Abstract
The current study investigated role of telocytes (TCs) in angiogenesis during embryonic development of quail using immunohistochemistry (IHC), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The angiogenic apparatus consisted of TCs, endothelial cells, and macrophages. TCs were identified morphologically by their telopodes and podoms using TEM and SEM and immunohistochemically using CD34, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). TCs also expressed CD68. TCs formed a three-dimensional network and established direct contact with blood vessels, sprouting endothelial cells, and active macrophages, while exerting their effect through paracrine signaling. VEGF was also expressed by endothelial cells and macrophages. Matrix metalloproteinase–9 (MMP-9) was expressed by TCs, endothelial cells, and macrophages. In conclusion, the expression of VEGF by TCs, endothelial cells, and macrophages is required for the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells and vascular growth. The expression of MMP-9 by TCs, endothelial cells, and macrophages is essential for the degradation of extracellular matrix (ECM) components during neoangiogenesis. Macrophages may facilitate phagocytosis and elimination of the degraded ECM components.
Subject terms: Cell biology, Developmental biology
Introduction
Telocytes (TCs) are a unique type of interstitial cells. They play a critical role during tissue development and hemostasis1. TCs consist of a cell body and telopodes (TPs), which contain focal dilatations and thin podomeres. TPs are the unique features that distinguish TCs by electron microscopy2. The cell body contains mitochondria, small Golgi apparatus, and smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum3,4. Podoms contain endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, caveolae, and secretory vesicles4.
Angiogenesis is a physiological process through which blood vessels grow. During embryogenesis, two mechanisms of angiogenesis occur: sprouting angiogenesis and intussusceptive angiogenesis. The latter occurs during splitting of the blood vessels in current vascular tissue. Sprouting angiogenesis is a well-known type in which endothelial sprouting occurs in response an angiogenic stimulus (vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGF). Sprouting is involved in the angiogenesisof tissues devoid of blood vessels. Endothelial sprouting requires sequential steps, including enzymatic degradation of capillary basement membrane, endothelial cell (EC) proliferation, directed migration of ECs, tubulogenesis, vessel fusion, vessel pruning, and pericyte stabilization5.
The role of TCs angiogenesis is described in many tissues and organs during development and tissue repair6,7. They express VEGF, which facilitates angiogenesis2. The current study aims to investigate the role of TCs in angiogenesis during embryonic development of quail bird using immunohistochemistry (IHC), transmission electron microcopy (TEM), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
Materials and methods
Sample collection
Fertile quail (Coturnix japonica) eggs were used in the current study. The source of the eggs was the Farm of Department of Histology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, South Valley University, Qena, Egypt. The egg incubation protocol was carried out according to Soliman8. Eggs were incubated at 37.5 °C at a relative humidity 65%. Quail embryos were collected from days 5 and 8 (five for each day). The eggs were kept at − 20 °C for 4 h and were opened from the wide end, with embryos carefully excised from the egg shells. The embryos were placed on a Petri dish and fixed after washing with saline 0.9% NaCl. Sample collection was conducting in accordance with the guidelines of the Institutional Ethical Committee of Veterinary Medicine, South Valley University, Egypt, and following the Egyptian animal laws.
Preparation of paraffin sections
Preparation of paraffin sections was performed in accidence with9. Embryos were fixed in Bouin’s fixative (Table 1) for 24 h10. Samples were dehydrated by ascending grades of alcohol, cleared by methyl benzoate (Table 1), impregnated, and embedded in paraffin wax (Table 1). Paraffin sections were cut using a Richert Leica RM 2125 microtome (Germany). Paraffin sections were cut at the neck region and stained by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)11. The stained sections were examined using a Leitz Dialux 20 microscope. Photos were taken using a Canon digital camera (Canon Powershot A95).
Table 1.
The processing time of the samples in paraffin embedding techniques.
| Age process | 5d | 8d |
|---|---|---|
| 1-Fixation | ||
| 1-F A-NBF | 8 h | 13 h |
| B_Bouin’s solution | 1/2 h | 1/2 h |
| 2-dehydration | ||
| Alcohol70%I | 2 h | 2 h |
| Alcohol 70%II | 2 d | 2d |
| Alchol70%III | ||
| Alchol80% | 1 h | 2 h |
| Alchol90% | 1 h | 2 h |
| Alchol100% | 1/2 h | 1/2 h |
| Alchol100% | 1/2 h | 1/2 h |
| 3-clearing with methylebenzot | ||
| MB I | 1 h | 1 h |
| MB II | 12 h | 12 h |
| MB III | 12 h | 12 h |
| 4-embedding in paraffin | ||
| P I | 2 h | 2 h |
| P II | 2 h | 2 h |
| PIII | 4 h | 4 h |
NBF neutral buffer formalin, h hours, d days, MB I methyl bonzoate1, MB II methyl benzoate II, P I paraffin I, P II paraffin II, P III paraffin III.
