signalling and target cell effects are mediated by high affinity interactions with the receptors CD74 (HLA class II histocompatibility antigen gamma chain or invariant chain [Ii]), CXCR2 and CXCR4.26,27 Importantly, CD74 is not only expressed on cell membranes but as a result of membrane proteolysis a shed, soluble form of the CD74 ectodomain (sCD74) exists that was first characterised in autoimmune liver disease.17,28 sCD74 binds to extracellular MIF within the circulation and acts as a decoy receptor resulting in neutralising effects of systemic and local MIF signalling.29 Serum sCD74 concentrations were found to be elevated in inflammatory diseases including acute lung injury as well as burn accompanied by more severe inflammatory injuries associated with worse clinical outcome.30,31 Moreover, sCD74 has been shown to be increased in patients with autoimmune disorders of the liver such as autoimmune hepatitis and primary biliary cholangitis as compared with healthy controls.17
In this study we investigated whether increased serum concentrations of MIF and sCD74 indicate manifested ACLF and predicted short-term mortality in a cohort of hospitalised patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis.
Materials and methods
Study population
Data on patients with decompensated cirrhosis were acquired as a single-centre study and collaboration with the Jena University Hospital, and 292 patients were included from 10/2010 to 06/2015. Patients were admitted to the hospital owing to an acute decompensation of underlying liver cirrhosis accompanied by new onset grade 2 or 3 or worsening ascites. Out-patients undergoing routine large volume paracentesis for refractory ascites were not eligible. Moreover, patients with ascites as a result of peritoneal carcinomatosis or secondary peritonitis were excluded. All specimens and clinical data were obtained at study inclusion, which was defined as the time point of diagnostic paracentesis. Primary endpoints were defined as death from any cause or liver transplantation within 90 days. For comparison of serum concentrations in acutely decompensated cirrhosis to compensated cirrhosis patients, serum concentrations were further determined in a control cohort of 41 patients with compensated cirrhosis.
In a second cohort, 120 patients with cirrhosis undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) implantation owing to variable indications were included in the collaborative study at the University Hospital of Bonn from 08/1998 to 08/2003. During the TIPS procedure blood was drawn at the TIPS insertion from the right atrium as well as the portal vein system.
In both cohorts, informed consent was obtained from patients before inclusion. Patients’ sera were extracted and stored at -80°C. Demographic and clinical data including aetiology of cirrhosis and CHILD Pugh/MELD score were documented at baseline. Blood parameters were determined using routine laboratory analysis. Fulfilment of ACLF criteria according to the chronic liver failure (CLIF) consortium criteria was assessed for patients of the first cohort included in 2013 or later at inclusion; for the remaining patients of the first cohort criteria were reviewed retrospectively. Both described patient cohorts were further characterised and published previously.7,[32], [33], [34], [35], [36], [37], [38]
Ethical approval
The study protocol conformed to the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics committee of the Jena University Hospital; 2880-08/10, 3683-02/3, 3150-06/11 and the Ethics committee of the Bonn University Clinic; 029/13. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects.
ELISA
Determination of MIF and sCD74 in patients’ sera was performed with a human MIF ELISA39 or human sCD74 ELISA17 as previously described. C-X-C motif chemokine (CXCL10) and IL-10 concentrations in serum were determined using the CXCL10/IP-10 DuoSet ELISA (R&D systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA) and the human IL-10 Antibody Pair Kit (ThermoFisher Scientific, Langerwehe, Germany) according to the manufacturers’ instructions.
Determination of MIF promoter polymorphisms -173 G/C (rs755622) and -794 CATT5–8 (rs5844572)
To determine the polymorphisms, genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral whole blood patient samples using a customised kit NucleoSpin® Blood (Macherey Nagel, Düren, Germany). Genotyping of patients for the SNP rs755622 (-173 G/C) was performed with genomic DNA with 5ʹ-endonuclease (TaqMan, Applied Biosystems, Darmstadt, Germany) assays as previously described.40
Fragment analysis to determine the repeat length of the tetra nucleotide marker rs5844572 (-794 CATT5–8) was performed using PCR as previously described.40 PCR products were run on an AB3130 genetic analyser (Applied Biosystems), and electrophoresis results were analysed with the GeneMapper® Software 5 (Applied Biosystems).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed with IBM SPSS Statistics 25 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) and STATA software version 16.1 (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA). Data presentation was performed using GraphPad software version 5.01 (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA). To compare 2 groups, we used Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney tests for continuous and Fisher’s exact test for nominal variables. Bivariate non-parametric correlation analysis (Spearman’s rho) was performed to identify correlations between continuous or ordinal variables. Univariate and multivariable analysis of risk factors for mortality were assessed by Cox regression analysis and binary logistic regression. Continuous variables were dichotomised according to the maximum Youden index in receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis. Time-to-event variables were determined by the Kaplan–Meier method and groups were contrasted by log-rank tests. For analysis of transplant-free and overall survival, patients were right-censored at loss-to-follow-up or at liver transplantation or after 90 days. Competing risk analysis was performed using Fine and Gray's proportional subhazards model using Stata version 16.1 (StataCorp).41 A 2-sided significance level of p = 0.05 was applied for all tests of the study.
Results
Baseline cohort characteristics
A total of 292 hospitalised patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis and ascites were included. The median age at the time of admission was 59 years (Table 1). Of all patients, 74% were males and almost 80% of them suffered from liver cirrhosis as a result of regular alcohol consumption. Approximately two-thirds of all patients were scored as Child-Pugh class C, the median model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) score was 17. In total, 78 (27%) fulfilled the CLIF consortium criteria for ACLF.1 The median time from hospital admission to study inclusion was 1 day (interquartiles 0–6 days). Sixty-five percent of patients were included within 72 h after hospital admission.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of patients with decompensated cirrhosis stratified for outcome at 90 days follow up.
