Significance
The mesoscopic p53-rich clusters that we discover represent a new class of biological condensate, distinct from amorphous and ordered aggregates and the dense liquids found with several physiologically active proteins. The demonstrated two-step mechanism of amyloid fibril nucleation, whereby the clusters host the nucleation of p53 amyloid fibrils, illustrates the potency of recently identified nonclassical nucleation concepts to understand intracellular processes. This finding establishes a new biophysical paradigm for the assembly of numerous ordered functional and pathological biological solids, such as tubules, filaments, sickle cell polymers, amyloids, and crystals.
Keywords: nucleation mechanism, fibrillization, precursors
Abstract
The protein p53 is a crucial tumor suppressor, often called “the guardian of the genome”; however, mutations transform p53 into a powerful cancer promoter. The oncogenic capacity of mutant p53 has been ascribed to enhanced propensity to fibrillize and recruit other cancer fighting proteins in the fibrils, yet the pathways of fibril nucleation and growth remain obscure. Here, we combine immunofluorescence three-dimensional confocal microscopy of human breast cancer cells with light scattering and transmission electron microscopy of solutions of the purified protein and molecular simulations to illuminate the mechanisms of phase transformations across multiple length scales, from cellular to molecular. We report that the p53 mutant R248Q (R, arginine; Q, glutamine) forms, both in cancer cells and in solutions, a condensate with unique properties, mesoscopic protein-rich clusters. The clusters dramatically diverge from other protein condensates. The cluster sizes are decoupled from the total cluster population volume and independent of the p53 concentration and the solution concentration at equilibrium with the clusters varies. We demonstrate that the clusters carry out a crucial biological function: they host and facilitate the nucleation of amyloid fibrils. We demonstrate that the p53 clusters are driven by structural destabilization of the core domain and not by interactions of its extensive unstructured region, in contradistinction to the dense liquids typical of disordered and partially disordered proteins. Two-step nucleation of mutant p53 amyloids suggests means to control fibrillization and the associated pathologies through modifying the cluster characteristics. Our findings exemplify interactions between distinct protein phases that activate complex physicochemical mechanisms operating in biological systems.
Wild-type p53 is a potent tumor suppressor, which is inactivated in almost every cancer, either through mutations in the TP53 gene (in 50% or more of human cancers) or deregulation of its associated pathways (1, 2). By contrast, p53 mutants emerge as effective cancer promoters because they exert a dominant-negative effect on the wild-type variant and also display oncogenic gain-of-function properties by inhibiting other cancer suppressors (1). Several mechanisms of cancer promotion by mutant p53 have been discussed (2–4). It was recently suggested that the mutant proteins’ aggregation into insoluble amyloid fibrils and cofibrillization with other cancer suppressors may play a decisive role in their oncogenicity (5–8); fibril suppression has been identified as a general way to fight cancer (5, 9). Further progress, however, has been impeded by the paucity of mechanistic details on the nucleation and growth of p53 fibrils.
Here, we focus on p53 R248Q, in which arginine (R) in position 248 is replaced with glutamine (Q). p53 R248Q is one of the most common mutants found in breast cancers (10) and is ranked among the strongest predictors of patient death in ovarian cancer (11). We examine the phase behaviors of p53 R248Q in two breast cancer cell lines expressing this mutant and in solutions of the purified protein. As p53 binds to DNA, the positive arginine embeds in the minor grove of the double helix to support the contact (Fig. 1A) (5). Mutations at this site are the most frequent oncogenic p53 mutations (5). Replacing arginine with glutamine not only weakens the binding to DNA (Fig. 1A) but also destabilizes the conformation of the DNA-binding domain [the free energy of unfolding drops from 42.5 kJ ⋅ mol−1 for the wild type to 34.6 kJ ⋅ mol−1 for R248Q (12)] and boosts the aggregation propensity of p53 (5). We employ light scattering and transmission electron microscopy analyses to establish that p53 R248Q forms mesoscopic clusters, a unique protein phase distinct from the recently highlighted macroscopic dense liquid (13–21), and the clusters host the nucleation of amyloid fibrils. We complement the findings on the thermodynamic and kinetic characteristics of the unusual aggregation behaviors of R248Q and wild-type p53 with molecular simulations, which reveal that p53 condensation is driven by the destabilization of the DNA-binding domain and not by interactions of its extensive disordered region.
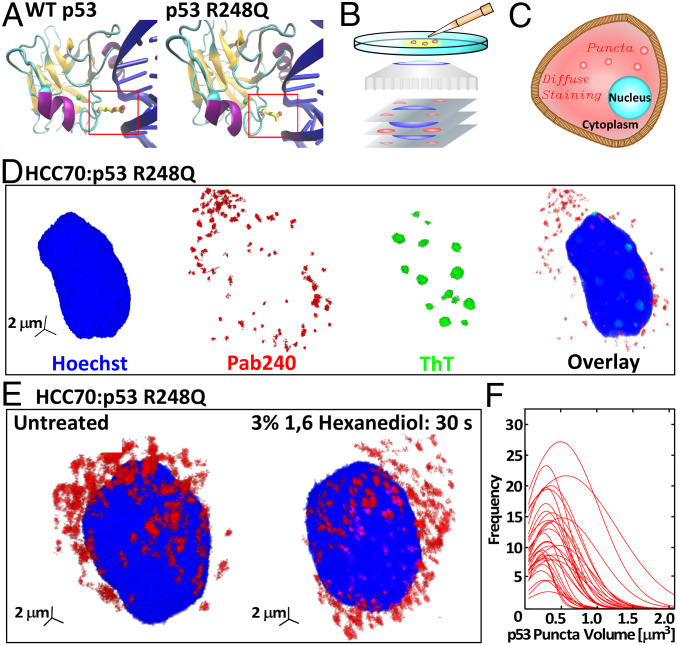
Fig. 1.
The R248Q mutation and aggregation on p53 R248Q in breast cancer cells. (A) The structure of the DBD (94 to 292) of wild-type p53 and the R248Q (Arg-248 Gln) mutant. Nitrogen atoms are colored in red, zinc in green, alpha helices in purple, beta sheets in orange, and DNA in blue. Protein Data Bank ID is 1TUP (23) for wild-type p53; prediction of p53 R248Q DNA interaction was done using Visual Molecular Dynamics (24). (B) Schematic of confocal immunofluorescence microscopy in which antibodies that specifically target cell components of interest are tagged with fluorescent dyes. The spatial distribution of the fluorescent signal collected by the microscope maps the 3D distribution of the target molecule. (C) Illustration of diffuse and punctate staining in the cytoplasm. (D) Combined staining of HCC70 cells with a Hoechst dye, which stains the nucleus, Pab240, which binds to unfolded or aggregated p53, and ThT, which recognizes amyloid structures. (E) Staining of HCC70 cells with Pab240 before and after treatment with 1,6-hexanediol, known to disperse dense liquid droplets of disordered proteins. (F) Distributions of the volumes of the puncta found in HCC70 cells treated with Pab240. Each trace represents the volume distribution of puncta from a single cell.
Results
Cytoplasmic Aggregation of p53 R248Q in Cancer Cells.
We explore the phase behaviors of p53 in two breast cancer cell lines, HCC70, which expresses p53 R248Q, and MCF7, expressing wild-type p53. We detect and quantify aggregated and unaggregated p53 by multicolor immunofluorescence three-dimensional (3D) confocal microscopy (Fig. 1B), which exploits the sensitivity of antibodies to their antigen to attach fluorescent dyes to specific targets within a cell and map the 3D distribution of the target molecule (22). Uniformly distributed targets present diffuse staining, whereas aggregates of target molecules appear as puncta (Fig. 1C). To identify the nucleus, each cell is treated with a Hoechst dye, which binds to DNA and emits a characteristic blue signal.
We combine staining with an antibody specific for misfolded or aggregated p53, Pab240, the antibody DO1, directed against the N-terminal transactivation domain of p53, and Thioflavin T (ThT), a common probe for amyloid structures. HCC70 cells, characterized at 37 °C, exhibit exclusively cytosolic, punctate Pab240 staining and lack of detectable p53 staining in the nucleus (Fig. 1D and SI Appendix, Fig. S2). ThT staining is pronounced in the nucleus, but no ThT staining is detectable in the cytoplasm (Fig. 1D). Treating the HCC70 cells with DO1 reveals diffuse staining in the cell nucleus (SI Appendix, Fig. S1A). The distinct staining patterns of the three reagents in the nucleus and the cytoplasm indicate that unaggregated p53 R248Q resides in the nucleus (where it elicits DO1 diffuse staining), whereas aggregated or misfolded p53 R248Q (revealed by Pab240 puncta) localizes in the cytoplasm. The amyloid structures in the nucleus (identified by ThT staining) are not comprised of p53 (no Pab240 binding). Importantly, the p53 R248Q aggregates in the cytoplasm are not amyloid structures since they do not evoke a ThT signal.
