Introduction
In a recent meta-analysis from our group based on a systematic review we have identified brain regions reported to be responsible for central mechanisms of itch processing (1). We also have discussed the central mechanisms of itch proceeding in the brain more in depth in a review paper (2). The research papers that have studied central mechanism of itch are presented in Table 1 while their results are presented in Table 2. Here in this paper, we are exploring a new idea in which we categorize the itch matrix in the brain into three matrixes that each of them is contributing to a specific aspect of itch perception. This conceptualizes the processing of itch signals into different itch matrices could be useful in order to model different aspects of itch. For example, it is possible, that an overactivity in second matrix cause a higher susceptivity to contagious itch.
Table 1.
Papers and methods which have been used in order to study central mechanism of itch.
| # | References | Scanner | Neuroimaging analysis | Itch induction | Itch stimulus | Number of subjects | Pathology | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hsieh et al. (3) | PET | Subtraction | Intracutaneous injection | Histamine | 10 | Healthy | |
| 2 | Darsow et al. (4) | PET | Subtraction | Skin prick | Histamine | 6 | Healthy | |
| 3 | Darsow et al. (4) | PET | Correlation | Skin prick | Histamine | 6 | Healthy | |
| 4 | Drzezga et al. (5) | PET | Correlation | Skin prick | Histamine | 6 | Healthy | |
| 5 | Mochizuki et al. (6) | PET | Subtraction | Iontophoresis | Histamine | 15 | Healthy | |
| 6 | Walter et al. (7) | fMRI | Correlation | Skin prick | Histamine | 6 | Healthy | |
| 7 | Herde et al. (8) | fMRI | Subtraction | Intracutaneous microdialysis | Histamine | 10 | Healthy | |
| 8 | Leknes et al. (9) | fMRI | Correlation | Skin prick | Histamine | 8 | Healthy | |
| 9 | Leknes et al. (9) | fMRI | Correlation | Allergan | 8 | Atopic cohort | ||
| 10 | Mochizuki et al. (10) | fMRI | Correlation | Iontophoresis | Histamine | 14 | Healthy | |
| 11 | Mochizuki et al. (10) | fMRI | Subtraction | Iontophoresis | Histamine | 14 | Healthy | |
| 12 | Valet et al. (11) | fMRI | Subtraction | Skin prick | Histamine | 12 | Healthy | |
| 13 | Valet et al. (11) | fMRI | Subtraction | Skin prick | Histamine | 12 | Healthy | Temperature modeling |
| 14 | Schneider et al. (12) | PET | Subtraction | Iontophoresis | Histamine | 6 | Healthy | |
| 15 | Schneider et al. (12) | PET | Subtraction | Iontophoresis | Histamine | 8 | Atopic dermatitis | |
| 16 | Schneider et al. (12) | PET | Subtraction | Iontophoresis | Histamine | 8 | Healthy < > AD | |
| 17 | Yosipovitch et al. (13) | fMRI | Subtraction | Scratching | 13 | Healthy | ||
| 18 | Ishiuji et al. (14) | fMRI | ASL | Iontophoresis | Histamine | 8 | Atopic dermatitis | |
| 19 | Ishiuji et al. (14) | fMRI | ASL | Iontophoresis | Histamine | 7 | Healthy | |
| 20 | Ishiuji et al. (14) | fMRI | ASL | Iontophoresis | Histamine | 7 | Healthy < > AD | |
| 21 | Mochizuki et al. (15) | fMRI | Subtraction | Electrically induced itch | 10 | Healthy | ||
| 22 | Mochizuki et al. (15) | MEG | Subtraction | Electrically induced itch | 10 | Healthy | ||
| 23 | Vierow et al. (16) | fMRI | Subtraction | Scratching | 15 | Healthy | ||
| 24 | Vierow et al. (16) | fMRI | Subtraction | Scratching in presence of itch | 15 | Healthy | ||
| 25 | Pfab et al. (17) | fMRI | Subtraction | Skin prick non lesion skin | Histamine | 13 | Atopic dermatitis | Thermal modulation |
| 26 | Pfab et al. (17) | fMRI | Subtraction | Skin prick lesion skin | Histamine | 13 | Atopic dermatitis | Thermal modulation |
| 27 | Bergeret et al. (18) | PET | Subtraction | Iontophoresis | Histamine | 28 | Healthy | |
| 28 | Bergeret et al. (18) | PET | Correlation | Iontophoresis | Histamine | 29 | Healthy | Itch sensation |
| 29 | Holle et al. (19) | fMRI | Subtraction | Audiovisual itch | 18 | Healthy | ||
| 30 | Holle et al. (19) | fMRI | Correlation | Audiovisual itch | 19 | Healthy | ||
| 31 | Kleyn et al. (20) | fMRI | Subtraction | Skin prick | Histamine | 16 | Healthy | |
| 32 | Kleyn et al. (20) | fMRI | Correlation | Skin prick | Histamine | 16 | Healthy | |
| 33 | Papoiu et al. (21) | fMRI | ASL | Iontophoresis | Histamine | 15 | Healthy | |
| 34 | Papoiu et al. (21) | fMRI | ASL | Spicules rubbing | Cowhage | 15 | Healthy | |
| 35 | Papoiu et al. (21) | fMRI | ASL | 15 | Healthy | Cowhage < >Histamine | ||
| 36 | Papoiu et al. (21) | fMRI | Subtraction | Audiovisual pain | 18 | Healthy | ||
| 37 | Papoiu et al. (21) | fMRI | Subtraction | Itch & Pain | 18 | Healthy | Itch & Pain | |
| 38 | Papoiu et al. (22) | fMRI | ASL-correlation | Scratching | 14 | Healthy | Correlated with the pleasurability | |
| 39 | Papoiu et al. (22) | fMRI | ASL-correlation | Scratching | 14 | Healthy | Correlated with itch relief | |
| 40 | Stumpf et al. (23) | fMRI | Subtraction | Microdialysis | Histamine | 33 | Healthy | Female>Males |
| 41 | Stumpf et al. (23) | fMRI | Subtraction | Microdialysis | Histamine | 33 | Healthy | Female>Males (with stroop task) |
| 42 | Napadow et al. (24) | fMRI | Subtraction | Skin prick | Allergen-induced | 14 | Atopic dermatitis | Temperature modeling |
| 43 | Napadow et al. (24) | fMRI | Subtraction | Skin prick | Allergen-induced | 14 | Atopic dermatitis | Temperature modeling and acupuncture intervention |
| 44 | Desbordes et al. (25) | fMRI | Connectivity | Skin prick | Allergen-induced | 14 | Atopic dermatitis | Right premotor as seed |
| 45 | Desbordes et al. (25) | fMRI | Connectivity | Skin prick | Allergen-induced | 14 | Atopic dermatitis | Right insula as seed |
| 46 | Desbordes et al. (25) | fMRI | Connectivity | Skin prick | Allergen-induced | 14 | Atopic dermatitis | Right putamen as seed |
| 47 | Desbordes et al. (25) | fMRI | Connectivity | Skin prick | Allergen-induced | 14 | Atopic dermatitis | Left superior parietal lobule as seed |