| All patients (n = 292) | Transplant-free survivors at 90 days∗ (n = 199) | Non-survivors/transplanted at 90 days (n = 93) | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 59 (52–67) | 58 (50–65) | 63 (56–71) | <0.001 |
| Male sex (%) | 216 (74) | 149 (75) | 67 (72) | 0.67 |
| HCC at baseline (%) | 42 (14) | 23 (12) | 19 (20) | 0.05 |
| Alcoholic liver disease (%) | 232 (79) | 165 (83) | 67 (72) | 0.04 |
| Child-Pugh class C (%) | 182 (62) | 115 (58) | 67 (72) | 0.02 |
| MELD score | 17 (12–22) | 15 (11–20) | 20 (16–28) | <0.001 |
| ACLF | 78 (27) | 36 (18) | 42 (45) | <0.001 |
| ACLF | ||||
| Grade 1 | 44 (15) | 25 (13) | 19 (20) | 0.004 |
| Grade 2 | 21 (7) | 10 (5) | 11 (12) | |
| Grade 3 | 13 (4) | 1 (1) | 12 (13) | |
| SBP at baseline (%) | 39 (13) | 16 (8) | 23 (25) | <0.001 |
| Bilirubin (μmol/L) | 40 (20–97) | 35 (19–75) | 65 (25–173) | <0.001 |
| ALT (μmol/L) | 0.57 (0.38–0.93) | 0.54 (0.37–0.76) | 0.65 (0.42–1.20) | 0.02 |
| AST (μmol/L) | 1.08 (0.70–1.89) | 1.03 (0.68–1.65) | 1.17 (0.76–2.66) | 0.09 |
| INR | 1.4 (1.2–1.7) | 1.4 (1.2–1.6) | 1.5 (1.3–1.9) | 0.001 |
| Creatinine (μmol/L) | 95 (64–147) | 81 (62–126) | 136 (81–185) | <0.001 |
| WBC (/nl) | 6.8 (5.0–10.1) | 6.3 (4.6–9,3) | 8.4 (5.6–11.9) | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 31 (16–61) | 25 (13–49) | 53 (25–87) | <0.001 |
Baseline characteristics are depicted as frequencies or median (IQR). Values of p are based on Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney test for continuous and Fisher’s exact test for categorial variables.
ACLF, acute-on-chronic liver failure; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; CRP, C-reactive protein; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; MELD, model for end-stage liver disease; SBP, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis; WBC, white blood cell count.
Including 40 patients lost to follow-up after a median of 14 days.
Within 90 days after inclusion, 83 (28%) died, 10 (3%) underwent liver transplantation, and 40 (14%) were lost to follow-up with a median follow-up of 14 days. In patients presenting with ACLF actuarial transplant-free 90-day survival was 43.4 ± 5.8% (standard error) as compared with 73 ± 3.2% in patients without ACLF (p <0.001). Moreover, patients with ACLF were characterised by higher MELD scores (median 25 vs. 14; p <0.001), white blood cell (WBC) counts (9.0 vs. 6.4/nl; p <0.001) and C-reactive protein (CRP) concentrations (42 vs. 29 mg/l; p = 0.02) than patients without ACLF.
MIF and sCD74 serum concentrations do not indicate presence or grade of ACLF
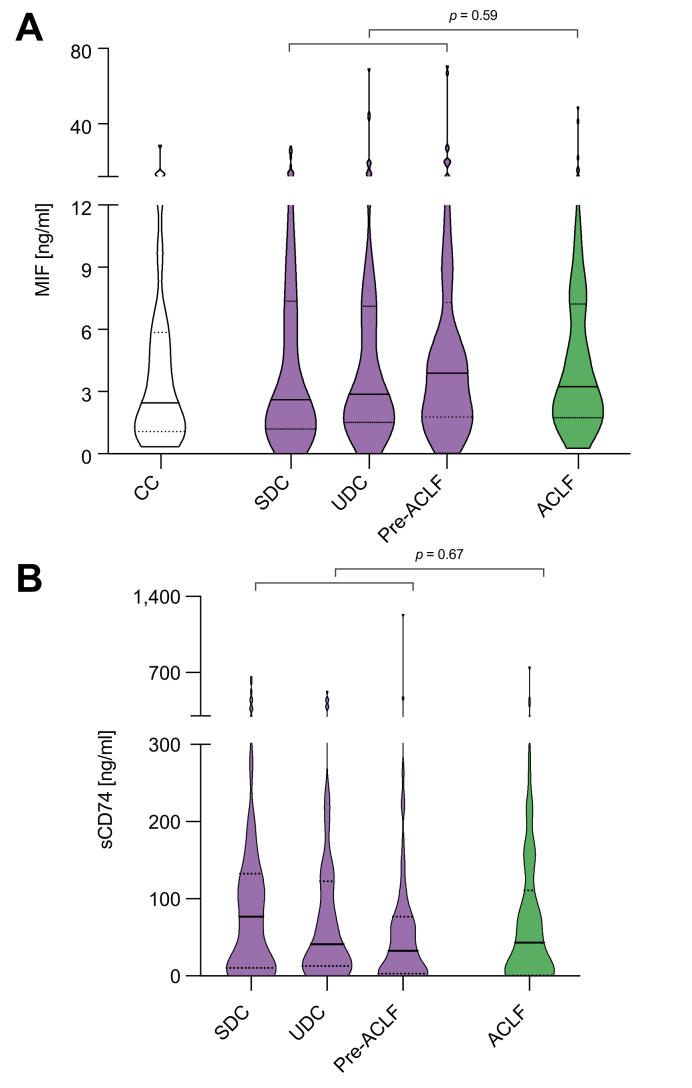
To investigate whether MIF and sCD74 serum concentrations might indicate presence and grade of ACLF both serum parameters were measured in the peripheral serum of included patients. MIF and sCD74 did neither differ between patients with and without ACLF nor in patients with distinct ACLF grades (Table 2, Fig. 1).
Table 2.
