Abstract
Accumulated reactive oxygen species (ROS) directly contribute to biomacromolecule damage and influence various inflammatory responses. Reactive oxygen species act as mediator between innate and adaptive immune cells, thereby influencing the antigen-presenting process that results in T cell activation. Evidence from patients with chronic granulomatous disease and mouse models support the function of ROS in preventing abnormal autoimmunity; for example, by supporting maintenance of macrophage efferocytosis and T helper 1/T helper 2 and T helper 17/ regulatory T cell balance. The failure of many anti-oxidation treatments indicates that ROS cannot be considered entirely harmful. Indeed, enhancement of ROS may sometimes be required. In a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), absence of NOX2-derived ROS led to higher prevalence and more severe symptoms. In patients with RA, naïve CD4+ T cells exhibit inhibited glycolysis and enhanced pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) activity, leading to ROS exhaustion. In this “reductive” state, CD4+ T cell immune homeostasis is disrupted, triggering joint destruction, together with oxidative stress in the synovium.
Keywords: reactive oxygen species, autoimmunity, macrophage, T cell, rheumatoid arthritis, metabolism
Introduction
Oxidative stress represents an imbalance between pro- and anti-oxidants, in favor of the former, and has generally been considered as potentially harmful, since it leads to phenomena including DNA damage, protein oxidation, and lipid peroxidation (1). Based on this dogma, items, such as antioxidant skin care products, natural foods, herbal medicine, and even vitamins have been in demand in recent decades. A typical example of the effects of oxidative stress is ROS-related cell aging. Strikingly, a recent study demonstrated that a modified oxidized form of cysteine residues in proteins is not elevated in old (80 weeks) compared with young (16 weeks) mice, providing strong evidence against the theory of oxidative aging, which involves accumulation of indiscriminate oxidation of biological macromolecules. This study found that protein oxidative state is tissue- and age-specific, and can influence various physiological networks. For example, reversible cysteine oxidation modification of hexokinase controls the flux of glycolysis and the PPP, and polymerization and dissociation of some protein complexes are also regulated by redox state. Researchers have proposed that oxidative modification site, rather than oxidative modification level, is the main target of anti-aging (2).
Numerous studies have demonstrated the role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of autoimmune disease, varying from biomacromolecule damage to pro-inflammatory responses (3); however, antioxidant supplements may be not beneficial for primary or secondary prevention (4, 5); indeed, beta carotene, vitamin A, and vitamin E supplements may increase mortality (6). In recent years, ROS has become widely regarded as a signaling molecule, involved in many immune cell relationships and functions (Figure 1). In this review, we discuss the importance of ROS in adaptive immune responses, and the damage to immune tolerance caused by excessive ROS elimination. Further, we provide a detailed review of the roles of redox regulation in the glycolytic/PPP equilibrium in CD4+ T cells, focusing on rheumatoid arthritis (RA) as a model autoimmune disease.
Figure 1.
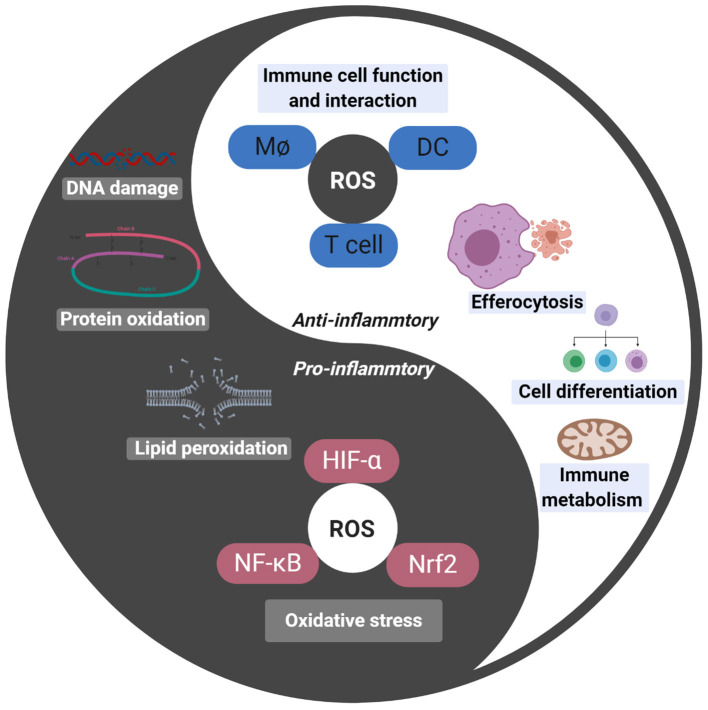
Darkness (oxidative stress) and light (signal molecule) of ROS. Oxidative stress induced by ROS lead to DNA damage, protein oxidation and lipid peroxidation, thus injuring cells. ROS also are involved in HIF-α, NF-κB, and Nrf2 mediated pro-inflammatory response. ROS act as important signal molecular in cell, which connect innate immunity and adaptive immunity, as well as participate in cell biological behaviors like metabolism, differentiation, and apoptosis.
ROS and Immune Cells
ROS Production and Disease
There are two main physiological sources of ROS: the NADPH oxidase complex, NOX2, and mitochondria. NOX2 is a multi-component enzyme system, composed of three cytoplasmic protein subunits (p47phox, encoded by NCF1; p67phox, encoded by NCF2; and p40phox, encoded by NCF4), two transmembrane protein subunits (p22phox, encoded by CYBA and gp91phox encoded by CYBB), and a small GTP-binding protein (Rac) (7, 8). In mitochondria, ROS production occurs when O2 receives an electron from the mitochondrial complex, which is a complex process influenced by the concentration of electron donors and O2, and the reactions rate constants between them (9). Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) is an inherited disease, characterized by non-functional NOX2. Patients with CGD always suffer from recurrent life-threatening infections, due to deficient neutrophil- and macrophage-mediated innate immune responses. Interestingly, patients with CGD patients also have an increased risk of developing autoimmune diseases, resulting from their adaptive immune response disorder (8). In contrast, mitochondrial disease pathology is invariably considered to involve elevation of ROS (10); however, a study found that double mutants of alternative oxidases and severe myopathic skeletal muscle-specific COX15 gene mutation led to decreased ROS production, and consequent impairment of PAX7/MYOD-dependent muscle regeneration. This study indicated the benefits of mitochondrial ROS (mtROS) signaling and the potential hazards arising from ROS elimination (11).
ROS in Antigen Presentation
Mononuclear phagocytes and dendritic cell are the main professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs), in which exogenous antigens are proteolytically processed, then complexed, generally with MHC class II, or with MHC class I by a special process referred to as cross-presentation. NOX2-derived ROS in phagosomes can kill ingested pathogenic microorganisms and prevent excessive reduction of proteolysis and disulfide bond formation, by modulating the redox microenvironment, including the pH and oxidative modification of cysteine residues (12–14). In this way, the stability of effective epitopes of antigenic peptides and efficiency of their presentation are enhanced, so that APCs can better activate T cells. For example, activation of CD4+ T cell clones is regulated by NOX2-derived ROS through alteration of phagosome cysteine cathepsin activity, based on the immunodominant peptide epitope presented in the context of MHC Class II (14). In contrast, dendritic cells from p47phox-null mutant NOD mice (a spontaneous mouse model of autoimmune diabetes) and patients with CGD showed reduced ability to activate CD8+ T cells, due to antigen degradation and deficient antigenic peptide loading on MHC Class I (15). In addition, discovery of many oxidation autoantigens in APCs from individuals with autoimmune diseases indicated that ROS can change antigen structure directly, thus affecting T cell behavior (16, 17).
The other main source of ROS, MtROS may also influence the antigen presentation process in more complex ways. One study found that increased mtROS in aged murine dendritic cells (DCs) hampered the cross-presentation process, which could be restored by scavenging of ROS in vitro. This change is not influenced by phagocytosis function and pH (18); however, in plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), mtROS-dependent pH alkalization and antigen protection are key factors in induction of cross-presentation. This obvious difference may result from specialized toll-like receptor (TLR) activation and NOX2 independence of pDCs (19, 20). In pDCs, ROS also participates in responses to damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) molecules (such as mitochondrial DNA), and influences their capacity to stimulate pDCs (21). NOX2-derived ROS and mtROS may act synergistically, since one study found that, in macrophages that had already engulfed bacteria, mitochondria translocated and juxtaposed to the phagosome (22), and mtROS can be packaged by Parkin-based mitochondrial vesicles and transferred to bacteria-containing phagosomes (23).
Costimulatory molecules on the surface of APCs also influence the activation of adaptive immune cell. NOX2-derived ROS in dendritic cells endocytosing tumor cell-derived microparticles can upregulate the costimulatory molecules, CD80 and CD86, thereby activating CD8+ T cells. The underlying mechanism involves generation of the ROS-activated calcium channel, Mcoln2, in the lysosomal membrane, leading to Ca2+ release and activation of the transcription factor EB (TFEB), which can bind to the promoters of the genes encoding CD80 and CD86 (24, 25); however, in human primary monocytes infected by Epstein-Barr virus, TLR signaling activation increases ROS production. Further, ROS is an important contributor to marked up-regulation of the inhibitory costimulatory molecule, PD-L1, leading to immune escape (25); interestingly, the antioxidants, N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) and apigenin, can offset this change (26). In addition, alloantibody-FcγR I/FcγR III-dependent ROS production in macrophages is an important mediator of humoral immune damage during liver graft rejection (27). Opsonization of IgG on IFN-γ-activated macrophages led to diminished phagosomal processing of proteins in a PKC/Syk- NOX2-dependent manner, which occurs at the level of the individual phagosome (28). Altered IgG subtype distribution and the resulting increase in IFN-γ production are observed in both patients with CGD and a CGD mouse model (29), indicating a possible feedback loop involving IFN-γ, IgG, FcγRs, and NOX2.
ROS and Macrophage Efferocytosis
Macrophages are responsible for anti-pathogen immunity and ROS is a powerful weapon in this context. Reactive oxygen species promotes both M1 and M2 macrophage polarization (30), which appears to be contradictory, as the M1 phenotype is pro-inflammatory while M2 polarization is anti-inflammatory; however, the mechanism occurs in the context of mixed M1/M2 populations present under physiological conditions, defective innate immunity, and the tendency toward autoimmunity in patients with CGD. Normally, macrophages do not require antioxidants to protect themselves from ROS-related oxidative stress, because they possess defensive measures against ROS-mediated damage, such as the Mst-Nrf2 axis (31). In contrast, the addition of anti-oxidants may disturb macrophage-mediated autoimmunity, by altering macrophage polarization and homeostasis (30).
Efferocytosis is the process by which macrophages engulf and clear billions of apoptotic cells. Impaired efferocytosis plays a vital role in inflammation in CGD patients. Peritoneal, bone marrow-derived, and alveolar macrophages from NOX2-deficient mice and primary macrophages from CGD patients showed diminished efferocytosis of apoptotic Jurkat T cells and human neutrophils both in vivo and in vitro (32, 33). The mechanism involved has several aspects: “find me” signals in the prepare phase, “eat me” signals in the implementation phase and “digest me” in the rehabilitation phase.
