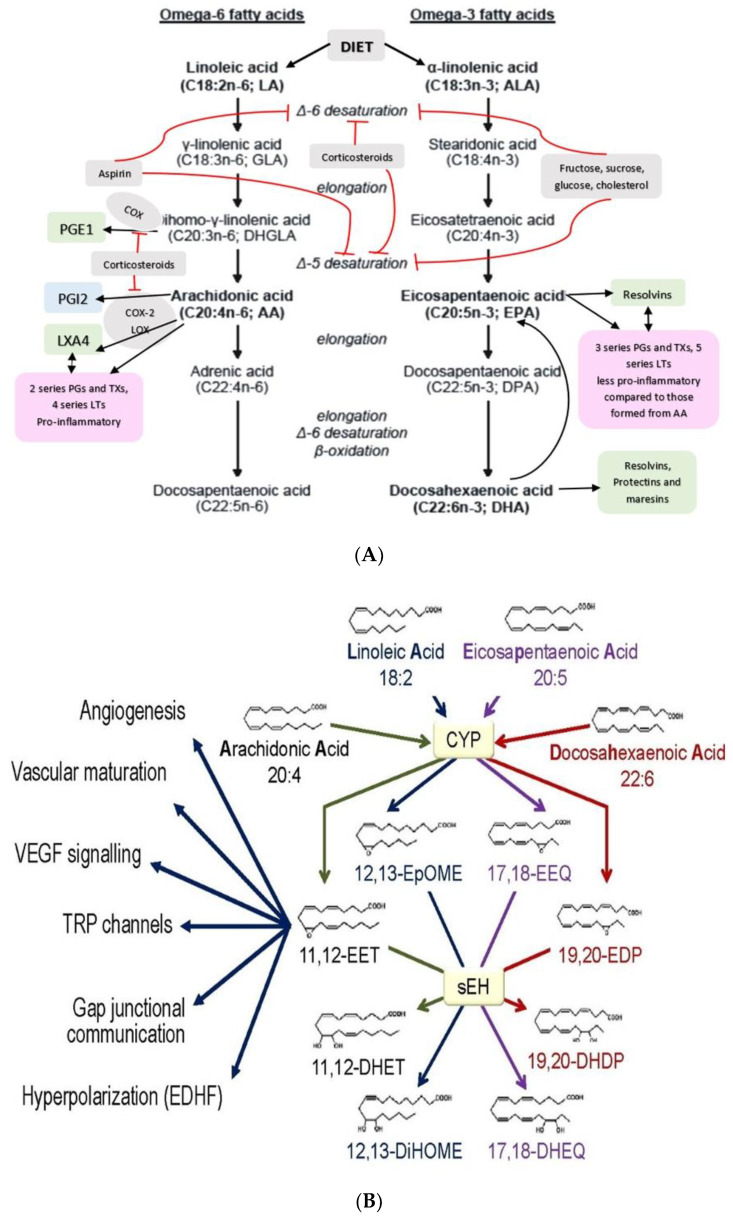
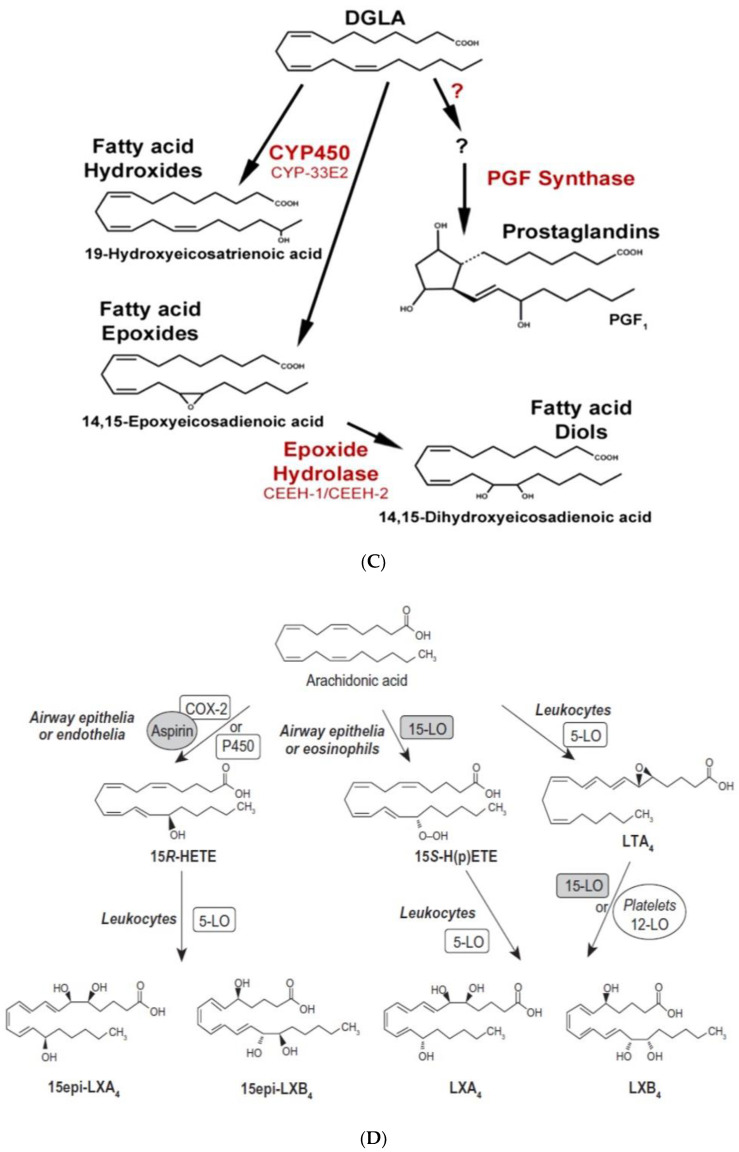
Figure 2.
(A) Scheme showing metabolism of essential fatty acids and their important products. (B) Scheme showing metabolism of AA, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) by cytochrome P450 enzymes. DHA, alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), LXA4 and possibly, other bioactive lipids (BALs) may inhibit sEH enzyme and thus, bring about some of their beneficial actions. Some of the beneficial actions of metabolites of AA, EPA and DHA formed due to the action of cytochrome P450 enzymes (such as 11,12-EET) is also shown. (C) Metabolism of dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid (DGLA) by cytochrome P450 enzymes. (D) Scheme showing the formation of leukotrienes (LTs) and lipoxins (LXs) in various types of cells from arachidonic acid. Similar metabolism occurs regarding EPA and DHA to form resolvins, protectins and maresins. Note the conversion of 15S-H(p)ETE to LXA4 and LTA4 to LXA4/LXB4 by the action of 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) and 12-lipoxygenase (12-LO). This could be one potential mechanism by which leukocytes and platelets at the site of inflammation can convert pro-inflammatory leukotrienes to anti-inflammatory lipoxins and thus, initiate resolution of inflammation.