Abstract
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
MCI was recently subdivided into sd-aMCI, sd-fMCI, and md-aMCI. The current investigation aimed to discriminate between MCI subtypes by using DTI.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
Sixty-six prospective participants were included: 18 with sd-aMCI, 13 with sd-fMCI, and 35 with md-aMCI. Statistics included group comparisons using TBSS and individual classification using SVMs.
RESULTS:
The group-level analysis revealed a decrease in FA in md-aMCI versus sd-aMCI in an extensive bilateral, right-dominant network, and a more pronounced reduction of FA in md-aMCI compared with sd-fMCI in right inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus and inferior longitudinal fasciculus. The comparison between sd-fMCI and sd-aMCI, as well as the analysis of the other diffusion parameters, yielded no significant group differences. The individual-level SVM analysis provided discrimination between the MCI subtypes with accuracies around 97%. The major limitation is the relatively small number of cases of MCI.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our data show that, at the group level, the md-aMCI subgroup has the most pronounced damage in white matter integrity. Individually, SVM analysis of white matter FA provided highly accurate classification of MCI subtypes.
Although there are currently no proven disease-modifying treatments for AD, several promising candidates have been evaluated to date.1,2 However, recent studies pointed to their limited performance in patients with clinically overt dementia.3,4 To date, the identification of patients at high risk for rapid cognitive decline is considered a prerequisite for future curative strategies in AD.
MCI represents a transition zone between normal aging and very early dementia, characterized by selective memory deficits associated, or not, with other cognitive dysfunctions.5 It was originally conceived as a functionally nondisabling amnestic disorder that was later expanded to include essentially any form of cognitive complaints.6 Based on the patterns of neuropsychologic deficits, MCI was recently subdivided into sd-aMCI with isolated memory impairment; sd-fMCI, characterized by early deficits confined to executive functions; and md-aMCI, which displays widespread cognitive dysfunctions that affect memory and also language, attention, and/or visuospatial abilities. For instance, md-aMCI is thought to progress to clinically overt AD with an annual rate of 10%–15%,6,7 whereas the other subgroups of MCI may remain stable or evolve to other forms of dementia.8
Structural MR imaging was initially used to differentiate patients with MCI from healthy controls in cross-sectional studies. Most earlier MR neuroimaging studies focused on the investigation of gray matter using voxel-based morphometry9 in MCI.10–15 A series of voxel-based morphometric studies revealed volume differences between patients with MCI and controls mainly distributed within the precuneus and cingulate gyrus.16 More recently, several contributions on various neurodegenerative diseases reported that the changes in WM microstructure assessed with DTI may be a more sensitive parameter compared with gray matter data17–21 for detecting mild structural changes occurring at the early stages of the degenerative process. Applying DTI analyses with voxelwise TBSS,22 an increasing number of contributions described the damage of long interhemispheric and intrahemispheric white matter tracts with homogeneously oriented fibers (ie, genu or splenium of the corpus callosum, superior longitudinal fasciculus, cingulus) and, more rarely, in frontal, parietal, and temporal white matter in patients with MCI compared with healthy controls.23–31
The biologic relevance of the description of MCI subtypes is still a challenging issue. In particular, it is unclear whether the neuropsychologic definition of these subtypes corresponds to distinct patterns of brain compromise. Earlier studies focusing on brain atrophy patterns reported a predominant mesio-inferior temporal lobe involvement in sd-aMCI and progressive damage of other neocortical association areas in md-aMCI. Cases of nonamnestic MCI are thought to have increased vascular burden as well as focal atrophy of basal forebrain and hypothalamus.32–35 In contrast to gray matter, MR imaging investigations of WM integrity in MCI subtypes are still very rare.36–38 They neither included the whole spectrum of MCI subtypes nor explored the usefulness of DTI parameters on the individual classification of cases of MCI. We recently investigated FA patterns in prospectively documented patients with MCI compared with healthy controls and reported their use in the a priori identification of progressive MCI.30 To explore the morphologic WM changes that characterize each subtype of MCI, we assessed all DTI