“Find me” signals are some soluble substances released by apoptotic cells themselves, which recruit macrophages and reshape their scavenging potential. Among these signals phingosine-1-phosphate and some metabolites (AMP, GMP, creatine, spermidine, and glycerol 3-phosphate) are reported as phagocyte gene expression modulators (34, 35). Interestingly, this characteristic of apoptotic cells seems to be changed in CGD mice. In zymosan A induced self-limited peritonitis CGD mice, researchers observed reduced macrophages/monocyte infiltration and delayed neutrophils clearance as well as diminished macrophage efferocytosis. The mechanism lays in defective respiratory burst in CGD neutrophils, thus failed to deplete local O2 and produce enough ROS to maintain HIF-1α protein stability that is essential to upregulate macrophage efferocytosis enhancer erythropoietin- PPARγ signals (36).
As for “eat me” signals exposed on the surface of apoptotic cells, phosphatidylserine (PS) is the strongest (37). Apoptotic neutrophils in patients with CGD are prevented from PS externalization, as this process requires the participation of NOX2-derived ROS (33, 38, 39), which is verified by treatment of normal neutrophils with NOX2 inhibitor diphenyleneiodonium (33). And peroxidized PS species (PSox) are even stronger “eat-me” signals than PS alone (40). Further, PS exposure seems to modulate macrophage program such as classical and alternative activation in M1/M2 balance, above and beyond its effect on phagocytosis (32). M2, rather M1, macrophages are the protagonists of efferocytosis; and CGD patients and NOX2-deficient mice have macrophages with an M1 phenotype that tend to promote inflammation (32, 41, 42). Finally, the difference in efferocytosis ability between M1 and M2 macrophages is primarily attributable to the central role of interleukin 4 (IL-4) signaling through peroxisome-proliferator activated receptor γ (PPARγ). Ex vivo treatment of macrophages from patients with CGD and NOX2-deficient mice with IL-4 or IL-13 leads to re-establishment of normal efferocytosis, as do monocytes treated with the PPARγ agonist, pioglitazone (a drug for treatment of type 2 diabetes) (32, 43). PPARγ agonist treatment can not only reverse impaired efferocytosis in CGD monocytes, but also enhances mtROS production (43, 44). Interestingly, mtROS production can promote M2 macrophage polarization in the intestine (45).
Works go on in macrophage after ingesting apoptotic cells. In contrast to function of preventing excessive antigen reduction characterized in previous section, NOX2-derived ROS in the degradation of apoptotic cells seems to be a positive correlation: efferosomes maturation (acquisition of LC3 and LAMP-1), enhanced acidic environment mediated by V-ATPases, competent proteolytic activity, and these are obviously delayed in macrophage of CGD patients. The key element of this difference lies on the nature of phagosomal protein cargo. Apoptotic neutrophils cargo contributes to activation of macrophage NOX2 in a CD11b-TLR2/TLR4-myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88)-dependent manner and the subsequent ROS production, which is significantly delayed in macrophages from NOX2-deficient mice (46). While IgG-opsonized antigen cargo activates NOX2 dependent on FcγR-PKC/Syk pathway rather than V-ATPase (13, 28, 46).
NOX2 deficiency has been identified as associated factor in autoimmune disease. For example, Ncf1 polymorphism is a stronger genetic factor of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (47). It is well-known that autoantigen triggered autoantibody plays a vital role in pathology of SLE, and this process is dramatically enhanced in experimental lupus in NOX2 deficient mice (48, 49). Failure in timely clearance of apoptotic cells that is founded in NOX2 deficient lupus mice contributes to accumulation of secondary necrotic cells leading to increased secretion of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines (50).
The Effects of ROS on T Helper 1/T Helper 2 and T Helper 17/Regulatory T Cell Balance
It is widely accepted that ROS is essential in adaptive immunity. T cell receptor (TCR) activation is accompanied by production of large amounts of ROS over a few minutes (51), which is associated with mTOR/AMPK axis-mediated metabolic reprogramming (52, 53). Reactive oxygen species is a critical link in the signaling events mediating T cell activation, proliferation, and differentiation (54, 55); however, number of studies have contradicted these findings (56). Here, we review understanding of the function of ROS in T helper 1 (Th1)/T helper 2 (Th2) cell, and T helper 17 (Th17) cell/regulatory T cell (Treg) balance, the importance of which in autoimmunity is universally acknowledged.
Th1/Th2 were the first CD4+ T helper cell subsets determined to contribute to autoimmune diseases (57). Characterized by IFN-γ and IL-2, Th1 cells mainly function in cellular immunity, while Th2 cells are focused on humoral immunity. The Th1/Th2 equilibrium manifests in both directions during autoimmune disease; for example, the Th1 predominance in RA (58) and Th2 advantage in SLE (59). Further the Th17/Treg equilibrium has a major role in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases (60). Interconnected developmental pathways facilitate the plasticity between Th17 and Treg phenotypes in various inflammatory (61) and oxidative (56) microenvironments.
Evidence from patients with CGD and NOX2-deficient mice includes experimental data on the “third signal” function of ROS in Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg balance (Table 1). In NOX2-deficient mice, the T cell phenotype is skewed toward the Th1 and Th17 lineages (62, 63, 67), while macrophage-restricted restoration of ROS production improved resistance to collagen-induced arthritis in NOX2-deficient mice (68). This effect may depend on Treg induction by macrophage-derived ROS, and was confirmed in experiments using macrophages from patients with CGD (64). Further, compared with wild-type mice, Tregs from NOX2-deficient mice exert much weaker inhibition of CD4+ effector T cells (65), and antioxidant NAC or NOX inhibitors also induce changes in the Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg balance (Table 2).
Table 1.
Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg related change in NOX2-deficient mice or CGD patients.
| Cell type | NOX2 mutation | Th1 change | Th2 change | Th17 change | Treg change | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD4+ T cell of C57BL/6 (62) | gp91phox- | IL-2 ↑ | IL-4 ↓ IL-5 ↓ | NA | NA | TNF ↑ |
| Total splenocytes of C57BL/6 (63) | gp91phox- | IFN-γ ↑ | NA | IL-17↑ | NA | NA |
| Naïve CD4+ T cells of C57BL/6 (63) | gp91phox- | IFN-γ ↑T-bet ↑ | IL-4 ↓ IL-4Rα↓ IL-5 ↓ GATA-3↓ | IL-17↑ | NA | STAT5Phosphorylation↓NA |
| PBMC from CGD patients (64) | p47phox- | NA | NA | NA | No change of CD4+CD25+ Foxp3+ cells | NA |
| Total spleen cell from C57BL/6 (65) | p47phox- | NA | NA | NA | No change of CD4+ Foxp3+ cells | NA |
| Spleen CD4 T cells of OT-II mouse (66) | p47phox- | IL-2 ↓IFN-γ↓CD4+T-bet+ cell↓ | IL-17A↓ | IL-10↓ | TNF-α↓TGF-β↓IL-5↓Il-12p70↓ |
Frequencies of Th1, Th2, Th17, Treg cells, or levels of related cytokines are compared between immune cells from NOX2 mutation mice/CGD patients and wild type mice/healthy people. ↑: levels of cytokines or frequencies of cells are higher than wild type mice/healthy people. ↓: levels of cytokines or frequencies of cells are lower than wild type mice/healthy people.
Table 2.
Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg related change in different treatments.
| Cell type | Treatment | Th1 change | Th2 change | Th17 change | Treg change | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD4+ T cell from BALB/c mice (63) | 10 mM NAC (ROS scavenger) | IFN-γ ↑ | IL-4 ↓ IL-5 ↓ | NA | NA | STAT5Phosphorylation↓ |
| Human CD4+CD25– T cells (64) | Primed with macrophage from p47phox-CGD patients | IFN-γ ↑ | NA | IL-17↑ | CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ cell ↓ | NA |
| CD4+ CD45RO– T-cells under Th1- and Th17-skewing conditions (69) | Tempol (ROS scavenger) | IFN-γ+ cells ↑ | NA | IL-17+ cells ↑ | NA | NA |
Thayer et al. (70) immune cells whether receiving ROS clearing treatment, or primed with macrophage from CGD patients and healthy people. ↑: levels of cytokines or frequencies of cells are higher than control group. ↓: levels of cytokines or frequencies of cells are lower than control group.
However, it is noteworthy that NOX2 deficiency in combination with transgenic mice shows different change of T cell subsets. For example, NOX2 deficiency in OT-II mice (a transgenic mouse model with antigen-specificity for chicken ovalbumin 323-339 in CD4+ T cell) lead to both decreased Th1 and Th17 lineages in contrast with NOX2-deficient mice (66). Further, NOX2 deficiency in NOD mice serves as protector reflected in significant reduction and delay in autoimmune diabetes development (67, 70, 71). And macrophage, CD4+ T cell, CD8+ T cell are involved in the protection (Table 3). Weakened Th1 lineage proficiency resulted from absence of Th1 transcription factors (T-bet, STAT4, and STAT1α) and Th17 proneness by STAT3 activation are observed in NOX2-deficient NOD mice (67). Followed research revealed that the protection afforded by NOX2 deficiency is rely on ROS lack in macrophages and DCs leading to reduced CD4+ T-cell autoreactivity [one possible mechanism is reduced MHC-II complex by macrophage (72)] and CD8+ T cell effector function [one possible mechanism is defective cross presentation by DC (15)], rather than isletβ-cell and neutrophils (70). Surprisingly, NOX2 deficiency in NOD.BDC-2.5 mice (a TCR transgenic mice whose TCR specifically recognizes islet antigen) that was meant to prevent from autoimmune diabetes has instead resulted in spontaneous type 1 diabetes. In followed adoptive transfer experiment, CD4+ T cells of NOX2-deficent NOD.BDC-2.5 mice were more diabetogenic upon adoptive transfer into NOD due to less suppressive Tregs (73). These studies implied the complication of ROS in immune cell response to heterogeneous microenvironment.
Table 3.
Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg related change in NOX2-deficient (NCF1 mutation) NOD mice.
| Cell type and mice | Type 1 diabetes | Macrophage related change | CD4/CD8+ T cell related change | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD4+ T cells of NOD mice (67) | Remission | NA | IFN-γ ↓, IL-2 ↓, T-bet ↓ IL-4 ↓, IL-17↑, IL-10↑ CD4+/IL-17A+ cell↑ No change of CD4+CD25+ Foxp3+ cells | TNF-α↓ TGF-β↑ |
| Spleen CD8+ T cells (70) of NOD mice | Remission | NA | CD8+/IFN-γ+ cells↓ CD8+/GzmB+ cells↓ | NA |
| BM-Mφs and CD4+ T cell of NOD mice (72) | Remission | MHC-II↑, TNF-α↓, IFN-β↓, TLR3↓, NF-κB↓ | No change of CD4+ Foxp3+ cells | NA |
| Islets and BM-Mφs with M1/M2 Polarization of NOD mice; (71) | Remission | M1 Marker↓ (cxcl10, ccl5, iNOS, TNF-α, IFN-γ,STAT1 )M2 Marker↑ (ccl17, Arg1, Retnla, CD206, STAT6) | NA | NA |
| Splenocytes of NOD.BDC-2.5 mice (73) | Exacerbation | NA | IFN-γ↑, IL-17↑ IL-2↑, IL-12Rβ2↑ Activation Markers↑ (CD25, CD44, CD69) | TNF-α↑IL-1β↑ |
Frequencies of Th1, Th2, Th17, Treg cells, or levels of related cytokines are compared between immune cells from NOX2 mutation NOD mice and NOD mice. ↑: levels of cytokines or frequencies of cells are higher than NOD mice. ↓: levels of cytokines or frequencies of cells are lower than NOD mice. BM-Mϕs, Bone marrow macrophages.
