In December 2019, in the Chinese city of Wuhan, Hubei province, a new pneumonia outbreak emerged, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2).1 The disease, known as COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019), quickly spread to the rest of the world, prompting the World Health Organization to declare a global pandemic on March 12, 2020.
Case series reported in China suggest that patients with cardiovascular disease are at higher risk for developing COVID-19 and have more severe complications and worse outcomes.1, 2, 3 Furthermore, SARS-CoV-2 infection appears to lead to acute myocardial injury, myocarditis and heart failure.3, 4 Preliminary data from Italy describe clinical presentations suggestive of acute coronary syndrome, with ischemic electrical and echocardiographic changes, without obstructive coronary artery disease in most patients.5, 6
We present the case of a 62-year-old woman with multiple cardiovascular risk factors, including hypertension, dyslipidemia, type 2 diabetes and previous smoking, previously followed for ischemic cardiomyopathy.
In 2017, the patient was admitted with acute myocardial infarction of the lateral wall and underwent emergent coronary angiography that showed total occlusion on the mid left circumflex coronary artery. Angioplasty was performed and a drug-eluting stent (2.0 mm×15 mm Resolute Onyx) was implanted. Her clinical course was favorable, with no pathological Q waves or major ST-T changes on the electrocardiogram (Figure 1 ), normal biventricular systolic function and akinesia in the left ventricular posterior wall. During an irregular cardiology follow-up of one year, she had no cardiovascular symptoms; two years after the event, she decided to discontinue her medication.
Figure 1.
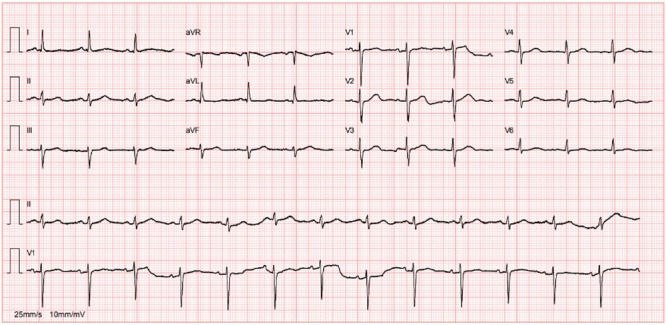
Baseline electrocardiogram performed during cardiology follow-up consultation: sinus rhythm, without pathological Q waves or major ST-T changes.
On March 16, 2020, due to fever and vomiting, she was tested for SARS-CoV-2 and the result was positive; a chest computed tomography scan revealed bilateral ground-glass opacities and an area of consolidation in the right lower lobe. She had no significant biochemical changes or respiratory failure (pH 7.48, pCO2 33.4 mmHg, pO2 75.4 mmHg in ambient air). Given the absence of criteria for hospital admission, the patient was discharged for home isolation, with telephone follow-up. Clinical improvement and sustained apyrexia were reported.
On March 27, 2020, she presented clinical worsening with oppressive chest pain radiating to the back and a prehospital emergency team was activated. An electrocardiogram was performed that revealed ST-segment elevation. Immediately, loading doses of aspirin plus clopidogrel were administered and she was transferred to the emergency department.
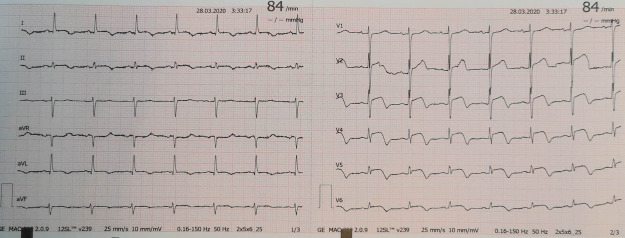
At the hospital, the patient was admitted to the isolation area for COVID-19 patients in the emergency ward. She was hemodynamically stable, apyretic, eupneic in ambient air, with a peripheral oxygen saturation of 97%. Despite intravenous nitrate and morphine, her chest pain persisted. Cardiopulmonary auscultation was not performed due to interposition of personal protective equipment (PPE). A new electrocardiogram was performed that revealed persistent ST-elevation in leads V2-V6 (Figure 2 ) and a rapid echocardiogram showed preserved biventricular systolic function with mid-apical and infero-posterolateral akinesia of the left ventricular wall.
Figure 2.
Electrocardiogram at admission performed in the emergency ward with acute coronary syndrome: sinus rhythm, with ST-segment elevation in leads V2-V6.
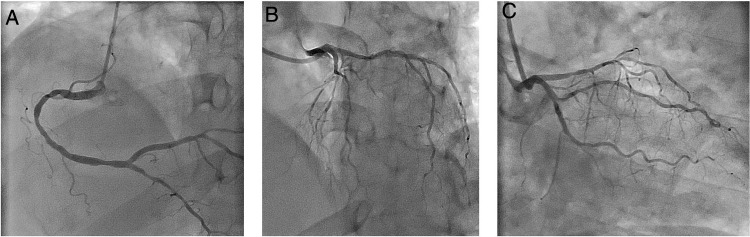
Using PPE for aerosol-generating procedures, emergent angiography performed 13 hours after symptom onset showed a good result of the previous angioplasty and non-obstructive coronary artery disease (Figure 3 ).
Figure 3.
Emergent coronary angiography. (A) Right coronary artery with moderate disease in mid segment and mild disease in distal segment; (B and C) left main coronary artery with no significant lesions; left anterior descending artery with diffuse disease; left circumflex artery with mild disease and stent in mid segment without restenosis.
For etiological clarification, cardiac magnetic resonance was considered, however, it was postponed due to concomitant infection with SARS-CoV-2.
The patient presented clinical improvement, without recurrence of chest pain after coronary angiography and without hemodynamic or electrical complications. Peak high-sensitivity troponin I was 23 000 ng/l. One week after admission, she was considered cured of COVID-19, after two negative tests for SARS-CoV-2, and was discharged, referred for cardiology follow-up.
In this report, we present a case of typical presentation of ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome, without epicardial obstruction, in a patient with mild COVID-19. This case report highlights the challenges facing cardiology in this global pandemic, in which COVID-19 can mimic a classic obstructive acute coronary syndrome. It also demonstrates the need to adjust inter- and in-hospital protocols associated with direct access to primary angioplasty and to ensure that the catheterization laboratory has the appropriate equipment and conditions.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- 1.Guan W.J., Ni Z.Y., Hu Y. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020 doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2002032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chen N., Zhou M., Dong X. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet. 2020;395:507–513. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ganatra S., Hammond S.P., Nohria A. The novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) threat for patients with cardiovascular disease and cancer. JACC CardioOncol. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2020.03.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Clerkin K.J., Fried J.A., Raikhelkar J. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 2020 doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.046941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zheng Y.-Y., Ma Y.-T., Zhang J.-Y. COVID-19 and the cardiovascular system. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020 doi: 10.1038/s41569-020-0360-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Maddalena L. ESC TV Special Edition Responding to COVID-19. 2020. Cardiac care in the COVID-19 pandemic [Webinar] Retrieved from: https://www.youtube.com/embed/crxtEVLJ7oQ?rel=0&autoplay=1. [Google Scholar]