Abstract
Intestinal parasitic infections, including those caused by Entamoeba species, are a persistent problem in rural areas of Thailand. The aims of this study were to identify pathogenic Entamoeba species and to analyze their genotypic diversity. Stool samples were collected from 1,233 students of three schools located in the Thai-Myanmar border region of Tak Province, Thailand. The prevalence of Entamoeba infection was measured by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using species-specific primers. Thirty-one (2.5%) positive cases were detected for E. histolytica, 55 (4.5%) for E. dispar, and 271 (22.0%) for E. coli. Positive samples for E. histolytica and E. dispar were exclusively obtained from a few school classes, whereas E. coli was detected in all grades. No infections caused by E. moshkovskii, E. nuttalli, E. chattoni, and E. polecki were detected in the students studied. The D-A locus of tRNA-linked short tandem repeats was analyzed in samples of E. histolytica (n = 13) and E. dispar (n = 47) to investigate their diversity and potential modes of transmission. Five genotypes of E. histolytica and 13 genotypes of E. dispar were identified. Sequences of the D-A were divergent, but several unique genotypes were significantly prevalent in limited classes, indicating that intra-classroom transmission has occurred. As it was unlikely that infection would have been limited within school classes if the mode of transmission of E. histolytica and E. dispar had been through the intake of contaminated drinking water or food, these results suggest a direct or indirect person-to-person transmission mode within school classes. Positive rates for three Entamoeba species were 2-fold higher in students who had siblings in the schools than in those without siblings, suggesting that transmission occurred even at home due to heavy contacts among siblings.
Author summary
Transmissions in endemic areas of the pathogen Entamoeba histolytica and other non-pathogenic Entamoeba species such as E. dispar and E. coli are caused by ingestion of drinking water and foods contaminated with cysts of the parasites. Cases of Entamoeba infections among school-aged children have been reported in several countries. However, it has not been demonstrated that transmission of protozoa of the Entamoeba genus occurs within school facilities. In addition, genetic information on E. histolytica and other morphologically indistinguishable species, including E. dispar and E. moshkovskii, in Thailand remains scarce. In the present study, we demonstrated that E. histolytica and/or E. dispar are prevalent among school-aged children, but limited to few classes in three rural schools in the Thai-Myanmar border region of northwest Thailand. Although various genotypes of these Entamoeba species were identified, identical genotypes were significantly more prevalent in certain school classes and also among siblings, suggesting that transmission occurred within the classrooms and at home. The possibility of person-to-person transmission among these students via direct or indirect contact during daily activities in classrooms and home is proposed.
Introduction
Intestinal parasitic infections are a persistent problem in rural areas of Thailand [1–5]. Chronic intestinal parasitic infections can cause malnutrition, anemia, growth retardation, and intellectual developmental delays in preschoolers and students. As such, cross-sectional studies on intestinal parasitic infections have been conducted in Thai children from various locations [6–9]. Microscopy studies also demonstrated the prevalence of Entamoeba. However, as Entamoeba histolytica is morphologically indistinguishable from species such as E. dispar and E. moshkovskii, the prevalence of each species in Thailand remains unknown. E. histolytica is the pathological agent of amebiasis, which is associated with an estimated 50 million cases of colitis and liver abscesses that result in 55,000 deaths per year worldwide. E. dispar has mainly been isolated from cysts in fecal samples from asymptomatic carriers and is described as non-pathogenic. E. moshkovskii is primarily free-living, but human infections have also been reported in many countries [10–12].
Recent studies have reported polymorphisms for a serine-rich protein gene, chitinase gene, and tRNA-linked short tandem repeats (tRNA-STR) in E. histolytica and E. dispar [13–15]. The tRNA-STR polymorphism is highly divergent, and several reports have correlated specific genotypes with symptoms [16–18]. Genotyping is a useful tool that can be used to investigate the dynamics of infection in families, communities, and schools [19–21]. However, epidemiological studies to identify Entamoeba species and characterize their genotypic diversity have not been previously conducted in schools in Thailand.
Here, we report the prevalence of intestinal parasites, including protozoa and helminths, with a special focus on Entamoeba, among students from schools located in the Thai-Myanmar border region in northwest Thailand. Genotypic analyses of E. histolytica and E. dispar suggested a mode of person-to-person transmission in classrooms and in the home.
Methods
Ethics statement
This study was conducted in accordance with ethical protocols approved by the Institutional Review Board in Human Research, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Thailand (IRB Nos. 236/54 and 246/61). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants or from their parents or guardians prior to stool sample collection.
Study area and collection of samples
A cross-sectional study was conducted at three schools (A to C) located in the Thai-Myanmar border region in Tha Song Yang, the northwestern-most district of Tak Province, Thailand, in July 2018 (Fig 1). School A has a kindergarten (2 grades), primary school (6 grades), and secondary school (3 grades). School B is located on a hill, and is a branch of school A, comprising a small-scale kindergarten and primary school. School C is a secondary school (6 grades).
Fig 1. Map of the study area, Tha Song Yang District in Tak Province, Thailand.
A, B, and C indicate the locations of the schools studied.
Clean, wide-mouthed screw-capped plastic containers and spatulas were distributed to the children (or their parents) with instructions for stool sample collection. All 1,788 students from three schools: school A (n = 1,144), school B (n = 82), and school C (n = 562), were requested to submit their stool samples. The next day, stool samples were collected, kept cool on ice, and transported to the laboratory at Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok. A total of 1,233 stool samples were obtained, accounting for 69% of total students from the three schools (70.6%, 53.7%, and 67.8% from schools A, B, and C, respectively). Main reasons for the students not providing their stool samples were no defecation on that morning or unwillingness to participate. Characteristics of students who participated in this study are summarized in Table 1. Herein, individual classrooms for kindergarten, primary, and secondary schools are referred to as ‘Kin-’, ‘Pri-,’ and ‘Sec-’, respectively, followed by classroom grades and specific rooms.
Table 1. General characteristics of students in the three schools.
| Characteristics | School A (n) n = 808 |
School B (n) n = 44 |
School C (n) n = 381 |
Total (n) n = 1,233 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Educational stage (n) | ||||
| Kindergarten | 121 | 2 | - | 123 |
| Primary school | 448 | 42 | - | 490 |
| Secondary school | 239 | - | 381 | 620 |
| Sex (n) | ||||
| Male | 370 | 18 | 137 | 525 |
| Female | 438 | 26 | 244 | 708 |
| Age (years)a | ||||
| Range | 4 to 19 | 4 to 12 | 11 to 24 | 4 to 24 |
| Average | 10.9 | 9.8 | 15.4 | 12.2 |
aA few Hill-tribe students started school significantly later than other Thai children.
Stool examination and culture
Stool samples were examined by light microscopy with iodine staining. Samples that contained Entamoeba quadrinucleate cysts were filtered through a Kim wipe, pelleted by centrifugation, and washed several times with distilled water. The samples were then cultured in Robinson’s medium at 37°C. Grown trophozoites were treated with a cocktail of antibiotics and were then cultured monoxenically with Crithidia fasciculata in YIMDHA-S medium supplemented with 15% adult bovine serum at 37°C [22]. Finally, some of the isolates were cultured axenically in the medium.