A key factor influencing Th1/Th2 differentiation from Th0 cells is the cytokine microenvironment, where APC represent a cytokine source. If glutathione (GSH; a major cellular antioxidant) is depleted in APCs over a short time period, production of Th1-associated cytokines will be inhibited and Th2-associated cytokine generation favored (74). Similarly, low doses of H2O2 can prevent activated Th1 clones from producing INF-γ and potentiate IL-4 secretion by activated Th2 clones (75). T cell activation-triggered IL-2 and IL-4 expression is partly dependent on ROS generation and follows oxidative signaling via mitochondrial respiration chain complex I. Inhibition of complex I function will decrease mtROS generation, thus blocking activation-induced secretion of IL-4 in CD4+ T cells from patients with atopic dermatitis, a disease characterized by elevated IL-4 and IgE. Prolonged ciprofloxacin treatment has the same effect on CD4+ T cells as the complex I inhibitor, rotenone, which may explain the immune regulation function of ciprofloxacin (76). The transcription factor, Bach2, plays a vital role in shaping the balance between CD4+ T cell subsets (77). TCR signaling induced by ROS specifically limits the degradation of the SUMO-specific protease, SENP3, leading to its rapid accumulation in Tregs. SENP3 promotes Bach2 deSUMOylation and prevents its nuclear export, which inhibits the expression of IFN-g, IL-17, and other effector cytokines, and maintains Treg-specific gene signatures (78). Reactive oxygen species promotes PAC1/DUSP2 expression by activating the transcription factor, EGR1, while PAC1 suppress the STAT3 signaling crucial for Th17 lineage differentiation (79, 80). In addition, we have described above that the post-translational oxidative modification is the main change in aging (2). Protein oxidative modification state is regulated by balance between ROS and methionine sulfoxide reductase (Mrs). Mrsb1 deficiency in DC delays its maturation and decreases DC-induced Th1 differentiation, and is associated with defective differentiation of follicular helper T cell cells in vivo (81).
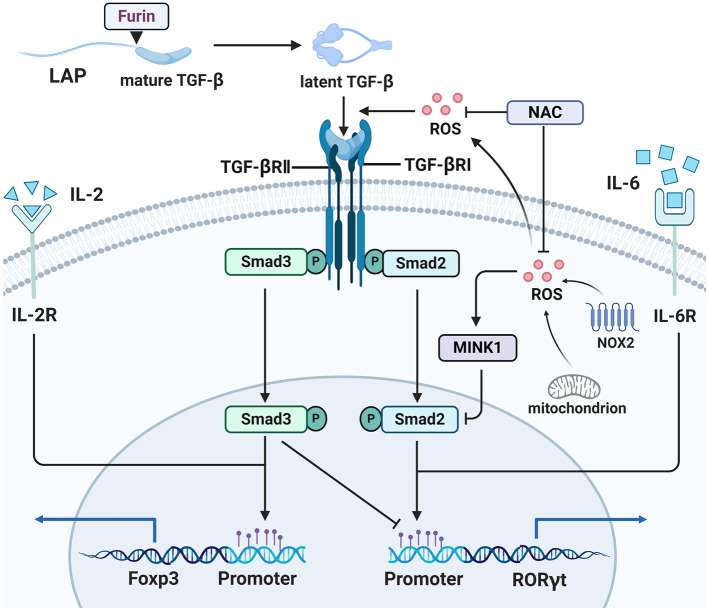
Transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) is a cytokine with broad regulatory functions in T cell development and differentiation. The complexity of TGF-β-related signaling is partly reflected in its contradictory functions and mechanisms in Th17/Treg differentiation. TGF-β is normally synthesized as a precursor, whose C-terminal portion is referred to as latency-associated peptide (LAP). LAP is cleaved by Furin, to generate latent TGF-β, which can occur both intracellularly and extracellularly (82). Latent TGF-β can be activated by various molecules, including integrin αvβ8 and ROS in T cells (83, 84). Human CD4+ CD25− naïve T cells can be induced to express Foxp3 by stimulation with anti-TCR and anti-CD28 antibodies plus ROS (85). This effect relies on production of latent TGF-β by TCR and CD28 engagement, as well as subsequent activation of latent TGF-β by ROS on TCR stimulation (84). Promotion of Th17 generation by high glucose and Treg generation by D-mannose are dependent on addition of exogenous latent LAP-TGF-β, rather than active TGF-β, indicating that activation related signals contribute to this effect, but not active TGF-β itself (86, 87) (Figure 2). Why active TGF-β does not function in this context and how the “activation-related signals” promote TGF-β signal transduction remain unclear; we speculate that intercellular communication, controlled by receptor-mediated TGF-β activation, may be a contributing factor, while “activation-related signals” may trigger some change that influences TGF-β signal transduction. Reactive oxygen species are key intermediary molecules for activation of latent TGF-β, and NAC abolishes the induction of Th17 cells and Tregs (86, 87). Reactive oxygen species not only acts as an upstream molecule to activate latent TGF-β, but also participates in TGF-β-Smad signaling. Misshapen (Msn)/NIK-related kinase 1 (MINK1) is a serine-threonine kinase that can induce Th17 differentiation by directly phosphorylating the T324 site at the α1 helix region of the Smad2 protein (88). Reactive oxygen species are involved in activation of MINK1 (89), and NAC treatment profoundly reduced MINK1 activity and increased the frequency of IL-17A+ cells, which did not occur in MINK1-deficient T cells. The processes described above are shown in Figure 2. Further, in Th17 cells differentiated from MOG35–55-immunized CD4+ T cells, NAC treatment resulted in more severe experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) disease after transfer into Rag1−/− mice (88), while knockout of GSH in T cells led to EAE resistance in mice. IsoalloLCA is a bile acid metabolite, which can enhance mtROS production in CD4+ T cells. Elevated mtROS increased H3K27 acetylation at the Foxp3 promoter region in a TGF-β-Smad3 signal dependent manner, thereby promoting Treg differentiation (90). Moreover, ROS also contributes to suppression of CD4+ effector T cells mediated by Tregs, which is partly dependent on TGF-β and can be blocked by thiol-containing antioxidants (65).
Figure 2.
ROS participate in Th17/Treg balance. ROS are involved in TGF-β mediated Th17/Treg balance. Latent TGF-β formed after LAP in the TGF-β precursor was cut by Furin, and then ROS activated TGF-β from its latent form. NOX2 or mitochondrion derived ROS activated MINK1 that inhibits the phosphorylation of Smad2 in T324 residue, so that expression of Th17-associted genes is blocked, and ROS scavenger NAC will reverse this function. ROS also participate in expression of Treg-associated genes.
Abnormal redox related Th subsets change has been identified in autoimmune diseases, such as RA. Naïve CD4+ T cells from RA patients possess a distinct carbohydrate metabolic signature, which is manifested as an excessive shunt of glucose into the PPP, resulting in high levels of reduction mediated by GSH and NADPH, and exhaustion of ROS (69, 91, 92). Low levels of ROS lead to ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) deficiency, causing rapid T cell proliferation and differentiation toward Th1 and Th17 lineages (69, 91); however, in a study of inflammasomes in RA, naïve CD4+T cells from RA patients produced more ROS compared with those from healthy controls (93); this contradictory result may be attributable to measurement being conducted as early as 8 h after anti-CD3/CD28 stimulation, which is much earlier than the 3–6 day time points used in two other studies (69, 92). In those reports, treatment of CD4+ T cells from RA patients with the pro-oxidant, plumbagin, reduced the frequencies of Th1 and Th17 cells, as well as decreasing production of the inflammatory cytokines, TNF-α and IL-6. The antioxidant, NAC, completely reversed the regulatory effects of plumbagin (94). These studies demonstrate the potential pro-inflammatory function of ROS exhaustion in RA CD4+ T cells, and anti-inflammatory benefits of supplementation with oxidants.
Based on the evidence reviewed above, it remains unclear how strong the effect of ROS is in autoimmunity-related Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg balance. Regarding patients with CGD, it is difficult to determine a clear role of CD4+ T cells in CGD-related autoimmunity risk. For example, one study reported that only gp91phox-deficient CGD is associated with diminished Tregs (95); however, a review demonstrated that oxidative stress leads to T-cell dysfunction in SLE by altering Th cell lineages and gene transcription (96).
ROS and Inflammatory Metabolism: Kyn-IDO1
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) has maintained a central role in tryptophan metabolism over hundreds of millions of years of evolution (97, 98). It is well-established that IDO has suppression and feedback roles in immune regulation (99), and clinical trials of IDO inhibitors for treatment of cancers were very successful. The normal dioxygenase activity of IDO is post-translationally activated by biological reduction of Fe3+ to Fe2+ in heme. Of these reducing agents, ROS, and particularly superoxide anion (O2?), are most widely studied in mice and rabbit (100, 101). Specifically, hyperbaric oxygen can increase kynurenine concentration in rat brains by 60% compared with air (102). In murine atopic dermatitis and psoriasis lesions, hyperbaric oxygen therapy can elevate ROS levels to attenuate disease, which may be mediated by enhanced IDO expression and Treg function (103, 104). Precisely because of the immunosuppressive effect of IDO and its ROS dependency, defective IDO activation and tryptophan metabolism were once considered to be important factors contributing to hyper inflammatory responses in murine CGD (101, 105). Interestingly, long-term evolution appears to have freed human IDO activity from ROS restriction. The IDO metabolic activity of leukocytes and monocyte-derived dendritic cells is fully maintained and intact in human patients with CGD (106–108), indicating that ROS is not indispensable for human IDO activity. Cytochrome b5, rather than ROS, has a major role in IDO reduction in human cells (100, 109); however, it is not clear whether the entire tryptophan metabolism process is independent of ROS in humans. LPS-induced ROS promotes DC maturation mediated by IDO and NF-κB activation, leading to expansion of CD4+ CD25high Tregs (110). A tryptophan catabolite of IDO, L-kynurenine (Kyn), can induce apoptosis of NK cells in a ROS-dependent manner. This pro-apoptotic effect can be entirely prevented by the antioxidant, NAC (111). In turn, Kyn also can elevate ROS levels in activated T cells and promote their proliferation, which relies on inhibition of sepiapterin reductase, the terminal enzyme in the de novo tetrahydrobiopterin synthesis pathway (112). Further, IDO1 can even produce single molecular oxygen in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. The generated 1O2 oxidizes L-tryptophan to a tricyclic hydroperoxide, thus regulating vascular tone and blood pressure under inflammatory conditions (112).
ROS and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Due to the physiological function of ROS, high levels of reducing equivalents and excessive ROS scavenging may lead to damage of the opposite type to oxidative stress, sometimes referred to as reductive (113) or antioxidative (114) stress.
Redox regulation treatments should be disease-specific as the different redox characteristics among diseases. For example, unlike the central role of oxidative stress in lupus pathogenesis, CD4+ T cells of RA patients experienced reductive stress (115). In addition, variations in redox state exist among types of lesions and cells in RA. In the next section, we discuss the metabolic origin of these variations and their influences on pathology.