The staining patterns of MCF7 cells (expressing wild-type p53) are simpler. No ThT response was detected, indicating the absence of amyloid structure in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The DO1 and Pab240 antibodies displayed strong perinuclear staining (SI Appendix, Figs. S1B and S3). The two observations are consistent with the accumulation of unaggregated misfolded protein in the vicinity of the nucleus.
To test whether the aggregates in the cytoplasm of HCC70 cells are droplets of macroscopic dense liquid, we determined the sensitivity of the cellular puncta to treatment with 1,6-hexanediol, an organic molecule known to destabilize liquid condensates (13). HCC70 cells treated with 1,6-hexanediol showed no reduction in the number of cytoplasmic p53 puncta (Fig. 1E), indicating the p53 R248Q aggregates are not dense liquid droplets. We measured the volume of the individual puncta of p53 R248Q in the HCC70 cells. The size distributions of 32 cells are similar and relatively narrow with average volumes ranging from 0.1 to 0.6 μm3 (Fig. 1F). A reproducible distribution that is narrow and weighted toward small sizes is not consistent with behaviors expected for disordered agglomerates, whose stochastic formation at low driving forces may result in broader distributions and greater variability between cells.
Collectively, imaging with Pab240 and DO1 antibodies and ThT, and the response to 1,6-hexanediol, demonstrate that the mutant p53 R248Q forms aggregates of narrow size distributions within the cytoplasm of breast cancer cells, whereas wild-type p53 does not aggregate within the probed cancer cells. The results with breast cancer cells establish that the p53 R248Q protein aggregates within the cytoplasm are not fibrils or droplets of stable dense liquid. For further insight into the mechanisms and properties of the observed aggregates, we turn to experiments under defined conditions in vitro.
Mesoscopic Protein-Rich Clusters in Solutions of p53 R248Q.
We monitored solutions of p53 R248Q with concentration 2 μM by oblique illumination microscopy (OIM, Fig. 2A) (25, 26). This method records speckles of light scattered by individual solution inhomogeneities and is particularly suited to detect aggregates of sizes ca. 100 nm since, according to the Rayleigh law, the scattered light intensity scales with the sixth power of the scatterers’ size. The solutions were filtered through low-protein binding 220-nm filters to remove extrinsic inhomogeneities and loaded on the microscope within 10 to 20 min of preparation. The OIM micrographs reveal speckles of light that correspond to protein aggregates (Fig. 2B). Notably, the aggregates are not amyloid structures since tests using a fluorescent dye specific for amyloid fibrils, discussed below, reveal that no fibrillization occurs at concentrations and times after solution preparation similar to those employed here.
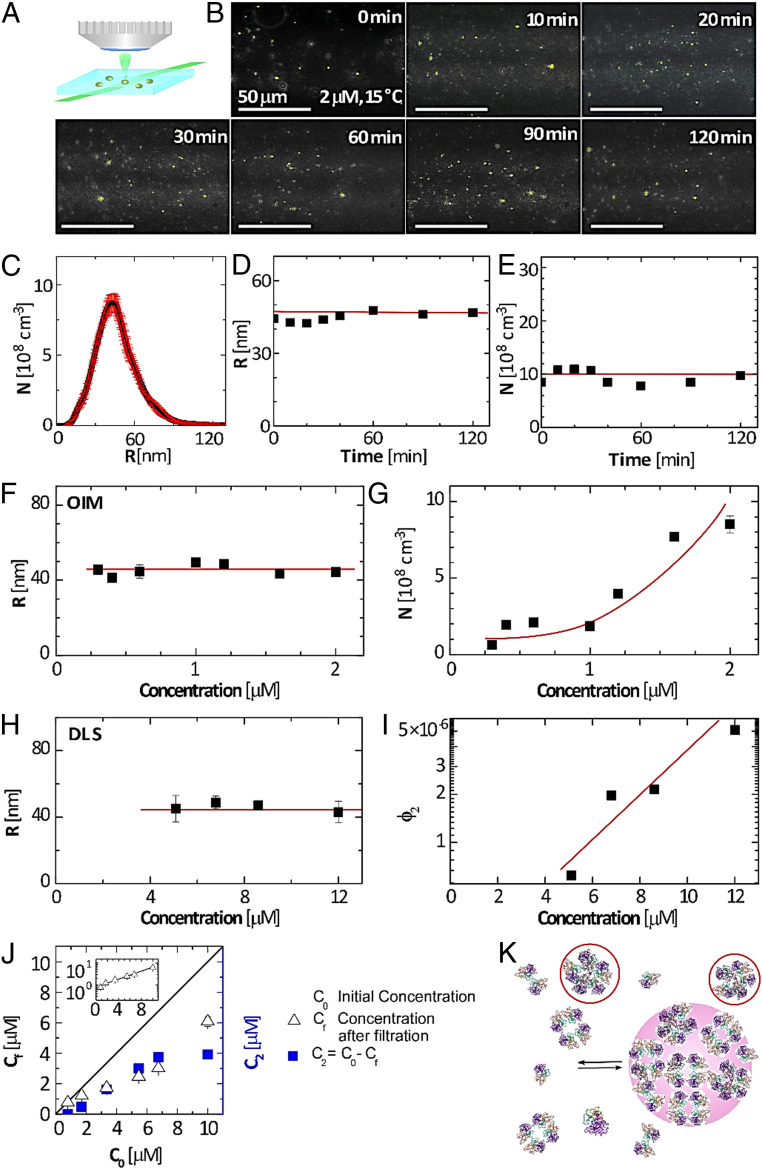
Fig. 2.
Mesoscopic protein-rich clusters of p53 R248Q. (A) Schematic of OIM. A 500-μm-thick solution layer is illuminated by a green laser (wavelength 532 nm) at an oblique angle. Upward scattered light is collected by a microscope lens. (B) Representative OIM micrographs tracing the evolution of aggregates in a 2-μM p53 R248Q solution at 15 °C. The observed volume is 5 × 80 × 120 μm3 depth × height × width. The clusters appear as gold speckles. (C) Number density distribution of the radii R of clusters determined by OIM at 2 μM and 15 °C. The averages of five measurements are displayed. The error bars represent the respective SDs. (D and E) The evolution of the average radius R and number N of clusters per unit solution volume in a 2-μM solution determined at 15 °C by OIM from images as in B. The averages of five measurements are displayed. The respective SDs are smaller than the symbol size. Horizontal lines denote the mean values of R and N. (F and G) The concentration dependence of R and N determined 15 °C by OIM. The averages of five measurements are displayed. The error bars represent the respective SDs and are smaller than the symbol size for most determinations. Horizontal line in F denotes the mean value of R; curve in G is a guide to the eye. (H and I) The concentration dependence of R and the cluster volume fraction ϕ2 determined at 15 °C by dynamic light scattering. The averages of five measurements are displayed. The error bars represent the respective SDs and are smaller than the symbol size for some determinations. Horizontal line in H denotes the mean value of R; the line in I is a guide to the eye. (J) Concentrations Cf and C2, defined in the plot after incubation for 20 min at 15 °C as a function of the initial solution concentration C0. (Inset) The Cf(C0) correlation in semilogarithmic coordinates. (K) Schematic of formation of mesoscopic p53-rich clusters owing to accumulation of transient misassembled oligomers, tentatively represented as pentamers and highlighted in ovals.
