Abstract
Background
This study aimed to develop and validate a model for mortality risk stratification of intensive care unit (ICU) patients with acute kidney injury (AKI) using the machine learning technique.
Methods
Eligible data were extracted from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care (MIMIC-III) database. Calibration, discrimination, and risk classification for mortality prediction were evaluated using conventional scoring systems and the new algorithm. A 10-fold cross-validation was performed. The predictive models were externally validated using the eICU database and also patients treated at the Second People’s Hospital of Shenzhen between January 2015 to October 2018.
Results
For the new model, the areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUROCs) for mortality during hospitalization and at 28 and 90 days after discharge were 0.91, 0.87, and 0.87, respectively, which were higher than for the Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS II) and Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA). For external validation, the AUROC was 0.82 for in-hospital mortality, higher than SOFA, SAPS II, and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) IV in the eICU database, but for the 28- and 90-day mortality, the new model had AUROCs (0.79 and 0.80, respectively) similar to that of SAPS II in the SZ2 database. The reclassification indexes were superior for the new model compared with the conventional scoring systems.
Conclusions
The new risk stratification model shows high performance in predicting mortality in ICU patients with AKI.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury (AKI), intensive care unit (ICU), machine learning, in-hospital mortality, severity score
Introduction
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common but complex disease in critically ill patients, leading to high morbidity and mortality (1,2). In addition, AKI is associated with increased length of hospital stay (LOS), total health-related costs, and mortality (3-6). In-hospital mortality in patients with AKI has recently been estimated to be between 20% and 25% (7,8), while critically ill patients with AKI requiring dialysis have a mortality rate exceeding 50% (9,10). Currently, the diagnosis criteria for AKI mostly depend on serum creatinine (SCr) assessment (3), and diagnosing AKI based on SCr might delay AKI detection, leading to a more advanced stage at diagnosis and irreversible damage and loss of organ function (11). Therefore, the development of new predictive models for risk stratification in patients with AKI in the intensive care unit (ICU) is crucial in reducing unnecessary kidney stress and improving patient outcomes (4,12).
The burden of care for critically ill patients is massive. The basis of critical care is a risk stratification approach for classifying patients by severity levels and thus optimizing personal care. Precision delivery is based on this prediction-personalization approach, deployed precisely at the right moment in the course of clinical management for improved clinical outcomes (13,14). Traditionally, several rule-based severities scoring systems, and their modifications, are used based on the clinical experiences of physicians; those systems include, for example, the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA), Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS II), and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) IV (15,16).
Machine-learning techniques are being increasingly used to examine the risk stratification of patients (17,18). Novel machine learning applications can offer improved predictive performance by maximally leveraging large-scale, complex electronic health record (EHR) and identifying the most robust signals within the noise (19,20). They can rapidly assess voluminous and complex data to identify clinically relevant risk levels by applying computationally intensive statistical modeling (19,20). Nevertheless, none of these models reaches sufficient precision to be used for an individual patient (21). In addition, studies have unanimously concluded that non-parametric methods might perform at least as well, if not better, than standard logistic regression-based techniques in predicting ICU mortality (22). Therefore, more robust methods for staging AKI are required (23).
Therefore, this study aimed to develop a risk stratification system for ICU patients with AKI at admission using machine-learning. We present the following article in accordance with the TRIPOD reporting checklist (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/atm-20-5723).
Methods
Study population
This study is a cohort retrospective study based on three different population. Three databases were used: the publicly available Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care (MIMIC-III) database (24) (internal validation), the publicly available eICU Collaborative Research Database (external validation), and Shenzhen Second Renmin Hospital database (SZ2) (also external validation). In this study, all patients diagnosed with AKI in the ICU according to the diagnostic criteria described in the “Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes” (KDIGO) clinical practice guidelines were included according to the diagnostic codes in the hospital information system (25). Therefore, the diagnosis of AKI was: (I) increase in SCr ≥0.3 mg/dL within 48 h or ≥50% within 7 days, and (II) urine output <0.5 mL/kg/h for 6 h. Baseline SCr was defined as the mean creatinine level before hospital admission within 3 months (25-27). If the patients had no available data, then the SCr was estimated using the back-calculation method from the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MRDR) formula with a GFR of 75 mL/min/1.73 m2 (28). The patients who had been hospitalized once or more were enrolled. The patients who received dialysis (renal replacement) in the ICU were identified (29) and excluded.
The predictive model was built and internally validated using data extracted from the publicly available MIMIC-III database (24). During the model building process, 10% of the data from the MIMIC cohort were not used for model building but for the validation process. Hence, it was defined as an internal validation (30).
External validation of the predictive performance of the developed algorithm was evaluated using the above metrics but in a completely independent dataset. The data used for external validation were extracted from the publicly available eICU Collaborative Research Database and SZ2. The eICU is a multi-center ICU database with high granularity data for over 200,000 admissions to ICUs monitored by the eICU Programs across the United States. It was created by the Laboratory for Computational Physiology (LCP) at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and the eICU Research Institute (eRI) at Philips Healthcare (31). A total of 1,087 events made by a total of 1,063 patients were included from the eICU database.
The other external dataset was obtained from our local hospital, and a total of 84 randomly selected patients with AKI admitted to the general adult ICU in the Second People’s Hospital of Shenzhen (a tertiary-care teaching hospital) from January 2015 to October 2018 were included. The study was approved by the ethics committee of the Second People’s Hospital of Shenzhen (#20180515001). For the data from this hospital, informed consent was obtained from all patients or their families by telephone. All patient privacy data were protected under the confidentiality policy.
For eICU and SZ2, the inclusion criteria were the septic shock 3.0 criteria: (I) persisting hypotension requiring vasopressors to maintain mean arterial pressure (MAP) ≥65 mmHg, and (II) blood lactate >2 mmol/L despite adequate volume resuscitation. The exclusion criteria were (I) <18 years of age, (II) history of chronic kidney disease and kidney transplantation, (III) end-stage malignant tumors, (IV) septic shock occurred 24 h after admission, (V) death within 12 h of admission despite cardiopulmonary and brain resuscitation, (VI) missing data (without creatinine in 24 h after admission), and (VII) trauma and other causes of renal contusion injury. In SZ2, the patients were followed by phone calls every week.