parameters and developed models of automatic individual classification in a community-based series of cases of sd-aMCI, md-aMCI, and sd-fMCI. First, a group-level analysis using TBSS,22 an improved voxel-based technique with respect to spatial normalization, was performed to identify regions with altered white matter structure between groups. As discussed above, recent investigations implementing this technique in the domain of MCI23,24,28 documented the presence of reduced FA primarily in white matter tracts with homogeneously oriented fibers (ie, genu or splenium of the corpus callosum, superior longitudinal fasciculus, cingulus) and, more rarely, in frontal, parietal, and temporal white matter. However, other studies led to negative data challenging this point of view.39 While such group-level data are fascinating from a research perspective, these cannot be applied in clinical neuroradiology for the diagnosis of individual patients. In addition to MCI subgroup comparisons, we report here an individual-level classification analysis to explore the association between WM changes and MCI subtype by using SVM analysis.40 The basic principle of such pattern recognition analyses can be illustrated in the example of face recognition. A single feature, for example, the nose, is generally not sufficient to detect an individual subject—even though the nose might show group differences, for example, between females and males. In contrast, individual faces can be identified by the combination of multiple features such as nose, ear, chin, eyebrow, and so on, even though each feature per se is not necessarily significantly different between groups (for a more detailed description of pattern recognition analyses, see Haller et al41). Originating from machine learning, this technique provided individual risk scores for MCI conversion to AD on the basis of gray matter voxel-based morphometry16,42–45 and WM DTI data.30 In contrast to these studies that focused on the discrimination between MCI versus controls, or stable versus progressive MCI, this work aims to explore the neuroradiologic background of the previously cited subgroups of MCI and to provide MR imaging tools for the individual classification of MCI subtypes.
Materials and Methods
Participants
After formal approval by the local ethics committee, informed written consent was obtained from all participants before inclusion in this study. Sixty-six right-handed elderly subjects (66.2 ± 5.0 years; 37 women) were recruited by using announcements in local newspapers. All participants with MCI had normal or corrected-to-normal visual acuity, and none reported a history of major medical disorders (cancer, cardiac illness), sustained head injury, psychiatric or neurologic disorders, or alcohol or drug abuse. All participants characterized by regular use of psychotropics, stimulants, and beta blockers, as well as those with severe physical illness that precluded the participation in either phase of the project, were excluded. The education level was defined according to the Swiss scholar system, where level 1 = less than 9 years (primary school), level 2 = between 9 and 12 years (high school), and level 3 = more than 12 years (university).
All subjects were screened with the Mini-Mental State Examination,46 the Lawton Instrumental Activities of Daily Living,47 and the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale.48 In addition, extensive neuropsychologic testing was performed on the basis of fully validated tools, with normative age- and education-corrected norms in Europe. It included attention (Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-Revised Code, Trail-Making Test A), working memory (verbal: Forward Digit Span Test;49 visuo-spatial: Corsi Block-Tapping Test50), episodic memory (verbal: Buschke Double Memory Test 48 items;51 visual: Shapes Test52), executive functions (Trail-Making Test A,53 Verbal Fluency Test,54,55 Wisconsin Card Sorting Test56), language (Boston Naming Test57), visual gnosis (Ghent Overlapping Figures Test58), and praxies (ideomotor,59 reflexive,60 and constructional61 tests). Global cognitive function was assessed by the Clinical Dementia Rating scale.62 Participants having a test score more than 1.5 standard deviations below the age-appropriate mean in any of the above tests, and a Clinical Dementia Rating score of 0.5 but no dementia, were diagnosed with possible MCI.63 Patients with MCI were further divided into subtypes based on the extensive neuropsychologic testing, according to the criteria by Petersen and collaborators64 as follows:
sd-aMCI: impaired memory function for age and education; decreased performance in the Buschke Double Memory Test 48 items.
sd-fMCI: impairment in a single cognitive domain other than memory, most commonly frontal alteration; decreased performance in the visual Shapes Test and/or the Trail Making Test B.