MIF and sCD74 serum concentrations stratified for clinical parameters and the presence and severity of ACLF.
| Serum MIF (ng/ml) |
Serum sCD74 (ng/ml) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (IQR) | p value | Median (IQR) | p value | |
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 2.7 (1.4–6.0) | 0.25 | 37.1 (7.2–85.0) | 0.20 |
| Male | 3.2 (1.7–7.6) | 49.3 (6.1–118.7) | ||
| Aetiology | ||||
| Alcoholic | 3.0 (1.5–7.3) | 0.61 | 39.2 (6.1–111.7) | 0.26 |
| Non-alcoholic | 3.2 (1.8–6.8) | 64.2 (10.2–128.4) | ||
| Child-Pugh class | ||||
| B | 3.0 (1.6–7.4) | 0.84 | 38.8 (14.7–84.8) | 0.94 |
| C | 3.1 (1.5–7.3) | 48.5 (2.6–115.0) | ||
| HCC | ||||
| No | 3.0 (1.5–7.2) | 0.32 | 42.3 (5.7–111.4) | 0.67 |
| Yes | 3.5 (1.9–7.9) | 50.5 (13.0–143.4) | ||
| ACLF | ||||
| No | 3.0 (1.5–7.2) | 0.63 | 46.5 (9.2–114.1) | 0.67 |
| Yes | 3.5 (1.9–7.9) | 43.4 (0.6–110.9) | ||
| ACLF grade | ||||
| Grade 1 | 3.1 (1.7–7.1) | 0.49 | 43.1 (1.6–147.1) | 0.90 |
| Grade 2 | 3.6 (1.4–8.0) | 48.9 (1.4–111.0) | ||
| Grade 3 | 3.4 (2.6–8.0) | 37.2 (0.4–74.3) | ||
Medians with IQRs are depicted and p values from the Mann-Whitney U test or Kruskal-Wallis test are shown. ACLF, acute-on-chronic liver failure; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; MIF, macrophage migration inhibitory factor; sCD74, soluble receptor CD74.
Fig. 1.
MIF and sCD74 concentrations in patients with cirrhosis and ascites in absence or presence of ACLF. Violin plots showing the distribution, median and IQRs of serum concentrations of (A) MIF and (B) sCD74 in patients with SDC, UDC, pre-ACLF, and ACLF. p values from Mann-Whitney U tests comparing patients with acute decompensation with and without ACLF are indicated (not significant). Serum concentrations of MIF from patients with CC (n = 41) are shown for comparison. ACLF, acute-on-chronic liver failure; CC, compensated cirrhosis; MIF, macrophage migration inhibitory factor; sCD74, soluble receptor CD74; SDC, stable decompensated cirrhosis; UDC, unstable decompensated cirrhosis.
Within the group of decompensated patients without ACLF at baseline, we performed post-hoc stratification into the 3 different trajectories of decompensated cirrhosis, that is stable decompensated cirrhosis (SDC), unstable decompensated cirrhosis (UDC) and occurrence of ACLF within 90 days (pre-ACLF) according to the PREDICT study.42 Overall, there were no significant differences between MIF and sCD74 concentrations in these 3 groups of acute decompensation when assessed using the Kruskal-Wallis test (Fig. 1, Table S1). In addition, MIF and sCD74 serum concentrations did not significantly differ between patients of different sex, aetiology of cirrhosis, Child-Pugh class or the presence of hepatocellular carcinoma (Table 2).
To assess whether MIF serum concentrations were elevated in patients with decompensated cirrhosis, we included an additional cohort of patients with compensated cirrhosis (Table S2). Median MIF concentrations did not significantly differ between these 2 groups (3.1 ng/ml vs. 2.45 ng/ml, Fig. 1).
Higher MIF and lower sCD74 serum concentrations indicate decreased 90-day transplant-free survival
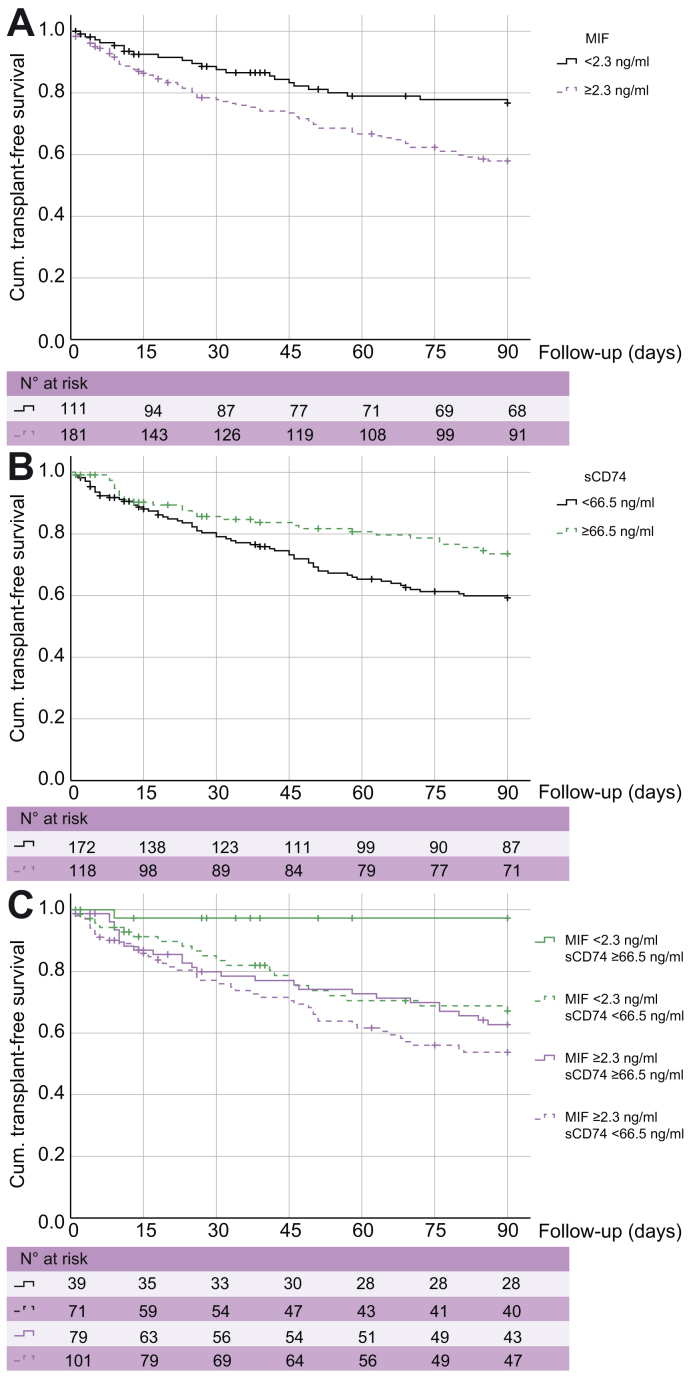
To determine the association of MIF and sCD74 with transplant-free 90-day survival in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis, we identified the optimum cut-off for both serum markers derived from ROC analysis and maximum Youden index. The estimates of cumulative transplant-free survival at 90 days were 57.9 ± 3.9% in patients with serum MIF concentrations ≥2.3 ng/ml as compared with 76.7 ± 4.3% in patients with low serum MIF concentrations <2.3 ng/ml (p = 0.003, log-rank test) (Fig. 2A). The estimates of cumulative transplant-free survival at 90 days were 73.5.9 ± 4.3% in patients with higher serum sCD74 concentrations ≥66.5 ng/ml as compared with 59.3 ± 3.9% in patients with low serum sCD74 concentrations <66.5 ng/ml (p = 0.018, log-rank test) (Fig. 2B).