The assessed features included baseline demographic features, vital signs, laboratory measurements, medications, and diagnostic codes. The averaged laboratory data (since a given indicator might have been measured more than once during the first 24 h) included in the model were those obtained within 24 h of admission to the ICU. The averaged values for biochemical parameters within 24 h of admission to the ICU were used for downstream analysis. If variables were missing, for laboratory results, we used the mean of the normal range; for the absent height and weight, we used age and sex to stratify the liner relationship then interpolation; for the other categorical variables, we used “null” as the default value.
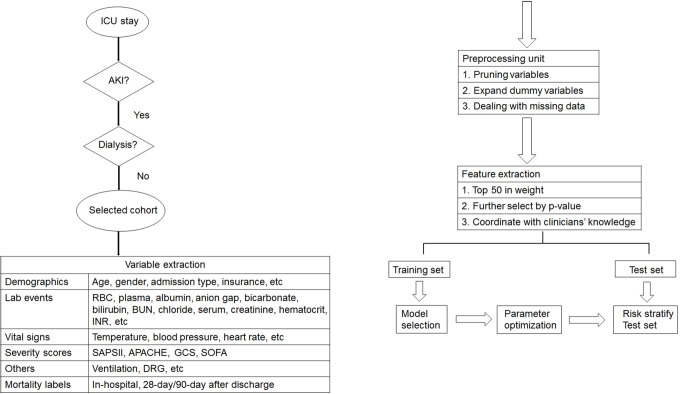
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (as revised in 2013). The study was approved by the institutional ethics board of the Second People’s Hospital of Shenzhen (No. 20180515001), and individual consent for this retrospective analysis was waived. The flowchart of data processing is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Flowchart of data processing. ICU, intensive care unit; AKI, acute kidney injury; RBC, red blood cell; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; INR, international normalized ratio; SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; SAPS II, Simplified Acute Physiology Score II; APACHE, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation.
Prediction algorithm
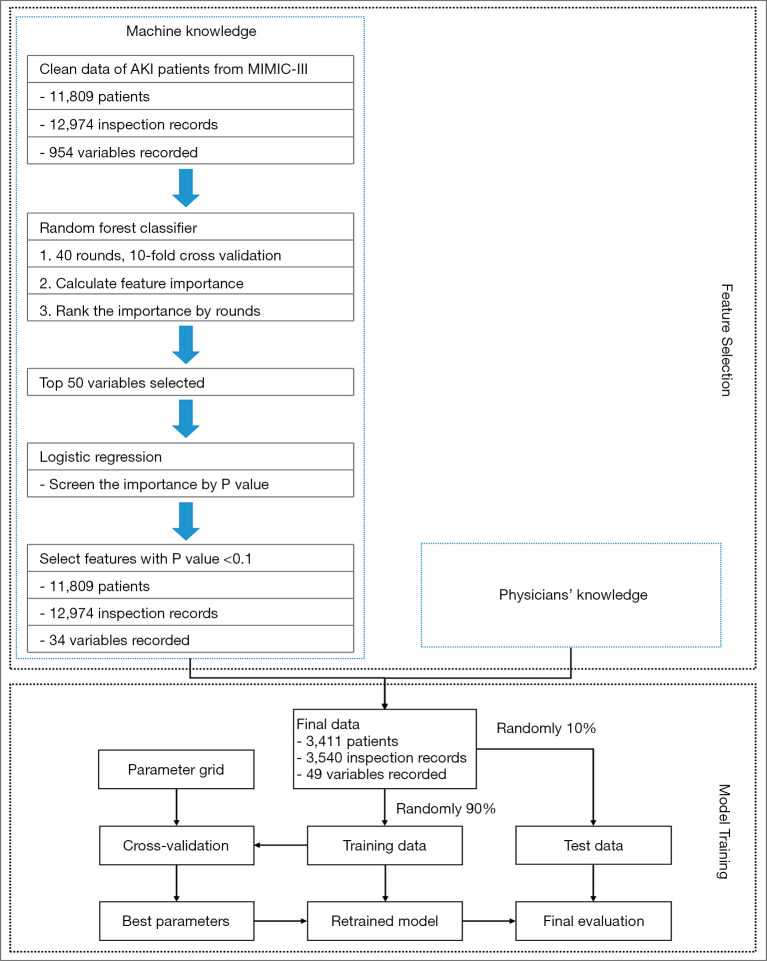
In this study, the proposed algorithm was built based on the random forest algorithm method (32) with improvement in feature selection (Figure 2) and consisted of two steps:
Figure 2.
Building procedure for the proposed risk stratification algorithms. The following features were finally selected for model building: age, gender, length of stay in intensive care unit (ICU) (los_icu), weight, height, body mass index (BMI), diabetes, heart-related diseases, lung-related diseases, no comorbidity, has two diseases, more than three diseases, hypertension, Simplified Acute Physiology Score II (SAPS II). The follow features were collected within 24 h after ICU admission: albumin serum (ALB), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), white blood cell (WBC), platelet count (PLT), neutrophil (NEUT), lymphocyte (LY), serum total bilirubin (TBIL), serum creatinine (SCr), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), red blood cell (RBC), hemoglobin (HBG), hematocrit (HCT), activated partial thromboplastin time (PTT), prothrombin time (PT), international normalized ratio (INR), neutrophils/lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet/lymphocyte ratio (PLR), PCO2, PO2, temperature, respirate, mean blood pressure (MEANBP), heart rate, glucose, SpO2, diastolic blood pressure (DIASBP), CO2, chloride (CL), lactate, sodium, plasma cells, mechanic ventilation (MV), min Glasgow coma scale (MINGCS), specimen.
Feature selection. Because the relative rank of each feature could be used to reflect its relative significance (12-14), a random forest algorithm was first applied to rank the contributions of the various features. Then, a stepwise multivariable regression analysis was performed to further screen the selected variables. Variables with P<0.10 were included in the final model building.
Model building. The risk stratification model was constructed based on the selected feature subspaces using the random forest algorithm. In addition, we developed a new version of the SAPS II score by fitting a main-term logistic regression model to our data using the same explanatory variables as those used in the original SAPS II score. The same procedure was used to build a new version of the APACHE IV and SOFA scores. Mortality prediction based on the traditional scores was obtained by regressing hospital mortality on the scores using a main-term logistic regression (22). The model was written in the Python scripting language (v3.6.5) [The Python Software Foundation (PSF), https://www.python.org; Wilmington, DE, USA].
