Abstract
Background
Evidence has been shown that long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) play an important role in the development of cervical cancer. Recently, lncRNA DARS-AS1 was reported to be dysregulated in several cancer types; however, the role of DARS-AS1 in cervical cancer remains unclear.
Methods
Flow cytometry and transwell invasion assays were performed to determine the apoptosis and invasion in cervical cancer cells. In addition, RNA pull-down and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) assays were conducted to assess the interaction between DARS-AS1 and IGF2BP3 in cervical cancer cells.
Results
Downregulation of DARS-AS1 significantly induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in cervical cancer cells. Meanwhile, the invasion ability of cervical cancer cells was inhibited by DARS-AS1 knockdown as well. RNA pull-down and FISH results showed that DARS-AS1 interacted with IGF2BP3. Mechanistically, DARS-AS1 positively regulated IGF2BP3 expression via stabilization of IGF2BP3 mRNA. Rescue assays confirmed that DARS-AS1 regulated the progression of cervical cancer through interacting with IGF2BP3 in vitro. In addition, in vivo experiments revealed that downregulation of DARS-AS1 inhibited tumor growth in SiHa xenograft model.
Conclusion
In this study, we found that downregulation of DARS-AS1 could inhibit the growth of cervical cancer cells via inhibition of IGF2BP3, suggesting DARS-AS1 might serve as a potential target for the treatment of cervical cancer.
Keywords: cervical cancer, lncRNAs, DARS-AS1, IGF2BP3, apoptosis
Introduction
Cervical cancer is one of the most common female malignancies worldwide and is one of the major causes of cancer death among women worldwide.1,2 History of smoking, parity, use of contraceptive methods and history of sexually transmitted disease are the main risk factors of cervical cancer.1,3 In addition, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is a necessary etiological agent of cervical cancer.4,5 Normally, cervical cancer could be prevented by cervical screening and HPV vaccination.6 However, the uptake of the HPV vaccine among adolescent females was about 34% in more-developed regions, but less than 3% in less-developed regions.7 It is estimated that there are still approximately 530,000 new cases and nearly 275,000 deaths due to cervical cancer annually.8 Moreover, incidence and mortality rates of cervical cancer elevated dramatically in China, particularly in young females.9 Therefore, the identification of novel promising targets may help to explore the strategy of diagnosis and treatment for patients with cervical cancer.
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are a class of noncoding RNAs with more than 200 nucleotides in length.10 It has been shown that some lncRNAs are dysregulated in multiple human cancers and may serve as useful diagnostic and prognostic markers for a variety of cancer types.11,12 In addition, lncRNAs have been shown to involve in a large variety of biological processes such as cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion.13,14 LncRNA DARS-AS1 has been found to play an oncogenic role in various human cancers including ovarian cancer and myeloma,15,16 however, the role and the regulatory mechanism of DARS-AS1 in cervical cancer remains unclear. Thus, this study aimed to investigate the role of DARS-AS1 in the progression of cervical cancer.
Materials and Methods
Cell Culture and Transfection
The human cervical cancer cell lines SiHa and Hela were obtained from Type Culture Collection of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China). Cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM, cat. no. 11965092; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, cat. no. 10091148; Thermo Fisher Scientific) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (cat. no. 15070063; Thermo Fisher Scientific), and maintained in atmosphere containing 5% CO2 at 37°C.
The DARS-AS1-siRNA1, DARS-AS1-siRNA2, siRNA negative control (siRNA-ctrl) were purchased from Guangzhou RiboBio Co., Ltd (Guangzhou, China). The DARS-AS1 siRNA1, DARS-AS1 siRNA2 and siRNA-ctrl were transfected into SiHa and Hela cells using Lipofectamine 2000 (cat. no. 11668019; Thermo Fisher Scientific) for 24 h according to the manufacturer’s protocols.
Lentivirus Infection
The IGF2BP3-overexpressing and control lentiviruses were obtained from RiboBio Co., Ltd (Guangzhou, China), named IGF2BP3-OE and vector-control. The 293 T cells (Type Culture Collection of the Chinese Academy of Sciences) were transfected with lentivirus carrying IGF2BP3 gene, lentiviral packaging plasmid (pAX2) and envelope plasmid (pMD2.G). After 72 h of incubation, virus-containing supernatant was collected, and the supernatant was used for infection of SiHa or Hela cells in the presence of 8 μg/mL polybrene (cat. no. sc-134220; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA). After 72 h of transduction, infected cells were cultured with 2.5 μg/mL puromycin (cat. no. A1113803; Thermo Fisher Scientific) to select stable IGF2BP3-overexpressing cells.
Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
The total RNA from SiHa and Hela cells was extracted using TRIzol reagent (cat. no. 15596018; Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. After that, total RNA was reverse transcribed into cDNA using the EntiLink™ 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (cat. no. EQ003; ELK Biotechnology, Hubei, China). Later on, real-time PCR was performed on the StepOnePlus System (Applied Biosystems, CA) using an EnTurbo™ SYBR Green PCR SuperMix reagent (cat. no. EQ001; ELK Biotechnology). The relative expressions of DARS-AS1, SRSF1, TAF15, ELAVL1, IGF2BP3, U2AF2 were calculated on the basis of 2−ΔΔCt method and β-actin was treated as an internal control. The primer pairs were as follows: DARS-AS1, forward: 5ʹ-CCACCTGTATCAGAATCCCATG-3ʹ; reverse: 5ʹ-TCCCACTTTTGAGTGAGAACATG-3ʹ. SRSF1, forward: 5ʹ-GCGACGGCTATGATTACGATG-3ʹ; reverse: 5ʹ-ACATACATCACCTGCTTCACGC-3ʹ. TAF15, forward: 5ʹ-GCAGCCATTGACTGGTTTGA-3ʹ; reverse: 5ʹ-GATTAGGGCAAACCCAATCC-3ʹ. ELAVL1, forward: 5ʹ-GTTTGGGCGGATCATCAACT-3ʹ; reverse: 5ʹ-GATGGGCTCAGAGGAACCTG-3ʹ. IGF2BP3, forward: 5ʹ-CTGCGGCTTGTAAGTCTATTCTG-3ʹ; reverse: 5ʹ-TCCTGCAATGGAGATATCGTG-3ʹ. U2AF2, forward: 5ʹ-CATCTTCCAGGGCCAGTCAC-3ʹ; reverse: 5ʹ-GTTCAGGTAGTTGGGTAAGCCC-3ʹ. β-actin, forward: 5ʹ-GTCCACCGCAAATGCTTCTA-3ʹ; reverse; 5ʹ-TGCTGTCACCTTCACCGTTC-3ʹ.
Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) Assay
Cell viability was determined using the CCK-8 assay. SiHa and Hela cells were transfected with DARS-AS1-siRNA1 and DARS-AS1-siRNA2 for 48 h. Later on, 10 μL of the CCK-8 reagent (cat. no. CK04; Dojindo Molecular Technologies, Inc., Kyushu, Japan) was added into each well, and cells were incubated for another 2 h. Subsequently, the absorbance of each well was measured at the wavelength of 450 nm using a microplate reader (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
Colony Formation Assay
SiHa and Hela cells (5 × 103 cells/well) were plated onto 6-well plates and cultured for 2 weeks at 37°C. After that, cells were stained with methylene blue solution for 1 h at room temperature. Subsequently, images were observed using a fluorescence microscope (Leica, Buffalo Grove, IL, USA) and the number of cell colonies and clusters were counted.
Validation of Gene Expression Based on the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) Database
A newly interactive web server GEPIA (http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/detail.php), for analyzing the RNA sequencing expression data of tumors and normal samples from the TCGA and the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) projects was used to explore the expression of IGF2BP3 between cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CESC) and adjacent normal tissue samples.17
Western Blot Assay
The protein concentration was quantified by the BCA Protein Assay Kit (cat. no. P0012; Beyotime, China). After that, 40 μg of each protein samples was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and then electrotransferred to a PVDF membrane (cat. no. 05317; Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). After blocking with 5% skim milk in TBST at room temperature for 1 h, the membrane was incubated with primary antibodies IGF2BP3 (cat. no. ab177477; 1:1000, Abcam Cambridge, MA, USA), c-Myc (cat. no. ab32072; 1;1000, Abcam), CDK6 (cat. no. ab124821; 1:1000, Abcam), β-actin (cat. no. ab8227; 1:1000, Abcam) at 4°C overnight. Later on, the membrane was incubated with HRP-conjugated goat-anti-rabbit secondary antibody (cat. no. ab7090; 1:5000, Abcam) at room temperature for 1 h. Subsequently, protein signals were visualized by an enhanced chemiluminescent substrate kit (cat. no. WP20005; Thermo Fisher Scientific).
RNA Pull-Down Assay
DARS-AS1 sequence was in vitro transcribed with biotin RNA-labeling mix (cat. no. 11685597910; Roche, Mannheim, Germany) and T7 RNA polymerase (cat. no. p2075; Promega, Madison, WI, USA). After that, biotinylated DARS-AS1 RNA were incubated with the total cell lysate and streptavidin-coated magnetic beads (cat. no. 29000701011150; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) for 2 h. Then, RNA-protein complexes were pulled down with streptavidin-coated magnetic beads. Subsequently, Western blot assay was conducted to analyze the abundance of IGF2BP3 in bound fractions.
RNA Fluorescence in situ Hybridization (FISH)
Fluorescence-conjugated DARS-AS1 probe was used for FISH, which was performed as described previously.18 Images were observed using a fluorescence microscope (Leica).
Immunofluorescence Assay
SiHa cells were permeabilized with 0.3% Triton X-100 for 15 min at room temperature. After that, cells were incubated with an IGF2BP3 antibody (Abcam) overnight at 4°C. Later on, cells were incubated with a goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody (cat. no. ab150077; Abcam) at 37°C for 1 h. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI for 15 min at room temperature. Subsequently, cells were observed with a fluorescence microscope (Leica).
