Abstract
The unfolded protein response (UPR) is an evolutionarily conserved adaptive signaling pathway triggered by a stress of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) lumen compartment, which is initiated by the accumulation of unfolded proteins. This response, mediated by three sensors-Inositol Requiring Enzyme 1 (IRE1), Activating Transcription Factor 6 (ATF6), and Protein Kinase RNA-Like Endoplasmic Reticulum Kinase (PERK)—allows restoring protein homeostasis and maintaining cell survival. UPR represents a major cytoprotective signaling network for cancer cells, which frequently experience disturbed proteostasis owing to their rapid proliferation in an usually unfavorable microenvironment. Increased basal UPR also participates in the resistance of tumor cells against chemotherapy. UPR activation also occurs during hematopoiesis, and growing evidence supports the critical cytoprotective role played by ER stress in the emergence and proliferation of leukemic cells. In case of severe or prolonged stress, pro-survival UPR may however evolve into a cell death program called terminal UPR. Interestingly, a large number of studies have revealed that the induction of proapoptotic UPR can also strongly contribute to the sensitization of leukemic cells to chemotherapy. Here, we review the current knowledge on the consequences of the deregulation of UPR signaling in leukemias and their implications for the treatment of these diseases.
Keywords: endoplasmic reticulum stress, unfolded protein response (UPR), leukemia, AML, CLL, ALL, CML
1. Introduction
About one-third of human genes encode secreted or transmembrane proteins as well as proteins resident of the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes. Most of these proteins are targeted to the ER. The endoplasmic reticulum is a complex network of membrane-enclosed tubules and vesicles, extending from the nuclear membrane throughout the cytoplasm. ER is the largest organelle of most eukaryotic cells, as its membrane may account for at least 50% of all cell membranes and even more for specialized secretory cell. Its total area is 10–30 times that of the plasma membrane. ER constitutes the first compartment of the secretory pathway in which secreted and transmembrane proteins are folded and post-translationally modified [1].
ER is also the most important compartment for intracellular calcium ions (Ca2+) storage, which is necessary for the physiological activities of the ER, allowing the maintenance of the oxidation–reduction potential [2,3]. In its lumen, a set of specialized proteins like chaperones, foldases, glycosylating enzymes, oxidoreductases, and cofactors ensures the correct folding of newly synthesized proteins. By interacting with the exposed hydrophobic segments present on the newly synthesized proteins or on misfolded proteins, the chaperones (BiP/GRP78, calnexin, GRP94, etc.) act both to complete the folding process and to correct folding errors [4]. After passing the protein quality control checkpoints in the ER, correctly folded proteins traffic via the Golgi to other organelles and/or to the plasma membrane. Despite this optimized environment in the ER luminal domain, the success rate for accurate folding is variable. In case of unsuccessful folding, proteins are released in the cytosol where they become ubiquitinated and targeted to degradation by the proteasome. This rigorous quality control system has been named ERAD for Endoplasmic Reticulum-Associated Degradation [5].
In addition, to cope with the perturbations caused by unfolded or misfolded proteins, cells set off an adaptive response called the unfolded protein response (UPR), which aims to restore normal ER functioning [6,7,8,9]. This is achieved by (i) lowering the biosynthesis of proteins to reduce accumulation of misfolded proteins in the ER; (ii) increasing the biosynthesis of chaperone proteins; (iii) increasing ER size through membrane synthesis, (i), and (ii) resulting in a boost of ER folding capabilities; and finally (iv) increasing the biosynthesis of ER-associated degradation proteins thus improving the cell’s ability to eliminate misfolded proteins. Consequently, “adaptive UPR” limits cell damages and allows cell recovery and survival to a new stressful environment. However, if stress overcomes cell recovery capacities UPR can switch from an adaptive to a “terminal UPR” program triggering cell death [10,11,12].
Perturbations in the ER stress response such as either chronic ER stress or defects in UPR signaling, have been associated with a number of pathologies: diabetes, atherosclerosis, inflammation, stroke, pulmonary fibrosis, several eye diseases, neurodegenerative disorders (including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s or Huntington’s diseases), and, of course, cancer [13,14,15,16]. The common feature among these seemingly different diseases is a cellular dysfunctioning leading to an accumulation of misfolded proteins in the ER.
With respect to cancer, the role of ER stress response/UPR signaling pathways was mainly studied in primary solid tumors in which a very unfavorable microenvironment mainly originating from inadequate vascularization and characterized by nutrient (e.g., amino acids, glucose) deprivation, hypoxia, acidosis leads to the activation of ER stress in the highly proliferative and metabolically active cancer cells [17,18,19,20,21]. However, in recent years our current knowledge on the essential functions played by the UPR in leukemia has also significantly improved.
In this review, after introducing the Unfolded Protein Response, we will summarize current findings on the involvement of ER stress in the progression of leukemia, and discuss the potential therapeutic effects of UPR activation or repression in these pathologies.
2. The Unfolded Protein Response
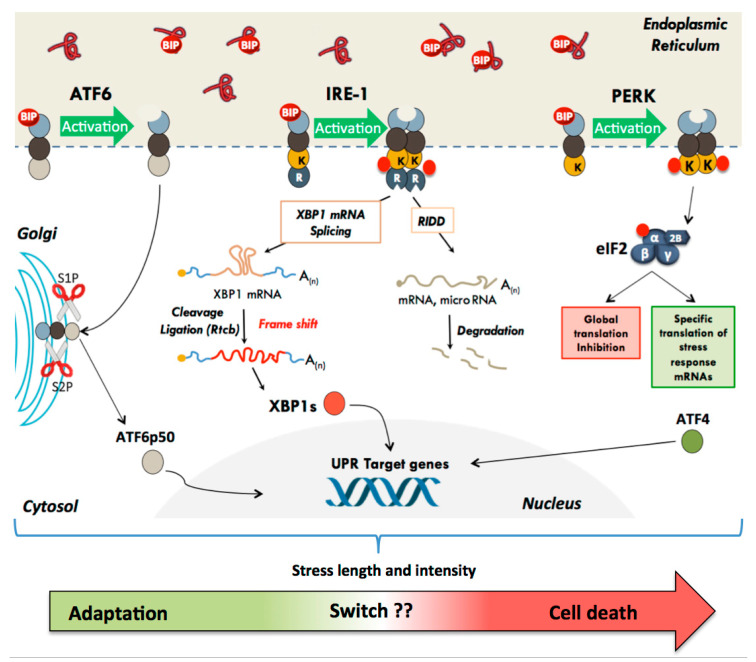
In mammals, UPR is triggered by activation of three ER transmembrane sensors: PERK (PKR-like ER-associated protein kinase), ATF6 (Activating Transcription Factor-6), and IRE1 (inositol-requiring enzyme-1) [6,10,22,23]. The luminal part of these proteins integrates the information coming from the ER lumen, whereas their cytosolic part interacts with their effectors and mediates the signaling cascades (Figure 1). In the absence of stress, the ER resident protein chaperone BiP also known as GRP78 (Glucose-regulated protein 78kDa) or HSPA5 (Heat Shock Protein Family A (Hsp70) Member 5) binds to the luminal domain of the three effectors and keep them in an inactive state. Upon accumulation of unfolded proteins in the ER lumen, BiP will act as a protein chaperone, interact with exposed hydrophobic segments of misfolded proteins, and thus be released from ATF6, IRE1, and PERK, leading to their activation [24,25]. In addition to BiP release, an activation of IRE1 by oligomerization induced by direct binding of unfolded proteins has also been reported, both in yeast [26] and mammalian cells [27]. Therefore, the relative ratios of three proteins complexes inside the endoplasmic reticulum, namely, those created by interaction between BiP and either unfolded proteins or UPR sensors, as well as those formed by direct interaction between unfolded proteins and the UPR sensors themselves, could contribute to a very precise and dynamic regulation of the UPR [28].
Figure 1.
The different UPR effectors and their modes of action. In the basal state, the three UPR effector transmembrane proteins (PERK, ATF6, and IRE-1) are maintained inactive through their interaction with the protein chaperone BiP. The accumulation of misfolded proteins in the ER lumen results in dissociation of BiP and activation of UPR. (1) PERK dimerizes and phosphorylates the eIF2α subunit, leading to a global inhibition of translation initiation. Specific mRNA subsets, containing cis-acting elements in their 5′UTR, such as uORF and IRES, escape translational inhibition triggered by eIF2 phosphorylation. (2) IRE-1 initiates an unconventional splicing of XBP-1 mRNA. IRE1α cleaves Xbp1u mRNA within two stem-loop structures, leading to excision of 26 nucleotides. Subsequent ligation of the Xbp1 mRNA by the tRNA ligase RTCB results in a frame shift and allows the translation of the active transcription factor XBP1s, which is imported into the nucleus and activates the expression of target genes. IRE1α mediates also the degradation of some RNAs (this mechanism has been called RIDD for Regulated Ire1-Dependent Decay). (3) BIP dissociation from ATF6 exposes its Golgi Localization Signal. ATF6 is translocated to the Golgi apparatus where proteolysis releases its transcription factor amino-terminal domain, which is imported into the nucleus and activates the expression of target genes. The UPR has a primary function in adaptive response in order to restore homeostasis and promote cell survival, but depending on the duration and intensity of the stress, a switch can induce cell death to get rid of the damaged cells.
As previously stated, the primary goal of the activated signaling cascades is to reestablish ER homeostasis by a two-step process: in a first stage, through the reduction of overall protein synthesis and the degradation of misfolded proteins, and in a second stage through the activation of cellular functions crucial for cell survival [6,10,22].
However, in the absence of protein homeostasis restoration, the adaptive UPR will switch to terminal UPR, which ultimately results in cell death. Cell fate is largely influenced by the intensity and duration of the stress. A long or intense stress leads to the activation of this terminal UPR [10,18]. The regulatory networks, which determine the transition from adaptive to terminal UPR, are complex and not fully understood. Regardless, the molecular events that will direct the cell towards either adaptive or terminal UPR involve to some extent each of the PERK, IRE1, and ATF6 signaling cascades. The contribution of each pathway to the execution of the adaptive or terminal UPR may be variable depending on the type of cell and on the nature and extent of damage experienced by the cell. The different UPR signaling cascades are described below.
2.1. The Translational Pathway: Activation of the PERK Kinase
Among the three key proteins involved in UPR, PERK (encoded by the EIF2AK3 gene for eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 3) is the first to be activated by autophosphorylation. The dissociation of BiP from its luminal domain causes dimerization or oligomerization and trans-autophosphorylation of PERK (threonine 981), thus activating the cytosolic serine/threonine kinase domain (Figure 1). The main substrate of PERK is the alpha subunit of the translation initiation factor eIF2 (eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2) [29,30,31,32]. The eIF2 factor, which possesses three subunits-α, β, and γ-links the initiator methionine tRNA (tRNA-Met) to the small ribosomal subunit. The regulatory α subunit contains a serine (ser51) strictly conserved in eukaryotes. By phosphorylating ser51, PERK induces a global inhibition of cap-dependent translation initiation and therefore overall protein synthesis in order to temporary reduce unfolded protein load, until favorable conditions return [33]. Mechanistically, the phosphorylation of the eIF2α ser51 increases the affinity of eIF2 for its own eIF2B guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF), which recycles the inactive form of eIF2-GDP into its active form eIF2-GTP. This strong interaction induces sequestration of the eIF2 factor by eIF2B, causing a blockade of active translation pre-initiation complex formation and thus inhibition of translation initiation [34]. This translation inhibition prevents further protein loading in the ER, reduces cell overall metabolism and saves energy to repair the damage caused by the stress [34].
In parallel to cap-dependent translation arrest, translation of specific messenger RNAs exhibiting particular features in their 5′ untranslated region is selectively induced [35]. This is the case of the Activating Transcription Factor 4 (ATF4) mRNA which contains several upstream open frames (uORFs) in its 5′ untranslated region, preventing translation of the main open reading frame (ORF) in normal conditions. Under stress conditions however, low levels of active eIF2α allow the ribosomes to reach the main ATF4 ORF and efficiently initiate translation of this transcription factor, which in turn activates the expression of chaperones and of genes involved in amino acid metabolism and resistance to oxidative stress [36,37]. Interestingly, some mRNA whose translation depends on the presence of internal ribosome entry sites (IRESs) in their 5′ untranslated region [35] and coding for stress response proteins are also activated when eIF2α is phosphorylated (Figure 1) [38,39,40,41].
The dephosphorylation of eIF2α is necessary to restore a normal protein synthesis level after stress. This reset to the basal state is achieved by two phosphatases, composed of a single catalytic subunit PP1 (Protein Phosphatase 1) and one of the two regulatory subunits GADD34 (Growth And DNA-Damage inducible protein 34) or CReP (Constitutive Repressor of eIF2α phosphorylation) [42]. In contrast to CReP, which is constitutively expressed, the expression of GADD34 is only induced in response to stress as a negative feedback loop [43]. Indeed, transcription of GADD34 is activated by ATF4 and its translation is, as for ATF4 itself, regulated by a uORF mechanism ensuring proper GADD34 expression despite eIF2α phosphorylation [44].
Under chronic stress, sustained activation of PERK and thus prolonged expression of ATF4 induce apoptosis by activating CHOP transcription (C/EBP Homologous protein, also known as GADD153-Growth And DNA-Damage inducible protein 153 or DDIT3-DNA-Damage Inducible Transcript 3) [45]. This transcription factor, a member of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) family, plays a central, multifunctional role in the UPR-induced apoptotic process [46]. CHOP can alone or cooperatively with other transcriptional factors function either as a transcriptional activator or repressor. It acts mainly by modulating the expression of various members of the BCL-2 protein family playing either pro-(Bim) or antiapoptotic (Bcl-2, BCL-XL and MCL-1) functions [47]. CHOP can however also induce cell death by many additional, non-exclusive, pathways such as restoration of protein synthesis (via GADD34 activation) which leads to increased proteins load detrimental to the cell (“proteotoxicity”) and by increased ROS production (through upregulation of the ER reductase ERO1α) [48].
It is interesting to note that eIF2α is not the only PERK substrate. Indeed, the transcription factor Nrf2 (Nuclear Factor (erythroid derived 2)-like2), which is involved in the response to oxidative stress, is normally maintained in the cytoplasm by association with Keap1. Under stress conditions, PERK phosphorylates Nrf2. This causes a dissociation of the Nrf2/Keap1 complex and allows the import of Nrf2 to nuclear compartment [49]. Nrf2 then bind to ARE sequences (Antioxidant response element) on the promoter of its target genes such as GCLC (Glutamate Cysteine Ligase Catalytic Subunit), HO-1 (Heme oxygenase 1) or NQO1 (NADPH dehydrogenase quinone 1) [50]. Thus, the activation of Nrf2 by PERK helps in maintaining the redox status of the cell subjected to ER stress.
2.2. The Transcriptional Pathway: Activation of ATF6α and IRE1α
In mammals, the transcriptional response to ER stress involves two families of transmembrane proteins: the IRE1 and ATF6 proteins (Figure 1).
The ATF6α (activating transcription factor 6 α) transcription factor is a type II transmembrane protein characterized by a C-terminal luminal domain, sensitive to misfolded proteins, and an N-terminal cytosolic portion containing a leucine zipper DNA binding domain (bZIP) and a transcriptional activation domain. In mammals, two ATF6 proteins, ATF6α and ATF6β, are produced form independent genes. Whereas both proteins are ubiquitously expressed, only ATF6α has proven to be an effective transcriptional activator and its it is currently accepted that only ATF6α plays a major role in the ATF6-dependent transduction of UPR signaling [51]. The amount and mode of contribution of ATF6β to the unfolded protein response remain poorly understood and need to be further investigated [52]. During ER stress, Bip dissociation from the ATF6α protein allows the exposure of two Golgi localization signals, and migration of ATF6α from ER to the Golgi apparatus where it undergoes 2 sequential cleavages by the proteins S1P and S2P (Site-1 and Site-2 Proteases) (Figure 1) [25,53]. These cleavages generate a transcriptionally active N-terminal short-lived fragment of 50 kDa called ATF6p50 which translocates into the nucleus to activate the transcription of chaperone and foldase proteins such as BiP, calreticulin, calnexin, and protein disulfide isomerases. ATF6p50 also activates the transcription of enzymes such as the calcium pump SERCA (sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase). This ER ATPAse transports calcium ions from the cytosol into the ER and plays a major role in the maintenance of calcium homeostasis which controls many essential cellular processes [54]. ATF6p50 also promotes the expression of different genes involved in lipid biosynthesis, thus participating to the expansion of the endoplasmic reticulum [55]. It also upregulates XBP1 (X-box binding protein 1), a transcription factor which acts immediately downstream of the third UPR sensor IRE1 (see below). Moreover, ATF6α can also form heterodimers with XBP1 and upregulate genes involved in the ERAD pathway like EDEM (ER Degradation Enhancing Alpha-Mannosidase Like Protein 1) or HERPUD1 (Homocysteine Inducible ER Protein With Ubiquitin Like Domain 1). ATF6α gene invalidation induces increased sensitivity to ER stress probably due to impaired induction of chaperone proteins such as BiP or GRP94 (Glucose-regulated protein 94 kDa) [56,57]. However, ATF6α can also activate the expression of the proapoptotic factor CHOP [58,59], and a very recent work suggested that ATF6α could play an important role in the decision from adaptive to terminal UPR by modulating early and late CHOP expression kinetics [60]. Therefore, the role played by ATF6α on cell survival or death appears complex. In addition, the ATF6α transactivator domain (more precisely the first N-terminal 93 amino acids) has been shown to be responsible for its own degradation by the proteasome [61]. As a result, ATF6α appears as a powerful transcriptional activator, but with a transient effect. This may contribute to finely tune the UPR machinery.