IHC
IHC staining using (CD34), CD68, and matrix metalloproteinase–9 (MMP-9)
Samples were fixed in Neutral buffered formalin NBF (Table 1). The detection of antigen localization was carried out using a combination of the avidin–biotin complex technique12 and the solution of the Ultra Vision Detection System (antipolyvalent, horseradish peroxidase [HRP]/3,3′-diaminobenzidine [DAB] manufactured by Thermo Fisher Scientific TP-015HD). Procedures were performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions13–15. The Richert Leica RM 2125 microtome was used to cut 5-µm paraffin sections. The sections were dewaxed by xylene, hydrated by ascending grades of alcohol, and washed by phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; pH 7.4) (Table 2) three times for 5 min. Hydrogen peroxide was applied to the sections at room temperature to bock endogenous peroxidase activity. The sections were washed by running tap water for 10 min. A 10-mm sodium citrate buffer (pH 6.0; Table 2) was used at 95–98 °C in a water bath for 20 min for antigen retrieval. Subsequently, the slides were cooled for 20 min at room temperature and washed by PBS (pH 7.4) three times for 5 min. To prevent nonspecific background staining, Ultra V block was used at room temperature and applied for only 5 min and not more than 10 min to avoid artifact. The primary antibody (Table 3) was applied on the sections overnight at 4 °C. The sections were rinsed using PBS (pH 7.4) three times for 5 min. The biotinylated secondary antibody (goat antipolyvalent, anti-mouse immunoglobulin G [IgG] + antirabbit IgG; Thermo Fisher Scientific, UK; Lab Vision Corporation; Table 3) was applied on sections at room temperature for 10 min. The sections were rinsed by PBS (pH 7.4) three times for 5 min and incubated using streptavidin–peroxidase complex (Thermo Fisher Scientific, UK; Lab Vision Corporation, USA) for 10 min at room temperature. Visualization of the bound antibodies was performed by incubation in a humid chamber at room temperature for 5 min using a mixture of one drop of DAB and chromogen to 2 mL of DAB plus substrate. The sections were stained by a counterstain, Harris hematoxylin, for 30 s and dehydrated using ethanol and isopropanol I and II, cleared in xylene, and covered by dibutylphthalate polystyrene xylene (DPX). Immunohistochemical staining was analyzed using a Leitz Dialux 20 microscope with the Canon Power Shot A95 digital camera.
Table 2.
Components of the fixative.
| Fixative | Components | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Karnovsky Fixative | Paraformaldehyde, 25% freshly prepared | 10 ml |
| Glutaraldehyde 50% | 10 ml | |
| Na-Phosphate buffer (0.1 M, pH 7.4) | 50 ml | |
| Distilled water | 30 ml | |
| Na-Phosphate buffer (0.1 M, pH 7.4) | Solution A | |
| Na2HPO4 2H2O | 17.02 gm | |
| Distilled water | 600 ml | |
| Solution B | ||
| NaH2PO4 H2 | 6 gm | |
| Distilled water | 200 ml | |
| Using solution | ||
| Solution A | 580 ml | |
| Solution B | 219 ml | |
| Citrate-buffer (pH 6.0) | Solution A | |
| Citrate C6H8O7 H2O | 21 g | |
| Distilled water | 1 L | |
| Solution B | ||
| Sodium citrate Na3C6H5O7 2H2O | 29.41 g | |
| Distilled water | 1 L | |
| Using solution | ||
| Solution A | 9 ml | |
| Solution B | 41 ml | |
| Distilled water | Add 500 ml |
Table 3.
Identity, sources, and working dilution of antibodies used in immunohistochemical studies.
| Target | Primary antibody supplier | Origin (catalog no) | Dilution | incubation | Antigen retrieval | secondary antibody-incubation time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD34 |
MOUSE ANTI CHICKEN CD34 (Bio rad) |
MOUSE ANTI CHICKEN CD34 Monoclonal Antibody (Clone: AV138) (Cat.no MBS224490) |
1:100 | Over night |
boiling in citrate buffer (pH 6.0), 20 min Goat |
Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H + L) Secondary Antibody Catalog # 31,569 Dilution ; 1:100 One hour at room temperature |
| VEGF | Rabbit anti -VEGF (Invitrogen by Thermo Fisher Scientific Waltham, MA, USA)) |
Rabbit VEGF Polyclonal Antibody (clone: RB-222-P0) (Cat.no PA1-21,796) |
1:100 | Overnight | boiling in citrate buffer (pH 6.0), 20 min |
Goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody (cat. no. K4003, EN Vision System Horseradish Peroxidase Labelled Polymer; Dako) Ready to use 30 min at room temperature |
| CD68 (Macrophage Marker) Ab-3 (Clone KP1) |
Mouse Anti-CD68 Thermo Fisher Scientific Lab Vision Corporation, Fremont, USA |
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Cat. #MS-397-R7 |
1:100 | Overnight | boiling in citrate buffer (pH 6.0), 20 min | |
| MMP9 / Gelatinase B |
Rabbit anti-MMP9 LifeSpan BioSciences |
Rabbit Polyclonal antibody Catalog # LS-C31757 |
1:100 | Overnight | boiling in citrate buffer (pH 6.0), 20 min |
Antibodies used that showed reactivity in Avian species.
Immunohistochemical procedures of VEGF
Two-step immunohistochemical staining procedures using the DAKO EN Vision System and HRP peroxidase were applied16, Paraffin sections 5-µm thick were cut using the Richert Leica RM 2125 microtome. The sections were dewaxed, rehydrated, and washed by PBS (pH 7.4) three times for 5 min. Blocking of the endogenous peroxidase was carried out using drops of 3% hydrogen peroxide in methanol for 20 min at room temperature. The section was thoroughly rinsed using running tap water for 10 min. Antigen retrieval was performed by applying 10-mm sodium citrate buffer (pH 6.0; Table 2). The sodium citrate buffer was heated in a water bath for 20 min to 95–98 °C followed by cooling for 20 min at room temperature. Sections were rinsed for 5 min by PBS (pH 7.4) three times. Blocking nonspecific background staining was carried out using drops of blocking serum (DAKO) to cover the sections for 5 min at room temperature. The primary antibody was incubated with the sections. The antibodies were successfully used in avian species17. Table 3 lists the identity, sources, and the working dilutions of the antibodies used in the immunohistochemical technique. The slides were washed in by PBS (pH 7.4) three times for 5 min and incubated with secondary antibody at room temperature for 30 min. The slides were washed again with PBS (pH 7.4) three times for 5 min and incubated for 5–10 min at room temperature with DAB and substrate chromogen, which revealed a brown color at the antigen site. The counterstain, Harris hematoxylin, was applied for 30 s. The sections were dehydrated by ethanol alcohol 90% and 100% II, cleared in xylene, and covered using DPX. Immunohistochemical stained sections were examined using the Leitz Dialux20 microscope provided with the Canon PowerShot A95 digital camera.