| 48 | Desbordes et al. (25) | fMRI | Connectivity | Skin prick | Allergen-induced | 14 | Atopic dermatitis | Right anterior mid-cingulate cortex as seed |
| 49 | Desbordes et al. (25) | fMRI | Connectivity | Skin prick | Allergen-induced | 14 | Atopic dermatitis | Right caudate as seed |
| 50 | Desbordes et al. (25) | fMRI | Connectivity | Skin prick | Allergen-induced | 14 | Atopic dermatitis | Right globus pallidus |
| 51 | Mochizuki et al. (26) | fMRI | Subtraction | Electrically induced itch | 16 | Healthy | ||
| 52 | Mochizuki et al. (26) | fMRI | Subtraction | Electrically induced itch | Passive scratching | 16 | Healthy | Scratching itch |
| 53 | Mochizuki et al. (26) | fMRI | Subtraction | Electrically induced itch | Passive scratching | 16 | Healthy | Scratching itch> scratching another region |
| 54 | Mochizuki et al. (26) | fMRI | Subtraction | Electrically induced itch | Passive scratching | 16 | Healthy | Deactivation scratching itch region |
| 55 | Mochizuki et al. (26) | fMRI | Subtraction | Electrically induced itch | Passive scratching | 16 | Healthy | Scratching another region |
| 56 | Papoiu et al. (27) | fMRI | ASL | Iontophoresis | Histamine | 13 | End-stage renal disease | |
| 57 | Papoiu et al. (27) | fMRI | ASL | Spicules rubbing | Cowhage | 13 | End-stage renal disease | |
| 58 | Kim et al. (28) | fMRI | Subtraction | Audiovisual itch | 14 | Neurodermatosis | Stress-induced pruritus | |
| 59 | Kim et al. (28) | fMRI | Subtraction | Audiovisual itch | 14 | Neurodermatosis | Stress-induced pruritus (after sedating antihistamine treatment) | |
| 60 | Kim et al. (28) | fMRI | Subtraction | Audiovisual itch | 14 | Neurodermatosis | Stress-induced pruritus (after non-sedating antihistamine treatment) | |
| 61 | Mochizuki et al. (29) | fMRI | ASL | Spicules rubbing | Cowhage | 10 | Healthy | Scratching |
| 62 | Mochizuki et al. (29) | fMRI | ASL | Spicules rubbing | Cowhage | 10 | Chronic itch patients | Scratching |
| 63 | Mochizuki et al. (29) | fMRI | ASL | Spicules rubbing | Cowhage | 20 | Patients>Healthy | Scratching |
| 64 | Mochizuki et al. (29) | fMRI | ASL | Spicules rubbing | Cowhage | 10 | Healthy | Scratching |
| 65 | Mochizuki et al. (29) | fMRI | ASL | Spicules rubbing | Cowhage | 10 | Chronic itch patients | Scratching |
| 66 | Mochizuki et al. (29) | fMRI | ASL | Spicules rubbing | Cowhage | 20 | Patients>Healthy | Scratching |
| 67 | Napadow et al. (30) | fMRI | Skin prick | Allergan | 14 | Atopic dermatitis | Nocebo > open saline | |
| 68 | Papoiu et al. (31) | fMRI | ASL | Iontophoresis | Histamine | 24 | Healthy | Areas significantly activated during the suppression of histamine itch by butorphanol |
| 69 | Papoiu et al. (31) | fMRI | ASL | Spicules rubbing | Cowhage | 25 | Healthy | Deactivation areas significantly correlated with the reduction in cowhage itch |
| 70 | Vierow et al. (32) | fMRI | Subtraction | Spicules rubbing | Capsaicin | 16 | Healthy | Placebo |
| 71 | Vierow et al. (32) | fMRI | Subtraction | Spicules rubbing | Capsaicin | 16 | Healthy | Naltrexone |
| 72 | Vierow et al. (32) | fMRI | Subtraction | Spicules rubbing | Histamine | 16 | Healthy | Placebo |
| 73 | Vierow et al. (32) | fMRI | Subtraction | Spicules rubbing | Histamine | 16 | Healthy | Naltrexone |
| 74 | Schut et al. (33) | fMRI | ASL-Subtraction | Audiovisual | 11 | Atopic dermatitis | ||
| 75 | Schut et al. (33) | fMRI | ASL-correlation | Audiovisual | 11 | Atopic dermatitis | ||
| 76 | Stumpf et al. (34) | fMRI | Subtraction | Microdialysis | Histamine | 33 | Healthy | Itch modulation by distraction (Itch>stroop) |
| 77 | van de Sand et al. (35) | fMRI | Subtraction | Skin patch | Histamine | 30 | Healthy | Nocebo modulation Itch-nocebo > itch only (temperature modulating) |
| 78 | van de Sand et al. (35) | fMRI | Connectivity with insula | Skin patch | Histamine | 30 | Healthy | Nocebo modulation Itch-nocebo > itch only (temperature modulating) |
| 79 | Wang et al. (36) | fMRI | Resting state | 40+40 | Chronic urticaria +Healthy | CSU > HC (amplitude of low frequency fluctuations) | ||
| 80 | Wang et al. (36) | fMRI | Resting state | 40+40 | Chronic urticaria +Healthy | CSU > HC (functional connectivity with right ventral striatum) | ||
| 81 | Wang et al. (36) | fMRI | Resting state | 40+40 | Chronic urticaria +Healthy | CSU > HC (functional connectivity with right putamen) | ||
| 82 | Wang et al. (37) | fMRI | Resting state | 40+40 | Chronic urticaria +Healthy | CSU > HC (regional homogeneity) | ||
| 83 | Wang et al. (37) | fMRI | Resting state | 40 | Chronic urticaria | After intervention > Before intervention (regional homogeneity) | ||
| 84 | Wang et al. (37) | fMRI | Resting state | 40+40 | Chronic urticaria +Healthy | CSU > HC (functional connectivity with Cerebellum) | ||
| 85 | Wang et al. (37) | fMRI | Resting state | 40 | Chronic urticaria | After intervention > Before intervention (functional connectivity with Cerebellum) | ||
| 86 | Wang et al. (37) | fMRI | Resting state | 40 | Chronic urticaria | After intervention > Before intervention (functional connectivity with SI/MI/SMA) | ||
| 87 | Min et al. (38) | fMRI | Resting state | Skin prick | Histamine | 20 | Healthy | Acupuncture (itch-baseline)> Non-responder (itch-baseline) (functional connectivity with left Putamen) |
| 88 | Min et al. (38) | fMRI | Resting state | Skin prick | Histamine | 20 | Healthy | Acupuncture (itch-baseline)> Non-responder (itch-baseline) (functional connectivity with right Putamen) |
| 89 | Min et al. (38) | fMRI | Resting state | Skin prick | Histamine | 20 | Healthy | Acupuncture (itch-baseline)> Non-responder (itch-baseline) (functional connectivity with Pallidum) |
| 90 | Mochizuki et al. (39) | fMRI | Subtraction | Electrically induced itch | 25 | Healthy | ||
| 91 | Mochizuki et al. (39) | fMRI | Connectivity | Electrically induced itch | 25 | Healthy |
Table 2.