ROS in RA: Every Coin Has Two Sides
RA pathogenesis is not well-understood, but can be summarized by loss of peripheral immune tolerance to autoantigens, followed by excessive activation of T and B cells, leading to increased levels of cytokines and autoantibodies (rheumatoid factor, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies, etc.). The homeostasis between pro- and anti-inflammatory states is destroyed, eventually leading to damage of multiple joints and other organs throughout the body.
Numerous studies have confirmed the vital role of ROS-related oxidative stress in joint pathology, including in angiogenesis, synovial proliferation, and inflammatory infiltration (116, 117). Further, functional genetic analysis showed that the rs201802880 polymorphism in the NCF1 coding region is associated with genetic susceptibility to RA (47). Patients with CGD also have increased susceptibility to RA (47, 118). Moreover, a study of NOX2-deficient mice demonstrated that the absence of ROS prevents resistance to autoimmune arthritis. A collagen-induced arthritis model generated by Ncf1 mutation in mice has more severe symptoms, higher anti-CII IgG levels, and stronger Th1 responses than wild-type mice, which can be reversed by restoration of functional Ncf1 solely in macrophages. Interestingly, this research also found that T cells from Ncf1-mutated mice responded more vigorously to APCs (68). Mice with mutated mouse collagen (MMC) have higher resistance to arthritis mediated by a mutated immunodominant epitope in collagen type II that binds to the MHC class II molecule. When these MMC mice are bred with NOX2-deficient mice, their immune tolerance to arthritis disappears, and they exhibit enhanced autoimmune T cell responses and higher anti-CII IgG levels (119).
Poly-N-isopropylacrylamide (PNiPAAm)-based polymers are new synthetic substances that can serve as adjuvants in inducing experimental arthritis. Mixture of these new “adjuvants” with natural CII triggers more severe arthritis and stronger autoantibody responses in Ncf1-mutated mice, in which macrophage ROS also plays a central role (120). DC function is also influenced by redox state. Mycobacterium tuberculosis-activated DC with ROS exhaustion (through incubation with SOD and catalase, or derived from NOX2-deficient mice) produced more IL-1β, TNF-α, TGF-β, and IL-6. NOX2 mutation breaks the resistance to arthritis of wild-type C57BL/6 mice, and this is CII specific, as Freund's complete adjuvant alone cannot induce arthritis. In addition, when DC from NOX2-deficient mice serve as APC, T cells produce more IL-17 after activation by toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1) (121); however, research into SKG mice (a spontaneous arthritis animal model caused by ZAP70 mutation) indicates that Ncf1 mutation-related ROS deficiency does not exhibit further alteration of T-cell activation or differentiation profile because of ZAP70 mutation, while transgenic restoration of functional Ncf1 in macrophages modified the arthritis in Ncf1-mutated SKG mice to the state observed in ROS-sufficient SKG mice. This research indicates that innate, but not adaptive, inflammation contributes to more severe arthritis related to ROS deficiency (122). Therapeutic strategy that increasing NOX2-derived ROS has been tested, in which phytol, an oxidative burst-inducing substance, ameliorated pristane induced rat arthritis in T cell and IFN-βdependent pathway (123, 124). Other free radicals, namely reactive nitrogen species, also contribute to arthritis pathogenesis in Ncf1-mutated mice, and may counteract the effects of ROS. Treatment with the NOS inhibitor, L-NAME, in the priming, rather than the effector, phase prevents Ncf1-mutated mice from developing CII-induced arthritis (125).
The Reductive State in RA Naïve CD4+ T Cells
Subsets of CD4+ T cells, including Th17 cells and Tregs, are recognized as important targets for the treatment of autoimmune disease; however, few studies have concentrated on the role of naïve CD4+ T cells. After recognizing the MHC complex, naïve CD4+ T cells initiate rapid clonal expansion, with a consequent explosive increase in energy and biosynthesis demands. The energy demands are dependent on transformation from oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis, referred to as metabolic reprogramming (52). This may appear to be a retrogression, where an efficient method of ATP generation is abandoned in favor of a wasteful method; however, glycolysis actually is the more logical choice for cells undergoing rapid proliferation. Oxidative phosphorylation has a much higher proteome costs than glycolysis, because of the prerequisite complicated mitochondrial infrastructure, that requires huge energy expenditure (126). The enhanced PPP and glutamine decomposition meet the NADPH and biosynthetic precursor needs during T cell growth and proliferation (127), and both participate in GSH generation. The balance of energy generation and biosynthesis is also very important. In contrast, deficiency of any of these processes will destroy the basic support for normal physiological activities after T cell activation. In contrast, excessive glycolysis is associated with pro-inflammatory T cell subsets (128) and excessive biosynthesis indicates a worse outcome (i.e., a tumor). In normal naïve CD4+ T cells, glycolysis activation occurs in response to upregulation of the glucose transporter, GLUT, which increases glucose uptake (129), and activities of several rate-limiting enzymes, including 6-phosphofructo-1-kinase (PFK-1) (130). PFK-1 activity is mainly dependent on allosteric activation by fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (F2,6P2), and production of F2,6P2 is primarily controlled by four fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase (PFKFB) isoenzymes (131), among which PFKFB3 is the strongest. During the activation of CD3+ T cells, PFKFB3 expression is increased in response to engagement of the TCR and the co-stimulatory receptor, CD28 (132). Two studies found that, compared with those from healthy people, naïve CD4+ T cells from patients with RA failed to upregulate PFKFB3 expression during the activation process, leading to reduced glycolytic flux and diminished ATP generation. As a rate-limiting enzyme of the PPP, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) initiates the PPP by dehydrogenation of glucose 6-phosphate. Unlike PFKFB3, these naïve CD4+ T cells successfully upregulated G6PD expression, which controls the fate of residual glucose, namely, influx to the PPP. Hence, there is an imbalance of energy generation and biosynthesis in naïve CD4+ T cells from patients with RA, resulting in accumulation of GSH and NADPH, reduced ATP generation, and ROS exhaustion (Figure 2) (60, 79).
Altered Metabolism Influences T Cell Differentiation and Proliferation
Glutaminolysis is a basic and widespread metabolic process that links oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), biosynthesis, and redox regulation. The main branch point hinges on glutamate, the first product of glutamine decomposition, which can serve as material for de novo synthesis of GSH to regulate oxidation, or transform into α-KG and enter the TCA cycle to generate ATP, mtROS, and biosynthetic precursors. Hence, the different destinies of glutamate generate counteracting metabolites (GSH and ROS), facilitating precise coordination of metabolic flux by altering enzyme activity (133). Activation of primary T cells requires rapid glutamine uptake mediated by the amino acid transporter, ASCT2 (127). Glutaminolysis inhibition of CD4+ T cells has an anti-inflammatory function in autoimmunity, promotes high levels of Foxp3 expression (134) and decreases Th17 differentiation in SLE and EAE (135, 136). In RA, fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) express increased levels of glutaminase 1, and inhibition of glutaminase 1 reduces RA-FLS proliferation (137); however, there has been no study of the glutaminolysis phenotype of RA naïve CD4+ T cells. Given the dysregulated redox state in RA T cells, whether or not glutaminolysis contributes to this phenomenon warrants discussion and study.
Other than sharing the same substrates, connections between PPP and glycolysis also include their interactions in metabolic signaling. Although excessive PPP and accumulated GSH lead to reductive stress in RA primary CD4+ T cells, T cells lacking GSH also appear to be incapable of initiating metabolic reprogramming, because of impaired Myc expression, NFAT activation, and mTOR activation. Higher ROS levels appear to be the protagonist, as ROS scavengers reverse the influence of lack of GSH (138). Briefly, both high levels of ROS and exhaustion of ROS harm normal transfer into glycolysis during metabolic reprogramming following T cell activation; recalling the old Chinese idiom, “Beyond is as wrong as falling short.”
Similar with the higher risk of fetal deformity occurring during the first 3 months of pregnancy, naïve CD4+ T cell may represent a stage at which pathogenic factors can readily influence T cells, with pathological changes at this stage having profound and lasting influences. Reactive oxygen species exhaustion disturbs normal DNA repair capabilities in naïve CD4+ T cells from patients with RA, and ATM insufficiency is a key factor influencing this phenomenon (69, 139). The resulting accumulation of DNA damage, ATP deficiency because of reduced glycolysis, and impaired autophagy induction (92) mean that naïve CD4+ T cells are more sensitive to apoptosis, leading to an abnormal loss of T cells. Since patients generally present with RA in middle-age, it is T cell auto proliferation, rather than newborn T cells, that maintain homeostasis of the T cell compartment. Remaining T cells are confronted with replicative stress, under the influence of lymphopenia, excessive biosynthesis, and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Consequently, the T cell immune aging process begins (140, 141). In addition, this imbalance supports pro-inflammatory functions, such as Th17 lineage expansion and enhanced synovial invasiveness (69, 142).
Division of Glycolysis Between Naïve CD4+ T Cell and Synovium in RA: Hypoxia, Lactic Acid, and ROS
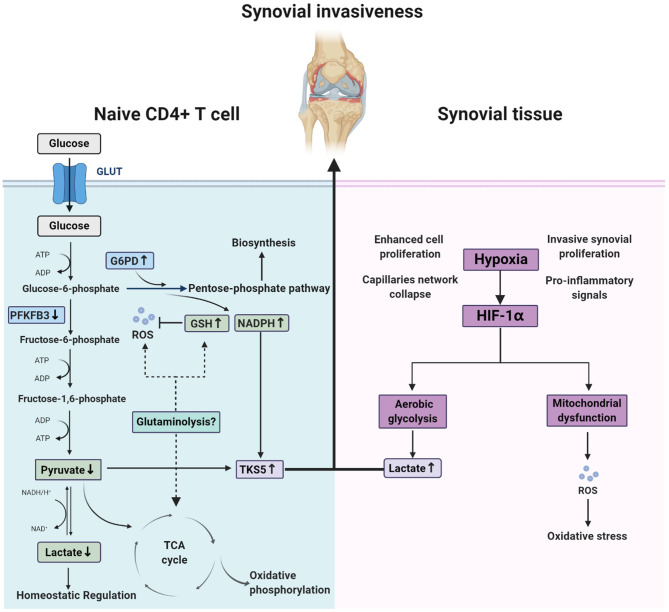
Hypoxia has been identified as a constant feature of RA synovial tissue, which occurs in the pre-arthritic phase because of increased cell proliferation, capillary network collapse, and maintenance of the inflammatory phase, due to invasive synovial proliferation, dysregulated architecture of the microvasculature, and pro-inflammatory signals, such as HIF-1α and JAK–STAT signaling (143). In energy metabolism, hypoxia is always accompanied by aerobic glycolysis and mitochondrial dysfunction, leading to accumulation of lactic acid and ROS (9). Indeed, accumulated lactic acid supports pro-inflammatory T cells to remain at the double-positive stage and produce more IL-17 (144, 145), while ROS causes oxidation with broad impacts (116, 117); however, as discussed above, in CD4+ T cells at the preliminary stages of RA, glycolysis is decreased and ROS is exhausted, resulting in a reductive metabolic microenvironment (low pyruvate and high NADPH) and triggering aberrant lipogenesis. This induces up-regulation of the podosome scaffolding protein, TKS5, and formation of cell membrane structures beneficial to T cell synovial invasion (142). Interestingly, this division of glycolysis between RA T cells and the synovium may combine to induce joint destruction: pro-inflammatory T cells invade synovial tissue quickly and easily, while departure is more difficult (Figure 3). In addition, lactate, which was once considered a metabolic waste product, is now thought to act as a homeostatic regulatory substance capable of counteracting the inflammatory responses caused by HIF1α and glycolysis metabolites, such as macrophage polarization, tumor immunity, and antiviral responses (146), and the newly discovered histone lysine lactate modification, lactylation, may be an important mechanism underlying these processes (147). Therefore, the decreased lactate levels in RA naïve CD4+ T cells, due to deficient glycolysis, may also contribute to the immune pathology of RA.