Performance evaluation
In this study, the predictive performances of scores yielded by the current and conventional models were comparatively assessed. A 10-fold cross-validation was performed in all experiments for the different classification methods. In addition to the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC), accuracy, specificity, sensitivity, and F-measure (F1) were also assessed to evaluate the performance of the constructed model. Discrimination was evaluated using AUROC, as well as the box plots of predicted probabilities of death for survivors and non-survivors, and the corresponding discrimination slopes, defined as the differences between the mean predicted risks in survivors and non-survivors. The calibration of the predictive model was assessed by the conventional Hosmer-Lemeshow test. Under perfect calibration, a prediction algorithm would satisfy the logistic regression equation (22). Summary reclassification measures, including continuous net reclassification index (cNRI) and integrated discrimination improvement (IDI), were relative metrics that have been designed to overcome the limitations of the usual discrimination and calibration measures (33-35). We computed the reclassification tables and associated summary measures to measure reclassification for the various methods. Finally, we used decision curve analysis (DCA) (36) to estimate the clinical usefulness and net benefit of different prediction models to facilitate the comparison among them.
Statistical analysis
Exploratory data analysis was performed for each selected variable. Median values with interquartile ranges or means with standard deviations (SDs) were calculated for continuous variables. Percentages were determined for categorical variables. Patient demographics, vital signs, laboratory results, and admission diagnoses were compared among databases by the Kruskal-Wallis rank-sum test, chi-square test, or Fisher’s exact test, as appropriate. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analyses were performed using Python 3.7.0 and R 3.6.3 Bell Labs (New Providence, NJ, USA) and EmpowerStats (www.empowerstats.com) on May 16, 2020.
Results
Patient characteristics
There were 3,411 patients with AKI were included from the MIMIC-III population (development set), with a total of 3,540 encounters, 1,063 patients with AKI were included from the eICU, with a total of 1,087 encounters, and 84 patients with AKI were included from the SZ2 (external validation sets). There was some heterogeneity among the different patient cohorts. All patient features are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Characteristics of the study population.
| Data source | MIMIC-III | eICU | SZ2 | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 3,540 | 1,087 | 84 | |
| Age (years) | 65.96 (52.72, 78.33) | 67.00 (57.50, 78.00) | 67.00 (52.75, 78.25) | 0.009 |
| Length of stay in ICU (days) | 4.07 (2.18, 8.14) | 3.79 (1.96, 7.79) | 7.00 (3.00, 19.25) | <0.001 |
| SAPS II | 43.00 (33.00, 54.00) | 93.00 (73.00, 118.00) | 30.50 (20.00, 36.00) | <0.001 |
| Albumin serum (g/dL) | 3.10 (2.57, 3.60) | 2.80 (2.40, 3.27) | 2.42 (2.04, 2.86) | <0.001 |
| Total bilirubin serum (mg/dL) | 0.68 (0.40, 1.30) | 0.80 (0.50, 1.50) | 1.13 (0.69, 1.78) | <0.001 |
| Creatinine serum (mg/dL) | 1.15 (0.83, 1.80) | 2.07 (1.52, 3.10) | 2.85 (2.12, 3.56) | <0.001 |
| Hematocrit | 32.20 (28.70, 36.34) | 32.50 (27.91, 37.69) | 33.20 (29.98, 37.75) | 0.217 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 10.79 (9.53, 12.25) | 10.55 (9.11, 12.25) | 11.00 (9.57, 12.30) | 0.008 |
| Platelet count | 210.00 (140.50, 289.50) | 187.17 (122.09, 251.00) | 120.00 (69.75, 196.25) | <0.001 |
| Prothrombin time (s) | 14.65 (13.40, 17.37) | 15.70 (12.90, 20.70) | 15.80 (13.90, 21.95) | <0.001 |
| Blood urea nitrogen (mg/dL) | 25.50 (16.00, 42.00) | 36.67 (25.93, 55.54) | 13.75 (10.68, 17.50) | <0.001 |
| White blood cell (×1,000) | 12.50 (8.70, 17.44) | 12.90 (9.23, 18.00) | 14.47 (9.53, 22.86) | 0.008 |
| Red blood cell (×1,000) | 3.69 (3.21, 4.36) | 3.61 (3.10, 4.18) | 3.66 (3.27, 4.42) | <0.001 |
| Alanine aminotransferase (U/L) | 30.50 (17.50, 67.00) | 34.00 (18.16, 98.00) | 50.00 (28.00, 109.75) | <0.001 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (U/L) | 43.25 (25.00, 96.56) | 52.75 (25.75, 180.50) | 59.00 (33.25, 266.75) | <0.001 |
| Mechanic ventilation | 2468 (69.7) | 570 (52.4) | 56 (66.7) | <0.001 |
| Gender (male) | 1953 (55.2) | 620 (57.0) | 53 (63.1) | 0.218 |
| In-hospital death | 838 (23.7) | 388 (35.7) | – | <0.001 |
| 28-day mortality | 966 (27.3) | – | 43 (51.2) | <0.001 |
| 90-day mortality | 1,179 (33.3) | – | 48 (57.1) | <0.001 |
| Stage KDIGO | <0.001 | |||
| 1 | 584 (16.5) | 368 (33.9) | 34 (40.5) | |
| 2 | 704 (19.9) | 358 (32.9) | 35 (41.7) | |
| 3 | 2,252 (63.6) | 361 (33.2) | 15 (17.9) |
Data are median (Q1–Q3), or n (%). P value: continuous variables were assessed by the Kruskal Wallis rank sum test, and count variables with a theoretical number <10 by the Fisher’s exact probability test. ICU, intensive care unit.
Feature selection
In most cases, models built on multiple variables perform better in prediction, but it is more cost-effective and efficient to use a few but important features. Since features built on the top of trees contribute more to predicting AKI in at-risk patients, the relative importance of each feature is provided in Figure 3.
Figure 3.