Results of the all the papers studied the central mechanism of itch.
| Parts of which matrix | 1 | 1 | 1/2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regions | Primary somatosensory cortex (BA 1, 2, 3) | Somatosensory associated/parietal cortex (BA 5, 7) | Primary motor cortex (BA 4) | Pre- motor and supplementary motor cortex (BA 6) | Cerebellum | Insular cortex (BA 13, 16) | Posterior cingulate cortex (BA 23,31) | Anterior cingulate cortex (BA 24, 32, 33) | Prefrontal cortex (BA 9) | Frontopolar and orbifrontal area (BA 8, 10, 11, 12) | Inferior and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (BA 44, 45, 46, 47) | Temporal gyrus (BA 20, 21, 22, 38) + fusiform | Prietal pole/Wernicke's area (BA 39, 40) Inferior parietal, supramarginal | Thalamus | Basal ganglia | Secondary somatosensory cortex (BA 40, 43) OPC | Precuneus (BA 7, 31) | Putamen | Visual association gyrus (BA 17, 18, 19) ocipital | Anterior entorhinal cortex (BA 34) | Hippocampus | Parahippocampal gyrus | Ventral tegmental area cum om Ventral tegmental area | Raphé nucleus | Red Nucleus | PAG | Substantia nigra | Clastrum | Midbrain | Amygdala | Brain steem | Lentiform nucleus | Pons | |
| # | Author | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | (3) | B | B | C | B | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | Darsow et al. (4) | B | C | B | C | C | C | C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | Darsow et al. (4) | B | B | B | C | C | B | C | C | C | C | B | I | C | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | Drzezga et al., (5) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | Mochizuki et al. (6) | I | I | C | B | I | C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | Walter et al. (7) | C | C | B | C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | Herde et al. (8) | C | C | B | B | B | B (m) | B | C | B | B | B | B | B | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | Leknes et al. (9) | B | B | B | I | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | Leknes et al. (9) | C | C | C | B | B | C | B | B | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | Mochizuki et al. (10) | I | B | C | C | I | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 | Mochizuki et al. (10) | I | B | C | I | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | Valet et al. (11) | B- | C- | I | C | I- | B- | B | B | B | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13 | Valet et al. (11) | C- | I | B | I- | B | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 | Schneider et al. (12) | C | C | C | C | I | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15 | Schneider et al. (12) | B | B | I | I | B | C | C | C | I | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | Schneider et al. (12) | C | I | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 17 | Yosipovitch et al. (13) | B- | B- | B,B- | B | B | B- | I,B- | I,B- | B | B | B | B | B- | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 | Ishiuji et al. (14) | B | B | I | B | B | B | B | B | I | C | B | C | B | C | |||||||||||||||||||
| 19 | Ishiuji et al. (14) | C | C | C | C | C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 | Ishiuji et al. (14) | C | C | C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 21 | Mochizuki et al. (15) | C | I | B | I | I | C | B | B | B | C | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 22 | Mochizuki et al. (15) | B | B | C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23 | Vierow et al. (16) | B | B | B | B | B | B | B | B | B | I | B | B | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 | Vierow et al. (16) | B | B | B | B | B | B | B | B | B | B | B | B | B | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 25 | Pfab et al. (17) | B- | B- | B- | B- | B | B | B- | B | I | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 26 | Pfab et al. (17) | B- | B- | B- | B | B- | B- | B | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27 | Bergeret et al. (18) | I | I | I | C | I | I | B | C | B | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 28 | Bergeret et al. (18) | C | I | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29 | Holle et al. (19) | L | L | L | B | B | L | B | B | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30 | Holle et al. (19) | L | L | L | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31 | Kleyn et al. (20) | I | B | B | C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 32 | Kleyn et al. (20) | C | B | B | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 33 | Papoiu et al. (21) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 34 | Papoiu et al. (21) | C | C | B | C | B | B | C | B | B | B | B | C | B | C | C | ||||||||||||||||||
| 35 | Papoiu et al. (21) | B | C | B | C | I | C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 36 | Papoiu et al. (21) | L | B | B | L | L | B | L | B | R | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 37 | Papoiu et al. (21) | L | B | L | L | L | B | L | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 38 | Papoiu et al. (22) | I | B | C | C | B | I | I | I | B | C | C | B | B | B | B | C | |||||||||||||||||
| 39 | Papoiu et al. (22) | C | C | I | I | I | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 40 | Stumpf et al. (23) | B | B | C | C | B | I | B | C | C, I- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 41 | Stumpf et al. (23) | I | C- | C | B | I | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 42 | Napadow et al. (24) | I | B | C | C | C | B | B | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 43 | Napadow et al. (24) | B | B | C | C | I | C | C | C | C | C | C | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 44 | Desbordes et al. (25) | R | L | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 45 | Desbordes et al. (25) | L | L | L | L | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 46 | Desbordes et al. (25) | L | L | B | L (42) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 47 | Desbordes et al. (25) | R | L | L | R | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 48 | Desbordes et al. (25) | R | R | R | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 49 | Desbordes et al. (25) | L | L | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 50 | Desbordes et al. (25) | L | R | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 51 | Mochizuki et al. (26) | L | R | R | B | B | R | L | B | B | B | B | B | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 52 | Mochizuki et al. (26) | B | B | B | B | B | B | B | B | B | B | B | B | B | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 53 | Mochizuki et al. (26) | B | B | L | L | B | R | L | B | L | L | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 54 | Mochizuki et al. (26) | B | B | L | L | B | L | B | B | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 55 | Mochizuki et al. (26) | B | B | R | B | R | B | B | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 56 | Papoiu et al. (27) | I | I | B | L | B | B | B | B | B | B | I | C | I | B | B | B | I | ||||||||||||||||