Fig. 2.
MIF and sCD74 concentrations and transplant-free 90-days survival. Kaplan-Meier analysis of transplant-free 90-day survival is shown for stratified serum (A) MIF and (B) sCD74 concentrations. Both parameters were analysed as dichotomised variables with cut-off values based on the maximal Youden index. In C, stratification was performed for all patients with available serum concentrations for both MIF and sCD74 serum concentrations. Values of statistical significance are (A) p = 0.003, (B) p = 0.018 and (C) p <0.001 in overall and pairwise log-rank test. MIF, macrophage migration inhibitory factor; sCD74, soluble receptor CD74.
To further examine the prognostic significance of MIF and sCD74 serum concentrations on short-term transplant-free survival in the presence of confounding parameters, univariate analysis and multivariable Cox regression analysis were performed. The unadjusted hazard ratio for death or transplant within 90 days was 2.01 (95% CI 1.26–3.22) for MIF concentrations ≥2.3 ng/ml and 0.59 (95% CI 0.38–0.92) for sCD74 concentrations ≥66.5 ng/ml (Table 3). Higher MIF concentrations and lower sCD74 remained significant predictors of death or transplant, when adjusted for the MELD score or the presence of ACLF (Table 3). Higher MIF concentrations remained robust indicators of poor outcome even after adjustment for inflammatory parameters (Table 3).
Table 3.
Dichotomised serum concentrations of MIF and sCD74 indicate an increased risk of death or transplant within 90 days.
| Serum MIF Dichotomised ≥2.3 ng/ml |
Soluble CD74 Dichotomised ≥66.5 ng/ml |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) | p value | Hazard ratio (95% CI) | p value | |
| Unadjusted | 2.01 (1.26–3.22) | 0.004 | 0.59 (0.38–0.92) | 0.02 |
| Adjusted for MELD | 1.70 (1.06–2.75) | 0.03 | 0.62 (0.40–0.97) | 0.03 |
| Adjusted for ACLF | 1.88 (1.17–3.02) | 0.009 | 0.59 (0.38–0.92) | 0.02 |
| Adjusted for WBC∗ | 1.75 (1.09–2.80) | 0.02 | 0.64 (0.41–1.00) | 0.05 |
| Adjusted for CRP∗ | 1.76 (1.10–2.84) | 0.02 | 0.65 (0.42–1.02) | 0.06 |
| Adjusted for ACLF and WBC∗ | 1.57 (1.07–2.32) | 0.02 | 0.63 (0.40–0.99) | 0.04 |
| Adjusted for ACLF and CRP∗ | 1.67 (1.04–2.70) | 0.03 | 0.64 (0.41–1.01) | 0.055 |
Univariate and multivariable Cox regression analysis of the risk for death or transplant within 90 days using dichotomised serum levels of MIF and sCD74. In multivariable analysis, hazard ratios were adjusted for the MELD, presence of ACLF, and the inflammatory parameters WBC and CRP as indicated. Serum MIF and sCD74 were dichotomised according to the maximum Youden index. ACLF, acute-on-chronic liver failure; CRP, C-reactive protein; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; MELD, model for end-stage liver disease; MIF, macrophage migration inhibitory factor; sCD74, soluble receptor CD74; WBC, white blood cell count.
Parameter was loge-normalised.
Among 290 patients, both serum sCD74 and MIF concentration could be determined. Here, 71 (24%) had low MIF and low sCD74 concentrations, 39 (13%) had low MIF and high sCD74, 101 (35%) had high MIF and low sCD74, and 79 (27%) had high MIF and high sCD74. Estimates of transplant-free 90-day survival was 97.3 ± 2.7% in patients with low MIF and high sCD74, whereas it was only 53.8 ± 5.2% in patients with high MIF and low sCD74 (p < 0.001, overall and pairwise log-rank test) (Fig. 2C).
Having analysed liver transplantation or death as a composite outcome, we went on to analyse 90-day mortality defining liver transplantation as a competing risk. In a multivariable Fine and Gray regression model, both MIF concentrations of 2.3 ng/ml or higher (subdistribution hazard ratio [SHR] 2.26; 95% CI 1.37–3.77; p = 0.002) and sCD74 concentrations of 66.5 ng/ml or higher (SHR 0.60; 95% CI 0.38–0.94; p = 0.026) were significant independent predictors of 90-day mortality.
Serum MIF concentrations do not correlate with hepatic dysfunction but with markers of systemic inflammation
To further investigate the role of MIF in decompensated cirrhosis from a context-dependent and functional point of view, we investigated whether MIF is rather associated with the intrahepatic organ function or with the state of systemic inflammation: Interestingly, MIF did not correlate with organ dysfunction but with the state of inflammation as characterised by white blood cell count, CRP, IL-10, and CXCL10 serum concentrations (Table 4). Notably, this correlation was not evident for sCD74.
Table 4.
Correlation of MIF and sCD74 serum concentrations with markers of liver dysfunction and systemic inflammation.
| MIF |
Soluble CD74 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-parametric correlation | p value | Non-parametric correlation | p value | |
| MELD score | 0.019 | 0.74 | -0.090 | 0.13 |
| Bilirubin | -0.067 | 0.25 | -0.062 | 0.29 |
| Albumin | 0.077 | 0.20 | 0.064 | 0.28 |
| WBC | 0.165 | 0.005 | -0.101 | 0.09 |
| CRP | 0.117 | 0.05 | -0.079 | 0.18 |
| IL-10∗ | 0.225 | 0.0006 | 0.013 | 0.85 |
| CXCL10∗ | 0.157 | 0.02 | 0.115 | 0.09 |
CRP, C-reactive protein; CXCL10, C-X-C motif chemokine; MELD, model for end-stage liver disease; MIF, macrophage migration inhibitory factor; sCD74, soluble receptor CD74; WBC, white blood cell count.
IL-10 and CXCL10 serum concentrations were available in 227 and 230 patients, respectively. Non-parametric Spearman’s rho correlation coefficients are shown.