Figure 3.
Different redox state between naïve CD4+ T cell and synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. In naïve CD4+ T cell of rheumatoid arthritis patients, glucose shunting into pentose phosphate pathway due to the change of metabolic key enzymes (PFKFB3 and G6PD) activity leads to a special microenvironment characterized by low ATP, high reducing equivalences (GSH and NADPH) and exhausted ROS. Whether glutaminolysis is associated with this remains to unclear. In contrast, synovium of patients experienced oxidative stress and abnormal aerobic glycolysis that result from hypoxia in the joint. These two split situation destruct joints together by the integration of up-regulated TKS5 in naïve CD4+ T cell and high lactates in synovium.
Progressive Opinion in Redox Modulation
Studies indicate that oxidatively modified lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, may be typical of atherosclerosis. Oxidation of low-density lipoprotein has been clearly identified as an important initial event for the onset of atherosclerosis (148). Further, regarding oxidative stress in immune-related disease, oxidatively modified autoantigens are a major topic of interest, because of their induction of loss of immune tolerance. Nevertheless, cardiovascular patients do not benefit from antioxidant supplements (5), and their effects in autoimmune diseases, such as RA, are highly contentious (149–151).
Several points may explain the failure of “one-size-fits-all” antioxidant supplements in human studies. First, the reactivity of antioxidants is dependent on the oxidants they encounter, and rate constants are highest in specific pairs: α-tocopherol and peroxyl radical, glutathione and peroxynitrous acid, ascorbic acid and carbonate anion radical, glutathione and hypochlorous acid, and β-carotene paired with singlet oxygen (152). In view of different types of oxidative modification of biological macromolecules in various degenerative and aging related diseases, as well as selectively or indiscriminately produced oxidation products, application of bulk antioxidants are expected to be more precise and targeted. Second, bioavailability in target organs is a key factor. Take ischemic stroke for example, edaravone works by eliminating free radicals and suppressing oxidative stress. However, low bioavailability and inefficient penetration across the blood-brain barrier limits the curative. Treatments based on drug nano-systems loading with edaravone possess better scavenging efficiency of free radicals (153, 154). Third, different roles of antioxidants between target organ and the others may be an important reason for side effects. In view of ROS as the key beneficial messenger in the barrier ecosystem, oral administration of antioxidants which is the main application way by people, may starts its disturbance on the body upon first barrier—gastrointestinal tract (155).
Inspired by these findings in exogenous antioxidants, new strategies may combat oxidative stress shifts by promoting innate redox modulation systems; For example, by increasing the level of endogenous NADPH (156). Another meaningful progress is the use of the SOD mimics. Superoxide dismutase 2 (MnSOD) is a part of innate redox modulation systems, which plays an important role in regulating the ROS level in mitochondria. Based on therapeutic potential of MnSOD in human diseases, SOD mimics have been developed and are currently in several clinical trials (157). Interestingly, due to the redox potential falling in between the potentials for the oxidation and reduction of O2•-, these MnSOD mimics are capable of role transformation from reductants to oxidants decided by chemical properties of the reaction and the cellular environment (157). Except for drug therapy, there are some special treatments promoting redox balance and deserve attention. A recent study found static magnetic and electric fields rapidly ameliorate insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in type 2 diabetes dependent on mitROS induction, and SOD2 application fully abolishes these positive effects (158). Further, exercise especially acute exercise is widely believed a process producing large numbers of ROS which causes skeletal muscle damage, fatigue and impair recovery. As a result, antioxidants supplement has become common practice. However, several reviews have well-characterized that increase of free radicals explain the health promotion effect of exercise, and antioxidants supplement reduce the positive effects of exercise (159–161). These discoveries imply the potential bidirectional therapy, which fits the point we mentioned in this review: enhancement of ROS may sometimes be required in diseases.
Conclusion
Unlike their past reputation as harmful factors, a focus on ROS as important signaling molecule has developed in recent years. A typical example of this change in research direction is illustrated by the fact that tissue-specific redox modification of proteins has replaced biomacromolecule damage as the main agent involved in the process of aging. Failures of clinical trials into antioxidant supplements led scientists to deeply consider the problems of whether and how antioxidation strategies should be implemented.
This review has discussed the important roles of ROS in various autoimmune functions. For example, ROS influences interactions between innate and adaptive immunity by controlling the antigen presentation and apoptotic cell clearance. Evidence from NOX2-deficient mice and patients with CGD support the functions of ROS in regulating Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg balance. Immunometabolism is an important process to which ROS contributes. Tryptophan metabolism deficiency contributes to the stronger, harmful inflammatory response in CGD mice. Regarding autoimmune diseases, such as RA, alterations in glucose metabolism-related redox imbalance have broad impacts. Due to glucose shunting into the PPP from glycolysis, naïve CD4+ T cells from RA patients are a good cellular level model system to explore T cell immune responses in a naturally ROS deficient environment. This special change in metabolism and redox balance leads to DNA repair deficiency, susceptibility to apoptosis, and differentiation into inflammatory subsets of RA naïve CD4+T cells. In addition, although the metabolism and redox state in RA synovial tissue are completely contrary to that of naïve CD4+T cells, we speculate that they act in combination to mediate joint destruction; however, the origin of this specific type of metabolic reprogramming remains unclear, and whether ROS contributes to triggering this process also awaits further investigation.
Overall, ROS clearance may be beneficial in specific situations, but harmful in others. Under no circumstances should we regard antioxidant supplements as completely safe treatments, particularly for immune disease. Moreover, antioxidant supplements are not equivalent to ROS clearance.
Author Contributions
WL: writing, original draft, and figures. PS: review and editing. YS: resources. YH: resources. ST: conceptualization. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
Figures were created using BioRender.com.
Footnotes
Funding. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81573802, 81503426, and 81874383) and the program of Tongji-Rongcheng Center for Biomedicine (HUST).
References
- 1.Sies H Oxidative stress: from basic research to clinical application . Am J Med. (1991) 91:31s−8s. 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90281-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Xiao H, Jedrychowski MP, Schweppe DK, Huttlin EL, Yu Q, Heppner DE, et al. A quantitative tissue-specific landscape of protein redox regulation during aging. Cell. (2020) 180:968–83.e24. 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Franchina DG, Dostert C, Brenner D. Reactive oxygen species: involvement in T cell signaling and metabolism. Trends Immunol. (2018) 39:489–502. 10.1016/j.it.2018.01.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bjelakovic G, Nikolova D, Gluud LL, Simonetti RG, Gluud C. Antioxidant supplements for prevention of mortality in healthy participants and patients with various diseases. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2012) 3:Cd007176. 10.1002/14651858.CD007176.pub2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Myung SK, Ju W, Cho B, Oh SW, Park SM, Koo BK, et al. Efficacy of vitamin and antioxidant supplements in prevention of cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ (Clin Res Ed.). (2013) 346:f10. 10.1136/bmj.f10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bjelakovic G, Nikolova D, Gluud LL, Simonetti RG, Gluud C. Mortality in randomized trials of antioxidant supplements for primary and secondary prevention: systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. (2007) 297:842–57. 10.1001/jama.297.8.842 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bedard K, Krause KH. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev. (2007) 87:245–313. 10.1152/physrev.00044.2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.O'Neill S, Brault J, Stasia MJ, Knaus UG. Genetic disorders coupled to ROS deficiency. Redox Biol. (2015) 6:135–56. 10.1016/j.redox.2015.07.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Murphy MP. How mitochondria produce reactive oxygen species. Biochem J. (2009) 417:1–13. 10.1042/BJ20081386 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lin DS, Huang YW, Ho CS, Hung PL, Hsu MH, Wang TJ, et al. Oxidative insults and mitochondrial DNA mutation promote enhanced autophagy and mitophagy compromising cell viability in pluripotent cell model of mitochondrial disease. Cells. (2019) 8:65. 10.3390/cells8010065 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dogan SA, Cerutti R, Benincá C, Brea-Calvo G, Jacobs HT, Zeviani M, et al. Perturbed redox signaling exacerbates a mitochondrial myopathy. Cell Metab. (2018) 28:764–5.e5. 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.07.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Savina A, Jancic C, Hugues S, Guermonprez P, Vargas P, Moura IC, et al. NOX2 controls phagosomal pH to regulate antigen processing during crosspresentation by dendritic cells. Cell. (2006) 126:205–18. 10.1016/j.cell.2006.05.035 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Rybicka JM, Balce DR, Khan MF, Krohn RM, Yates RM. NADPH oxidase activity controls phagosomal proteolysis in macrophages through modulation of the lumenal redox environment of phagosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2010) 107:10496–501. 10.1073/pnas.0914867107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Allan ER, Tailor P, Balce DR, Pirzadeh P, McKenna NT, Renaux B, et al. NADPH oxidase modifies patterns of MHC class II-restricted epitopic repertoires through redox control of antigen processing. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md.: 1950). (2014) 192:4989–5001. 10.4049/jimmunol.1302896 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Liu C, Whitener RL, Lin A, Xu Y, Chen J, Savinov A, et al. Neutrophil cytosolic factor 1 in dendritic cells promotes autoreactive CD8(+) T cell activation via cross-presentation in type 1 diabetes. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:952. 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00952 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yang M, Haase C, Viljanen J, Xu B, Ge C, Kihlberg J, et al. Cutting edge: processing of oxidized peptides in macrophages regulates T cell activation and development of autoimmune arthritis. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md.: 1950). (2017) 199:3937–42. 10.4049/jimmunol.1700774 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Prolo C, Alvarez MN, Radi R. Peroxynitrite, a potent macrophage-derived oxidizing cytotoxin to combat invading pathogens. BioFactors (Oxford, England). (2014) 40:215–25. 10.1002/biof.1150 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chougnet CA, Thacker RI, Shehata HM, Hennies CM, Lehn MA, Lages CS, et al. Loss of phagocytic and antigen cross-presenting capacity in aging dendritic cells is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md.: 1950). (2015) 195:2624–32. 10.4049/jimmunol.1501006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Oberkampf M, Guillerey C, Mouriès J, Rosenbaum P, Fayolle C, Bobard A, et al. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species regulate the induction of CD8(+) T cells by plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:2241. 10.1038/s41467-018-04686-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mouriès J, Moron G, Schlecht G, Escriou N, Dadaglio G, Leclerc C. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells efficiently cross-prime naive T cells in vivo after TLR activation. Blood. (2008) 112:3713–22. 10.1182/blood-2008-03-146290 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pazmandi K, Agod Z, Kumar BV, Szabo A, Fekete T, Sogor V, et al. Oxidative modification enhances the immunostimulatory effects of extracellular mitochondrial DNA on plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Free Radic Biol Med. (2014) 77:281–90. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.09.028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Geng J, Sun X, Wang P, Zhang S, Wang X, Wu H, et al. Kinases Mst1 and Mst2 positively regulate phagocytic induction of reactive oxygen species and bactericidal activity. Nat Immunol. (2015) 16:1142–52. 10.1038/ni.3268 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Abuaita BH, Schultz TL, O'Riordan MX. Mitochondria-derived vesicles deliver antimicrobial reactive oxygen species to control phagosome-localized Staphylococcus aureus. Cell Host Microbe. (2018) 24:625–36.e5. 10.1016/j.chom.2018.10.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kantengwa S, Jornot L, Devenoges C, Nicod LP. Superoxide anions induce the maturation of human dendritic cells. Am J Resp Crit Care Med. (2003) 167:431–7. 10.1164/rccm.200205-425OC [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ma J, Wei K, Zhang H, Tang K, Li F, Zhang T, et al. Mechanisms by which dendritic cells present tumor microparticle antigens to CD8(+) T cells. Cancer Immunol Res. (2018) 6:1057–68. 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-17-0716 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gilardini Montani MS, Santarelli R, Falcinelli L, Gonnella R, Granato M, Di Renzo L, et al. EBV up-regulates PD-L1 on the surface of primary monocytes by increasing ROS and activating TLR signaling and STAT3. J Leukoc Biol. (2018) 104:821–32. 10.1002/JLB.2A0118-029RR [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zimmerer JM, Liu XL, Blaszczak A, Avila CL, Pham TA, Warren RT, et al. Critical role of macrophage FcγR signaling and reactive oxygen species in alloantibody-mediated hepatocyte rejection. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md.: 1950). (2018) 201:3731–40. 10.4049/jimmunol.1800333 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Balce DR, Rybicka JM, Greene CJ, Ewanchuk BW, Yates RM. Ligation of FcγR alters phagosomal processing of protein via augmentation of NADPH oxidase activity. Traffic (Copenhagen, Denmark). (2016) 17:786–802. 10.1111/tra.12396 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cachat J, Deffert C, Alessandrini M, Roux-Lombard P, Le Gouellec A, Stasia MJ, et al. Altered humoral immune responses and IgG subtypes in NOX2-deficient mice and patients: a key role for NOX2 in antigen-presenting cells. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:1555. 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01555 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tan HY, Wang N, Li S, Hong M, Wang X, Feng Y. The reactive oxygen species in macrophage polarization: reflecting its dual role in progression and treatment of human diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2016) 2016:2795090. 10.1155/2016/2795090 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wang P, Geng J, Gao J, Zhao H, Li J, Shi Y, et al. Macrophage achieves self-protection against oxidative stress-induced ageing through the Mst-Nrf2 axis. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:755. 10.1038/s41467-019-08680-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Fernandez-Boyanapalli RF, Frasch SC, McPhillips K, Vandivier RW, Harry BL, Riches DW, et al. Impaired apoptotic cell clearance in CGD due to altered macrophage programming is reversed by phosphatidylserine-dependent production of IL-4. Blood. (2009) 113:2047–55. 10.1182/blood-2008-05-160564 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sanmun D, Witasp E, Jitkaew S, Tyurina YY, Kagan VE, Ahlin A, et al. Involvement of a functional NADPH oxidase in neutrophils and macrophages during programmed cell clearance: implications for chronic granulomatous disease. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2009) 297:C621–31. 10.1152/ajpcell.00651.2008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Medina CB, Mehrotra P, Arandjelovic S, Perry JSA, Guo Y, Morioka S, et al. Metabolites released from apoptotic cells act as tissue messengers. Nature. (2020) 580:130–5. 10.1038/s41586-020-2121-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Luo B, Gan W, Liu Z, Shen Z, Wang J, Shi R, et al. Erythropoeitin signaling in macrophages promotes dying cell clearance and immune tolerance. Immunity. (2016) 44:287–302. 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.01.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Luo B, Wang J, Liu Z, Shen Z, Shi R, Liu YQ, et al. Phagocyte respiratory burst activates macrophage erythropoietin signalling to promote acute inflammation resolution. Nat Commun. (2016) 7:12177. 10.1038/ncomms12177 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Fadok VA, Voelker DR, Campbell PA, Cohen JJ, Bratton DL, Henson PM. Exposure of phosphatidylserine on the surface of apoptotic lymphocytes triggers specific recognition and removal by macrophages. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md.: 1950). (1992) 148:2207–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Arroyo A, Modrianský M, Serinkan FB, Bello RI, Matsura T, Jiang J, et al. NADPH oxidase-dependent oxidation and externalization of phosphatidylserine during apoptosis in Me2SO-differentiated HL-60 cells. Role in phagocytic clearance. J Biol Chem. (2002) 277:49965–75. 10.1074/jbc.M204513200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hampton MB, Vissers MC, Keenan JI, Winterbourn CC. Oxidant-mediated phosphatidylserine exposure and macrophage uptake of activated neutrophils: possible impairment in chronic granulomatous disease. J Leukoc Biol. (2002) 71:775–81. 10.1189/jlb.71.5.775 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tyurin VA, Balasubramanian K, Winnica D, Tyurina YY, Vikulina AS, He RR, et al. Oxidatively modified phosphatidylserines on the surface of apoptotic cells are essential phagocytic ‘eat-me' signals: cleavage and inhibition of phagocytosis by Lp-PLA2. Cell Death Differ. (2014) 21:825–35. 10.1038/cdd.2014.1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zeng MY, Pham D, Bagaitkar J, Liu J, Otero K, Shan M, et al. An efferocytosis-induced, IL-4-dependent macrophage-iNKT cell circuit suppresses sterile inflammation and is defective in murine CGD. Blood. (2013) 121:3473–83. 10.1182/blood-2012-10-461913 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Yi L, Liu Q, Orandle MS, Sadiq-Ali S, Koontz SM, Choi U, et al. p47(phox) directs murine macrophage cell fate decisions. Am J Pathol. (2012) 180:1049–58. 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.11.019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Fernandez-Boyanapalli RF, Falcone EL, Zerbe CS, Marciano BE, Frasch SC, Henson PM, et al. Impaired efferocytosis in human chronic granulomatous disease is reversed by pioglitazone treatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2015) 136:1399–401.e3. 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.07.034 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Fernandez-Boyanapalli RF, Frasch SC, Thomas SM, Malcolm KC, Nicks M, Harbeck RJ, et al. Pioglitazone restores phagocyte mitochondrial oxidants and bactericidal capacity in chronic granulomatous disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2015) 135:517–27.e12. 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.10.034 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Formentini L, Santacatterina F, Núñez de Arenas C, Stamatakis K, López-Martínez D, Logan A, et al. Mitochondrial ROS production protects the intestine from inflammation through functional M2 macrophage polarization. Cell Rep. (2017) 19:1202–13. 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.04.036 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bagaitkar J, Huang J, Zeng MY, Pech NK, Monlish DA, Perez-Zapata LJ, et al. NADPH oxidase activation regulates apoptotic neutrophil clearance by murine macrophages. Blood. (2018) 131:2367–78. 10.1182/blood-2017-09-809004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zhao J, Ma J, Deng Y, Kelly JA, Kim K, Bang SY, et al. A missense variant in NCF1 is associated with susceptibility to multiple autoimmune diseases. Nat Genet. (2017) 49:433–7. 10.1038/ng.3782 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Campbell AM, Kashgarian M, Shlomchik MJ. NADPH oxidase inhibits the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Sci Transl Med. (2012) 4:157ra141. 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004801 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kienhöfer D, Hahn J, Stoof J, Csepregi JZ, Reinwald C, Urbonaviciute V, et al. Experimental lupus is aggravated in mouse strains with impaired induction of neutrophil extracellular traps. JCI Insight. (2017) 2:92920. 10.1172/jci.insight.92920 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hahn J, Euler M, Kilgus E, Kienhöfer D, Stoof J, Knopf J, et al. NOX2 mediates quiescent handling of dead cell remnants in phagocytes. Redox Biol. (2019) 26:101279. 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101279 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Yang Y, Bazhin AV, Werner J, Karakhanova S. Reactive oxygen species in the immune system. Int Rev Immunol. (2013) 32:249–70. 10.3109/08830185.2012.755176 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.MacIver NJ, Michalek RD, Rathmell JC. Metabolic regulation of T lymphocytes. Ann Rev Immunol. (2013) 31:259–83. 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032712-095956 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Waickman AT, Powell JD. mTOR, metabolism, and the regulation of T-cell differentiation and function. Immunol Rev. (2012) 249:43–58. 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01152.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sena LA, Li S, Jairaman A, Prakriya M, Ezponda T, Hildeman DA, et al. Mitochondria are required for antigen-specific T cell activation through reactive oxygen species signaling. Immunity. (2013) 38:225–36. 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.10.020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Previte DM, O'Connor EC, Novak EA, Martins CP, Mollen KP, Piganelli JD. Reactive oxygen species are required for driving efficient and sustained aerobic glycolysis during CD4+ T cell activation. PLoS ONE. (2017) 12:e0175549. 10.1371/journal.pone.0175549 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Moro-García MA, Mayo JC, Sainz RM, Alonso-Arias R. Influence of inflammation in the process of T lymphocyte differentiation: proliferative, metabolic, oxidative changes. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:339. 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00339 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bond MW, Giedlin MA, Coffman RL. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md.: 1950). (1986) 136:2348–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Schulze-Koops H, Kalden JR. The balance of Th1/Th2 cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. (2001) 15:677–91. 10.1053/berh.2001.0187 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Wisłowska M, Kuczewska-Stanecka K. Current views of etiopathogenesis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Polski tygodnik lekarski (Warsaw, Poland: 1960). (1986) 41:506–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Noack M, Miossec P. Th17 and regulatory T cell balance in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Autoimmun Rev. (2014) 13:668–77. 10.1016/j.autrev.2013.12.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Sakaguchi S, Vignali DA, Rudensky AY, Niec RE, Waldmann H. The plasticity and stability of regulatory T cells. Nat Rev Immunol. (2013) 13:461–7. 10.1038/nri3464 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Jackson SH, Devadas S, Kwon J, Pinto LA, Williams MS. T cells express a phagocyte-type NADPH oxidase that is activated after T cell receptor stimulation. Nat Immunol. (2004) 5:818–27. 10.1038/ni1096 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Shatynski KE, Chen H, Kwon J, Williams MS. Decreased STAT5 phosphorylation and GATA-3 expression in NOX2-deficient T cells: role in T helper development. Eur J Immunol. (2012) 42:3202–11. 10.1002/eji.201242659 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Kraaij MD, Savage ND, van der Kooij SW, Koekkoek K, Wang J, van den Berg JM, et al. Induction of regulatory T cells by macrophages is dependent on production of reactive oxygen species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2010) 107:17686–91. 10.1073/pnas.1012016107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Efimova O, Szankasi P, Kelley TW. Ncf1 (p47phox) is essential for direct regulatory T cell mediated suppression of CD4+ effector T cells. PLoS ONE. (2011) 6:e16013. 10.1371/journal.pone.0016013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Padgett LE, Tse HM. NADPH oxidase-derived superoxide provides a third signal for CD4 T cell effector responses. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md.: 1950). (2016) 197:1733–42. 