md-aMCI: multiple areas of cognitive impairment that fall outside of predicted norms, but none sufficiently severe to constitute dementia; decreased performance in the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test and/or the Trail-Making Test A and/or the Corsi Block-Tapping test.65
These patients were reviewed independently by 2 highly experienced clinicians, blinded to each other's findings, and were included in the respective MCI groups only if both clinicians concurred on the diagnosis. The final sample included 18 patients with sd-aMCI (65.8 ± 5.4 years; 7 women), 13 patients with sd-fMCI (67.0 ± 4.7 years; 8 women), and 35 patients with md-aMCI (66.2 ± 5.23 years; 22 women). In agreement with community-based data in this field, there was a predominance of patients with md-aMCI in our sample. Moreover, sd-fMCI had a prevalence close to that of sd-aMCI.66
MR Imaging
MR imaging was performed on a 3T clinical routine whole-body scanner (Magnetom Trio; Siemens, Erlangen, Germany). We used a standard DTI sequence: 12 diffusion directions isotropically distributed on a sphere, 1 B0 image with no diffusion weighting, 128 × 128 × 64 matrix, 1.8 × 1.8 × 2.0 mm voxel size, TE 76 ms, TR 7800 ms, 1 average, 2:48 minutes. Additional sequences (3D T1WI, 8:42 minutes; T2WI, 4:02 minutes; 3D FLAIR, 7:02 minutes) were acquired and analyzed to exclude brain pathology such as ischemic stroke, subdural hematomas, or space-occupying lesions. In particular, white matter lesions were analyzed according to the Fazekas score.67
Statistical Analysis
Demographic and Clinical Data.
Demographic and clinical characteristics, as well as neuropsychologic values were compared among groups by using the nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis group test. A pair-wise Dunn Multiple Comparison posttest was performed if overall P was < .05.
DTI TBSS Analysis.
Preprocessing of the FA data was carried out by using the standard procedure of TBSS, as described in detail before22,68 in the FSL software package (http://www.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/fsl),69 notably obtaining a spatial normalization of the DTI data, which is the basis for the following analyses. In principle, TBSS projects all subjects' FA data onto a mean FA tract skeleton by using nonlinear registration. The tract skeleton is the basis for voxelwise cross-subject statistics and reduces potential misregistrations as the source for false-positive or false-negative analysis results. The other DTI-derived parameters—longitudinal, radial, and mean diffusivity were analyzed in the same way by using spatial transformation parameters that were estimated in the initial FA analysis. Voxelwise statistical analyses were corrected for multiple comparisons implementing threshold-free cluster enhancement, considering fully corrected P values <.05 as significant.70 Age and sex were used as nonexplanatory coregressors. We used the Johns Hopkins University DTI-based white matter atlases (http://www.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/fsldownloads/), which is distributed in the FSL package, for anatomic labeling of the suprathreshold voxels.
SVM Individual Classification Analysis.
The individual SVM classification analysis is, in principle, identical to a previous study.30 The individual classification was analyzed in the freely available WEKA software package (Version 3.6.1; http://www.cs.waikato.ac.nz/ml/weka/). It is based on the TBSS preprocessed data, which notably include a spatial normalization into Montreal Neurological Institute; standard space and a selection of the voxels of the white matter skeleton. This dataset contained 149,775 voxels. After conversion of the preprocessed DTI FA data in a WEKA-compatible data format, 3 separate analyses were performed for the differences between each pair of MCI subgroups. The analysis included 2 steps. In the first step, we performed a feature selection. The rationale behind this step is that not all voxels discriminate between groups. On the one hand, inclusion of nondiscriminative voxels results in overlapping features (or voxels), which reduces the accuracy of the classification. On the other hand, exclusion of discriminative features also reduces the accuracy of the classification. To identify the optimum number of voxels, we used the feature selection algorithm “RELIEFF.”71 In principle, this method ranks features (or voxels) that distinguish most between classes. These are known as the relevant features. To avoid selection-related bias, we selected the top 1000 features implementing 10 repetitions of a 10-fold cross-validation. This means that the data were divided into 10 parts; 9 parts were used for training and the remaining part was used for testing. This was repeated 10 times such that each part was once used for testing. To further reduce selection-related bias, we repeated this entire process 10 times. The second step consisted of the “actual” classification analyses for each comparison by using the SVM algorithm “sequential minimal optimization”72 (distributed in the WEKA package) with a radial basis function kernel.73 We chose the commonly used radial basis function kernel, which nonlinearly maps samples into a higher dimensional space, because this kernel provided slightly better classification accuracy in the present study and in a related previous study30 than a linear kernel. Unlike linear kernels, radial basis function can handle the case when the relation between class labels and attributes is nonlinear. There are 2 parameters while using radial basis function kernels: C and GAMMA. GAMMA represents the width of the radial basis function, and C represents the error/trade-off parameter that adjusts the importance of the separation error in the creation of the separation surface. Based on our previous experience, GAMMA was iteratively explored from 0.01 to 0.09, with an increment of 0.01, while C was fixed to 1.00. Equivalent to the feature selection discussed above, we implemented 10 repetitions of a 10-fold cross-validation to reduce selection-related bias. We present the average results of 10 repetitions of 10-fold cross-validations for the best parameter settings. The 3 MCI subgroups were pair-wise compared in 3 distinct SVM analyses.