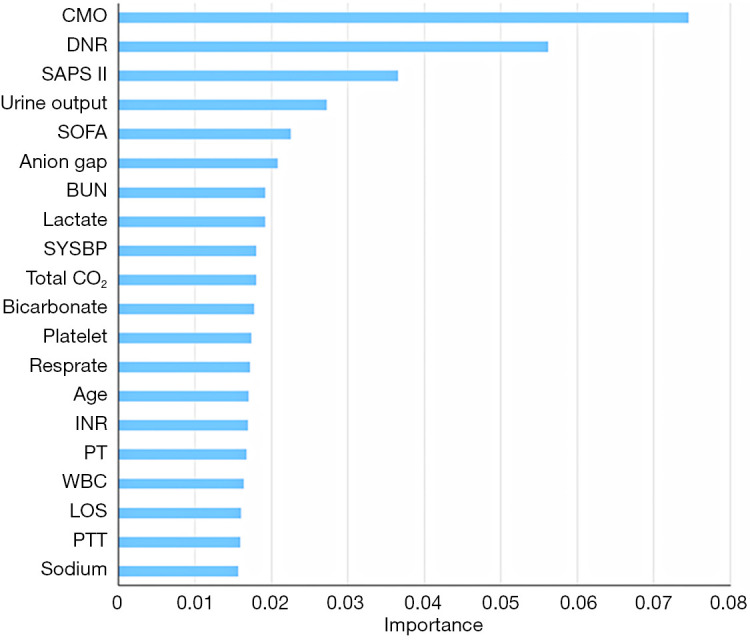
Variables selected by machine knowledge, ranking by their importance levels. AKI, acute kidney injuries. CMO, comfort measures only; DNR, do not resuscitate; SAPS II, Simplified Acute Physiology Score II; SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; SYSBP, systolic blood pressure; INR, international normalized ratio; PT, prothrombin time; WBC, white blood cells; LOS, length of stay; PTT, partial thromboplastin time.
Model building and validation performance
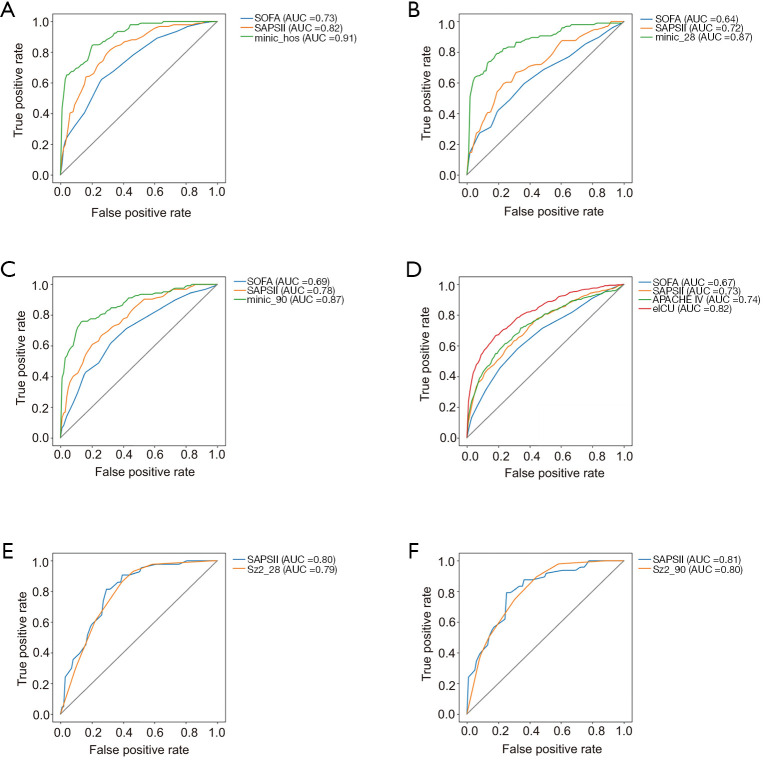
Three predictive models were built based on the above procedure (Figure 2). Feature selection was first conducted by machine learning, then the features were further selected after discussion with our physicians, unfavorable features were deleted and useful features were added before training. These three predictive models were targeted on identifying patient mortality during hospitalization (Model_inpatient) and at 28 (Model_28) and 90 (Model_90) days after discharge. The AUROCs for Model_inpatient, Model_28, and Model_90 were 0.91, 0.87, and 0.87, respectively. Compared with traditional scoring systems (SAPS II and SOFA), all three newly developed models had better predictive performances based on AUROCs (Figure 4A,B,C).
Figure 4.
Performances of the newly developed prediction models and traditional scoring systems for internal and external validation. Internal validation performance: The new predictive model targeted on identifying patient mortality in the MIMIC-III database during hospitalization (A), and at 28 (B) and 90 (C) days, versus the SOFA and SAPS II models. External validation performance: (D) the new predictive model targeted on identifying patient mortality during hospitalization in eICU database, versus the SOFA, SAPS II, and APACHE IV models. (E) The new predictive model targeted on identifying 28-day mortality after discharge in the SZ2 database, versus the SAPS II model. (F) The new predictive model targeted on identifying 90-day mortality after discharge in the SZ2 database, versus the SAPS II model. SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; SAPS II, Simplified Acute Physiology Score II; APACHE, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation.
The performances of the three models were externally validated in the eICU and SZ2 dataset. Since eICU only has inpatient records, while SZ2 only records post-discharge mortality, Model_inpatient was evaluated in the eICU dataset and Model_28 and Model_90 in the SZ2 dataset. The ROC curves for hospital mortality prediction in the external validation are provided in Figure 4D,E,F. For the eICU dataset, AUROCs were 0.67 and 0.73 for the SOFA and SAPS II scores, respectively; similar results were obtained for the APACHE IV, which yielded an AUROC of 0.74. Model_inpatient substantially outperformed the traditional scoring systems. The AUROC was 0.82, revealing a clear advantage of the newly developed algorithm over traditional scores (Figure 4D). For the SZ2 dataset, the performance of Model_28 and Model_90 behaved similarly compared to SAPS II (Figure 4E,F).
