Abstract
Objective
To identify the impact of segmentation methods and intensity discretization on radiomic features (RFs) extraction from 68Ga-DOTA-TOC PET images in patients with neuroendocrine tumors.
Methods
Forty-nine patients were retrospectively analyzed. Tumor contouring was performed manually by four different operators and with a semi-automatic edge-based segmentation (SAEB) algorithm. Three SUVmax fixed thresholds (20, 30, 40%) were applied. Fifty-one RFs were extracted applying two different intensity rescale factors for gray-level discretization: one absolute (AR60 = SUV from 0 to 60) and one relative (RR = min-max of the VOI SUV). Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) was calculated to quantify segmentation agreement between different segmentation methods. The impact of segmentation and discretization on RFs was assessed by intra-class correlation coefficients (ICC) and the coefficient of variance (COVL). The RFs’ correlation with volume and SUVmax was analyzed by calculating Pearson’s correlation coefficients.
Results
DSC mean value was 0.75 ± 0.11 (0.45–0.92) between SAEB and operators and 0.78 ± 0.09 (0.36–0.97), among the four manual segmentations. The study showed high robustness (ICC > 0.9): (a) in 64.7% of RFs for segmentation methods using AR60, improved by applying SUVmax threshold of 40% (86.5%); (b) in 50.9% of RFs for different SUVmax thresholds using AR60; and (c) in 37% of RFs for discretization settings using different segmentation methods. Several RFs were not correlated with volume and SUVmax.
Conclusions
RFs robustness to manual segmentation resulted higher in NET 68Ga-DOTA-TOC images compared to 18F-FDG PET/CT images. Forty percent SUVmax thresholds yield superior RFs stability among operators, however leading to a possible loss of biological information. SAEB segmentation appears to be an optimal alternative to manual segmentation, but further validations are needed. Finally, discretization settings highly impacted on RFs robustness and should always be stated.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s40658-021-00367-6.
Keywords: Texture analysis, Radiomics, Neuroendocrine tumor, Robustness, 68Ga-DOTATOC PET/CT, Semi-automatic segmentation
Introduction
Neuroendocrine tumors (NET) are a heterogeneous group of malignancies represented by different histological subtypes and different primary locations [1]. Histopathology is crucial in tumor classification and Ki-67 is currently used to define tumor grading in GEP NET [2]. However, the assessment of tumor aggressiveness is generally assessed by lesion biopsy, leading to a potential grading underestimation [3], since tumor heterogeneity is both spatial (inter- and intra-tumoral heterogeneity) and time-related (more aggressive cell clones developing over time) [4, 5]. Thus, although multiple-lesion biopsy sampling is not feasible, grading heterogeneity among primary and secondary lesions is not negligible [6]. New generation imaging technologies, including positron emission tomography (PET), might offer its contribution in the evaluation of tumor heterogeneity [7–9]. At present, PET imaging with 68Ga-DOTA-peptides analog to the somatostatin receptors (SSTR) is considered the state of the art to quantify SST receptors in vivo [10, 11], while 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) PET-CT is used to metabolically characterize more aggressive and higher grade NET lesions [12]. This dual approach has been recently evaluated leading to the development of the NETPET score [13]. Nevertheless, the simple in vivo quantification of receptor expression is not sufficient to characterize the biology of the tumor and the intra-patients and intra-tumor heterogeneity. This drawback might be solved with a better characterization of tumor heterogeneity by the extraction of radiomic features (RFs), as a surrogate biomarker for NET lesions characterization [14], from the 68Ga-DOTA-peptide PET-CT [15–18]. While scientific interest in radiomics applied to PET imaging is rapidly increasing, the methodological approach needs to be validated and standardized and, thus, harmonization among protocols is needed [19–21]. Indeed, imaging analysis procedures such as tumor segmentation methods, gray-level intensity discretization, and image reconstruction algorithm can affect the RFs [22–25]. Robustness analysis measures the variability of RFs concerning these factors. The identification of robust RFs for 68Ga-DOTA-TOC PET-CT is fundamental since this innovative modality might be used as a prognostic and predictive tool for evaluating tumor heterogeneity in NET. To our knowledge, there is only one study evaluating the robustness of RFs in function of image acquisition and reconstruction parameters for 68Ga-DOTA-peptides PET/CT (without considering the consequences of different segmentation approaches) [26], while the extraction of RFs and the assessment of RFs robustness in 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging has been broadly explored [27–31]. There are several reasons to evaluate the RFs robustness specifically in 68Ga-DOTA-peptide tracers: a diverse range of positrons compromising the resolution in PET in a different way comparing to 18F-FDG [32–34]; a different physiological distribution of 68Ga-DOTA-peptide; and a high inter-patient and intra-patient heterogeneity for both physiological and pathological uptake comparing to 18F-FDG [35], leading to the necessity to provide different segmentation methods and discretization settings.
The objective of this study was to evaluate the robustness of RFs in function of segmentation methods and discretization settings in 68Ga-DOTATOC PET/CT images.
Materials and methods
Patient selection
270 consecutive patients affected by NET referred to our institution to perform 68Ga-DOTA-TOC PET/CT between February 2017 and July 2019 were reviewed (IRB protocol: CS2/477). The inclusion criteria of the present study were (1) histologically proven NET, (2) patients who underwent 68Ga-DOTA-TOC PET/CT for staging in treatment-naïve patients or restaging after surgery, and (3) willing to sign an informed consent form (ICF). Exclusion criteria were (1) age < 18 years and (2) previous systemic therapies (e.g., somatostatin analogs, chemotherapy, everolimus, and peptide receptor radionuclide therapy). Forty-nine patients with a total of 60 lesions matched the inclusion criteria and were considered in this analysis. Primary tumor sites were GEP-NET, lung NET, and others NET in 77.5% (38/49), 18.4% (9/49), and 4.1% (2/49) of cases, respectively. Patients’ characteristics are exposed in detail in Table 1.
Table 1.
Demographic data and NET characteristics of study subjects (values are given as mean ± standard deviation and range)
| Demographic data and tumor characteristics | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | n | % | |
| Number of patients | 49 | 100% | |
| Sex | Female | 22 | 44.9% |
| Male | 27 | 55.1% | |
|
Age, years mean ± sd (range) |
61.7 ± 14.1 (18–83) | ||
|
Weight, kg mean ± sd (range) |
76.2 ± 17.1 (48–115) | ||
|
Injected tracer activity, MBq mean ± sd (range) |
145.1 ± 25.2 (100–212) | ||
| Primary | GEP-NET total | 38 | 77.5% |
| Pancreatic | 22 | 57.9% | |
| Gastro-enteric | 16 | 42.1% | |
| Lung | 9 | 18.4% | |
| Other | 2 | 4.1% | |
| NET histological sub-types | G1 | 33 | 67.4% |
| G2 | 6 | 12.2% | |
| G3 | 1 | 2.0% | |
| Atypical carcinoid | 4 | 8.2% | |
| Typical carcinoid | 5 | 10.2% | |
|
KI67, % mean ± sd (range) |
4.2 ± 12.9 (1–90) | ||
| Number of lesions | Primary | 42 | 70.0% |
| Liver metastasis | 8 | 13.3% | |
| Bone metastasis | 0 | 0% | |
| Lymph node metastasis | 9 | 15.0% | |
| Other metastasis | 1 | 1.7% | |
PET/CT acquisition and image reconstruction
All patients underwent PET/CT on an analog 3-dimensional (3D) PET scanner (Philips Gemini Dual-slice EXP scanner—PET AllegroTM system with Brilliance CT scanner—Philips Medical Systems, Cleveland, OH). In accordance with the procedural guidelines for PET imaging [36–38], the injected tracer activity was 145.1 ± 25.3 MBq of 68Ga-DOTA-TOC (range, 100–212 MBq). After 60 min of uptake and following free-breathing CT acquisition for attenuation correction from the vertex of the skull to the mid-thighs (5 mm slice, 40 mAs, and 120 kVp), PET data were acquired in 3-dimensional (3D) mode, covering the same anatomical region of the CT, with 2.5 min per bed position and 6–8 bed positions per patient. The PET scans were reconstructed by ordered subset expectation maximization (OSEM) algorithm (3D-RAMLA), with the following settings: 4 iterations, 8 subsets, and field of view (FOV) of 576 mm. For all reconstructions, matrix size was 144 × 144 voxels, resulting in isotropic voxels of 4.0 × 4.0 × 4.0 mm3. All acquisitions were corrected for photon attenuation (using the corresponding CT image), as well as for scatter and random coincidences.
Lesion segmentation
For each lesion, a three-dimensional volume of interest (VOI) was manually delineated (VOIm), slice-by-slice, in the OSEM PET images by four independent observers, all nuclear medicine physicians (FC, VL, GP, and BD with 10, 7, 5, and 3 years of expertise, respectively), by using the software LifeX v. 4.81 (IMIV/CEA, Orsay, France—www.lifexsoft.org) [39].
