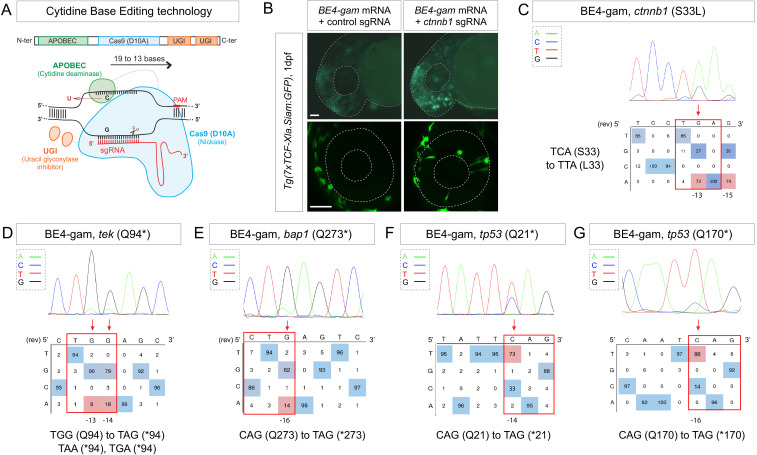
Figure 1. Efficient endogenous activation of Wnt signaling pathway and tumor suppressor genes targeting using BE4-gam in zebrafish.
(A) Schematic representation of the cytidine base editor technology. (B) Activation of Wnt signaling via S33L mutation in β-catenin. 1 dpf Tg(7xTCF-Xla.Siam:GFP) representative embryos injected with BE4-gam mRNA and ctnnb1 (S33L) sgRNA or control scrambled sequence. The upper panel shows an overall increase of GFP-positive cells in the head/anterior region upon the injection of the BE4-gam mRNA and ctnnb1 (S33L) sgRNA compared to the control situation. The lower panel shows maximal z-projection of lateral view of the injected embryos where ectopic GFP signal in retinal progenitor cells (white stars) can be detected, whereas control embryos do not show any fluorescence in the retina at this stage. (C–G) DNA sequencing chromatogram of targeted loci with the BE4-gam and obtained C-to-T conversion efficiencies. The chromatograms correspond to the highest efficiency reported for the single embryos analyzed as detailed in Table 2. (C) S33L mutation in β-catenin upon C-to-T conversion in ctnnb1 reached 73% of gene-editing efficiency. The other edited C led to a silent mutation GAC (D) to GAT (D). (D) Q94* mutation in Tek upon C-to-T conversion in tek reached 18% of gene-editing efficiency. (E) Q273* mutation in Bap1 upon C-to-T conversion in bap1 reached 14% of gene-editing efficiency. (F) Q21* mutation in p53 upon C-to-T conversion in tp53 reached 73% of gene-editing efficiency. (G) Q170* mutation in p53 upon C-to-T conversion in tp53 reached 86% of gene-editing efficiency. For (C) and (E), the reverse complement of the sgRNA sequence is shown. Scale bars: (B) 50 µm. (D–G) Numbers in the boxes represent the percentage of each base at that sequence position. In red are highlighted the base substitutions introduced by base editing, while the original bases are in blue. The color code of the chromatogram is indicated in the upper left corner (Adenine green, Cytosine blue, Thymine red, Guanine black). The distance from the PAM sequence of the targeted C base is indicated below each chromatogram. It is considered that the quantifications under 5% are due to the background signal from Sanger sequencing and are thus non-significant (Kluesner et al., 2018).