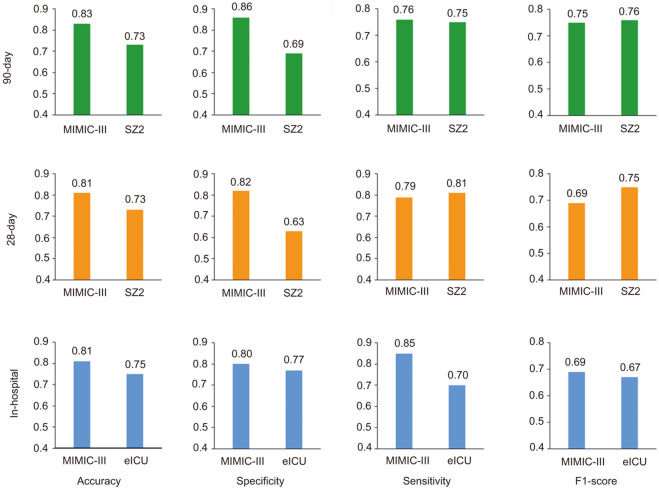
The accuracies, specificities, sensitivities, and F1 scores of the new risk stratification model for internal and external validation are shown in Figure 5. Even though external validation performed well, internal validation results were slightly better in general.
Figure 5.
Predictive performances of the new proposed models. Predictive performances measured by accuracy, specificity, and sensitivity of the three predictive models for mortality during hospitalization, and at 28 and 90 days after discharge, respectively, based on the internal MIMIC-III database and two external validation datasets (the eICU database for mortality during hospitalization, and the SZ2 dataset for 28/90-day mortality).
Discrimination and calibration
To better evaluate the discrimination potential of our predicted results, the whole population was grouped into five categories based on predicted risk scores. The observed mortality rate was determined for each group. As demonstrated in Table 2, the lower the relative rate of patient mortality, the lower the predicted risk score, especially in patients with risk scores greater than 60% or lower than 20%. These results suggested that the new algorithm could successfully identify survivors and non-survivors, especially among patients with very high (0.8–1.0) and low (<0.2) risk scores.
Table 2. Relative risk ratios for various risk groups in both external validation datasets.
| Risk | Model_inpatient | Model_28 | Model_90 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients, n | Mortality, % | RR | Patients, n | Mortality, % | RR | Patients, n | Mortality, % | RR | |||
| >80% | 221 | 81.40 | 2.3 | 17 | 76.50 | 1.5 | 17 | 82.40 | 1.4 | ||
| 60–79% | 216 | 43.50 | 1.2 | 17 | 70.60 | 1.4 | 17 | 70.60 | 1.2 | ||
| 40–59% | 216 | 26.40 | 0.7 | 16 | 62.50 | 1.2 | 17 | 70.60 | 1.2 | ||
| 20–39% | 220 | 18.60 | 0.5 | 17 | 41.20 | 0.8 | 16 | 50 | 0.9 | ||
| <19% | 214 | 7.50 | 0.2 | 17 | 6.90 | 0.1 | 17 | 11.80 | 0.2 | ||
| Total | 1,087 | 35.70 | 84 | 51.20 | 84 | 57.10 | |||||
RR, relative ratio.
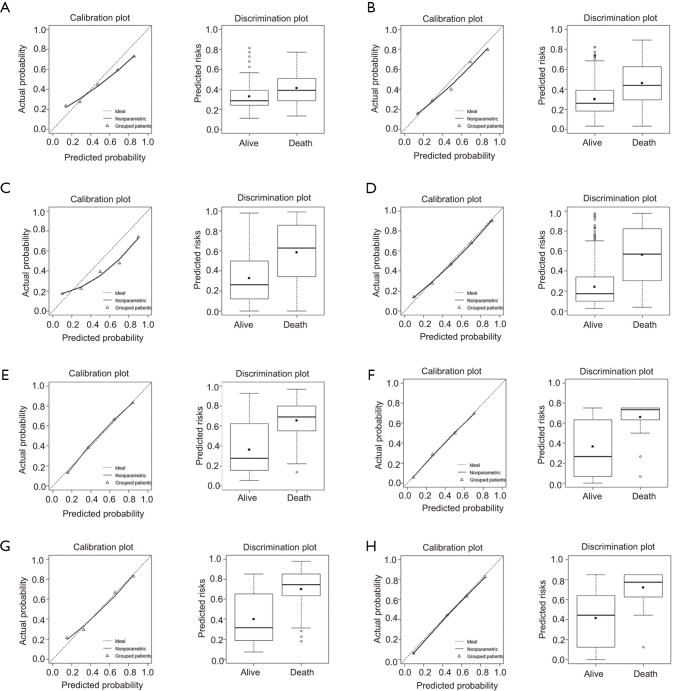
Discrimination was also evaluated by assessing differences between the predicted probabilities of death among survivors and non-survivors using each prediction algorithm (Figure 6). The discrimination slopes were 0.085 for the SOFA score, 0.16 for the SAPS II score, 0.257 for the APACH IV score, and 0.32 for the RF score. The plots indicated a lack of fit for the traditional scores.
Figure 6.
Calibration and discrimination potentials of the new RF-based algorithm and traditional scoring systems in external validation. (A,B,C,D) In-hospitalization mortality. (A) SOFA score (Brier score =0.210; χ2=4.992, P=0.759; discrimination slope =0.085); (B) SAPS II score (Brier score =0.192; χ2=7.188, P=0.517; discrimination slope =0.16); (C) APACHE IV score (Brier score =0.203; χ2=249.148, P=0; discrimination slope =0.257); (D) the newly developed algorithm (Brier score =0.159; χ2=4.185, P=0.84; discrimination slope =0.32). (E,F) Mortality within 28 days after discharge. (E) 28_SAPS II score (Brier score =0.177; χ2=1.181, P=0.554; discrimination slope =0.291); (F) 28_RF score (Brier score =0.177; χ2=0.064, P=0.969; discrimination slope =0.294). (G,H) Mortality within 90 days after discharge. (G) 90_SAPS II score (Brier score =0.172; χ2=0.404, P=0.817; discrimination slope =0.302); (H) 90_RF (Brier score =0.170; χ2=0.472, P=0.79; discrimination slope =0.306). SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; SAPS II, Simplified Acute Physiology Score II; APACHE, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation.
