Abstract
Objective
Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are injuries to the musculoskeletal (MSK) system that occur due to repetitive or singular trauma and negatively affect one’s daily life. Dentistry is a field that exposes professionals to the highest rate of work-related MSDs. This study aimed to assess the prevalence and predictors of MSK pain among a sample of dental students.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted among a sample of 377 dental students and interns at the dental school of King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. We distributed a validated questionnaire, the Nordic Back Pain Questionnaire, which included additional questions, to all dental students participating in clinical practice and to dental interns. Categorical variables were described by presenting frequencies and percentages, and continuous variables by displaying means and standard deviations. Logistic regression was performed to identify predictors for developing MSK pain over the last 12 months.
Results
Overall, 91.2% of the participants experienced MSK pain or discomfort in one or more body parts over the last 12 months. The highest prevalence was for neck pain (69.2%), followed by shoulder pain (67.1%) and lower back pain (65%). Females were more likely than males to experience MSK pain (odds ratio [OR] = 2.98, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.3–6.7), and those who exercised regularly were less likely to experience MSK pain than were those who did not (OR = 0.27, 95% CI: 0.1–0.6).
Conclusion
This study showed a concerningly high prevalence of MSD symptoms among dental students, especially in the neck, shoulders, and lower back. Educational and occupational health programs in preclinical years could be effective for reducing MSK pain.
Keywords: occupational hazards, dental students, musculoskeletal disorders, occupational health, ergonomics
Introduction
Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are defined as injuries to the musculoskeletal (MSK) system that can happen due to repetitive or singular trauma and that adversely affect an individual’s daily life.1 The dental field exposes professionals to a high rate of job-related MSDs. These occupational MSDs result from multiple factors, such as working in a restricted working field for prolonged hours while maintaining static posture, making repetitive wrist movements, and maintaining a bent neck.2–5 These problems could lead to a decline in dental professionals’ health, which could increase the amount of sick leave.6
MSDs are one of the most common work-related health hazards for healthcare professionals, particularly among dentists.7 Several studies have been conducted to assess MSK pain among dental students. In the United States, 46% to 71% of dental students reported body pain, with the percentage increasing by school year.8 Research in the United Kingdom showed that the lower back was the most common area for pain at a rate of 54%.9 Another study in Europe showed that 92% of participants reported neck, shoulder, elbow, wrist, or hip pain,10 while research in Indonesia showed that 63.5% of dentists experienced MSD symptoms.11 High MSK pain rates for dental students have also been reported in local studies. In a cross-sectional study of 68 dentists in Hail, Saudi Arabia, the prevalence of MSK pain was 77.9%.12 A study involving the observation of 134 dental students’ postural positions found that 89% of students had poor to medium levels of postural awareness, which was reflected in the high prevalence of MSDs (75%).13
Dentistry is considered to be a continuously developing profession in Saudi Arabia. The Saudi Ministry of Health reported that there were 16,752 dentists in 2018, 12,430 of whom were residents, thus comprising 74.2% of all dentists working in Saudi Arabia.14 MSK pain is a major occupational health concern in the dental field,15 and the high rates of MSK pain among dentists can be attributed to various physiological and ergonomic factors related to the profession.16
Identifying the prevalence and predictors of MSDs will allow better understanding of its early development among dental students, as well as influence planning of preventive measures, such as the employment of ergonomic and proper posture principles within their curricula later on. Furthermore, data regarding MSD among dental students in Saudi Arabia is limited. Therefore, this study was conducted to assess the prevalence and predictors of MSK pain in a sample of undergraduate dental students.
Methods
Study Design
This cross-sectional study was conducted at King Abdulaziz University, Faculty of Dentistry (KAUFD) in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
Participants and Data Collection
In order to assess MSK pain, we distributed a self-report questionnaire to all dental students in clinical years (4th, 5th, and 6th year) and dental interns (n= 625). Students at KAUFD start their clinical exposure in their fourth year, working around 12 hours per week. Data were collected from February 2018 to July 2018. The questionnaire was distributed to dental students during their clinical sessions and to interns during their mandatory weekly teaching lectures.