Negative controls were performed using the same procedures, except using the primary antibodies.
Preparations of resin embedding samples18
Resin-embedding technique was performed using Karnovsky’s fixative19. The fixative was prepared as follows: 10 mL of 25% paraformaldehyde, 10 mL of 50% glutaraldehyde, 50 mL phosphate buffer, and 30 mL distilled water. Five samples were used for each age (i.e., days 5 and 8 of incubation). The neck skin was carefully excised and trimmed to a small-sized length of 2.0 to 3.0 mm. Karnovsky fixative (Table 2) was used at 4 °C overnight. The samples underwent postfixation by osmium tetroxide, dehydration, impregnation in a mixture of alcohol/resin and pure resin, resin embedding, and crystallization in an oven at 60 °C. Semithin sections were taken at 1 μm using an ultramicrotome Ultracut E (Reichert-Leica, Germany) and stained with toluidine blue20,21 and Periodic acid–Schiff (PAS)22. Staining of semithin sections was performed after dissolving the resin using a saturated alcoholic solution of sodium hydroxide. The stained sections were examined by a Leitz Dialux 20 microscope and a Canon digital camera (Canon PowerShot A95).
TEM
Ultra-thin sections (60 nm) of resin-embedded samples at embryonic days 5 and 8 were cut using the Reichert ultra-microtome. The sections were stained using uranyl acetate followed by lead citrate for 15 min for each stain. The stained grids were examined using a JEOL100CX II transmission electron microscope at the central laboratory of South Valley University, Egypt.
SEM
The samples were fixed in Karnovsky’s fixative and washed. Sample washing was performed using the Na–phosphate buffer (pH 7.3) for four times at 15 min. Samples were postfixed in 1% osmic acid in 0.1 M Na–phosphate buffer for an additional 2 h at room temperature and washed in Na–phosphate buffer. The samples were dehydrated by ascending grades of alcohol (50%, 70%, and 90%) for 30 min at each concentration and 100% for 2 days with many changes. Samples were treated with isoamyl acetate for 2 days and dried using the critical-point drying method with the Critical Point Drying Procedure Polaron E3000 CPD apparatus (Germany). Sample coating with gold was performed using the JEOL 1100 E-ion sputtering device (Japan) and examined with a JEOL SEM (JSM 5500 LV) at 10 kV, at the central laboratory of South Valley University, Egypt.
Coloring of TEM and SEM images
To distinguish different types of cells and structures, coloring of TEM and SEM images was performed using the Photo Filter 6.3.2 program. The black and white image was colored using adjust then color balance to change the color to a desirable colors and degrees. Coloring transfer was performed by the stamp tool located at the right panel. Changing color was performed again using adjust then color balance to color another cell or structure. The methods used were previously described by many authors2,4,23–31.
Ethical approval
The National Ethics Committee of South Valley University and veterinary authorities in South Valley University Province, Egypt, approved the method of this study. ‘All procedures were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations32. Arrival guidelines the study was carried out in compliance with the ARRIVE guidelines33.
Results
