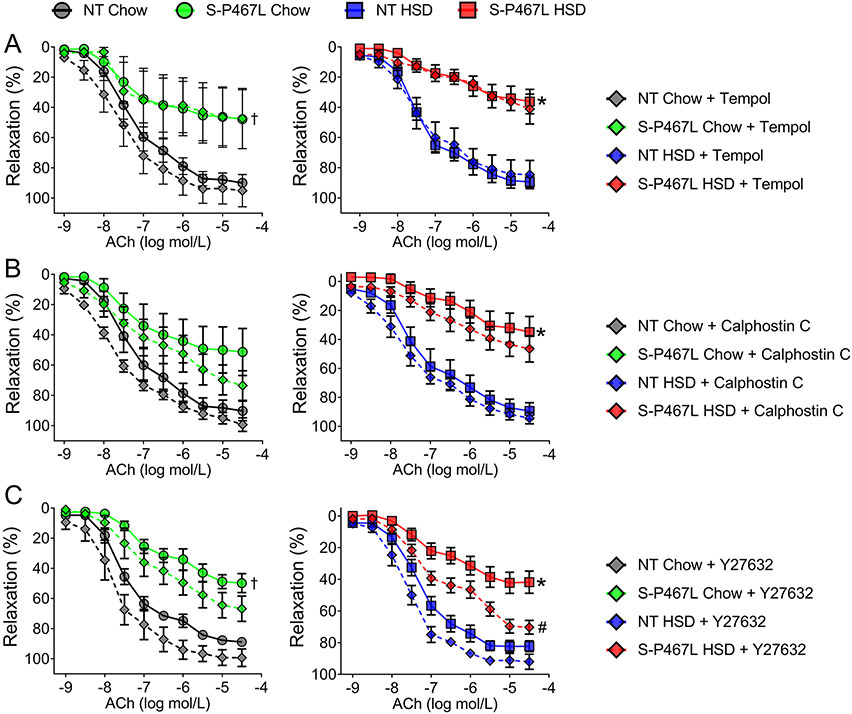
Figure 1. Vasodilation: Role of Superoxide, Protein Kinase C, and Rho kinase.
Dose-dependent vasodilation (following precontraction with thromboxane A2 receptor agonist U46619) in response to acetylcholine (ACh). Vessel segments were pre-incubated with pharmacological inhibitors or vehicle for 30 min prior to U46619. Effects of A) superoxide dismutase mimetic Tempol (1 mmol/L, n=4-8), B) a protein kinase C inhibitor Calphostin C (50 nmol/L, n=4-6), and C) a Rho kinase inhibitor Y27632 (1 μmol/L, n=4-8) were shown in curves with diamonds. Curves with filled circles (chow) or squares (HSD) represent vehicle-treated vessel segments. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Two-way ANOVA Repeated Measurements (RM) was performed to determine whether two curves were different (main-group effect, denoted by statistical symbols on the right of the curve). †p<0.05, S-P467L Chow Diet vs NT Chow Diet; *p<0.05, S-P467L HSD vs NT HSD; #p<0.05, Y-27632-treated VS vehicle-treated. Dose response curves were analyzed by nonlinear regression to generate EC50 and Emax values listed in Supplemental Table S1.