Extraction of DNA and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis
Genomic DNA was isolated from the stool samples using a QIAamp Fast DNA Stool Mini Kit (Qiagen). Genomic DNA from cultured trophozoites was isolated using a DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit (Qiagen). PCR amplification of the partial 18S rRNA genes of E. histolytica, E. dispar, E. nuttalli, E. coli, and E. chattoni was performed using primers specific for each species [23–25]. PCR amplification of the 18S gene from E. moshkovskii was performed following the same condition described in a previous study but using newly designed primers [26]. Sequences of primers and annealing temperatures used are shown in Table 2. Genomic DNA isolated from cultured trophozoites of E. histolytica HM-1:IMSS, E. dispar SAW1734RclAR, E. moshkovskii Laredo, and E. nuttalli P19-061405 was used as a positive control. For E. chattoni and E. polecki, genomic DNA extracted from cysts in fecal samples of macaques and pigs was used as the positive control, respectively. The D-A locus of tRNA-STR was also amplified using common primers for E. histolytica and E. dispar [27].
Table 2. List of primers used for PCR analysis.
| Primer name | Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Size of amplicon (bp) | Annealing temperature (°C) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ehist-18S-S | GTTTTATACATTTTGAAGACTTTATG | 434 | 60 | [23] |
| Ehist-18S-AS | CAGATCTAGAAACAATGCTTCTCT | [23] | ||
| Edisp-18S-S | ATTTTATACATTTTGAAGACTTTACATT | 458 | 60 | [23] |
| Edisp-18S-AS | GAACAAGGTAGTATTGATATACTTG | [23] | ||
| Enut-18S-S | TTTTATACATTTTGAAGACTTTGCATA | 452 | 60 | [23] |
| Enut-18S-AS | AAGGTAATATTGATATACTCAGATTA | [23] | ||
| Ecoli-18S-S | GAATGTCAAAGCTAATACTTGACG | 160 | 60 | [24] |
| Ecoli-18S-AS | GATTTCTACAATTCTCTTGGCATA | [24] | ||
| Echattoni1 | AGGATTTGTTTTATAACAAGTTC | 215 | 55 | [25] |
| Echattoni2 | TAAATAACCTTTCTCCTTTTTCTATC | [25] | ||
| Epolecki1 | TCGATATTTATATTGATTCAAATG | 201 | 55 | [25] |
| Epolecki2 | CCTTTCTCCTTTTTTTAT ATTAG | [25] | ||
| Emoshkov3 | TGACGACAAATAACTCTCGAGG | 200 | 60 | Present study |
| Emoshkov4 | GCCTTCAAAATGATTAAAACCACC | Present study | ||
| D-A5 (EhR1) | CTGGTTAGTATCTTCGCCTGT | 364–540a | 58 | [27] |
| D-A3 (EhR2) | GCTACACCCCCATTAACAAT | [27] |
aSize range obtained in this study.
Sequencing
PCR products were purified with either a QIAquick PCR purification kit (Qiagen) or QIAquick Gel Extraction Kit (Qiagen), and were sequenced using a BigDye Terminator v3.1 cycle sequencing kit (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA, USA) with an Applied Biosystems 3500 Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems).
Data analysis
Categorical data were computed as odds ratio (OR) with the 95% confidence interval (CI), and were compared between groups with the Chi-square test, with a difference considered to be statistically significant at p < 0.05. Data analysis was performed using Prism ver. 6.
Results
Prevalence of intestinal parasites observed by microscopy
The prevalence of each parasite was measured by microscopy, and is summarized in Table 3. Of the 1,233 students sampled, 393 (31.9%) were infected with at least one intestinal parasite. However, the prevalence varied significantly between schools. Only one student from school B (2.3%) was negative for intestinal parasites. In contrast, most of the students from schools A (69.6%) and C (72.7%) were negative. The most prevalent protozoon identified was Blastocystis hominis (10.5%), followed by Endolimax nana (10%), E. coli (9%), and G. intestinalis (4.9%). E. histolytica-like species was observed in 46 (3.7%) samples. Ascaris lumbricoides (5.1%) and Trichuris trichiura (1.5%) were the most prevalent helminths identified. Parasites that are transmitted through contaminated soil were highly prevalent in school B, with the highest prevalence observed for A. lumbricoides (61.4%) and T. trichiura (25%). In contrast, A. lumbricoides (0.8%) had a low prevalence and T. trichiura was not detected at school C.
Table 3. Prevalence of parasites observed by direct microscopy of simple fecal smears from students in Ta Song Yang District, Tak Province, Northwest Thailand.
| Species | No. of positives (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| School A n = 808 |
School B n = 44 |
School C n = 381 |
Total n = 1,233 |
|
| Protozoa | ||||
| Entamoeba histolytica-like spp. | 28 (3.5) | 7 (15.9) | 11 (2.9) | 46 (3.7) |
| Entamoeba coli | 78 (9.6) | 10 (22.7) | 23 (6.0) | 111 (9.0) |
| Entamoeba hartmanni | 18 (2.2) | 10 (22.7) | 10 (2.6) | 38 (3.1) |
| Endolimax nana | 81 (10.0) | 10 (22.7) | 32 (8.4) | 123 (10.0) |
| Iodamoeba buetschlii | 6 (0.7) | 8 (18.2) | 4 (1.0) | 18 (1.5) |
| Giardia intestinalis | 49 (6.1) | 3 (6.8) | 8 (2.1) | 60 (4.9) |
| Chilomastix mesnili | 3 (0.4) | 3 (6.8) | 0 (0) | 6 (0.5) |
| Blastocystis hominis | 62 (7.7) | 17 (38.6) | 51 (13.4) | 130 (10.5) |
| Helminths | ||||
| Ascaris lumbricoides | 33 (4.1) | 27 (61.4) | 3 (0.8) | 63 (5.1) |
| Trichuris trichiura | 7 (0.9) | 11 (25.0) | 0 (0) | 18 (1.5) |
| Hookworm | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (0.5) | 2 (0.2) |
| Strongyloides stercoralis | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.1) |
| Taenia spp. | 1 (0.1) | 0 (0) | 2 (0.5) | 3 (0.2) |
| No. of negatives (%) | 562 (69.6) | 1 (2.3) | 277 (72.7) | 840 (68.1) |
Prevalence of Entamoeba species detected by PCR
PCR was performed to increase the sensitivity of detection and to distinguish between E. histolytica and morphologically similar species. Thirty-one (2.5%) of the samples were positive for E. histolytica, 55 (4.5%) were positive for E. dispar, and 271 (22.0%) were positive for E. coli (Table 4). The prevalence of each species was the highest in school B and was the lowest in school C. The prevalence of E. histolytica and E. dispar was 2.5% and 4.8% in school A, 6.8% and 20.5% in school B, and 2.1% and 1.8% in school C, respectively. The prevalence of E. dispar significantly differed among the three schools (p < 0.0001 for school A vs B and B vs C; p = 0.0126 for school A vs C), whereas no significant difference was found among schools for the prevalence of E. histolytica (S1 Table). E. histolytica and E. dispar mixed infection was observed in only a single sample from school A. The positive rates for E. coli in schools A, B, and C were 23.4%, 72.7%, and 13.1%, respectively (p < 0.0001 among the three schools). Mixed infections of E. histolytica and E. coli, and of E. dispar and E. coli were observed in 2.6% and 7.4% of samples, respectively. No infections caused by E. moshkovskii, E. nuttalli, E. chattoni, or E. polecki were detected in all schools studied.
