Figure 3.
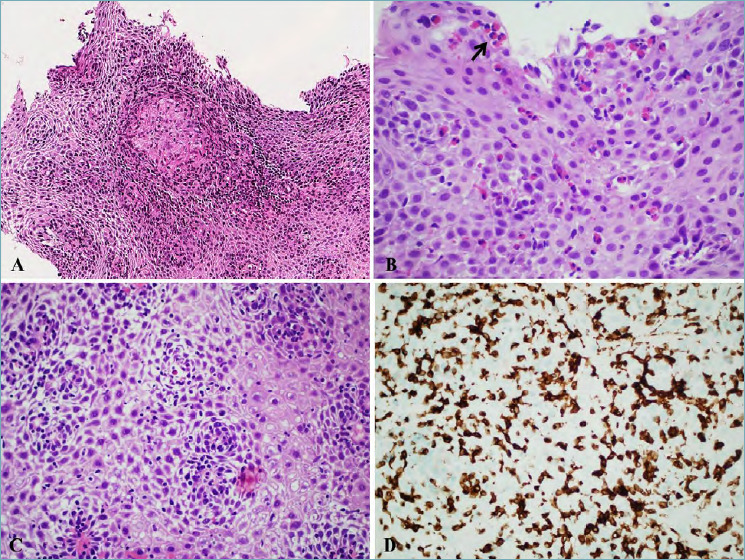
(A) Esophageal Crohn’s disease (magnification 20x). Presence of an epithelioid granuloma within squamous epithelium, diagnostic for esophageal localization of Crohn’s disease in a patient with previous diagnosis in the distal ileum; (B) Eosinophilic esophagitis (magnification 40x). A high number of intraepithelial eosinophils is present, also forming microabscesses (black arrow) in the superficial layer. (C) Lymphocytic esophagitis (magnification 40x). Marked spongiosis is present with an increase in intraepithelial lymphocytes in the peri-papillary areas. (D) Lymphocytic esophagitis (magnification 40x). Immunostains for CD3 showing a marked increase in intraepithelial T lymphocytes.