Questionnaire
The questionnaire was divided into 4 sections, with a total of 61 questions. The first section was used to collect sociodemographic data: gender, age, weight, height, body mass index (BMI), school year, physical activity level, and whether they stretch after exercise (8 questions). The second section was the English version of the validated Nordic Back Pain Questionnaire,17 which includes 36 “Yes or No” questions to collect information regarding history of trouble (such as, ache, pain, discomfort, numbness), in the 12 months and in the past 7 days preceding the survey, in a respondent’s neck, shoulders, elbows, upper back, wrists/hands, lower back, hips/thighs, knees, and ankles/feet experienced. This section also asks whether respondents sought medical attention in the past 12 months, and if the pain prevented them from performing normal activities in the past 12 months, with regards to the anatomical sites listed above. The psychometric properties of the Nordic Back Pain Questionnaire showed good reliability and validity which makes it adequate for assessing health-related factors at work.18 The third section included a numeric rating scale from one to 5, which was used to identify the severity of pain in respondents’ eyes, neck, shoulders, upper back, elbows, lower back, arms, wrists/hands, thighs, knees, calves, and feet/ankles (12 questions). A score of one indicates extremely comfortable and a score of 5 indicates extremely uncomfortable. An overall score for each body part was calculated by summing the scores of the different questions for the respective body part. The fourth section of the questionnaire included 5 questions added by the investigators to evaluate work-related actions that might influence MSK pain: repeated neck bending, arms outstretched for long periods, repetitive movements during work, stretching exercises between patients, and regular wear of dental loupes.
Ethical Considerations
We obtained ethical approval from the ethical approval committee at King Abdulaziz University, Faculty of Dentistry, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia (ethical approval number: 032–02-18). This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Implied consent was obtained from all participants. They were informed that participation was voluntary and that filling out the questionnaire indicated their agreement to participate in the study. The questionnaire was accompanied by a cover letter explaining the study’s objective and reassuring respondents of the confidentiality of the data.
Statistical Analyses
For descriptive statistics, categorical variables were presented as frequencies and percentages, while continuous variables as means and standard deviations (SD). A chi-square test was used to assess the associations between categorical variables. Degree of discomfort scores were checked for normality by using Shapiro–Wilk and Kolmogorov–Smirnov tests. Scores between males and females were compared by conducting a two-sample t-test. Logistic regression analysis was performed to identify predictors of developing MSK pain over the last 12 months. Variables that were significant in the univariate analyses were entered into a multivariate model. P-values of ≤0.05 were considered statistically significant. Analyses were performed with SPSS, version 23.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
Results
A total of 377 out of 625 dental students agreed to participate, yielding a response rate of 60.3% (50.8% for males, and 68.4% for females). The mean age was 22.8 ± 1.4 years, and 61.5% were females. Half of the males (49.3%) and 28.4% of the females reported performing physical exercise regularly (Table 1). The majority of respondents had MSK pain or discomfort in one or more body parts during the last 12 months (91.2%).
Table 1.
Demographic and Physical Activity Characteristics of Participants, Stratified by Gender
| Variables | Male (n = 145) |
Female (n = 232) |
P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD | 23.0 ± 1.5 | 22.7 ± 1.3 | 0.022^ |
| Weight, mean ± SD | 76.9 ± 18.3 | 54.9 ± 10.1 | <0.001^ |
| Height, mean ± SD | 172.0 ± 10.3 | 158.7 ± 5.5 | <0.001^ |
| Body mass index, mean ± SD | 26.1 ± 6.7 | 21.8 ± 3.6 | <0.001^ |
| School year | |||
| 4th year | 53 (36.6%) | 70 (30.2%) | 0.209# |
| 5th year | 46 (31.7%) | 65 (28%) | |
| 6th year | 28 (19.3%) | 52 (22.4%) | |
| Intern | 18 (12.4%) | 45 (19.4%) | |
| Exercise regularly | |||
| No | 73 (50.7%) | 166 (71.6%) | <0.001# |
| Yes | 71 (49.3%) | 66 (28.4%) | |
| Stretch after workout* | |||
| No | 38 (56%) | 24 (36.4%) | 0.024# |
| Yes | 30 (44%) | 42 (63.6%) |
Notes: Values given as n (%) except where otherwise indicated. Some numbers do not add up to the total because of missing values. ^Two-sample t-test. #Chi-square test. *Only participants who exercised were asked this question.