Table 4. Prevalence of Entamoeba infection detected by PCR analysis.
| Species | No. of positives (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| School A n = 808 |
School B n = 44 |
School C n = 381 |
Total n = 1,233 |
|
| Entamoeba histolytica | 20 (2.5) | 3 (6.8) | 8 (2.1) | 31 (2.5) |
| Entamoeba dispar | 39 (4.8) | 9 (20.5) | 7 (1.8) | 55 (4.5) |
| Entamoeba coli | 189 (23.4) | 32 (72.7) | 50 (13.1) | 271 (22.0) |
| Entamoeba moshkovskii | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Entamoeba nuttalli | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Entamoeba polecki ST1 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Entamoeba chattoni (E. polecki S2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
Distribution of students positive for Entamoeba in each grade and class
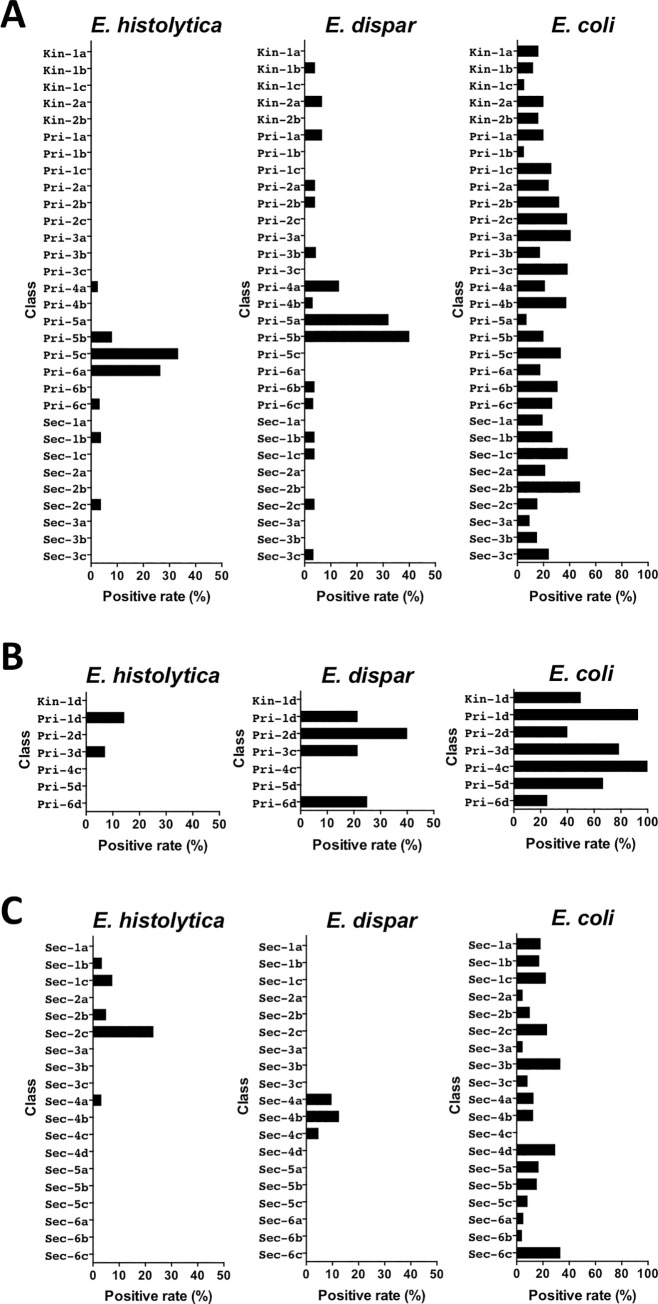
The distribution of students in school A who were positive for Entamoeba is represented in Table 5. The 20 students who were positive for E. histolytica were exclusively from grade 4 of primary school through grade 2 of secondary school, with the greatest number of positives found in grades 5 (n = 7) and 6 (n = 10) of primary school. However, the distribution of students who were positive for E. histolytica was different among classes in grades 5 and 6 (Fig 2A). Of students who were positive, 5 (33.3%) were from class Pri-5c, 2 (8%) from Pri-5b, 9 (26.5%) from Pri-6a, and 1 (3.3%) from Pri-6c. No students from classes Pri-5a or Pri-6b were positive, whereas E. dispar was detected in all grades. However, the majority of students who were positive were from grades 4 and 5 (6 and 19 of 39, respectively) of primary school. Nine (32.1%) students from class Pri-5a and 10 (40%) students from Pri-5b were positive, but there was no positive result for E. dispar detected among students from Pri-5c. In contrast, E. coli was detected in all grades with a prevalence ranging from 13.6% to 32.4%. E. coli was also detected in all classes, with a prevalence varying from 5% to 48%.
Table 5. Distribution of Entamoeba positives in each grade for school A.
| Educational stage | Grade | No. of students | No. of positives (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. histolytica | E. dispar | E. coli | |||
| Kindergarten | 1 | 66 | 0 (0) | 1 (1.5) | 9 (13.6) |
| 2 | 55 | 0 (0) | 2 (3.6) | 10 (18.2) | |
| Primary school | 1 | 75 | 0 (0) | 2 (2.7) | 13 (17.3) |
| 2 | 74 | 0 (0) | 2 (2.7) | 22 (29.7) | |
| 3 | 71 | 0 (0) | 1 (1.4) | 23 (32.4) | |
| 4 | 70 | 1 (1.4) | 6 (8.6) | 20 (28.6) | |
| 5 | 68 | 7 (10.3) | 19 (27.9) | 12 (17.6) | |
| 6 | 90 | 10 (11.1) | 2 (2.2) | 22 (24.4) | |
| Secondary school | 1 | 83 | 1 (1.2) | 2 (2.4) | 23 (27.7) |
| 2 | 77 | 1 (1.3) | 1 (1.3) | 22 (28.6) | |
| 3 | 79 | 0 (0) | 1 (1.3) | 13 (16.5) | |
| Total | 808 | 20 (2.5) | 39 (4.8) | 189 (23.4) | |
Fig 2.
Distribution of students positive for Entamoeba in each class from schools A, B, and C.
In school B, we found that students who were positive for E. histolytica were exclusively from grades 1 and 3 of primary school (Table 6 and Fig 2B). Similarly, 8 of the 9 students who were positive for E. dispar were also from grades 1 to 3. However, students who were positive for E. coli were distributed across all grades, with prevalence varying from 25% to 100%.
Table 6. Distribution of Entamoeba positives in each grade for school B.
| Educational stage | Grade | No. of students | No. of positives (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. histolytica | E. dispar | E. coli | |||
| Kindergarten | 1 | 2 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (50.0) |
| Primary school | 1 | 14 | 2 (14.3) | 3 (21.4) | 13 (92.9) |
| 2 | 5 | 0 (0) | 2 (40.0) | 2 (40.0) | |
| 3 | 14 | 1 (7.1) | 3 (21.4) | 11 (78.6) | |
| 4 | 2 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (100.0) | |
| 5 | 3 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (66.7) | |
| 6 | 4 | 0 (0) | 1 (25.0) | 1 (25.0) | |
| Total | 44 | 3 (6.8) | 9 (20.5) | 32 (72.7) | |
In school C, 7 of 8 students who were positive for E. histolytica were from grades 1 and 2 of secondary school (Table 7). One (3.4%) student from class Sec-1b, 2 (7.4%) from Sec-1c, 3 (23.1%) from Sec-2c, and 1 (5%) from Sec-2b were positive. No student in classes Sec-1a and Sec-2a was positive (Fig 2C). All 7 students who were positive for E. dispar were from grade 4 of secondary school. Three (9.7%) students from class Sec-4a, 3 (12.5%) from Sec-4b, and 1 (4.7%) from Sec-4c were positive, but no positives were detected in Sec-4d. In contrast, E. coli was detected in all grades, with the prevalence varying from 8.8% to 19.2%. Only class Sec-4c had no cases of E. coli infections; in other classes, the prevalence ranged from 4% to 33.3%.