The third UPR sensor is IRE1 (Inositol-requiring protein 1 also known as ERN1 for Endoplasmic reticulum-to-nucleus signaling 1), a 110 kDa protein initially identified in yeast where it is the only ER stress sensor. In mammals this protein is expressed as two isoforms: IRE1α, which is ubiquitously expressed, and IRE1β expressed only in the epithelial cells of the digestive system [62,63,64,65,66]. IRE1α possesses a luminal structure and an activation mode similar to that of PERK. However, in addition to a Ser/Thr kinase enzymatic activity, the IRE1α cytosolic domain also retains an atypical endoribonuclease (RNAse) activity, which becomes functional after IRE1α homodimerization under stress conditions [67]. This dimerization is essential for endoribonuclease activation, which is also dependent on IRE1α phosphorylation status [68]. The IRE1α RNAse domain catalyzes the excision of a 26-nucleotide sequence within the Xbp1 (X-box binding protein1) mRNA by an unconventional cytoplasmic splicing mechanism independent of the spliceosome (Figure 1) [69]. This cleavage, followed by a ligation step mediated by the RTCB tRNA ligase [70], generates a frame shift in the open reading frame, which leads to the expression of XBP1s (XBP1 spliced), a transcription factor belonging to the ATF/CREB family. The activation of the IRE1α/XBP1s signaling axis induces the expression of genes encoding proteins of the ERAD pathway (EDEM, HRD1) and factors that modulate protein translocation into the ER and folding, including the protein BiP [53,71]. Importantly, the non-spliced Xbp1 mRNA encodes the protein XBP1u (XBP1 unspliced), which is an inactive form with no transcriptional activity because it lacks the transactivating domain, and is an extremely short-lived protein. Interestingly, however, XBP1u was also found to interact with XBP1s under ER stress conditions, functioning as a negative feedback regulator [72,73].
IRE1α’s endoribonuclease activity has also been shown to induce rapid and specific degradation of some RNAs by a mechanism called RIDD (Regulated Ire1-Dependent Decay) (Figure 1) [74,75]. Currently, only a limited number of direct targets have been identified and validated, including 4 microRNAs (miR-17, 96, 125b, 34a) [76] and some mRNAs notably PER1 [77], SPARC [78], BLOS1 [79], and DR5 (death receptor 5), but bioinformatic studies coupled with transcriptomic studies suggest a wider spectrum of action [80,81]. Several studies indicate that the RIDD mechanism contributes to ER stress-induced cell death, notably by degrading several miRNAs involved in the repression of caspase-2 mRNA expression [75,76]. However, other studies propose that RIDD activity, by targeting mRNAs specifically translated at the endoplasmic reticulum, reduces the influx of newly synthesized proteins, and thus participates in the adaptive survival process [82]. Moreover, the IRE1α-mediated targeting through RIDD of the mRNA coding for the death receptor 5 protein, a cell surface transducer of apoptotic signals could also limit ER stress-induced cell death [83].
The IRE1α activation level, stability, conformation, and oligomerization status appear to be also regulated by the interaction with many different protein partners such as for example HSP47 which facilitates the dissociation of BiP from its luminal domain thus helping in activation of IRE1α signaling under low stress conditions [10,84,85].
IRE1α associates also with additional partners through its cytosolic domain to induce different signaling pathways. TRAF2 (TNF receptor-associated factor), an adaptor protein, associates with IRE1α’s kinase domain. The IRE1α/TRAF2 complex was found to interact with ASK1 (apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1) to activate the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and induce apoptosis [62,86]. Thus, the JNK arm of IRE1α pathway was initially thought to promote cell death. However, the function of this pathway in vivo is still controversial and has been described in some cases as pro-death and in other cases as pro-survival [62,86]. The nature and the intensity of the stimulus may account for these results. As in the case of ATF6α, IRE1α behaves as a sensor of the general cellular state through its multiple interactions with cofactors, regulators, and other members of the UPR signaling cascades and centralizes a set of signals in order to balance between anti- and proapoptotic signals.
Recent work has demonstrated that the activity of PERK and ATF6α can also be regulated by specific interacting proteins (reviewed in [10]). These results indicate that the activity of the three UPR effectors is extremely finely tuned. In addition, these effectors can establish crosstalk between each other during the UPR response and therefore more detailed analyses of these proteins and their identified partners remain necessary to better understand how they contribute on their own and altogether to the overall cell’s response during UPR activation.
3. Hematopoiesis and Leukemias
3.1. Hematopoiesis
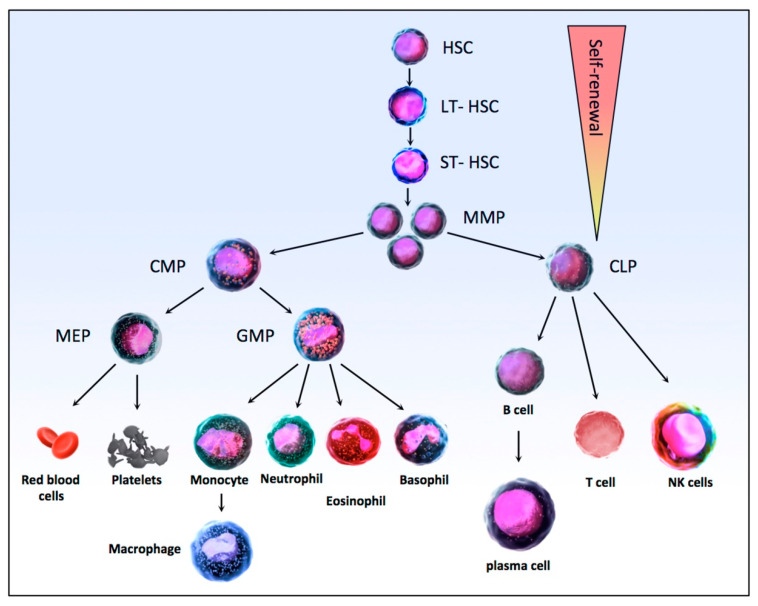
Hematopoiesis is the physiological process that is responsible for the production of the mature pools of blood cells from undifferentiated precursors, the stem cells. Hematopoiesis, which takes place mainly in the bone marrow of long and flat bones, is a crucial process as it allows the maintenance of blood cell homeostasis, producing approximately 1012 blood cells daily in a healthy adult. The hematopoietic system functions as a pyramid-like hierarchy organized from a hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) at the top, able to self-renew or differentiate to produce all the cells of the hematopoietic system (Figure 2). In the bone marrow, long-term hematopoietic stem cells (LT-HSC) are quiescent, in the G0 phase of the cell cycle with a very low mitochondrial activity, but a high self-renewal potential [87]. These cells are maintained throughout life. In classical hematopoiesis, LT-HSC division leads to the generation of new LT-HSC or ST-HSC, for Short-Term Hematopoietic Stem Cell, which are able to produce all mature hematopoietic lineages [88,89]. These cells then differentiate into multipotent progenitors (MPPs) and then either in common lymphoid progenitors (CLPs) or in common myeloid progenitors (CMPs) [90]. CLPs produce B and T lymphocytes and natural killer cells, while CMPs generate granulocyte-macrophage progenitors (GMPs), which, as their name implies, are then differentiated into granulocytes and macrophages, and megakaryocyte–erythrocyte progenitors (MEPs) which themselves differentiate into red blood cells and platelets [91,92] (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Schematic of the HSC differentiation hierarchy in normal hematopoiesis. HSC, Hematopoietic stem cells; LT-HSCs (Long-Term Hematopoietic Stem Cell) are able to generate new LT-HSC or to differentiate into ST-HSC (Short-Term Hematopoietic Stem Cell) then into MPPs (MultiPotent Progenitors) with reduced self-renewal capacity. Downstream of MPPs, a strict separation takes place between the myeloid (CMP, Common Myeloid Progenitors) and lymphoid (CLP, Common Lymphoid Progenitors) lineages. CMP then produce MEPs (Megakaryocyte–Erythrocyte Progenitors), which differentiate into platelets and erythrocytes, and GMPs (Granulocyte-Macrophage Progenitors) produce granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils) and macrophages. In the lymphoid lineage, the CLPs then produce T and B lymphocytes and natural killer cells. The whole hematopoietic differentiation process is tightly regulated by a number of intrinsic and extrinsic factors, like cytokines and transcription factors.
Hematopoiesis is a tightly regulated mechanism, and therefore impaired hematopoiesis can be the cause of leukemias, malignant disorders resulting from defects of the stem cells at different stages of maturation, with subsequent clonal expansion [92]. Leukemias include acute and chronic leukemia and are also classified into lymphoblastic and myeloblastic leukemias according to the cell type affected. Acute leukemias are characterized by the proliferation of immature, unfunctional white blood cells called “blasts”, decreasing normal hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow while chronic leukemias are characterized by the expansion of differentiated cells in the blood [93]. Acute leukemias are divided into acute myeloid leukemias (AML) or acute lymphoblastic leukemias (ALL) and chronic leukemia into chronic myeloid leukemias (CML) or chronic lymphoblastic leukemias (CLL).
3.2. Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a group of phenotypically and genetically heterogeneous diseases, which is among the most common adult leukemia (it accounts for about 80% of leukemias in adults), with an average age of first diagnosis over 60 years [94]. This is a complex pathology triggered by the accumulation of chromosomal translocations and/or multiple mutations and resulting in the transformation and clonal expansion of hematopoietic progenitors. AML is thought to initially develop from at least two types of somatically acquired genetic alterations: mutations that confer advantages in terms of proliferation and survival and mutations that interfere with cell differentiation and apoptosis mechanisms [95]. Recent advances in sequencing methodologies have shown that AML represents a dynamic disorder in which multiple sub-clones compete and coexist, not only during the normal progression of the disease but also under pressure generated by anticancer agents [96]. While the majority of patients are in complete remission after the initial chemotherapy, AML has been associated with a poor prognosis because most patients tend to relapse due to the emergence of therapy-resistant clones [97]. Identifying the genetic alterations associated with resistance to chemotherapy is essential for risk stratification and to predict response to treatment of each AML patient. Three main classes of genetic aberrations have been described in AML: non-random chromosomal alterations, multiple gene mutations, and epigenetic alterations [98,99]. The most common of these chromosomal alterations include rearrangements leading to the formation of genes coding for chimeric proteins and upregulation of gene expression by juxtaposition with strong promoters. Among these rearrangements, we find translocations t(8;21) AML1-ETO or RUNX1, t(15;17) PML-RARA, inv(16) CBFB-MYH11, and t(9;11) MLL-AF9, which are associated with a better prognosis, whereas translocations t(11;19) MLL-ENL, t(6;11) MLL-AF6, t(10;11) MLL-AF10, or complex karyotypes are associated with a worse prognosis [100]. One of these translocations, t(15;17) (q22;q12), is peculiar because it is characteristic of a subtype of acute myeloid leukemia named acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) [101]. This specific chromosomal translocation leads to the expression of the PML-RARα fusion protein. APL is unique among all leukemias because of its high level of sensitivity to all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), the vitamin A acid form [102]. The prognosis of this pathology is very good in general [103,104]. Among the genes that have been found mutated in AML we can mention retinoic acid receptor-α (RAR-α), core binding factor (CBF), HOX gene family or MLL. Mutations in oncogenes such as FLT3, KIT, N-RAS, GATA-1, JUN B, MYC, p53, PU.1, RB, FES, FOS, MPL, WT1, WNT, CEBPA, and NPM1 or mutations affecting epigenetic modifiers such as DNMT3A, ASXL1, TET2, IDH1, and IDH2 have also been characterized [105,106,107].
3.3. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), also called acute lymphocytic leukemia, is a rare genetically heterogeneous clonal malignant disorder of the bone marrow characterized by immature lymphoid precursors proliferation leading to the crowd out of normal hematopoietic cells [108]. ALL, which can occur at virtually any age, is more frequently seen in children and adolescents. This pathology results from clonal proliferation of abnormal B cell progenitors (B-ALL) accounting for approximately 85% of ALL or T cell progenitors (T-ALL) accounting for roughly 15% of ALL. Most of the genetic alterations leading to leukemogenesis, including chromosomal translocations, somatic mutations, aneuploidy, and gene copy number alterations have been characterized in both T-ALL and B-ALL. Like in AML, these genetic alterations are important prognostic factors for disease-risk stratification and treatment [109,110]. Among the genetic alterations found in B-ALL, TCF3–PBX1 t(1;19), ETV6–RUNX1 t(12;21), and hyperdiploidy are associated with a favorable outcome while MLL rearrangements, TCF3–HLF t(1;19) and rearrangements of CRLF2, JAK2A, or BL-class tyrosine kinase genes are of poor prognosis [111,112]. Alterations involving the KRAS, NRAS, FTL3, PTPN11, and epigenetic modifiers like CREBBP or WHSC1 are frequent genetic events [111,113].
The genetics of T-ALL is extremely heterogeneous, with chromosomal abnormalities in nearly all patients. Mutations in the NOTCH1 gene leading to constitutive activation of NOTCH signaling is the main oncogenic pathway found in the majority of patients. These alterations are generally associated with loss of p16 (INK4A) and p14 (ARF) suppressor genes at the CDKN2A locus. In addition, in 50% of patients with T-ALL, chromosomal translocations affect genes encoding oncogenic transcription factors like TAL1, TAL2, MYC, MYB, LYL1, TLX1 (HOX11), TLX3 (HOX11L2), or HOXA genes, placing these genes under the control of powerful T cell specific activators [114].
As for the AML example, it is not possible to exhaustively list all the genetic alterations and different combinations encountered, so we refer the reader to references dealing more specifically with this pathology [115,116,117].
3.4. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a slow-growing myeloproliferative neoplasm characterized in more than 95% of cases by the t(9;22) (q34.1;q11.2) chromosomal translocation leading to the formation of the Philadelphia chromosome (Ph*), resulting in the BCR-ABL1 gene fusion. The subsequent BCR/ABL1 chimeric protein is a constitutively active tyrosine kinases oncoprotein which activates transduction pathways involved in cell growth and differentiation such as RAS, MYC, STAT, AKT RAF, or JUN, and is therefore capable of transforming hematopoietic stem cell into neoplastic one [118,119].
Before targeted therapies became available, the main treatment options for CML included allogeneic stem cell transplantation and chemotherapy. However, the prognosis for CML improved considerably since the use of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), most notably imatinib in the early 2000s, which inhibit the BCR-ABL1 fusion protein by blocking its kinase domain [120]. Several generations of TKI have been developed since, but the appearance of TKI resistances remains a major issue [121]. It is therefore also crucial for this pathology to identify new therapeutic approaches in order to better stop its progression and avoid evolution to advanced disease states which may account for as much as 15% of all CML deaths [121].
3.5. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is characterized by a clonal proliferation and accumulation of mature but defective lymphocytes in the blood, bone marrow, lymph nodes, and spleen. CLL is the most common form of leukemia in Western countries. It is highly heterogeneous in its evolution, with some patients needing chemotherapy early after diagnosis and others never requiring specific treatment and having a survival rate similar to the general population. More than 95% of people with CLL develop the B cell type [122]. CLL is a heterogeneous disease, which divides into an aggressive form that expresses a wild type immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable region (IGVH) gene, and an indolent form that expresses a mutated IGVH, reflecting the stage of normal B cell differentiation [123,124]. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells exhibit many complex genetic alterations, which have been used by clinicians as prognostic biomarkers in order to predict survival and disease progression and guide treatment decisions [124]. Many recurrent cytogenetic abnormalities are encountered in CLL. The main ones are (i) deletion of the long arm of chromosome 13 (del(13q)), leading to the loss of the DLEU2/MIR15A/MIR16-1 genes, which is found in more than 50% of CLL cases and is of good prognosis when isolated; (ii) trisomy 12, associated with an intermediate prognosis with median overall survival; (iii) deletion of the long arm of chromosome 11 (del(11q)) that leads a more aggressive disease due to the loss of the ATM gene (for Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated) which is essential for the regulation of the cell cycle; and (iv) deletion of the short arm of chromosome 17 (del(17p)) resulting in the loss of the TP53 gene which is of poor prognosis [125,126,127]. At least one of these abnormalities can be found in approximately 80% of patients [122,128,129]. Translocations are reported in approximately 20% of CLL [130]. These translocations predominantly involve the immunoglobulin genes, mainly IGH, and the 13q14 locus. Common partners are CCND1, BCL2, and BCL3 [130]. In addition to chromosomal rearrangements, sequencing studies have also revealed numerous recurrent mutations in CLL mostly in the P53, ATM, NOTCH1, SF3B1 (Splicing Factor 3B subunit 1), and BIRC3 genes [131].