| 57 | Papoiu et al. (27) | C | I | B | C | I | B | C | I | C | C | B | C | C | I | C | ||||||||||||||||||
| 58 | Kim et al. (28) | R | R | R | L | L | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 59 | Kim et al. (28) | B | R | L | L | B | L | R | R | L | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 60 | Kim et al. (28) | B | B | B | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 61 | Mochizuki et al. (29) | B | B | B | B | I | B | B | I | B | I | B | B | B | C | C | ||||||||||||||||||
| 62 | Mochizuki et al. (29) | C | B | C | B | B | I | I | B | C | B | B | C | I | B | C | ||||||||||||||||||
| 63 | Mochizuki et al. (29) | C,I- | B,I- | B- | I- | C | B | C | I- | C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 64 | Mochizuki et al. (29) | C | B | C | I | B | B | B | B | B | B | B | I | B | C | B | B | |||||||||||||||||
| 65 | Mochizuki et al. (29) | B | B | B | B | I | I | I | C | B | B | B | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 66 | Mochizuki et al. (29) | I | I | C | B | C | C,I- | I | C | I | C | I- | C | I- | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 67 | Napadow et al. (30) | C | I | C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 68 | Papoiu et al. (31) | I | B | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 69 | Papoiu et al. (31) | C | B | I | C | I | I | C | B | B | I | C | I | I | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 70 | Vierow et al. (32) | B | I- | B | B | B,C- | B | B | B | C | B- | B- | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 71 | Vierow et al. (32) | B | I- | B | B | B | B | B | B | C | C- | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 72 | Vierow et al. (32) | B | I- | B | B | B | B | B | C | B | C | C- | B- | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 73 | Vierow et al. (32) | B | I- | B | B | I | B | B | C | B | C | C- | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 74 | Schut et al. (33) | B | I | C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 75 | Schut et al. (33) | I | I | I | I | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 76 | Stumpf et al. (34) | B- | C | C | B- | B- | I- | I | I- | I | B- | C- | I- | I- | B- | |||||||||||||||||||
| 77 | van de Sand et al. (35) | C | I | I- | C | I,C- | C | B | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 78 | van de Sand et al. (35) | C- | C | I | I,C- | C | I | I | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 79 | Wang et al. (36) | R | R | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 80 | Wang et al. (36) | R- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 81 | Wang et al. (36) | L- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 82 | Wang et al. (37) | B | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 83 | Wang et al. (37) | B | B | B | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 84 | Wang et al. (37) | B | B | R | R | R | B | R | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 85 | Wang et al. (37) | R- | R- | R- | R- | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 86 | Wang et al. (37) | B- | L- | R- | L- | L- | L- | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 87 | Min et al. (38) | L | L | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 88 | Min et al. (38) | L | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 89 | Min et al. (38) | C | L | C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 90 | Mochizuki et al. (39) | C | C | C | B | L | B | B | B | B | B | B | B |
If laterality applicable: B, Bilateral; C, Contralateral to stimulus; I, Ipsilateral to stimulus. If laterality not applicable: B, Bilateral; L, Left; R, Right.
When only the peak locations were reported the sprout022 tool (Dept. of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging, Yale School of Medicine) was used to identify the regions.
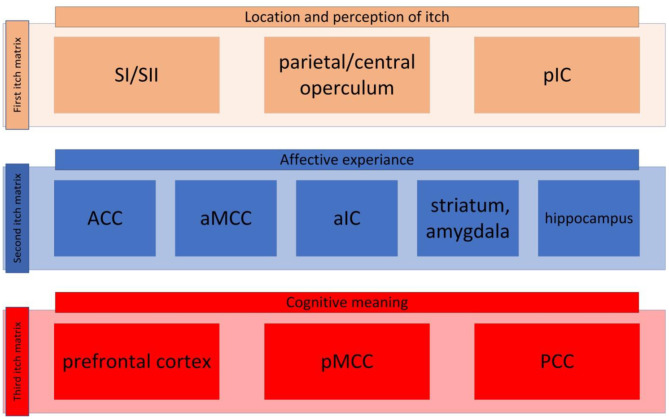
Unlike the visual system pain and itch can evoke multitude of regions in the brain, which we call pain matrix and itch matrix respectively. Recent studies have proposed that the pain matrix can be categorized into three different pain matrixes (40, 41): one contributing to perception and the location of pain; another matrix responsible for the affective aspect of the pain; and a third involving decoding the cognitive aspect of pain. In the same manner, we guardedly propose that the itch processing network can be broken down into three main matrixes although many data are still lacking. These three matrixes have been presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
The itch matrix categorized into three itch matrixes. First itch matrix consisted of primary and secondary sensorimotor cortex (SI and SII, respectively), the parietal/central operculum, and the posterior insular cortex (pIC) (here presented in brown, this matrix is also presented in Figure 2A). The second itch matrix consisting of anterior singular cortex (ACC), anterior part of the middle cingulate cortex (aMCC), anterior part of the insular cortex (aIC), amygdala, striatum and hippocampus (here presented in blue, this matrix is also presented in Figure 2B). The third matrix contains prefrontal cortex, posterior part of the middle cingulate cortex (pMCC), and posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) (here presented in red, this matrix is also presented in Figure 2C).
First Itch Matrix
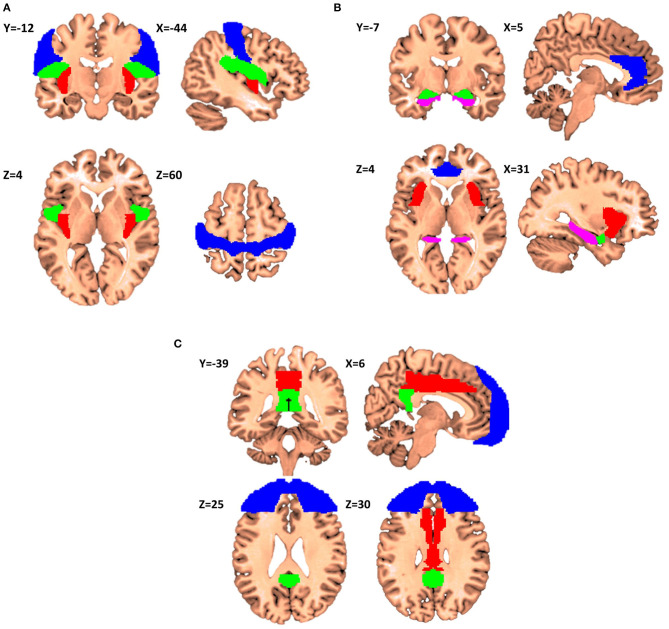
The first itch matrix includes but is not restricted to the primary sensorimotor cortex, the parietal/central operculum, and the posterior insular cortex (Figure 2A).
Figure 2.