To distinguish the aggregates observed with p53 R248Q from macroscopic dense protein liquids and amorphous agglomerates, we measure their individual radii R and the number of aggregates per unit volume N. We determine the aggregates’ radii from their Brownian trajectories, extracted from sequences of OIM images, treated with a Stokes–Einstein procedure (25, 26). In consequence, OIM assess sizes as low as 20 nm, much smaller than the diffraction limit of conventional optical microscopy (21, 25–28). The aggregates exhibit a relatively narrow size distribution (Fig. 2C) with an average R = 45 ± 5 nm at 15 °C. Such clusters would hold ca. 1,000 moderately packed p53 tetramers, whose molecular weight, ca. 173 kDa (29), corresponds to a ca. 8 nm diameter (21). Both R and N are steady for at least 2 h (Fig. 2 D and E), behaviors that stand in contrast to expectations for liquid–liquid separation, a first-order phase transition (30, 31), for which nucleation of new liquid droplets and their growth persist and R and N increase in time (32, 33). Remarkably, at 37 °C, R increases to ca. 150 nm (34), which is consistent with the average volume of the intracellular clusters in HCC70 cells (Fig. 1F).
The reversibility of the observed aggregates is revealed by the correlations of R and ϕ2with the protein concentration (Fig. 2 G and I). The concentration N declines from 8.7 × 108 cm−3 to 0.4 × 108 cm−3, ca. 20-fold, in response to a sevenfold reduction of concentration from 2.0 to 0.3 μM. Similarly, ϕ2, determined independently by dynamic light scattering (DLS), shrinks from 5 × 10−6 to 0.5 × 10−6, a 10-fold decrease driven by 2.5-fold lower concentration. The two techniques complement their respective concentration ranges and demonstrate that R is consistently ca. 45 nm at C0 between 0.2 and 12 μM (Fig. 2 F and H). The OIM measurement of N is consistent with the DLS determination of ϕ2: the product at 2 μM is close to the ϕ2 value extrapolated for that concentration. The exaggerated response of N and ϕ2 to reduced concentration indicates that the aggregates are not irreversibly disordered agglomerates, whose concentration is diluted in parallel with that of the protein, but rather condensates existing in dynamic equilibrium with the host solution.
These behaviors of wild-type p53 and p53 R248Q aggregates cohere with previous observations of mesoscopic protein-rich clusters of globular proteins (21, 25, 35, 36). We conclude that the aggregates are mesoscopic p53-rich clusters. According to recent models, the mesoscopic clusters of multichain proteins, such as tetrameric p53, form because of accumulation of transient misassembled oligomers (Fig. 2K, where the misassembled oligomers are tentatively represented as pentamers) (21, 37, 38). In the clusters, the transient misassembled oligomers coexist with native p53 tetramers and other stable p53 species, such as octamers, dimers, and monomers (7, 39). This kinetic model accounts for the conversion of native molecules to misassembled oligomers and the diffusion of native molecules to fill the void created by this conversion as well as the outflow and decay of the transient misassembled oligomers (36, 37, 40). The cluster size appears as a square root of the product of the diffusivity of the misassembled oligomers and their lifetime and is, hence, independent of the protein concentration and steady in time (36, 37, 40). By contrast, the amount of protein captured in the clusters and the related number of clusters and cluster population volume increase exponentially with the protein concentration as a consequence of the thermodynamic equilibrium between the clusters and the bulk solution (37, 40, 41); this equilibrium is discussed in further detail below. The mesoscopic clusters of p53 R248Q appear to comply with the predictions of this model remarkably well.
The Enlarged Aggregation Capacity of p53 R248Q.
p53 R248Q manifests an enlarged capacity to form clusters, exposed by cluster formation at 15 °C and C0 = 2 μM (Fig. 2B), in contrast to wild-type p53, which exhibits no clusters at these temperature and concertation (21). This exaggerated cluster formation is reaffirmed by tests at C0 as high as 8 μM. Previous tests with wild-type p53 reveal that the concentration of the solution in equilibrium with the clusters Cf, measured after removing the clusters by filtration, is equal to the initial C0, conforming to the lack of clusters in the respective OIM tests (21); wild-type p53 only forms clusters at T = 18 °C and higher. By contrast, filtration to remove the clusters in a p53 R248Q solution lowers Cf from C0 by about half (Fig. 2J), indicating that that the clusters hold ca. 50% of the dissolved mutant.
The Mesoscopic Clusters of p53 R248Q Lack Constant Solubility owing to Their Distinct Chemical Composition.
Surprisingly , which represents the concentration of solution in equilibrium with clusters, is not constant but instead increases quasi-exponentially with C0 (Fig. 2 J, Inset). The finding of increasing terminal concentration is in striking contrast with examples of dense protein liquids, which, in the absence of additional solution components, equilibrate with solutions of constant concentration (15–17, 42–45). The correlation between Cf and C0 is likely represented by a thermodynamic model originally developed for the mesoscopic clusters of wild-type p53 (21). Analogously to the kinetic scheme that predicts a steady and concentration-independent cluster size, we assume that in the clusters, native p53 tetramers convert to misassembled oligomers. With this, the equilibrium between the solution and the cluster phases integrates a chemical transformation. This assumption naturally invokes a varying as the equilibrium concentration governed by a reversible chemical process always depends on the initial concentrations of the reactants.
We represent the chemical potential of native p53 R248Q tetramers in the clusters as , where is the amount of protein captured in the clusters per unit solution volume (Fig. 2J), and the entropy term accounts for their translational and rotational degrees of freedom. The parameter incorporates two terms, . The first addend is the standard chemical potential of p53 R248Q in the clusters that likely differs from that in the solution , owing to the distinct composition of the clusters that accumulate misassembled oligomers; is the activity coefficient of native p53 tetramers in the clusters, determined by the local concentration in the clusters. We assume that is controlled by the parameters of conversion to misassembled oligomers. Owing to the kinetically fixed cluster size and chemically controlled , increasing drives the production of more clusters and increases N but does not impact , , and .
In the solution, we account for the nonideality because of interactions between the solute p53 R248Q molecules by modeling the activity coefficient as , where is the second osmotic virial coefficient and is the p53 molecular weight (46). We obtain for the chemical potential of p53 R248Q in the solution . Supported by the reversibility of the p53-rich clusters (Fig. 2 G and I), we assume equilibrium between the clusters and the solution, which leads to . We solve this equation for the amount of p53 R248Q captured in the clusters . If and , as with wild-type p53 (21), this relation predicts that is comparable to and that increases quasi-exponentially with . The found dependence resolves the mystery of the experimentally observed variable (Fig. 2J).
The Mesoscopic Protein-Rich Clusters Host the Nucleation of p53 R248Q Fibrils.
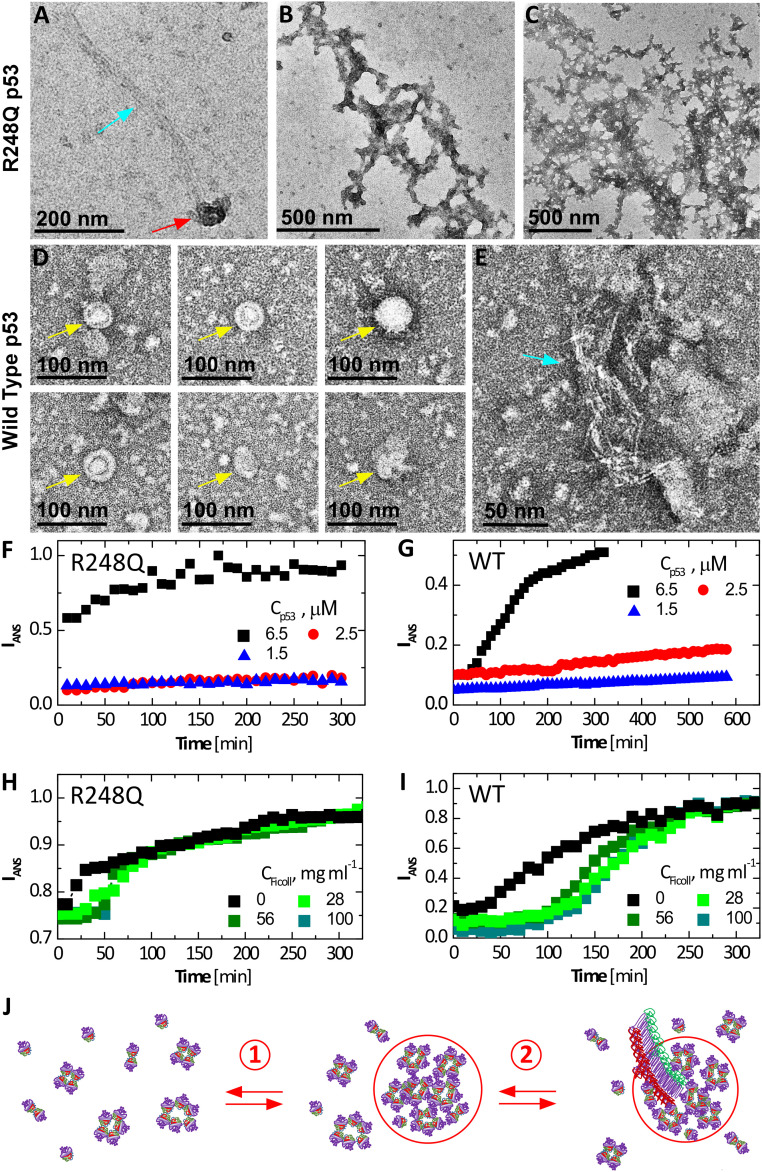
Formation of amyloid fibrils of mutant and wild-type p53 is a distinguishing behavior of this protein (7, 47, 48). To examine whether the mesoscopic protein-rich clusters appertain to the mechanisms of nucleation and growth of the P53 R248Q fibrils, we imaged the aggregates in solutions of p53 R248Q and, for comparison, wild-type p53 by negative staining transmission electron microscopy (EM) (Fig. 3 A–E) (49). The electron micrographs reveal three classes of p53 aggregates: isometric round aggregates of diameter about 60 to 80 nm (Fig. 3 A and D), whose narrow size distribution is consistent with the mesoscopic p53-rich clusters observed by immunofluorescence (Fig. 1F) and scattering techniques (Fig. 2C); linear structures that likely are amyloid fibrils (Fig. 3 A and E); and amorphous agglomerates that either coat fibrils (Fig. 3B) or exist independently (Fig. 3C). Remarkably, fibrils originate in the round aggregates tentatively identified as mesoscopic p53-rich clusters (Fig. 3 A and E).