Results
Clinical Data
The distribution of MCI subtypes in our series was similar to that previously reported in community-based series.65,66 Age, sex, education, and Fazekas score did not differ significantly between the 3 groups (Table 1). Among cases of MCI, patients with sd-aMCI had a significantly lower Buschke total score than both patients with md-aMCI and those with sd-fMCI (Table 2). In contrast, patients with sd-aMCI were quicker in the Trail-Making Test B than both patients with md-aMCI and sd-fMCI, and in the Trail-Making Test A compared with patients with md-aMCI. Patients with md-aMCI had significantly lower Corsi scores than those with sd-fMCI (P = .008).
Table 1:
Demographic and clinical characteristics
| Variables | sd-aMCI | md-aMCI | sd-fMCI | sd-aMCI Compared with md-aMCI | sd-aMCI Compared with sd-fMCI | md-aMCI Compared with sd-fMCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 65.8 ± 5.4 | 66.2 ± 5.2 | 67.0 ± 4.7 | .897 (NS) | .445 (NS) | .358 (NS) |
| Gender (F/M) | 7/11 | 22/13 | 8/5 | .100 (NS) | .220 (NS) | .933 (NS) |
| Education | 2.6 ± 0.6 | 1.9 ± 0.7 | 1.9 ± 0.8 | .019 (NS) | .120 (NS) | .284 (NS) |
| MMSE | 28.4 ± 1.5 | 27.7 ± 1.8 | 28.5 ± 1.5 | .115 (NS) | .884 (NS) | .141 (NS) |
| IADL | 8.8 ± 0.8 | 8.3 ± 0.8 | 7.8 ± 1.2 | .018 (NS) | .016 (NS) | .310 (NS) |
| HAD (anxiety) | 4.8 ± 3.3 | 6.1 ± 3.0 | 5.9 ± 3.0 | .147 (NS) | .176 (NS) | .726 (NS) |
| HAD (depression) | 1.9 ± 1.9 | 2.1 ± 1.7 | 2.9 ± 3.3 | .645 (NS) | .514 (NS) | .382 (NS) |
| Fazekas score | 0.7 ± 0.5 | 1.1 ± 0.9 | 1.2 ± 1.0 | .090 (NS) | .851 (NS) | .148 (NS) |
Note:—Data are presented as mean ± SD. Demographic and clinical characteristics did not differ between the 3 groups. NS refers to the Dunn Multiple comparison test adjusted P-value threshold for each demographic and clinical characteristic. sd-fMCI, n = 13; sd-aMCI, n = 18; md-aMCI, n = 35. HAD indicates Hospital Anxiety & Depression; IADL, Instrumental Activities of Daily Living; MMSE, Mini-Mental State Examination.