A variety of targeted drugs including BCR signaling pathway inhibitors, anti-CD20 antibodies and BCL-2 inhibitors have been used in therapeutics and have significantly improved the management of this disease [132,133]. However, despite the increasing number of available therapeutic alternatives, chemotherapy does not currently provide a definitive cure and additional strategies are still required.
4. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Induction in Hematopoietic and Leukemic Cells
4.1. ER Stress Activation in HSCs
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are sitting at the apex of the hematopoietic hierarchy. They are the most immature cells and are capable of replenishing all hematopoietic cell types [134,135]. As long-life cells, HSCs require a highly regulated protein quality control in order to avoid the accumulation of damages that could ultimately affect their DNA integrity and promote tumorigenesis. At steady state, HSCs are quiescent and display lower protein synthesis rates in vivo and in vitro compared to their progeny [136]. Furthermore, HSCs have been associated with low protein folding capacity that can be explained by a lower expression of chaperones proteins compared to hematopoietic progenitors [137]. Moreover, protein synthesis deregulation has a great impact on HSCs’ viability and self-renewal capacities and can lead to HSCs loss [136,138]. Investigation of ER stress role in regulating hematopoietic stem cells fate, revealed a high expression of PERK and a low expression of eIF2α in HSCs when compared to progenitor cells [139,140]. PERK upregulation in HSCs appears to increase their sensitivity to ER stress, compared to more committed progenitor cells, through activation of the PERK-peIF2α-ATF4/CHOP arm that can trigger apoptosis. It has been suggested that this sensitivity to ER stress could prevent accumulation of damaged cells in the HSCs compartment and potential subsequent malignant transformation [139]. In agreement with this hypothesis, Miharada et al. showed that reducing ER stress levels in vitro in HSCs through the overexpression of the RNA binding protein Dppa5 (Developmental pluripotency-associated 5) improved their self-renewal activity by protecting them from apoptosis [141]. However, the IRE1α-XBP1 UPR branch can also be activated in HSCs and in this case plays a significant cytoprotective role. For example, estrogen treatment of HSCs activates the IRE1α-XBP1 branch and increases repopulation capacities of HSCs upon transplantation [142]. In a mouse model system, Liu et al. also showed that IRE1α-XBP1 activation in HSCs in vivo prevents ER stress-induced apoptosis, preserves HSC clonogenicity and improves reconstitution capacity [143]. Xie et al. also demonstrated that increased cytoprotective ER stress (induced by the pharmacological inhibition of the sphingolipid enzyme DEGS1) participates together with autophagy in the setting up of a prosurvival response aimed to maintain stemness properties [144].
Increased ERAD has also been recently reported to actively participate in the maintenance of proteins homeostasis in HSCs and appeared to be essential for stem cell pool maintenance [145]. In addition to low protein synthesis rates and low folding capacity, it has been reported that protein quality control by ERAD maintains HSCs pool. Altogether currently known data indicate that increased basal UPR induced at least in part by unfavorable growing conditions in the bone marrow environment, such as, e.g., hypoxia [146], helps in maintaining HSC integrity as well as clearing damaged HSCs and therefore play critical functions at the early steps of hematopoiesis [147]. Of note, in our article we refer to “basal UPR” as the activation status of the different signaling pathways of the UPR in cells growing either in vitro or in vivo without any treatment by chemotherapeutic drugs or chemical compounds.
4.2. ER Stress Activation in Leukemic Cells
Recent lines of evidence link activation of the three UPR branches to most hallmarks of cancer and especially those aimed to protect the cells against the numerous aggressions they undergo during their growth inside tumors [20]. This is especially true for solid tumors, which develop in a highly adverse environment but also for leukemic cells. Indeed, hematopoietic cells, either normal or leukemic, are exposed in the bone marrow to an adverse environment caused by hypoxia, high levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and nutrient deprivation, often resulting in ER stress activation [13,16,23,148]. Thus, many studies have reported the activation, to variable extents, of each of the three UPR branches (IRE1α, PERK, and ATF6α) in a wide range of hematopoietic tumors (leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma) [137,149,150,151]. As in solid cancers, UPR plays a fundamental role in the adaptation of leukemic cells to cellular stress by inducing different mechanisms, which attempt to reestablish ER homeostasis in order to restore its proper functions.
In AML patients, increased expression of XBP1, BiP, and Calreticulin has been detected in 17.4% of cases [152]. Schardt et al. demonstrated a correlation between a high expression of XBP1s and complex karyotype in AML [152]. Another clinical study from Tanimura et al. reported activation of the IRE1α-XBP1 pathway in AML patients; however, no significant correlation between ER stress activation and genetic features could be revealed [153].
Interestingly, UPR activation in some hematological malignancies is not always the consequence of stress integration but can also be induced through aberrant pathway activation. For example, in chronic lymphoid leukemia (CLL), UPR activation is observed in response to surface immunoglobulin M stimulation and activation of the kinases BTK and SYK [154]. In pre-B-ALL, Xbp1 expression is activated by various oncogenic tyrosine kinases via STAT5 signaling [155]. Moreover, the transcription factor c-Jun, overexpressed in AML and CML, promotes the transcription of general UPR target genes such as Xbp1 and Atf4 by a direct mechanism [156]. The modulation of expression of some UPR effectors in leukemia has been shown to involve epigenetic modifications in their promoters [157,158].
In addition, mutations in epigenetic splicing factors, which are considered as first hit mutations, have pleiotropic effects that might be linked to ER stress activation (Figure 3). The comparison between healthy donor and AML patient samples revealed hypomethylation of Xbp1′s promoter that has been suggested to lead to overexpression of XBP1. On the contrary, in large diffuse B cells lymphoma, IRE1α expression is reduced through a mechanism involving the histone methyltransferase, EZH2 (Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2).
Figure 3.
Activation of UPR signaling in leukemia. Different mechanisms of ER stress activation have been reported in leukemia, which include (epi)genetic modifications and genomic instability (e.g., mutations, translocations, hypomethylation), oncogenic signaling, and metabolism rewiring due to a high proliferation in blasts. Microenvironment is also a well-known source of ER stress (e.g., hypoxia) that contributes to UPR activation.
Furthermore, transcription of ER stress-related proteins by oncogenic pathways also participates in the UPR activation in leukemia. For instance, the MAPK pathway promotes the transcription of Xbp1 through STAT5 activation. In pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), BCR-ABL1 or NRASG12D signals through MAPK-STAT5-XBP1 [155]. Indirectly, in lymphomagenesis the transcription factor MYC, by promoting a rapid cell proliferation, increases the rate of misfolded proteins in ER that triggers the UPR [159].
Compared to HSC, in which both cytoprotective (IRE1α-XBP1) and cell death-promoting (PERK) UPR pathways can be activated in the basal state, the activation of an adaptive UPR (mainly via IRE1α signaling) appears to be preferred in leukemic cells. However, the increase in basal UPR could sensitize these cells to additional stress induced, for example, by chemotherapy treatment (see next chapter). By analogy with what is observed in HSCs under normal growth conditions, the UPR response may represent a real checkpoint influencing cell fate of leukemic cells experiencing chemotherapy: either the stress can be resolved via an adaptive phase and cancer progresses or the damage accumulates and becomes unrecoverable. In this latter case, excessive or prolonged stress triggers proapoptotic signaling through a terminal process [137,150,151,160]. This important issue is discussed below.
4.3. UPR Modulation: A Double-Edged Sword to Fight Against Leukemia
Despite the numerous pieces of evidence of reticulum stress activation in multiple cancers, the question of whether UPR reduces or promotes tumor growth in patients is still the subject of intense debate [149]. Two therapeutic strategies exploiting ER stress and UPR could be possible in order to induce leukemic cell death: either inhibition of the adaptive UPR response (cytoprotective) or activation of the terminal UPR response (cytotoxic). The choice between these two strategies may be difficult as their relative efficacy may be highly dependent on the cellular deregulation that led to the disease.
As mentioned above, various studies have shown that leukemic cells often possess basal UPR activity with a cytoprotective function, which favors tumor progression and additionally may increase chemoresistance of the cells to various drugs. For example, the ER stress sensor BiP was found to be highly expressed in B-ALL and its pharmacological inhibition by epigallocatechin gallate (a polyphenolic compound purified from green tea) sensitized cells to the anti-leukemic drug vincristine [161]. In the same pathology, the increase in expression and activity of BiP and the IRE1α/XBP1 pathway were found to be essential for cell survival and pharmacological inhibition of IRE1α RNAse domain by the drug STF-083010 reduced the proliferation and survival of patient-derived pre-B ALL cells [155]. Of note, increased Xbp1 mRNA levels at diagnosis appear of poor prognosis for patients with the disease [155]. In CML, activation of the PERK-eIF2α pathway has a cytoprotective effect and increases their resistance to imatinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor widely used in cancer chemotherapy [162]. Resistance to imatinib in CML was also shown to result from the activation of ATF6α, which appears mediated by the protein disulfide isomerase 5 (PDIA5) upon ER stress and a PDIA5 inhibitor, 16F16, increased cells’ sensitivity to treatment with imatinib [163]. Moreover, a pharmacological inhibitor of IRE1α, B109, was reported to suppress CLL tumor cell progression in a murine model and to sensitize human CLL cells to the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib [164]. A pro-survival role for IRE1α was also reported in AML and the pharmacological inhibition of IRE1α by 2-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde (HNA) switched the cells towards apoptosis and in addition synergized with treatments with bortezomib and arsenic trioxide, two widely used anticancer drugs [157]. Moreover, analysis of Philadelphia chromosome (Ph)-positive AML patient samples revealed increased expression of the BiP, CHOP, and Xbp1s mRNAs and the authors demonstrated that inhibition of the IRE1α and ATF6α pathways sensitized cells expressing the Bcr-Abl fusion protein to imatinib- and etoposide-induced apoptosis [165]. More recently it was shown that Jun itself induces the expression of several UPR effectors thereby enhancing UPR induction and this appeared essential to AML cell proliferation and survival, thus demonstrating that Jun could contribute to induce an adaptive UPR in some AML subtypes [156].
Altogether, the data presented above have largely validated the inhibition of adaptive UPR as an effective means of fighting leukemia and a significant number of pharmacological inhibitors of central UPR effectors are currently under preclinical studies or clinical trials [137,150].
However, these promising results should not lead us to neglect the other strategy aimed at inducing a cytotoxic response in the cell through terminal UPR induction, the “second edge of the sword”. Indeed, leukemic cells, which usually experience unfavorable growth conditions and maintain increased levels of ER stress and basal UPR, may show an increased susceptibility to enter terminal UPR in response to different treatments. Indeed, artificially increasing the unfolded protein load can lead to a cytotoxic cellular response in some leukemic models. Thus, in ALL treatment with the drug pevonedistat, which inhibits the NEDD8 conjugation pathway and impairs degradation of misfolded proteins by the proteasome, induces a reorientation of UPR towards apoptosis [166]. Interestingly, inhibiting the ER-associated degradation (ERAD) pathway of proteins by knockdown of one of its components, UFD1, also results in the induction of a terminal UPR process in T-ALL cells in response to the accumulation of unfolded proteins [167]. In mast cell leukemia, it was demonstrated that moderate pharmacological inhibition of IRE1α could stop leukemic cell proliferation by impairing adaptive UPR but with non-significantly induced cell death. Interestingly, stronger inhibition of IRE1α induced a switch from adaptive to terminal UPR. Enhancing ER stress by pharmacological inhibition of proteasome activity with bortezomib also induced terminal UPR in this model [168]. In Philadelphia-positive ALL, pharmacological inhibition of IRE1α with MKC-8866 also appeared able to reorient the initial cytoprotective UPR program towards cell death induction when combined with the inhibition of BCR-ABL1 with nilotinib [169].
Few studies describing the induction of cell death in leukemic cells by a strategy deliberately aimed at redirecting the cell response towards terminal UPR has yet been described. However, the analysis of data published over the last two decades and describing the use of antileukemic drugs shows, strikingly, that for many of them (see Table 1) their mode of action involves the induction of a terminal UPR pathway or related UPR-induced cell death processes. Indeed, although adaptive UPR was found to contribute to chemoresistance in 10 out of the 91 chemical compounds tested against leukemic cells and listed in Table 1, for the remaining compounds (i.e., 89% of the whole) the induction of UPR signaling pathways was associated with cytotoxicity. There appears to be no apparent correlation between the type of leukemia and the final response, cytoprotective or cytotoxic, to UPR induction. This also seems to be the case if we consider the mode of action of the drugs used. Similarly, no strict correlation can be found between the UPR pathways activated in response to the drugs and the final response of the cell (pro-survival or pro-death) and all UPR pathway have been reported to be induced whatever the final outcome on leukemic cell’s viability. It can be noted, however, that the CHOP pathway is very frequently activated when UPR induction results in cell death. This appears not surprising as the PERK-peIF2α/ATF4/CHOP signaling pathway plays a crucial function in inducing cell apoptosis in the cell [46] and was reported to be a major cell death-inducing UPR pathway in hematopoietic stem cells, as described above (see Chapter 4.1). However, induction of the PERK-peIF2α/ATF4/CHOP signaling pathway can also be detected in leukemic cells responding to treatment by an adaptive UPR. As in other pathological models, leukemic cell response to UPR induction is a complex process, which may rely on a subtle balance between the activation levels of the different branches of the UPR. Anyway, it appears that for a large number of chemotherapeutic agents or candidate compound, this process is critical for the final death/survival outcome of leukemic cells.
Table 1.
Consequences of UPR induction by drugs in leukemic cells. For each drug, the chemical nature, the pubchem compound ID, and the molecular target are provided when available. The type of leukemia on which the work was carried out was provided as well as the inferred or demonstrated role of UPR activation. The involved effectors are also indicated, when they have been identified (n.d.: not determined).