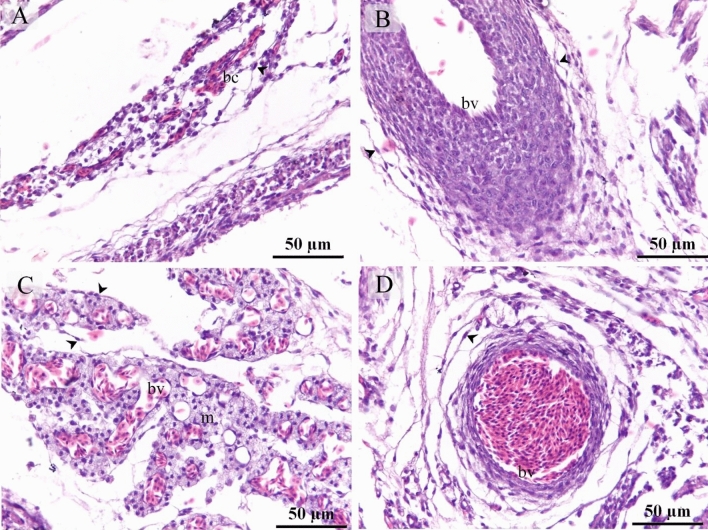
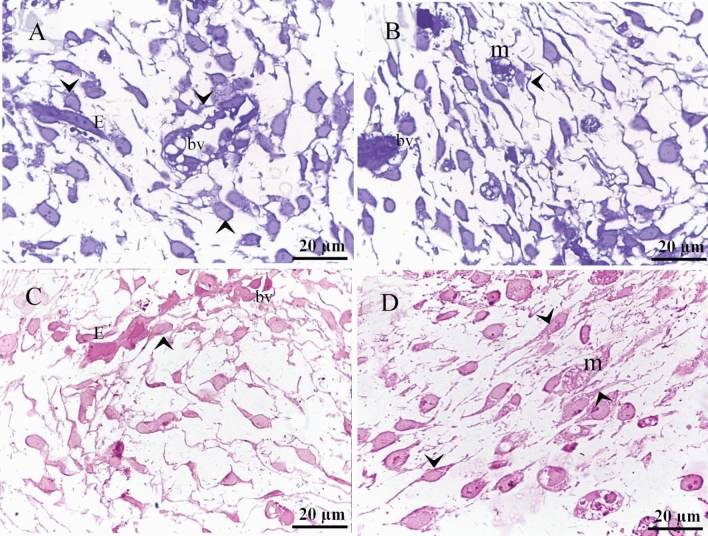
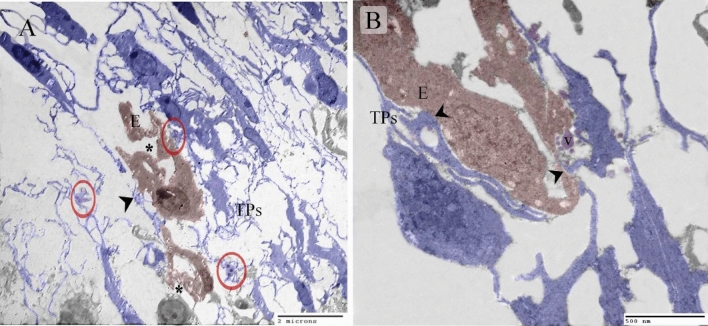
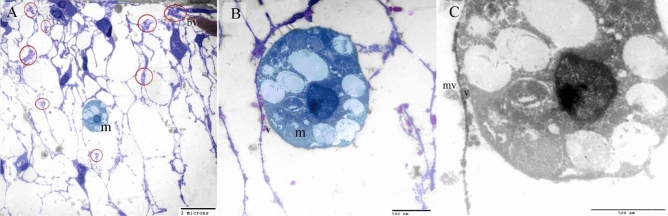
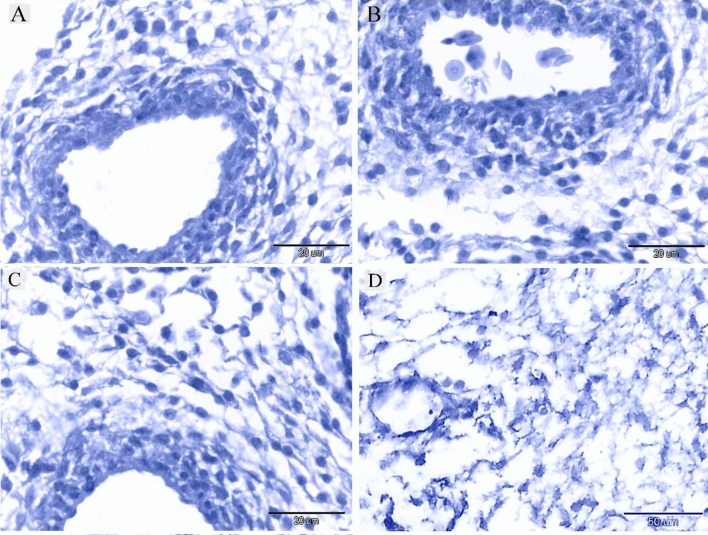
TCs were recognized around blood capillaries (Fig. 1A), large vessels (Fig. 1B), the vascular plexus (Fig. 1C) and small vessels (Fig. 1D). Perivascular TCs were also identified using semithin sections stained by toluidine blue (Fig. 2A,B) and PAS (Fig. 2C,D). They were also located in contact with sprouting ECs (Fig. 2A,C) and active macrophages (Fig. 2B,C). By TEM, TCs were identified by TPs that had distinguished podoms. TCs formed an extensive three-dimensional (3D) network (Fig. 3A). The established contact with the sprouting ECs occurred post constriction (Fig. 3A) as well as blood vessels (Fig. 3B). They released numerous secretory vesicles (Fig. 3B). TCs formed physical contact with active macrophages that had phagosomes containing materials of different stages of digestion and lipid inclusions (Fig. 4A–C). CD34 + ve TCs associated with the macrophages (Fig. 5A) and blood vessels (Fig. 5B). CD34 + ve TCs were also located around the sprouting endothelial cells (Fig. 5B). VEGF + ve TCs located around the macrophages (Fig. 6A) and the blood vessels (Fig. 6B). MMP-9 + ve TCs were detected closed to the blood vessel and macrophages and (Fig. 7A, B). TCs expressed MMP-9 (Fig. 7A,B). TCs expressed markers specific for monocyte-macrophage marker CD68 (Fig. 8A–F).
Figure 1.
Recognition of perivascular TCs. Paraffin sections of the neck skin of day 8 quail embryos stained by H&E. (A) TC (arrowhead) was located around the blood capillary (bc). (B,D): TCs (arrowheads) were located around the blood vessels (bv). (C): TCs (arrowheads) were closely related to the vascular plexus. Note that the macrophage (m) had a vacuolated cytoplasm.
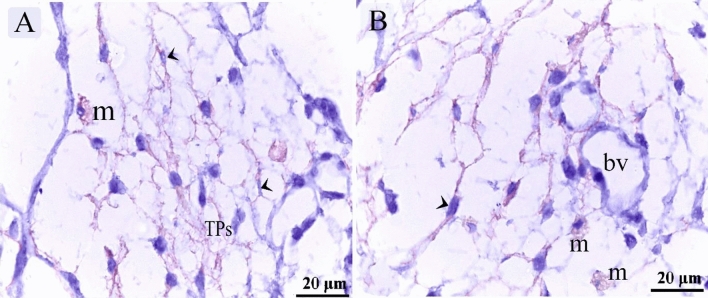
Figure 2.
Recognition of perivascular TCs using semithin sections. Semithin sections of the neck skin of day 5 quail embryos stained by toluidine blue (A,B) and PAS (C,D). (A,C) TCs (arrowheads) located around sprouting endothelial cells (E) and blood vessel (bv). (B,D) TCs (arrowheads) located around active macrophages (m), which exhibited vesicular cytoplasm. Note the blood vessel (bv).
Figure 3.
Identification of TCs using TEM. Ultrathin sections of the neck skin of day 5 quail embryos. (A) TCs (blue colored) identified by TPs and podoms (red circles). TCs formed an extensive 3D network. Note the sprouting endothelial cells (brown colored) that occurred after constriction (asterisk). TCs established contact with the endothelial cells (arrowhead). (B) TCs (blue colored) established contact with the endothelial cells (arrowhead). Note the secretory vesicles (v).
Figure 4.
Identification of TCs using TEM. Ultrathin sections of the neck skin of day 8 quail embryos. (A,B) TCs (blue colored) identified by TPs and podoms (red circles). TCs formed an extensive 3D network. Note the TPs connected to the macrophage (m) and secretory vesicles (v). (C): physical contact was observed between TPs and macrophage (arrows) that had phagosomes (p) contained materials of different stages of digestion and lipid inclusions (l). Note secretory vesicles (v) and multivesicular body (mv).