Table 7. Distribution of Entamoeba positives in each grade for school C.
| Educational stage | Grade | No. of students | No. of positives (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. histolytica | E. dispar | E. coli | |||
| Secondary school | 1 | 78 | 3 (3.8) | 0 (0) | 15 (19.2) |
| 2 | 55 | 4 (7.3) | 0 (0) | 6 (10.9) | |
| 3 | 40 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4 (9.8) | |
| 4 | 93 | 1 (1.1) | 7 (7.5) | 12 (12.9) | |
| 5 | 56 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 8 (14.3) | |
| 6 | 59 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 5 (8.8) | |
| Total | 381 | 8 (2.1) | 7 (1.8) | 50 (13.1) | |
Isolation of E. histolytica and E. dispar
Successful in vitro culture of samples containing quadrinucleate Entamoeba cysts in Robinson’s medium was achieved for 14 isolates. Of these, PCR identified E. histolytica in 5 isolates (school A, n = 2; school B, n = 3), while 9 isolates belonged to E. dispar (school A, n = 7; school B, n = 1; school C, n = 1). Genotypic analysis was subsequently performed. Three E. histolytica isolates (school A, n = 1; school B, n = 2) were established as axenic strains in YIMDHA-S medium.
Genotypic analysis of E. histolytica
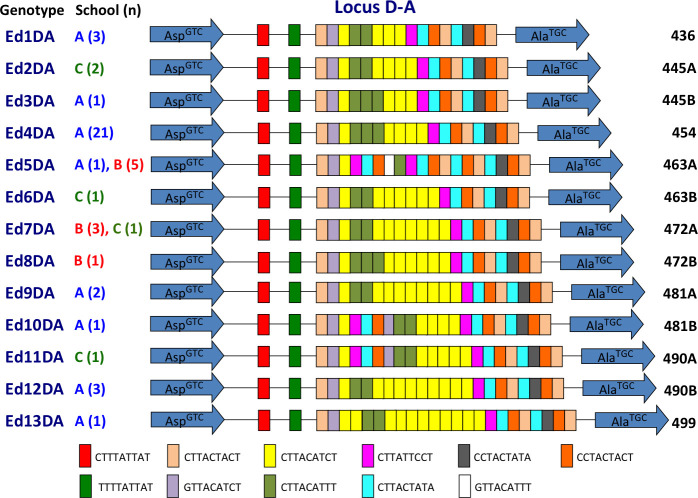
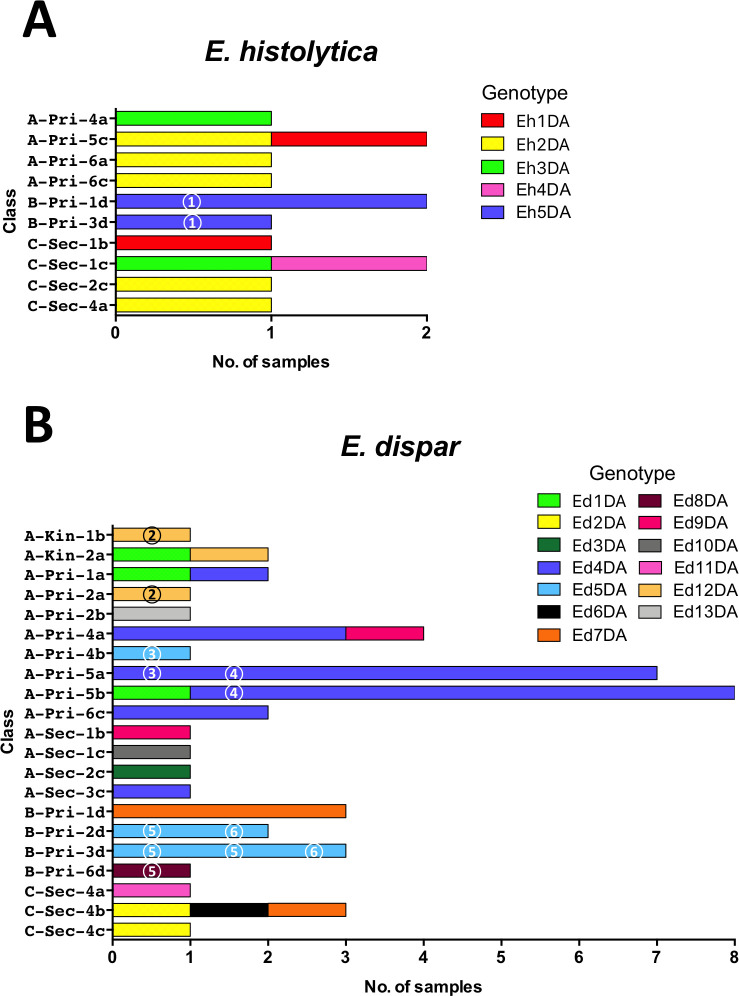
Sequencing was used to identify polymorphisms of tRNA-STR at the D-A locus. Sequences were successfully obtained for 13 (including 5 cultures) of 31 E. histolytica samples, and 47 (including 9 cultures) of 55 E. dispar samples. Five E. histolytica genotypes were identified (Fig 3). Three genotypes were identified in school A, 1 in school B, and 4 in school C. Of the 5 genotypes, 3 were common to schools A and C, and 2 were found exclusively in school B or school C (Fig 3). The most prevalent genotype (Eh2DA) was observed in 5 samples. The exclusive prevalence of genotype Eh5DA in school B was significant (p = 0.0047 in school A vs B and B vs C) (S2 Table). The prevalence in B-Pri-1d was also significnatly higher than the total prevalence from the other classes of the three schools (p = 0.0050).
Fig 3. Schematic representation of tRNA-linked STR fragments at the D-A locus in E. histolytica.
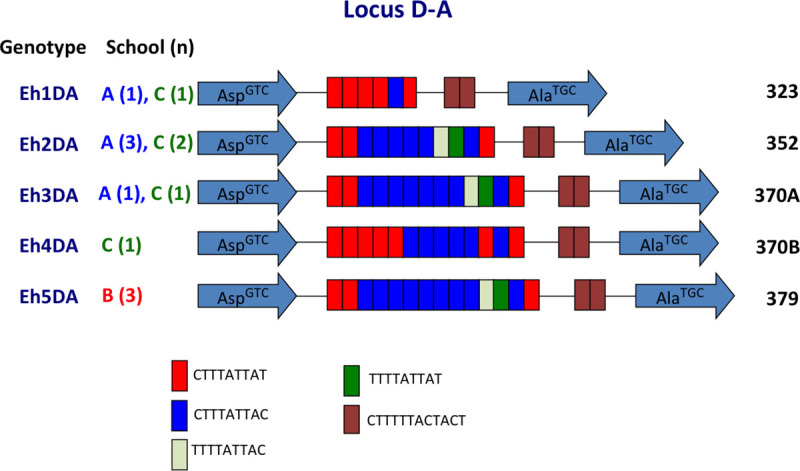
Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of samples with each genotype from each school. Numbers on the far right show the length of fragments excluding the primer sequences.