Proposals for itch matrixes (X,Y,Z denotes the location of the corresponding slice in Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) coordinate system). (A) Elements of the first matrix contributing to encoding of the recognition, localization, and intensity of itch. Primary sensorimotor cortex is presented in Blue, parietal operculum in Green, and posterior insular cortex in Red (Regions have been extracted from Automated Anatomical Labeling and Harvard-Oxford atlases). (B) The second matrix itch processing matrix consenting of anterior cingulate cortex (Blue), anterior insular cortex (Red), amygdala (Green) and hippocampus (Violet). This matrix is in charge of affective and motivational aspects of itch. (C) The third matrix consists of frontal cortex (Blue), middle cingulate cortex (Red), and posterior cingulate cortex (Green), and it is involved in the interpretation of the cognitive meaning of itch.
Among these three regions the primary sensorimotor cortex is involved in the encoding of the recognition, localization, and intensity of painful stimuli (42). In pain studies, activation in this region bears a linear relationship with pain intensity (43–47). In a positron emission tomography (PET) study by Drzezga et al. (5) the authors reported that SI activity, is positively correlated with itch intensity. Six years after Drzezga, in 2007, Mochizuki et al. added the secondary somatosensory cortex (SII) demonstrating an increase of activity in this region after itch induction with histamine (10). The increase was statistically not different than the proven one observed in the painful condition (pain vs. itch) but did not reach a statistically corrected threshold when comparing itch against no itch.
In another study which includes both AD patients and healthy controls, itch was found to activate the post-central gyrus in the right hemisphere (12). This study together with Drzezga study in 2001 are reported in the meta-analysis on Itch from Lee et al. (48). Out of 56 regions listed in the parietal cortex (31 Left and 25 Right) from 18 studies (Table 1). Brain activity upon itch stimulation in (48), left SI appears to be activated eight times against two only in the right hemisphere. On the contrary, right SII is reported five times against two only in the left hemisphere. The other regions mentioned (n = 39) are in both left and right parietal cortices sometime very near to the SI/SII regions (i.e., SMG, SPL, IPL, anterior parietal cortex).
In the meta-analysis from Roberts et al. (49), the authors suggest the possibility of a specificity of these regions for the itching process as they appear to be better activated by itching than by pain. Interestingly, they also group these regions with the central operculum. In a recent meta-analysis of our group (1), SI/SII region was not clearly identified but we discussed this point regarding the diversity of studies we included. Our results on correlations with itch intensity also showed two important clusters in bilateral insular cortices (5068 voxels right 4589 voxels left) that spread to a great extent on the post-central gyri.
The co-activation of the central operculum together with SI/SII cortex is widely reported in itch literature both in healthy subjects and patients. Indeed, central operculum corresponding to the junction of pre- and post-central gyri accompanied with the region located laterally to the posterior convolution of the insula is often confounded with insula itself or even SI. In the regions abbreviated OPC, also named rolandic operculum elsewhere, itch intensity was also correlated with PET signal both in healthy subjects and AD patients (4, 33).
Finally, we propose that the insular cortex, and especially its posterior portion, takes part into this first matrix. As a common point between these regions, their gradual response with itch intensity seems important to highlight. In Leknes et al. bilateral insular and left posterior insular activity (BOLD) is correlated with histamine-induced itch intensity (9). Following Craig (50, 51), Mochizuki et al. postulate that the posterior part of insula plays a different role than its anterior part (52, 53). A distinction that can also find its basis on cytoarchitectural composition of these structures and their connectives with other brain areas (50, 54).
Despite weak evidences in itch literature, other evidences can help to understand the insula role in processing the sensations which are common to itch and pain. Mazzola et al. explain that the two thirds of posterior insula submitted to low electrical stimulation (SEEG) directly translate these stimulations as pain sensations (55). Another study from Frot et al. showed that once pain feeling is reached, the posterior insular cortex activity still correlates with noxious thermal stimulation intensity (47).
In summary, all these regions encode the feeling of itchy sensation and are somewhat translating its intensity level as well as their location following a somatotopic representation. When compared to Xiang et al. study (41), this first matrix includes all already reported regions for pain. However, studies reporting activities in those regions only for itch are rare and some studies need to be carefully interpreted given approximations inherent to main peak reporting. Effectively, secondary peaks of wide clusters or percentage of anatomical regions covered by these clusters are most often not indicated. As an example, the absence of parietal operculum in Roberts et al. study (49) needs to be put in perspective. Indeed, the point that the contrast pain—itch shows an increased activity in the parietal operculum does not mean that this region is silent in itch. Moreover, in the same study, the opposite contrast itch—pain, which reveals an implication of both right supramarginal gyrus and central operculum, could have led us to add more parietal areas to this first matrix.
So far, we have dealt with the membership of each of these brain regions in the matrix separately. However, interesting arguments reside in the fact that new pathological conditions can appear when these regions grouped and malfunction together. Hence, some studies reported that SI/SII together with the insular cortex participate in creating the allodynia phenomenon (56–59). Consecutively, these regions once activated lead to an ignition of the pain network inducing activity in the PAG, the prefrontal cortex, the thalamus, the amygdala, the ACC and many other regions within the pain network. Allodynia has repercussions on the way normal brain areas react to tactile stimuli and authors do not only consider the condition through the scope of pain matrix. Many brain areas are those involved in tactile or thermal sensitivity and this allows more faithful comparison with itch perception. The difficulty with allodynia is that even when it is spontaneous, painful sensation is quickly reached and its intensity then depends on other brain region listed above.
To illustrate this phenomenon, we adduce together both Ducreux et al. study (60) and an article from Geuter et al. (61) about predictive coding. In Ducreux et al. authors demonstrated with noxious and non-noxious cold stimulation (4° and 22°C) that while non-noxious cold in control subjects activates SII and the insular cortex (mostly its anterior part), the same non-noxious stimulation did activates SII and mid-posterior insula in allodynic patients together with other regions of the pain network (60). In Geuter et al. work, the authors used the predictive coding theory of brain functioning to demonstrate a difference within the anterior and the posterior part of the insula. While the anterior part would be dedicated to pain feelings as a prediction error on perceived sensations, the posterior part only responds to pain intensity with no comparisons to any predicted sensation (61). We propose that in Ducreux et al. even if the feeling is non-noxious in control subjects, it remains unpredictable and then activates the anterior part of the insula. However, allodynic patients are prepared to feel painful stimulation and then, the anterior part shut down as painful sensation are correctly predicted. Meanwhile, the posterior part of the insula starts to encode its intensity like it was demonstrated by Frot et al. (47) in implanted subjects when stimulation becomes noxious.