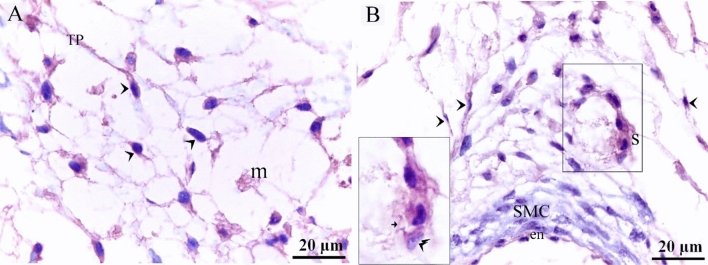
Figure 5.
Immunohistochemical staining of the neck skin of quail embryos at day 8 using CD34. (A) CD34 + ve TCs (arrowheads) located around the macrophages (m). (B) CD34 + ve TCs (arrowheads) located around the blood vessel that consisted of endothelial cell (en) and smooth muscle cell (SMC). CD34 + ve TCs (double arrowheads) were also located around the sprouting endothelial cells (s).
Figure 6.
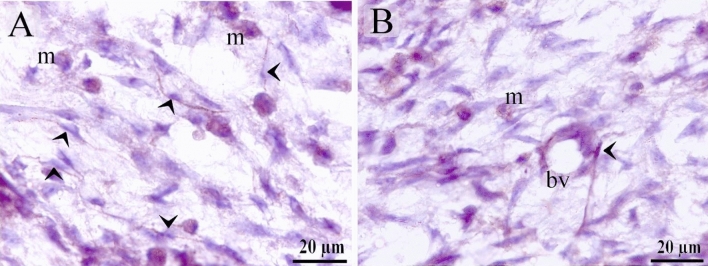
Immunohistochemical staining of the neck skin of quail embryos at day 8 using VEGF. (A) VEGF + ve TCs (arrowheads) located around the macrophages (m). (B) VEGF + ve perivascular TCs (arrowheads). Note the blood vessels (bv).
Figure 7.
Immunohistochemical staining of the neck skin of quail embryos at day 8 using MMP-9. (A,B) TCs (arrowheads) expressed MMP-9. Note macrophages (m) and blood vessel (bv).
Figure 8.
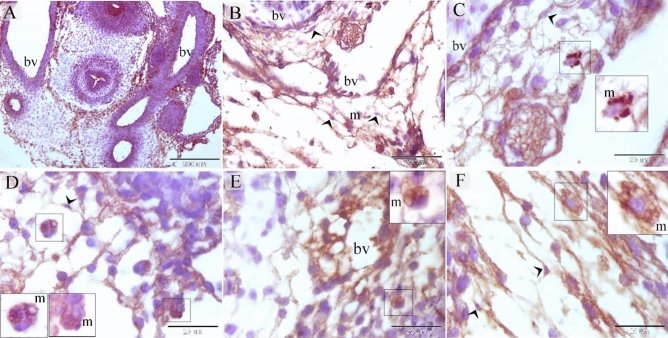
Immunohistochemical staining of the neck skin at day 5 and day 8 using CD68. (A) general view of the neck region at day 5 showing blood vessels (bv). (B,C,D) Vascular area of the neck skin of quail embryos at day 8. Note CD68 + ve macrophage (m), CD68 + ve TCs (arrowheads), blood vessel (bv). (E,F) Vascular area of the neck skin of quail embryos at day 5. CD68 + ve macrophage (m), CD68 + ve TCs (arrowheads), blood vessel (bv).
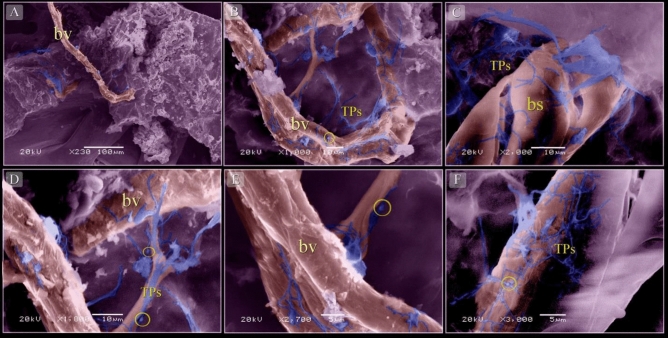
By SEM, TCs were distinguished by TPs that formed a 3D network around blood vessels (Fig. 9A,B,D–F) and blood sinusoids (Fig. 9C). Negative control was performed for CD34 (Fig. 10A), VEGF (Fig. 10B), MMP-9 (Fig. 10C), CD68 (Fig. 10D).
Figure 9.
Scanned samples of the neck skin of quail embryos at day 8. (A,B,D–F) TCs (blue colored) surrounded the blood vessels (bv). Note that the TPs formed a 3D network, podoms (yellow circles). (C) TCs (blue colored) surrounded the blood sinusoids (bs).
Figure 10.
Negative control of IHC. (A) Negative control for CD34. (B) Negative control for VEGF. (C): Negative control for MMP-9. (D): negative control of the CD68.
Discussion
The current study investigated the role of TCs during the early stages of angiogenesis in embryonic quail. Using TEM, SEM, and IHC, typical TCs were identified forming a 3D network in the neck skin. TCs had strong immunoaffinity for CD34 CD34 is a member protein of the transmembrane sialomucin protein family and is used for the identification of hematopoietic stem cells and non-hematopoietic progenitors, including vascular endothelial progenitors and embryonic fibroblasts, multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells, interstitial dendritic cells, and epithelial progenitors. Functional implications of CD34 are linked to cell adhesion34, proliferation, and inhibition of differentiation of stem or progenitor cells35.