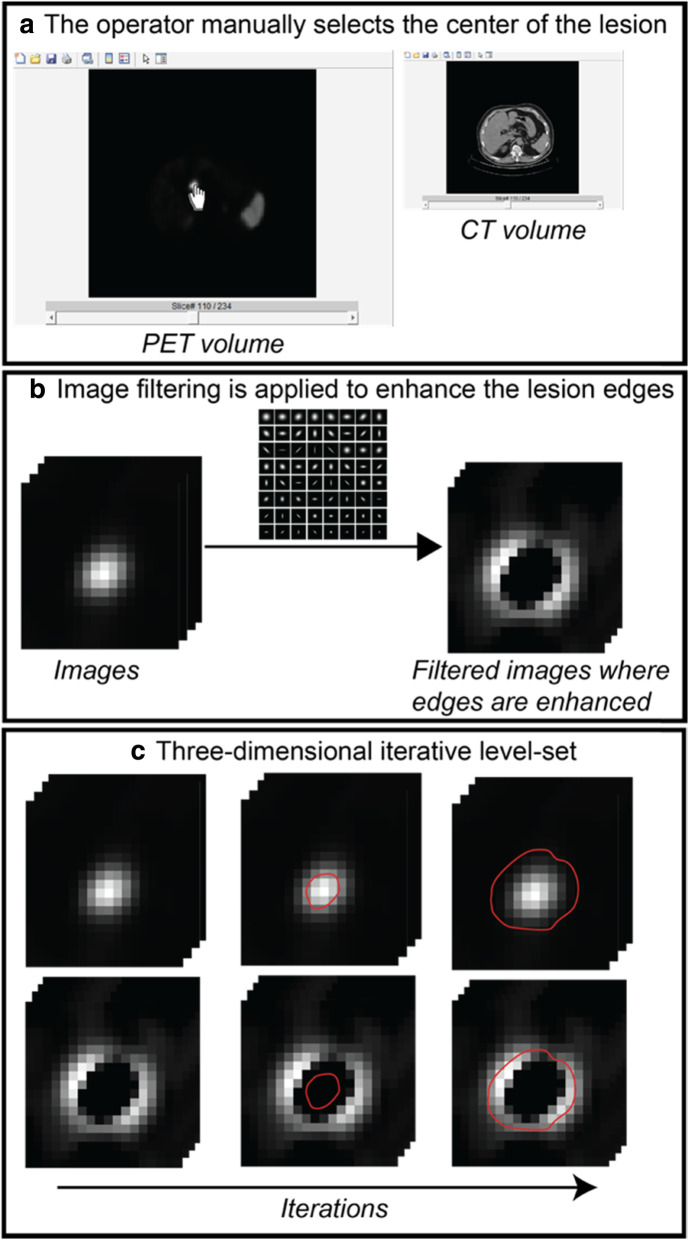
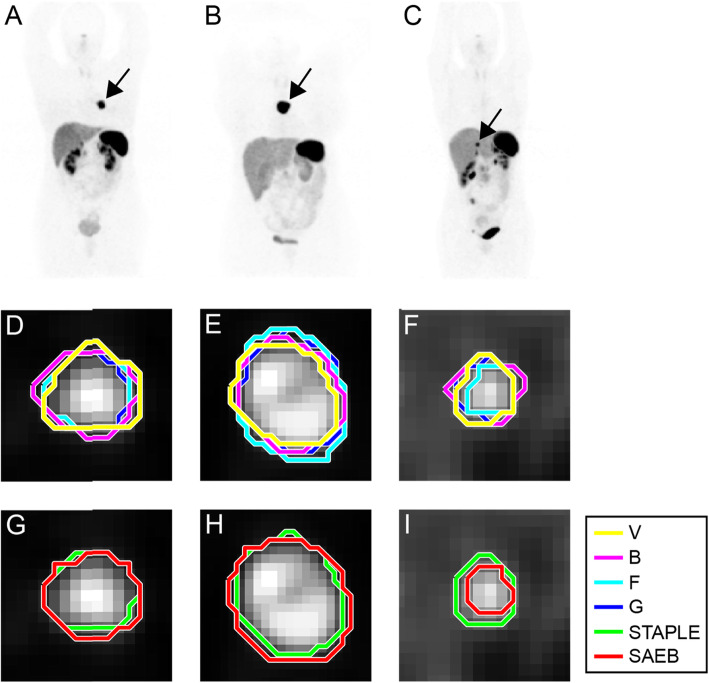
In additional, each lesion was also contoured using a semi-automatic edge-based (SAEB) algorithm (VOISAEB), homemade implemented in MATLAB (MathWorks) code, based on the active contour model proposed by Chan and Vese [40]. The algorithm is semi-automatic since the operator intervention was required in order to insert the central point of the lesion (Fig. 1a). The developed MATLAB graphical user interface allowed the operator to view both the PET and the CT images separately. Edge enhancement filters were applied to emphasize the edges of the lesion (Fig. 1b) and, subsequently, a curve was evolved iteratively on both the original and the edge-enhanced image in order to match the lesion contours by using a level-set formulation (Fig. 1c). The iteration 0 of the level-set, which is the initialization, was the center of the lesion indicated by the operator. The final contour of the lesion (VOISAEB) was achieved at the end of the iterative level-set.
Fig. 1.
Semi-automatic edge-based (SAEB) algorithm workflow. The algorithm requires the intervention of an operator to insert the central point of the lesion (a) through an interface created in MATLAB, the operator can view both the PET and the CT images separately. As a second step, edge-preserving filters are applied to the image to emphasize the edge of the lesion (b) and, after that, and a level-set is used which is a shape that evolves iteratively over the image (c). The level-set acts both on the original image of the lesion and on the filtered image in which the contours are highlighted. The iteration 0 of the level set, which would be the initialization, is the center of the lesion indicated by the operator. The final outline of the lesion is achieved at the end of the process
A threshold-based segmentation approach was implemented applying three different thresholds on both manual VOIm and VOISAEB, defined as 20, 30, and 40% of the SUVmax (VOI20, VOI30, and VOI40, respectively), as recently suggested by Toriihara et al. [41]. This approach is different from the well-established isocontouring methods frequently used for 18F-FDG PET/CT, in which the threshold is applied to larger regions of interest containing the tumor [42, 43]. In 68Ga-DOTA-peptide tracers, the methodology proposed by Toriihara is preferable to exclude surrounding physiological uptake, especially for the segmentation of liver metastases which are very prevalent in metastatic neuroendocrine tumors.
Intensity discretization
To perform RFs calculation, in particular of textural features, voxels values were redefined considering a limited number of SUV intensity values (gray-level intensity discretization process). To investigate the effect of gray-level discretization, the analysis was performed with two different settings of intensity discretization:
Absolute resampling with 64 number of gray levels (bins) between 0 and 60 SUV units (“fixed bin size” equal to 0.95, using the IBSI nomenclature [44]), called AR60, since most of the lesions presented a SUVmax between 0 and 60, as showed in supplemental material (Figure S1A);
Relative resampling (RR), between minimum and-maximum SUV of the VOI, using a “fixed bin number” equal to 64 number of gray levels (using the IBSI nomenclature [44]) and different sizes of bin, according to the uptake characteristic of each lesion/VOI.
Number of gray levels was set to 64 based on the results of previous studies regarding RFs robustness in 18F-FDG PET/CT [45–47]. The spatial resampling was of 4 × 4 × 4 mm3, according to the resolution limits of the Philips Gemini Dual-slice EXP PET/CT scanner.
Radiomic features extraction
Radiomics features were extracted from PET images in all the VOIm segmented by each nuclear medicine physician, in all the VOISAEB and in all the corresponding VOI20, VOI30, and VOI40 using the two intensity rescaling factors (AR60 and RR). Hence, a total of 40 combinations of VOI, threshold, and intensity rescaling factors were tested, as shown in Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.
Flow chart of the ICC and COVL analysis applied to assess radiomic features robustness according to segmentation and discretization
A total of fifty-one semi-quantitative PET parameters and RFs were extracted, using LifeX description:
Ten conventional PET parameters: such as SUVmax, SUVmean, SUVmin, SUVpeak, SUVstd SUV quartiles (SUVQ1, SUVQ2, and SUVQ3) and total lesion somatostatin receptor expression (TLSRE);
Five descriptors of the image intensity histogram: HISTO_Skewness (asymmetry), HISTO_Kurtosis (flatness), HISTO_Energy (uniformity), HISTO_Entropy_log2, and _log10 (randomness);
Four shape-based features, that describe shape and size of VOI: SHAPE_Volume (mL), SHAPE_Volume (voxels), SHAPE_Sphericity, and SHAPE_Compacity; and
Thirty-two textural features: (a) seven features from gray-level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM): describing the correlation between pair of voxels in 13 directions of a three-dimensional space; (b) eleven features from gray-level run length matrix (GLRLM): describing the number and length of run with a certain level of gray in 13 directions of a three-dimensional space; (c) eleven features from gray-level zone length matrix (GLZLM): describing the number and size of zone with a certain level of gray in 13 directions of a three-dimensional space; (d) three features from neighborhood gray-level different matrix (NGLDM): describing the difference between a voxel and its connected neighbors.