Prediction based on the RF exhibited excellent calibration properties (Figure 6), as reflected by a Brier scores of 0.159 (χ2=4.185, P=0.84) for Model_inpatient, 0.177 (χ2=0.064, P=0.969) for Model_28, and 0.170 (χ2=0.472, P=0.79) for Model_90. The calibration plots indicated a lack of fit for the traditional scoring methods. The newly developed algorithm performed better for the entire range of death probability.
Reclassification
We calculated the risk of each individual in the entire external validation cohort and divided all patients into three groups based on the risk cut-off at 95% sensitivity and 95% specificity (37). The reclassification tables involving the RF score and traditional scores are provided in Table 3. The results show that the RF score proposals resulted in a large proportion of patients being reclassified.
Table 3. Reclassification (reclassification tables).
| Initial model | Updated model | Predicted probability according to initial model | % Reclassified | Statistics | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <12% | 12–64% | >64% | NRI (95% CI) | P | |||
| SOFA | Model_inpatient | 0.628 (0.555–0.701) | |||||
| <12% | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | <0.001 | ||
| 12–64% | 260 | 600 | 189 | 43 | |||
| >64% | 0 | 15 | 22 | 41 | |||
| APACHE IV | Model_inpatient | 0.176 (0.100–0.252) | |||||
| <12% | 126 | 74 | 6 | 39 | <0.001 | ||
| 12–64% | 132 | 390 | 66 | 34 | |||
| >64% | 3 | 151 | 139 | 53 | |||
| SAPS II | Model_inpatient | 0.457 (0.386–0.528) | |||||
| <12% | 49 | 12 | 0 | 20 | <0.001 | ||
| 12–64% | 212 | 566 | 136 | 38 | |||
| >64% | 0 | 37 | 75 | 33 | |||
| Model_28 | <13% | 13–70% | >70% | 0.287 (0.039–0.535) | |||
| <13% | 7 | 1 | 0 | 12 | 0.023 | ||
| 13–70% | 11 | 25 | 13 | 49 | |||
| >70% | 0 | 5 | 22 | 19 | |||
| Model_90 | <15% | 15–83% | >83% | 0.340 (0.058–0.623) | |||
| <15% | 4 | 1 | 0 | 20 | 0.018 | ||
| 15–83% | 12 | 31 | 18 | 49 | |||
| >83% | 0 | 7 | 11 | 39 | |||
SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; SAPS II, Simplified Acute Physiology Score II; APACHE, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation; NRI, net reclassification index.
We computed the cNRI and IDI considering RF as the updated model, and the SOFA, SAPS II, and APACHE IV scores as the initial models. In this case, positive values for the cNRI and IDI would indicate that RF has a better discriminative ability than the traditional methods, whereas negative values indicate the opposite. The results are summarized in Table 4. Compared with the SOFA, SAPS II, and APACHE IV systems, both cNRI and IDI showed positive values for the new algorithm. These findings indicated the superiority of the newly developed model in predicting mortality in AKI patients in the ICU.
Table 4. Reclassification (reclassification statistics).
| Model_inpatient | Model_28 | Model_90 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOFA | |||
| cNRI | 0.864 (0.752, 0.977) | – | – |
| IDI | 0.235 (0.207, 0.263) | – | – |
| SAPS II | |||
| cNRI | 0.814 (0.700, 0.928) | 0.001 (–0.427, 0.429) | 0.097 (–0.334, 0.529) |
| IDI | 0.160 (0.136, 0.184) | 0.003 (–0.074, 0.079) | 0.005 (–0.075, 0.085) |
| APACHE IV | |||
| cNRI | 0.205 (0.084, 0.327) | – | – |
| IDI | 0.063 (0.031, 0.095) | – | – |
SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; SAPS II, Simplified Acute Physiology Score II; APACHE, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation; cNRI, continuous net reclassification index; IDI, integrated discrimination improvement.
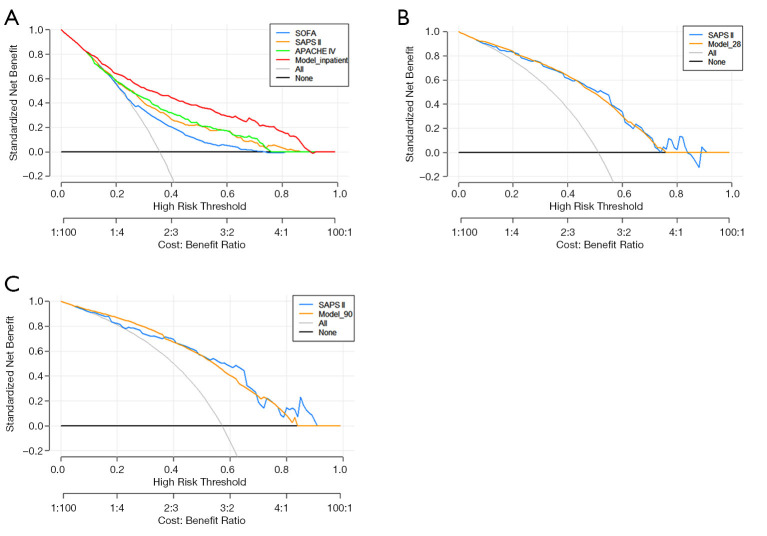
Decision curve analysis
The decision curve of the three predictive models and traditional scores is provided in Figure 7A,B,C. The DCA graphically shows the clinical usefulness of each model based on a continuum of potential thresholds for major risk (X-axis) and the standardized net benefit of using the model to stratify the patients (Y-axis). In this analysis, for the eICU dataset, RF provided a larger standardized net benefit across the range of major high risk compared with the SOFA, SAPS II, and APACHE IV systems (Figure 7A). For the SZ2 dataset, RF had a superior overall standardized net benefit within the wide and practical ranges of threshold probabilities, and this is similar to the performance of the SAPS II (Figure 7B,C).
Figure 7.
DCA of the new RF-based algorithm and traditional scoring systems in external validation. (A) In-hospitalization mortality; (B) mortality within 28 days after discharge; (C) mortality within 90 days after discharge. DCA, decision curve analysis.