Fig. 3.
Fibrillization of wild type and p53 R248Q. (A–E) Negative staining EM micrographs reveal clusters, fibrils, and amorphous agglomerates of p53 R248Q in A–C and wild-type p53 in D and E. Gold arrows point to empty clusters; red arrows, clusters that spawn fibrils; and blue arrows, fibrils. (B) Branched fibrils coated with amorphous agglomerates. (C) Stand-alone amorphous agglomerates. (F–I) Evolution of the intensity of fluorescence at wavelength 500 nm of ANS in the presence of p53 at 37 °C. ANS concentrations were 200 µM in all tests. (F and G) At the listed concentrations of R248Q, in F, and wild type, in G, in the absence of Ficoll. (H and I) At 6.5 μM of R248Q, in H, and wild type, in I, and in the presence of varying concentrations of Ficoll. (J) Schematic of two-step nucleation of fibrils; step 1) Mesoscopic p53-rich clusters, comprised of misassembled p53 oligomers (depicted here as pentamers), native tetramers, and additional p53 species, assemble and step 2) Fibrils, which likely represent stacks of refolded p53 monomers (7), nucleate within the mesoscopic clusters by the assembly of p53 monomers. Fibril growth proceeds classically, via sequential association of p53 monomers from the solution. Compare to EM micrograph in A.
For additional evidence for the role of the mesoscopic p53-rich clusters in fibril nucleation, we probed the response of the fibrillization kinetics to Ficoll. We monitored the growth of the amyloid population with the dye 1-anilino-8-naphthalenesulfonate (ANS), which binds to amyloid fibrils and emits fluorescence at 500 nm (50); ANS is a well-established assay to detect amyloid fibrils and monitor their growth (50–52). Notably, ANS also binds to exposed hydrophobic regions abundant in partially unfolded proteins (50); the pronounced fluorescence intensity in both wild-type and mutant p53 solutions immediately after ANS introduction (Fig. 3 A and B) may be due to the binding of the dye to the disordered segments in the transactivation and proline-rich domains (5). The stronger initial fluorescence of the mutant solution attests to the abundance of hydrophobic residues exposed, owing to the lower stability of its core domain (5, 12).
In the absence of Ficoll, solutions of wild-type p53 emit steady fluorescence intensity for ca. 40 min at the highest tested concentration, 6.5 μM, and for up to 9 h at the two lower concentrations (Fig. 3F). After this lag time, the intensity ascended. The observed fibrillation delay is likely due to the known slow nucleation of amyloid structures (6, 53). The R248Q p53 at 6.5 μM fibrilizes after a shorter lag time, ca. 20 min (Fig. 3G), indicating fast nucleation of the mutant fibrils; at the lower tested concentrations, the nucleation of R248Q p53 fibrils is delayed by at least 5 h (Fig. 3G).
Time-dependent ANS fluorescence reveals that added Ficoll invokes significantly longer lag times with both wild type and p53 R248Q (Fig. 3 H and J). Ficoll-enforced nucleation delay is counterintuitive since the excluded volume effects of Ficoll and the associated surge of the protein chemical potential (54) would hasten fibril nucleation. The faster fibril growth in the presence of Ficoll, manifesting as a steeper gain of ANS fluorescence after the lag time for both wild-type and mutant p53 (Fig. 3 H and J), concurs with a crowding-enforced chemical potential boost. On the other hand, suppressed nucleation in the presence of Ficoll coheres with nuclei growth hosted within the clusters. Ficoll sequesters in the clusters (21), where it may obstruct the migration of the p53 molecules to a fibril nucleus. The accelerated fibril growth in the presence of Ficoll suggests that after nucleation, the fibrils emerge from the clusters and grow in the p53 solution.
The EM and ANS fluorescence data (Fig. 3) support a nonclassical two-step mechanism of fibril nucleation assisted by preformed mesoscopic clusters and followed by classical growth by association of solute monomers, as illustrated in Fig. 3J. This nucleation pathway is similar to a precursor mechanism suggested for the nucleation of polyglutamine peptides, whose aggregation leads to several neurological disorders (55).
Why Is p53 R248Q More Prone to Aggregate than the Wild-Type p53?
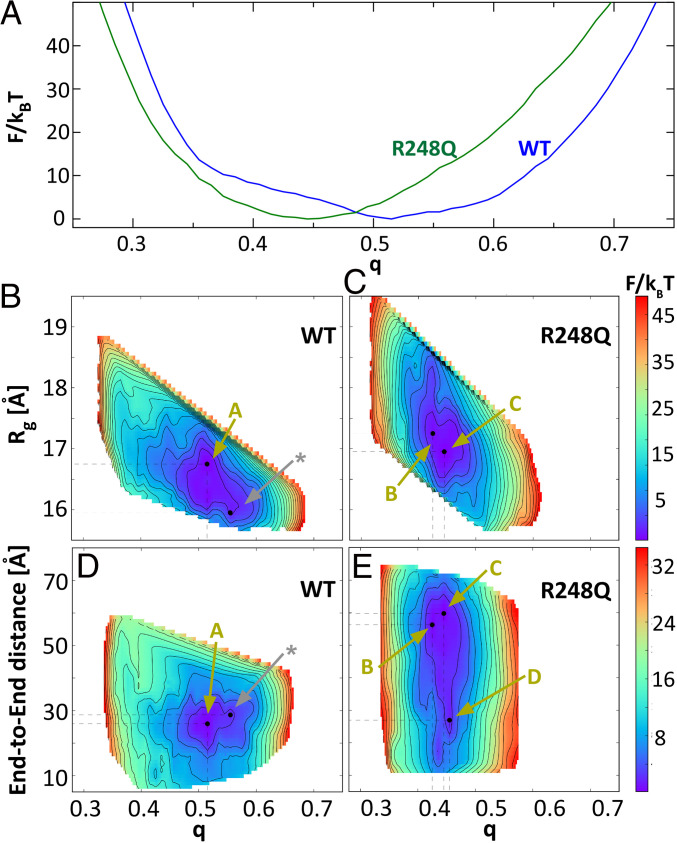
To understand how a mutation located in the ordered DNA-binding domain (DBD, comprised of residues 94 to 289) of p53 lowers the stability of the molecule and promotes aggregation, we modeled the conformational changes in the p53 structure driven by the R248Q mutation. We use the Associative Memory, Water Mediated, Structure and Energy Model for Molecular Dynamics (AWSEM-MD) (56). For a coarse estimate of the conformational modifications enforced by the mutation, we first evaluate the free energy profiles F of the wild type and P53 R248Q DBDs (56). We introduce a reaction coordinate q that measures the similarity of the DBD conformation to an experimentally known DBD structure (q = 0 for random coils and q = 1 for structures identical to the protein database entry). Notably, the experimental structure of reference used here is of the DBD bound to DNA (23), which might be significantly different from the unbound structure that we model. Indeed, we found that the free energy minima for both wild type and p53 R248Q locate at q values below 0.7; this value indicates a high degree of similarity between structures. q < 1 manifests the divergence between the DNA-bound and unassociated structures. Importantly, the one-dimensional free energy profile F(q) reveals that wild type and p53 R248Q explore distinct conformational spaces (Fig. 4A). Whereas the free energy minimum for the wild type is at q > 0.5, it is closer to 0.45 for the R248Q mutant.