Table 2:
Neuropsychologic data
| Variables | sd-aMCI | md-aMCI | sd-fMCI | sd-aMCI Compared with md-aMCI | sd-aMCI Compared with sd-fMCI | md-aMCI Compared with sd-fMCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attention | ||||||
| WAIS-R; Code | 63.1 ± 11.4 | 55.0 ± 13.1 | 53.0 ± 12.8 | .01461 (NS) | .1458 (NS) | .3150 (NS) |
| Trail-Making Test A (s) | 35.7 ± 7.3 | 47.9 ± 18.1 | 45.0 ± 11.3 | .001 (S) | .151 (NS) | .4354 (NS) |
| Working Memory | ||||||
| Verbal (Digit) | 6.8 ± 2.2 | 6.1 ± 1.6 | 7.0 ± 1.8 | .233 (NS) | .839 (NS) | .135 (NS) |
| Visuospatial (Corsi) | 5.7 ± 1.4 | 4.4 ± 1.4 | 5.9 ± 1.1 | .008 (NS) | .246 (NS) | .0015 (S) |
| Episodic Memory | ||||||
| Verbal (Buschke 48) | ||||||
| Total score | 19.2 ± 4.2 | 23.63 ± 6.0 | 24.62 ± 2.3 | .0004 (S) | .0003 (S) | .201 (NS) |
| Immediate recall | 38.0 ± 5.2 | 37.3 ± 3.4 | 39.5 ± 3.9 | .720 (NS) | .376 (NS) | .230 (NS) |
| Differed cued recall | 18.4 ± 3.7 | 23.6 ± 6.4 | 24.6 ± 2.3 | .163 (NS) | .395 (NS) | .900 (NS) |
| Intrusions | 3.8 ± 3.5 | 4.0 ± 2.9 | 3.6 ± 4.9 | .501 (NS) | .597 (NS) | .202 (NS) |
| Visual (Shapes) | 11.8 ± 0.7 | 11.0 ± 1.5 | 12.0 ± 0.0 | .147 (NS) | .443 (NS) | .049 (NS) |
| Executive functions | ||||||
| Trail-Making Test B (s) | 54.2 ± 14.3 | 90.3 ± 41.0 | 96.50 ± 41.3 | .000032 (S) | .00015 (S) | .33006 (NS) |
| Verbal Fluency | 22.7 ± 6.9 | 22.5 ± 7.1 | 21.2 ± 6.1 | .798 (NS) | .335 (NS) | .709 (NS) |
| Wisconsin | 5.6 ± 2.1 | 4.7 ± 1.8 | 4.0 ± 2.5 | .104 (NS) | .049 (NS) | .407 (NS) |
| Language (Boston) | 19.4 ± 0.8 | 19.1 ± 0.9 | 19.6 ± 0.7 | .157 (NS) | .570 (NS) | .055 (NS) |
| Visual gnosis (Ghent) | 5.0 ± 0.0 | 5.0 ± 0.0 | 5.0 ± 0.0 | .500 (NS) | .500 (NS) | .500 (NS) |
| Standardized praxies | ||||||
| Ideomotor | 19.1 ± 1.0 | 18.9 ± 1.3 | 19.2 ± 1.1 | .188 (NS) | .148 (NS) | .919 (NS) |
| Reflexive | 7.7 ± 0.5 | 7.0 ± 1.0 | 6.9 ± 0.9 | .0161 (NS) | .0139 (NS) | .2942 (NS) |
| Constructional | 9.6 ± 0.9 | 9.1 ± 1.2 | 3.4 ± 0.5 | .806 (NS) | .371 (NS) | .499 (NS) |
Note:—Data are presented as mean ± SD. sd-fMCI, n = 13; sd-aMCI, n = 18; md-aMCI, n = 35. S and NS refer to the significant and nonsignificant Dunn multiple comparison test adjusted P-value threshold for each demographic and clinical characteristic. Wisconsin: number of completed categories (/6); ideomotor praxis: transitive and intransitive (/30). WAIS-R indicates Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-Revised.
TBSS Group Differences
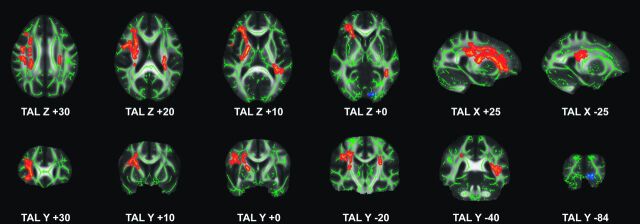
Compared with patients with sd-aMCI, those with md-aMCI had significantly reduced FA in a bilateral, right-dominant network, including right uncinate fasciculus, forceps minor, and internal capsule as well as bilateral inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus, anterior thalamic radiation, superior longitudinal fasciculus, inferior longitudinal fasciculus, and corticospinal tract (Fig 1, Table 3). The inverse comparison and the analysis of longitudinal diffusivity, radial diffusivity, or mean diffusivity yielded no significant differences. Importantly, md-aMCI displayed a significant FA decrease in right inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus and inferior longitudinal fasciculus compared with sd-fMCI (Fig 1, Table 3). Again, the inverse comparison and the analysis of longitudinal diffusivity, radial diffusivity, or mean diffusivity yielded no significant differences. The comparison between sd-aMCI and sd-fMCI yielded no significant differences.
Fig 1.