Flow Cytometry Assay
For detection of cell apoptosis, SiHa and Hela cells were stained with 5 μL of annexin V-FITC and 5 μL of propidium iodide (PI) using the FITC Annexin V/Dead cell apoptosis kit (cat. no. V13242; Thermo Fisher Scientific). Subsequently, the percentage of apoptotic cells was analyzed on the flow cytometry (FACScan; BD Biosciences, Franklin Lake, NJ, USA) using the CellQuest software (BD Biosciences).
For detection of cell cycle, SiHa cells were stained with PI/RNase Staining Buffer (cat. no. F10797; Thermo Fisher Scientific) for 30 min, and then cell cycle distribution was analyzed by flow cytometry (FACScan; BD Biosciences).
Transwell Invasion Assay
Cell invasion was analyzed using 24‐well transwell chambers (0.8 μm; Corning Incorporated, Corning, New York, NY, USA). SiHa and Hela cells were seed into the upper chamber pre-coated with matrigel (cat. no. 356234; BD Biosciences), and DMEM medium containing 10% FBS was added into the lower chamber. After 24 h of incubation, the cells on the lower surface of the chamber were stained with 0.2% crystal violet for 20 min. Subsequently, cells were imaged using a fluorescence microscope (Leica). ImageJ software was used to quantify the number of invasive cells.
Animal Study
BALB/c nude mice (4–6-weeks old) were purchased from the Shanghai SLAC Animal Center (Shanghai, China). All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Ethical Committee of the 2nd Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University (No. D20190408), and animals were maintained following the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 1 × 107 SiHa cells (in 100 μL of PBS) were injected subcutaneously into the left flank of nude mice. When the tumors reach about 200 mm3, animals were randomized into 2 groups: control and DARS-AS1 siRNA2 group. 50 nM siRNA control or 50 nM DARS-AS1 siRNA2 was directly injected into the tumors of mice in control or DARS-AS1 siRNA2 group twice a week, respectively. Tumor volume was monitored weekly with a caliper and tumor size was calculated as following: volume = length × width2/2. After 4 weeks’ treatment, mice were sacrificed, and the neoplasm was excised for weighting.
Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism software (version 7.0, La Jolla, CA, USA). The comparison between two groups was analyzed by Student’s t-test. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey’s tests were carried out for multiple group comparisons. Data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (S.D.) and all experiments were performed at least three times. *P < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Downregulation of DARS-AS1 Inhibits the Proliferation of Cervical Cancer Cells
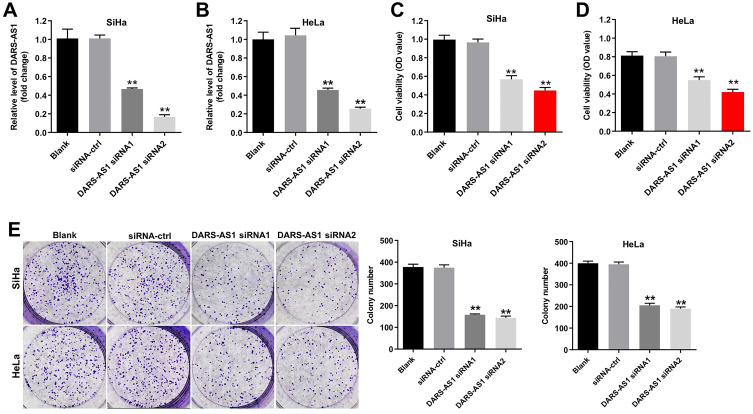
To investigate the role of DARS-AS1 in cervical cancer cells, we knockdown of DARS-AS1 in SiHa and HeLa with siRNAs. As shown in Figure 1A and B, the level of DARS-AS1 was markedly decreased in SiHa and Hela cells following transfection with DARS-AS1-siRNA1 or DARS-AS1-siRNA2. In addition, CCK-8 and colony formation assays indicated that downregulation of DARS-AS1 notably suppressed the viability and proliferation of SiHa and HeLa cells (Figure 1C–E). These data suggested that downregulation of DARS-AS1 could inhibit the proliferation of cervical cancer cells. Regarding as knockdown efficacy, DARS-AS1-siRNA2 was much better than DARS-AS1-siRNA1 in SiHa and HeLa cells (Figure 1A and B). Thus, DARS-AS1-siRNA2 was utilized in the following experiments.
Figure 1.
Downregulation of DARS-AS1 inhibits the proliferation of cervical cancer cells. SiHa and HeLa cells were transfected with DARS-AS1-siRNA1 or DARS-AS1-siRNA2, respectively. (A and B) The level of DARS-AS1 in SiHa and HeLa cells was analyzed by RT-qPCR. (C and D) Cell viability was analyzed by CCK-8 assay. (E) Colony formation assay was used to determine the cell proliferation. **P < 0.01, compared with the siRNA-ctrl group.