The prevalence of MSK pain in the neck, wrist/hand, upper back, and lower back in the past 12 months is shown in Table 2. Neck pain in the last 12 months was most common, reported by 69.2% of the participants, followed by shoulder pain (67.1%) and then lower back pain (65%). Students were most frequently prevented from performing normal activities in the last 12 months due to shoulder pain (18.8%) and lower back pain (18.6%). Less than 10% had visited a physician for their MSD in the 12 months preceding the survey. The most frequent reason for the visit was shoulder pain (8.2%) and the least common was hip/thigh pain (3.2%). In addition, 37% of the students reported pain that affected the neck, shoulders, or lower back over the past 7 days.
Table 2.
Prevalence of Musculoskeletal Disorders in Different Body Parts (n = 377)
| Body Part | Have You at Any Time During the Last 12 Months Had Trouble (Such as Ache, Pain, Discomfort, Numbness) in: n (%) |
During the Last 12 Months Have you Been Prevented from Carrying Out Normal Activities (eg Job, Housework, Hobbies) Because of This Trouble in: n (%) |
During the Last 12 Months Have You Seen a Physician for This Condition: n (%) |
During the Last 7 Days Have You Has Trouble in: n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neck | 261 (69.2) | 64 (17.0) | 23 (6.1) | 140 (37.1) |
| Shoulders | 253 (67.1) | 71 (18.8) | 31 (8.2) | 139 (36.9) |
| Upper back | 177 (46.9) | 54 (14.3) | 18 (4.8) | 101 (26.8) |
| Elbows | 69 (18.3) | 38 (10.1) | 24 (6.4) | 31 (8.2) |
| Wrists/hands | 171 (45.4) | 59 (15.6) | 20 (5.3) | 71 (18.8) |
| Lower back | 245 (65.0) | 70 (18.6) | 23 (6.1) | 138 (36.6) |
| Hips/thighs | 75 (19.9) | 26 (6.9) | 12 (3.2) | 29 (7.7) |
| Knees | 107 (28.4) | 42 (11.1) | 18 (4.8) | 46 (12.2) |
| Ankles/feet | 117 (31.0) | 39 (10.3) | 17 (4.5) | 54 (14.3) |
Note: The results presented in this table were obtained from the validated Nordic Back Pain Questionnaire.
Table 3 illustrates the mean discomfort scores for the different body parts. Females had higher levels of discomfort than males did in the eyes, neck, shoulders, lower back, arms, wrists/hands and knees. There was no difference in the level of discomfort between genders for other body parts. The highest discomfort score among females was in the neck (3.2 ±1.1), followed by the lower back (3.1 ±1.4) and shoulders (3.1 ±1.2); whereas the highest score among males was for the lower back (2.6 ±1.4) followed by the neck (2.4 ±1.2). Overall, the lowest levels of discomfort were reported for the thighs (1.67 ± 1.1) and the calves (1.69 ± 1.1) (data not shown).
Table 3.
Respondents’ Scores for Degree of Discomfort in Different Body Parts Within the Last 7 Days, Stratified by Gender (n = 377)
| Body Part | Male Mean (SD) |
Female Mean (SD) |
P-value* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eyes | 1.92 (1.1) | 2.4 (1.2) | <0.001 |
| Neck | 2.4 (1.2) | 3.2 (1.13) | <0.001 |
| Shoulders | 2.2 (1.3) | 3.1 (1.2) | <0.001 |
| Upper back | 2.3 (1.3) | 2.6 (1.4) | 0.12 |
| Elbows | 1.6 (1.1) | 1.7 (1.1) | 0.58 |
| Lower back | 2.6 (1.4) | 3.1 (1.4) | <0.001 |
| Arms | 1.6 (1.1) | 1.9 (1.2) | 0.03 |
| Wrists/hands | 1.9 (1.2) | 2.2 (1.4) | 0.05 |
| Thighs | 1.5 (1.04) | 1.8 (1.1) | 0.06 |
| Knees | 1.6 (0.9) | 2 (1.3) | 0.009 |
| Calves | 1.6 (1.1) | 1.7 (1.2) | 0.41 |
| Feet/ankles | 1.8 (1.2) | 2.1 (1.3) | 0.082 |
Notes: The results presented in this table were obtained from the third section of the questionnaire. *Two-sample t-test.