TBSS analysis between MCI subtypes. md-aMCI compared with sd-aMCI had significantly reduced FA (red to yellow) in a bilateral right-dominant network including right uncinate fasciculus, forceps minor, and internal capsule, as well as bilateral inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus, anterior thalamic radiation, superior longitudinal fasciculus, inferior longitudinal fasciculus, and corticospinal tract. md-aMCI compared with sd-fMCI had less pronounced reduction in FA in right inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus and inferior longitudinal fasciculus (blue to light blue). Axial, sagittal, and coronal sections at the indicated position in Montreal Neurological Institute; standard space coordinates (radiologic convention with right hemisphere on left-hand side). Gray, mean FA value; green, average skeleton. Threshold-free cluster enhancement–corrected for multiple comparisons at P < .05. Suprathreshold voxels were enlarged by using TBSS fill (part of FSL) for illustrative purposes.
Table 3:
List of suprathreshold clusters (threshold-free cluster enhancement–corrected at P < .05) for the comparison of MCI subgroups
| Cluster Index | Voxels | Z-MAX | Z-MAX X (mm) | Z-MAX Y (mm) | Z-MAX Z (mm) | Z-COG X (mm) | Z-COG Y (mm) | Z-COG Z (mm) | Side | Anatomic Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sd-fMCI versus md-aMCI | ||||||||||
| 1 | 40 | .952 | −12 | −86 | −7 | −12.8 | −85.2 | −4.18 | Right | Inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus (occipital) |
| Inferior longitudinal fasciculus (occipital) | ||||||||||
| 2 | 12 | .951 | −7 | −84 | −3 | −7.17 | −83.8 | −2.5 | Right | Inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus (occipital) |
| Inferior longitudinal fasciculus (occipital) | ||||||||||
| sd-aMCI versus md-aMCI | ||||||||||
| 1 | 3409 | .973 | 25 | 28 | 0 | 29.6 | 4.3 | 20.3 | Right | Inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus (frontal) |
| Uncinate fasciculus | ||||||||||
| Anterior thalamic radiation | ||||||||||
| Internal capsule | ||||||||||
| Superior longitudinal fasciculus | ||||||||||
| Corticospinal tract | ||||||||||
| 2 | 694 | .966 | −25 | −24 | 24 | −32.4 | −35.5 | 13.1 | Left | Anterior thalamic radiation |
| Superior longitudinal fasciculus | ||||||||||
| Corticospinal tract | ||||||||||
| Inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus | ||||||||||
| Inferior longitudinal fasciculus | ||||||||||
| 3 | 175 | .959 | 15 | −8 | 56 | 16.4 | −7.61 | 52.9 | Right | Superior longitudinal fasciculus |
| 4 | 66 | .954 | 17 | 47 | −9 | 17.1 | 48.9 | −6.96 | Right | Forceps minor |
| Uncinate fasciculus | ||||||||||
| Anterior thalamic radiation |
Note:—Cluster index, number of suprathreshold voxels in cluster, maximum P value, location of maximum P value per cluster in Montreal Neurological Institute; standard space (X, Y, Z), and center of gravity of the cluster in NMI standard space (X, Y, Z).
SVM Individual Classification Analysis
Confirming the strength of the association between these patterns of WM changes and MCI subtypes, SVM analysis of FA provided a correct classification between the MCI subgroups with accuracies of 98.40 (±5.90)% for md-aMCI versus sd-fMCI; 97.70 (±6.61)% for md-aMCI versus sd-aMCI; and 99.67 (±3.33)% for sd-fMCI versus sd-aMCI (Table 4).
Table 4:
Individual SVM classification based on DTI FA TBSS
| md-aMCI versus sd-fMCI | md-aMCI versus sd-aMCI | sd-fMCI versus sd-aMCI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of subjects | 34/11 | 34/15 | 11/15 |
| Chance rate | 0.76 | 0.69 | 0.58 |
| SVM analysis | |||
| Accuracy | 98.40 (5.90) | 97.70 (6.61) | 99.67 (3.33) |
| TP rate | 1.00 (0.00) | 1.00 (0.00) | 1.00 (0.00) |
| FP rate | 0.06 (0.23) | 0.07 (0.20) | 0.01 (0.05) |
| TN rate | 0.94 (0.23) | 0.94 (0.20) | 1.00 (0.05) |
| FN rate | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) |
Note:—Accuracy, true-positive (TP), false-positive (FP), true-negative (TN), and false-negative (FN) rates for individual classifications using a SVM classifier. Note that the accuracy is calculated as average accuracy of 10 repetitions using 10-fold cross-validation (average and standard deviation).