Discussion
Since mortality prediction remains challenging in patients with AKI in the ICU, the current study developed and validated a machine learning technique for the risk stratification of such patients. The new risk stratification model was superior in predicting mortality in ICU patients with AKI compared with the conventional severity scoring systems (SOFA, SAPS II, and APACHE IV) based on in-hospital mortality as well as mortality at 28 and 90 days post-discharge.
Based on the retrospective MIMIC-III dataset and the KDIGO definition of AKI (25), a tree-based predictive algorithm was proposed to build three predictive models (Model_inpatient, Model_28, and Model_90). The prediction outcomes of these three models were mortality during hospitalization and at 28 and 90 days after discharge, respectively. Their performances were validated both internally and externally, both in terms of discrimination and calibration, compared with traditional scoring systems. The results indicated that the tree-based predictive algorithm was robust in building prediction models for mortality during hospitalization and at 28 and 90 days after discharge. As shown above, the new model performed better than the traditional scoring systems, including APACHE IV, SOFA, and SAPS II, which are commonly used to stratify critically ill patients on the day of hospital admission (38,39). The results showed that the lower the relative rate of patient mortality, the lower the predicted risk score, indicating the excellent ability of our model in grading ICU patients with AKI.
The proposed predictive model provides advantages over currently used systems. Unlike the traditional scoring systems, including SOFA, SAPS II, and APACHE IV, which assess general disease severity scores, the developed method is specific to AKI in ICU settings. Besides, the SOFA score is based on logistic regression (40). The process leading to ICU death is highly complex, and accurately predicting mortality through linear relationships with explanatory variables is challenging. The newly proposed algorithm may also provide advantages over manual AKI detection methods, which might not be implemented unless a physician already suspects AKI and are subject to potential human error.
Non-parametric techniques have been advocated for the early detection of AKI and ICU mortality prediction but may not be applicable to AKI. Mohamadlou et al. have developed a decision tree-based machine learning algorithm with a strong predictive performance compared with the SOFA score in terms of AUROC (41), but these results were challenged by Kim et al. (42), who reported no clear benefit from neural networks and support vector machines compared with APACHE-IV. Rather, in the latter study, the optimal performance was achieved with a decision tree.
Interestingly, the new algorithms were externally validated for performance based on two separate datasets. In addition, its predictive ability, as well as calibration and discrimination potential, were also tested. As shown above, the current models yielded good results in both datasets. Therefore, this new algorithm might provide an efficient real-time risk stratification tool because of its accuracy and computational speed.
Based on the above findings, the newly developed model should be applied for the risk stratification of ICU patients with AKI, which would help provide appropriate care and improve the quality of life of the patients. In addition, similar specific models could be developed for various diseases to improve risk stratification.
The limitations of this study should be mentioned. First, due to incomplete datasets, the current models could not be compared to all the widely used scoring systems for predictive performance. The APACHE IV and SOFA systems serve as references in most hospitals, and performance comparison between each of these scores and the proposed algorithm should be carried out, especially in local hospitals. Second, since eICU only includes inpatient records, while the SZ2 only contained mortality information after discharge, external validation of Model_inpatient was only possible based on eICU, while Model_28 and Model_90 could only be tested using the SZ2. Third, there were differences in baseline features of patients among the three sources, including the training (MIMIC-III) and validation (eICU and SZ2) sets, which could bias the results. Nevertheless, validation was still good in the different populations, demonstrating the generalizability of these models. Third, the data from the public databases are limited. AKI stage and the changes in kidney condition during ICU stay could not be examined in this study. Finally, the sample size was relatively small in the validation cohorts. Therefore, including additional variables and enlarging the sample size for external validation would be beneficial.
Conclusions
The prediction algorithms developed in this study have a significantly improved performance compared with currently available methods, including the SOFA, SAPS II, and APACHE IV systems, constituting promising tools for building mortality prediction models in both the clinical and research settings. This model was developed to predict the in-hospital, 28-day (after discharge), and 90-day (after discharge) death risk of ICU patients who developed AKI, thus guiding the physicians to pay more attention to high-risk patients and anticipate potential complications.
Supplementary
The article’s supplementary files as
Acknowledgments
Funding: This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61601302) and the Shenzhen peacock plan (No. KQTD2016053112051497); the Startup funding for Youth Faculty by Shenzhen University (No. 2018009).
Ethical Statement: The authors are accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (as revised in 2013). The study was approved by the institutional ethics board of the Second People’s Hospital of Shenzhen (No. 20180515001), and individual consent for this retrospective analysis was waived.
Footnotes
Reporting Checklist: The authors have completed the TRIPOD reporting checklist. Available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/atm-20-5723
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/atm-20-5723). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- 1.Hobson C, Ozrazgat-Baslanti T, Kuxhausen A, et al. Cost and mortality associated with postoperative acute kidney injury. Ann Surg 2015;261:1207-14. 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000732 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chawla LS, Amdur RL, Amodeo S, et al. The severity of acute kidney injury predicts progression to chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2011;79:1361-9. 10.1038/ki.2011.42 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pozzoli S, Simonini M, Manunta P. Predicting acute kidney injury: current status and future challenges. J Nephrol 2018;31:209-23. 10.1007/s40620-017-0416-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lewington AJ, Sayed A. Acute kidney injury: how do we define it? Ann Clin Biochem 2010;47:4-7. 10.1258/acb.2009.009249 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Palevsky PM, Liu KD, Brophy PD, et al. KDOQI US commentary on the 2012 KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Am J Kidney Dis 2013;61:649-72. 10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.02.349 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Silver SA, Chertow GM. The Economic Consequences of acute kidney injury. Nephron 2017;137:297-301. 10.1159/000475607 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Susantitaphong P, Cruz DN, Cerda J, et al. World incidence of AKI: a meta-analysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2013;8:1482-93. 10.2215/CJN.00710113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Selby NM, Kolhe NV, McIntyre CW, et al. Defining the cause of death in hospitalised patients with acute kidney injury. PLoS One 2012;7:e48580. 10.1371/journal.pone.0048580 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Palevsky PM, Zhang JH, O'Connor TZ, et al. Intensity of renal support in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. N Engl J Med 2008;359:7-20. 10.1056/NEJMoa0802639 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Uchino S, Bellomo R, Morimatsu H, et al. Continuous renal replacement therapy: a worldwide practice survey. The beginning and ending supportive therapy for the kidney (B.E.S.T. kidney) investigators. Intensive Care Med 2007;33:1563-70. 10.1007/s00134-007-0754-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bagshaw SM, George C, Dinu I, et al. A multi-centre evaluation of the RIFLE criteria for early acute kidney injury in critically ill patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2008;23:1203-10. 10.1093/ndt/gfm744 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lieske JC, Chawla L, Kashani K, et al. Biomarkers for acute kidney injury: where are we today? Where should we go? Clin Chem 2014;60:294-300. 10.1373/clinchem.2012.201988 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Parikh RB, Schwartz JS, Navathe AS. Beyond genes and molecules - a precision delivery initiative for precision medicine. N Engl J Med 2017;376:1609-12. 10.1056/NEJMp1613224 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Che Z, Purushotham S, Khemani R, et al. Interpretable deep models for ICU outcome prediction. AMIA Annu Symp Proc 2017;2016:371-80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Le Gall JR, Loirat P, Alperovitch A, et al. A simplified acute physiology score for ICU patients. Crit Care Med 1984;12:975-7. 10.1097/00003246-198411000-00012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, et al. The SOFA (Sepsis-Related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. Intensive Care Med 1996;22:707-10. 10.1007/BF01709751 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Liu VX, Prescott HC. Precision delivery in critical care: balancing prediction and personalization. In: Vincent JL. Annual update in intensive care and emergency medicine 2019. Cham: Springer, 2019:15-27. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Davoodi R, Moradi MH. Mortality prediction in intensive care units (ICUs) using a deep rule-based fuzzy classifier. J Biomed Inform 2018;79:48-59. 10.1016/j.jbi.2018.02.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R. The elements of statistical learning. New York: Springer series in statistics, 2001.