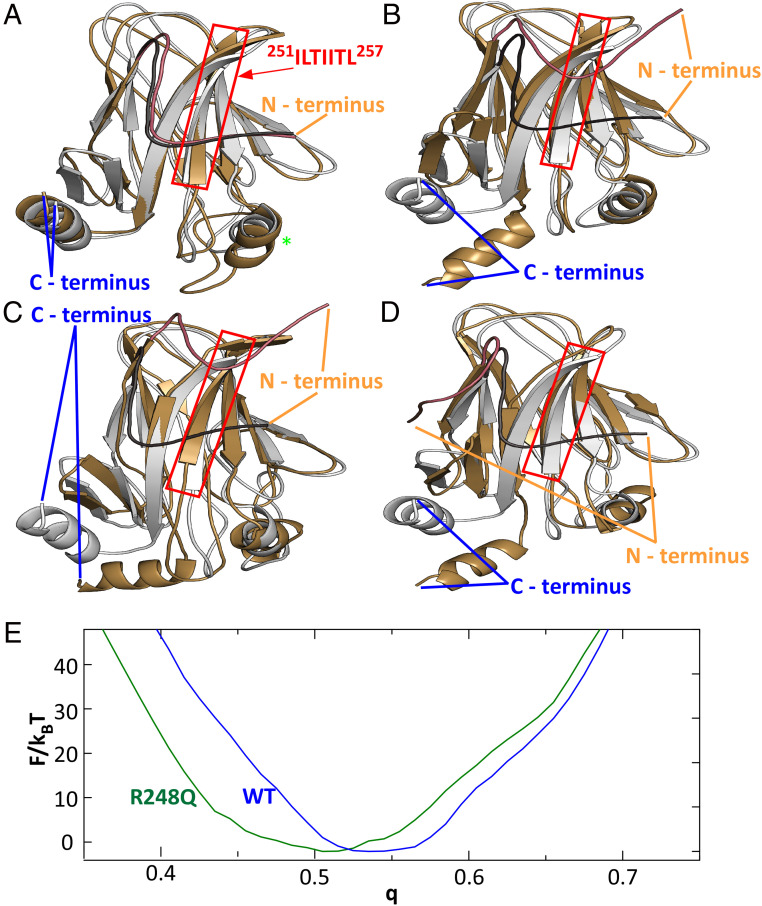
Fig. 4.
The free energy F of the conformations of wild type and p53 R248Q DBD. (A) As a function of the reaction coordinate q, which measures the similarity of the DBD conformation to a structure determined by X-ray crystallography (23). (B–E) 2D profiles of F as function of q and radius of gyration, Rg, in B and C, and end-to-end distance, D, in D and E, of the DBD chain. Gold arrows labeled with letters A through C point to the states of the structures in the respective panels in Fig. 5. The silver arrow labeled with a star indicates the state of the reference structure depicted with silver ribbons in Fig. 5 A–D.
For further insight, we explore the free energy as a function of two additional metrics of protein confirmation: the radius of gyration, Rg, and end-to-end distance, D, of the DBD chain. The two-dimensional (2D) free energy profiles F(q,Rg) and F(q,D) reveal that there are at least two local minima with F below kBT (kB, Boltzmann constant and T, temperature) for both wild-type and mutant p53 (Fig. 4 B–E). For wild-type p53, F(q,Rg) minima locate at at q = 0.515 and Rg = 16.75 Å and at q = 0.555 and Rg = 15.95 Å (Fig. 4B). For the mutant, the minima are at q = 0.425 and Rg = 17.25 Å and q = 0.445 and Rg = 16.95 Å (Fig. 4C). Thus, the mutant explores structures characterized with lower q and higher Rg. Consistently, the F(q,D) free energy profiles of the wild type exhibit two minima, at the same q as F(q,Rg) and end-to-end distances 26 Å and 28.6 Å, both 30 Å (Fig. 4D). For the mutant, however, we identify three local minima at q values 0.425, 0.445, and 0.455. While the minimum at q = 0.455 has end-to-end distance comparable to that of the wild type, ca. 27 Å, the minima at q = 0.425 and q = 0.445 have larger D values of 56 Å and 60 Å, respectively. The F(q,Rg) and F(q,D) profiles indicate that the mutant DBD can adopt extended conformations that have less similarity to the reference DNA-bound structure than the wild-type DBD.
We further explored the conformations of the wild type and mutant p53 DBD near the free energy minima in the F(q,Rg) and F(q,D) profiles. Pairwise comparisons of representative structures reveal that the conformations associated with two local minima of the F(q,Rg) and F(q,D) profiles of the wild type are similar (Fig. 5A). The largest difference is associated with a region containing a small helix and a large loop between residues 168 and 193. Both the N-terminal tail and the C-terminal helix, roughly defined as the first and last 13 residues of DBD, are tightly wrapped around the domain at all times. Importantly, the N-terminal tail binds to the ILTIITL motif (residues 251 to 257), known to promote p53 aggregation (7, 53). The mutant structures are, however, very different. The largest changes are associated with the N-terminal and C-terminal tails that are both found in various unbound conformations (Fig. 5 B–D). The unbinding of the N-terminal loop and C-terminal helix can lead to significant changes to the full-length p53 structure and dynamics. Importantly, the unbinding of the N-terminal tail leads to the exposure of the 252ILTIITL257 motif known to promote p53 aggregation (7). The exposure of the aggregation prone sequence in the p53 R248Q may be a part of the molecular mechanism of enhanced cluster formation, oligomerization, and aggregation of this mutant.
Fig. 5.
Conformational changes induced by the R248Q mutation. (A) Comparison of wild-type DBD structures corresponding to F(q) minima at q = 0.555 (silver) and q = 0.515 (gold). Red box highlights the aggregation prone sequence, protected by the N terminus tail in wild-type p53 and exposed in p53 R248Q. Green star indicates residues 168 to 193, the location of the strongest deviation of between the two modeled wild-type conformations. (B–D) Comparisons of wild-type DBD structures corresponding to the F(q) minimum at q = 0.555 (silver) to the DBD structures of p53 R248Q (gold) at F(q) minima at q = 0.425 in B; at q = 0.445 in C; and at q = 0.455 in D. In A–D, the N terminus tail of the reference structure is highlighted in charcoal and that of the second structure in copper. (E) Free energy profiles F(q) for the cores of the DBDs (residues 107 to 276) of wild type and p53 R248Q.
To understand how a mutation near the center of the DBD drives strong displacements of both DBD chain termini, we evaluated the F(q) profiles for the DBD core, comprised of residues 107 to 276 and omitting 13 residues from both N and C ends of the DBD, for both the wild type and the mutant. The F(q) minimum shifts from ca. 0.54 to ca. 0.51 (Fig. 5E). The modified F(q) profile indicates that the mutation induces conformation changes in the DBD core, albeit more subtle than for the entire DBD (Fig. 4A). The conformational changes in the DBD core illuminate how the structure perturbation introduced by the mutation propagates allosterically to the C and N termini and how the mutation drives the interactions of the α-helix at the C terminus and the tail at the N terminus with the core.
Discussion
The mesoscopic protein-rich clusters of p53 R248Q, observed in breast cancer cells and in solutions of purified protein, represent a unique protein condensed phase. The defining features of the clusters are the decoupling of the cluster sizes from the total cluster population volume, the independence of the cluster size on the p53 concentration, and the variable concentration of the solution in equilibrium with the clusters. These behaviors are incompatible with protein-dense liquids seen in solutions of numerous proteins, which represent macroscopic equilibrium phases (14–16, 57). Inevitably, the clusters share certain characteristics with other condensed phases of proteins or other materials (58), such as crystals (59), amyloid fibrils (60), and dense liquids (14–16, 57): their formation is reversible, they are in equilibrium with the solution, and they capture up to 80% of the available protein. The dramatic differences of their fundamental structural and thermodynamic characteristics from those of protein-dense liquid phases, however, certify the distinction of the clusters from dense liquid droplets.