DARS-AS1 Interacts with IGF2BP3 in SiHa Cells
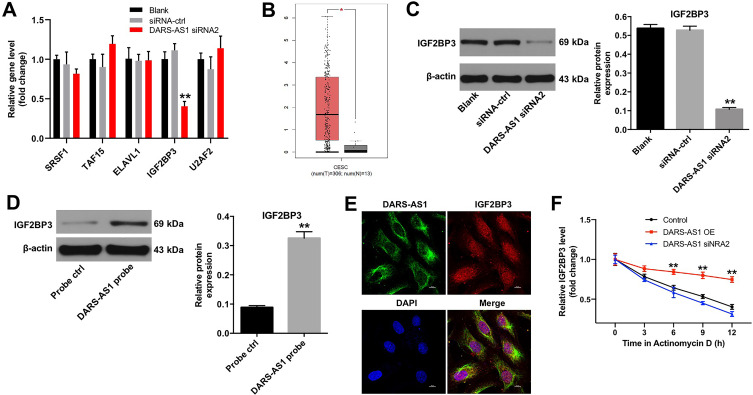
Evidence has been shown that most of the lncRNA mechanisms involve RNA–protein interactions.19 The data in Starbase (http://starbase.sysu.edu.cn) indicated that RNA binding proteins SRSF1, TAF15, ELAVL1, IGF2BP3 and U2AF2 were closely associated with DARS-AS1. In addition, RT-qPCR results indicated that downregulation of DARS-AS1 markedly decreased the level of IGF2BP3 in SiHa cells; however, the expressions of SRSF1, TAF15, ELAVL1 and U2AF2 were not affected (Figure 2A). Moreover, the expression of IGF2BP3 in patients with cervical cancer in GEPIA dataset was downloaded. The data revealed that IGF2BP3 levels in 306 CESC tissues were higher than that in 13 normal tissues (Figure 2B). Base on UCSC database (http://genome.ucsc.edu/), we found that IGF2BP3 was a nearby gene for DARS-AS1 (Supplementary Figure 1). Meanwhile, downregulation of DARS-AS1 notably suppressed the expression of IGF2BP3 in SiHa cells (Figure 2C). Furthermore, the results of RNA pull-down assay manifested that IGF2BP3 was pulled down by biotin-labeled DARS-AS1 (Figure 2D). The FISH and immunofluorescence assays indicated that DARS-AS1 and IGF2BP3 were partially co-localized in the cytoplasm (Figure 2E). All these results indicated that DARS-AS1 directly interacted with IGF2BP3. Additionally, we found that overexpression of DARS-AS1 led to the fortified mRNA stability of IGF2BP3, while knockdown of DARS-AS1 decreased IGF2BP3 mRNA stability in SiHa cells (Figure 2F). Taken together, these results suggested that DARS-AS1 modulated IGF2BP3 via regulating the mRNA stability of IGF2BP3.
Figure 2.
DARS-AS1 interacts with IGF2BP3 in SiHa cells. (A) SiHa cells were transfected with DARS-AS1-siRNA2 for 72 h. RT-qPCR was used to detect the levels of SRSF1, TAF15, ELAVL1, IGF2BP3 and U2AF2 in SiHa cells. **P < 0.01, compared with the siRNA-ctrl group. (B) Relative expression of IGF2BP3 expression in CESC tissues (n = 306), T and in normal tissues (n = 13), N in TCGA dataset. *P < 0.05. (C) SiHa cells were transfected with DARS-AS1-siRNA2 for 72 h. Western blot assay was used to detect the expression of DARS-AS1 in SiHa cells. **P < 0.01, compared with the siRNA-ctrl group. (D) RNA pull-down analysis determined the IGF2BP3−DARS-AS1 interaction. **P < 0.01, compared with the probe ctrl group. (E) The cellular localization of DARS-AS1 and IGF2BP3 in SiHa cells was analyzed using FISH and immunofluorescence assays. FISH analysis of DARS-AS1 (green) and immunofluorescence detection of IGF2BP3 (red) in SiHa cells. (F) SiHa cells were treated with actinomycin D to reduce the mRNA generation. RT-qPCR assay was applied to determine the mRNA stability of IGF2BP3 upon the upregulation and downregulation of DARS-AS1. **P < 0.01, compared with the control group.
