Fig. 2.
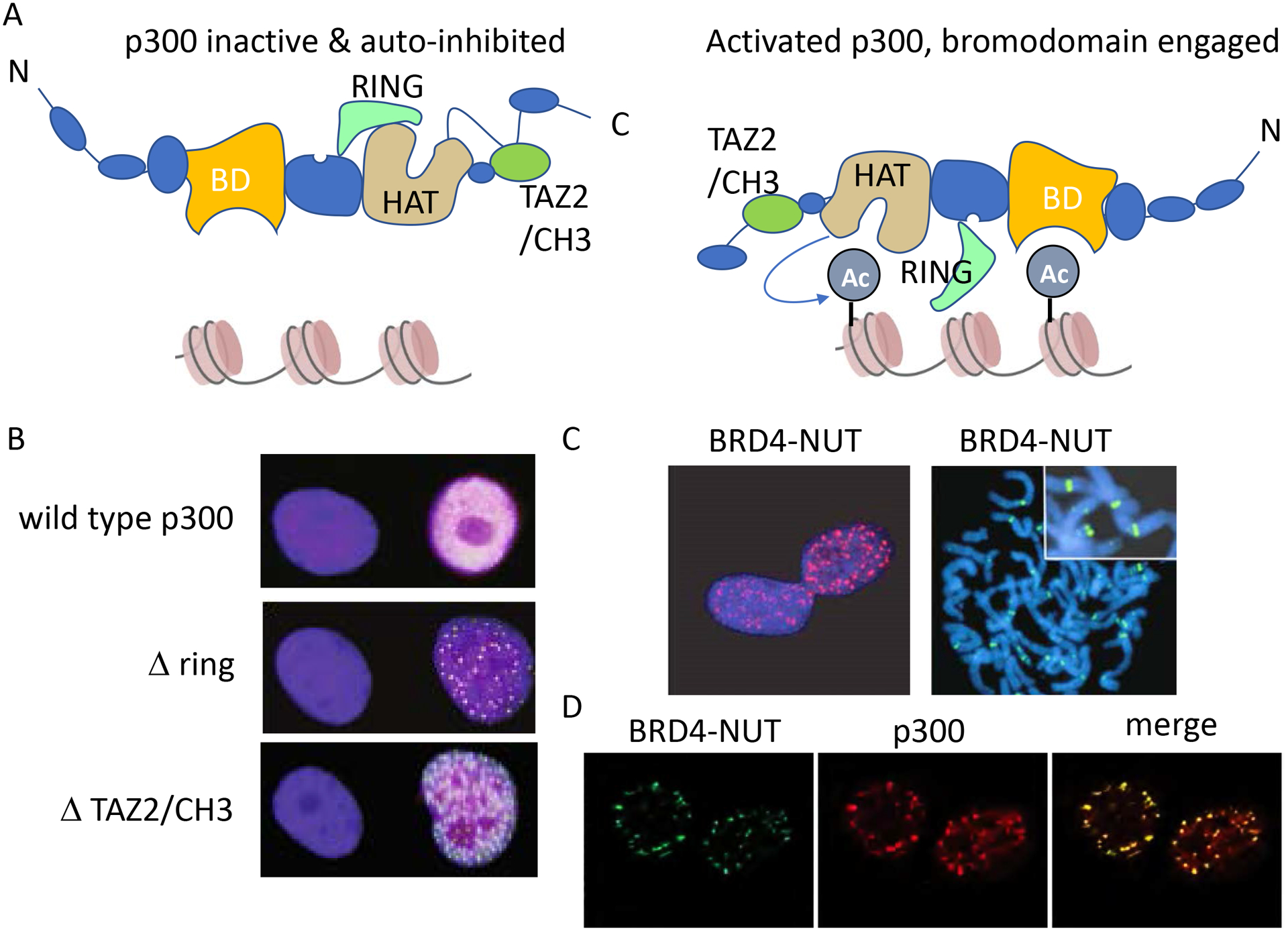
De-repression of p300 causes p300 foci to form, resembling BRD4-NUT. A. Cartoons of inactive and activated conformations of p300. These cartoons derived and simplified by those presented in Ortega E et al., 2018. In this model, p300 activation requires dimerization (not shown), and removal of the auto-inhibitory CH3/TAZ2 and RING domains to allow for HAT activation and engagement of the bromodomain, BD, with acetylated histones. B. Constitutionally activated p300, through deletion of its ring or CH3 domains, results in the formation of nuclear foci. HA-tagged p300 was stained with anti-HA antibody and the images shown are from Ortega E et al., 2018. C. BRD4-NUT immunofluorescence is seen in the NC cell line, TC-797. Left are interphase nuclei, and right are metaphase chromosomes revealing that megadomains cover discrete, chromosomal regions. Immunofluorescence was performed using an antibody to NUT protein (anti-NUT, clone C52B1). Images taken from Alekseyenko A et al., 2015. D. NUT and p300 co-immunofluorescence in the BRD4-NUT+ NC cell line, HCC2429. Taken from Reynoird N et al., 2010.