Detailed descriptions of these features can be found in the LifeX documentation (www.lifexsoft.org) [39]. Supplementary Table 1 reports the complete list of computed RFs and the comparison between LifeX and the Imaging Biomarker Standardization Initiative (IBSI) nomenclatures [44]. The GLZLM features of LifeX correspond to gray-level size zone matrix (GLSZM) of IBSI; the two features categories gray-level distance zone matrix (GLDZM) and neighboring gray tone difference matrix (NGTDM) are not measurable in LifeX.
Statistical analyses
Quantitative comparisons between VOIm and VOISAEB were evaluated through the Dice similarity coefficient (DSC), which measures spatial overlap between two different segmentations of the same lesion:
where |V1| and |V2| were the volumes of the two segmentations to be compared, |V1 ∩ V2| was the volume of the overlap between V1 and V2. DSC values can range from 0, when the two segmentations have no overlap, to 1 when the two segmentations are coincident [42].
The algorithm for simultaneous truth and performance level estimation (STAPLE), which takes a collection of segmentations of an image and computes a probabilistic estimate of the true segmentation [48], was also used to compare VOISAEB with the “true” segmentation (VOISTAPLE) derived by the four VOIm.
Robustness of RFs was assessed by two-way mixed effects intra-class correlation coefficients (ICC) to evaluate consistency and coefficient of variance for each lesion (COVL) to evaluate agreement in the various settings.
The intra-class correlation coefficients (ICC) was defined as:
where BMS is the between-subjects mean square, RMS is the residual mean square and N is the number of measurements of the RF (e.g., 2 in the case of intensity discretization, being AR60 and RR). RFs were considered highly robust in case of ICC > 0.9, robust if ICC > 0.8, moderately robust if ICC was between 0.5 and 0.8 and poorly robust if ICC was < 0.5 [25, 49, 50].
The coefficient of variation (COVL), which is commonly used to measure relative dispersion, calculated for each lesion (L) was defined as:
where is the measurement of RFs for lesion L for a specific segmentation and intensity discretization (k) and is the mean value of lesion L over the considered combinations of segmentation and discretization approaches, as presented in the study of Bailly et al. [26]. RFs with low percentage of COVL are characterized by low dispersion, on contrary RFs with high percentage of COVL are characterized by high dispersion.
To investigate the relationship between RFs and lesion volume and SUVmax, a Pearson’s correlation analysis was carried out. To consider a unique RF value for every segmentation, RFs values were averaged across segmentations.
All analyses were performed using statistical R software (R Foundation, Vienna, Austria [51]).
Results
Quantitative comparison of manual and SAEB segmentation
Mean value of DSC comparing VOISAEB with VOISTAPLE was 0.75 ± 0.11 (0.45–0.92), while mean value of DSC among VOIm was 0.78 ± 0.03 (0.75–0.83). Examples of segmentation performed by SAEB and operators for three different lesions are shown in Fig. 3. DSC boxplots between VOISAEB and the different VOIm and between manual operators for each lesion are reported in Fig. 4a, b.
Fig. 3.
Example of segmentation (single slice images) of lesions extracted from three different examined patients. Panels a, d, and g show a lung primary NET; panels b, e, and h show metastatic lesion in a mediastinal lymph node; panels c, f, and i show a metastatic liver lesion. The first row shows the maximum intensity projection (MIP) of 68Ga-DOTATOC of the three different patients where black arrows point at the segmented lesions. In the second row, manual contours performed by the four operators are represented in different colors. The third row shows the STAPLE contour (in green) and the semi-automatic edge-based segmentation (SAEB) algorithm result (in red)
Fig. 4.
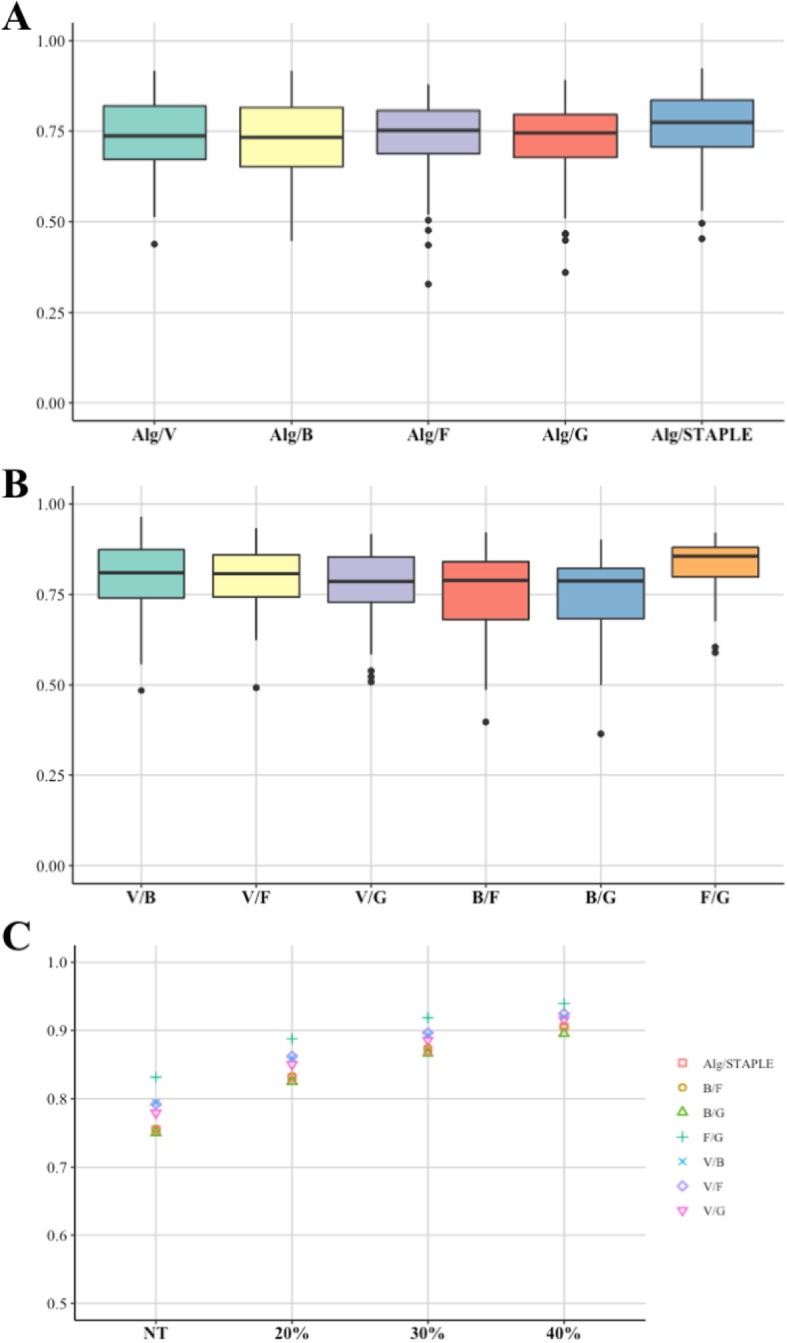
Boxplots of mean DSC comparing the semi-automatic edge-based algorithm (Alg) with manual segmentations and with STAPLE (a), comparing manual segmentations by different operators (b) and comparing different manual segmentations and Alg with STAPLE for different SUVmax thresholds (NT, no threshold applied) (c)
Comparison between operators showed a perfect segmentation overlap (DSC = 1) for 24 out of 60 lesions, applying the 40% SUVmax threshold; mean DSC using different SUVmax threshold are reported in Fig. 4c.
Mean DSC values improved as the SUVmax threshold applied increases. The volume distributions for different thresholds are shown in supplementary material (Figure S1B).
Impact of different segmentation approaches on RF
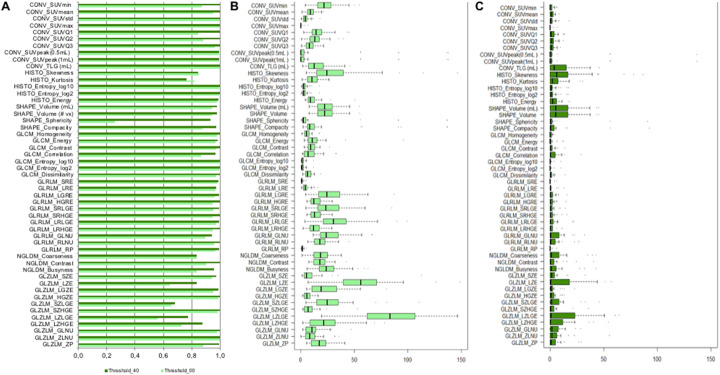
Using no threshold and applying AR60 intensity rescale factors, 64.7% of RFs showed high robustness (ICC > 0.9) to segmentation (7/10 conventional, 3/6 histogram, 2/4 shape, and 21/31 textural) (Fig. 5a).
