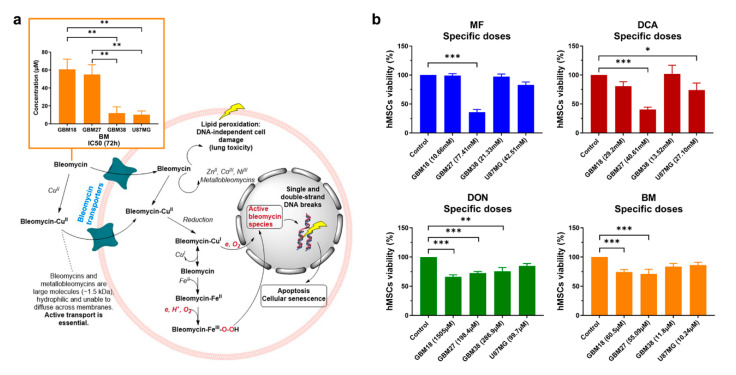
Figure 4.
(a) IC50 values at 72 h and mechanism of action of radiomimetic drug bleomycin (BM). Bleomycin is a large molecule (~1.5 kDa) and cannot freely diffuse cell membranes; it is transported into cells either alone or as a bleomycin-Cu(II) complex, then reduced to bleomycin-Cu(I), which reacts with oxygen leading to DNA strand breaks. Successful chemotherapy with bleomycin is dependent on active transport; however, there is currently no consensus about the uptake mechanism or the transporters involved. Bleomycin-Cu(I) can also dissociate inside the cell to form bleomycin-Fe(II) complexes, transforming into «activated bleomycin species» resulting in DNA fragmentation and chromosomal aberrations. Complexes with zinc (II), iron (II) and cobalt (III) have also been characterized. Calculated IC50, as per inner salt (MTS) assay, with a minimum of two biological replicates. One-way ANOVA with Tukey correction, p < 0.05 *; p < 0.01 **; p < 0.001 ***. (b) Viability profiles relative to control mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) treated with all calculated 72h-IC50 doses (n = 2). One-way ANOVA with Dunn’s correction, p < 0.05 *; p < 0.01 **; p < 0.001 ***.