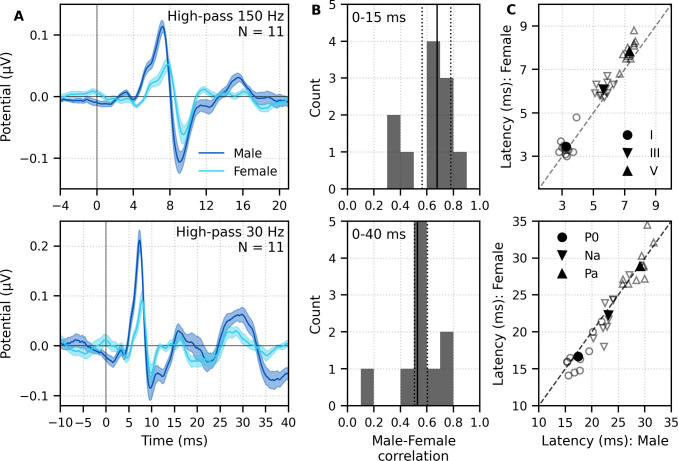
Figure 5. Comparison of responses to 32 min each of male- (dark blue) and female-narrated (light blue) re-synthesized broadband peaky speech.
(A) Average waveforms across subjects (areas show ±1 SEM) are shown for auditory brainstem response (ABR) time lags with high-pass filtering at 150 Hz (top), and both ABR and middle latency response (MLR) time lags with a lower high-pass filtering cutoff of 30 Hz (bottom). (B) Histograms of the correlation coefficients between responses evoked by male- and female-narrated broadband peaky speech during ABR (top) and ABR/MLR (bottom) time lags. Solid lines denote the median and dotted lines the interquartile range. (C) Comparison of ABR (top) and MLR (bottom) wave peak latencies for individual subjects (gray) and the group mean (black). ABR and MLR responses were similar to both types of input but are smaller for female-narrated speech, which has a higher glottal pulse rate. Peak latencies for female-evoked speech were delayed during ABR time lags but faster for early MLR time lags.