Second Itch Matrix
The second itch matrix could consist of the ACC, aMCC, aIC, amygdala, striatum and hippocampus (Figure 2B). This network could encode the affective and motivational aspects of itch. Significant activation in the ACC, especially dorsal, extending to the anterior part of the middle cingulate cortex (aMCC), has been linked to the reward network and the positive or negative emotional response (40). Noteworthy, Vogt has reported that the aMCC reflects emotional awareness and fear leading to the questioning of the enrolment of the aMCC to the ACC gross function (62, 63). Considering the anterior insula, it is reported to be involved in the awareness of emotions and subjective feelings (50) as well as errors of predictions like mentioned above. Another literature about lesions in the aIC would cause deficits in emotional awareness (e.g., alexithymia) (64). Several studies have reported that activity in the aIC is significantly correlated with the unpleasantness of itch (8–10, 18, 21). For the hippocampus, it has been also shown that this structure is fully integrated in the itch network (13, 21, 22). For example, only active scratching can relief activity in ipsi-hippocampal structure (53). The role of hippocampus together with amygdala, dACC and insular cortex are well-documented in Sanders and Akiyama (65). The authors noticed and argued that “amygdala and hippocampus activation appears to go hand-in-hand in most studies of itch, suggesting that the memory of previous itch experiences may be a significant factor in itch-related anxiety.” Stratum possibly involved with motivation aspects of itch and/or the carving for scratching.
According to original paradigms, two other studies have reported diminished activation of these regions in tasks that change the nature of pain perception with context variations (66) or with analgesia induced by meditation (67). While the first of these shows a diminished activation in dorsal ACC and insula as the subjects switch their perception from unpleasant to pleasant (or less unpleasant) revealing the link between emotional and motivational function. The second demonstrate that experienced Zen meditators can reduce activity of their prefrontal medial cortex, amygdala and hippocampus regions at the expense of an increased activity in dorsal ACC or insula which still belong to this second matrix but are more related to mindfulness. These articles suggest that making things more conscious by bringing activities closer to the awareness matrix (with insula as a common region) putatively lead to less harmful psychological consequences. This second matrix is more robust than the first one. Many arguments in the itch literature exist and converge about its functional role.
Third Itch Matrix
The third itch matrix would include parts of the prefrontal cortex, pMCC, and PCC (Figure 2C). This network should be involved in the subjective perception of itch. The cognitive state of the mind can affect the itch sensation e.g., emotions, obsessions, religious beliefs, disgusts, expectations, and past experiences. This pattern of activation is also present in the distraction from itch caused by the Stroop task (e.g., in the DLPFC) (14, 30, 34). The third matrix receives and integrates information from the foregoing two and triggers behavioral response.
Conclusion
Knowledge of itch processing in the brain is growing thanks to brain imaging (2, 68). A better understanding of interactions between itch matrixes would allow a better understanding of pruritus in different cutaneous or extra-cutaneous etiologies (69).
Author Contributions
LM, J-LC, DB, and OD contributed to conception and design of the study. PN organized the database and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. OD wrote sections of the manuscript. All authors contributed to manuscript revision, read, and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We thank the French Society of Dermatology for providing a grant.
Glossary
Abbreviations
- ACC
Anterior Cingulate Cortex
- AD
Atopic Dermatitis
- aIC
Anterior part of the Insular Cortex
- aMCC
Anterior part of the Middle Cingulate Cortex
- BOLD
Blood Oxygenation Level Dependent
- dACC
Dorsal part of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex
- DLPFC
Dorso-Lateral Pre-Frontal Cortex
- IPL
Inferior Parietal Lobule
- OPC
Operculum Central
- PAG
Peri-Aqueductal Gray matter
- PCC
Posterior Cingulate Cortex
- PET
Positron Emission Tomography
- pIC
Posterior Insular Cortex
- pMCC
Posterior part of the Middle Cingulate Cortex
- SI
Primary Somatosensory cortex
- SII
Secondary Somatosensory cortex
- SEEG
Stereo-Electro-Encephalo-Graphy
- SMG
Supra-Marginal Gyrus
- SPL
Superior Parietal Lobule.
References
- 1.Najafi P, Carré JL, Ben Salem D, Brenaut E, Misery L, Dufor O. Central mechanisms of itch: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J Neuroradiol. (2020) 47:450–7. 10.1016/j.neurad.2019.11.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Najafi P, Dufor O, Ben Salem D, Misery L, Carré JL. Itch processing in the brain. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2020) 47:400–1. 10.1111/jdv.17029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hsieh JC, Hagermark O, Stahle-Backdahl M, Ericson K, Eriksson L, Stone-Elander S, et al. Urge to scratch represented in the human cerebral cortex during itch. J Neurophysiol. (1994) 72:3004–8. 10.1152/jn.1994.72.6.3004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Darsow U, Drzezga A, Frisch M, Munz F, Weilke F, Bartenstein P, et al. Processing of histamine-induced itch in the human cerebral cortex: a correlation analysis with dermal reactions. J Invest Dermatol. (2000) 115:1029–33. 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2000.00193.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Drzezga A, Darsow U, Treede RD, Siebner H, Frisch M, Munz F, et al. Central activation by histamine-induced itch: analogies to pain processing: a correlational analysis of O-15 H2O positron emission tomography studies. Pain. (2001) 92:295–305. 10.1016/S0304-3959(01)00271-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mochizuki H, Tashiro M, Kano M, Sakurada Y, Itoh M, Yanai K. Imaging of central itch modulation in the human brain using positron emission tomography. Pain. (2003) 105:339–46. 10.1016/S0304-3959(03)00249-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Walter B, Sadlo MN, Kupfer J, Niemeier V, Brosig B, Stark R, et al. Brain activation by histamine prick test-induced itch. J Gen Intern Med. (2005) 20:380–2. 10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23817.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Herde L, Forster C, Strupf M, Handwerker HO. Itch induced by a novel method leads to limbic deactivations— a functional MRI study. J Neurophysiol. (2007) 98:2347–56. 10.1152/jn.00475.2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Leknes SG, Bantick S, Willis CM, Wilkinson JD, Wise RG, Tracey I. Itch and motivation to scratch: an investigation of the central and peripheral correlates of allergen- and histamine-induced itch in humans. J Neurophysiol. (2007) 97:415–22. 10.1152/jn.00070.2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mochizuki H, Sadato N, Saito DN, Toyoda H, Tashiro M, Okamura N, et al. Neural correlates of perceptual difference between itching and pain: A human fMRI study. Neuroimage. (2007) 36:706–17. 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.04.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Valet M, Pfab F, Sprenger T, Wöller A, Zimmer C, Behrendt H, et al. Cerebral Processing of histamine-induced itch using short-term alternating temperature modulation - an fMRI study. J Invest Dermatol. (2007) 128:426–33. 