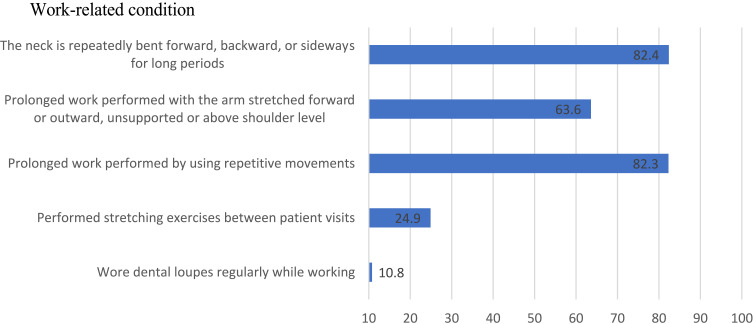
As presented in Figure 1, most of the respondents reported bending their necks and performing repetitive movements during work for prolonged periods (82%). A quarter of the respondents reported performing a stretching exercise between patient appointments; only 11% of the respondents reported wearing dental loupes regularly while working.
Figure 1.
Distribution of participant responses by prolonged work-related condition (n = 377).
Predictors of MSK pain are displayed in Table 4. Females were more likely than males to have MSK pain in the 12 months preceding the survey (odds ratio [OR] = 2.98, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.3–6.7), and students who exercised regularly were less likely to report MSK pain in the year prior to the survey than were those who did not (OR = 0.27, 95% CI: 0.1–0.6). Univariate regression revealed that increased height was a predictive factor for developing MSK pain (OR = 2.05, 95% CI: 1.0–4.45), but it lost its statistical significance when entered in the multivariate model (data not shown).
Table 4.
Predictors of MSK Pain in the Last 12 Months
| Variables | No MSK Pain (n = 33) | MSK Pain (n = 344) | Univariate OR (95% CI) | Multivariate OR (95% CI) |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 23 | 122 | 1 | 1 |
| Female | 10 | 222 | 4.19 (1.9–9.1) | 2.98 (1.3–6.7) |
| School year | – | |||
| 4th and 5th years | 13 | 179 | 1 | |
| 6th year and interns | 20 | 123 | 1.08 (0.5–2.3) | |
| Regular exercise | ||||
| No | 9 | 227 | 1 | 1 |
| Yes | 24 | 117 | 0.22 (0.1–0.5) | 0.27 (0.1–0.6) |
| Body mass index | – | |||
| Underweight | 2 | 27 | 1 | |
| Average | 20 | 219 | 0.81 (0.2–3.7) | |
| Overweight/obese | 8 | 82 | 0.76 (0.2–3.8) | |
| Neck bending during work | ||||
| No | 10 | 56 | 1 | 1 |
| Yes | 22 | 286 | 2.32 (1.0–5.2) | 2.06 (0.9–4.8) |
| Wear dental loupes during work | – | |||
| No | 26 | 288 | 1 | |
| Yes | 5 | 33 | 0.60 (02–1.7) |
Note: Some results do not add up to the total because of missing values.
Abbreviations: MSK, musculoskeletal; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
Discussion
MSDs are a global work-related disorder and the second most common cause of disability in the workplace.19,20 It has been estimated that half of work absences of more than 3 days and almost all work absences of more than 2 weeks are caused by MSDs.21 MSK pain is common among dentists and dental students, with several risk factors increasing its prevalence.8,9,12,22 In the current study, we aimed to determine the prevalence of MSK pain and identify the potential predictors among a sample of undergraduate dental students by using a modified validated questionnaire. The study revealed a high prevalence of MSK pain, with neck pain being reported by the highest number of students, followed by shoulder pain.