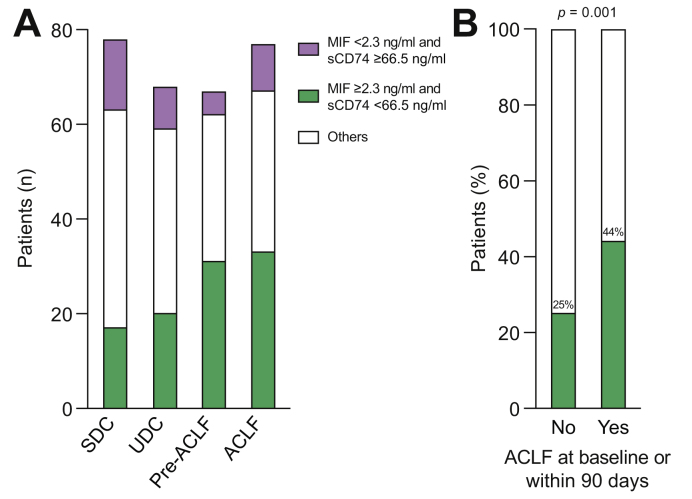
As systemic inflammation is a driver of ACLF and mortality in patients with cirrhosis, we first confirmed that the majority of deaths in patients with acute decompensation at baseline were a consequence of developing ACLF (Table S1). Although patients with the high-risk constellation, MIF ≥2.3 ng/ml and sCD74 <66.5 ng/ml, could be identified in patients from all trajectories of acute decompensation (Fig. 3A), a high-risk constellation was found more often in patients presenting with or developing ACLF within 90 days as compared with patients free of ACLF at baseline or during follow-up (p = 0.001) (Fig. 3B).
Fig. 3.
The frequency of patients with high MIF/low sCD74 serum concentrations differs within different phenotypes of patients with acutely decompensated cirrhosis. (A) Absolute numbers of patients with different MIF/sCD74 serum constellations within the different phenotype subgroups SDC, UDC, pre-ACLF as well as ACLF are depicted. Only patients with available data for both MIF as well as sCD74 serum concentrations were included in this figure. (B) The percentage of patients with high MIF/low sCD74 serum concentrations was significantly increased within the subgroup of patients, who presented with or developed ACLF within 90 days after inclusion (pre-ACLF, ACLF) as compared with patients without ACLF at baseline and within 90 days (SDC, UDC). Value of statistical significance is indicated as p = 0.001 from Fisher’s exact test. ACLF, acute-on-chronic liver failure; MIF, macrophage migration inhibitory factor; sCD74, soluble receptor CD74; SDC, stable decompensated cirrhosis; UDC, unstable decompensated cirrhosis.
The investigated MIF promoter variants G/C -173 and (CATT)5-8 -794 correlate with sCD74 concentrations but do not indicate outcome
Next, we set out to evaluate if elevated MIF concentrations, associated with decreased survival in patients with decompensated cirrhosis, are determined by genetic variants. Therefore, we assessed the distribution of 2 predominant MIF promoter polymorphisms associated with MIF expression alterations in our cohort: the SNP rs755622 and rs5844572 – a microsatellite marker of the tetra nucleotide motive ‘CATT’. Less frequent genotypes (C/C; CATT7/X) of both polymorphisms show increased basal transcriptional activity of the MIF promoter.12,24,25 In our cohort, the MIF promoter variant SNP -173C correlated with sCD74 concentrations as patients with the C/C genotype had significantly decreased sCD74 serum concentrations (Table S3). A similar trend was seen for patients with the genotype CATT 7/X of the microsatellite CATT5-8 (p = 0.07, not significant). However, both investigated promoter variants did not correlate with MIF serum concentrations stating that genetic predisposition does not represent the leading factor regarding the determination of MIF serum concentrations in our cohort. Additionally, neither SNP -173C nor microsatellite CATT5-8 indicated short-term outcome (Table S4).
Liver cirrhosis is a significant source of MIF in decompensated cirrhosis
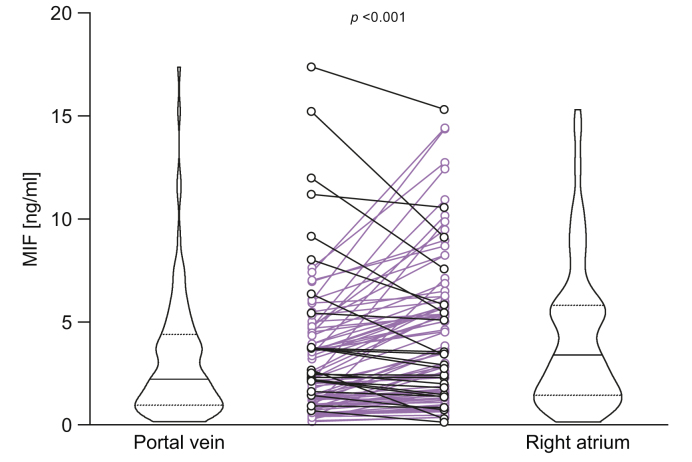
To evaluate the source of MIF within the systemic circulation, an independent cohort of patients undergoing TIPS insertion was analysed. TIPS was implanted for different indications (Table S5), 44% of patients had ascites. Blood was drawn during TIPS insertion from the right atrium and the portal vein. MIF concentrations were significantly higher in plasma from the right atrium than the portal vein, consistent with the liver representing a significant source of MIF in patients with decompensated liver disease (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4.
MIF plasma concentrations in the right atrium exceed MIF concentrations in the portal vein in cirrhotic patients undergoing procedure of TIPS insertion. Matching plasma samples were drawn from the right atrium and portal vein during TIPS insertion in cirrhotic patients. MIF plasma concentrations were measured by ELISA. The value of statistical significance is p <0.001 with Wilcoxon’s signed rank test. MIF, macrophage migration inhibitory factor; TIPS, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
Discussion
The present study demonstrates for the first time that higher concentrations of circulating MIF and lower concentrations of its soluble receptor CD74 are associated with decreased short-term transplant-free survival in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis. This association remained significant after adjustment for MELD, age, and presence of ACLF, and was independent of the presence or severity of ACLF. Consistent with publications characterising MIF as a relevant pro-inflammatory cytokine in inflammatory diseases,12,20,21 MIF serum concentrations correlated with markers of systemic inflammation, but were largely independent of genetic predisposition determined by common MIF promoter polymorphisms. We were able to identify the liver as an important source of circulating MIF in patients with decompensated cirrhosis.