10.1038/sj.jid.5701002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Schneider G, Stander S, Burgmer M, Driesch G, Heuft G, Weckesser M. Significant differences in central imaging of histamine-induced itch between atopic dermatitis and healthy subjects. Eur J Pain. (2008) 12:834–41. 10.1016/j.ejpain.2007.12.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yosipovitch G, Ishiuji Y, Patel TS, Hicks MI, Oshiro Y, Kraft RA, et al. The brain processing of scratching. J Invest Dermatol. (2008) 128:1806–11. 10.1038/jid.2008.3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ishiuji Y, Coghill R, Patel T, Oshiro Y, Kraft R, Yosipovitch G. Distinct patterns of brain activity evoked by histamine-induced itch reveal an association with itch intensity and disease severity in atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. (2009) 161:1072–80. 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2009.09308.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mochizuki H, Inui K, Tanabe HC, Akiyama LF, Otsuru N, Yamashiro K, et al. Time course of activity in itch-related brain regions: a combined MEG -fMRI study. J Neurophysiol. (2009) 102:2657–66. 10.1152/jn.00460.2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Vierow V, Fukuoka M, Ikoma A, Dörfler A, Handwerker HO, Forster C. Cerebral representation of the relief of itch by scratching. J Neurophysiol. (2009) 102:3216–24. 10.1152/jn.00207.2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pfab F, Valet M, Sprenger T, Huss-Marp J, Athanasiadis GI, Baurecht HJ, et al. Temperature modulated histamine-itch in lesional and nonlesional skin in atopic eczema - a combined psychophysical and neuroimaging study. Allergy. (2010) 65:84–94. 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2009.02163.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bergeret L, Black D, Theunis J, Misery L, Chauveau N, Aubry F, et al. Validation of a model of itch induction for brain positron emission tomography studies using histamine iontophoresis. Acta Derm Venereol. (2011) 91:504–10. 10.2340/00015555-1067 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Holle H, Warne K, Seth AK, Critchley HD, Ward J. Neural basis of contagious itch and why some people are more prone to it. PNAS. (2012) 109:19816–21. 10.1073/pnas.1216160109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kleyn C e, McKie S, Ross A, Elliott R, Griffiths CEM. A temporal analysis of the central neural processing of itch. Br J Dermatol. (2012) 166:994–1001. 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2012.10849.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Papoiu AD, Coghill RC, Kraft RA, Wang H, Yosipovitch G. A tale of two itches. Common features and notable differences in brain activation evoked by cowhage and histamine induced itch. Neuroimage. (2012) 59:3611–23. 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.10.099 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Papoiu AD, Nattkemper LA, Sanders KM, Kraft RA, Chan YH, Coghill RC, et al. Brain's reward circuits mediate itch relief: a functional MRI study of active scratching. PLoS ONE. (2013) 8:e82389. 10.1371/journal.pone.0082389 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Stumpf A, Burgmer M, Schneider G, Heuft G, Schmelz M, Phan NQ, et al. Sex differences in itch perception and modulation by distraction - an fMRI pilot study in healthy volunteers. PLoS ONE. (2013) 8:e0079123. 10.1371/journal.pone.0079123 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Napadow V, Li A, Loggia ML, Kim J, Schalock PC, Lerner E, et al. The brain circuitry mediating antipruritic effects of acupuncture. Cereb Cortex. (2014) 24:873–82. 10.1093/cercor/bhs363 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Desbordes G, Li A, Loggia ML, Kim J, Schalock PC, Lerner E, et al. Evoked itch perception is associated with changes in functional brain connectivity. Neuroimage Clin. (2014) 7:213–21. 10.1016/j.nicl.2014.12.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Mochizuki H, Tanaka S, Morita T, Wasaka T, Sadato N, Kakigi R. The cerebral representation of scratching-induced pleasantness. J Neurophysiol. (2014) 111:488–98. 10.1152/jn.00374.2013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Papoiu ADP, Emerson NM, Patel TS, Kraft RA, Valdes-Rodriguez R, Nattkemper LA, et al. Voxel-based morphometry and arterial spin labeling fMRI reveal neuropathic and neuroplastic features of brain processing of itch in end-stage renal disease. J Neurophysiol. (2014) 112:1729–38. 10.1152/jn.00827.2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kim HJ, Park JB, Lee JH, Kim I-H. How stress triggers itch: a preliminary study of the mechanism of stress-induced pruritus using fMRI. Int J Dermatol. (2015) 55:434–42. 10.1111/ijd.12864 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mochizuki H, Papoiu ADP, Nattkemper LA, Lin AC, Kraft RA, Coghill RC, et al. Scratching induces overactivity in motor-related regions and reward system in chronic itch patients. J Invest Dermatol. (2015) 135:2814–23. 10.1038/jid.2015.223 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Napadow V, Li A, Loggia ML, Kim J, Mawla I, Desbordes G, et al. The imagined itch: brain circuitry supporting nocebo-induced itch in atopic dermatitis patients Allergy. (2015) 70:1485–92. 10.1111/all.12727 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Papoiu ADP, Kraft RA, Coghill RC, Yosipovitch G. Butorphanol suppression of histamine itch is mediated by nucleus accumbens and septal nuclei: a pharmacological fMRI study. J Invest Dermatol. (2015) 135:560–8. 10.1038/jid.2014.398 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Vierow V, Forster C, Vogelgsang R, Dörfler A, Handwerker H. Cerebral networks linked to itch-related sensations induced by Histamine and Capsaicin. Acta Dermato Venereologica. (2015) 95:645–52. 10.2340/00015555-2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Schut C, Mochizuki H, Grossman SK, Lin AC, Conklin CJ, Mohamed FB, et al. Brain processing of contagious itch in patients with atopic dermatitis. Front Psychol. (2017) 8:1267. 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01267 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Stumpf A, Pfleiderer B, Schneider G, Heuft G, Schmelz M, Phan NQ, et al. Distraction from itch shows brainstem activation without reduction in experimental itch sensation. Acta Derm Venereol. (2017) 97:1074–80. 10.2340/00015555-2732 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.van de Sand MF, Menz MM, Sprenger C, Büchel C. Nocebo-induced modulation of cerebral itch processing - an fMRI study. NeuroImage. (2018) 166:209–18. 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.10.056 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wang Y, Fang J-L, Cui B, Liu J, Song P, Lang C, et al. The functional and structural alterations of the striatum in chronic spontaneous urticarial. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:1725. 10.1038/s41598-018-19962-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wang Y, Fang J, Song P, Bao Y, Song W, Liu J, et al. The dysfunction of the cerebellum and its cerebellum-reward-sensorimotor loops in chronic spontaneous urticaria. Cerebellum. (2018) 17:507–16. 10.1007/s12311-018-0933-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Min S, Kim K-W, Jung W-M, Lee M-J, Kim Y-K, Chae Y, et al. Acupuncture for histamine-induced itch: association with increased parasympathetic tone and connectivity of putamen-midcingulate cortex. Front Neurosci. (2019) 13:215. 