The results of the current study showed that 91.2% of participants had MSK pain or discomfort in one or more body parts during the 12 months preceding the survey. This finding is higher than the reported prevalence of MSK pain among dental students and dentists in other countries, such as the United States (46–71%),8 the United Kingdom (54%),9 Indonesia (63.5%),11 Australia (64%),7 and the Czech Republic (39%).23 In our study, the highest prevalence for pain was related to the neck (69.2%), followed by the shoulder (67.1%) and then the lower back (65%). The current study showed a slightly higher prevalence of neck pain compared to that found in the studies by Al-Mohrej et al15 in 2016 in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia (34.3%), by Akesson et al10 in 1999 in Sweden (48%), and by Vijay and Ide9 in 2016 in the United Kingdom (50%). The reported prevalence of shoulder pain in the current study was also higher than that found in the studies by Al-Mohrej et al15 (34.3%) and Akesson et al10 (44%). The prevalence of lower back pain in the current study was comparable to that in previous studies, such as those by Al-Mohrej et al15 (68%), and Vijay and Ide9 (54%). Some results of our study, however, differed from those of previous studies.9,10,16 These differences may be due to differences in the inclusion criteria for multiple dentist specialties and different workloads.
Our participants reported that they were most frequently unable to perform their usual activities during the last 12 months due to shoulder pain (18.8%). Furthermore, 8.2% of participants visited a physician for shoulder pain. Our finding of a high MSK pain prevalence, especially neck pain, followed by shoulder pain and lower back pain, may be attributable to dental students’ sitting positions and work environments. These risks need to be improved in order to reduce MSK pain in dentists.16 Ergonomic hazards are a dominant factor in dental practice and include repetitive motions such as long hours of bending, static posture, and other environmental factors in dental clinics.15 When individuals sit unsupported, which is a frequent position in dental practice, lumbar and cervical lordosis flattens out. In turn, intradiscal pressure and tension over the paraspinal musculature increase, causing neck and low back pain.22 The consequence of MSK pain for dental professionals’ health could have an impact on work efficiency and working hours, increase the amount of sick leave, influence early retirement rates, and affect daily life activity.6,24
Females were three times as likely as males to have MSK pain. Females also reported higher levels of discomfort than males did in their eyes, neck, shoulders, lower back, arms, and knees. Similarly, a study in the Czech Republic reported that females were more prone to MSK pain than males.23 A systematic review showed a positive correlation between female gender and severity of MSK pain in dental health practitioners.25 Some studies have attributed these gender disparities to the difference in muscle tone between the two genders.26,27 Another possible explanation is that pain is related to the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle. Interestingly, a more stable hormonal profile suggests that sex hormones may play an important role in explaining the variation in pain sensitivity between genders.28
A comparison of fourth- and sixth-year students showed that sixth-year students had more MSK pain than fourth-year students did. This may be attributable to the increased workload of sixth-year students. In the sixth year, students treat larger numbers of patients and experience more psychological stress as a result of the pressure of final graduation requirements. The present study also showed that regular physical exercise may decrease the risk of MSK pain and discomfort. Previous studies found that regular exercise (mostly aerobics and stretching) is crucial for preventing MSK damage and reducing symptoms of MSDs in dental professionals.29 For individuals with chronic lower back pain, lumbar stabilization and walking exercises may be recommended: they not only relieve back pain, but they also prevent chronic back pain by enhancing muscle endurance.30 In our study, height seemed to be a predictive factor for MSK pain. This was in line with a previous study conducted in Iran that showed an increase of 1% in neck pain occurrence for each centimeter increase in height.31 According to a cross-sectional study conducted in Portugal, there is a positive association between MSK pain and reported symptoms related to the shoulder and wrist/hand and BMI.32 We did not present height in the regression model of our study, because it had a lot of missing values, which could have compromised the statistical power of the multivariate regression model. Furthermore, in our study, we could not correlate BMI with a high prevalence of MSK pain, as most of our participants were of average BMI.
The high prevalence of MSK pain in our study may reflect a lack of posture awareness among our participants. In light of these results, we recommend implementing sessions in the curricula during preclinical years. The sessions should aim to improve postural techniques, emphasize positioning strategies, teach stress-reduction techniques, and to encourage the use of magnification loupes.
