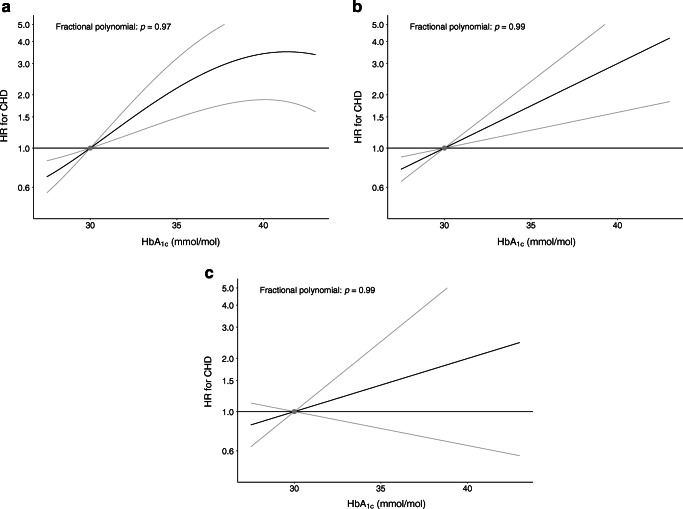
Fig. 1.
Non-linear Mendelian randomisation investigating the relationship between genetically proxied average blood glucose levels (measured by HbA1c) and risk of incident CHD in individuals without diabetes mellitus: (a) men and women combined; (b) men only; and (c) women only. The x-axis depicts HbA1c levels in mmol/mol. The y-axis depicts the hazard ratio for coronary heart disease (HR for CHD) with respect to the reference, plotted on a log scale. Reference is set to an HbA1c of 30 mmol/mol (4.9%). The grey lines represent the 95% CIs. The fractional polynomial test is a goodness-of-fit test that assesses whether any improvement of fit when using a non-linear function to model the association, compared with a linear function, is greater than would be expected due to chance (a significant p value indicates that a non-linear model is preferred to a linear model)