Genotypic analysis of E. dispar
Thirteen E. dispar genotypes were identified in 47 samples, suggesting that it had relatively greater diversity (Fig 4). Eight genotypes were identified in school A, 3 in school B, and 4 in school C. Only two genotypes were common to different schools, and the 11 other genotypes were unique to each school. The most prevalent genotype, Ed4DA, was observed in 21 samples from school A, including all 7 positive samples from class Pri-5a and 7 of 8 samples from Pri-5b (Fig 5). The prevalence in Pri-5a was significantly higher than that in the remaining classes of school A (p = 0.0242) (S3 Table). The prevalence of Ed4DA in grade 5 (Pri-5a and Pri-5b) was also significantly higher than that in the remaining classes of primary school (p = 0.0204). These results indicated that transmission of Entamoeba occurred within classes and grades. Genotype Ed4DA was also prevalent in grades 4 (class Pri-4a) and 6 (class Pri-6c), whereas genotype Ed12DA was found exclusively in the lower grades of school A, including classes Kin-1b, Kin-2a, and Pri-2a. In contrast, the genotypes Ed3DA and Ed10DA were found exclusively in school A’s secondary school. In school B, genotype Ed7DA was prevalent in grade 1 (class Pri-1d), whereas genotype Ed5DA was prevalent in grades 2 (class Pri-2d) and 3 (class Pri-3d). The prevalence of Ed7DA in Pri-1d was significantly higher than that in the remaining classes of school B (p = 0.0027), indicating that intra-class transmission occurred (S4 Table). The prevalence of Ed5DA in Pri-3d and Pri-2d was also significantly higher than that in other classes of school B (p = 0.0027) (S5 Table). In class Sec-4b of school C, the 3 E. dispar samples had different genotypes: Ed2DA, Ed6DA, and Ed7DA.
Fig 4. Schematic representation of tRNA-linked STR fragments at the D-A locus in E. dispar.
Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of samples with each genotype from each school. Numbers on the far right show the length of fragments excluding the primer sequences.
Fig 5.
Distribution of genotypes of tRNA-linked STR fragments at the D-A locus from E. histolytica (A) and E. dispar (B) in classes from three schools. Different colors represent different genotypes. Identical numbers within circles represent siblings.
Entamoeba prevalence and genotypes in siblings
Of the 1,233 students included in this study, 400 had siblings in the same schools. The positive rates for three Entamoeba species among students who had siblings were about 2-fold higher than those among students who did not have siblings in their school (p = 0.0028 for E. dispar and p < 0.0001 for E. coli) (Table 8). Although the difference in E. histolytica infection prevalence was not statistically meaningful (p = 0.055), it almost reached a significant level. To study the transmission of Entamoeba within families, genotyping was used to identify siblings who were positive (Fig 5). Two pairs of siblings were among the 31 E. histolytica-positive children. The Eh5DA genotype of E. histolytica was shared with a sibling (circled 1) from school B, whereas genotypes from the other siblings from school A could not be analyzed. Moreover, siblings from six families were among the 55 E. dispar-positive children. Genotypes for E. dispar were compared in siblings from 5 families. In school A, siblings from 2 families (circles 2 and 4) had identical genotypes (Ed12DA and Ed4DA), but one pair of siblings (circle 3) had different genotypes (Ed4DA and Ed5DA). Genotypes from the remaining siblings from school A could not be analyzed. In school B, a pair of siblings (circle 6) had an identical genotype (Ed5DA), but a set of four siblings (circle 5) had different genotypes, with Ed8DA found in 1 sibling and Ed5DA in the others. No siblings from school C were found to be positive for E. histolytica and E. dispar.
Table 8. Comparison of Entamoeba infection prevalence between students with and without siblings in the school.
| No. of students | No. of positives (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. histolytica | E. dispar | E. coli | ||
| Students with siblings in the school | 400 | 15 (3.8) | 28 (7.0) | 137 (34.3) |
| Students without siblings in the school | 833 | 16 (1.9) | 27 (3.2) | 134 (16.1) |
| Chi-square | 3.689 | 8.959 | 51.991 | |
| p value | 0.055 | 0.0028 | <0.0001 | |
| Odds ratio (95%CI) | 1.99 (0.97–4.07) | 2.25 (1.31–3.87) | 2.72 (2.06–3.59) | |
| Total | 1,233 | 31 (2.5) | 55 (4.5) | 271 (22.0) |
Discussion
This study revealed that the prevalence of intestinal parasites differed significantly among three schools located in the same district. School B, which is rural and small, had the highest prevalence, especially for nematodes transmitted through soil, such as A. lumbricoides and T. trichiura. In Thailand, a high prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections such as those caused by nematodes has been reported in children of the Karen Hill tribe and in immigrants from Myanmar [2,28,29]. We observed a much higher prevalence of A. lumbricoides in school B compared to that previously reported in Thailand [1–3]. Students who attended school B lived in close proximity to the school. Most of them lacked household latrines and drank untreated water from streams running through their villages. Therefore, the main reason for the high prevalence of parasitic infections in school B would be the poor hygiene. Further studies will be needed to investigate if the prevalence of this parasite is also relatively high within these students’ families.
The prevalence of E. histolytica/E. dispar and E. coli as detected by PCR was 6.9% and 22%, respectively, with a single mixed infection of E. histolytica and E. dispar detected. This was about twice as high as the prevalence observed by microscopy. Although concentration techniques may increase detection by microscopy, some studies have reported no difference for protozoa [3,29,30]. We showed that E. dispar, but not E. histolytica, was prevalent in the studied populations. Previous studies have reported that E. dispar was more prevalent than E. histolytica in hospitals in Bangkok [31,32] and that E. histolytica was prevalent in the Thai-Myanmar border region, such as in Phang-Nga Province [33].
Our main finding was that E. histolytica and E. dispar infections were distributed in a limited number of classes. In school A’s grade 5 of primary school, the number of samples positive for E. histolytica was 0 (0%) in class Pri-5a, 2 (8%) in Pri-5b, and 5 (33.3%) in Pri-5c. In the same classes, the number of samples positive for E. dispar was 9 (32.1%), 10 (40%), and 0 (0%), respectively, suggesting that the transmission occurred within classes. This also suggested that transmission of these two species must have occurred independently, even if both species shared the same mode of transmission. It has previously been reported that the D-A locus of tRNA-STR is highly variable and is thus useful for Entamoeba fingerprinting [15,19,21,34–36]. The present study showed that the prevalence of genotypes such as Ed4DA and Ed7DA was significantly higher in several classes, indicating that transmission occurred within the classroom. To our knowledge, this is the first report revealing the transmission of Entamoeba species within the classroom setting.
Concerning the high prevalence of Ed4DA in both Pri-5a and Pri-5b, in addition to intra-class transmission, the possibility that inter-class transmission between these two classes occurred could not be ruled out. However, it is difficult to prove whether transmission between these two classes occurred once (subsequent intra-class transmission), a few times, frequently, or did not occur at all (independent intra-class transmission) because of the cross-sectional nature of the present study. It is also reasonable to consider that contact between school children is longer and more extensive in the same classroom than in different classrooms. In fact, there was no E. dispar-positive case in A-Pri5c, despite being part of the same grade. Therefore, it is also reasonable that the incidence of intra-classroom transmission is higher than that of inter-classroom transmission. As different genotypes were found in secondary schools, this also suggests that children in primary schools have more person-to-person contact than older students. This study also provides evidence about the great genetic diversity of E. dispar, and demonstrates that the mobility of the parasite is restricted to relatively small areas where transmission is maintained [19–21].