Perivascular TCs formed a heterocontact with the blood vessels and release of secretory vesicles for paracrine singling. TCs established contact with sprouting ECs, which indicated neovascularization. They also expressed VEGF, which is essential for the development and growth of the circulatory system and for the regulation of proliferation and migration of vascular ECs36. The findings of the current study suggest the role of TCs in angiogenesis, which is supported by previous studies. They secrete VEGF and endothelial growth factor, which regulate angiogenesis and the proliferation of ECs6. The angiogenic role of TCs is also noted during myocardial infarction. TCs produce angiogenic microRNAs, such as let‐7e, 10a, 21, 27b, 100, 126‐3p, 130a, 143, 155, and 50337.
TCs communicated through direct contact and paracrine signaling with active macrophages. Avian macrophage identified by their rounded profile and contained large phagosomes with materials of different stages of digestion38. The relation between TCs and macrophages may reveal that TCs involved in the phagocytic activities via indirect pathway. The effect of TCs on the activation of macrophages has been studied using an in vitro coculture of peritoneal macrophages (pMACs). The authors showed that communication between pMACs and TCs occurs through heterocellular junctions and the paracrine mode, and they suggest that activation of pMACs occurs via the mitochondrial signaling pathway39.
MMP, or matrixins, are a type of endopeptidases. They are specialized to degrade the extracellular matrix components and other proteins and contribute to tissue remodeling40. Based on the biochemical properties, MMP subtypes are categorized as collagenases, gelatinases, stromelysins, and membrane-type MMPs (MT-MMPs)41. Gelatinases are gelatinase A (MMP-2) and gelatinase B (MMP-9)42. MMP-9 plays a critical role in angiogenesis, immune cell migration, activation of cytokines and chemokines, and progression and metastasis of cancer cells43–45. MMP-9 degrades collagen types IV, V, XIk´, XIVl´, elastin, aggrecan, link protein, decorinr, lamininn, entactin, SPARCq, myelin basic proteinm, ∞2Mn, ∞1Pli, IL-1βj, and proTNF-∞k46,47. In the current study, TCs exhibited proteolytic activities that had a strong immunoaffinity for MMP-9. MMP-9 plays an essential role in the steps of angiogenesis and degrades the basement membrane of capillaries. MMP-9 also promotes EC migration43. Vascular pruning requires post hypoxia activation of MMP-948. CD68 is a sialomucin belongs to class D scavenger receptor. CD68 protein is common in late endosomes and lysosomes. Thus, CD68 protein is found in the granules of macrophages, and other cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system such as Kupffer in the liver, microglial cells in the brain, Hofbauer cell in the placenta, osteoclast in bone49. CD68 is also expressed by other immune cells including dendritic cells, neutrophils, basophils, and mast cells, activated T-cells and some proportion of mature B-cells as well as epithelium of renal tubules50. Increased CD68 expression in macrophage is associated with high vascularity51. In the current study, TCs expressed CD68 as well as macrophages. Stromal cells/telocytes express CD68 in the human adult trigeminal ganglion52. Cd68 is one of the complement Receptors that expressed by antigen presenting cells. Complement Receptors are implicated in in cell migration and phagocytosis and immune regulation. Complement regulatory proteins that expressed by antigen presenting cells have an essential role in limiting cell activation. Complement receptors cooperate with different receptors to regulate myeloid cell responses53.
In the current study, TCs formed 3D network at the site of neovascularization. Nehls and his colleagues noticed that the initial endothelial sprouting may not depend on pericyte. Despite of pericyte is one of the initiative types of cells that invade the nascent vascular tissue and distribute at the tip of the growing endothelial sprouts54. Pericyte has an essential role during angiogenesis. Development of the endothelial tube is associated with pericytes, that the endothelial sprouting act as a migration sign. pericytes are derived from the differentiation of resident mesenchymal precursors or migration from the adventitia of the adjacent vessel55. This process is known as pericyte-driven angiogenic process in which endothelial cells are preceded and guided by migrating pericytes56. pericytes may inhibit endothelial growth and migration57,58. Previous studies revealed a remarkable correlation between pericyte contribution and microvessel stabilization59,60. pericyte investment is linked to maintenance of capillary integrity in vivo61.Formation of vascular basal lamina and investment of the pericytes occurs at the end of the proliferative stage and the onset of the mature or quiescent stage of capillary activity62. endothelial cell-pericyte interactions stimulate upregulation of basal lamina-encoding genes and proteins, including fibronectin laminin, and integrins63. On the other hand, pericytes invasion may establish tubes and enhance the subsequent penetration of endothelial cells64. NG2 expressing pericyte progenitors located in close proximity to blood vessels located closed to blood vessels65. Thus, the reciprocal interaction between endothelial cells and pericytes has a fundamental role in angiogenic process.
In conclusion, TCs facilitate angiogenesis. They express VEGF, which promotes endothelial proliferation and migration. They also release MMP-9, which plays a critical role in the degradation of the capillary basement membrane, EC migration, and vascular pruning.
Supplementary Information
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank EKB editing service for thorough English editing that greatly improved the manuscript.
Author contributions
The work was performed by Soha A. Soliman. The author designed the research study, analysed and interpreted the data, arranged the images and wrote the paper. The author has read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are available on the author.
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41598-021-85166-w.
References
- 1.Chaitow L. Telocytes: Connective tissue repair and communication cells. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2017;21(2):231–233. doi: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2017.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Abd-Elhafeez HH, Abou-Elhamd AS, Soliman SA. Morphological and immunohistochemical phenotype of TCs in the intestinal bulb of Grass carp and their potential role in intestinal immunity. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:14039. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70032-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Yang P, Liu Y, Ahmed N, Ullah S, Chen Q. Ultrastructural identification of telocytes in the muscularis of chicken ileum. Exp. Therap. Med. 2015;10(6):2325–2330. doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Abdel-Maksoud FM, Abd-Elhafeez HH, Soliman SA. Morphological changes of telocytes in camel efferent ductules in response to seasonal variations during the reproductive cycle. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:4507. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41143-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Adair, T. H. & Montani, J. P. in Chapter 1, Overview of Angiogenesis (2010).
