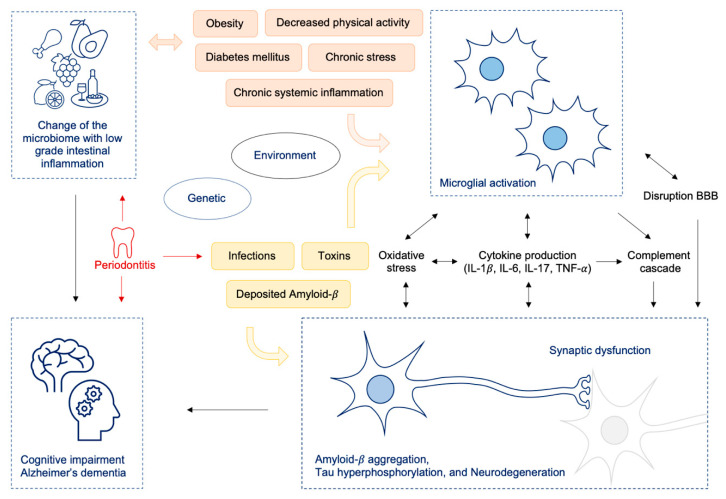
Figure 2.
Change of the microbiome (e.g., by Western diet) resulting in intestinal dysbiosis leads to low grade inflammation in the gut and to increased intestinal and BBB permeability and consecutively to neuroinflammation and cognitive decline; oral pathobionts like P. gingivalis lead to oralisation of gut microbiota on the one hand, thus additionally driving gut inflammation and on the other hand promoting neuroinflammatory processes by translocation of bacteria to the brain via toxic proteases. Abbreviations: IL = interleukin, TNF = tumor necrosis factor; BBB = blood brain barrier.