The formation of p53 fibrils starts with nucleation, whereby local fluctuations of the p53 concentration beget regions of concentrated and ordered p53 molecules that serve as nuclei for the growth of fibrils (61). The creation of a nucleus encounters significant free energy barriers (62–66). Hence, successful nucleation events are extremely rare. The finding that nucleation of p53 fibrils is hosted in the mesoscopic clusters suggests that the exaggerated p53 concentration in the clusters increases the probability of a fluctuation that overcomes the free energy barrier and evolves to a fibril nucleus. The proposed mechanism of fibrillization hosted and facilitated by mesoscopic clusters drastically deviates from the accepted sequential association of single solute molecules. Nonclassical nucleation is a recently proposed mechanism of phase transformation that diverges from the canon of J.W Gibbs (62–64); it guides the assembly and defines the properties of numerous other protein solids such as crystals (18–20, 67) and sickle cell hemoglobin polymers (68, 69).
The mesoscopic p53-rich clusters reported here are strikingly similar to condensates reported in two experimental investigations of the exon 1 encoded region of the huntingtin protein (70, 71). The found condensates, referred to by the authors as S phases, are round and relatively monodisperse with a size ca. 25 nm, close to the size range of the clusters identified here for mutant p53. The S phases appear to slow the conversion to fibrils and may represent a condensation pathway distinct from the one presented by the p53 clusters, which host and enhance fibrillization.
The clusters may represent a fibril-independent pathway to oncogenicity: unidentified nonfibrillar aggregates of two p53 mutants (R282W and R100P) were shown to sequester the tumor suppressors p63 and p73 (7). In this respect, the p53 liquid condensates may be akin to other protofibrillar assemblies known to trigger disease (72). Two-step nucleation of mutant p53 amyloids suggests means to control fibrillization and the associated pathologies through modifying the cluster behaviors. In addition, formation of clusters that combine mutant p53 with cancer suppressors (wild-type p53, p63, p73, and others) may expedite the fibrillization of the suppressors into one-component fibrils or in fibrils that also incorporate mutant p53. The suggested two-step mechanism of coaggregation presents an alternative to the generally accepted templating pathway, which relies on a pattern provided by an existing fibril to guide the assembly of fibrils of a distinct protein. In a broader context, findings reported here exemplify interactions between distinct protein phases that activate complex physicochemical mechanisms operating in biological systems.
The enhanced cluster formation of the R248Q mutant is not due to enhanced interactions in the disordered transactivation and proline-rich segments that are identical to those of wild-type p53. Molecular models of the conformations of the wild type and p53 R248Q indicate that the enhanced cluster formation by the mutant is due to changes in the structured DBD that are promoted by the mutation and which propagate allosterically to the N and C termini of the DBD. The shift of the N terminus tail exposes the aggregation prone motif ILTIITL (residues 251 to 257) and reinforces aggregation. Destabilization of the core domain in p53 condensation is consistent with the localization of most cancer-associated mutations in the structured DBD (8) and the role of mutant p53 aggregation in cancer.
Materials and Methods
Detailed descriptions of all methods used in this work are provided in SI Appendix.
Immunofluorescence Imaging of Human Breast Cancer Cells.
MCF7 (American Type Culture Collection), a human breast adenocarcinoma cell line, and HCC70 (American Type Culture Collection), a human breast carcinoma with mutant p53, were cultured in Eagle’s minimum essential medium (Quality Biological, Inc., 112-018-101) and Roswell Park Memorial Institute medium (RPMI) (HyClone Laboratories, Inc., SH3002701), respectively. Some of the HCC70 cells were treated with 1,6-hexanediol. For this, the cells were washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; HyClone, 16750-122), and 250 µl no-serum RPMI was added. An equal volume of 1,6-hexanediol (Sigma, 240117, 6%) in no-serum RPMI was added on the Petri dish. For immunofluorescence imaging, the cells were washed twice with PBS and fixed by incubating in 4% paraformaldehyde. Antibody staining was performed separately for Pab240 and DO-1 antibodies. The nucleus was stained with Hoechst 33342 (Sigma, 14533, 10 µg/mL) for 20 min at 37 °C and washed twice with PBS before acquiring the images.
A Nikon (Minato) Eclipse Ti2 inverted confocal microscope was used for imaging. 3D images (z-stacks, 0.2 µm steps, ∼60 slices) were taken from different fields of view. Z-stacks of 16-bit images were extracted for each channel and processed in ImageJ (NIH) using a series of plugins. A series of methods including background subtraction, 3D watershed, 3D object counter plugin2, 3D ROI Manager plugin2, and 3D Viewer were applied to construct the 3D images and measure the volume of p53 puncta (SI Appendix, Fig. S4).
Bacterial Expression and Purification.
The protein p53 was expressed in plasmid pET15b-TP 53, containing N-terminal 6-His-WT-p53 (1-303) (Addgene, 24859). For p53 R248Q, a point mutation was introduced in pET15b-TP 53 by PCR and Gibson Assembly. The culture was grown at 15 °C at 250 rpm overnight (73, 74). The cells were pelleted by centrifugation at 5 °C, and each aliquot was sonicated on ice four times for 30 s with 15 min intervals between each sonication. After sonication, the lysate was centrifuged at 5 °C with 13,000 rpm. The supernatant from centrifugation was filtered with 0.45 μm surfactant-free cellulose acetate syringe filters prior to purification. We used a 10 mL of Ni Sepharose Fast Flow column (GE Healthcare Life Sciences, 17531801), equilibrated with 50 mM of binding buffer containing 100 mM KH2PO4/K2HPO4, 300 mM NaCl, 5% glycerol, 25 mM imidazole (Sigma-Aldrich, 792527), and 1 mM tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TCEP) with pH 8.0. p53 R48Q was eluted with linear gradient of imidazole. Two fractions with most p53 R248Q (based on sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) were collected. Fractions were diluted 1:3 with binding buffer for heparin purification, including 20 mM KH2PO4/K2HPO4, 2 mM TCEP, and 5% glycerol at pH = 5.9 for HiTrap Heparin HP column (GE Healthcare Life Sciences, 17040601). p53 R248Q is eluted with linear gradient of NaCl. Two fractions with most p53 R248Q were collected again for buffer exchange (SI Appendix, Fig. S5 A and B). The concentrated fraction was mixed and was into a PD-10 desalting column (GE Healthcare Life Sciences, 17085101) for buffer exchange. The solution concentration was determined by absorbance measurement using a DU 800 Spectrophotometer (Beckman Coulter) and extinction coefficient ε = 0.763 mL ⋅ mg−1 ⋅ cm−1 at 280 nm (74, 75). The identity of p53 was confirmed with Western blotting (SI Appendix, Fig. S5C).
Transmission EM.
A total of 3 μL of 10 μM p53 solution was applied to EM grids with carbon support film (CF200-Cu, Electron Microscopy Sciences, Inc.) for 20 to 30 s followed by blotting with filter paper and application of 3 μL uranyl acetate (2% aqueous solution, pH 4).
OIM.
p53 R248Q was monitored with OIM known as Brownian microscopy or particle tracking (25–28). In this method, a green laser illuminates a thin solution layer at an oblique angle such that the incident beam avoids the lens of a microscope positioned above the sample (Fig. 2A) (26). This method enables the detection of nano- and microscale objects through light scattered at wave vectors of order µm−1. The scattered intensity is proportional to the sixth power of the scatterers’ sizes; thus, in a solution containing objects of varying size, the scattering signal is dominated by larger particles. This feature makes this technique particularly well suited to characterize the size and number distribution of the aggregates that appear as bright cyan spots in OIM micrographs (Fig. 2B). The spots are counted by a custom-made image package from NanoSight. The concentration of the observed aggregates is determined from the number of spots in a frame and the observed volume (27, 76). OIM records the Brownian trajectory of each particles in the image plane (SI Appendix, Fig. S6A) and calculates diffusion coefficient from correlation between the mean squared displacement and the lag time (SI Appendix, Fig. S6B) (76), , where D is the diffusion coefficient of the observed aggregate.
DLS.