- 20.Kuhn M, Johnson K. Applied predictive modeling. New York: Springer, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Salluh JI, Soares M. ICU severity of illness scores: APACHE, SAPS and MPM. Curr Opin Crit Care 2014;20:557-65. 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000135 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pirracchio R, Petersen ML, Carone M, et al. Mortality prediction in intensive care units with the Super ICU Learner Algorithm (SICULA): a population-based study. Lancet Respir Med 2015;3:42-52. 10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70239-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Husain-Syed F, Ronco C. The odyssey of risk stratification in acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Nephrol 2018;14:660-2. 10.1038/s41581-018-0053-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Johnson AE, Pollard TJ, Shen L, et al. MIMIC-III, a freely accessible critical care database. Sci Data 2016;3:160035. 10.1038/sdata.2016.35 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Inter Suppl 2012;2:1-138. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ali T, Khan I, Simpson W, et al. Incidence and outcomes in acute kidney injury: a comprehensive population-based study. J Am Soc Nephrol 2007;18:1292-8. 10.1681/ASN.2006070756 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Jenq CC, Tsai MH, Tian YC, et al. RIFLE classification can predict short-term prognosis in critically ill cirrhotic patients. Intensive Care Med 2007;33:1921-30. 10.1007/s00134-007-0760-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bellomo R, Ronco C, Kellum JA, et al. Acute renal failure - definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: the Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit Care 2004;8:R204-12. 10.1186/cc2872 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Abhyankar S, Demner-Fushman D, Callaghan FM, et al. Combining structured and unstructured data to identify a cohort of ICU patients who received dialysis. J Am Med Inform Assoc 2014;21:801-7. 10.1136/amiajnl-2013-001915 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Alba AC, Agoritsas T, Walsh M, et al. Discrimination and calibration of clinical prediction models: users' guides to the medical literature. JAMA 2017;318:1377-84. 10.1001/jama.2017.12126 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pollard TJ, Johnson AEW, Raffa JD, et al. The eICU Collaborative Research Database, a freely available multi-center database for critical care research. Sci Data 2018;5:180178. 10.1038/sdata.2018.178 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Breiman L. Bagging predictors. Machine Learning 1996;24:123-40. 10.1007/BF00058655 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Cook NR. Use and misuse of the receiver operating characteristic curve in risk prediction. Circulation 2007;115:928-35. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.672402 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Cook NR. Statistical evaluation of prognostic versus diagnostic models: beyond the ROC curve. Clin Chem 2008;54:17-23. 10.1373/clinchem.2007.096529 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Pencina MJ, D'Agostino RB, Sr, D'Agostino RB, Jr, et al. Evaluating the added predictive ability of a new marker: from area under the ROC curve to reclassification and beyond. Stat Med 2008;27:157-72; discussion 207-12. 10.1002/sim.2929 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kerr KF, Brown MD, Zhu K, et al. Assessing the clinical impact of risk prediction models with decision curves: guidance for correct interpretation and appropriate use. J Clin Oncol 2016;34:2534-40. 10.1200/JCO.2015.65.5654 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Liang W, Yao J, Chen A, et al. Early triage of critically ill COVID-19 patients using deep learning. Nat Commun 2020;11:3543. 10.1038/s41467-020-17280-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sun D, Ding H, Zhao C, et al. Value of SOFA, APACHE IV and SAPS II scoring systems in predicting short-term mortality in patients with acute myocarditis. Oncotarget 2017;8:63073-83. 10.18632/oncotarget.18634 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lee JH, Hwang SY, Kim HR, et al. Effectiveness of the sequential organ failure assessment, acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II, and simplified acute physiology score II prognostic scoring systems in paraquat-poisoned patients in the intensive care unit. Hum Exp Toxicol 2017;36:431-7. 10.1177/0960327116657602 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Schoe A, Bakhshi-Raiez F, de Keizer N, et al. Mortality prediction by SOFA score in ICU-patients after cardiac surgery; comparison with traditional prognostic-models. BMC Anesthesiol 2020;20:65. 10.1186/s12871-020-00975-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mohamadlou H, Lynn-Palevsky A, Barton C, et al. Prediction of acute kidney injury with a machine learning algorithm using electronic health record data. Can J Kidney Health Dis 2018;5:2054358118776326. 10.1177/2054358118776326 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kim SY, Kim S, Cho J, et al. A deep learning model for real-time mortality prediction in critically ill children. Crit Care 2019;23:279. 10.1186/s13054-019-2561-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
The article’s supplementary files as