MIF is expressed by several immune cells, epithelial and endothelial cells and exerts multifaceted pro-inflammatory functions in immune cell recruitment and macrophage survival.21 Consistently, higher MIF circulating concentrations have been shown to be associated with the severity of various inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.12 MIF has been identified to play a key regulatory role in rapid innate immune responses as it is pre-formed in cell types and can be released in response to pathogen-associated factors such as LPS,43 which renders this cytokine as an attractive readily accessible marker for the early diagnosis of new diseases in the clinical practice. Subsequently, MIF promotes macrophage surveillance and survival21 and amplifies inflammatory responses.44 In line with these observations, MIF serum concentrations are increased in patients with critical illness and septic shock and correlate with short-term outcome.45
Patients with decompensated cirrhosis are at high risk for bacterial infections and organ failure, characterised and often amplified by systemic inflammatory responses. Inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, often involved in leukocyte migration and chemotaxis pathways, are elevated in decompensated cirrhosis as compared with non-cirrhotic controls.8,46 This study reveals that patients with decompensated cirrhosis exert higher MIF serum concentrations, which correlate with prognostic markers of systemic inflammation such as white blood cell count and CRP. In contrast to other inflammatory cytokines and acute phase proteins, there was no correlation of serum MIF with the presence and severity of organ failure in decompensated cirrhosis.
Our data reveal that high MIF and low sCD74 serum concentrations are associated with impaired survival in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis. In contrast to our hypothesis, neither MIF nor sCD74 reliably indicated the presence of already established ACLF. However, as patients with the high-risk constellation, high MIF and low sCD74, as well as with the low-risk constellation, low MIF and high sCD74, were found across the 3 subgroups, it is tempting to speculate that the determination of serum MIF and sCD74 could help for risk stratification and prognosis prediction in acutely decompensated patients beyond the existing phenotypic characterisation,42 which relies on knowing the outcome after 90 days. Given that the major cause of death in our cohort was ACLF and we observed an enrichment of patients with the high-risk constellation (high MIF/low sCD74) in patients presenting with or developing ACLF, we speculate that the balance of MIF and sCD74 may indicate patients at risk even before the development of ACLF. However, 1 important limitation in interpreting MIF/sCD74 as a predictor of ACLF is the retrospective study design and the post-hoc stratification of patients into the 3 trajectories of acute decompensation.
Consistent with data on alcoholic hepatitis,16 we were able to demonstrate the liver as a relevant source of circulating MIF in decompensated cirrhosis. MIF levels in the right atrium were higher than in the portal vein in patients undergoing TIPS insertion even in the absence of acute liver injury.
Importantly, our data suggest a prognostic relevance of the interplay of MIF and sCD74 in decompensated cirrhosis. The function of sCD74 as a decoy receptor of circulating MIF has first been characterised in autoimmune liver disease and primary biliary cirrhosis,17 where serum sCD74/MIF negatively correlated with disease severity. These data prompted the question whether the relation of sCD74 and MIF distinguishes between levels of systemic inflammation or predict disease progression in advanced liver disease: Our data show the largest differences in short-term transplant-free survival between patients with high MIF and low sCD74 serum concentrations and patients with low MIF and high sCD74 serum concentrations. Therefore, it is tempting to speculate that MIF and sCD74 serum concentrations might exert functions beyond biomarkers of liver-related endpoints: Soluble CD74 would be able to neutralise MIF in the systemic circulation and specifically antagonise its proinflammatory function, which may be therapeutically employed. This is supported by the fact that patients with MIF promoter polymorphisms promoting higher MIF serum concentrations (SNP -173C C/C genotype and microsatellite CATT5-8 7/X genotype)12,17 had decreased sCD74, presumably as a consequence of binding to MIF. Apart from chronic liver diseases there is also evidence regarding a prognostically and functionally relevant interaction of MIF and sCD74 in ischaemia/reperfusion injury during cardiac surgery,47,48 where the presence of sCD74/MIF complexes correlated with less acute kidney injury improved oxidative stress, and altered MIF signalling in vitro.
In addition to using sCD74 as a decoy for MIF, strategies antagonising MIF using small molecule inhibitors, DNA-based vaccination strategies, or nanobodies have been successfully tested in animal models of glomerulonephritis49 and sepsis;50,51 further therapeutic strategies have been published in detail in a recent review.52 Based on our data it might be another important and promising approach to block the pro-inflammatory activities of MIF in inflammatory end-organ damage including decompensated cirrhosis.
Conclusions
In summary, higher MIF and lower sCD74 serum concentrations independently indicate poor 90-day transplant-free survival in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis. Using MIF/sCD74 concentrations for risk stratification in patients with decompensated cirrhosis is intriguing as MIF serum concentrations were largely independent of underlying hepatic and extrahepatic organ dysfunction. Given our observation, that higher concentrations of its soluble receptor sCD74 were associated with improved outcome, it is tempting to speculate that sCD74 could have therapeutic relevance in patients with decompensated liver disease.
Financial support
This study was supported by the German Research Foundation Grant SFB/TRR 57 to M.-L.B., J.B. and C.T. (Project ID 36842431), CRC1382 to M.-L.B., T.B. and C.T. (Project ID 403224013), BR 4905/3-1 to T.B, STO 1099/8-1 to C.S. and BE1977/14-1 to J.B. Further funding was provided by the BMBF (Federal Ministry of Education and Research, Germany) LiSyM project (FKZ 031L0041) to M.-L.B and C.T.
Authors’ contributions
Performed all experiments: THW, PF, IB, CB, CE. Assisted with performing the experiments: EFB, JR, MTK. Analysed the data: THW, TB. Drafted the manuscript: THW. Supported data analysis: CS, KMS, PAR, HWZ. Collected patients’ samples and obtained clinical data: NK-V, PAR, RS, MJB, JC, MP, JT, TB. Helped with performance of fluorescence-based genotyping and critically reviewed the manuscript: CB, TE, IK. Helped with performance of sCD74 ELISA: RB, JB
Critically edited the manuscript: JB, CT, JT, MP, AS. Designed the study, supervised the analysis of the data, and edited the manuscript: M-LB, TB
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author, THW.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest that pertain to this work.