Establishment of IGF2BP3 Overexpressing Cervical Cancer Cells
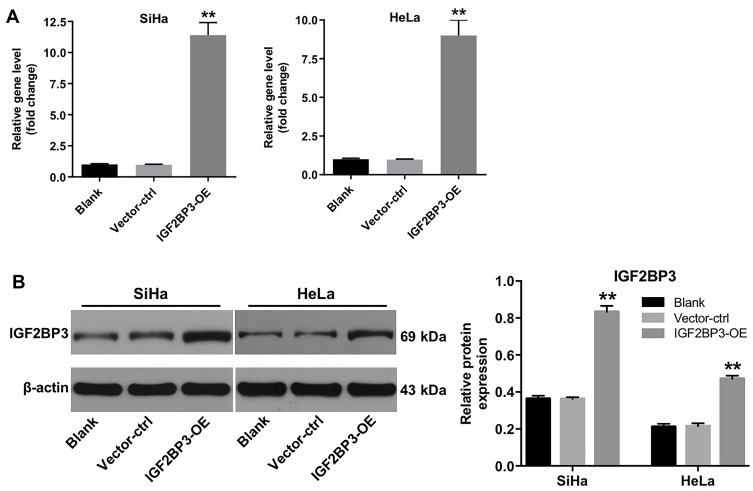
Next, we established cervical cancer cell lines (SiHa and HeLa) with IGF2BP3 stable overexpression. The 293 T cells were transfected with lentivirus carrying IGF2BP3 gene. After that, the virus-containing cell supernatant was then used for transduction of SiHa and HeLa cells. Subsequently, the lentivirus-transduced cells were cultured with puromycin to select stable IGF2BP3-overexpressing cells. As shown in Figure 3A and B, RT-qPCR and Western blot assays showed that the mRNA and protein levels of IGF2BP3 were significantly increased in IGF2BP3-overexpressing SiHa and HeLa cells, respectively. These data suggested that IGF2BP3 was successfully overexpressed in cervical cancer cells.
Figure 3.
IGF2BP3 is overexpressed in cervical cancer cells. SiHa and HeLa cells were infected with IGF2BP3-OE plasmids, respectively. (A) The level of IGF2BP3 in SiHa and HeLa cells was analyzed by RT-qPCR. (B) The expression of IGF2BP3 in SiHa and HeLa cells were analyzed by Western blotting. **P < 0.01, compared with the vector-ctrl group.
Downregulation of DARS-AS1 Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Invasion in Cervical Cancer Cells via Inhibition of IGF2BP3
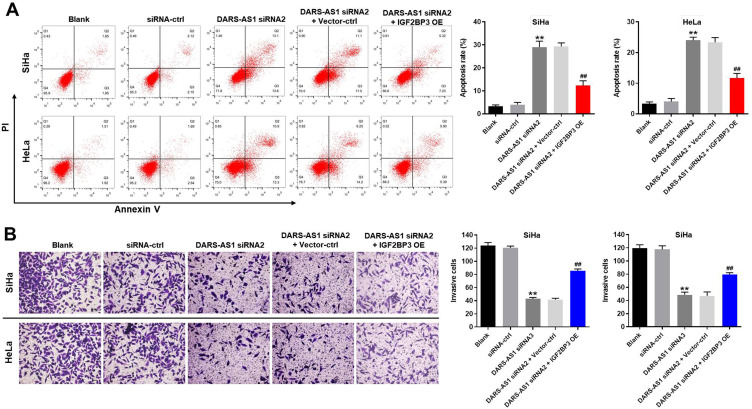
Previous studies have indicated that IGF2BP3 is overexpressed in human cancer cells.20 Hence, we wondered whether downregulation of DARS-AS1 inhibited the growth of cervical cancer cells via interacting with IGF2BP3. As shown in Figure 4A, downregulation of DARS-AS1 markedly induced the apoptosis of SiHa and HeLa cells; however, this phenomenon was partially reversed by IGF2BP3 overexpression. Interestingly, IGF2BP3 overexpression alone caused no major change in apoptosis in SiHa and Hela cells (Supplementary Figure 2A). In addition, downregulation of DARS-AS1 obviously inhibited the invasive ability of SiHa and HeLa cells; however, that effect was partially reversed by IGF2BP3 overexpression (Figure 4B). These results illustrated that downregulation of DARS-AS1 could induce apoptosis and inhibit invasion in cervical cancer cells via interacting with IGF2BP3.
Figure 4.
Downregulation of DARS-AS1 induces apoptosis and inhibits invasion of cervical cancer cells via inhibition of IGF2BP3. SiHa and HeLa cells were transfected with DARS-AS1-siRNA2 or DARS-AS1-siRNA2 + IGF2BP3-OE plasmids, respectively. (A) Apoptotic cells were detected by flow cytometry. (B) Cell invasion was detected using transwell invasion assay. **P < 0.01, compared with the siRNA-ctrl group. ##P < 0.01, compared with the DARS-AS1 siRNA2 group.