- 6.Zheng Y, et al. Human lung telocytes could promote the proliferation and angiogenesis of human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells in vitro. Mol. Cell. Therap. 2014;2:3. doi: 10.1186/2052-8426-2-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kucybała I, et al. A comprehensive guide to telocytes and their great potential in cardiovascular system. Bratisl. Lek. Listy. 2017;118:302–309. doi: 10.4149/bll_2017_059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Soliman, A. S. Potential role of telocytes in differentiation of embryonic skeletal progenitor cells. SF J Stem Cell.1 (2017).
- 9.Soliman SA. Organization and pattering of mesenchymal cells in quail embryonic cartilage. SF J Stem Cell. 2018;1:1. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Suvarna K, Layton C, Bancroft J. Bancroft’s Theory and Practice of Histological. Techniques. Churchill Livingstone: Elsevier; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Harris H. On the rapid conversion of haematoxylin into haematein in staining reactions. J. Appl. Microsc. Lab. Methods. 1900;3:777. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1981;29:577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Abd-Elhafeez HH, Abou-Elhamd AS, Soliman SA. Morphological and immunohistochemical phenotype of TCs in the intestinal bulb of Grass carp and their potential role in intestinal immunity. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:14039. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70032-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mustafa FE-Z, Elhanbaly R. Distribution of estrogen receptor in the rabbit cervix during pregnancy with special reference to stromal elements: an immunohistochemical study 10. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:13655. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70323-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Abd-Elkareem M, Abou-Elhamd A. Immunohistochemical localization of progesterone receptors alpha (PRA) in ovary of the pseudopregnant rabbit. Anim. Reprod. 2019;16:302–310. doi: 10.21451/1984-3143-AR2018-0128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kämmerer UKM, et al. A new rapid immunohistochemical staining technique using the EnVision antibody complex. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2001;49:623–630. doi: 10.1177/002215540104900509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chen Q, et al. Sexual differences in cell proliferation in the ventricular zone, cell migration and differentiation in the HVC of juvenile Bengalese finch. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e97403. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Spurr AR. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1969;26:31–43. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Karnovsky MJ. A formaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative of high osmolarity for use in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 1965;27:137A–138A. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Soliman SA, Ahmed YA, Abdelsabour-Khalaf M. Histogenesis of the stomach of the pre-hatching quail: a light microscopic study. Anat. Sci. Int. 2016;91:407–418. doi: 10.1007/s12565-015-0318-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Soliman S, Emeish W. Morphological Alternations of Intraepithelial and Stromal Telocytes in Response to Salinity Challenges. bioRxiv. 2017 doi: 10.1101/115881. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Soliman SA. Morphological and histochemical description of quail feather development. Anatom. Rec. 2019 doi: 10.1002/ar.24276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Fatma El-Zahraa AM, Abd-Elhafez EA. A histological histochemical and ultrastructural characterization of uterine vessels at early stages of pregnancy. J. Histol. Histopathol. Res. 2018;2:41–47. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Soliman S. Potential role of telocytes in differentiation of embryonic skeletal progenitor cells. SF J. Stem Cell. 2017;1:1. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Soliman SA. A comparative analysis of the organization of the sensory units in the beak of duck and quail. Histol. Cytol. Embryol. 2017 doi: 10.15761/HCE.1000122. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Soliman SA. Telocytes during organogenesis: Relations to nephrogenic cords in mesonephros of quail embryos. Histol. Cytol. Embryol. 2017;1:1–6. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Abd-Elhafeez HH, Abou-Elhamd AS, Abdo W, Soliman SA. Migratory activities and stemness properties of rodlet cells. Microsc. Microanal. 2020;21:1–18. doi: 10.1017/S1431927620001828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mustafa FEZA, El-Desoky SM. Architecture and cellular composition of the spleen in the Japanese Quail (Coturnix japonica) Microsc. Microanal. 2020;12:1–10. doi: 10.1017/S143192762000152X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Fatma El-Zahraa AM, Abd-Elhafez EA. A histological, histochemical and ultrastructural characterization of uterine vessels at early stages of pregnancy. J. Histol. Histopathol. Res. 2018;2:41–47. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yousef MS, Abd-Elhafeez HH, Talukder AK, Miyamoto A. Ovulatory follicular fluid induces sperm phagocytosis by neutrophils, but oviductal fluid around oestrus suppresses its inflammatory effect in the buffalo oviduct in vitro. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2019;86:835–846. doi: 10.1002/mrd.23164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Abdel-Hakeem SS, Mahmoud GA, Abdel-Hafeez HH. Evaluation and microanalysis of parasitic and bacterial agents of Egyptian fresh Sushi, Salmo salar. Microsc .Microanal. 2019;25:1498–1508. doi: 10.1017/S143192761901506X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Matar A, Silverman H. Perspectives of Egyptian research ethics committees regarding their effective functioning. J. Empir. Res. Hum. Res. Ethics. 2013;8:32–44. doi: 10.1525/jer.2013.8.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Percie du Sert N, et al. Reporting animal research: Explanation and elaboration for the ARRIVE guidelines 2.0. PLOS Biol. 2020;18:e3000411. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sidney LE, Branch MJ, Dunphy SE, Dua HS, Hopkinson A. Concise review: evidence for CD34 as a common marker for diverse progenitors. Stem Cells. 2014;32:1380–1389. doi: 10.1002/stem.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Nielsen JS, McNagny KM. Novel functions of the CD34 family. J. Cell Sci. 2008;121:3683–3692. doi: 10.1242/jcs.037507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Duffy, A. M., Bouchier-Hayes, D. J. & Harmey, J. H. (2000–2013).