Fig. 5.
a Bar diagrams of intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) values of RFs robustness to segmentation (different operators and semi-automatic algorithm), using AR60 and applying different SUVmax thresholds (no threshold and 40% SUVmax threshold applied). b Boxplot of percentage COVL for segmentation (for the first operator, results similar for the other operators) for each RFs, using AR60 and applying no SUVmax threshold. c Boxplot of percentage COVL applying 40% SUVmax threshold. TLG (total lesion glycolysis) conventional parameter in our study corresponded to the TLSRE (total lesion somatostatin receptor expression)
Using a 40% SUVmax threshold, the robustness of RFs to segmentation (ICC > 0.9) increased to 86.5% of RFs. An increase of the SUVmax threshold produced a substantial increase of ICC of the following features: CONV_SUVmin, CONV_SUVQ1, CONV_SUVQ2, SHAPE_Sphericity, SHAPE_Compacity, GLCM_Correlation, NGLDM_Contrast, NGLDM_Busyness, GLZLM_LZE, GLZLM_LZLGE, GLZLM_LZHGE, and GLZLM_ZP while lower increase was observed for the rest of features (Fig. 5a). Further, using a 40% SUVmax threshold, textural features were not computed in 22 lesions due to low number of voxels.
About the corresponding COVL analysis, when no threshold was applied, the grade of dispersion of the majority of RFs was rather low: median COVL values were below 10% for 47% of RFs and below 20% for 75% of RFs (Fig. 5b). Only two RFs (GLZLM_LZE and GLZLM_LZLGE) showed a COVL > 50%. Using a 40% SUVmax threshold, median values of COVL were lower than 10% for all the RFs (Fig. 5c).
ICC and COVL analysis regarding robustness to SUVmax thresholds (no threshold, 20%, 30%, 40%) using AR60 are shown in the supplemental material (Figure S2). 50.9% of RFs (5/10 conventional, 3/6 histogram, 0/4 shape and 18/31 textural) showed high robustness (ICC > 0.9). The results of COVL showed a high variability of the majority of RFs in function of different SUVmax thresholds. Median value of COVL was < 10% for few RFs, namely SUVmax, SUVpeak (0.5 ml and 1 ml), HISTO_Entropy (log10 and log2), GLCM_Homogeneity, GLCM_Contrast, GLCM_Entropy (log10 and log2), GLCM_Dissimilarity, GLRLM_SRE, GLRLM_LRE, GLRLM_RP, GLZLM_SZE, and GLZM_ZP.
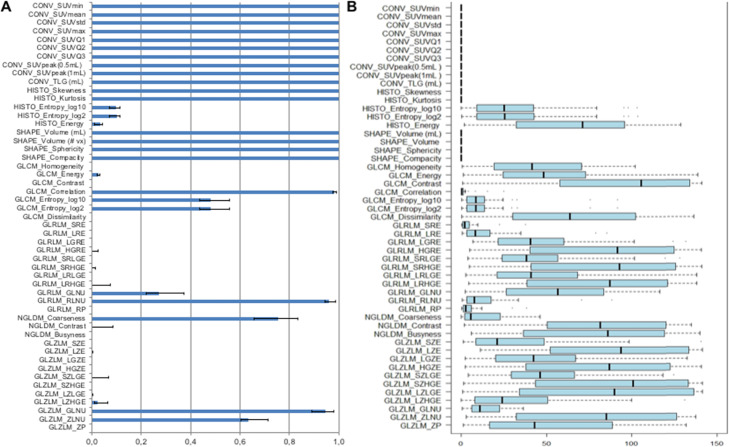
Impact of different discretization settings on RFs
Comparing the five VOI delineations (4 VOIm and VOISAEB) and applying no SUVmax threshold (Fig. 6a), median value of ICC for the two intensity discretization approaches (AR60 and RR) was equal to 1 for all conventional and shape features, HISTO_Skewness and HISTO_Kurtosis (not affected by the discretization), and for only three textural features, namely GLCM_Correlation, GLRLM_RLNU, and GLZLM_GLNU. Overall, the percentage of highly robust features was 37% (10/10 conventional, 2/5 histogram, 4/4 shape, and 3/32 textural). The majority of the remaining textural features showed very poor robustness to discretization settings except for NGLDM_Coarseness which had a median ICC > 0.7. The COVL analysis (Fig. 6b) highlighted in general low COVL values for all the RFs with high ICC (conventional, shape, HISTO_Skewness and HISTO_Kurtosis, GLCM_Correlation, GLRLM_RLNU, and GLZLM_GLNU). The majority of the other textural features were characterized by a very high dispersion, corresponding to a high percentage of COVL value. Only GLCM_Entropy (log10 and log2), GLRLM_SRE, GLRLM_LRE, GLRLM_RP presented a COVL < 10%, despite a corresponding low ICC for these RFs.
Fig. 6.
a Bar diagrams of intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) values of RFs robustness to different intensity rescale factors (RR and AR60) when no threshold was applied for different operators and semi-automatic algorithm. Bars in blue show the median ICC between different segmentations, applying no threshold. Range error bars (in black) encompass the lowest and highest values for different operators. b Boxplot of COVL for different intensity rescale factors (RR and AR60), applying no threshold, for the first operator (results superposable for the other operators). TLG (total lesion glycolysis) conventional parameter in our study corresponds to the TLSRE (total lesion somatostatin receptor expression)
RFs correlation with SUVmax and volume
Pearson correlation coefficients of RFs with volume (for AR60, without SUVmax threshold and with 40% SUVmax threshold applied, respectively) and with SUVmax of the ROI (AR60 and RR, no threshold applied) are shown in Fig. 7.
Fig. 7.
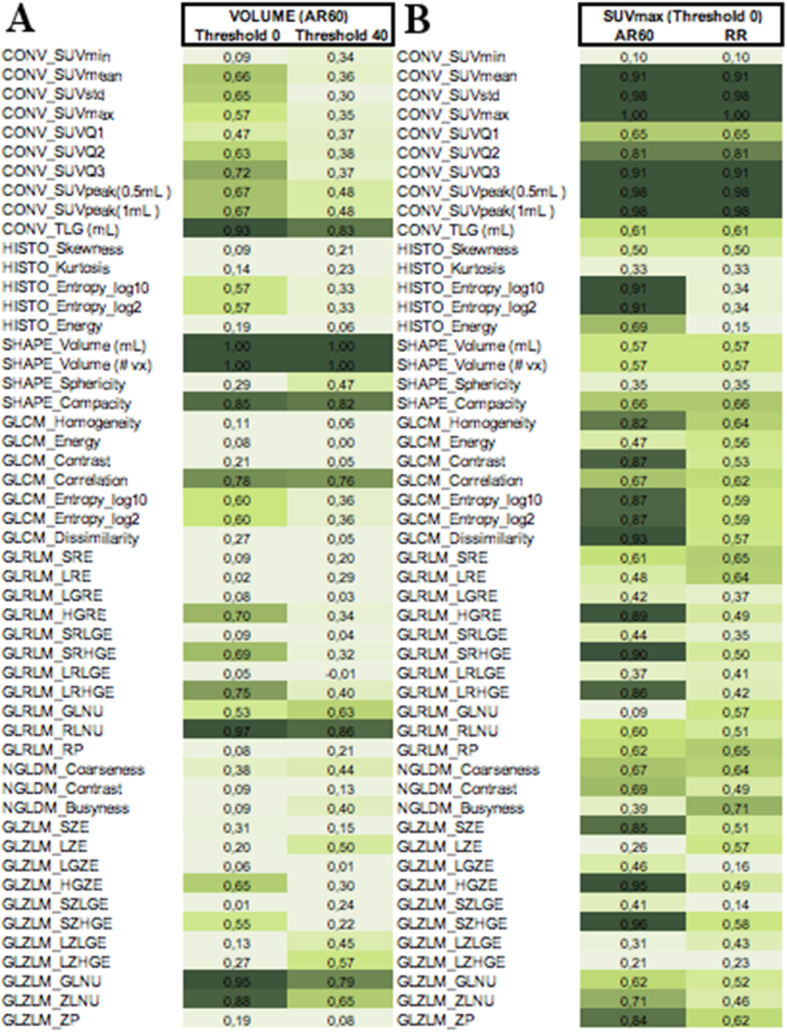
Pearson correlation coefficients (mean values between different operators) respectively (a) between RFs values and volume (for no threshold and 40% SUVmax threshold applied); and (b) between RFs and SUVmax (for AR60 and RR intensity rescale factors) without threshold. TLG (total lesion glycolysis) conventional parameter in our study corresponds to the TLSRE (total lesion somatostatin receptor expression)
The following RFs showed high correlation (r > 0.9) with volume, regardless of SUVmax threshold: TLSRE, SHAPE_Compacity, GLRLM_RLNU, and GLZLM_GLNU. Regarding correlation with SUVmax, the following RFs showed very high correlation (r > 0.9) when AR60 was employed: HISTO_Entropy (both_log10 and_log2), GLCM_Dissimilarity, GLRLM_SRHGE, GLZLM_HGZE, and GLZLM_SZHGE. When RR was used, no RFs were highly correlated with SUVmax (except for most part of conventional SUV features).