Downregulation of DARS-AS1 Induces Cell Cycle Arrest in Cervical Cancer Cells via Inhibition of IGF2BP3
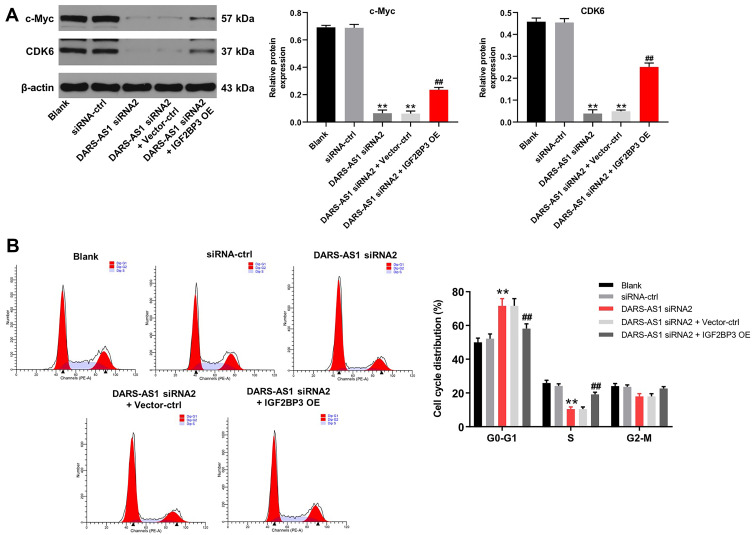
We next investigated whether DARS-AS1 could regulate cell cycle distribution in cervical cancer cells via interacting with IGF2BP3. Western blot assays indicated that downregulation of DARS-AS1 significantly decreased the expressions of c-Myc and CDK6 in SiHa cells, and these changes were partially reversed by IGF2BP3 overexpression (Figure 5A). In addition, downregulation of DARS-AS1 notably increased the percentage of SiHa cells in G0/G1 phase but decreased the percentage of cells in S-phase; however, these changes were partially reversed by IGF2BP3 overexpression (Figure 5B). Interestingly, IGF2BP3 overexpression caused no major difference in cell cycle distribution in SiHa cells (Supplementary Figure 2B). These data suggested that downregulation of DARS-AS1 could induce cell cycle arrest in cervical cancer cells via inhibition of IGF2BP3.
Figure 5.
Downregulation of DARS-AS1 induces cell cycle arrest in cervical cancer cells via inhibition of IGF2BP3. SiHa and HeLa cells were transfected with DARS-AS1-siRNA2 or DARS-AS1-siRNA2 + IGF2BP3-OE plasmids, respectively. (A) The expressions of c-Myc and CDK6 in SiHa cells were analyzed by Western blotting. The relative expressions of c-Myc and CDK6 in SiHa cells were normalized to β-actin, respectively. (B) Flow cytometry was used to analyze cell cycle distribution. **P < 0.01, compared with the siRNA-ctrl group; ##P < 0.01, compared with the DARS-AS1 siRNA2 group.
Downregulation of DARS-AS1 Inhibits Tumor Growth of SiHa Subcutaneous Xenografts in vivo
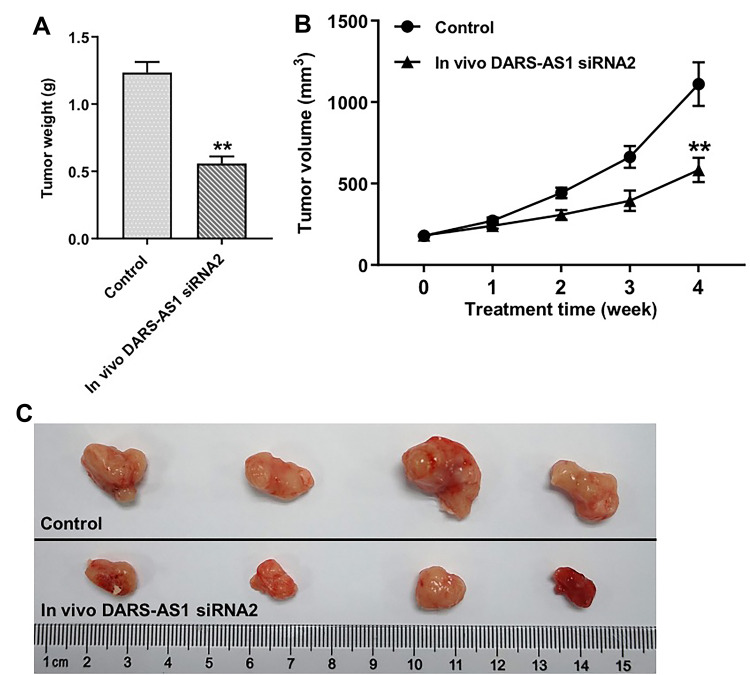
To investigate the role of DARS-AS1 in regulating the tumor growth of cervical cancer in vivo, SiHa subcutaneous xenograft model was established. As shown in Figure 6A–C, downregulation of DARS-AS1 significantly inhibited the tumor weight and tumor volume of SiHa subcutaneous xenografts, compared with the control group. These results indicated that downregulation of DARS-AS1 could inhibit the tumorigenesis of SiHa subcutaneous xenografts in vivo.
Figure 6.
Downregulation of DARS-AS1 inhibits tumorigenesis of SiHa subcutaneous xenografts in vivo. (A) Xenograft tumor volume was monitored weekly. (B and C) Xenografts tumors were weighted and photographed. **P < 0.01, compared with the control group.
