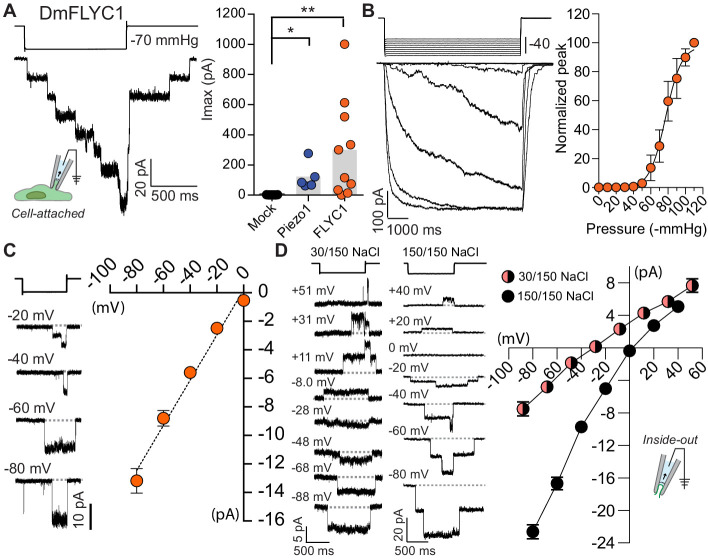
Figure 4. FLYC1 induces stretch-activated currents.
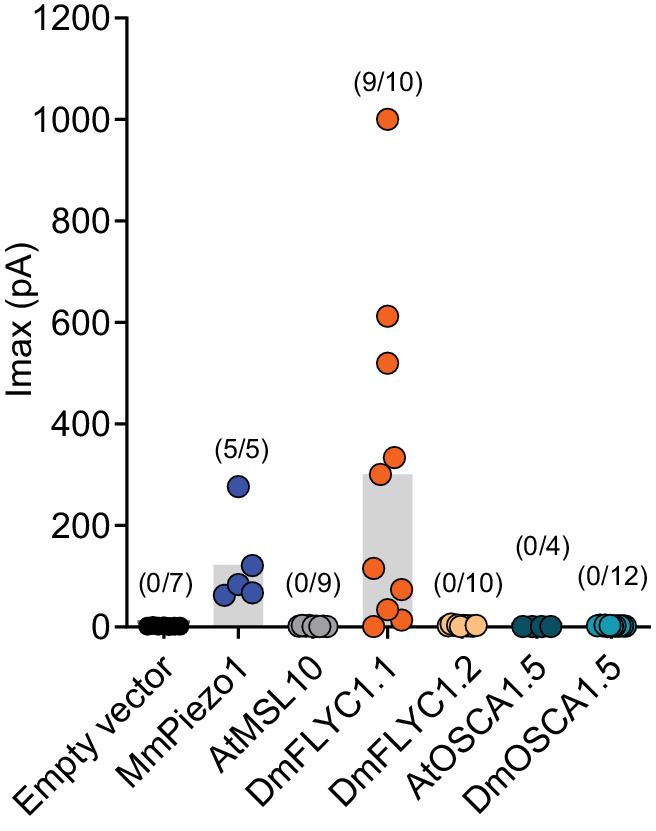
(A) Left, representative trace of stretch-activated current recorded from FLYC1-expressing HEK-P1KO cells in the cell-attached patch clamp configuration at −80 mV membrane potential in response to −70 mmHg pipette pressure. Stimulus trace illustrated above the current trace. Right, quantification of maximal current response from cells transfected with mock (N = 7), mouse PIEZO1 (N = 5), or FLYC1 plasmid (N = 10). p=0.0251 (mock vs. PIEZO1); p=0.0070 (mock vs. FLYC1); Dunn’s multiple comparison test. (B) Left, currents in response to graded negative pressure steps from 50 to 90 mmHg (Δ5 mmHg) at −60 mV membrane potential. Right, average pressure–response curve normalized to peak current across cells (pressure–response curve for absolute peak values is plotted in Figure 4—figure supplement 2). A fit with Boltzmann equation revealed P50 value of 77 mmHg (N = 9). (C) Left, representative single-channel traces in response to stretch at the indicated membrane potential. Right, average I–V relationship of stretch-activated single-channel currents from FLYC1-transfected cells (N = 6). (D) Left, representative stretch-activated single-channel currents recorded from excised inside-out patch configuration in asymmetrical or symmetrical NaCl solution at the indicated membrane potential. Right, average I–V of stretch-activated single-channel currents in asymmetrical NaCl solution (N = 7, red/black circles) or symmetrical NaCl solution (N = 8, black cirlces). Data for both conditions were collected from separate patches/cells. Scatter plots in B–D are mean ± s.e.m.
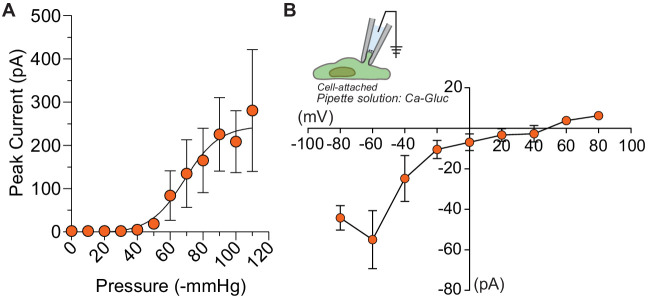
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. DmFLYC2 and DmOSCA functionality.