Discussion
Our study sought to identify robust RFs in 68Ga-DOTA-TOC PET/CT, as a result of different segmentation and gray-level intensity discretization methods of the images. The major findings of our study were the following: (a) 64.7% of RFs (7/10 conventional, 3/6 histogram, 2/4 shape, and 21/31 textural) showed high robustness in terms of consistency (ICC > 0.9) and agreement (low median COVL value) to different operators without SUVmax threshold applied (manual segmentation); (b) increasing the SUVmax isocontouring threshold had a positive effect on RFs robustness to segmentation. However, this approach might lead to a loss of important biological information on the population studied and reduction of analyzable lesions with textural features due to low number of voxels; (c) quantitative comparison between a semi-automatic edge-based (SAEB) algorithm and manual segmentation showed a dice similarity coefficient (DSC) of 0.75 ± 0.11 comparable to DSC between operators (0.78 ± 0.03). These results suggest that a semi-automatic algorithm might be able to aid expert segmentation to reduce operator variability and analysis time [36, 42]; (d) the use of absolute intensity rescaling factor (AR60) achieved higher robustness of RFs to segmentation than relative (RR) intensity rescaling factor.
In monocentric studies, image segmentation is one of the first step to take into account in radiomic analysis, since it is a possible source of RFs variability. Overall, RFs robustness to segmentation resulted to be quite good applying no SUVmax threshold (ICC > 0.9 for 64.7% RFs), using AR60 intensity discretization method (Fig. 5a). Only one morphological feature, SHAPE_Sphericity, resulted not robust to segmentation. However, its ICC value was furtherly decreased from Lifex software due to an assigned artificial feature value equal to zero for VOIs smaller than 64 voxels rather than a Not A Number (NAN) as other RFs. This occurred also for SHAPE_Compacity for a total of 7 lesions and only for some operator, leading to a high inter-operator variability. After removing these lesions, the ICC increased for both SHAPE_Sphericity (from ICC = 0.27 to ICC = 0.59) and SHAPE_Compacity (from ICC = 0.88 to ICC = 0.95).
In line with previous studies [52, 53], GLZLM (also called GLSZM) features and in particular the ones measuring zones with low gray-level (SZLGE and LZLGE) resulted to have a moderate robustness (ICC from 0.5 to 0.8) to segmentation (Fig. 5a). This is likely related to the lower uptake in lesions edges, where operators and SAEB segmentation showed a higher variability (Fig. 3).
When using AR60 intensity discretization method, the SUVmax thresholding had a considerable impact on inter-segmentation ICC values of conventional, shape, and GLRLM features (Fig. 5a). At the same time, however, it is clear that the SUVmax thresholding has an important impact on the dispersion (agreement) of RFs, reducing it significantly, with a progressive flattening of all RFs COVL values toward zero (Fig. 5b, c). These results lead to considering segmentation with a 40% SUVmax threshold as preferable from the point of view of robustness, increasing the similarity between segmentations (Fig. 4c). However, its use may lead to a significant loss of relevant information for diagnosis and prognosis. These findings are in accordance with previous studies, reporting that segmentation with 40% SUVmax threshold yields superior inter-observer reproducibility of texture features in 18F-FDG PET/CT images, despite the loss of information about tumor heterogeneity related to exclusion of voxel intensities below the fixed 40% threshold, such as those arising from low-activity tumor regions or tumor boundaries. However, as early demonstrated by the study of Biehl et al in 18F-FDG PET/CT images [54], there is no consensus in the use of SUVmax threshold, because this parameter can lead to an over- and/or underestimation of lesion PET volume compared with CT volume related to low resolution, inherent noise, high uncertainties in lesion boundaries, and motion blurring of the lesion related to the tomography characteristics [42]. Further, from a technical point of view, the use of high SUVmax threshold could reduce number of voxels of the VOI denying computation of textural features. In our opinion, the concern related to the use of threshold-based segmentation methods in 68Ga-DOTA-peptide PET-CT images must be even higher due to the aforementioned heterogeneity of somatostatin receptors expression in neuroendocrine tumors which may explain that currently the few studies of radiomics with 68Ga-DOTA-peptide in the literature has been made on a manual-based segmentation [55–58].
Image gradient showed to be useful for tumor segmentation in 18F-FDG PET/CT images, as highlighted by Pfeahler et al. [59] and Foster et al. [42]. In this study, we demonstrated the suitability and added value of using an automatic image gradient segmentation in 68Ga-DOTA-peptide PET images, given the high SUV variability and the presence of high SUV values for normal tissues. For these reasons, we believe that automatic and semi-automatic segmentation methods are crucial for the radiomics analysis of NET in 68Ga-DOTA-peptide images.
Our results regarding tumor segmentation accuracy are promising since DSC comparing the SAEB segmentation with the manual segmentations was 0.75 ± 0.11 (median 0.77). The SAEB algorithm is characterized by its hybrid nature: the curve evolves in the image looking to both the original image (important for homogeneity) and the edge-enhanced image (important for discontinuities detection). This feature allows the SAEB algorithm to behave reproducibly within lesions in different locations, with different image appearances and different background uptakes, such as blob-like lesions with dark background (Fig. 3a, d and g), heterogeneous lesions (Fig. 3b, e, and h) and liver lesions where background present SUV values comparable to the lesion (Fig. 3c, f, and i). Thus, the use of automatic and semi-automatic segmentation methods, such as SAEB algorithm, appears to be crucial in future studies assessing robustness or clinical significance of RFs in 68Ga-DOTA SSTR-peptide PET/CT imaging, in order to reduce inter- and intra-reader variability of manual segmentation methods, which is also time-consuming [42, 44], and in order to reduce relevant information loss secondary to the application of 40% SUVmax threshold. However, further studies are needed to validate our semi-automatic segmentation methods (SAEB).
Another interesting result of our study is related to the negative impact of the relative resampling intensity discretization (which corresponded to the fixed bin number) on the robustness to segmentation of the majority of textural features analyzed. As the rescaling is carried out according to the minimum and maximum values of the VOI, the same image is rescaled differently depending on the segmentation operator/method used, leading to high variability also in RFs values. Recently, Zwanenburg et al. [20] highlighted that, as both discretization methods have their particular advantages and disadvantages, they should not be treated as equivalent. Hence, an image biomarker should be considered different to consist of the discretization method and level, in addition to its scale and base feature definition.
Anyway, the use of relative resampling is not recommended in PET images, as already observed in 18F-FDG PET/CT [45–47]. At least in clinical cases, the “fixed bin number” is intuitively less appropriate: it is based on the range of SUV intensities found in the volume of interest, with low SUVs corresponding to low bin numbers and high SUVs corresponding to high bin numbers; hence bin width (in SUV) and SUV range may vary between images in a cohort, even though the number of bins is consistent [20]. For the identification of RFs as new cancer-specific biomarker (e.g., NET), it is important that the textural features values would, be directly comparable, both inter- and intra-patient, in order to derive meaningful conclusions. Moreover, NETs are characterized by an extremely variable expression of somatostatin receptors in 68Ga-DOTA-peptides with a corresponding broader range for SUV values (from close to 0 up to higher than 100) compared to 18F-FDG PET/CT, causing a greater impact of the RR in the final discretized uptake values. This concept has been already emphasized by several studies: beyond all the variabilities related to the tomographs, segmentations, and post-processing settings, the robustness of RFs is also related to the tumor characteristic and behavior [52, 60–62] and to the radiotracer analyzed, as recently demonstrated by Lu et al. [63] that studied the stability of RFs for nasopharyngeal carcinoma on both 11C-choline and 18F-FDG PET/CT images, with different results. In accordance with previous studies [20, 25], the impact of intensity discretization on textural features was stronger than segmentation. This is exactly the case of textural features, where differentiation between high and low-gray levels is needed, and thus, the choice of the discretization setting is relevant. When using no SUVmax threshold, only four textural features resulted to be consistent: GLCM_Correlation, GLRLM_RLNU, NGLDM_Coarseness, and GLZLM_GLNU (Fig. 6).
ICC and COVL provided in general similar information. Generally, we reported low ICC and high COVL or the opposite. Anyway, there were also RFs with low consistency (low ICC) and high agreement (low COVL) or high consistency (high ICC) and low agreement (high COVL). Representative examples were GLCM_Entropy (both _log10 and _log2), GLRLM_SRE, GLRLM_LRE, and GLRLM_RP which had low consistency but good agreement (COVL < 10%) to discretization. For these RFs, although measurements were not correlated when changing intensity discretization methods, the relative percentage of deviation was low (Figure S3). On the other hand, when evaluating robustness to SUVmax threshold, ICC was sometimes high even if COVL was also high because, despite the great variability, the RFs remained correlated by changing the parameters, as we can observe in particular for GLRLM_LGRE, GLRLM_SRLGE, GLRLM_LRLGE, and GLZLM_LZLGE for the threshold variability (Fig. 6 and Figure S4). This behavior was due to the very small, close to zero, values of these RFs, which produced high COVL values. Our study highlights the importance of the discretization settings chosen due to its high impact on the RFs robustness, which seems even higher in 68Ga-DOTA-peptide comparing to 18F-FDG PET/CT images (due to the widest range of SUV values in 68Ga-DOTA-peptide images in NET). However, discretization is a controllable variable, while segmentations do not. Respect of segmentation, there are essentially three categories of features: a first group of features almost not sensitive to segmentation with high ICC and low COVL values (e.g. SUVmean, figure S5 a), a second group of features with high ICC with relative high COVL values (e.g., TLG, figure S5 b) and a third group with low ICC and high COVL values (e.g., GLZLM_SZLGE, figure S5 c), that could probably be useless in the absence of a universally standardized and totally automatic segmentation method.