| Molecule | Chemical Nature | Pubchem Compound CID | Target | Type of Leukemia | Proposed Role of ER Stress/UPR Activation | Mainly Implicated Pathways/Effectors | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIX-01294 | 25150857 | Histone methyltransferase G9A | AML | Adaptive | PERK (prosurvival, via NRF2) | [170] | |
| SCH727965 (Dinaciclib) | 46926350 | CDKs 1,2,5 and 9 | AML, CML, T-ALL | Adaptive | XBP1s | [171] | |
| Ski, ROMe | 16760659 | spingosine kinases 1 and 2 | T-ALL | Adaptive | unclear | [172] | |
| MDA-7/IL-24) | cytokine | - | n.d. | AML, APL | Adaptive | GRP78/Bip, IRE1α, GADD34 | [173] |
| sorafenib | multikinase inhibitor | 216239 | MEK/ERK pathway | U937 cell line | Adaptive | PERK | [174] |
| Digoxine | cardiac glycoside | 2724385 | Na+/K+ ATPase | K562 (erythroleukemic) and THP-1 (acute monocytic leukemia) cell lines | Adaptive | PERK, IRE1α | [175] |
| Shikonin | naphthoquinone | 479503 | pyruvate kinase-M2 (PKM2), proteasome inhibition, NFkB, Thioredoxin reductase (TrxR1) | HL60 | Adaptive | ERP57 and Calreticulin | [176] |
| 3-deazaneplanocin A (DZNeP) | cyclopentenyl analog of 3-deazaadenosine | 73087 | histone methyltransferase | MV4-11, MOLM-14, Mono-Mac-1, THP-1, HL60 and KG-1 AML cell lines | Adaptive | GRP78, GRP94, PERK, PDIA isoform 3, 4, and 5 | [177] |
| wolfberry phytochemicals | n.d. | - | n.d. | Jurkat cell line | Adaptive | all UPR pathways | [178] |
| Imatinib | 5291 | tyrosine kinases inhibitor | CML/LAMA-84 CML cell line and murine myeloid progenitor primary cells | The constitutive activation of PERK in CML cells protects from imatinib treatment | PERK | [162] | |
| Metformin | 4091 | multiple, see PMID: 28776086 | T-ALL, B-ALL | Switch form adaptive to terminal | IRE1α, CHOP | [179] | |
| Nilotinib + MKC8866 | 644241 | Tyrosine kinases (Nilotinib); IRE1α (MKC8866) | ALL (Ph+) | Switch form adaptive to terminal | IRE1α (cytoprotective); PERK and ATF6α (cytotoxic) | [169] | |
| 2-deoxy-D-glucose | glucose analog | 108223 | n.d. | ALL Cell Lines | Switch form adaptive to terminal | GRP78/Bip, CHOP | [180,181] |
| Selenite | sodium selenite | 24934 | n.d. | NB4 cell line (APL) | Switch form adaptive to terminal | PERK/eIF2α/ATF4 | [182] |
| Asperuloside | iridoid glycoside | 84298 | n.d. | cell lines HL60 and U937, primary leukemic cells | Terminal: apoptosis induction | all UPR pathways | [183] |
| JA3 & JA7 | Aldehyde biphenyl chalcones | 134820953 | n.d. | (AML); T-ALL; CML | Terminal: immunogenic apoptosis-like cell death | CHOP; PERK | [184] |
| Oprozomib | tripeptide analog of carfilzomib | 25067547 | immunoproteasome subunit β5i/LMP7 (ubiquitin–proteasome pathway) | CML | Terminal: apoptosis induction | PERK, IRE1α (via ASK/JNK/Bim) | [185] |
| VAS3947 | given in [186] fig 1a | 7471335 | NADPH oxidases | AML | Terminal: apoptosis induction | IRE1α, PERK | [186] |
| Arsenic trioxide + Gilteritinib | 14888/49803313 | FLT3 (for Gilteritinib) | AML (FLT3-ITD) | Terminal: apoptosis induction | IRE1α | [187] | |
| GSK-J4 | 71729975 | H3K27me3 demethylase | AML | Terminal: apoptosis induction | PKCα; Bcl2 phosphorylation | [188] | |
| CXL146 | 4H-chromene derivative | - | AML (or APL): HL60; CML | Terminal: apoptosis induction | PERK, IRE1α, ATF6α | [189] | |
| FF-10501 | given in paper | 124343 | inosine monophosphate deshydrogenase | AML | Terminal: necrotic cell death | CHOP | [190] |
| Retinoic acid+Tunicamycin+ arsenic trioxide | 444795/11104835 | n.d. | AML | Terminal: Cytotoxic UPR | CHOP, XBP1s | [191] | |
| [Retinoic acid or arsenic trioxide] + tunicamycin | 444795/11104835 | n.d. | APL | Terminal: Cytotoxic UPR | [192] | ||
| MIM1 and UMI-77 | 135691163/992586 | n.d. | AML; T-ALL | Terminal: Cytotoxic UPR | NOXA | [193] | |
| PFR | peptide | - | n.d. | AML | Terminal: necroptosis | [193] | |
| Genistein | Isoflavone | 5280961 | n.d. | AML or APL (HL60 cell line) | Terminal: Cytotoxic UPR | [194] | |
| Camalexin | Phytoalexin (structure given in paper) | 636970 | n.d. | AML | Terminal: apoptosis induction | PERK, CHOP | [195] |
| Ibrutinib (PCI-32765) | 24821094 | Bruton’s tyrosine kinase | B-ALL | Terminal: apoptosis induction | ATF4; CHOP | [196] | |
| OT-55 | bis-coumarine derivative | - | n.d. | CML | Terminal: Immunogenic cell death induction; apoptosis induction | not well documented | [197] |
| RS-F3 | fistularin-3 stereoisomer | - | AML | Terminal: Cytotoxic UPR (assumed) | PERK; XBP1s; CHOP | [198] | |
| Bardoxolone methyl (CDDO-Me) | triterpenoid | 400769 | Nrf2 and NF-κB | Chronic myeloid leukemia, K562 cell line | Terminal: apoptosis induction | PERK, IRE1α, CHOP | [199] |
| 3-O-trans-p-coumaroyl-alphitolic acid (3OTPCA) | triterpenoid | - | n.d. | U937, Molt-4 and Jurkat cell lines. | Terminal: apoptosis induction | XBP-1 and CHOP | [200] |
| Nelfinavir | 64143 | HIV protease inhibitors | T-ALL, B-ALL, and AML; CLL primary leukemic cells | Terminal: apoptosis induction; In CLL, contributes to the induction of cell death in choroquine treated cells | CHOP | [201,202] | |
| CB-5083 | 1-[4-(benzylamino)-5H,7H,8H-pyrano[4,3-d]pyrimidin-2-yl]-2-methyl-1H-indole-4-carboxamide | 439268 | Valosin-Containing Protein/p97 | B-ALL Cell Lines (BALL1, REH, NALM6, OP1, ALL-PO, 697, RS4;11, BV173, SEM, and SUPB15) | Terminal: apoptosis induction | all UPR pathways | [203] |
| Tunicamycin ± Quizartinib (AC220) | AC220 | 11104835 + 24889392 | FLT3 | AML (FLT3-ITD) | Terminal: apoptosis induction | PERK, CHOP | [204] |
| Cryptotanshinone | lipophilic diterpene quinone | 160254 | n.d. | CCRF-CEM cell line (ALL) | Terminal: apoptosis induction | IRE1α-XBP1, PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 | [205] |
| Oxalicumone A | dihydrothiophene-condensed sulfur chromone | 90676613 | n.d. | KG-1a, HL60, U937, and K562 cell lines (AML) | Terminal: apoptosis induction | IRE1α-XBP1, PERK--CHOP | [206] |
| Pevonedistat (MLN4924) | adenosine sulfamate analog | 16720766 | NEDD8-activating enzyme | T-ALL (CCRF-CEM, Jurkat) and B-ALL (REH, NALM6, SupB15) cell lines | Terminal: apoptosis induction | all UPR pathways | [166] |
| Carfilzomib (PR-171) | tetrapeptide epoxyketone | 11556711 | ubiquitin–proteasome pathway | CLL MEC1 and MEC2 cell lines and primary leukemic cells | Terminal: apoptosis induction | ATF4, CHOP | [207] |
| Miltirone | abietane-type norditerpenoid quinone | 160142 | n.d. | Jurkat, U937, AML and ALL primary leukemic cells | Terminal: apoptosis induction | PERK | [208] |
| Arsenic trioxide | 14888 | n.d. | NB4 cell line (AML)/CML | Terminal: apoptosis induction | IRE1α-XBP1/GRP78/Bip, CHOP, Xbp1 (unspliced…) | [209,210] | |
| JPH203 | O-[(5-Amino-2-phenyl-7-benzoxazolyl)methyl]-3,5-dichloro-L-tyrosine dihydrochloride | 24853505 | LAT1 (L-type amino-acid transporter 1) | Ke37, DND41, Sil-ALL, Peer, Molt-16, Jurkat and SupT1 T-ALL cell lines | Terminal: apoptosis induction | CHOP | [211] |
| Wogonin | 5,7-dihydroxy-8-methoxyflavone | 5281703 | n.d. | HL-60 cell line. | Terminal: apoptosis induction | all UPR pathways-CHOP | [212] |
| Farnesol | acyclic sesquiterpene alcohol | 445070 | n.d. | Molt4 T-ALL cell line | Terminal: apoptosis induction | PERK-eIF2α-ATF3/4 | [213] |
| APO866 | (E)-N-[4-(1-benzoylpiperidin-4-yl)butyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide | 6914657 | nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT) | OCI/AML2, OCI/AML3, HL-60, HEL, KG1a, SET1, MV4-11, MEC.1, MEC.2, LAMA-84 cell lines and B-CLL and AML primary leukemic cells | Terminal: apoptosis induction | IRE1α-CHOP | [214] |
| Bortezomib | boronic acid | 387447 | proteasome (26S) | NB4 cell line (APL) | Terminal: apoptosis induction | Nd | [215] |
| CX-4945 | 5-(3-chloroanilino)benzo[c][2,6]naphthyridine-8-carboxylic acid | 24748573 | casein kinase 2 | T-ALL cell lines and primary cells | Terminal: apoptosis induction | GRP78/BIP-IRE1α-CHOP | [216] |
| compound 3 (Pyrimidine analogue) | 1-(5,5,5-trichloro-2-methoxy-4-oxopenten-2-yl)-4-trichloromethyl-pyrimidin-2(1H)-one | - | n.d. | L1210, CEM, JURKAT cell line (ALL) | Terminal: apoptosis induction | CHOP and caspase-12 | [217] |
| R7, R13 | Naphtylchalcones | n.d. | murine lymphoblastic leukemia | Terminal: apoptosis induction (assumed) | CHOP | [218] | |
| S1 (BH mimetic) | APL | Terminal: cytotoxic through NOXA induction | PERK; XBP1s, NOXA | [219] | |||
| Gossypol (BH3 mimetic) | polyphenol | 3503 | phospholipase A2 | AML, APL | Terminal: cytotoxic through NOXA induction | PERK; NOXA | [220] |
| Cariporide | 151172 | Na + H+ exchanger 1 (NHE1) | CML, APL, T-ALL | Terminal: sensitizes to extrinsic, TRAIL-induced, apoptosis | CHOP | [221] | |
| Auranofin | 6333901 | thioredoxin reductase | CLL | Terminal: contributes to the induction of cell death in treated cells | PERK; XBP1s, CHOP | [222] | |
| [Cu(thp)4][PF6] | phosphine copper(I) complex | n.d. | B-ALL | Terminal: apoptosis induction | Xbp1s, CHOP | [223] | |
| Z-Leu-Leu-Nle-CHO | leupeptin analog | - | γ-Secretase | CLL primary leukemic cells | Terminal: apoptosis induction | IRE1α, CHOP | [224] |
| curcumin | Diferuloylmethane | 969516 | n.d. | WEHI-3 myelomonocytic leukemia cell line/NB4 and UF-1 APL cell lines/HL60 cell line | Terminal: apoptosis induction | IRE1α, ATF6α, CHOP/PERK, CHOP, ASK | [225,226,227] |
| LQB 118 | pterocarpanquinone | 46233300 | n.d. | K562 and Jurkat cell lines | Terminal: apoptosis induction (assumed) | caspase 12 | [228] |
| Flavopiridol | Flavonoid alkaloid | 5287969 | CDKs inhibitor | CLL primary leukemic cells | Terminal: contributes to the induction of cell death in choroquine treated cells | IRE1α/XBP1 and CHOP | [229] |
| Safrole | 5144 | AML (HL-60) | Terminal: apoptosis induction (assumed) | ATF6α, CHOP | [230] | ||
| Clofibrate | 2796 | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) alpha | T-ALL | Terminal: apoptosis induction (assumed) | ASAPK/JNK | [231] | |
| Abnobaviscum F ® | Mitletoe aqueous extract | 135343633 | n.d. | CML | Terminal: contribution to the induction of cell death in treated cells (assumed) | GRP78/Bip, CHOP | [232] |
| MJ-29 | Quinazolinone | - | n.d. | murine myelomonocytic leukemia | Terminal: apoptosis induction | GRP78/Bip, CHOP, PERK | [233] |
| Imatinib (STI571) | 5291 | BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase | Terminal: apoptosis induction | not well documented | [234] | ||
| glycyrrhizic acid | 14982 | n.d. | murine myelomonocytic leukemia | Terminal: contributes to the induction of cell death in treated cells | GRP78/Bip, CHOP | [235] | |
| Gypenosides | - | n.d | HL-60 AML cell line | Terminal: apoptosis induction | ATF6α and ATF4 | [236] | |
| AICAr (+ methotrexate) | 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide (AICA) riboside | 266934 | n.d | Nalm6 and CCRF-CEM cell lines (ALL) | Terminal: apoptosis induction | CHOP (C/EPB homologous protein) | [237] |
| Emodin | 6-methyl-1,3,8-trihydroxyanthraquinone | 3220 | n.d. | WEHI-3 murine myelomonocytic leukemia cell line | Terminal: apoptosis induction (assumed) | n.d. | [238] |
| Syrbactin | azamacrocyclic product | - | proteasome (26S) | REH ALL cell line | Terminal: apoptosis induction | CHOP (C/EPB homologous protein) | [239] |
| ABT-737 and GX15-070 | BH3 mimetics | 11228183/46930997 | BCL2 family proteins | Jurkat, NB4 and K562 cell lines | Terminal: Cytotoxic UPR | ATF4, ATF3, CHOP and NOXA, | [240] |
| NPB001-05 | n.d. | - | BCR-ABL | K562 cell line | Terminal: apoptosis induction (assumed) | not well documented | [241] |
| Ras inhibitor farnesylthiosalicylic acid (FTS, Salirasib) | 2-[[(2E,6E)-3,7,11-trimethyl-2,6,10-dodecatrien-1-yl]thio]-benzamide | 5469318 | RAS | K562 cell line | Terminal: Cytotoxic UPR | not well documented | [242] |
| PYZD-4409 | 3,5-dioxopyrazolidine compound, 1-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-4-[(5-nitro-2-furyl)methylene]-3,5-pyrazolidinedione | 60111983 | ubiquitin-activating enzyme UBA1 | K562, NB4, THP1, and U937 cell lines and AML primary leukemic cells | Terminal: apoptosis induction | PERK, CHOP, ATF4 | [243] |
| Korbazol | n.d. | - | n.d. | CLL primary leukemic cells | Terminal: apoptosis induction (assumed) | n.d. | [244] |
| Polymethoxyflavone tangeretin (TAN) | Flavonoids | - | n.d. | K562 cell line | Terminal: apoptosis induction | IRE1α, PERK, CHOP | [245] |
| Shiga toxine type 1 (Stx1) | n.d. | - | ribosomes (protein synthesis) | THP-1 cell line | Terminal: apoptosis induction | CHOP, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), DR5 and calpain | [246] |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid | 446284 | n.d. | HL60 (AML or APL) | Terminal: apoptosis induction (assumed) | PERK | [247] | |
| Xanthohumol | prenylated chalcone | 639665 | n.d. | CLL (patient samples) | Terminal: apoptosis induction | PERK, CHOP | [248] |
| Tunicamycin (UPR inducer) | 11104835 | N-acetylglucosamine phophotransferase | AML (U937 and HL60) | Terminal: cytotoxic through induction of lysosomal apoptotic pathway | GRP78/Bip, CHOP | [249] | |
| arsenic sulfide | [As4S4 (AS)] | 61569 | n.d. | BCR/ABL-positive K562 cell line | Terminal: apoptosis induction | not well documented | [250] |
| Fenretinide | synthetic retinoid derivative (related to vitamin A) | 5288209 | n.d. | NB4, U937 and HL60 cell lines | Terminal: apoptosis induction | PERK/eIF2α-CHOP (C/EPB homologous protein) | [251,252] |
| PABA/NO | O2-[2,4-dinitro-5-(N-methyl-N-4-carboxyphenylamino)phenyl]1-(N,N-dimethylamino)diazen-1-ium-1,2-diolate | - | PDI | HL60 cell line | Terminal: Cytotoxic UPR | CHOP (C/EPB homologous protein) | [253] |
| alkyl gallate and gallamide derivatives | - | n.d. | HL60 cell line | Terminal: apoptosis induction | not well documented | [254] | |
| Trichosanthin | type I ribosome-inactivating protein | 596174 | Ribosomes | HL60 cell line | Terminal: apoptosis induction | CHOP (C/EPB homologous protein) | [255] |
| auraptene | monoterpene coumarin ether | 1550607 | n.d. | Jurkat cell line | Terminal: apoptosis induction | Caspase 8 | [256] |
| 4-hydroxybenzylretinone | fenretinide analogue/synthetic retinoid derivative (related to vitamin A) | - | n.d. | HL60 cell line | Terminal: Cytotoxic UPR | CHOP (C/EPB homologous protein) | [257] |
| tipifarnib combined with bortezomib | quinolone and boronic acid | 159324/387447 | Farnesyltransferase Inhibiteur and 26 s proteasome inhibitor | KG-1, and U937 cell lines | Terminal: Cytotoxic UPR | not well documented | [258] |
| AEBSF | 4-(2-aminoethyl) benzenesulfonyl fluoride hydrochloride | 186136 | serine protease inhibitor | NB4 cel line | Terminal: Cytotoxic UPR | not well documented | [259] |
| Thapsigargin (UPR inducer) | sesquiterpene lactone | 446378 | sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca++ ATPase | K562 cell line | Terminal: apoptosis induction | not well documented | [260,261] |
| arsenic trioxide (ATO) + kinase inhibitor imatinib mesylate (STI571) | 14888/5291 | BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase | K562 cell line and CML primary leukemic cells | Terminal: apoptosis induction | not well documented | [262] | |
| Tetrocarcin-A | 54681516 | n.d. | CLL/T-ALL | Terminal: apoptosis induction | not well documented | [263,264] |
Therefore, it seems important to further investigate terminal UPR induction, on its own as well as in combination with other pharmacological treatments, for the improvement of therapeutic strategies in leukemia.