10.4049/jimmunol.1502581 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Tse HM, Thayer TC, Steele C, Cuda CM, Morel L, Piganelli JD, et al. NADPH oxidase deficiency regulates Th lineage commitment and modulates autoimmunity. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md.: 1950). (2010) 185:5247–58. 10.4049/jimmunol.1001472 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Gelderman KA, Hultqvist M, Pizzolla A, Zhao M, Nandakumar KS, Mattsson R, et al. Macrophages suppress T cell responses and arthritis development in mice by producing reactive oxygen species. J Clin Invest. (2007) 117:3020–8. 10.1172/JCI31935 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Yang Z, Shen Y, Oishi H, Matteson EL, Tian L, Goronzy JJ, et al. Restoring oxidant signaling suppresses proarthritogenic T cell effector functions in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Transl Med. (2016) 8:331ra38. 10.1126/scitranslmed.aad7151 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Thayer TC, Delano M, Liu C, Chen J, Padgett LE, Tse HM, et al. Superoxide production by macrophages and T cells is critical for the induction of autoreactivity and type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. (2011) 60:2144–51. 10.2337/db10-1222 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Padgett LE, Burg AR, Lei W, Tse HM. Loss of NADPH oxidase-derived superoxide skews macrophage phenotypes to delay type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. (2015) 64:937–46. 10.2337/db14-0929 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Seleme MC, Lei W, Burg AR, Goh KY, Metz A, Steele C, et al. Dysregulated TLR3-dependent signaling and innate immune activation in superoxide-deficient macrophages from nonobese diabetic mice. Free Radic Biol Med. (2012) 52:2047–56. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.01.027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Padgett LE, Anderson B, Liu C, Ganini D, Mason RP, Piganelli JD, et al. Loss of NOX-derived superoxide exacerbates diabetogenic CD4 T-cell effector responses in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. (2015) 64:4171–83. 10.2337/db15-0546 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Peterson JD, Herzenberg LA, Vasquez K, Waltenbaugh C. Glutathione levels in antigen-presenting cells modulate Th1 versus Th2 response patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (1998) 95:3071–6. 10.1073/pnas.95.6.3071 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Frossi B, De Carli M, Piemonte M, Pucillo C. Oxidative microenvironment exerts an opposite regulatory effect on cytokine production by Th1 and Th2 cells. Mol Immunol. (2008) 45:58–64. 10.1016/j.molimm.2007.05.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Kaminski MM, Sauer SW, Klemke CD, Süss D, Okun JG, Krammer PH, et al. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species control T cell activation by regulating IL-2 and IL-4 expression: mechanism of ciprofloxacin-mediated immunosuppression. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md.: 1950). (2010) 184:4827–41. 10.4049/jimmunol.0901662 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Yang L, Chen S, Zhao Q, Sun Y, Nie H. The critical role of bach2 in shaping the balance between CD4(+) T cell subsets in immune-mediated diseases. Mediat Inflamm. (2019) 2019:2609737. 10.1155/2019/2609737 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Yu X, Lao Y, Teng XL, Li S, Zhou Y, Wang F, et al. SENP3 maintains the stability and function of regulatory T cells via BACH2 deSUMOylation. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:3157. 10.1038/s41467-018-05676-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Lu D, Liu L, Ji X, Gao Y, Chen X, Liu Y, et al. The phosphatase DUSP2 controls the activity of the transcription activator STAT3 and regulates TH17 differentiation. Nat Immunol. (2015) 16:1263–73. 10.1038/ni.3278 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Dan L, Liu L, Sun Y, Song J, Yin Q, Zhang G, et al. The phosphatase PAC1 acts as a T cell suppressor and attenuates host antitumor immunity. Nat Immunol. (2020) 21:287–97. 10.1038/s41590-019-0577-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Lee HJ, Park JS, Yoo HJ, Lee HM, Lee BC, Kim JH. The selenoprotein MsrB1 instructs dendritic cells to induce T-helper 1 immune responses. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland). (2020) 9:9101021. 10.3390/antiox9101021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Travis MA, Sheppard D. TGF-β activation and function in immunity. Ann Rev Immunol. (2014) 32:51–82. 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032713-120257 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Worthington JJ, Kelly A, Smedley C, Bauché D, Campbell S, Marie JC, et al. Integrin αvβ8-mediated TGF-β activation by effector regulatory T cells is essential for suppression of T-cell-mediated inflammation. Immunity. (2015) 42:903–15. 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.04.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Amarnath S, Dong L, Li J, Wu Y, Chen W. Endogenous TGF-beta activation by reactive oxygen species is key to Foxp3 induction in TCR-stimulated and HIV-1-infected human CD4+CD25- T cells. Retrovirology. (2007) 4:57. 10.1186/1742-4690-4-57 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Walker MR, Kasprowicz DJ, Gersuk VH, Benard A, Van Landeghen M, Buckner JH, et al. Induction of FoxP3 and acquisition of T regulatory activity by stimulated human CD4+CD25- T cells. J Clin Invest. (2003) 112:1437–43. 10.1172/JCI19441 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Zhang D, Jin W, Wu R, Li J, Park SA, Tu E, et al. High glucose intake exacerbates autoimmunity through reactive-oxygen-species-mediated TGF-β cytokine activation. Immunity. (2019) 51:671–81.e5. 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.08.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Zhang D, Chia C, Jiao X, Jin W, Kasagi S, Wu R, et al. D-mannose induces regulatory T cells and suppresses immunopathology. Nat Med. (2017) 23:1036–45. 10.1038/nm.4375 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Fu G, Xu Q, Qiu Y, Jin X, Xu T, Dong S, et al. Suppression of Th17 cell differentiation by misshapen/NIK-related kinase MINK1. J Exp Med. (2017) 214:1453–69. 10.1084/jem.20161120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Nicke B, Bastien J, Khanna SJ, Warne PH, Cowling V, Cook SJ, et al. Involvement of MINK, a Ste20 family kinase, in Ras oncogene-induced growth arrest in human ovarian surface epithelial cells. Mol Cell. (2005) 20:673–85. 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.10.038 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Hang S, Paik D, Yao L, Kim E, Trinath J, Lu J, et al. Bile acid metabolites control T(H)17 and T(reg) cell differentiation. Nature. (2019) 576:143–8. 10.1038/s41586-019-1785-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Gelderman KA, Hultqvist M, Holmberg J, Olofsson P, Holmdahl R. T cell surface redox levels determine T cell reactivity and arthritis susceptibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2006) 103:12831–6. 10.1073/pnas.0604571103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Yang Z, Fujii H, Mohan SV, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM. Phosphofructokinase deficiency impairs ATP generation, autophagy, and redox balance in rheumatoid arthritis T cells. J Exp Med. (2013) 210:2119–34. 10.1084/jem.20130252 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Zhao C, Gu Y, Zeng X, Wang J. NLRP3 inflammasome regulates Th17 differentiation in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Immunol (Orlando, Fla.). (2018) 197:154–60. 10.1016/j.clim.2018.09.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Abimannan T, Peroumal D, Parida JR, Barik PK, Padhan P, Devadas S. Oxidative stress modulates the cytokine response of differentiated Th17 and Th1 cells. Free Radic Biol Med. (2016) 99:352–63. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.08.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.van de Geer A, Cuadrado E, Slot MC, van Bruggen R, Amsen D, Kuijpers TW. Regulatory T cell features in chronic granulomatous disease. Clin Exp Immunol. (2019) 197:222–9. 10.1111/cei.13300 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Perl A. Oxidative stress in the pathology and treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2013) 9:674–86. 10.1038/nrrheum.2013.147 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Efimov I, Basran J, Thackray SJ, Handa S, Mowat CG, Raven EL. Structure and reaction mechanism in the heme dioxygenases. Biochemistry. (2011) 50:2717–24. 10.1021/bi101732n [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Thomas SR, Terentis AC, Cai H, Takikawa O, Levina A, Lay PA, et al. Post-translational regulation of human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity by nitric oxide. J Biol Chem. (2007) 282:23778–87. 10.1074/jbc.M700669200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Mándi Y, Vécsei L. The kynurenine system and immunoregulation. J Neural Transm (Vienna, Austria: 1996). (2012) 119:197–209. 10.1007/s00702-011-0681-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Maghzal GJ, Thomas SR, Hunt NH, Stocker R. Cytochrome b5, not superoxide anion radical, is a major reductant of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in human cells. J Biol Chem. (2008) 283:12014–25. 10.1074/jbc.M710266200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Romani L, Fallarino F, De Luca A, Montagnoli C, D'Angelo C, Zelante T, et al. Defective tryptophan catabolism underlies inflammation in mouse chronic granulomatous disease. Nature. (2008) 451:211–5. 10.1038/nature06471 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Dang Y, Dale WE, Brown OR. Comparative effects of oxygen on indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase of the kynurenine pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. (2000) 28:615–24. 10.1016/S0891-5849(99)00272-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Kim HR, Lee A, Choi EJ, Hong MP, Kie JH, Lim W, et al. Reactive oxygen species prevent imiquimod-induced psoriatic dermatitis through enhancing regulatory T cell function. PLoS ONE. (2014) 9:e91146. 10.1371/journal.pone.0091146 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Kim HR, Kim JH, Choi EJ, Lee YK, Kie JH, Jang MH, et al. Hyperoxygenation attenuated a murine model of atopic dermatitis through raising skin level of ROS. PLoS ONE. (2014) 9:e109297. 10.1371/journal.pone.0109297 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Popov A, Abdullah Z, Wickenhauser C, Saric T, Driesen J, Hanisch FG, et al. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-expressing dendritic cells form suppurative granulomas following Listeria monocytogenes infection. J Clin Investig. (2006) 116:3160–70. 10.1172/JCI28996 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.De Ravin SS, Zarember KA, Long-Priel D, Chan KC, Fox SD, Gallin JI, et al. Tryptophan/kynurenine metabolism in human leukocytes is independent of superoxide and is fully maintained in chronic granulomatous disease. Blood. (2010) 116:1755–60. 10.1182/blood-2009-07-233734 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Jürgens B, Fuchs D, Reichenbach J, Heitger A. Intact indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity in human chronic granulomatous disease. Clin Immunol (Orlando, Fla.). (2010) 137:1–4. 10.1016/j.clim.2010.05.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Maghzal GJ, Winter S, Wurzer B, Chong BH, Holmdahl R, Stocker R. Tryptophan catabolism is unaffected in chronic granulomatous disease. Nature. (2014) 514:E16–7. 10.1038/nature13844 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Vottero E, Mitchell DA, Page MJ, MacGillivray RT, Sadowski IJ, Roberge M, et al. Cytochrome b(5) is a major reductant in vivo of human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expressed in yeast. FEBS Lett. (2006) 580:2265–8. 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.03.034 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Hill M, Tanguy-Royer S, Royer P, Chauveau C, Asghar K, Tesson L, et al. IDO expands human CD4+CD25high regulatory T cells by promoting maturation of LPS-treated dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol. (2007) 37:3054–62. 10.1002/eji.200636704 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Song H, Park H, Kim YS, Kim KD, Lee HK, Cho DH, et al. L-kynurenine-induced apoptosis in human NK cells is mediated by reactive oxygen species. Int Immunopharmacol. (2011) 11:932–8. 10.1016/j.intimp.2011.02.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Cronin SJF, Seehus C, Weidinger A, Talbot S, Reissig S, Seifert M, et al. The metabolite BH4 controls T cell proliferation in autoimmunity and cancer. Nature. (2018) 563:564–8. 10.1038/s41586-018-0701-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Korge P, Calmettes G, Weiss JN. Increased reactive oxygen species production during reductive stress: the roles of mitochondrial glutathione and thioredoxin reductases. Biochimica et biophysica acta. (2015) 1847:514–25. 