DLS data were collected by an ALV instrument (ALV-GmbH), which includes an ALV goniometer, a He-Ne laser with a wavelength at 632.8 nm, and an ALV-5000/EPP Multiple Tau Digital Correlator. Normalized intensity correlation functions were collected at a fixed scattering angle of 90° for 60 s. The characteristic diffusion times and for monomers and aggregates were calculated by fitting the normalized correlation function with an exponential fit (35, 77). To calculate the average radii of monomers Ru and clusters R, we used the Strokes–Einstein relation, with and . In this relation, is the Boltzmann constant, is temperature, and is the independently determined solution viscosity (21).
ANS Assays for Characterization of p53 R248Q Aggregation.
The fibrillization kinetics of p53 R248Q was monitored at 37 °C with ANS (Sigma-Aldrich) assay (51–53). Ficoll PM-70 (Sigma-Aldrich) was used with the ANS assay. Stock concentration of Ficoll was 250 mg ⋅ mL−1 with 200 mM NaCl in deionized water for ionic strength of the buffer (21).
Simulation and Visualization of p53 Structures.
The structure of wild-type p53 was based on Protein Data Bank structure 1TUP. We introduced the mutation R248Q in the 1TUP structure by choosing the lowest score to optimize structure with mutation in Swiss-PdbViewer (78). These images were made with VMD/NAMD/BioCoRE/JMV/other software support (www.ks.uiuc.edu/Research/vmd/). VMD/NAMD/BioCoRE/JMV/ is developed with NIH support by the Theoretical and Computational Biophysics group at the Beckman Institute, University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign (24).
Coarse-Grained Simulations of the p53 DBD Domain.
Molecular dynamics simulations of DBD of p53 were carried out using the AWSEM coarse-grained model (57). In this model, each amino acid is represented by three beads placed at the positions of Cα, Cβ, and O atoms. The interactions between those beads are governed by a combination of physically motivated potentials responsible for proper backbone geometry, secondary structure and long-range tertiary interactions, and bioinformatics terms that supplement the former potentials.
Starting from the equilibrated states of wild type and R248Q mutant of the DBD (as well as for the DBD core), we performed free energy calculations along the reaction coordinate q, which is defined as a similarity measure to a reference structure. Given the instantaneous coordinates r and the coordinates of the reference structurer r', q is as , where N is the number of atoms in the structure and is the SD of the differences; q takes values from 0 to 1. The free energy calculations were performed using the umbrella sampling and the weighted histogram analysis method (79). The structural diversity of p53 DBD was studied by clustering conformations near the local minimums of the 2D free energy profiles F(q, Rg) and F(q, D). The clustering was performed using the hierarchical clustering algorithm (80). Consequently, several distinct conformations of DBD were identified for both wild type and the R248Q mutant (see Results).
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Clifford Brangwynne, Dominique Maes, Frederic Rousseau, and Joost Schymkowitz for valuable discussions of p53 aggregation, protein conformational stability, and protein expression and translocation and the latter two for providing the cell lines used in this work. This work was supported by the NIH (Award No. 1R21AI126215-01), the NSF (Award Nos. DMR-1710354 and DMR-1705464), Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs (Award No. CA160591), Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (Award No. RP180466), Melanoma Research Alliance (Award No. 509800), and NASA (Award No. NNX14AD68G). Additional support was provided by the Center for Theoretical Biological Physics at Rice University sponsored by NSF (Grant PHY-1427654) and the Sealy Center for Structural Biology and Molecular Biophysics at the University of Texas Medical Branch.
Footnotes
The authors declare no competing interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
This article contains supporting information online at https://www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.2015618118/-/DCSupplemental.
Data Availability
All study data are included in the article and/or SI Appendix.
References
- 1.Bieging K. T., Mello S. S., Attardi L. D., Unravelling mechanisms of p53-mediated tumour suppression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 14, 359–370 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Levine A. J., Targeting therapies for the p53 protein in cancer treatments. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 3, 21–34 (2019). [Google Scholar]
- 3.Muller P. A. J., Vousden K. H., p53 mutations in cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 15, 2–8 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Aramayo R., et al., Quaternary structure of the specific p53-DNA complex reveals the mechanism of p53 mutant dominance. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, 8960–8971 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Joerger A. C., Fersht A. R., The p53 pathway: Origins, inactivation in cancer, and emerging therapeutic approaches. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 85, 375–404 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wilcken R., Wang G., Boeckler F. M., Fersht A. R., Kinetic mechanism of p53 oncogenic mutant aggregation and its inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109, 13584–13589 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Xu J., et al., Gain of function of mutant p53 by coaggregation with multiple tumor suppressors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 7, 285–295 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Leroy B., Anderson M., Soussi T., TP53 mutations in human cancer: Database reassessment and prospects for the next decade. Hum. Mutat. 35, 672–688 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Soragni A., et al., A designed inhibitor of p53 aggregation rescues p53 tumor-suppression in ovarian carcinomas. Cancer Cell 29, 90–103 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ungerleider N. A., et al., Breast cancer survival predicted by TP53 mutation status differs markedly depending on treatment. Breast Cancer Res. 20, 115 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Seagle B.-L. L., et al., Survival of patients with structurally-grouped TP53 mutations in ovarian and breast cancers. Oncotarget 6, 18641–18652 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bullock A. N., Henckel J., Fersht A. R., Quantitative analysis of residual folding and DNA binding in mutant p53 core domain: Definition of mutant states for rescue in cancer therapy. Oncogene 19, 1245–1256 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chong S., et al., Imaging dynamic and selective low-complexity domain interactions that control gene transcription. Science 361, eaar2555 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Shin Y., Brangwynne C. P., Liquid phase condensation in cell physiology and disease. Science 357, eaaf4382 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wei M.-T., et al., Phase behaviour of disordered proteins underlying low density and high permeability of liquid organelles. Nat. Chem. 9, 1118–1125 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Uversky V. N., Intrinsically disordered proteins in overcrowded milieu: Membrane-less organelles, phase separation, and intrinsic disorder. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 44, 18–30 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Galkin O., Chen K., Nagel R. L., Hirsch R. E., Vekilov P. G., Liquid-liquid separation in solutions of normal and sickle cell hemoglobin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99, 8479–8483 (2002). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sleutel M., Van Driessche A. E., Role of clusters in nonclassical nucleation and growth of protein crystals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 111, E546–E553 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Schubert R., et al., Real-time observation of protein dense liquid cluster evolution during nucleation in protein crystallization. Cryst. Growth Des. 17, 954–958 (2017). [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yamazaki T., et al., Two types of amorphous protein particles facilitate crystal nucleation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 114, 2154–2159 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Safari M. S., et al., Anomalous dense liquid condensates host the nucleation of tumor suppressor p53 fibrils. iScience 12, 342–355 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mandrell R. E., Griffiss J. M., Macher B. A., Lipooligosaccharides (LOS) of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis have components that are immunochemically similar to precursors of human blood group antigens. Carbohydrate sequence specificity of the mouse monoclonal antibodies that recognize crossreacting antigens on LOS and human erythrocytes. J. Exp. Med. 168, 107–126 (1988). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cho Y., Gorina S., Jeffrey P. D., Pavletich N. P., Crystal structure of a p53 tumor suppressor-DNA complex: Understanding tumorigenic mutations. Science 265, 346–355 (1994). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Humphrey W., Dalke A., Schulten K., VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graphics 14, 33–38 (1996). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Vorontsova M. A., Chan H. Y., Lubchenko V., Vekilov P. G., Lack of dependence of the sizes of the mesoscopic protein clusters on electrostatics. Biophys. J. 109, 1959–1968 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Li Y., Lubchenko V., Vekilov P. G., The use of dynamic light scattering and brownian microscopy to characterize protein aggregation. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 82, 053106 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Maes D., et al., Do protein crystals nucleate within dense liquid clusters? Acta Crystallogr. F Struct. Biol. Commun. 71, 815–822 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Filipe V., Hawe A., Jiskoot W., Critical evaluation of Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) by NanoSight for the measurement of nanoparticles and protein aggregates. Pharm. Res. 27, 796–810 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chalkley G. E., Knowles P. P., Whitehead P. C., Coffer A. I., Biochemical characterisation of purified human wild-type p53 overexpressed in insect cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 221, 167–175 (1994). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Brangwynne C. P., et al., Germline P granules are liquid droplets that localize by controlled dissolution/condensation. Science 324, 1729–1732 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Feric M., et al., Coexisting liquid phases underlie nucleolar subcompartments. Cell 165, 1686–1697 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Chaikin P. M., Lubensky T. C., Principles of Condensed Matter Physics (Cambridge Unversity Press, Cambridge, 1995). [Google Scholar]