10.3389/fnins.2019.00215 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mochizuki H, Hernandez LE, Yosipovitch G, Sadato N, Kakigi R. The functional network processing acute electrical itch stimuli in humans. Front Physiol. (2019) 10:555. 10.3389/fphys.2019.00555 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Fenton BW, Shih E, Zolton J. The neurobiology of pain perception in normal and persistent pain. Pain Manage. (2015) 5:297–317. 10.2217/pmt.15.27 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Xiang Y, Wang Y, Gao S, Zhang X, Cui R. Neural mechanisms with respect to different paradigms and relevant regulatory factors in empathy for pain. Front Neurosci. (2018) 12:507. 10.3389/fnins.2018.00507 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Apkarian AV, Bushnell MC, Treede RD, Zubieta JK. Human brain mechanisms of pain perception and regulation in health and disease. Eur J Pain. (2005) 9:463–84. 10.1016/j.ejpain.2004.11.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Dong WK, Salonen LD, Kawakami Y, Shiwaku T, Kaukoranta EM, Martin RF. Nociceptive responses of trigeminal neurons in SII-7b cortex of awake monkeys. Brain Res. (1989) 484:314–24. 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90375-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Dong WK, Chudler EH, Sugiyama K, Roberts VJ, Hayashi T. Somatosensory, multisensory, and task-related neurons in cortical area 7b (PF) of unanesthetized monkeys. J Neurophysiol. (1994) 72:542–64. 10.1152/jn.1994.72.2.542 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Timmermann L, Ploner M, Haucke K, Schmitz F, Baltissen R, Schnitzler A. Differential coding of pain intensity in the human primary and secondary somatosensory cortex. J Neurophysiol. (2001) 86:1499–503. 10.1152/jn.2001.86.3.1499 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bornhövd K, Quante M, Glauche V, Bromm B, Weiller C, Büchel C. Painful stimuli evoke different stimulus–response functions in the amygdala, prefrontal, insula and somatosensory cortex: a singletrial fMRI study. Brain. (2002) 125:1226–36. 10.1093/brain/awf137 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Frot M, Magnin M, Mauguière F, Garcia-Larrea L. Human SII and posterior insula differently encode thermal laser stimuli. Cereb Cortex. (2007) 17:610–20. 10.1093/cercor/bhk007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lee JS, Han JS, Lee K, Bang J, Lee H. The peripheral and central mechanisms underlying itch. BMB Rep. (2016) 49:474–96. 10.5483/BMBRep.2016.49.9.108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Roberts CA, Stancak A, Fallon N, Thomas A, Kirkham TC. Where is itch represented in the brain, and how does it differ from pain? An activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis of experimentally-induced itch. J Invest Dermatol. (2019) 139:2245–8. 10.1016/j.jid.2019.04.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Craig AD. The sentient self. Brain Struct Funct. (2010) 214:563–77. 10.1007/s00429-010-0248-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Craig AD. Significance of the insula for the evolution of human awareness of feelings from the body. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2011) 1225:72–82. 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.05990.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Mochizuki H, Kakigi R. Central mechanisms of itch Clin Neurophysiol. (2015) 126:1650–60. 10.1016/j.clinph.2014.11.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Mochizuki H, Yosipovitch G. Neuroimaging of itch as a tool of assessment of chronic itch and its management. Handb Exp Pharmacol. (2015) 226:57–70. 10.1007/978-3-662-44605-8_4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kurth F, Eickhoff SB, Schleicher A, Hoemke L, Zilles K, Amunts K. Cytoarchitecture and probabilistic maps of the human posterior insular cortex. Cereb Cortex. (2010) 20:1448–61. 10.1093/cercor/bhp208 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Mazzola L, Isnard J, Peyron R, Guenot M, Mauguiere F. Somatotopic organization of pain responses to direct electrical stimulation of the human insular cortex. Pain. (2009) 146:99–104. 10.1016/j.pain.2009.07.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Iadarola MJ, Berman KF, Zeffiro TA, Byas-Smith MG, Gracely RH, Max MB, et al. Neural activation during acute capsaicin-evoked pain and allodynia assessed with PET. Brain. (1998) 121:931–47. 10.1093/brain/121.5.931 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Peyron R, Schneider F, Faillenot I, Convers P, Barral FG, Garcia-Larrea L, et al. An fMRI study of cortical representation of mechanical allodynia in patients with neuropathic pain. Neurology. (2004) 63:1838–46. 10.1212/01.WNL.0000144177.61125.85 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Schweinhardt P, Glynn C, Brooks J, Mcquay H, Jack T, Chessell I, et al. An fMRI study of cerebral processing of brush-evoked allodynia in neuropathic pain patients. Neuroimage. (2006) 32:256–65. 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.03.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Seifert F, Maihöfner C. Representation of cold allodynia in the human brain—a functional MRI study. Neuroimage. (2007) 35:1168–80. 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.01.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Ducreux D, Attal N, Parker F, Bouhassira D. Mechanisms of central neuropathic pain: a combined psychophysical and fMRI study in syringomyelia. Brain. (2006) 129:963–76. 10.1093/brain/awl016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Geuter S, Boll S, Eippert F, Büchel C. Functional dissociation of stimulus intensity encoding and predictive coding of pain in the insula. eLife. (2017) 6:e24770. 10.7554/eLife.24770.016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Vogt BA. Pain and emotion interactions in subregions of the cingulate gyrus. Nat Neurosci. (2005) 6:533–44. 10.1038/nrn1704 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Vogt BA. Midcingulate cortex: Structure, connections, homologies, functions and diseases. J Chem Neuroanat. (2016) 74:28–46. 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2016.01.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Gu X, Hof PR, Friston KJ, Fan J. Anterior insular cortex and emotional awareness. J Comp Neurol. (2013) 521:3371–88. 10.1002/cne.23368 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Sanders KM, Akiyama T. The vicious cycle of itch and anxiety. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2018) 87:17–26. 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.01.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Leknes S, Berna C, Lee MC, Snyder GD, Biele G, Tracey I. The importance of context: when relative relief renders pain pleasant. Pain. (2013) 154:402–10. 10.1016/j.pain.2012.11.018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Grant J, Courtemanche J, Rainville P. A non-elaborative mental stance and decoupling of executive and pain-related cortices predicts low pain sensitivity in Zen meditators. Pain. (2011) 152:150–6. 10.1016/j.pain.2010.10.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Cheddad El Aouni M, Ben Salem D, Misery L. Functional MRI of pruritus. J Neuroradiol. (2020) 47:400–1. 10.1016/j.neurad.2020.09.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Najafi P, Ben Salem D, Carré JL, Misery L, Dufor O. Functional and anatomical brain connectivity in psoriasis patients and healthy controls: a pilot brain imaging study after exposure to mentally induced itch. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2020) 34:2557–65. 10.1111/jdv.16441 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]