Finally, regarding Pearson’s correlation between RFs and SUVmax and volume, most of the RFs extracted showed a poor correlation with volume. Only two textural features had a strong correlation (coefficient values > 0.8 or < − 0.8) with the volume, for all thresholds and discretization (GLRM_RLNU and GLZLM_GLNU). Regarding the correlation with SUVmax, no features showed a strong correlation for all thresholds and discretization. These results suggest that RFs could provide additional information to better characterize NETs, regardless of volume and SUV parameters.
The extraction of robust RFs from 68Ga-DOTA SSTR-peptide PET/CT might contribute to solve some limitations related to the clinical evaluation of the SSTR expression in NET. At present, no consensus has been already reached regarding the assessment of patients who need to be investigated with both 18F-FDG and 68Ga-DOTA-peptide PET/CT (even if it is more probable that NET neoplasms with Ki67 > 15% will have positive lesions in 18F-FDG PET/CT [64, 65]). Furthermore, an early detection of more aggressive disease with 18F-FDG PET/CT does not necessarily reflect a change in the therapeutic strategy. Finally, conventional semi-quantitative PET parameters showed a sub-optimal feasibility to select patients for receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) and to evaluate response to PRRT. In this scenario, the quantitative analysis offered by radiomics might be applied as prognostic biomarker and predictor of tumor heterogeneity in NET.
Limitation
This study is not exempt from limitations. First, we did not initially perform a phantom study. To overcome this limitation, as recommended in the radiomics quality score (RQS) proposed by Lambin et al. [66], we are currently adapting our methodology for a study on an anthropomorphic phantom filled with synthetic lesions as obtained from PET/CT images and created by the 3D printer. This model will reflect realistic tumor shapes and heterogeneity uptakes for a prospective evaluation of RFs robustness. Second, we limited our analysis to the RFs provided by the LIFEx software. Even if LIFEx’s RFs are the most representative ones, they are only a limited set of the biggest group of RFs provided by the IBSI nomenclature, furthermore, two IBSI categories are not included; further and more comprehensive studies on this aspect are needed. Third, NET are rare tumors and G3 NET and G3 NEC are rarely evaluated with 68Ga-DOTA SSTR-peptide; for this reason, our sample size is yet too small and heterogeneous (as shown in Table 1) to evaluate the possible correlation between robust RFs with the histological NET grading system. The phantom study will lead to the possibility to enrolled NET patients from different centers, solving also limitations regarding sample size. Fourth, the difficulty of edge-based algorithms in the segmentation of lesions with a similar uptake background or with small (< 16 cm3) or large dimension (> 160 cm3) [50] has been previously highlighted. However, we acknowledge that the number of cases analyzed in this study is not enough to quantitatively validate the algorithm in the aforementioned conditions. Nevertheless, these results encouraged us to start evaluating also this on the 3D-printer based phantom study aimed to assess the performance of SAEB analyzing both spherical lesions, non-uniform and non-spherical volumes with different sizes and different backgrounds, reproducing the human-like lesions [60, 67].
Conclusion
Our results suggest that the use of RFs is feasible also in 68Ga-DOTA-TOC PET/CT. The manual delineation of VOI had an impact on RFs values dependent on RF type, preserving the correlation with high ICC values in most cases despite some relatively high COVL values. The 40% SUVmax threshold increased the RFs robustness, but with a potential loss of information and analyzable lesions. Finally, the gray-level discretization influences the robustness of RFs, which vary depending on the use of relative or absolute resampling. In our opinion, an absolute resampling better suited to the evaluation of NETs with functional imaging (68Ga-DOTA-TOC PET/CT).
These results suggest the needing to standardize the methodology used in the radiomic PET studies in 68Ga-DOTA-TOC PET/CT. Moreover, a semi-automatic segmentation algorithm might be helpful to solve both the impact of different manual segmentations on RFs robustness and the loss of valuable information due to SUVmax threshold segmentation method.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1. LifeX radiomic features description according to the Imaging Biomarker Standardization Initiative (IBSI) description (update 17 December 2019). LifeX version was 4.81. Figure S1. Box plots showing the distribution of SUVmax (panel A) and Volume (panel B). Figure S2. (A) Bar diagrams of intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) values of RFs for robustness to SUVmax thresholding. Bars show the median ICC between the different segmentations for the absolute intensity rescale factor AR60. Range error bars (in black) encompass the lowest and highest values for different operators. (B) Boxplot of COVL for different threshold (20, 30, 40%) for each RFs, for the first operator (results superposable for the other operators). TLG (total lesion glycolysis) conventional parameter in our study corresponds to the TLSRE (total lesion somatostatin receptor expression). Figure S3. Radiomic features with moderate or poor consistency (ICC < 0.80), but high agreement (median COVL < 10%) to intensity discretization. The RFs were: GLCM_Entropy_log2, GLCM_Entropy_log10 (not shown), GLRLM_SRE, GLRLM_LRE and GLRLM_RP. Value of the RFs for each lesion are presented in the top row; boxplots of COVL for the first operator are presented in the bottom row. Figure S4. Radiomic features with high consistency (ICC > 0.90), but low agreement (median COVL > 10%) to SUVmax thresholds (0, 20, 30 and 40%). The RFs were: GLRLM_LGRE, GLRLM_SRLGE, GLZLM_LGZE and GLZLM_LZLGE. Value of the RFs for each lesion are presented in the top row; boxplots of COVL for the first operator are presented in the bottom row. Figure S5. Boxplot showing the distribution of RF value for each operator. The three RFs chosen are the most representative of the impact of segmentation on ICC. Segmentation did not affect SUVmean (A) and TLG (B) in terms of ICC, although TLG was characterized by not negligible dispersion (percentage of COVL) in our study. In contrast, segmentation had a high impact on GLZLM_SZLGE (C) in terms of both ICC and COVL. Mean COVL of SUVmean, TLG and GLZLM_SZLGE was 8.33±3.96, 13.38±8.52 and 30.67±27.29, respectively.
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to the anonymous patients on whom this work is based and the staff of the Division of Nuclear Medicine for their excellent technical support.
Abbreviations
- 18F-FDG
18F-fluorodeoxyglucose
- CT
Computed tomography
- FOV
Field of view
- GLCM
Gray-level co-occurrence matrix
- GLNUr
Gray-level non-uniformity for run
- GLNUz
Gray-level non-uniformity for zone
- GLRLM
Gray-level run length matrix
- GLZLM
Gray-level zone length matrix
- HGRE
High gray-level run emphasis
- HGZE
High gray-level zone emphasis
- IBSI
Imaging biomarker standardization initiative
- ICH – GCP
International Conference on Harmonization - Good Clinical Practice
- LGRE
Low gray-level run emphasis
- LGZE
Low gray-level zone emphasis
- LRE
Long-run emphasis
- LRHGE
Long-run high gray-level emphasis
- LRLGE
Long-run low gray-level emphasis
- LZE
Long-zone emphasis
- LZHGE
Long-zone high gray-level emphasis
- LZLGE
Long-zone low gray-level emphasis
- MIP
Maximum intensity projection
- MTV
Metabolic tumor volume
- NET
Neuroendocrine tumor
- NGLDM
Neighborhood gray-level different matrix
- OSEM
Ordered subset expectation maximization
- PET
Positron emission tomography
- RF
Radiomic features
- RLNU
Run length non-uniformity
- ROI
Region of interest
- RP
Run percentage
- SAEB
Semi-automatic edge-based
- SRE
Short-run emphasis
- SRHGE
Short-run high gray-level emphasis
- SRLGE
Short-run low gray-level emphasis
- SSTR
Somatostatin receptor
- SZE
Short-zone emphasis
- SZHGE
Short-zone high gray-level emphasis
- SZLGE
Short-zone low gray-level emphasis
- SUV
Standardized uptake value
- TLSRE
Total lesion somatostatin receptor expression
- VOI
Volume of interest
- ZLNU
Zone length non-uniformity
- ZP
Zone percentage
Authors’ contributions
DD, FM, VL, BDS, and OR designed the study; VL collect the data; VL, BD, FC, and GP performed the manual segmentation; BDS and FM create the MATLAB homemade code for the semi-automatic algorithm; VL, BDS, OR, and EG conducted the statistical analysis; PT, FC, FM, and DD contributed in the review of the data and the statistical analysis; VL and BDS wrote the manuscript; all the authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Nuclear Medicine of A.O.U. Città della Salute e della Scienza di Torino, University of Turin, is supported by a grant from CRT Foundation (Fondazione Cassa di Risparmio di Torino) for the project “Radiomics in the Study of Neuroendocrine Tumors in Nuclear Medicine: Innovative Method for the Study of Tumor Heterogeneity”. No further specific grants from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors were received for this study.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This is a retrospective, observational study approved by the ethical committee A.O.U. Città della Salute e della Scienza di Torino (IRB protocol: CS2/477) and only patients with documented willingness to the use of their medical data for research were included.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in relation to the present study.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Oronsky B, Ma PC, Morgensztern D, Carter CA. Nothing But NET: a review of neuroendocrine tumors and carcinomas. Neoplasia (United States). 2017; 991–1002. [cited 2019 Dec 11]. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29091800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 2.Hofland J, Kaltsas G, de Herder WW. Advances in the diagnosis and management of well-differentiated neuroendocrine neoplasms. Endocr Rev. 2020;41:371–403. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnz004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gerlinger M, Rowan AJ, Horswell S, Larkin J, Endesfelder D, Gronroos E, et al. Intratumor heterogeneity and branched evolution revealed by multiregion sequencing. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:883–892. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1113205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ziv E, Durack JC, Solomon SB. The importance of biopsy in the era of molecular medicine. Cancer J. (United States). 2016. p. 418–22. [cited 2019 Dec 11] Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27870685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 5.McQuerry JA, Chang JT, Bowtell DDL, Cohen A, Bild AH. Mechanisms and clinical implications of tumor heterogeneity and convergence on recurrent phenotypes. J. Mol. Med. 2017; 1167–78. [cited 2019 Dec 11]. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28871446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 6.Grillo F, Albertelli M, Brisigotti MP, Borra T, Boschetti M, Fiocca R, et al. Grade increases in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumor metastases compared to the primary tumor. Neuroendocrinol. 