5. Conclusions
We have reviewed the currently available data in the literature dealing with the various roles played by UPR in leukemia. We also presented some of the UPR-mediated molecular processes that can induce cytoprotection of leukemic cells or direct them towards cell death through apoptosis induction. In the light of all of the currently reported data from studies carried out to dissect the role of UPR in the progression of leukemia, it is clear that the cytoprotective/cytotoxic balance regulation is a complex, highly dynamic machinery, still poorly understood and that a wide and integrative approach is needed to discover the genuine mechanisms underlying this crucial process. The specific networks that regulate ER stress-induced cytoprotection or apoptosis may be dependent on the nature, the intensity and the length of the stimuli. It is probable, even if contradictory results have sometimes been published, that it also depends on the cell type being stressed.
A better understanding of the UPR mechanisms acting in response to chemotherapy appears also essential to provide new therapeutic pathways aimed to eradicate neoplastic cells either by inhibiting the adaptive UPR, or by activating UPR-mediated cell death pathways [265].
Funding
This work was supported the Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale (INSERM), Université Toulouse III (Paul Sabatier) and Association Laurette Fugain (ALF2018/03 awarded to CT). KRP’s lab is funded by Kay Kendall Leukaemia Fund #KKL1149, Academy of Medical Sciences #SBF0041099 and Barts Charity. CP and MJ were supported by a fellowship from the French ministry of higher education and research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Alberts B., Johnson A., Lewis J., Morgan D., Raff M., Roberts K., Walter P. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 6th ed. Garland Science; New York, NY, USA: 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Araki K., Nagata K. Protein folding and quality control in the ER. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011;3:a007526. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a007526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Eletto D., Chevet E., Argon Y., Appenzeller-Herzog C. Redox controls UPR to control redox. J. Cell Sci. 2014;127:3649–3658. doi: 10.1242/jcs.153643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sun Z., Brodsky J.L. Protein quality control in the secretory pathway. J. Cell Biol. 2019;218:3171–3187. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201906047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Li C., Xia B., Wang S., Xu J. Folded or Degraded in Endoplasmic Reticulum. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020;1248:265–294. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-3266-5_12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hetz C. The unfolded protein response: Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012;13:89–102. doi: 10.1038/nrm3270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ron D., Walter P. Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;8:519–529. doi: 10.1038/nrm2199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Moore K.A., Hollien J. The unfolded protein response in secretory cell function. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2012;46:165–183. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-110711-155644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kaufman R.J. Stress signaling from the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum: Coordination of gene transcriptional and translational controls. Genes. Dev. 1999;13:1211–1233. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.10.1211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hetz C., Zhang K., Kaufman R.J. Mechanisms, regulation and functions of the unfolded protein response. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020;21:421–438. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-0250-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sicari D., Igbaria A., Chevet E. Control of Protein Homeostasis in the Early Secretory Pathway: Current Status and Challenges. Cells. 2019;8:1347. doi: 10.3390/cells8111347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Maurel M., McGrath E.P., Mnich K., Healy S., Chevet E., Samali A. Controlling the unfolded protein response-mediated life and death decisions in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015;33:57–66. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hetz C., Chevet E. Theme Series—UPR in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015;33:1–2. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hosoi T., Ozawa K. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in disease: Mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Clin. Sci. 2009;118:19–29. doi: 10.1042/CS20080680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hetz C., Axten J.M. Pharmacological targeting of the unfolded protein response for disease intervention. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019;15:764–775. doi: 10.1038/s41589-019-0326-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hetz C., Chevet E., Harding H.P. Targeting the unfolded protein response in disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013;12:703–719. doi: 10.1038/nrd3976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Corazzari M., Gagliardi M., Fimia G.M., Piacentini M. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Unfolded Protein Response, and Cancer Cell Fate. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017;7:78. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Oakes S.A. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Signaling in Cancer Cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2020;190:934–946. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.01.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Oakes S.A. Endoplasmic reticulum proteostasis: A key checkpoint in cancer. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2017;312:C93–C102. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00266.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Urra H., Dufey E., Avril T., Chevet E., Hetz C. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and the Hallmarks of Cancer. Trends Cancer. 2016;2:252–262. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2016.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chevet E., Hetz C., Samali A. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-activated cell reprogramming in oncogenesis. Cancer Discov. 2015;5:586–597. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-1490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Korennykh A., Walter P. Structural basis of the unfolded protein response. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012;28:251–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101011-155826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hetz C., Papa F.R. The Unfolded Protein Response and Cell Fate Control. Mol. Cell. 2018;69:169–181. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.06.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bertolotti A., Zhang Y., Hendershot L.M., Harding H.P., Ron D. Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000;2:326–332. doi: 10.1038/35014014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Shen J., Chen X., Hendershot L., Prywes R. ER stress regulation of ATF6 localization by dissociation of BiP/GRP78 binding and unmasking of Golgi localization signals. Dev. Cell. 2002;3:99–111. doi: 10.1016/S1534-5807(02)00203-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gardner B.M., Walter P. Unfolded proteins are Ire1-activating ligands that directly induce the unfolded protein response. Science. 2011;333:1891–1894. doi: 10.1126/science.1209126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Karagoz G.E., Acosta-Alvear D., Nguyen H.T., Lee C.P., Chu F., Walter P. An unfolded protein-induced conformational switch activates mammalian IRE1. eLife. 2017;6:e30700. doi: 10.7554/eLife.30700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bakunts A., Orsi A., Vitale M., Cattaneo A., Lari F., Tade L., Sitia R., Raimondi A., Bachi A., van Anken E. Ratiometric sensing of BiP-client versus BiP levels by the unfolded protein response determines its signaling amplitude. eLife. 2017;6:e27518. doi: 10.7554/eLife.27518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Harding H.P., Zhang Y., Ron D. Protein translation and folding are coupled by an endoplasmic-reticulum-resident kinase. Nature. 1999;397:271–274. doi: 10.1038/16729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Harding H.P., Novoa I., Zhang Y., Zeng H., Wek R., Schapira M., Ron D. Regulated translation initiation controls stress-induced gene expression in mammalian cells. Mol. Cell. 2000;6:1099–1108. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)00108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Marciniak S.J., Garcia-Bonilla L., Hu J., Harding H.P., Ron D. Activation-dependent substrate recruitment by the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 kinase PERK. J. Cell Biol. 2006;172:201–209. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200508099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.DuRose J.B., Scheuner D., Kaufman R.J., Rothblum L.I., Niwa M. Phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2alpha coordinates rRNA transcription and translation inhibition during endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009;29:4295–4307. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00260-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Koumenis C., Naczki C., Koritzinsky M., Rastani S., Diehl A., Sonenberg N., Koromilas A., Wouters B.G. Regulation of protein synthesis by hypoxia via activation of the endoplasmic reticulum kinase PERK and phosphorylation of the translation initiation factor eIF2alpha. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002;22:7405–7416. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.21.7405-7416.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wek R.C., Cavener D.R. Translational control and the unfolded protein response. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007;9:2357–2371. doi: 10.1089/ars.2007.1764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jaud M., Philippe C., Di Bella D., Tang W., Pyronnet S., Laurell H., Mazzolini L., Rouault-Pierre K., Touriol C. Translational Regulations in Response to Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Cancers. Cells. 2020;9:540. doi: 10.3390/cells9030540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Vattem K.M., Wek R.C. Reinitiation involving upstream ORFs regulates ATF4 mRNA translation in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2004;101:11269–11274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400541101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Palam L.R., Baird T.D., Wek R.C. Phosphorylation of eIF2 facilitates ribosomal bypass of an inhibitory upstream ORF to enhance CHOP translation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011;286:10939–10949. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.216093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bonnet-Magnaval F., Philippe C., Van Den Berghe L., Prats H., Touriol C., Lacazette E. Hypoxia and ER stress promote Staufen1 expression through an alternative translation mechanism. Cancers. 2016;479:365–371. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.09.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Jaud M., Philippe C., Van Den Berghe L., Ségura C., Mazzolini L. The PERK Branch of the Unfolded Protein Response Promotes DLL4 Expression by Activating an Alternative Translation Mechanism. Cancers. 2019;11:142. doi: 10.3390/cancers11020142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Philippe C., Dubrac A., Quelen C., Desquesnes A., Van Den Berghe L., Ségura C., Filleron T., Pyronnet S., Prats H., Brousset P., et al. PERK mediates the IRES-dependent translational activation of mRNAs encoding angiogenic growth factors after ischemic stress. Sci. Signal. 2016;9:ra44. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaf2753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Fernandez J., Bode B., Koromilas A., Diehl J.A., Krukovets I., Snider M.D., Hatzoglou M. Translation mediated by the internal ribosome entry site of the cat-1 mRNA is regulated by glucose availability in a PERK kinase-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:11780–11787. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110778200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Reid D.W., Tay A.S., Sundaram J.R., Lee I.C., Chen Q., George S.E., Nicchitta C.V., Shenolikar S. Complementary Roles of GADD34- and CReP-Containing Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2α Phosphatases during the Unfolded Protein Response. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016;36:1868–1880. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00190-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ma Y., Hendershot L.M. Delineation of a negative feedback regulatory loop that controls protein translation during endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:34864–34873. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301107200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lee Y.Y., Cevallos R.C., Jan E. An upstream open reading frame regulates translation of GADD34 during cellular stresses that induce eIF2alpha phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009;284:6661–6673. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806735200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ma Y., Brewer J.W., Diehl J.A., Hendershot L.M. Two distinct stress signaling pathways converge upon the CHOP promoter during the mammalian unfolded protein response. J. Mol. Biol. 2002;318:1351–1365. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(02)00234-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Hu H., Tian M., Ding C., Yu S. The C/EBP Homologous Protein (CHOP) Transcription Factor Functions in Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Apoptosis and Microbial Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018;9:3083. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Rozpedek W., Pytel D., Mucha B., Leszczynska H., Diehl J.A., Majsterek I. The Role of the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP Signaling Pathway in Tumor Progression During Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Curr. Mol. Med. 2016;16:533–544. doi: 10.2174/1566524016666160523143937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Marciniak S.J., Yun C.Y., Oyadomari S., Novoa I., Zhang Y., Jungreis R., Nagata K., Harding H.P., Ron D. CHOP induces death by promoting protein synthesis and oxidation in the stressed endoplasmic reticulum. Genes. Dev. 2004;18:3066–3077. doi: 10.1101/gad.1250704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Cullinan S.B., Zhang D., Hannink M., Arvisais E., Kaufman R.J., Diehl J.A. Nrf2 is a direct PERK substrate and effector of PERK-dependent cell survival. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003;23:7198–7209. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.20.7198-7209.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Cullinan S.B., Diehl J.A. PERK-dependent activation of Nrf2 contributes to redox homeostasis and cell survival following endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:20108–20117. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M314219200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Bobrovnikova-Marjon E., Diehl J.A. Coping with stress: ATF6alpha takes the stage. Dev. Cell. 2007;13:322–324. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2007.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hillary R.F., FitzGerald U. A lifetime of stress: ATF6 in development and homeostasis. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018;25:48. doi: 10.1186/s12929-018-0453-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Yamamoto K., Sato T., Matsui T., Sato M., Okada T., Yoshida H., Harada A., Mori K. Transcriptional induction of mammalian ER quality control proteins is mediated by single or combined action of ATF6alpha and XBP1. Dev. Cell. 2007;13:365–376. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2007.07.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Chemaly E.R., Troncone L., Lebeche D. SERCA control of cell death and survival. Cell Calcium. 2018;69:46–61. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2017.07.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bommiasamy H., Back S.H., Fagone P., Lee K., Meshinchi S., Vink E., Sriburi R., Frank M., Jackowski S., Kaufman R.J., et al. ATF6alpha induces XBP1-independent expansion of the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Sci. 2009;122:1626–1636. doi: 10.1242/jcs.045625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Yamamoto K., Takahara K., Oyadomari S., Okada T., Sato T., Harada A., Mori K. Induction of liver steatosis and lipid droplet formation in ATF6alpha-knockout mice burdened with pharmacological endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2010;21:2975–2986. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-02-0133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wu J., Rutkowski D.T., Dubois M., Swathirajan J., Saunders T., Wang J., Song B., Yau G.D., Kaufman R.J. ATF6alpha optimizes long-term endoplasmic reticulum function to protect cells from chronic stress. Dev. Cell. 2007;13:351–364. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2007.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Guan D., Xu Y., Yang M., Wang H., Wang X., Shen Z. N-acetyl cysteine and penicillamine induce apoptosis via the ER stress response-signaling pathway. Mol. Carcinog. 2010;49:68–74. doi: 10.1002/mc.20578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Yoshida H., Okada T., Haze K., Yanagi H., Yura T., Negishi M., Mori K. ATF6 activated by proteolysis binds in the presence of NF-Y (CBF) directly to the cis-acting element responsible for the mammalian unfolded protein response. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000;20:6755–6767. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.18.6755-6767.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Yang H., Niemeijer M., van de Water B., Beltman J.B. ATF6 Is a Critical Determinant of CHOP Dynamics during the Unfolded Protein Response. iScience. 2020;23:100860. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.100860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Thuerauf D.J., Morrison L.E., Hoover H., Glembotski C.C. Coordination of ATF6-mediated transcription and ATF6 degradation by a domain that is shared with the viral transcription factor, VP16. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:20734–20739. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M201749200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Urano F., Bertolotti A., Ron D. IRE1 and efferent signaling from the endoplasmic reticulum. Pt 21J. Cell Sci. 2000;113:3697–3702. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113.21.3697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Tirasophon W., Welihinda A.A., Kaufman R.J. A stress response pathway from the endoplasmic reticulum to the nucleus requires a novel bifunctional protein kinase/endoribonuclease (Ire1p) in mammalian cells. Genes. Dev. 1998;12:1812–1824. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.12.1812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Wang X.Z., Harding H.P., Zhang Y., Jolicoeur E.M., Kuroda M., Ron D. Cloning of mammalian Ire1 reveals diversity in the ER stress responses. EMBO J. 1998;17:5708–5717. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.19.5708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Bertolotti A., Wang X., Novoa I., Jungreis R., Schlessinger K., Cho J.H., West A.B., Ron D. Increased sensitivity to dextran sodium sulfate colitis in IRE1beta-deficient mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2001;107:585–593. doi: 10.1172/JCI11476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Martino M.B., Jones L., Brighton B., Ehre C., Abdulah L., Davis C.W., Ron D., O’Neal W.K., Ribeiro C.M. The ER stress transducer IRE1beta is required for airway epithelial mucin production. Mucosal Immunol. 2013;6:639–654. doi: 10.1038/mi.2012.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Shamu C.E., Walter P. Oligomerization and phosphorylation of the Ire1p kinase during intracellular signaling from the endoplasmic reticulum to the nucleus. EMBO J. 1996;15:3028–3039. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1996.tb00666.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Liu C.Y., Schröder M., Kaufman R.J. Ligand-independent dimerization activates the stress response kinases IRE1 and PERK in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:24881–24885. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M004454200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Peschek J., Acosta-Alvear D., Mendez A.S., Walter P. A conformational RNA zipper promotes intron ejection during non-conventional XBP1 mRNA splicing. EMBO Rep. 2015;16:1688–1698. doi: 10.15252/embr.201540955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Lu Y., Liang F.X., Wang X. A synthetic biology approach identifies the mammalian UPR RNA ligase RtcB. Mol. Cell. 2014;55:758–770. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.06.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Acosta-Alvear D., Zhou Y., Blais A., Tsikitis M., Lents N.H., Arias C., Lennon C.J., Kluger Y., Dynlacht B.D. XBP1 controls diverse cell type- and condition-specific transcriptional regulatory networks. Mol. Cell. 2007;27:53–66. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.06.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Guo F., Lin E.A., Liu P., Lin J., Liu C. XBP1U inhibits the XBP1S-mediated upregulation of the iNOS gene expression in mammalian ER stress response. Cell. Signal. 2010;22:1818–1828. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Byrd A.E., Brewer J.W. Intricately Regulated: A Cellular Toolbox for Fine-Tuning XBP1 Expression and Activity. Cells. 2012;1:738–753. doi: 10.3390/cells1040738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Hollien J., Weissman J.S. Decay of endoplasmic reticulum-localized mRNAs during the unfolded protein response. Science. 2006;313:104–107. doi: 10.1126/science.1129631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Maurel M., Chevet E., Tavernier J., Gerlo S. Getting RIDD of RNA: IRE1 in cell fate regulation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014;39:245–254. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2014.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Upton J.P., Wang L., Han D., Wang E.S., Huskey N.E., Lim L., Truitt M., McManus M.T., Ruggero D., Goga A., et al. IRE1alpha cleaves select microRNAs during ER stress to derepress translation of proapoptotic Caspase-2. Science. 2012;338:818–822. doi: 10.1126/science.1226191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Pluquet O., Dejeans N., Bouchecareilh M., Lhomond S., Pineau R., Higa A., Delugin M., Combe C., Loriot S., Cubel G., et al. Posttranscriptional regulation of PER1 underlies the oncogenic function of IREalpha. Cancer Res. 2013;73:4732–4743. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Dejeans N., Pluquet O., Lhomond S., Grise F., Bouchecareilh M., Juin A., Meynard-Cadars M., Bidaud-Meynard A., Gentil C., Moreau V., et al. Autocrine control of glioma cells adhesion and migration through IRE1alpha-mediated cleavage of SPARC mRNA. J. Cell Sci. 2012;125:4278–4287. doi: 10.1242/jcs.099291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Bright M.D., Itzhak D.N., Wardell C.P., Morgan G.J., Davies F.E. Cleavage of BLOC1S1 mRNA by IRE1 Is Sequence Specific, Temporally Separate from XBP1 Splicing, and Dispensable for Cell Viability under Acute Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015;35:2186–2202. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00013-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Han D., Lerner A.G., Vande Walle L., Upton J.P., Xu W., Hagen A., Backes B.J., Oakes S.A., Papa F.R. IRE1alpha kinase activation modes control alternate endoribonuclease outputs to determine divergent cell fates. Cell. 2009;138:562–575. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.07.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.So J.S., Hur K.Y., Tarrio M., Ruda V., Frank-Kamenetsky M., Fitzgerald K., Koteliansky V., Lichtman A.H., Iwawaki T., Glimcher L.H., et al. Silencing of lipid metabolism genes through IRE1alpha-mediated mRNA decay lowers plasma lipids in mice. Cell Metab. 2012;16:487–499. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.09.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Moore K., Hollien J. Ire1-mediated decay in mammalian cells relies on mRNA sequence, structure, and translational status. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2015;26:2873–2884. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-02-0074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Lu M., Lawrence D.A., Marsters S., Acosta-Alvear D., Kimmig P., Mendez A.S., Paton A.W., Paton J.C., Walter P., Ashkenazi A. Opposing unfolded-protein-response signals converge on death receptor 5 to control apoptosis. Science. 2014;345:98–101. doi: 10.1126/science.1254312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Hetz C., Glimcher L.H. Fine-tuning of the unfolded protein response: Assembling the IRE1alpha interactome. Mol. Cell. 2009;35:551–561. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.08.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Sepulveda D., Rojas-Rivera D., Rodriguez D.A., Groenendyk J., Kohler A., Lebeaupin C., Ito S., Urra H., Carreras-Sureda A., Hazari Y., et al. Interactome Screening Identifies the ER Luminal Chaperone Hsp47 as a Regulator of the Unfolded Protein Response Transducer IRE1alpha. Mol. Cell. 2018;69:238–252.e237. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.12.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Urano F., Wang X., Bertolotti A., Zhang Y., Chung P., Harding H.P., Ron D. Coupling of stress in the ER to activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase IRE1. Science. 2000;287:664–666. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5453.664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Zhang Y., Gao S., Xia J., Liu F. Hematopoietic Hierarchy—An Updated Roadmap. Trends Cell Biol. 2018;28:976–986. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2018.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Chao M.P., Seita J., Weissman I.L. Establishment of a normal hematopoietic and leukemia stem cell hierarchy. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2008;73:439–449. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2008.73.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Warr M.R., Pietras E.M., Passegué E. Mechanisms controlling hematopoietic stem cell functions during normal hematopoiesis and hematological malignancies. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2011;3:681–701. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Noetzli L.J., French S.L., Machlus K.R. New Insights into the Differentiation of Megakaryocytes from Hematopoietic Progenitors. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019;39:1288–1300. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.312129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Akashi K., Traver D., Miyamoto T., Weissman I.L. A clonogenic common myeloid progenitor that gives rise to all myeloid lineages. Nature. 2000;404:193–197. doi: 10.1038/35004599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Passegué E., Jamieson C.H., Ailles L.E., Weissman I.L. Normal and leukemic hematopoiesis: Are leukemias a stem cell disorder or a reacquisition of stem cell characteristics? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2003;100(Suppl. 1):11842–11849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2034201100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Sawyers C.L., Denny C.T., Witte O.N. Leukemia and the disruption of normal hematopoiesis. Cell. 1991;64:337–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90643-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.De Kouchkovsky I., Abdul-Hay M. Acute myeloid leukemia: A comprehensive review and 2016 update. Blood Cancer J. 2016;6:e441. doi: 10.1038/bcj.2016.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Grove C.S., Vassiliou G.S. Acute myeloid leukaemia: A paradigm for the clonal evolution of cancer? Dis. Models Mech. 2014;7:941–951. doi: 10.1242/dmm.015974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Klco J.M., Spencer D.H., Miller C.A., Griffith M., Lamprecht T.L., O’Laughlin M., Fronick C., Magrini V., Demeter R.T., Fulton R.S., et al. Functional heterogeneity of genetically defined subclones in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2014;25:379–392. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.01.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Hackl H., Astanina K., Wieser R. Molecular and genetic alterations associated with therapy resistance and relapse of acute myeloid leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017;10:51. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0416-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Lagunas-Rangel F.A., Chávez-Valencia V., Gómez-Guijosa M., Cortes-Penagos C. Acute Myeloid Leukemia-Genetic Alterations and Their Clinical Prognosis. Int. J. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Res. 2017;11:328–339. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Goldman S.L., Hassan C., Khunte M., Soldatenko A., Jong Y., Afshinnekoo E., Mason C.E. Epigenetic Modifications in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Prognosis, Treatment, and Heterogeneity. Front. Genet. 2019;10:133. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Pourrajab F., Zare-Khormizi M.R., Hashemi A.S., Hekmatimoghaddam S. Genetic Characterization and Risk Stratification of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020;12:2231–2253. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S242479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Benedetti L., Levin A.A., Scicchitano B.M., Grignani F., Allenby G., Diverio D., Lo Coco F., Avvisati G., Ruthardt M., Adamo S., et al. Characterization of the retinoid binding properties of the major fusion products present in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Blood. 1997;90:1175–1185. doi: 10.1182/blood.V90.3.1175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Visani G., Buonamici S., Malagola M., Isidori A., Piccaluga P.P., Martinelli G., Ottaviani E., Grafone T., Baccarani M., Tura S. Pulsed ATRA as single therapy restores long-term remission in PML-RARalpha-positive acute promyelocytic leukemia patients: Real time quantification of minimal residual disease. A pilot study. Leukemia. 2001;15:1696–1700. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2402266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Cicconi L., Divona M., Ciardi C., Ottone T., Ferrantini A., Lavorgna S., Alfonso V., Paoloni F., Piciocchi A., Avvisati G., et al. PML-RARα kinetics and impact of FLT3-ITD mutations in newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukaemia treated with ATRA and ATO or ATRA and chemotherapy. Leukemia. 2016;30:1987–1992. doi: 10.1038/leu.2016.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Martinelli G., Ottaviani E., Visani G., Testoni N., Montefusco V., Tura S. Long-term disease-free acute promyelocytic leukemia patients really can be cured at molecular level. Haematologica. 1998;83:860–863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Haferlach T., Bacher U., Haferlach C., Kern W., Schnittger S. Insight into the molecular pathogenesis of myeloid malignancies. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2007;14:90–97. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0b013e3280168490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Haferlach T., Kohlmann A., Bacher U., Schnittger S., Haferlach C., Kern W. Gene expression profiling for the diagnosis of acute leukaemia. Br. J. Cancer. 2007;96:535–540. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Prada-Arismendy J., Arroyave J.C., Röthlisberger S. Molecular biomarkers in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Rev. 2017;31:63–76. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2016.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Inaba H., Greaves M., Mullighan C.G. Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet. 2013;381:1943–1955. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)62187-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Teitell M.A., Pandolfi P.P. Molecular genetics of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2009;4:175–198. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pathol.4.110807.092227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Armstrong S.A., Look A.T. Molecular genetics of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2005;23:6306–6315. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.05.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Moorman A.V. New and emerging prognostic and predictive genetic biomarkers in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. 2016;101:407–416. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2015.141101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Palmi C., Savino A.M., Silvestri D., Bronzini I., Cario G., Paganin M., Buldini B., Galbiati M., Muckenthaler M.U., Bugarin C., et al. CRLF2 over-expression is a poor prognostic marker in children with high risk T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncotarget. 2016;7:59260–59272. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Malinowska-Ozdowy K., Frech C., Schönegger A., Eckert C., Cazzaniga G., Stanulla M., zur Stadt U., Mecklenbräuker A., Schuster M., Kneidinger D., et al. KRAS and CREBBP mutations: A relapse-linked malicious liaison in childhood high hyperdiploid acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2015;29:1656–1667. doi: 10.1038/leu.2015.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Van Vlierberghe P., Ferrando A. The molecular basis of T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2012;122:3398–3406. doi: 10.1172/JCI61269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Malard F., Mohty M. Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet. 2020;395:1146–1162. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)33018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Brown L.M., Lonsdale A., Zhu A., Davidson N.M., Schmidt B., Hawkins A., Wallach E., Martin M., Mechinaud F.M., Khaw S.L., et al. The application of RNA sequencing for the diagnosis and genomic classification of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Adv. 2020;4:930–942. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019001008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Waanders E., Gu Z., Dobson S.M., Antić Ž., Crawford J.C., Ma X., Edmonson M.N., Payne-Turner D., van der Vorst M., Jongmans M.C.J., et al. Mutational landscape and patterns of clonal evolution in relapsed pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Cancer Discov. 2020;1:96–111. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.BCD-19-0041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Apperley J.F. Chronic myeloid leukaemia. Lancet. 2015;385:1447–1459. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Siveen K.S., Prabhu K.S., Achkar I.W., Kuttikrishnan S., Shyam S., Khan A.Q., Merhi M., Dermime S., Uddin S. Role of Non Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Hematological Malignances and its Targeting by Natural Products. Mol. Cancer. 2018;17:31. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0788-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Steegmann J.L., Baccarani M., Breccia M., Casado L.F., García-Gutiérrez V., Hochhaus A., Kim D.W., Kim T.D., Khoury H.J., Le Coutre P., et al. European LeukemiaNet recommendations for the management and avoidance of adverse events of treatment in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia. 2016;30:1648–1671. doi: 10.1038/leu.2016.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Westerweel P.E., Te Boekhorst P.A.W., Levin M.D., Cornelissen J.J. New Approaches and Treatment Combinations for the Management of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2019;9:665. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Kipps T.J., Stevenson F.K., Wu C.J., Croce C.M., Packham G., Wierda W.G., O’Brien S., Gribben J., Rai K. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017;3:16096. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Hamblin T.J., Davis Z., Gardiner A., Oscier D.G., Stevenson F.K. Unmutated Ig V(H) genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1999;94:1848–1854. doi: 10.1182/blood.V94.6.1848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Rodríguez-Vicente A.E., Díaz M.G., Hernández-Rivas J.M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A clinical and molecular heterogenous disease. Cancer Genet. 2013;206:49–62. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2013.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Puiggros A., Blanco G. Genetic abnormalities in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Where we are and where we go. Biomed Res. Int. 2014;2014:435983. doi: 10.1155/2014/435983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Kiefer Y., Schulte C., Tiemann M., Bullerdiek J. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia-associated chromosomal abnormalities and miRNA deregulation. Appl. Clin. Genet. 2012;5:21–28. doi: 10.2147/tacg.s18669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Nabhan C., Raca G., Wang Y.L. Predicting Prognosis in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia in the Contemporary Era. Jama Oncol. 2015;1:965–974. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.0779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Kipps T.J. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Curr. Opini. Hematol. 2000;7:223–234. doi: 10.1097/00062752-200007000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Döhner H., Stilgenbauer S., Benner A., Leupolt E., Kröber A., Bullinger L., Döhner K., Bentz M., Lichter P. Genomic aberrations and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000;343:1910–1916. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200012283432602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Haferlach C., Dicker F., Schnittger S., Kern W., Haferlach T. Comprehensive genetic characterization of CLL: A study on 506 cases analysed with chromosome banding analysis, interphase FISH, IgV(H) status and immunophenotyping. Leukemia. 2007;21:2442–2451. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2404935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Zent C.S., Burack W.R. Mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and how they affect therapy choice: Focus on NOTCH1, SF3B1, and TP53. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2014;2014:119–124. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2014.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Kipps T.J., Choi M.Y. Targeted Therapy in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancer J. 2019;25:378–385. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0000000000000416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Burger J.A. Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;383:460–473. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1908213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Doulatov S., Notta F., Laurenti E., Dick J.E. Hematopoiesis: A human perspective. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10:120–136. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Vedi A., Santoro A., Dunant C.F., Dick J.E., Laurenti E. Molecular landscapes of human hematopoietic stem cells in health and leukemia. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016;1370:5–14. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Signer R.A., Magee J.A., Salic A., Morrison S.J. Haematopoietic stem cells require a highly regulated protein synthesis rate. Nature. 2014;509:49–54. doi: 10.1038/nature13035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Khateb A., Ronai Z.A. Unfolded Protein Response in Leukemia: From Basic Understanding to Therapeutic Opportunities. Trends Cancer. 2020;6:960–973. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.05.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Hidalgo San Jose L., Sunshine M.J., Dillingham C.H., Chua B.A., Kruta M., Hong Y., Hatters D.M., Signer R.A.J. Modest Declines in Proteome Quality Impair Hematopoietic Stem Cell Self-Renewal. Cell Rep. 2020;30:69–80.e66. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.12.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.van Galen P., Kreso A., Mbong N., Kent D.G., Fitzmaurice T., Chambers J.E., Xie S., Laurenti E., Hermans K., Eppert K., et al. The unfolded protein response governs integrity of the haematopoietic stem-cell pool during stress. Nature. 2014;510:268–272. doi: 10.1038/nature13228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.van Galen P., Mbong N., Kreso A., Schoof E.M., Wagenblast E., Ng S.W.K., Krivdova G., Jin L., Nakauchi H., Dick J.E. Integrated Stress Response Activity Marks Stem Cells in Normal Hematopoiesis and Leukemia. Cell Rep. 2018;25:1109–1117.e1105. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.10.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Miharada K., Sigurdsson V., Karlsson S. Dppa5 improves hematopoietic stem cell activity by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Rep. 2014;7:1381–1392. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.04.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Chapple R.H., Hu T., Tseng Y.J., Liu L., Kitano A., Luu V., Hoegenauer K.A., Iwawaki T., Li Q., Nakada D. ERalpha promotes murine hematopoietic regeneration through the Ire1alpha-mediated unfolded protein response. eLife. 