In general, the mode of transmission for Entamoeba is through ingestion of contaminated drinking water or food [37–42]. However, the supplied drinking water at school A was filtered, and for lunch, children either bought food that was sold at the school or were provided with side dishes that were cooked in a central kitchen at the school. If water or food was the source of infection, it is unlikely that infections would be limited to specific classes. Therefore, the most likely route of transmission would be through direct or indirect person-to-person contact during daily activities in classes and in grades. It is also improbable that Entamoeba was transmitted through sexual behavior in children. As such, we propose a possible mode of transmission that is similar to that of Enterobius vermicularis. Although the prevalence of E. vermicularis was not investigated in this study, a prevalence of 7.8% has previously been reported in 2 primary schools in Tak Province [43]. Further study is required to test this hypothesis through simultaneous detection of Entamoeba cysts and E. vermicularis eggs in samples of dirt collected from under the fingernails. Indeed, cleanliness of the fingernails has been shown to have a significant effect on the prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections in school children [44].
In the present study, students who had siblings in the same school showed a significantly higher prevalence of E. dispar and E. coli infections than students who did not have siblings in the school, although the higher prevalence of E. histolytica was not significant, suggesting that transmission of Entamoeba between siblings occurred at home. Indeed, the fact that four of six sets of siblings with E. histolytica and E. dispar infections had identical genotypes at the D-A locus further supports the significance of this transmission route. The prevalence of genotype Ed5DA in Pri-3d and Pri-2d of school B may be due to familial transmission. Because there were siblings infected with E. dispar showing an identical genotype, Ed4DA, in Pri-5a and Pri-5b, it might be possible that the siblings transmitted the infection from home to two classrooms in the school. Another possibility is that one of the siblings was infected in a classroom of the school, carried the infection to home and transmitted it to siblings, and then transmission was extended to another classroom from home. There is also a possibility of transmission from school to home and vice versa [20]. It is interesting and important to follow the direction of transmission. For further analysis, the following questions are important and need to be answered: Are the children infected before they enter into the school? Are their families exposed to the parasite or infected? Were children infected in the school? Initial infection might occur at home; however, it is difficult to prove the direction of transmission and to ascertain how to transmit the infections between home and school in this study, because of the limitations of it being a cross sectional study. Further studies would be required for answering these questions.
By contrast, we previously reported different E. dispar genotypes in a couple from a family in Nepal [21]. Different E. dispar genotypes at another locus have also been observed in children and their relatives in Mexico [20]. There may be differences in behavior between adults and children that affect transmission. It is probable that contact with siblings is closer than that with the parents at home. Further analysis of family members is required to confirm transmission within families, as the possibility of transmission by contaminated drinking water and foods in the homes could not be excluded.
Outbreaks of amebiasis have also been reported in institutions for individuals with mental disabilities [45–49]. Abnormal behaviors such as pica and fecal play (coprophilia) are suggested to be factors that promote the transmission of Entamoeba. However, the teachers reported that no such behavior was observed in the students from the schools studied.
A high prevalence of E. moshkovskii infection has recently been reported in rural communities of many countries. A prevalence rate of 18.2% was reported in Yemen [50], 15.9% in South Africa [30], 21.1% in preschoolers in Bangladesh [51], 12.3% in Malaysia [52], 61.8% in patients in Australia [53], and 13% for suspected HIV or HIV-positive inpatients in Tanzania [54]. However, no E. moshkovskii infections were detected in this study or in our previous study in Nepal [21]. In the present study, we designed a new primer set for amplification of the E. moshkovskii 18S rRNA gene, which covered the sequences recently stored in DNA databases. These sequences were from E. moshkovskii isolates from human (KP722601-KP722605), snake (MN536488), cockroach (MN535795, MN535796, MN536492), beetle (MN536495), and various water sediments (MN536493, MN536494, MN536496-MN536501). The primer set was shown to effectively amplify the partial 18S sequence of Laredo strain (AF149906) (S1 Fig). Although E. moshkovskii has previously been detected in clinical samples, its prevalence may be lower or may not be widely distributed in Thailand [31,32].
E. nuttalli and E. chattoni infections were also not detected. Macaques are the natural host of these parasites, and although we had previously reported E. chattoni infection in Nepal where macaques live in the same area as the study participants, few macaques are found in the studied area in Thailand [21]. Despite the presence of pigs that were kept near school B, E. polecki infection was not detected.
In conclusion, the mode of transmission of E. histolytica and E. dispar among school children on the Thai-Myanmar border region appears to be through direct or indirect person-to-person contact within classes, and it also seems to occur in siblings at home due to their more extensive contact. These findings suggest that specific measures are necessary to prevent transmission in both schools and at home.
Supporting information
Genomic DNA isolated from E. moshkovskii Laredo strain was serially diluted and used as a template for PCR (lanes 1 to 7). Predicted 200-bp products were clearly detected from 1 pg of template DNA (lane 5). Lane 8, without template DNA; M, 100-bp DNA ladder.
(TIF)
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Napaporn Kuamsab, Rattiporn Kosuwin, Sunisa Songsaigath, Yoshiro Takashima, and Sedthawud Chaikigosiyakul from Chulalongkorn University for their assistance. We are especially grateful to the students of Tha Song Yang for their participation, and to the teachers for their cooperation. We would also like to thank the staff from the Support Center for Medical Research and Education, Tokai University for their help.
Data Availability
Nucleotide sequences have been deposited at the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank database, accession numbers LC546869-LC546886.