2016;103:452–459. doi: 10.1159/000439434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Serkova NJ. Translational imaging endpoints to predict treatment response to novel targeted anticancer agents. Drug Resist Updat. 2011 [cited 2019 Dec 11];14:224–35. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21640633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 8.James ML, Gambhir SS. A molecular imaging primer: modalities, imaging agents, and applications. Physiol. Rev. 2012 [cited 2019 Dec 11]. p. 897–965. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22535898. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 9.Jennings M, Marcu LG, Bezak E. PET-specific parameters and radiotracers in theoretical tumour modelling. Comput Math Methods Med. 2015 [cited 2019 Dec 11];2015:415923. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25788973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 10.Tirosh A, Kebebew E. The utility of 68Ga-DOTATATE positron-emission tomography/computed tomography in the diagnosis, management, follow-up and prognosis of neuroendocrine tumors. Futur Oncol. 2018;14:111–122. doi: 10.2217/fon-2017-0393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Giovannini E, Giovacchini G, Borsò E, Lazzeri P, Riondato M, Leoncini R, et al. [ 68 Ga]-Dota Peptide PET/CT in Neuroendocrine Tumors: Main Clinical Applications. Curr Radiopharm. 2018;12:11–22. [cited 2019 Dec 11] Available from: http://www.eurekaselect.com/168288/article. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 12.Carideo L, Prosperi D, Panzuto F, Magi L, Pratesi MS, Rinzivillo M, et al. Role of Combined [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-SST analogues and [18F]FDG PET/CT in the management of GEP-NENs: a systematic review. J Clin Med. 2019 [cited 2019 Dec 11];8:1032. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/8/7/1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 13.Chan DLH, Pavlakis N, Schembri GP, Bernard EJ, Hsiao E, Hayes A, et al. Dual somatostatin receptor/FDG PET/CT imaging in metastatic neuroendocrine tumours: Proposal for a novel grading scheme with prognostic significance. Theranostics. 2017;7:1149–1158. doi: 10.7150/thno.18068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hatt M, Tixier F, Pierce L, Kinahan PE, Le Rest CC, Visvikis D. Characterization of PET/CT images using texture analysis: the past, the present… any future? Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol; 2017. 151–65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 15.Ha S, Choi H, Paeng JC, Cheon GJ. Radiomics in oncological PET/CT: a methodological overview. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging (2010). 2019 [cited 2019 Dec 11]. p. 14–29. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30828395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 16.Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, Carvalho S, Van Stiphout RGPM, Granton P, et al. Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48:441–446. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.11.036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H. Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiol. 2016;278:563–577. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015151169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sanduleanu S, Woodruff HC, de Jong EEC, van Timmeren JE, Jochems A, Dubois L, et al. Tracking tumor biology with radiomics: a systematic review utilizing a radiomics quality score. Radiother. Oncol.; 2018. p. 349–360. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 19.Cook GJR, Azad G, Owczarczyk K, Siddique M, Goh V. Challenges and promises of PET radiomics. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018;102:1083–9. [cited 2019 Dec 11] Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29395627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 20.Zwanenburg A. Radiomics in nuclear medicine: robustness, reproducibility, standardization, and how to avoid data analysis traps and replication crisis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019;46:2638–55. [cited 2019 Dec 11] Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31240330. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 21.Castiglioni I, Gilardi MC. Radiomics: is it time to compose the puzzle? Clin Transl Imaging. 2018;6:411–3. [cited 2019 Dec 11] Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30416989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 22.Gatta R, Depeursinge A, Ratib O, Michielin O, Leimgruber A. Integrating radiomics into holomics for personalised oncology: from algorithms to bedside. Eur. Radiol. Exp; 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 23.Duron L, Balvay D, Perre S Vande, Bouchouicha A, Savatovsky J, Sadik JC, et al. Gray-level discretization impacts reproducible MRI radiomics texture features. PLoS One; 2019;14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 24.Mayerhoefer ME, Materka A, Langs G, Häggström I, Szczypiński P, Gibbs P, et al. Introduction to radiomics. J. Nucl. Med. NLM (Medline); 2020. p. 488–95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 25.Traverso A, Wee L, Dekker A, Gillies R. Repeatability and reproducibility of radiomic features: a systematic review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018;102:1143–1158. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.05.053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bailly C, Bodet-Milin C, Couespel S, Necib H, Kraeber-Bodéré F, Ansquer C, et al. Revisiting the robustness of PET-based textural features in the context of multi-centric trials. PLoS One. 2016;11:154–191. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Orlhac F, Thézé B, Soussan M, Boisgard R, Buvat I. Multiscale texture analysis: from 18F-FDG PET images to histologic images. J Nucl Med. 2016;57:1823–8. [cited 2019 Dec 11] Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27261515. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 28.Tixier F, Hatt M, Le Rest CC, Le Pogam A, Corcos L, Visvikis D. Reproducibility of tumor uptake heterogeneity characterization through textural feature analysis in 18F-FDG PET. J Nucl Med. J Nucl Med. 2012;53:693–700. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.111.099127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Leijenaar RTH, Carvalho S, Velazquez ER, Van Elmpt WJC, Parmar C, Hoekstra OS, et al. Stability of FDG-PET radiomics features: an integrated analysis of test-retest and inter-observer variability. Acta Oncol (Madr) 2013;52:1391–1397. doi: 10.3109/0284186X.2013.812798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.van Velden FHP, Kramer GM, Frings V, Nissen IA, Mulder ER, de Langen AJ, et al. Repeatability of radiomic features in non-small-cell lung cancer [18F]FDG-PET/CT studies: impact of reconstruction and delineation. Mol Imaging Biol. 2016;18:788–795. doi: 10.1007/s11307-016-0940-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Weber WA, Gatsonis CA, David Mozley P, Hanna LG, Shields AF, Aberle DR, et al. Repeatability of 18F-FDG PET/CT in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: prospective assessment in 2 multicenter trials. J Nucl Med. 2015;56:1137–1143. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.114.147728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Jodal L, Le Loirec C, Champion C. Positron range in PET imaging: an alternative approach for assessing and correcting the blurring. Phys Med Biol. 2012;57:3931–43. [cited 2020 Nov 22] Available from: http://iopscience.iop.org/0031-9155/57/12/3931. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 33.Bailly C, Bodet-Milin C, Couespel S, Necib H, Kraeber-Bodéré F, Ansquer C, et al. Revisiting the robustness of PET-based textural features in the context of multi-centric trials. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0159984. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lindström E, Lindsjö L, Sundin A, Sörensen J, Lubberink M. Evaluation of block-sequential regularized expectation maximization reconstruction of 68Ga-DOTATOC, 18F-fluoride, and 11C-acetate whole-body examinations acquired on a digital time-of-flight PET/CT scanner. EJNMMI Phys. Springer; 2020 [cited 2020 Nov 18];7. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32542512/. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 35.Kroiss A, Putzer D, Decristoforo C, Uprimny C, Warwitz B, Nilica B, et al. 68Ga-DOTA-TOC uptake in neuroendocrine tumour and healthy tissue: Differentiation of physiological uptake and pathological processes in PET/CT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging; 2013 [cited 2020 Nov 22];40:514–23. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23291643/. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 36.Balon HR, Brown TLY, Goldsmith SJ, Silberstein EB, Krenning EP, Lang O, et al. The SNM practice guideline for somatostatin receptor scintigraphy 2.0. J Nucl Med Technol. 2011;39:317–324. doi: 10.2967/jnmt.111.098277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Oberg K, Modlin IM, De Herder W, Pavel M, Klimstra D, Frilling A, et al. Consensus on biomarkers for neuroendocrine tumour disease. Lancet Oncol; 2015; e435–46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 38.Bozkurt MF, Virgolini I, Balogova S, Beheshti M, Rubello D, Decristoforo C, et al. Guideline for PET/CT imaging of neuroendocrine neoplasms with 68Ga-DOTA-conjugated somatostatin receptor targeting peptides and 18F–DOPA. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017;44:1588–1601. doi: 10.1007/s00259-017-3728-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nioche C, Orlhac F, Boughdad S, Reuze S, Goya-Outi J, Robert C, et al. Lifex: a freeware for radiomic feature calculation in multimodality imaging to accelerate advances in the characterization of tumor heterogeneity. Cancer Res. 2018;78:4786–4789. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chan TF, Vese LA. Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2001;10:266–277. doi: 10.1109/83.902291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Toriihara A, Baratto L, Nobashi T, Park S, Hatami N, Davidzon G, et al. Prognostic value of somatostatin receptor expressing tumor volume calculated from 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT in patients with well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019;46:2244–2251. doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-04455-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Foster B, Bagci U, Mansoor A, Xu Z, Mollura DJ. A review on segmentation of positron emission tomography images. Comput. Biol. Med; 2014. p. 76–96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 43.Boellaard R, Delgado-Bolton R, Oyen WJG, Giammarile F, Tatsch K, Eschner W, et al. FDG PET/CT: EANM procedure guidelines for tumour imaging: version 2.0. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2015. p. 328–54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 44.Zwanenburg A, Leger S, Vallières M, Löck S. Image biomarker standardisation initiative. 2016 [cited 2020 Jan 10]; Available from: http://arxiv.org/abs/1612.07003.