- 33.Debenedetti P. G., Metastable Liquids (Princeton Univ Press, Princeton, 1996). [Google Scholar]
- 34.Yang D. S., et al., Mesoscopic liquid clusters represent a distinct condensate of mutant. bioRxiv [Preprint] (2020). 10.1101/2020.02.04.931980 (Accessed 15 February 2021). [DOI]
- 35.Safari M. S., Vorontsova M. A., Poling-Skutvik R., Vekilov P. G., Conrad J. C., Differential dynamic microscopy of weakly scattering and polydisperse protein-rich clusters. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin. Soft Matter Phys. 92, 042712 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chan H. Y., Lubchenko V., A mechanism for reversible mesoscopic aggregation in liquid solutions. Nat. Commun. 10, 2381 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Pan W., Vekilov P. G., Lubchenko V., Origin of anomalous mesoscopic phases in protein solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 114, 7620–7630 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Chan H. Y., Lankevich V., Vekilov P. G., Lubchenko V., Anisotropy of the coulomb interaction between folded proteins: Consequences for mesoscopic aggregation of lysozyme. Biophys. J. 102, 1934–1943 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Rajagopalan S., Huang F., Fersht A. R., Single-Molecule characterization of oligomerization kinetics and equilibria of the tumor suppressor p53. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, 2294–2303 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Safari M. S., Byington M. C., Conrad J. C., Vekilov P. G., Polymorphism of lysozyme condensates. J. Phys. Chem. B 121, 9091–9101 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Li Y., Lubchenko V., Vorontsova M. A., Filobelo L., Vekilov P. G., Ostwald-like ripening of the anomalous mesoscopic clusters in protein solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 116, 10657–10664 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Broide M. L., Berland C. R., Pande J., Ogun O. O., Benedek G. B., Binary-liquid phase separation of lens protein solutions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 5660–5664 (1991). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Muschol M., Rosenberger F., Liquid-liquid phase separation in supersaturated lysozyme solutions and associated precipitate formation/crystallization. J. Chem. Phys. 107, 1953–1962 (1997). [Google Scholar]
- 44.Chen Q., Vekilov P. G., Nagel R. L., Hirsch R. E., Liquid-liquid phase separation in hemoglobins: Distinct aggregation mechanisms of the β6 mutants. Biophys. J. 86, 1702–1712 (2004). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Choi J.-M., Dar F., Pappu R. V., LASSI: A lattice model for simulating phase transitions of multivalent proteins. PLOS Comput. Biol. 15, e1007028 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Dill K., Bromberg S., Molecular Driving Forces: Statistical Thermodynamics in Biology, Chemistry, Physics, and Nanoscience (Garland Science, ed. 2, New York, 2011). [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wang G., Fersht A. R., Propagation of aggregated p53: Cross-reaction and coaggregation vs. seeding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112, 2443–2448 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ano Bom A. P. D., et al., Mutant p53 aggregates into prion-like amyloid oligomers and fibrils: Implications for cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 28152–28162 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Harris J. R., De Carlo S., “Negative staining and cryo-negative staining: Applications in biology and medicine” in Electron Microscopy: Methods and Protocols, Kuo J., Ed. (Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, 2014), pp. 215–258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hawe A., Sutter M., Jiskoot W., Extrinsic fluorescent dyes as tools for protein characterization. Pharm. Res. 25, 1487–1499 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Frare E., et al., Characterization of oligomeric species on the aggregation pathway of human lysozyme. J. Mol. Biol. 387, 17–27 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Munishkina L. A., Fink A. L., Fluorescence as a method to reveal structures and membrane-interactions of amyloidogenic proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1768, 1862–1885 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Wang G., Fersht A. R., Multisite aggregation of p53 and implications for drug rescue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 114, E2634–E2643 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ellis R. J., Minton A. P., Cell biology: Join the crowd. Nature 425, 27–28 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Vitalis A., Pappu R. V., Assessing the contribution of heterogeneous distributions of oligomers to aggregation mechanisms of polyglutamine peptides. Biophys. Chem. 159, 14–23 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Davtyan A., et al., AWSEM-MD: Protein structure prediction using coarse-grained physical potentials and bioinformatically based local structure biasing. J. Phys. Chem. B 116, 8494–8503 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kamagata K., et al., Liquid-like droplet formation by tumor suppressor p53 induced by multivalent electrostatic interactions between two disordered domains. Sci. Rep. 10, 580 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Debenedetti P. G., Thermodynamics: When a phase is born. Nature 441, 168–169 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Vekilov P. G., Chernov A. A., “The Physics of protein crystallization” in Solid State Physics, Ehrenreich H., Spaepen F., Eds. (Academic Press, New York, 2002), vol. 57, pp. 1–147. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Xu Y., et al., Steady, symmetric, and reversible growth and dissolution of individual amyloid-β fibrils. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 10, 2967–2976 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kashchiev D., Cabriolu R., Auer S., Confounding the paradigm: Peculiarities of amyloid fibril nucleation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 1531–1539 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Gibbs J. W., On the equilibrium of heterogeneous substances, First Part. Trans. Connect. Acad. Sci. 3, 108–248 (1876). [Google Scholar]
- 63.Gibbs J. W., On the equilibrium of heterogeneous substances (concluded). Trans. Connect. Acad. Sci. 3, 343–524 (1878). [Google Scholar]
- 64.Gibbs J. W., The Scientific Papers of J.W. Gibbs: Thermodynamics (Oxbow Press, Woodbridge, CT, 1993), vol. 1. [Google Scholar]
- 65.Kashchiev D., Nucleation. Basic Theory with Applications (Butterworth, Heinemann, Oxford, 2000), p. 529. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Zheng W., Tsai M.-Y., Chen M., Wolynes P. G., Exploring the aggregation free energy landscape of the amyloid-β protein (1-40). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 113, 11835–11840 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Vekilov P. G., Nucleation. Cryst. Growth Des. 10, 5007–5019 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Galkin O., et al., Two-step mechanism of homogeneous nucleation of sickle cell hemoglobin polymers. Biophys. J. 93, 902–913 (2007). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Lu L., et al., Quantitative prediction of erythrocyte sickling for the development of advanced sickle cell therapies. Sci. Adv. 5, eaax3905 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Crick S. L., Ruff K. M., Garai K., Frieden C., Pappu R. V., Unmasking the roles of N- and C-terminal flanking sequences from exon 1 of huntingtin as modulators of polyglutamine aggregation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 20075–20080 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Posey A. E., et al., Profilin reduces aggregation and phase separation of huntingtin N-terminal fragments by preferentially binding to soluble monomers and oligomers. J. Biol. Chem. 293, 3734–3746 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Lansbury P. T., Lashuel H. A., A century-old debate on protein aggregation and neurodegeneration enters the clinic. Nature 443, 774–779 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Bell S., Klein C., Müller L., Hansen S., Buchner J., p53 contains large unstructured regions in its native state. J. Mol. Biol. 322, 917–927 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Wong K. B., et al., Hot-spot mutants of p53 core domain evince characteristic local structural changes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96, 8438–8442 (1999). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Gill S. C., von Hippel P. H., Calculation of protein extinction coefficients from amino acid sequence data. Anal. Biochem. 182, 319–326 (1989). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Vorontsova M. A., Vekilov P. G., Maes D., Characterization of the diffusive dynamics of particles with time-dependent asymmetric microscopy intensity profiles. Soft Matter 12, 6926–6936 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Safari M. S., Poling-Skutvik R., Vekilov P. G., Conrad J. C., Differential dynamic microscopy of bidisperse colloidal suspensions. NPJ Microgravity 3, 21 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Guex N., Peitsch M. C., SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: An environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 18, 2714–2723 (1997). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Souaille M., Roux B., Extension to the weighted histogram analysis method: Combining umbrella sampling with free energy calculations. Comput. Phys. Commun. 135, 40–57 (2001). [Google Scholar]
- 80.Rokach L., Maimon O., “Clustering methods” in Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery Handbook, Maimon O., Rokach L., Eds. (Springer US, Boston, MA, 2005), pp. 321–352. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All study data are included in the article and/or SI Appendix.