- 37.Manole C, Cismaşiu V, Gherghiceanu M, Popescu L. Experimental acute myocardial infarction: Telocytes involvement in neo-angiogenesis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2011;15:2284–2296. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01449.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Moujahid A, Navascués J, Marín-Teva JL, Cuadros MA. Macrophages during avian optic nerve development: Relationship to cell death and differentiation into microglia. Anat. Embryol. 1996;193:131–144. doi: 10.1007/bf00214704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Jiang X-J, Cretoiu D, Shen Z-J, Yang X-J. An in vitro investigation of telocytes-educated macrophages: Morphology, heterocellular junctions, apoptosis and invasion analysis. J. Transl. Med. 2018;16:85. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1457-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Nagase H, Visse R, Murphy G. Structure and function of matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006;69:562–573. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Jabłońska-Trypuć A, Matejczyk M, Rosochacki S. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), the main extracellular matrix (ECM) enzymes in collagen degradation, as a target for anticancer drugs. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016;31:177–183. doi: 10.3109/14756366.2016.1161620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Toth M, Sohail A, Fridman R. Assessment of gelatinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) by gelatin zymography. Methods Mol. Biol. (Clifton, NJ) 2012;878:121–135. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-854-2_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Quintero-Fabián S, et al. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in angiogenesis and cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019;9:1370–1370. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Deleon-Pennell KY, Altara R, Yabluchanskiy A, Modesti A, Lindsey ML. The circular relationship between matrix metalloproteinase-9 and inflammation following myocardial infarction. IUBMB Life. 2015;67:611–618. doi: 10.1002/iub.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Klein T, Bischoff R. Physiology and pathophysiology of matrix metalloproteases. Amino Acids. 2011;41:271–290. doi: 10.1007/s00726-010-0689-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Laronha H, Caldeira J. Structure and function of human matrix metalloproteinases. Cells. 2020;9:1076. doi: 10.3390/cells9051076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Shiomi T, Lemaître V, D'Armiento J, Okada Y. Matrix metalloproteinases, a disintegrin and metalloproteinases, and a disintegrin and metalloproteinases with thrombospondin motifs in non-neoplastic diseases. Pathol. Int. 2010;60:477–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2010.02547.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Boroujerdi A, Welser-Alves J, Milner R. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 mediates post-hypoxic vascular pruning of cerebral blood vessels by degrading laminin and claudin-5. Angiogenesis. 2015 doi: 10.1007/s10456-015-9464-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Nuovo, G. J. in In Situ Molecular Pathology and Co-Expression Analyses (ed Gerard J. Nuovo) 167–196 (Academic Press, Cambridge, 2013).
- 50.Naeim, F. in Hematopathology (eds Faramarz Naeim, P. Nagesh Rao, & Wayne W. Grody) 27–55 (Academic Press, Cambridge, 2008).
- 51.Yu, X., Guo, C., Fisher, P. B., Subjeck, J. R. & Wang, X.-Y. in Advances in Cancer Research Vol. 128 (eds Xiang-Yang Wang & Paul B. Fisher) 309–364 (Academic Press, Cambridge, 2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 52.Rusu MC, Mănoiu VS, Creţoiu D, Creţoiu SM, Vrapciu AD. Stromal cells/telocytes and endothelial progenitors in the perivascular niches of the trigeminal ganglion. Ann. Anat. Anatomischer Anzeiger. 2018;218:141–155. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2017.12.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Gordon, S. & Plüddemann, A. in Kelley and Firestein's Textbook of Rheumatology (Tenth Edition) (eds Gary S. Firestein et al.) 145–168.e143 (Elsevier, 2017).
- 54.Nehls V, Denzer K, Drenckhahn D. Pericyte involvement in capillary sprouting during angiogenesis in situ. Cell Tissue Res. 1992;270:469–474. doi: 10.1007/bf00645048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Gerhardt H, Betsholtz C, Gerhardt H, Betsholtz C. Endothelial-pericyte interactions in angiogenesis. Cell Tissue Res. 2003;314:15–23. doi: 10.1007/s00441-003-0745-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Virgintino D, et al. An intimate interplay between precocious, migrating pericytes and endothelial cells governs human fetal brain angiogenesis. Angiogenesis. 2007;10:35–45. doi: 10.1007/s10456-006-9061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Orlidge A, D'Amore PA. Inhibition of capillary endothelial cell growth by pericytes and smooth muscle cells. J. Cell Biol. 1987;105:1455–1462. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Sato Y, Rifkin DB. Inhibition of endothelial cell movement by pericytes and smooth muscle cells: Activation of a latent transforming growth factor-beta 1-like molecule by plasmin during co-culture. J. Cell Biol. 1989;109:309–315. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.von Tell D, Armulik A, Betsholtz C. Pericytes and vascular stability. Exp. Cell Res. 2006;312:623–629. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.10.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Bergers G, Song S. The role of pericytes in blood-vessel formation and maintenance. Neuro Oncol. 2005;7:452–464. doi: 10.1215/s1152851705000232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Benjamin LE, Hemo I, Keshet E. A plasticity window for blood vessel remodelling is defined by pericyte coverage of the preformed endothelial network and is regulated by PDGF-B and VEGF. Development. 1998;125:1591–1598. doi: 10.1242/dev.125.9.1591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Blood CH, Zetter BR. Tumor interactions with the vasculature: angiogenesis and tumor metastasis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) Rev. Cancer. 1990;1032:89–118. doi: 10.1016/0304-419X(90)90014-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Stratman AN, Malotte KM, Mahan RD, Davis MJ, Davis GE. Pericyte recruitment during vasculogenic tube assembly stimulates endothelial basement membrane matrix formation. Blood. 2009;114:5091–5101. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-05-222364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Ozerdem U, Stallcup WB. Early contribution of pericytes to angiogenic sprouting and tube formation. Angiogenesis. 2003;6:241–249. doi: 10.1023/B:AGEN.0000021401.58039.a9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Rajantie I, et al. Adult bone marrow- derived cells recruited during angiogenesis comprise precursors for periendothelial vascular mural cells. Blood. 2004;104:2084–2086. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-01-0336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during this study are available on the author.