Please refer to the accompanying ICMJE disclosure forms for further details.
Footnotes
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhepr.2020.100221
Appendix A. Supplementary data
References
- 1.Moreau R., Jalan R., Gines P., Pavesi M., Angeli P., Cordoba J. Acute-on-chronic liver failure is a distinct syndrome that develops in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2013;144:1426–1437. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.02.042. e1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Claria J., Arroyo V., Moreau R. The acute-on-chronic liver failure syndrome, or when the innate immune system goes astray. J Immunol. 2016;197:3755–3761. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Claria J., Stauber R.E., Coenraad M.J., Moreau R., Jalan R., Pavesi M. Systemic inflammation in decompensated cirrhosis: characterization and role in acute-on-chronic liver failure. Hepatology. 2016;64:1249–1264. doi: 10.1002/hep.28740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Claria J., Moreau R., Fenaille F., Amoros A., Junot C., Gronbaek H. Orchestration of tryptophan-kynurenine pathway, acute decompensation, and acute-on-chronic liver failure in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2019;69:1686–1701. doi: 10.1002/hep.30363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Monteiro S., Grandt J., Uschner F.E., Kimer N., Madsen J.L., Schierwagen R. Differential inflammasome activation predisposes to acute-on-chronic liver failure in human and experimental cirrhosis with and without previous decompensation. Gut. 2020 doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-320170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Moreau R., Claria J., Aguilar F., Fenaille F., Lozano J.J., Junot C. Blood metabolomics uncovers inflammation-associated mitochondrial dysfunction as a potential mechanism underlying ACLF. J Hepatol. 2020;72:688–701. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.11.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Queck A., Bode H., Uschner F.E., Brol M.J., Graf C., Schulz M. Systemic MCP-1 levels derive mainly from injured liver and are associated with complications in cirrhosis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:354. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Trebicka J., Amoros A., Pitarch C., Titos E., Alcaraz-Quiles J., Schierwagen R. Addressing profiles of systemic inflammation across the different clinical phenotypes of acutely decompensated cirrhosis. Front Immunol. 2019;10:476. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gronbaek H., Rodgaard-Hansen S., Aagaard N.K., Arroyo V., Moestrup S.K., Garcia E. Macrophage activation markers predict mortality in patients with liver cirrhosis without or with acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) J Hepatol. 2016;64:813–822. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.11.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Calandra T., Bernhagen J., Metz C.N., Spiegel L.A., Bacher M., Donnelly T. MIF as a glucocorticoid-induced modulator of cytokine production. Nature. 1995;377:68–71. doi: 10.1038/377068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bacher M., Metz C.N., Calandra T., Mayer K., Chesney J., Lohoff M. An essential regulatory role for macrophage migration inhibitory factor in T-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:7849–7854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.15.7849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Radstake T.R., Sweep F.C., Welsing P., Franke B., Vermeulen S.H., Geurts-Moespot A. Correlation of rheumatoid arthritis severity with the genetic functional variants and circulating levels of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:3020–3029. doi: 10.1002/art.21285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wu S.P., Leng L., Feng Z., Liu N., Zhao H., McDonald C. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promoter polymorphisms and the clinical expression of scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:3661–3669. doi: 10.1002/art.22179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nohara H., Okayama N., Inoue N., Koike Y., Fujimura K., Suehiro Y. Association of the -173 G/C polymorphism of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor gene with ulcerative colitis. J Gastroenterol. 2004;39:242–246. doi: 10.1007/s00535-003-1284-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Heinrichs D., Knauel M., Offermanns C., Berres M.L., Nellen A., Leng L. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) exerts antifibrotic effects in experimental liver fibrosis via CD74. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:17444–17449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1107023108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Marin V., Poulsen K., Odena G., McMullen M.R., Altamirano J., Sancho-Bru P. Hepatocyte-derived macrophage migration inhibitory factor mediates alcohol-induced liver injury in mice and patients. J Hepatol. 2017;67:1018–1025. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.06.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Assis D.N., Leng L., Du X., Zhang C.K., Grieb G., Merk M. The role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in autoimmune liver disease. Hepatology. 2014;59:580–591. doi: 10.1002/hep.26664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sadek K.H., Ezzat S., Abdel-Aziz S.A., Alaraby H., Mosbeh A., Abdel-Rahman M.H. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) gene promotor polymorphism is associated with increased fibrosis in biliary atresia patients, but not with disease susceptibility. Ann Hum Genet. 2017;81:177–183. doi: 10.1111/ahg.12199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Barnes M.A., McMullen M.R., Roychowdhury S., Pisano S.G., Liu X., Stavitsky A.B. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor contributes to ethanol-induced liver injury by mediating cell injury, steatohepatitis, and steatosis. Hepatology. 2013;57:1980–1991. doi: 10.1002/hep.26169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bacher M., Meinhardt A., Lan H.Y., Mu W., Metz C.N., Chesney J.A. Migration inhibitory factor expression in experimentally induced endotoxemia. Am J Pathol. 1997;150:235–246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kang I., Bucala R. The immunobiology of MIF: function, genetics and prospects for precision medicine. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15:427–437. doi: 10.1038/s41584-019-0238-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schober A., Bernhagen J., Weber C. Chemokine-like functions of MIF in atherosclerosis. J Mol Med. 2008;86:761–770. doi: 10.1007/s00109-008-0334-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Merk M., Baugh J., Zierow S., Leng L., Pal U., Lee S.J. The Golgi-associated protein p115 mediates the secretion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. J Immunol. 2009;182:6896–6906. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Donn R., Alourfi Z., Zeggini E., Lamb R., Jury F., Lunt M. A functional promoter haplotype of macrophage migration inhibitory factor is linked and associated with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:1604–1610. doi: 10.1002/art.20178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Banos-Hernandez C.J., Navarro-Zarza J.E., Bucala R., Hernandez-Bello J., Parra-Rojas I., Ramirez-Duenas M.G. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor polymorphisms are a potential susceptibility marker in systemic sclerosis from southern Mexican population: association with MIF mRNA expression and cytokine profile. Clin Rheumatol. 2019;38:1643–1654. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04459-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bernhagen J., Krohn R., Lue H., Gregory J.L., Zernecke A., Koenen R.R. MIF is a noncognate ligand of CXC chemokine receptors in inflammatory and atherogenic cell recruitment. Nat Med. 2007;13:587–596. doi: 10.1038/nm1567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Leng L., Metz C.N., Fang Y., Xu J., Donnelly S., Baugh J. MIF signal transduction initiated by binding to CD74. J Exp Med. 2003;197:1467–1476. doi: 10.1084/jem.20030286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Levine S.J. Molecular mechanisms of soluble cytokine receptor generation. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:14177–14181. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R700052200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Soppert J., Kraemer S., Beckers C., Averdunk L., Mollmann J., Denecke B. Soluble CD74 reroutes MIF/CXCR4/AKT-mediated survival of cardiac myofibroblasts to necroptosis. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018;7 doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.009384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wu G., Sun Y., Wang K., Chen Z., Wang X., Chang F. Relationship between elevated soluble CD74 and severity of experimental and clinical ALI/ARDS. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30067. doi: 10.1038/srep30067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kim B.S., Stoppe C., Grieb G., Leng L., Sauler M., Assis D. The clinical significance of the MIF homolog d-dopachrome tautomerase (MIF-2) and its circulating receptor (sCD74) in burn. Burns. 2016;42:1265–1276. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2016.02.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bruns T., Nuraldeen R., Mai M., Stengel S., Zimmermann H.W., Yagmur E. Low serum transferrin correlates with acute-on-chronic organ failure and indicates short-term mortality in decompensated cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2017;37:232–241. doi: 10.1111/liv.13211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Benz F., Bogen A., Praktiknjo M., Jansen C., Meyer C., Wree A. Serum levels of bone sialoprotein correlate with portal pressure in patients with liver cirrhosis. PLoS One. 2020;15 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Berres M.L., Asmacher S., Lehmann J., Jansen C., Gortzen J., Klein S. CXCL9 is a prognostic marker in patients with liver cirrhosis receiving transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. J Hepatol. 2015;62:332–339. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.09.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Berres M.L., Lehmann J., Jansen C., Gortzen J., Meyer C., Thomas D. Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 11 levels predict survival in cirrhotic patients with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Liver Int. 2016;36:386–394. doi: 10.1111/liv.12922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lehmann J.M., Claus K., Jansen C., Pohlmann A., Schierwagen R., Meyer C. Circulating CXCL10 in cirrhotic portal hypertension might reflect systemic inflammation and predict ACLF and mortality. Liver Int. 2018;38:875–884. doi: 10.1111/liv.13610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nielsen M.J., Lehmann J., Leeming D.J., Schierwagen R., Klein S., Jansen C. Circulating elastin fragments are not affected by hepatic, renal and hemodynamic changes, but reflect survival in cirrhosis with TIPS. Dig Dis Sci. 2015;60:3456–3464. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3783-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Torner M., Mangal A., Scharnagl H., Jansen C., Praktiknjo M., Queck A. Sex specificity of kidney markers to assess prognosis in cirrhotic patients with TIPS. Liver Int. 2020;40:186–193. doi: 10.1111/liv.14230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Strussmann T., Tillmann S., Wirtz T., Bucala R., von Hundelshausen P., Bernhagen J. Platelets are a previously unrecognised source of MIF. Thromb Haemost. 2013;110:1004–1013. doi: 10.1160/TH13-01-0049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wirtz T.H., Fischer P., Backhaus C., Bergmann I., Brandt E.F., Heinrichs D. Genetic variants in the promoter region of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor are associated with the severity of hepatitis C virus-induced liver fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:3753. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wolbers M., Koller M.T., Witteman J.C., Steyerberg E.W. Prognostic models with competing risks: methods and application to coronary risk prediction. Epidemiology. 2009;20:555–561. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0b013e3181a39056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Trebicka J., Fernandez J., Papp M., Caraceni P., Laleman W., Gambino C. The PREDICT study uncovers three clinical courses of acutely decompensated cirrhosis that have distinct pathophysiology. J Hepatol. 2020;73:842–854. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.06.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Uhlen M., Fagerberg L., Hallstrom B.M., Lindskog C., Oksvold P., Mardinoglu A. Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science. 2015;347:1260419. doi: 10.1126/science.1260419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Gao X.M., Liu Y., White D., Su Y., Drew B.G., Bruce C.R. Deletion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor protects the heart from severe ischemia-reperfusion injury: a predominant role of anti-inflammation. J Mol Cel Cardiol. 2011;50:991–999. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2010.12.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bozza F.A., Gomes R.N., Japiassu A.M., Soares M., Castro-Faria-Neto H.C., Bozza P.T. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor levels correlate with fatal outcome in sepsis. Shock. 2004;22:309–313. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000140305.01641.c8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sole C., Sola E., Morales-Ruiz M., Fernandez G., Huelin P., Graupera I. Characterization of inflammatory response in acute-on-chronic liver failure and relationship with prognosis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32341. doi: 10.1038/srep32341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Stoppe C., Werker T., Rossaint R., Dollo F., Lue H., Wonisch W. What is the significance of perioperative release of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in cardiac surgery? Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;19:231–239. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.5015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Stoppe C., Rex S., Goetzenich A., Kraemer S., Emontzpohl C., Soppert J. Interaction of MIF family proteins in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion damage and their influence on clinical outcome of cardiac surgery patients. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015;23:865–879. doi: 10.1089/ars.2014.6243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Leng L., Chen L., Fan J., Greven D., Arjona A., Du X. A small-molecule macrophage migration inhibitory factor antagonist protects against glomerulonephritis in lupus-prone NZB/NZW F1 and MRL/lpr mice. J Immunol. 2011;186:527–538. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Tohyama S., Onodera S., Tohyama H., Yasuda K., Nishihira J., Mizue Y. A novel DNA vaccine-targeting macrophage migration inhibitory factor improves the survival of mice with sepsis. Gene Ther. 2008;15:1513–1522. doi: 10.1038/gt.2008.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Sparkes A., De Baetselier P., Brys L., Cabrito I., Sterckx Y.G., Schoonooghe S. Novel half-life extended anti-MIF nanobodies protect against endotoxic shock. FASEB J. 2018;32:3411–3422. doi: 10.1096/fj.201701189R. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Sinitski D., Kontos C., Krammer C., Asare Y., Kapurniotu A., Bernhagen J. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF)-based therapeutic concepts in atherosclerosis and inflammation. Thromb Haemost. 2019;119:553–566. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1677803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author, THW.