The current study has several limitations, we cannot exclude the possibility of recall bias. In addition, some types of dental practices deal with small instruments (for example, root canal treatment, scaling) that may contribute to more MSK pain, but we were not able to assess the effect of the type of dental work on MSK pain, as dental students perform all types of dental treatment. A major strength of our study is that all participants were trained in the same dental environment with equal workloads. Moreover, we used the English version of the validated Nordic Back Pain Questionnaire, which showed good psychometric properties.18 Furthermore, the response rate in our study was above 60%. The response rates in medical research have been estimated to have a mean of 54% to 61% for physicians.33,34
Conclusion
The current study showed a concerningly high prevalence of MSK pain among dental students, especially in the neck, shoulders, and lower back; women were more at risk than men. This study also showed that regular physical exercise is a protective factor for MSK pain among dental students. These results suggest that early awareness and ergonomic education should be included in dental curricula and physical exercise, especially for women. Furthermore, clinical trials, including occupational, ergonomic, physical therapy, might help assess the best interventions to reduce MSK pain among undergraduate dental students.
Funding Statement
This research did not receive any grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Data Sharing Statement
Data will be made available upon request.
Ethical Approval, Consent to Participate and Consent for Publication
Participation in the study was voluntary, and the questionnaire was accompanied by a cover letter explaining the purpose of the study and reassuring respondents of the confidentiality of the survey.
Ethical approval was obtained from the ethical approval committee at King Abdulaziz University, Faculty of Dentistry, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia (ethical approval number: 032-02-18).
Author Contributions
Felemban RA, Sofi RA, Alharbi SG, and Alhebshi SG contributed to conceiving the research idea, collected the data, performed data cleaning and statistical analyses, and wrote the manuscript. Farsi NJ supervised the statistical analyses, interpreted the results. She also participated in writing the manuscript, and critically reviewed it. Abduljabbar FH contributed to conceiving the research idea and questionnaire construction. He also critically reviewed the manuscript. Farsi JM contributed to conceiving the research idea and supervised the interns in proposal writing and ethical approval application. She also critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors made significant contributions to conception and design of the study, data collection, or statistical analysis and interpretation of results; took part in writing the manuscript or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to this journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be responsible for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest for this work.
References
- 1.Hayes MJ, Smith DR, Taylor JA. Musculoskeletal disorders in a 3 year longitudinal cohort of dental hygiene students. J Dent Hyg. 2014;88(1):36–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Graham C. Ergonomics in dentistry, Part 1. Dent Today. 2002;21(4):98–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Finsen L, Christensen H, Bakke M. Musculoskeletal disorders among dentists and variation in dental work. Appl Ergon. 1998;29(2):119–125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lake J. Musculoskeletal dysfunction associated with the practice of dentistry – proposed mechanisms and management: literature review. Univ Tor Dent J. 1995;9(1):7,9–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lindfors P, von Thiele U, Lundberg U. Work characteristics and upper extremity disorders in female dental health workers. J Occup Health. 2006;48(3):192–197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Leggat PA, Kedjarune U, Smith DR. Occupational health problems in modern dentistry: a review. Ind Health. 2007;45(5):611–621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Marshall ED, Duncombe LM, Robinson RQ, Kilbreath SL. Musculoskeletal symptoms in New South Wales dentists. Aust Dent J. 1997;42(4):240–246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rising DW, Bennett BC, Hursh K, Plesh O. Reports of body pain in a dental student population. J Am Dent Assoc. 2005;136(1):81–86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Vijay S, Ide M. Musculoskeletal neck and back pain in undergraduate dental students at a UK dental school - a cross-sectional study. Br Dent J. 2016;221(5):241–245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Akesson I, Johnsson B, Rylander L, Moritz U, Skerfving S. Musculoskeletal disorders among female dental personnel – clinical examination and a 5-year follow-up study of symptoms. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1999;72(6):395–403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Phedy P, Gatam L. Prevalence and associated factors of musculoskeletal disorders among young dentists in Indonesia. Malays Orthop J. 2016;10(2):1–5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Aljanakh M, Shaikh S, Siddiqui AA, Al-Mansour M, Hassan SS. Prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders among dentists in the Hail Region of Saudi Arabia. Ann Saudi Med. 2015;35(6):456–461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kanaparthy A, Kanaparthy R, Boreak N. Postural awareness among dental students in Jizan, Saudi Arabia. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2015;5(Suppl 2):S107–111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ministry of Health. MOH Statistics and Indicators. http://www.moh.gov.sa/en/Ministry/Statistics/Pages/default.aspx.