Funding Statement
This study was supported by JSPS (https://www.jsps.go.jp) KAKENHI (grant number 24406013, JP16H05819, JP17K08811, JP20H03482 to H.T., JP20K07466 to N.Y.), the Thailand Research Fund (https://www.trf.or.th) (RSA5980054 to C.P.), and the Matsumae International Foundation (https://wwww.mif-japan.org) (2017 Research Fellowship Program to U.P.). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Suntaravitun P, Dokmaikaw A. Prevalence of intestinal parasites and associated risk factors for infection among rural communities of Chachoengsao Province, Thailand. Korean J Parasitol. 2018;56(1):33–9. Epub 2018/03/14. 10.3347/kjp.2018.56.1.33 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Yanola J, Nachaiwieng W, Duangmano S, Prasannarong M, Somboon P, Pornprasert S. Current prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections and their impact on hematological and nutritional status among Karen hill tribe children in Omkoi District, Chiang Mai Province, Thailand. Acta Trop. 2018;180:1–6. Epub 2018/01/08. 10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.01.001 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chaisiri K, Jollivet C, Della Rossa P, Sanguankiat S, Wattanakulpanich D, Lajaunie C, et al. Parasitic infections in relation to practices and knowledge in a rural village in Northern Thailand with emphasis on fish-borne trematode infection. Epidemiol Infect. 2018:1–12. Epub 2018/11/16. 10.1017/S0950268818002996 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Boonjaraspinyo S, Boonmars T, Kaewsamut B, Ekobol N, Laummaunwai P, Aukkanimart R, et al. A cross-sectional study on intestinal parasitic infections in rural communities, northeast Thailand. Korean J Parasitol. 2013;51(6):727–34. Epub 2014/02/12. 10.3347/kjp.2013.51.6.727 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Punsawad C, Phasuk N, Bunratsami S, Thongtup K, Siripakonuaong N, Nongnaul S. Prevalence of intestinal parasitic infection and associated risk factors among village health volunteers in rural communities of southern Thailand. BMC Public Health. 2017;17(1):564. Epub 2017/06/11. 10.1186/s12889-017-4486-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Waikagul J, Krudsood S, Radomyos P, Radomyos B, Chalemrut K, Jonsuksuntigul P, et al. A cross-sectional study of intestinal parasitic infections among schoolchildren in Nan Province, Northern Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2002;33(2):218–23. Epub 2002/09/19. . [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wongstitwilairoong B, Srijan A, Serichantalergs O, Fukuda CD, McDaniel P, Bodhidatta L, et al. Intestinal parasitic infections among pre-school children in Sangkhlaburi, Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007;76(2):345–50. Epub 2007/02/14. . [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jongwutiwes S, Kraivichian P, Kulkumthorn M, Sitthichareonchai P, Jaroenkorn M. Cryptosporidiosis among orphanage children in Thailand: a one year prospective study. Southeast Asian J Tropi Med Public Health. 1990;21(3):458–64. Epub 1990/09/01. . [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Doi R, Itoh M, Chakhatrakan S, Uga S. Epidemiological investigation of parasitic infection of schoolchildren from six elementary schools in Sakon Nakhon Province, Thailand. Kobe J Med Sci. 2017;62(5):E120–E8. Epub 2017/03/16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2095–128. Epub 2012/12/19. 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Heredia RD, Fonseca JA, Lopez MC. Entamoeba moshkovskii perspectives of a new agent to be considered in the diagnosis of amebiasis. Acta Trop. 2012;123(3):139–45. Epub 2012/06/06. 10.1016/j.actatropica.2012.05.012 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ximenez C, Moran P, Rojas L, Valadez A, Gomez A, Ramiro M, et al. Novelties on amoebiasis: a neglected tropical disease. J Glob Infect Dis. 2011;3(2):166–74. Epub 2011/07/07. 10.4103/0974-777X.81695 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ayeh-Kumi PF, Ali IM, Lockhart LA, Gilchrist CA, Petri WA Jr., Haque R. Entamoeba histolytica: genetic diversity of clinical isolates from Bangladesh as demonstrated by polymorphisms in the serine-rich gene. Exp Parasitol. 2001;99(2):80–8. Epub 2001/12/26. 10.1006/expr.2001.4652 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zaki M, Clark CG. Isolation and characterization of polymorphic DNA from Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39(3):897–905. Epub 2001/03/07. 10.1128/JCM.39.3.897-905.2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Haghighi A, Kobayashi S, Takeuchi T, Masuda G, Nozaki T. Remarkable genetic polymorphism among Entamoeba histolytica isolates from a limited geographic area. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40(11):4081–90. Epub 2002/11/01. 10.1128/jcm.40.11.4081-4090.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Escueta-de Cadiz A, Kobayashi S, Takeuchi T, Tachibana H, Nozaki T. Identification of an avirulent Entamoeba histolytica strain with unique tRNA-linked short tandem repeat markers. Parasitol Int. 2010;59(1):75–81. Epub 2009/11/10. 10.1016/j.parint.2009.10.010 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ali IK, Haque R, Alam F, Kabir M, Siddique A, Petri WA Jr, Evidence for a link between locus R-R sequence type and outcome of infection with Entamoeba histolytica. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012;18(7):E235–7. Epub 2012/03/28. 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2012.03826.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Das K, Mukherjee AK, Chowdhury P, Sehgal R, Bhattacharya MK, Hashimoto T, et al. Multilocus sequence typing system (MLST) reveals a significant association of Entamoeba histolytica genetic patterns with disease outcome. Parasitol Int. 2014;63(2):308–14. Epub 2013/12/11. 10.1016/j.parint.2013.11.014 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zaki M, Reddy SG, Jackson TF, Ravdin JI, Clark CG. Genotyping of Entamoeba species in South Africa: diversity, stability, and transmission patterns within families. J Infect Dis. 2003;187(12):1860–9. Epub 2003/06/07. 10.1086/375349 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rojas L, Moran P, Valadez A, Gomez A, Gonzalez E, Hernandez E, et al. Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar infection in Mexican school children: genotyping and phylogenetic relationship. BMC Infect Dis. 2016;16:485. 10.1186/s12879-016-1812-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Feng M, Pandey K, Yanagi T, Wang T, Putaporntip C, Jongwutiwes S, et al. Prevalence and genotypic diversity of Entamoeba species in inhabitants in Kathmandu, Nepal. Parasitol Res. 2018;117(8):2467–72. 10.1007/s00436-018-5935-2 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kobayashi S, Imai E, Haghighi A, Khalifa SA, Tachibana H, Takeuchi T. Axenic cultivation of Entamoeba dispar in newly designed yeast extract-iron-gluconic acid-dihydroxyacetone-serum medium. J Parasitol. 2005;91(1):1–4. Epub 2005/04/29. 10.1645/GE-3386 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Tachibana H, Yanagi T, Pandey K, Cheng XJ, Kobayashi S, Sherchand JB, et al. An Entamoeba sp. strain isolated from rhesus monkey is virulent but genetically different from Entamoeba histolytica. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2007;153(2):107–14. Epub 2007/04/04. 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2007.02.006 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tachibana H, Yanagi T, Akatsuka A, Kobayashi S, Kanbara H, Tsutsumi V. Isolation and characterization of a potentially virulent species Entamoeba nuttalli from captive Japanese macaques. Parasitology. 2009;136(10):1169–77. Epub 2009/07/29. 10.1017/S0031182009990576 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Verweij JJ, Polderman AM, Clark CG. Genetic variation among human isolates of uninucleated cyst-producing Entamoeba species. J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39(4):1644–6. Epub 2001/04/03. 10.1128/JCM.39.4.1644-1646.2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tachibana H, Yanagi T, Lama C, Pandey K, Feng M, Kobayashi S, et al. Prevalence of Entamoeba nuttalli infection in wild rhesus macaques in Nepal and characterization of the parasite isolates. Parasitol Int. 2013;62(2):230–5. Epub 2013/02/02. 10.1016/j.parint.2013.01.004 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ali IK, Zaki M, Clark CG. Use of PCR amplification of tRNA gene-linked short tandem repeats for genotyping Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43(12):5842–7. Epub 10.1128/JCM.43.12.5842-5847.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sagnuankiat S, Wanichsuwan M, Bhunnachet E, Jungarat N, Panraksa K, Komalamisra C, et al. Health status of immigrant children and environmental survey of child daycare centers in Samut Sakhon Province, Thailand. J Immigr Minor Health. 