2018;7:e31159. doi: 10.7554/eLife.31159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Liu L., Zhao M., Jin X., Ney G., Yang K.B., Peng F., Cao J., Iwawaki T., Del Valle J., Chen X., et al. Adaptive endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling via IRE1alpha-XBP1 preserves self-renewal of haematopoietic and pre-leukaemic stem cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019;21:328–337. doi: 10.1038/s41556-019-0285-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Xie S.Z., Garcia-Prat L., Voisin V., Ferrari R., Gan O.I., Wagenblast E., Kaufmann K.B., Zeng A.G.X., Takayanagi S.I., Patel I., et al. Sphingolipid Modulation Activates Proteostasis Programs to Govern Human Hematopoietic Stem Cell Self-Renewal. Cell Stem Cell. 2019;25:639–653.e637. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2019.09.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Xu L., Liu X., Peng F., Zhang W., Zheng L., Ding Y., Gu T., Lv K., Wang J., Ortinau L., et al. Protein quality control through endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation maintains haematopoietic stem cell identity and niche interactions. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020;22:1162–1169. doi: 10.1038/s41556-020-00581-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Rouault-Pierre K., Hamilton A., Bonnet D. Effect of hypoxia-inducible factors in normal and leukemic stem cell regulation and their potential therapeutic impact. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016;16:463–476. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2016.1133582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Sigurdsson V., Miharada K. Regulation of unfolded protein response in hematopoietic stem cells. Int. J. Hematol. 2018;107:627–633. doi: 10.1007/s12185-018-2458-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Doultsinos D., Avril T., Lhomond S., Dejeans N., Guédat P., Chevet E. Control of the Unfolded Protein Response in Health and Disease. Slas Discov. Adv. Life Sci. R D. 2017;22:787–800. doi: 10.1177/2472555217701685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Siwecka N., Rozpędek W., Pytel D., Wawrzynkiewicz A., Dziki A., Dziki Ł., Diehl J.A., Majsterek I. Dual role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Unfolded Protein Response Signaling Pathway in Carcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:4354. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Martelli A.M., Paganelli F., Chiarini F., Evangelisti C. The Unfolded Protein Response: A Novel Therapeutic Target in Acute Leukemias. Cancers. 2020;12:333. doi: 10.3390/cancers12020333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Kharabi Masouleh B., Chevet E., Panse J., Jost E., O’Dwyer M., Bruemmendorf T.H., Samali A. Drugging the unfolded protein response in acute leukemias. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015;8:87. doi: 10.1186/s13045-015-0184-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Schardt J.A., Weber D., Eyholzer M., Mueller B.U., Pabst T. Activation of the unfolded protein response is associated with favorable prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2009;15:3834–3841. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Tanimura A., Yujiri T., Tanaka Y., Tanaka M., Mitani N., Nakamura Y., Ariyoshi K., Tanizawa Y. Activation of the unfolded protein response in primary acute myeloid leukemia cells. Int. J. Hematol. 2011;94:300–302. doi: 10.1007/s12185-011-0918-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Krysov S., Steele A.J., Coelho V., Linley A., Sanchez Hidalgo M., Carter M., Potter K.N., Kennedy B., Duncombe A.S., Ashton-Key M., et al. Stimulation of surface IgM of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells induces an unfolded protein response dependent on BTK and SYK. Blood. 2014;124:3101–3109. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-04-567198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Kharabi M.B., Geng H., Hurtz C., Chan L.N., Logan A.C., Chang M.S., Huang C., Swaminathan S., Sun H., Paietta E., et al. Mechanistic rationale for targeting the unfolded protein response in pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:E2219–E2228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1400958111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Zhou C., Martinez E., Di Marcantonio D., Solanki-Patel N., Aghayev T., Peri S., Ferraro F., Skorski T., Scholl C., Fröhling S., et al. JUN is a key transcriptional regulator of the unfolded protein response in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2017;31:1196–1205. doi: 10.1038/leu.2016.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Sun H., Lin D.C., Guo X., Kharabi M.B., Gery S., Cao Q., Alkan S., Ikezoe T., Akiba C., Paquette R., et al. Inhibition of IRE1α-driven pro-survival pathways is a promising therapeutic application in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget. 2016;7:18736–18749. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Bujisic B., De Gassart A. Impairment of both IRE1 expression and XBP1 activation is a hallmark of GCB DLBCL and contributes to tumor growth. Blood. 2017;129:2420–2428. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-09-741348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Hart L.S., Cunningham J.T., Datta T., Dey S., Tameire F., Lehman S.L., Qiu B., Zhang H., Cerniglia G., Bi M., et al. ER stress-mediated autophagy promotes Myc-dependent transformation and tumor growth. J. Clin. Investig. 2012;122:4621–4634. doi: 10.1172/JCI62973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Brancolini C., Iuliano L. Proteotoxic Stress and Cell Death in Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2020;12:2385. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Uckun F.M., Qazi S., Ozer Z., Garner A.L., Pitt J., Ma H., Janda K.D. Inducing apoptosis in chemotherapy-resistant B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cells by targeting HSPA5, a master regulator of the anti-apoptotic unfolded protein response signalling network. Br. J. Haematol. 2011;153:741–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2011.08671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Kusio-Kobialka M., Podszywalow-Bartnicka P., Peidis P., Glodkowska-Mrowka E., Wolanin K., Leszak G., Seferynska I., Stoklosa T., Koromilas A.E., Piwocka K. The PERK-eIF2α phosphorylation arm is a pro-survival pathway of BCR-ABL signaling and confers resistance to imatinib treatment in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Cell Cycle. 2012;11:4069–4078. doi: 10.4161/cc.22387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Higa A., Taouji S., Lhomond S., Jensen D., Fernandez-Zapico M.E., Simpson J.C., Pasquet J.M., Schekman R., Chevet E. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-activated transcription factor ATF6α requires the disulfide isomerase PDIA5 to modulate chemoresistance. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014;34:1839–1849. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01484-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Tang C.H., Ranatunga S., Kriss C.L., Cubitt C.L., Tao J., Pinilla-Ibarz J.A., Del Valle J.R., Hu C.C. Inhibition of ER stress-associated IRE-1/XBP-1 pathway reduces leukemic cell survival. J. Clin. Investig. 2014;124:2585–2598. doi: 10.1172/JCI73448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Tanimura A., Yujiri T., Tanaka Y., Hatanaka M., Mitani N., Nakamura Y., Mori K., Tanizawa Y. The anti-apoptotic role of the unfolded protein response in Bcr-Abl-positive leukemia cells. Leuk. Res. 2009;33:924–928. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2009.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Leclerc G.M., Zheng S., Leclerc G.J., DeSalvo J., Swords R.T., Barredo J.C. The NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor pevonedistat activates the eIF2α and mTOR pathways inducing UPR-mediated cell death in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2016;50:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2016.09.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Huiting L.N., Samaha Y., Zhang G.L., Roderick J.E., Li B., Anderson N.M., Wang Y.W., Wang L., Laroche F., Choi J.W., et al. UFD1 contributes to MYC-mediated leukemia aggressiveness through suppression of the proapoptotic unfolded protein response. Leukemia. 2018;32:2339–2351. doi: 10.1038/s41375-018-0141-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Wilhelm T., Bick F., Peters K., Mohta V., Tirosh B., Patterson J.B., Kharabi-Masouleh B., Huber M. Infliction of proteotoxic stresses by impairment of the unfolded protein response or proteasomal inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for mast cell leukemia. Oncotarget. 2018;9:2984–3000. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Vieri M., Preisinger C., Schemionek M., Salimi A., Patterson J.B., Samali A., Brummendorf T.H., Appelmann I., Kharabi Masouleh B. Targeting of BCR-ABL1 and IRE1α induces synthetic lethality in Philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Carcinogenesis. 2020:bgaa095. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgaa095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Jang J.E., Eom J.I., Jeung H.K., Chung H., Kim Y.R., Kim J.S., Cheong J.W., Min Y.H. PERK/NRF2 and autophagy form a resistance mechanism against G9a inhibition in leukemia stem cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR. 2020;39:66. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01565-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Nguyen T.K., Grant S. Dinaciclib (SCH727965) inhibits the unfolded protein response through a CDK1- and 5-dependent mechanism. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014;13:662–674. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Evangelisti C., Evangelisti C., Teti G., Chiarini F., Falconi M., Melchionda F., Pession A., Bertaina A., Locatelli F., McCubrey J.A., et al. Assessment of the effect of sphingosine kinase inhibitors on apoptosis, unfolded protein response and autophagy of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells; indications for novel therapeutics. Oncotarget. 2014;5:7886–7901. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Rahmani M., Mayo M., Dash R., Sokhi U.K., Dmitriev I.P., Sarkar D., Dent P., Curiel D.T., Fisher P.B., Grant S. Melanoma differentiation associated gene-7/interleukin-24 potently induces apoptosis in human myeloid leukemia cells through a process regulated by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol. Pharm. 2010;78:1096–1104. doi: 10.1124/mol.110.068007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Rahmani M., Davis E.M., Crabtree T.R., Habibi J.R., Nguyen T.K., Dent P., Grant S. The kinase inhibitor sorafenib induces cell death through a process involving induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007;27:5499–5513. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01080-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Zhang X.H., Wang X.Y., Zhou Z.W., Bai H., Shi L., Yang Y.X., Zhou S.F., Zhang X.C. The combination of digoxin and GSK2606414 exerts synergistic anticancer activity against leukemia in vitro and in vivo. Biofactors. 2017;43:812–820. doi: 10.1002/biof.1380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Trivedi R., Müller G.A., Rathore M.S., Mishra D.P., Dihazi H. Anti-Leukemic Activity of Shikonin: Role of ERP57 in Shikonin Induced Apoptosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharm. 2016;39:604–616. doi: 10.1159/000445652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Zhou J., Bi C., Cheong L.L., Mahara S., Liu S.C., Tay K.G., Koh T.L., Yu Q., Chng W.J. The histone methyltransferase inhibitor, DZNep, up-regulates TXNIP, increases ROS production, and targets leukemia cells in AML. Blood. 2011;118:2830–2839. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-07-294827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Jiang Y., Zhang Y., Wark L., Ortiz E., Lim S., He H., Wang W., Medeiros D., Lin D. Wolfberry Water Soluble Phytochemicals Down-Regulate ER Stress Biomarkers and Modulate Multiple Signaling Pathways Leading to Inhibition of Proliferation and Induction of Apoptosis in Jurkat Cells. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2011:S2. doi: 10.4172/2155-9600.S2-001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Leclerc G.M., Leclerc G.J., Kuznetsov J.N., DeSalvo J., Barredo J.C. Metformin induces apoptosis through AMPK-dependent inhibition of UPR signaling in ALL lymphoblasts. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e74420. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Gu L., Yi Z., Zhang Y., Ma Z., Zhu Y., Gao J. Low dose of 2-deoxy-D-glucose kills acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells and reverses glucocorticoid resistance via N-linked glycosylation inhibition under normoxia. Oncotarget. 2017;8:30978–30991. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.DeSalvo J., Kuznetsov J.N., Du J., Leclerc G.M., Leclerc G.J., Lampidis T.J., Barredo J.C. Inhibition of Akt potentiates 2-DG-induced apoptosis via downregulation of UPR in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR. 2012;10:969–978. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-12-0125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Jiang Q., Li F., Shi K., Wu P., An J., Yang Y., Xu C. Involvement of p38 in signal switching from autophagy to apoptosis via the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4 axis in selenite-treated NB4 cells. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e1270. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Rong C., Wei W., Yu-Hong T. Asperuloside exhibits a novel anti-leukemic activity by triggering ER stress-regulated apoptosis via targeting GRP78. Biomed. Pharm. Biomed. Pharm. 2020;125:109819. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Maioral M.F., Stefanes N.M., Neuenfeldt P.D., Chiaradia-Delatorre L.D., Nunes R.J., Santos-Silva M.C. Aldehyde biphenyl chalcones induce immunogenic apoptotic-like cell death and are promising new safe compounds against a wide range of hematologic cancers. Future Med. Chem. 2020;12:673–688. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2019-0228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Fang W., Xin W., Na L., Juan L., Lin Z., Lingyun H., Ai F., Zhonglin W., Yawen W. Prolonged unfolded protein reaction is involved in the induction of CML cell death upon oprozomib treatment. Cancer Sci. 2020;112:133–143. doi: 10.1111/cas.14696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.El Dor M., Dakik H., Polomski M., Haudebourg E., Brachet M., Gouilleux F., Prié G., Zibara K., Mazurier F. VAS3947 Induces UPR-Mediated Apoptosis through Cysteine Thiol Alkylation in AML Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:5470. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Hu X., Cai J., Zhu J., Lang W., Zhong J., Zhong H., Chen F. Arsenic trioxide potentiates Gilteritinib-induced apoptosis in FLT3-ITD positive leukemic cells via IRE1a-JNK-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:250. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01341-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Chu X., Zhong L., Yu L., Xiong L., Li J., Dan W., Ye J., Liu C., Luo X., Liu B. GSK-J4 induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via ER stress and the synergism between GSK-J4 and decitabine in acute myeloid leukemia KG-1a cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:209. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01297-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Bian T., Tagmount A., Vulpe C., Vijendra K.C., Xing C. CXL146, a Novel 4H-Chromene Derivative, Targets GRP78 to Selectively Eliminate Multidrug-Resistant Cancer Cells. Mol. Pharm. 2020;97:402–408. doi: 10.1124/mol.119.118745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Matsumoto T., Jimi S., Migita K., Terada K., Mori M., Takamatsu Y., Suzumiya J., Hara S. FF-10501 induces caspase-8-mediated apoptotic and endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated necrotic cell death in hematological malignant cells. Int. J. Hematol. 2019;110:606–617. doi: 10.1007/s12185-019-02722-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Masciarelli S., Capuano E., Ottone T., Divona M., Lavorgna S., Liccardo F., Śniegocka M., Travaglini S., Noguera N.I., Picardi A., et al. Retinoic acid synergizes with the unfolded protein response and oxidative stress to induce cell death in FLT3-ITD+ AML. Blood Adv. 2019;3:4155–4160. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Masciarelli S., Capuano E., Ottone T., Divona M., De Panfilis S., Banella C., Noguera N.I., Picardi A., Fontemaggi G., Blandino G., et al. Retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide sensitize acute promyelocytic leukemia cells to ER stress. Leukemia. 2018;32:285–294. doi: 10.1038/leu.2017.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Mallick D.J., Soderquist R.S., Bates D., Eastman A. Confounding off-target effects of BH3 mimetics at commonly used concentrations: MIM1, UMI-77, and A-1210477. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:185. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1426-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Hsiao Y.C., Peng S.F., Lai K.C., Liao C.L., Huang Y.P., Lin C.C., Lin M.L., Liu K.C., Tsai C.C., Ma Y.S., et al. Genistein induces apoptosis in vitro and has antitumor activity against human leukemia HL-60 cancer cell xenograft growth in vivo. Environ. Toxicol. 2019;34:443–456. doi: 10.1002/tox.22698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Yang Y., Wang G., Wu W., Yao S., Han X., He D., He J., Zheng G., Zhao Y., Cai Z., et al. Camalexin Induces Apoptosis via the ROS-ER Stress-Mitochondrial Apoptosis Pathway in AML Cells. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018;2018:7426950. doi: 10.1155/2018/7426950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Li Z., Wu J., Sheng L. Ibrutinib improves the development of acute lymphoblastic leukemia by activating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cell death. Pharmazie. 2018;73:294–299. doi: 10.1691/ph.2018.8306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Mazumder A., Lee J.Y., Talhi O., Cerella C., Chateauvieux S., Gaigneaux A., Hong C.R., Kang H.J., Lee Y., Kim K.W., et al. Hydroxycoumarin OT-55 kills CML cells alone or in synergy with imatinib or Synribo: Involvement of ER stress and DAMP release. Cancer Lett. 2018;438:197–218. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.07.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Florean C., Kim K.R., Schnekenburger M., Kim H.J., Moriou C., Debitus C., Dicato M., Al-Mourabit A., Han B.W., Diederich M. Synergistic AML Cell Death Induction by Marine Cytotoxin (+)-1(R), 6(S), 1′(R), 6′(S), 11(R), 17(S)-Fistularin-3 and Bcl-2 Inhibitor Venetoclax. Mar. Drugs. 2018;16:518. doi: 10.3390/md16120518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Wang X.Y., Zhang X.H., Peng L., Liu Z., Yang Y.X., He Z.X., Dang H.W., Zhou S.F. Bardoxolone methyl (CDDO-Me or RTA402) induces cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and autophagy via PI3K/Akt/mTOR and p38 MAPK/Erk1/2 signaling pathways in K562 cells. Am. J. Trans. Res. 2017;9:4652–4672. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Mitsuhashi Y., Furusawa Y., Aradate T., Zhao Q.L., Moniruzzaman R., Kanamori M., Noguchi K., Kondo T. 3-O-trans-p-coumaroyl-alphitolic acid, a triterpenoid from Zizyphus jujuba, leads to apoptotic cell death in human leukemia cells through reactive oxygen species production and activation of the unfolded protein response. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0183712. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Meier-Stephenson V., Riemer J., Narendran A. The HIV protease inhibitor, nelfinavir, as a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of refractory pediatric leukemia. Oncotargets. 2017;10:2581–2593. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S136484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Mahoney E., Maddocks K., Flynn J., Jones J., Cole S.L., Zhang X., Byrd J.C., Johnson A.J. Identification of endoplasmic reticulum stress-inducing agents by antagonizing autophagy: A new potential strategy for identification of anti-cancer therapeutics in B-cell malignancies. Leuk. Lymphoma. 2013;54:2685–2692. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2013.781168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Gugliotta G., Sudo M., Cao Q., Lin D.C., Sun H., Takao S., Le Moigne R., Rolfe M., Gery S., Müschen M., et al. Valosin-Containing Protein/p97 as a Novel Therapeutic Target in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Neoplasia. 2017;19:750–761. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2017.08.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Tsitsipatis D., Jayavelu A.K., Müller J.P., Bauer R., Schmidt-Arras D., Mahboobi S., Schnöder T.M., Heidel F., Böhmer F.D. Synergistic killing of FLT3ITD-positive AML cells by combined inhibition of tyrosine-kinase activity and N-glycosylation. Oncotarget. 2017;8:26613–26624. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Wu C.F., Seo E.J., Klauck S.M., Efferth T. Cryptotanshinone deregulates unfolded protein response and eukaryotic initiation factor signaling in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2016;23:174–180. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2015.12.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Wang J., Wang Q.L., Nong X.H., Zhang X.Y., Xu X.Y., Qi S.H., Wang Y.F. Oxalicumone A, a new dihydrothiophene-condensed sulfur chromone induces apoptosis in leukemia cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Eur. J. Pharm. 