- 45.Leijenaar RTH, Nalbantov G, Carvalho S, Van Elmpt WJC, Troost EGC, Boellaard R, et al. The effect of SUV discretization in quantitative FDG-PET Radiomics: the need for standardized methodology in tumor texture analysis. Sci Rep. 2015;5:1–10. doi: 10.1038/srep11075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Orlhac F, Soussan M, Chouahnia K, Martinod E, Buvat I. 18F-FDG PET-derived textural indices reflect tissue-specific uptake pattern in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One. Public Library of Science; 2015 [cited 2020 Feb 18];10:e0145063. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26669541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 47.Orlhac F, Nioche C, Soussan M, Buvat I. Understanding changes in tumor texture indices in PET: a comparison between visual assessment and index values in simulated and patient data. J Nucl Med; 2017;58:387–92. [cited 2020 Feb 18] Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27754906. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 48.Warfield SK, Zou KH, Wells WM. Simultaneous truth and performance level estimation (STAPLE): an algorithm for the validation of image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2004;23:903–921. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2004.828354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Koo TK, Li MY. A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J Chiropr Med. Elsevier USA. 2016;15:155–163. doi: 10.1016/j.jcm.2016.02.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Pfaehler E, van Sluis J, Merema BBJ, van Ooijen P, Berendsen RCM, van Velden FHP, et al. Experimental multicenter and multivendor evaluation of the performance of PET radiomic features using 3-dimensionally printed phantom inserts. J Nucl Med. NLM (Medline); 2020;61:469–76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 51.RFSC. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. 2008 [cited 2020 Feb 28]. Available from: https://www.gbif.org/tool/81287/r-a-language-and-environment-for-statistical-computing.
- 52.Altazi BA, Zhang GG, Fernandez DC, Montejo ME, Hunt D, Werner J, et al. Reproducibility of F18-FDG PET radiomic features for different cervical tumor segmentation methods, gray-level discretization, and reconstruction algorithms. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2017;18:32–48. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Bashir U, Azad G, Siddique MM, Dhillon S, Patel N, Bassett P, et al. The effects of segmentation algorithms on the measurement of 18F-FDG PET texture parameters in non-small cell lung cancer. EJNMMI Res. 2017;7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 54.Biehl KJ, Kong FM, Dehdashti F, Jin JY, Mutic S, El Naqa I, et al. 18F-FDG PET definition of gross tumor volume for radiotherapy of non-small cell lung cancer: is a single standardized uptake value threshold approach appropriate? Society of Nuclear Medicine. 2006;47:1808–1812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Werner RA, Lapa C, Ilhan H, Higuchi T, Buck AK, Lehner S, et al. Survival prediction in patients undergoing radionuclide therapy based on intratumoral somatostatin-receptor heterogeneity. Oncotarget. 2017;8:7039–7049. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Werner RA, Ilhan H, Lehner S, Papp L, Zsótér N, Schatka I, et al. Pre-therapy Somatostatin receptor-based heterogeneity predicts overall survival in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor patients undergoing peptide receptor radionuclide therapy. Mol Imaging Biol. 2019;21:582–590. doi: 10.1007/s11307-018-1252-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Weber M, Kessler L, Schaarschmidt B, Fendler WP, Lahner H, Antoch G, et al. Textural analysis of hybrid DOTATOC-PET/MRI and its association with histological grading in patients with liver metastases from neuroendocrine tumors. Nucl Med Commun. 2020;41:363–369. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0000000000001150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Weber M, Kessler L, Schaarschmidt B, Fendler WP, Lahner H, Antoch G, et al. Treatment-related changes in neuroendocrine tumors as assessed by textural features derived from 68Ga-DOTATOC PET/MRI with simultaneous acquisition of apparent diffusion coefficient. BMC Cancer; 2020 [cited 2020 Oct 6];20. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32299391/. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 59.Werner-Wasik M, Nelson AD, Choi W, Arai Y, Faulhaber PF, Kang P, et al. What is the best way to contour lung tumors on PET scans? Multiobserver validation of a gradient-based method using a NSCLC digital PET phantom. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;82:1164–1171. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.12.055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Halt M, Le Rest CC, Turzo A, Roux C, Visvikis D. A fuzzy locally adaptive Bayesian segmentation approach for volume determination in PET. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2009;28:881–893. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2008.2012036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Parmar C, Leijenaar RTH, Grossmann P, Velazquez ER, Bussink J, Rietveld D, et al. Radiomic feature clusters and prognostic signatures specific for lung and head &neck cancer. Sci Rep. 2015;5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 62.Messerli M, Kotasidis F, Burger IA, Ferraro DA, Muehlematter UJ, Weyermann C, et al. Impact of different image reconstructions on PET quantification in non-small cell lung cancer: a comparison of adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Radiol. 2019;92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 63.Lu L, Lv W, Jiang J, Ma J, Feng Q, Rahmim A, et al. Robustness of radiomic features in [11C]choline and [18F]FDG PET/CT imaging of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: impact of segmentation and discretization. Mol Imaging Biol. 2016;18:935–45. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 64.Binderup T, Knigge U, Loft A, Federspiel B, Kjaer A. 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography predicts survival of patients with neuroendocrine tumors. Clin Cancer Res. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:978–985. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Oberg K, Krenning E, Sundin A, Bodei L, Kidd M, Tesselaar M, et al. A delphic consensus assessment: imaging and biomarkers in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumor disease management. Endocr Connect. 2016;5:174–87. [cited 2020 Feb 7] Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27582247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 66.Radiomics: the bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. - PubMed - NCBI. [cited 2020 Feb 7]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Lambin++Radiomics%3A+the+bridge+between+medical+imaging+and+personalized+medicine. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 67.Geets X, Lee JA, Bol A, Lonneux M, Grégoire V. A gradient-based method for segmenting FDG-PET images: Methodology and validation. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2007;34:1427–38. [cited 2020 Jan 9] Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17431616. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1. LifeX radiomic features description according to the Imaging Biomarker Standardization Initiative (IBSI) description (update 17 December 2019). LifeX version was 4.81. Figure S1. Box plots showing the distribution of SUVmax (panel A) and Volume (panel B). Figure S2. (A) Bar diagrams of intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) values of RFs for robustness to SUVmax thresholding. Bars show the median ICC between the different segmentations for the absolute intensity rescale factor AR60. Range error bars (in black) encompass the lowest and highest values for different operators. (B) Boxplot of COVL for different threshold (20, 30, 40%) for each RFs, for the first operator (results superposable for the other operators). TLG (total lesion glycolysis) conventional parameter in our study corresponds to the TLSRE (total lesion somatostatin receptor expression). Figure S3. Radiomic features with moderate or poor consistency (ICC < 0.80), but high agreement (median COVL < 10%) to intensity discretization. The RFs were: GLCM_Entropy_log2, GLCM_Entropy_log10 (not shown), GLRLM_SRE, GLRLM_LRE and GLRLM_RP. Value of the RFs for each lesion are presented in the top row; boxplots of COVL for the first operator are presented in the bottom row. Figure S4. Radiomic features with high consistency (ICC > 0.90), but low agreement (median COVL > 10%) to SUVmax thresholds (0, 20, 30 and 40%). The RFs were: GLRLM_LGRE, GLRLM_SRLGE, GLZLM_LGZE and GLZLM_LZLGE. Value of the RFs for each lesion are presented in the top row; boxplots of COVL for the first operator are presented in the bottom row. Figure S5. Boxplot showing the distribution of RF value for each operator. The three RFs chosen are the most representative of the impact of segmentation on ICC. Segmentation did not affect SUVmean (A) and TLG (B) in terms of ICC, although TLG was characterized by not negligible dispersion (percentage of COVL) in our study. In contrast, segmentation had a high impact on GLZLM_SZLGE (C) in terms of both ICC and COVL. Mean COVL of SUVmean, TLG and GLZLM_SZLGE was 8.33±3.96, 13.38±8.52 and 30.67±27.29, respectively.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.