10.1016/j.bbabio.2015.02.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Poljsak B, Milisav I. The neglected significance of antioxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2012) 2012:480895. 10.1155/2012/480895 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Perl A. Review: metabolic control of immune system activation in rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol (Hoboken, N.J.). (2017) 69:2259–70. 10.1002/art.40223 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Balogh E, Veale DJ, McGarry T, Orr C, Szekanecz Z, Ng CT, et al. Oxidative stress impairs energy metabolism in primary cells and synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2018) 20:95. 10.1186/s13075-018-1592-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Mateen S, Moin S, Zafar A, Khan AQ. Redox signaling in rheumatoid arthritis and the preventive role of polyphenols. Clinica Chimica Acta. (2016) 463:4–10. 10.1016/j.cca.2016.10.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Battersby AC, Braggins H, Pearce MS, Cale CM, Burns SO, Hackett S, et al. Inflammatory and autoimmune manifestations in X-linked carriers of chronic granulomatous disease in the United Kingdom. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2017) 140:628–30.e6. 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.02.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Hultqvist M, Bäcklund J, Bauer K, Gelderman KA, Holmdahl R. Lack of reactive oxygen species breaks T cell tolerance to collagen type II and allows development of arthritis in mice. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md.: 1950). (2007) 179:1431–7. 10.4049/jimmunol.179.3.1431 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Shakya AK, Kumar A, Holmdahl R, Nandakumar KS. Macrophage-derived reactive oxygen species protects against autoimmune priming with a defined polymeric adjuvant. Immunology. (2016) 147:125–32. 10.1111/imm.12546 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.George-Chandy A, Nordström I, Nygren E, Jonsson IM, Postigo J, Collins LV, et al. Th17 development and autoimmune arthritis in the absence of reactive oxygen species. Eur J Immunol. (2008) 38:1118–26. 10.1002/eji.200737348 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Guerard S, Holmdahl R, Wing K. Reactive oxygen species regulate innate but not adaptive inflammation in ZAP70-mutated SKG arthritic mice. Am J Pathol. (2016) 186:2353–63. 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.05.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Hultqvist M, Olofsson P, Gelderman KA, Holmberg J, Holmdahl R. A new arthritis therapy with oxidative burst inducers. PLoS Med. (2006) 3:e348. 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030348 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Olofsson P, Nerstedt A, Hultqvist M, Nilsson EC, Andersson S, Bergelin A, et al. Arthritis suppression by NADPH activation operates through an interferon-beta pathway. BMC Biol. (2007) 5:19. 10.1186/1741-7007-5-19 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Zhong J, Yau ACY, Holmdahl R. Regulation of T cell function by reactive nitrogen and oxygen species in collagen-induced arthritis. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2020) 32:161–72. 10.1089/ars.2019.7788 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Basan M, Hui S, Okano H, Zhang Z, Shen Y, Williamson JR, et al. Overflow metabolism in Escherichia coli results from efficient proteome allocation. Nature. (2015) 528:99–104. 10.1038/nature15765 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Nakaya M, Xiao Y, Zhou X, Chang JH, Chang M, Cheng X, et al. Inflammatory T cell responses rely on amino acid transporter ASCT2 facilitation of glutamine uptake and mTORC1 kinase activation. Immunity. (2014) 40:692–705. 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.04.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Gerriets VA, Kishton RJ, Nichols AG, Macintyre AN, Inoue M, Ilkayeva O, et al. Metabolic programming and PDHK1 control CD4+ T cell subsets and inflammation. J Clin Investig. (2015) 125:194–207. 10.1172/JCI76012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Frauwirth KA, Riley JL, Harris MH, Parry RV, Rathmell JC, Plas DR, et al. The CD28 signaling pathway regulates glucose metabolism. Immunity. (2002) 16:769–77. 10.1016/S1074-7613(02)00323-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Maciver NJ, Jacobs SR, Wieman HL, Wofford JA, Coloff JL, Rathmell JC. Glucose metabolism in lymphocytes is a regulated process with significant effects on immune cell function and survival. J Leukoc Biol. (2008) 84:949–57. 10.1189/jlb.0108024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Okar DA, Wu C, Lange AJ. Regulation of the regulatory enzyme, 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. Adv Enzyme Regul. (2004) 44:123–54. 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2003.11.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Telang S, Clem BF, Klarer AC, Clem AL, Trent JO, Bucala R, et al. Small molecule inhibition of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase suppresses t cell activation. J Transl Med. (2012) 10:95. 10.1186/1479-5876-10-95 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Rashida Gnanaprakasam JN, Wu R, Wang R. Metabolic reprogramming in modulating T cell reactive oxygen species generation and antioxidant capacity. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:1075. 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01075 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Metzler B, Gfeller P, Guinet E. Restricting glutamine or glutamine-dependent purine and pyrimidine syntheses promotes human T cells with high FOXP3 expression and regulatory properties. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md.: 1950). (2016) 196:3618–30. 10.4049/jimmunol.1501756 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Kono M, Yoshida N, Maeda K, Suárez-Fueyo A, Kyttaris VC, Tsokos GC. Glutaminase 1 inhibition reduces glycolysis and ameliorates lupus-like disease in MRL/lpr mice and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Arthritis Rheumatol (Hoboken, NJ). (2019) 71:1869–78. 10.1002/art.41019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Johnson MO, Wolf MM, Madden MZ, Andrejeva G, Sugiura A, Contreras DC, et al. Distinct regulation of Th17 and Th1 cell differentiation by glutaminase-dependent metabolism. Cell. (2018) 175:1780–95.e19. 10.1016/j.cell.2018.10.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Takahashi S, Saegusa J, Sendo S, Okano T, Akashi K, Irino Y, et al. Glutaminase 1 plays a key role in the cell growth of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2017) 19:76. 10.1186/s13075-017-1283-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Mak TW, Grusdat M, Duncan GS, Dostert C, Nonnenmacher Y, Cox M, et al. Glutathione primes T cell metabolism for inflammation. Immunity. (2017) 46:675–89. 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.03.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Shao L, Fujii H, Colmegna I, Oishi H, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM. Deficiency of the DNA repair enzyme ATM in rheumatoid arthritis. J Exp Med. (2009) 206:1435–49. 10.1084/jem.20082251 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Weyand CM, Fujii H, Shao L, Goronzy JJ. Rejuvenating the immune system in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2009) 5:583–8. 10.1038/nrrheum.2009.180 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Li Y, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM. DNA damage, metabolism and aging in pro-inflammatory T cells: rheumatoid arthritis as a model system. Exp Gerontol. (2018) 105:118–27. 10.1016/j.exger.2017.10.027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Shen Y, Wen Z, Li Y, Matteson EL, Hong J, Goronzy JJ, et al. Metabolic control of the scaffold protein TKS5 in tissue-invasive, proinflammatory T cells. Nat Immunol. (2017) 18:1025–34. 10.1038/ni.3808 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Fearon U, Canavan M, Biniecka M, Veale DJ. Hypoxia, mitochondrial dysfunction and synovial invasiveness in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2016) 12:385–97. 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.69 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Haas R, Smith J, Rocher-Ros V, Nadkarni S, Montero-Melendez T, D'Acquisto F, et al. Lactate regulates metabolic and pro-inflammatory circuits in control of T cell migration and effector functions. PLoS Biol. (2015) 13:e1002202. 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002202 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Pucino V, Bombardieri M, Pitzalis C, Mauro C. Lactate at the crossroads of metabolism, inflammation, and autoimmunity. Eur J Immunol. (2017) 47:14–21. 10.1002/eji.201646477 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Ivashkiv LB The hypoxia-lactate axis tempers inflammation . Nat Rev Immunol. (2020) 20:85–6. 10.1038/s41577-019-0259-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Zhang D, Tang Z, Huang H, Zhou G, Cui C, Weng Y, et al. Metabolic regulation of gene expression by histone lactylation. Nature. (2019) 574:575–80. 10.1038/s41586-019-1678-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Devaraj S, Jialal I. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein and atherosclerosis. Int J Clin Lab Res. (1996) 26:178–84. 10.1007/BF02592979 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Batooei M, Tahamoli-Roudsari A, Basiri Z, Yasrebifar F, Shahdoust M, Eshraghi A, et al. Evaluating the effect of oral N-acetylcysteine as an adjuvant treatment on clinical outcomes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, double blind clinical trial. Rev Recent Clin Trials. (2018) 13:132–8. 10.2174/1574887113666180307151937 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.León Fernández OS Viebahn-Haensler R Cabreja GL Espinosa IS Matos YH Roche LD . Medical ozone increases methotrexate clinical response and improves cellular redox balance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Pharmacol. (2016) 789:313–8. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.07.031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Abdollahzad H, Aghdashi MA, Asghari Jafarabadi M, Alipour B. Effects of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6) and oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Med Res. (2015) 46:527–33. 10.1016/j.arcmed.2015.08.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Niki E Oxidant-specific biomarkers of oxidative stress . Association with atherosclerosis and implication for antioxidant effects. Free Radic Biol Med. (2018) 120:425–40. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.04.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Sun T, Jiang D, Rosenkrans ZT, Ehlerding EB, Ni D, Qi C, et al. A melanin-based natural antioxidant defense nanosystem for theranostic application in acute kidney injury. Adv Funct Mater. (2019) 29:1904833. 10.1002/adfm.201904833 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Bao Q, Hu P, Xu Y, Cheng T, Wei C, Pan L, et al. Simultaneous blood-brain barrier crossing and protection for stroke treatment based on edaravone-loaded ceria nanoparticles. ACS Nano. (2018) 12:6794–805. 10.1021/acsnano.8b01994 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Aviello G, Knaus UG. NADPH oxidases and ROS signaling in the gastrointestinal tract. Mucosal Immunol. (2018) 11:1011–23. 10.1038/s41385-018-0021-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Nóbrega-Pereira S, Fernandez-Marcos PJ, Brioche T, Gomez-Cabrera MC, Salvador-Pascual A, Flores JM, et al. G6PD protects from oxidative damage and improves healthspan in mice. Nat Commun. (2016) 7:10894. 10.1038/ncomms10894 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Batinic-Haberle I, Tome ME. Thiol regulation by Mn porphyrins, commonly known as SOD mimics. Redox Biol. (2019) 25:101139. 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Carter CS, Huang SC, Searby CC, Cassaidy B, Miller MJ, Grzesik WJ, et al. Exposure to static magnetic and electric fields treats type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab. (2020) 32:1076. 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.11.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Ristow M, Schmeisser K. Mitohormesis: promoting health and lifespan by increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Dose Response. (2014) 12:288–341. 10.2203/dose-response.13-035.Ristow [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Merry TL, Ristow M. Do antioxidant supplements interfere with skeletal muscle adaptation to exercise training? J Physiol. (2016) 594:5135–47. 10.1113/JP270654 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Ristow M, Zarse K. How increased oxidative stress promotes longevity and metabolic health: the concept of mitochondrial hormesis (mitohormesis). Exp Gerontol. (2010) 45:410–8. 10.1016/j.exger.2010.03.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]