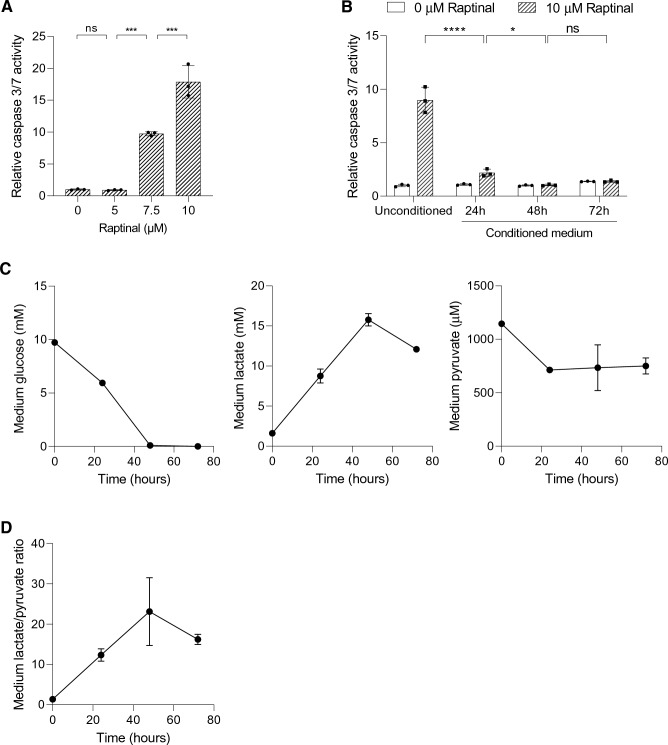
Fig. 1.
HepG2-conditioned medium protects against Raptinal-induced apoptosis. a HepG2 cells were treated with different concentrations of Raptinal for 1.5 h and caspase 3/7 activity was measured. Data is normalized to 0 µM Raptinal (vehicle, 0.1% DMSO) condition. Shown are the mean ± SD of a representative experiment (N = 2). One-way ANOVA with multiple comparison (Tukey) with ***p < 0.001, ns; not significant. b HepG2 cells were pre-incubated with the conditioned media for 1 h and thereafter treated with vehicle (0.1% DMSO) or 10 µM Raptinal for 1.5 h. Caspase 3/7 activity was then measured. Data is normalized to vehicle in unconditioned medium and shown are the mean ± SD of a representative experiment (N = 2). Two-way ANOVA with multiple comparison (Tukey) with ****p < 0.001, *p < 0.05, ns; not significant. c The medium glucose, lactate, and pyruvate of cultured HepG2 cells were measured at 24, 48 and 72 h after seeding. Shown are the mean ± SD of a representative experiment (N = 2). d The lactate-to-pyruvate (L/P) ratio in the medium conditioned by HepG2 cells over time. The ratios are derived from (c)