2016;783:47–55. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.04.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Lamothe B., Wierda W.G., Keating M.J., Gandhi V. Carfilzomib Triggers Cell Death in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia by Inducing Proapoptotic and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Responses. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2016;22:4712–4726. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Zhou L., Jiang L., Xu M., Liu Q., Gao N., Li P., Liu E.H. Miltirone exhibits antileukemic activity by ROS-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction pathways. Sci. Rep. 2016;6:20585. doi: 10.1038/srep20585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Wang F.F., Liu M.Z., Sui Y., Cao Q., Yan B., Jin M.L., Mo X. Deficiency of SUMO-specific protease 1 induces arsenic trioxide-mediated apoptosis by regulating XBP1 activity in human acute promyelocytic leukemia. Oncol. Lett. 2016;12:3755–3762. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.5162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Chen J., Wei H., Xie B., Wang B., Cheng J., Cheng J. Endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis in drug-sensitive and -resistant leukemia cells. Leuk. Res. 2012;36:1526–1535. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2012.08.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Rosilio C., Nebout M., Imbert V., Griessinger E., Neffati Z., Benadiba J., Hagenbeek T., Spits H., Reverso J., Ambrosetti D., et al. L-type amino-acid transporter 1 (LAT1): A therapeutic target supporting growth and survival of T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma/T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2015;29:1253–1266. doi: 10.1038/leu.2014.338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Hu C., Xu M., Qin R., Chen W., Xu X. Wogonin induces apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress in HL-60 leukemia cells through inhibition of the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2015;33:3146–3154. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.3896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Joo J.H., Ueda E., Bortner C.D., Yang X.P., Liao G., Jetten A.M. Farnesol activates the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis and the ATF4-ATF3-CHOP cascade of ER stress in human T lymphoblastic leukemia Molt4 cells. Biochem. Pharm. 2015;97:256–268. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.08.086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Cagnetta A., Caffa I., Acharya C., Soncini D., Acharya P., Adamia S., Pierri I., Bergamaschi M., Garuti A., Fraternali G., et al. APO866 Increases Antitumor Activity of Cyclosporin-A by Inducing Mitochondrial and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Leukemia Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2015;21:3934–3945. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-3023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Takenokuchi M., Miyamoto K., Saigo K., Taniguchi T. Bortezomib Causes ER Stress-related Death of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Cells Through Excessive Accumulation of PML-RARA. Anticancer Res. 2015;35:3307–3316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Buontempo F., Orsini E., Martins L.R., Antunes I., Lonetti A., Chiarini F., Tabellini G., Evangelisti C., Evangelisti C., Melchionda F., et al. Cytotoxic activity of the casein kinase 2 inhibitor CX-4945 against T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Targeting the unfolded protein response signaling. Leukemia. 2014;28:543–553. doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Winter E., Dal Pizzol C., Filippin-Monteiro F.B., Brondani P., Silva A.M., Silva A.H., Bonacorso H.G., Martins M.A., Zanatta N., Creczynski-Pasa T.B. Antitumoral activity of a trichloromethyl pyrimidine analogue: Molecular cross-talk between intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2014;27:1040–1049. doi: 10.1021/tx500094x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Winter E., Chiaradia L.D., Silva A.H., Nunes R.J., Yunes R.A., Creczynski-Pasa T.B. Involvement of extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways together with endoplasmic reticulum stress in cell death induced by naphthylchalcones in a leukemic cell line: Advantages of multi-target action. Toxicol. Vitr. 2014;28:769–777. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2014.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Soderquist R., Pletnev A.A., Danilov A.V., Eastman A. The putative BH3 mimetic S1 sensitizes leukemia to ABT-737 by increasing reactive oxygen species, inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress, and upregulating the BH3-only protein NOXA. Apoptosis Int. J. Program. Cell Death. 2014;19:201–209. doi: 10.1007/s10495-013-0910-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Soderquist R.S., Danilov A.V., Eastman A. Gossypol increases expression of the pro-apoptotic BH3-only protein NOXA through a novel mechanism involving phospholipase A2, cytoplasmic calcium, and endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2014;289:16190–16199. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.562900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Li H., Chang G., Wang J., Wang L., Jin W., Lin Y., Yan Y., Wang R., Gao W., Ma L., et al. Cariporide sensitizes leukemic cells to tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand by up-regulation of death receptor 5 via endoplasmic reticulum stress-CCAAT/enhancer binding protein homologous protein dependent mechanism. Leuk. Lymphoma. 2014;55:2135–2140. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2013.861064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Fiskus W., Saba N., Shen M., Ghias M., Liu J., Gupta S.D., Chauhan L., Rao R., Gunewardena S., Schorno K., et al. Auranofin induces lethal oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress and exerts potent preclinical activity against chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Res. 2014;74:2520–2532. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-2033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Bortolozzi R., Viola G., Porcù E., Consolaro F., Marzano C., Pellei M., Gandin V., Basso G. A novel copper(I) complex induces ER-stress-mediated apoptosis and sensitizes B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells to chemotherapeutic agents. Oncotarget. 2014;5:5978–5991. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Rosati E., Sabatini R., De Falco F., Del Papa B., Falzetti F., Di Ianni M., Cavalli L., Fettucciari K., Bartoli A., Screpanti I., et al. γ-Secretase inhibitor I induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells by proteasome inhibition, endoplasmic reticulum stress increase and notch down-regulation. Int. J. Cancer. 2013;132:1940–1953. doi: 10.1002/ijc.27863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Huang A.C., Chang C.L., Yu C.S., Chen P.Y., Yang J.S., Ji B.C., Lin T.P., Chiu C.F., Yeh S.P., Huang Y.P., et al. Induction of apoptosis by curcumin in murine myelomonocytic leukemia WEHI-3 cells is mediated via endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondria-dependent pathways. Environ. Toxicol. 2013;28:255–266. doi: 10.1002/tox.20716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Ng A.P., Chng W.J., Khan M. Curcumin sensitizes acute promyelocytic leukemia cells to unfolded protein response-induced apoptosis by blocking the loss of misfolded N-CoR protein. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR. 2011;9:878–888. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Pae H.O., Jeong S.O., Jeong G.S., Kim K.M., Kim H.S., Kim S.A., Kim Y.C., Kang S.D., Kim B.N., Chung H.T. Curcumin induces pro-apoptotic endoplasmic reticulum stress in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007;353:1040–1045. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.12.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.de Sá Bacelar T., da Silva A.J., Costa P.R., Rumjanek V.M. The pterocarpanquinone LQB 118 induces apoptosis in tumor cells through the intrinsic pathway and the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Anti-Cancer Drugs. 2013;24:73–83. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0b013e3283592da8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Mahoney E., Byrd J.C., Johnson A.J. Autophagy and ER stress play an essential role in the mechanism of action and drug resistance of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor flavopiridol. Autophagy. 2013;9:434–435. doi: 10.4161/auto.23027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.Yu C.S., Huang A.C., Yang J.S., Yu C.C., Lin C.C., Chung H.K., Huang Y.P., Chueh F.S., Chung J.G. Safrole induces G0/G1 phase arrest via inhibition of cyclin E and provokes apoptosis through endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrion-dependent pathways in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Anticancer Res. 2012;32:1671–1679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.Penna F., Pin F., Costamagna D., Reffo P., Baccino F.M., Bonelli G., Costelli P. Caspase 2 activation and ER stress drive rapid Jurkat cell apoptosis by clofibrate. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e45327. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232.Park Y.K., Do Y.R., Jang B.C. Apoptosis of K562 leukemia cells by Abnobaviscum F®, a European mistletoe extract. Oncol. Rep. 2012;28:2227–2232. doi: 10.3892/or.2012.2026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 233.Lu C.C., Yang J.S., Chiang J.H., Hour M.J., Lin K.L., Lin J.J., Huang W.W., Tsuzuki M., Lee T.H., Chung J.G. Novel quinazolinone MJ-29 triggers endoplasmic reticulum stress and intrinsic apoptosis in murine leukemia WEHI-3 cells and inhibits leukemic mice. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e36831. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234.Pattacini L., Mancini M., Mazzacurati L., Brusa G., Benvenuti M., Martinelli G., Baccarani M., Santucci M.A. Endoplasmic reticulum stress initiates apoptotic death induced by STI571 inhibition of p210 bcr-abl tyrosine kinase. Leuk. Res. 2004;28:191–202. doi: 10.1016/S0145-2126(03)00218-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 235.Chueh F.S., Hsiao Y.T., Chang S.J., Wu P.P., Yang J.S., Lin J.J., Chung J.G., Lai T.Y. Glycyrrhizic acid induces apoptosis in WEHI-3 mouse leukemia cells through the caspase- and mitochondria-dependent pathways. Oncol. Rep. 2012;28:2069–2076. doi: 10.3892/or.2012.2029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 236.Lin J.J., Hsu H.Y., Yang J.S., Lu K.W., Wu R.S., Wu K.C., Lai T.Y., Chen P.Y., Ma C.Y., Wood W.G., et al. Molecular evidence of anti-leukemia activity of gypenosides on human myeloid leukemia HL-60 cells in vitro and in vivo using a HL-60 cells murine xenograft model. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2011;18:1075–1085. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2011.03.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237.Kuznetsov J.N., Leclerc G.J., Leclerc G.M., Barredo J.C. AMPK and Akt determine apoptotic cell death following perturbations of one-carbon metabolism by regulating ER stress in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011;10:437–447. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 238.Chang Y.C., Lai T.Y., Yu C.S., Chen H.Y., Yang J.S., Chueh F.S., Lu C.C., Chiang J.H., Huang W.W., Ma C.Y., et al. Emodin Induces Apoptotic Death in Murine Myelomonocytic Leukemia WEHI-3 Cells In Vitro and Enhances Phagocytosis in Leukemia Mice In Vivo. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. ECAM. 2011;2011:523596. doi: 10.1155/2011/523596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 239.Anshu A., Thomas S., Agarwal P., Ibarra-Rivera T.R., Pirrung M.C., Schönthal A.H. Novel proteasome-inhibitory syrbactin analogs inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in hematological tumor cell lines. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011;82:600–609. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.06.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 240.Albershardt T.C., Salerni B.L., Soderquist R.S., Bates D.J., Pletnev A.A., Kisselev A.F., Eastman A. Multiple BH3 mimetics antagonize antiapoptotic MCL1 protein by inducing the endoplasmic reticulum stress response and up-regulating BH3-only protein NOXA. J. Biol. Chem. 2011;286:24882–24895. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.255828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 241.Wagh V., Mishra P., Thakkar A., Shinde V., Sharma S., Padigaru M., Joshi K. Antitumor activity of NPB001-05, an orally active inhibitor of Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase. Front. Biosci. 2011;3:1349–1364. doi: 10.2741/338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 242.Yaari-Stark S., Shaked M., Nevo-Caspi Y., Jacob-Hircsh J., Shamir R., Rechavi G., Kloog Y. Ras inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress in human cancer cells with amplified Myc. Int. J. Cancer. 2010;126:2268–2281. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 243.Xu G.W., Ali M., Wood T.E., Wong D., Maclean N., Wang X., Gronda M., Skrtic M., Li X., Hurren R., et al. The ubiquitin-activating enzyme E1 as a therapeutic target for the treatment of leukemia and multiple myeloma. Blood. 2010;115:2251–2259. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-07-231191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 244.Popovic S., Baskic D., Djurdjevic P., Zelen I., Mitrovic M., Nikolic I., Avramovic D., Radenkovic M., Arsenijevic N. Endoplasmic reticulum stress associated with caspases-4 and -2 mediates korbazol-induced B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell apoptosis. J. B.U. Off. J. Balk. Union Oncol. 2010;15:783–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 245.Lust S., Vanhoecke B., Van Gele M., Philippé J., Bracke M., Offner F. The flavonoid tangeretin activates the unfolded protein response and synergizes with imatinib in the erythroleukemia cell line K562. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010;54:823–832. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200900186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 246.Lee M.S., Cherla R.P., Lentz E.K., Leyva-Illades D., Tesh V.L. Signaling through C/EBP homologous protein and death receptor 5 and calpain activation differentially regulate THP-1 cell maturation-dependent apoptosis induced by Shiga toxin type 1. Infect. Immun. 2010;78:3378–3391. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00342-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 247.Slagsvold J.E., Pettersen C.H., Follestad T., Krokan H.E., Schønberg S.A. The antiproliferative effect of EPA in HL60 cells is mediated by alterations in calcium homeostasis. Lipids. 2009;44:103–113. doi: 10.1007/s11745-008-3263-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 248.Lust S., Vanhoecke B., Van Gelle M., Boelens J., van Melckebeke H., Kaileh M., Vanden Berghe W., Haegeman G., Philippé J., Bracke M., et al. Xanthohumol activates the proapoptotic arm of the unfolded protein response in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:3797–3805. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 249.Huang W.C., Lin Y.S., Chen C.L., Wang C.Y., Chiu W.H., Lin C.F. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta mediates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced lysosomal apoptosis in leukemia. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009;329:524–531. doi: 10.1124/jpet.108.148122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 250.Zhang Q.Y., Mao J.H., Liu P., Huang Q.H., Lu J., Xie Y.Y., Weng L., Zhang Y., Chen Q., Chen S.J., et al. A systems biology understanding of the synergistic effects of arsenic sulfide and Imatinib in BCR/ABL-associated leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:3378–3383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0813142106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 251.Wang K., Fang H., Xiao D., Zhu X., He M., Pan X., Shi J., Zhang H., Jia X., Du Y., et al. Converting redox signaling to apoptotic activities by stress-responsive regulators HSF1 and NRF2 in fenretinide treated cancer cells. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e7538. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 252.Lai W.L., Wong N.S. The PERK/eIF2 alpha signaling pathway of Unfolded Protein Response is essential for N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide (4HPR)-induced cytotoxicity in cancer cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2008;314:1667–1682. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 253.Townsend D.M., Manevich Y., He L., Xiong Y., Bowers R.R., Jr., Hutchens S., Tew K.D. Nitrosative stress-induced s-glutathionylation of protein disulfide isomerase leads to activation of the unfolded protein response. Cancer Res. 2009;69:7626–7634. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 254.Dodo K., Minato T., Noguchi-Yachide T., Suganuma M., Hashimoto Y. Antiproliferative and apoptosis-inducing activities of alkyl gallate and gallamide derivatives related to (-)-epigallocatechin gallate. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2008;16:7975–7982. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.07.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 255.Li J., Xia X., Ke Y., Nie H., Smith M.A., Zhu X. Trichosanthin induced apoptosis in HL-60 cells via mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling pathways. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2007;1770:1169–1180. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2007.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 256.Jun D.Y., Kim J.S., Park H.S., Han C.R., Fang Z., Woo M.H., Rhee I.K., Kim Y.H. Apoptogenic activity of auraptene of Zanthoxylum schinifolium toward human acute leukemia Jurkat T cells is associated with ER stress-mediated caspase-8 activation that stimulates mitochondria-dependent or -independent caspase cascade. Carcinogenesis. 2007;28:1303–1313. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgm028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 257.Anding A.L., Chapman J.S., Barnett D.W., Curley R.W., Jr., Clagett-Dame M. The unhydrolyzable fenretinide analogue 4-hydroxybenzylretinone induces the proapoptotic genes GADD153 (CHOP) and Bcl-2-binding component 3 (PUMA) and apoptosis that is caspase- dependent and independent of the retinoic acid receptor. Cancer Res. 2007;67:6270–6277. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 258.Yanamandra N., Colaco N.M., Parquet N.A., Buzzeo R.W., Boulware D., Wright G., Perez L.E., Dalton W.S., Beaupre D.M. Tipifarnib and bortezomib are synergistic and overcome cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance in multiple myeloma and acute myeloid leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2006;12:591–599. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 259.Ng A.P., Howe Fong J., Sijin Nin D., Hirpara J.L., Asou N., Chen C.S., Pervaiz S., Khan M. Cleavage of misfolded nuclear receptor corepressor confers resistance to unfolded protein response-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2006;66:9903–9912. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 260.Feng X.Q., You Y., Xiao J., Zou P. Thapsigargin-induced apoptosis of K562 cells and its mechanism. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2006;14:25–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 261.Feng X.Q., Xiao J., Nie S.M., Liu F., You Y., Zou P. Expression and significance of melanoma antigen gene-3 in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis of K562 cells. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2005;13:741–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 262.Du Y., Wang K., Fang H., Li J., Xiao D., Zheng P., Chen Y., Fan H., Pan X., Zhao C., et al. Coordination of intrinsic, extrinsic, and endoplasmic reticulum-mediated apoptosis by imatinib mesylate combined with arsenic trioxide in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2006;107:1582–1590. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-06-2318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 263.Anether G., Tinhofer I., Senfter M., Greil R. Tetrocarcin-A—Induced ER stress mediates apoptosis in B-CLL cells via a Bcl-2--independent pathway. Blood. 2003;101:4561–4568. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-08-2501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 264.Tinhofer I., Anether G., Senfter M., Pfaller K., Bernhard D., Hara M., Greil R. Stressful death of T-ALL tumor cells after treatment with the anti-tumor agent Tetrocarcin-A. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2002;16:1295–1297. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-0020fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 265.Walczak A., Gradzik K., Kabzinski J. The Role of the ER-Induced UPR Pathway and the Efficacy of Its Inhibitors and Inducers in the Inhibition of Tumor Progression. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019;2019:5729710. doi: 10.1155/2019/5729710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]