2016;18(1):21–7. Epub 2014/12/17. 10.1007/s10903-014-0146-0 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Piangjai S, Sukontason K, Sukontason KL. Intestinal parasitic infections in hill-tribe schoolchildren in Chiang Mai, northern Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2003;34 Suppl 2:90–3. Epub 2003/01/01. . [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Samie A, Mahlaule L, Mbati P, Nozaki T, ElBakri A. Prevalence and distribution of Entamoeba species in a rural community in northern South Africa. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2020;18:e00076. Epub 2020/03/11. 10.1016/j.fawpar.2020.e00076 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hamzah Z, Petmitr S, Mungthin M, Leelayoova S, Chavalitshewinkoon-Petmitr P. Differential detection of Entamoeba histolytica, Entamoeba dispar, and Entamoeba moshkovskii by a single-round PCR assay. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44(9):3196–200. Epub 2006/09/07. 10.1128/JCM.00778-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hamzah Z, Petmitr S, Mungthin M, Leelayoova S, Chavalitshewinkoon-Petmitr P. Development of multiplex real-time polymerase chain reaction for detection of Entamoeba histolytica, Entamoeba dispar, and Entamoeba moshkovskii in clinical specimens. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010;83(4):909–13. Epub 2010/10/05. 10.4269/ajtmh.2010.10-0050 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Intarapuk A, Kalambaheti T, Thammapalerd N, Mahannop P, Kaewsatien P, Bhumiratana A, et al. Identification of Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar by PCR assay of fecal specimens obtained from Thai/Myanmar border region. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2009;40(3):425–34. Epub 2009/10/22. . [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Haghighi A, Kobayashi S, Takeuchi T, Thammapalerd N, Nozaki T. Geographic diversity among genotypes of Entamoeba histolytica field isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41(8):3748–56. Epub 2003/08/09. 10.1128/jcm.41.8.3748-3756.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Mojarad EN, Haghighi A, Kazemi B, Rostami Nejad M, Abadi A, Zali MR. High genetic diversity among Iranian Entamoeba dispar isolates based on the noncoding short tandem repeat locus D-A. Acta Trop. 2009;111(2):133–6. Epub 2009/06/16. 10.1016/j.actatropica.2009.03.008 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pinheiro SM, Maciel RF, Morais MA Jr., Aca IS, Carvalho LB Jr., Coimbra MR. Genetic characterization of Entamoeba dispar isolates in Northeast Brazil. Acta Trop. 2005;94(1):35–40. Epub 2005/03/22. 10.1016/j.actatropica.2005.01.012 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Berhe B, Bugssa G, Bayisa S, Alemu M. Foodborne intestinal protozoan infection and associated factors among patients with watery diarrhea in Northern Ethiopia; a cross-sectional study. J Health Popul Nutr. 2018;37(1):5. Epub 2018/03/04. 10.1186/s41043-018-0137-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Duedu KO, Yarnie EA, Tetteh-Quarcoo PB, Attah SK, Donkor ES, Ayeh-Kumi PF. A comparative survey of the prevalence of human parasites found in fresh vegetables sold in supermarkets and open-aired markets in Accra, Ghana. BMC Res Notes. 2014;7:836. Epub 2014/11/27. 10.1186/1756-0500-7-836 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mohamed MA, Siddig EE, Elaagip AH, Edris AM, Nasr AA. Parasitic contamination of fresh vegetables sold at central markets in Khartoum state, Sudan. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2016;15:17. Epub 2016/03/13. 10.1186/s12941-016-0133-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Baldursson S, Karanis P. Waterborne transmission of protozoan parasites: review of worldwide outbreaks – an update 2004–2010. Water Res. 2011;45(20):6603–14. Epub 2011/11/04. 10.1016/j.watres.2011.10.013 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Craun GF, Brunkard JM, Yoder JS, Roberts VA, Carpenter J, Wade T, et al. Causes of outbreaks associated with drinking water in the United States from 1971 to 2006. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010;23(3):507–28. Epub 2010/07/09. 10.1128/CMR.00077-09 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Plutzer J, Karanis P. Neglected waterborne parasitic protozoa and their detection in water. Water Res. 2016;101:318–32. Epub 2016/06/10. 10.1016/j.watres.2016.05.085 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Tomanakan K, Sanpool O, Chamavit P, Lulitanond V, Intapan PM, Maleewong W. Genetic variation of Enterobius vermicularis among schoolchildren in Thailand. J Helminthol. 2018;94:e7. Epub 2018/10/30. 10.1017/S0022149X18000962 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sitotaw B, Shiferaw W. Prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections and associated risk factors among the first-cycle primary schoolchildren in Sasiga District, Southwest Ethiopia. J Parasitol Res. 2020;2020:8681247. Epub 2020/04/02. 10.1155/2020/8681247 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nagakura K, Tachibana H, Tanaka T, Kaneda Y, Tokunaga M, Sasao M, et al. An outbreak of amebiasis in an institution for the mentally retarded in Japan. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1989;42(2):63–76. Epub 1989/04/01. 10.7883/yoken1952.42.63 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Nagakura K, Tachibana H, Kaneda Y, Suzuki H, Sasaoka K, Kobayashi S, et al. Amebiasis in institutions for the mentally retarded in Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1990;43(4):123–31. Epub 1990/08/01. 10.7883/yoken1952.43.123 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Nishise S, Fujishima T, Kobayashi S, Otani K, Nishise Y, Takeda H, et al. Mass infection with Entamoeba histolytica in a Japanese institution for individuals with mental retardation: epidemiology and control measures. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 2010;104(5):383–90. Epub 2010/09/08. 10.1179/136485910X12743554760388 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Rivera WL, Santos SR, Kanbara H. Prevalence and genetic diversity of Entamoeba histolytica in an institution for the mentally retarded in the Philippines. Parasitol Res. 2006;98(2):106–10. Epub 2005/11/15. 10.1007/s00436-005-0024-8 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Tachibana H, Kobayashi S, Nagakura K, Kaneda Y, Takeuchi T. Asymptomatic cyst passers of Entamoeba histolytica but not Entamoeba dispar in institutions for the mentally retarded in Japan. Parasitol Int. 2000;49(1):31–5. Epub 2000/03/24. 10.1016/s1383-5769(99)00032-x . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Al-Areeqi MA, Sady H, Al-Mekhlafi HM, Anuar TS, Al-Adhroey AH, Atroosh WM, et al. First molecular epidemiology of Entamoeba histolytica, E. dispar and E. moshkovskii infections in Yemen: different species-specific associated risk factors. Trop Med Int Health. 2017;22(4):493–504. 10.1111/tmi.12848 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ali IK, Hossain MB, Roy S, Ayeh-Kumi PF, Petri WA Jr., Haque R, et al. Entamoeba moshkovskii infections in children, Bangladesh. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9(5):580–4. Epub 2003/05/10. 10.3201/eid0905.020548 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Anuar TS, Al-Mekhlafi HM, Ghani MK, Azreen SN, Salleh FM, Ghazali N, et al. First molecular identification of Entamoeba moshkovskii in Malaysia. Parasitology. 2012:1–5. Epub 2012/09/04. 10.1017/S0031182012001485 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Fotedar R, Stark D, Beebe N, Marriott D, Ellis J, Harkness J. PCR detection of Entamoeba histolytica, Entamoeba dispar, and Entamoeba moshkovskii in stool samples from Sydney, Australia. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45(3):1035–7. Epub 2007/01/19. 10.1128/JCM.02144-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Beck DL, Dogan N, Maro V, Sam NE, Shao J, Houpt ER. High prevalence of Entamoeba moshkovskii in a Tanzanian HIV population. Acta Trop. 2008;107(1):48–9. Epub 2008/05/13. 10.1016/j.actatropica.2008.03.013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Genomic DNA isolated from E. moshkovskii Laredo strain was serially diluted and used as a template for PCR (lanes 1 to 7). Predicted 200-bp products were clearly detected from 1 pg of template DNA (lane 5). Lane 8, without template DNA; M, 100-bp DNA ladder.
(TIF)
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
Data Availability Statement
Nucleotide sequences have been deposited at the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank database, accession numbers LC546869-LC546886.