Discussion
LncRNAs can regulate gene expression at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels.21 Many studies have been shown that lncRNAs play crucial roles in the tumorigenesis and progression of cervical cancer.22,23 Our previous study indicated that downregulation of DARS-AS1 could inhibit the proliferation of cervical cancer cells via sponging miR-188-5p.24 Chen et al found that DARS-AS1 could promote the proliferation of cervical cancer cells via miR-628-5p/JAG1 axis.25 However, the mechanisms by which DARS-AS1 regulates the proliferation, apoptosis and invasion in cervical cancer cells remain largely unclear. In the present study, we found that downregulation of DARS-AS1 significantly inhibited the proliferation of cervical cancer cells via inducing apoptosis. Moreover, downregulation of DARS-AS1 markedly suppressed cervical cancer tumorigenesis in vivo. Huang et al also observed similar effects of DARS-AS1 on cell proliferation and invasion in ovarian cancer.15 These data suggested that DARS-AS1 may function as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target in cervical cancer.
The data in Starbase indicated that SRSF1, TAF15, ELAVL1, IGF2BP3 and U2AF2 proteins were closely associated with DARS-AS1. Considering these five proteins play important roles in cancer progression,26–30 whether DARS-AS1 is involved in the regulation of expression of these proteins in cervical cancer remains unclear. In this study, we observed that DARS-AS1 interacted with IGF2BP3, and DARS-AS1 positively regulated IGF2BP3 expression in cervical cancer cells. Wang et al indicated that lncRNA LINRIS could stabilize IGF2BP2 via blocking K139 ubiquitination of IGF2BP2.31 Then, we investigated the detailed mechanism whereby DARS-AS1 regulated IGF2BP3. In this study, we found that knockdown of DARS-AS1 decreased IGF2BP3 mRNA stability in SiHa cells. These data indicated that DARS-AS1 modulated IGF2BP3 via regulating the mRNA stability of IGF2BP3. In addition, our data showed that downregulation of DARS-AS1 significantly induced apoptosis and inhibited invasion in cervical cancer cells; however, these changes were reversed by IGF2BP3 overexpression. Moreover, downregulation of DARS-AS1 markedly induced cell cycle arrest in cervical cancer cells accompanied with the decreased expressions of c-Myc and CDK6; however, these phenomena were partially reversed by IGF2BP3 overexpression. All these data indicated that DARS-AS1 knockdown could induce apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in cervical cancer cells via downregulation of IGF2BP3.
Interestingly, we found that IGF2BP3 overexpression had limited effect on apoptosis and cell cycle distribution of SiHa cells, thus we speculated that IGF2BP3 might modulate tumor growth through indirect mechanisms. Ma et al found that FGF13-AS1 reduced the expression of c-Myc by binding RNA-binding proteins (IGF2BPs) and interrupting the interaction between IGF2BPs and c-Myc.32 Bao et al indicated that CERS6-AS1 enhances the stability of CERS6 mRNA and acts as an oncogene in breast cancer through binding to IGF2BP3.33 Based on previous studies, we speculated that DARS-AS1 may mediate the progression of cervical cancer via interacting with IGF2BP3 to regulate the expressions of oncogenes (for example, c-Myc gene). However, the detailed mechanisms whereby DARS-AS1/IGF2BP3 regulated the growth and invasion of cervical cancer cells remains unknown. Thus, further studies are needed to clarify the detailed mechanisms by which DARS-AS1 regulates tumor development in cervical cancer progression.
Conclusion
Collectively, our data indicated that downregulation of DARS-AS1 could inhibit the tumorigenesis of cervical cancer cells via downregulation of IGF2BP3. Therefore, DARS-AS1 might serve as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of cervical cancer.
Disclosure
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- 1.Saei Ghare Naz M, Kariman N, Ebadi A, et al. Educational interventions for cervical cancer screening behavior of women: a systematic review. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018;19(4):875–884. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.4.875 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Olusola P, Banerjee HN, Philley JV, Dasgupta S. Human papilloma virus-associated cervical cancer and health disparities. Cells. 2019;8(6):622. doi: 10.3390/cells8060622 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Partridge EE, Abu-Rustum N, Giuliano A, et al. Cervical cancer screening. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2014;12(3):333–341; quiz 341. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2014.0035 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Shrestha AD, Neupane D, Vedsted P, Kallestrup P. Cervical cancer prevalence, incidence and mortality in low and middle income countries: a systematic review. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018;19(2):319–324. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.2.319 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Muñoz N, Bosch FX, Castellsagué X, et al. Against which human papillomavirus types shall we vaccinate and screen? The international perspective. Int J Cancer. 2004;111(2):278–285. doi: 10.1002/ijc.20244 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Canfell K. Towards the global elimination of cervical cancer. Papillomavirus Res. 2019;8:100170. doi: 10.1016/j.pvr.2019.100170 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bruni L, Diaz M, Barrionuevo-Rosas L, et al. Global estimates of human papillomavirus vaccination coverage by region and income level: a pooled analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2016;4(7):e453–463. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(16)30099-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wei M, Zhou W, Bi Y, et al. Rising mortality rate of cervical cancer in younger women in Urban China. J Gen Intern Med. 2019;34(2):281–284. doi: 10.1007/s11606-018-4732-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(2):115–132. doi: 10.3322/caac.21338 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sanchez Calle A, Kawamura Y, Yamamoto Y, Takeshita F, Ochiya T. Emerging roles of long non-coding RNA in cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018;109(7):2093–2100. doi: 10.1111/cas.13642 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jen J, Tang YA, Lu YH, et al. Oct4 transcriptionally regulates the expression of long non-coding RNAs NEAT1 and MALAT1 to promote lung cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 2017;16(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0674-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature. 