- 15.Al-Mohrej OA, AlShaalan NS, Al-Bani WM, Masuadi EM, Almodaimegh HS. Prevalence of musculoskeletal pain of the neck, upper extremities and lower back among dental practitioners working in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2016;6(6):e011100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Aghahi RH, Darabi R, Hashemipour MA. Neck, back, and shoulder pains and ergonomic factors among dental students. J Educ Health Promot. 2018;7:40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kuorinka I, Jonsson B, Kilbom A, et al. Standardised Nordic questionnaires for the analysis of musculoskeletal symptoms. Appl Ergon. 1987;18(3):233–237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wännström I, Peterson U, Asberg M, Nygren A, Gustavsson JP. Psychometric properties of scales in the General Nordic Questionnaire for Psychological and Social Factors at Work (QPS): confirmatory factor analysis and prediction of certified long-term sickness absence. Scand J Psychol. 2009;50(3):231–244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Horton R. GBD 2010: understanding disease, injury, and risk. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2053–2054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Armijo-Olivo S, Woodhouse LJ, Steenstra IA, Gross DP. Predictive value of the DASH tool for predicting return to work of injured workers with musculoskeletal disorders of the upper extremity. Occup Environ Med. 2016;73(12):807–815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cammarota A. The European Commission Initiative on WRMSDs: Recent Developments, Presentation to EUROFOUND Conference on ‘Musculoskeletal Disorders’. Lisbon; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Valachi B, Valachi K. Preventing musculoskeletal disorders in clinical dentistry: strategies to address the mechanisms leading to musculoskeletal disorders. J Am Dent Assoc. 2003;134(12):1604–1612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kapitán M, Pilbauerova N, Vavrickova L, Sustova Z, Machac S. Prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders symptoms among Czech dental students. Part 1: a Questionnaire Survey. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2018;61(4):131–136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Picavet HS, Schouten JS. Musculoskeletal pain in the Netherlands: prevalences, consequences and risk groups, the DMC(3)-study. Pain. 2003;102(1–2):167–178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hayes M, Cockrell D, Smith DR. A systematic review of musculoskeletal disorders among dental professionals. Int J Dent Hyg. 2009;7(3):159–165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Meisha DE, Alsharqawi NS, Samarah AA, Al-Ghamdi MY. Prevalence of work-related musculoskeletal disorders and ergonomic practice among dentists in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2019;11:171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hodacova L, Sustova Z, Cermakova E, Kapitan M, Smejkalova J. Self-reported risk factors related to the most frequent musculoskeletal complaints among Czech dentists. Ind Health. 2015;53(1):48–55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Craft RM, Mogil JS, Aloisi AM. Sex differences in pain and analgesia: the role of gonadal hormones. Eur J Pain. 2004;8(5):397–411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kumar DK, Rathan N, Mohan S, Begum M, Prasad B, Prasad ER. Exercise prescriptions to prevent musculoskeletal disorders in dentists. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8(7):ZE13–16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Suh JH, Kim H, Jung GP, Ko JY, Ryu JS. The effect of lumbar stabilization and walking exercises on chronic low back pain: a randomized controlled trial. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(26):e16173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Madadizadeh F, Vali L, Rafiei S, Akbarnejad Z. Risk factors associated with musculoskeletal disorders of the neck and shoulder in the personnel of Kerman University of Medical Sciences. Electron Physician. 2017;9(5):4341–4348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Moreira-Silva I, Santos R, Abreu S, Mota J. Associations between body mass index and musculoskeletal pain and related symptoms in different body regions among workers. Sage Open. 2013;3(2):2158244013491952. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Asch DA, Jedrziewski MK, Christakis NA. Response rates to mail surveys published in medical journals. J Clin Epidemiol. 1997;50(10):1129–1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Cummings SM, Savitz LA, Konrad TR. Reported response rates to mailed physician questionnaires. Health Serv Res. 2001;35(6):1347–1355. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]