2010;464(7291):1071–1076. doi: 10.1038/nature08975 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Foroughi K, Amini M, Atashi A, et al. Tissue-Specific down-regulation of the long non-coding RNAs PCAT18 and LINC01133 in gastric cancer development. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(12):3881. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123881 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bartonicek N, Maag JL, Dinger ME. Long noncoding RNAs in cancer: mechanisms of action and technological advancements. Mol Cancer. 2016;15(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0530-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Huang K, Fan WS, Fu XY, Li YL, Meng YG. Long noncoding RNA DARS-AS1 acts as an oncogene by targeting miR-532-3p in ovarian cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(6):2353–2359. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201903_17379 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tong J, Xu X, Zhang Z, et al. Hypoxia-induced long non-coding RNA DARS-AS1 regulates RBM39 stability to promote myeloma malignancy. Haematologica. 2020;105(6):1630–1640. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2019.218289 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, et al. GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(W1):W98–w102. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx247 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wang P, Xue Y, Han Y, et al. The STAT3-binding long noncoding RNA lnc-DC controls human dendritic cell differentiation. Science. 2014;344(6181):310–313. doi: 10.1126/science.1251456 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gawronski AR, Uhl M, Zhang Y, et al. MechRNA: prediction of lncRNA mechanisms from RNA-RNA and RNA-protein interactions. Bioinformatics. 2018;34(18):3101–3110. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty208 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Xu W, Sheng Y, Guo Y, et al. Increased IGF2BP3 expression promotes the aggressive phenotypes of colorectal cancer cells in vitro and vivo. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10):18466–18479. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28483 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Xu S, Wang P, Zhang J, et al. Ai-lncRNA EGOT enhancing autophagy sensitizes paclitaxel cytotoxicity via upregulation of ITPR1 expression by RNA-RNA and RNA-protein interactions in human cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1017-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jin X, Chen X, Hu Y, et al. LncRNA-TCONS_00026907 is involved in the progression and prognosis of cervical cancer through inhibiting miR-143-5p. Cancer Med. 2017;6(6):1409–1423. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1084 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yang W, Hong L, Xu X, et al. LncRNA GAS5 suppresses the tumorigenesis of cervical cancer by downregulating miR-196a and miR-205. Tumour Biol. 2017;39(7):1010428317711315. doi: 10.1177/1010428317711315 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhu J, Han S. DARS-AS1 knockdown inhibits the growth of cervical cancer cells via downregulating HMGB1 via sponging miR-188-5p. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020;19:1533033820971669. doi: 10.1177/1533033820971669 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chen Y, Wu Q, Lin J, Wei J. DARS-AS1 accelerates the proliferation of cervical cancer cells via miR-628-5p/JAG1 axis to activate notch pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20(1):535. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01592-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dong M, Dong Z, Zhu X, Zhang Y, Song L. Long non-coding RNA MIR205HG regulates KRT17 and tumor processes in cervical cancer via interaction with SRSF1. Exp Mol Pathol. 2019;111:104322. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.104322 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kume K, Ikeda M, Miura S, et al. α-Amanitin restrains cancer relapse from drug-tolerant cell subpopulations via TAF15. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):25895. doi: 10.1038/srep25895 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Xue F, Li QR, Xu YH, Zhou HB. MicroRNA-139-3p inhibits the growth and metastasis of ovarian cancer by inhibiting ELAVL1. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:8935–8945. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S210739 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 29.Wang Z, Tong D, Han C, et al. Blockade of miR-3614 maturation by IGF2BP3 increases TRIM25 expression and promotes breast cancer cell proliferation. EBioMedicine. 2019;41:357–369. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.12.061 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Li J, Cheng D, Zhu M, et al. OTUB2 stabilizes U2AF2 to promote the warburg effect and tumorigenesis via the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Theranostics. 2019;9(1):179–195. doi: 10.7150/thno.29545 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wang Y, Lu JH, Wu QN, et al. LncRNA LINRIS stabilizes IGF2BP2 and promotes the aerobic glycolysis in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1105-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ma F, Liu X, Zhou S, et al. Long non-coding RNA FGF13-AS1 inhibits glycolysis and stemness properties of breast cancer cells through FGF13-AS1/IGF2BPs/Myc feedback loop. Cancer Lett. 2019;450:63–75. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.02.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bao G, Huang J, Pan W, Li X, Zhou T. Long noncoding RNA CERS6-AS1 functions as a malignancy promoter in breast cancer by binding to IGF2BP3 to enhance the stability of CERS6 mRNA. Cancer Med. 2020;9(1):278–289. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2675 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]