Discussion
Our investigation led to 2 main findings. Paralleling the multiple cognitive deficits that characterize their clinical expression, patients with md-aMCI displayed a more widespread damage of long interhemispheric pathways, mainly in the right hemisphere compared with the single-MCI subgroups. The most relevant data concern the possibility of using the SVM technique to correctly classify each patient in the MCI subgroups with an accuracy higher than 95%.
DTI Parameters in MCI Subtypes
Among the different DTI parameters studied, only the FA correlated with the clinical diagnosis of MCI subtypes. Interestingly, the other DTI-derived diffusion parameters—longitudinal diffusivity, mean diffusivity, and radial diffusivity—yielded no significant group differences. This is consistent with a recent (2012) study by Bosch and colleagues,28 indicating that FA more closely correlates to the cognitive profile than longitudinal diffusivity or radial diffusivity in patients with MCI and healthy controls. However, another recent TBSS study assessing the same diffusion parameters in clinically overt AD cases compared with healthy controls led to the opposite results.74 The few available recent investigations on the different diffusion parameters in normal aging, MCI, and AD28,74–77 provided inconsistent data with respect to the regional differences in the distribution of significant changes in FA, longitudinal diffusivity, radial diffusivity, and mean diffusivity. For example, in the above mentioned study of subjects with MCI and AD, FA was more closely related to the cognitive profile than longitudinal diffusivity or radial diffusivity.28 In contrast, another study in AD showed stronger differences in longitudinal diffusivity, radial diffusivity, and mean diffusivity than FA.74 It is likely that the sensitivity of the different diffusion parameters may vary substantially as a function of the disease severity. Research using these different diffusion indices is still at an early stage, as is our understanding of the relevance of longitudinal diffusivity and radial diffusivity changes in terms of myelin or axonal damage. FA changes without parallel modifications in other diffusion parameters as those observed in our cases of MCI support the idea of group differences at the level of fiber tract coherence rather than myelin or axonal integrity loss.78 In clinically overt AD, the predominance of myelin loss is accompanied by concomitant changes in DTI parameters. Finally, wallerian degeneration suggested by increased mean diffusivity, without significant changes in FA, may take place only in advanced stages of the degenerative process.79 Future work is clearly warranted to elucidate the biologic significance of DTI parameter changes over time in aging, MCI, and AD.
TBSS Analysis
The number of previous DTI studies of MCI subtypes implementing a similar voxelwise TBSS analysis is still limited. Most investigations included only 1 (not further specified) MCI group,23–25 or only the sd-aMCI subtype,26–29 or a mix of several subtypes, with the aim of discriminating stable versus progressive MCI.30 Only 3 recent contributions compared DTI patterns in aMCI versus non-MCI.36,37 In their study of 55 patients with aMCI and 41 patients with non-MCI, Chua et al36 reported significantly lower FA in the splenium of corpus callosum and significantly higher mean diffusivity in the left parahippocampal subgyrus in the aMCI compared with the non-MCI group. Zhuang et al37 included 96 patients with aMCI and 69 patients with non-MCI. Despite the higher number of cases, the comparison between aMCI versus non-MCI yielded no significant differences in this investigation. A possible explanation for this observation might be the heterogeneous constitution of the non-MCI group, which included cases with various neuropsychologic profiles (and presumably FA-related patterns). Another recent study by O'Dwyer et al31 implemented a very similar analysis approach as did our previous work in stable versus progressive MCI.30 The use of SVM analysis of TBSS-preprocessed DTI data provided highly accurate discriminations of patients with MCI versus controls, patients with aMCI versus patients with non-MCI and controls, as well as patients with non-MCI versus patients with aMCI and controls. In contrast to the present study, O'Dwyer et al31 did not specifically assess the classification between MCI subtypes. Moreover, this contribution explored only aMCI and non-MCI, while the current study uses a more detailed discrimination of MCI into 3 subtypes. Using a careful neuropsychologic characterization, the present study is the first, to our knowledge, that describes distinct patterns of WM changes among the 3 MCI subtypes. The widespread involvement of long intrahemispheric connections within the right hemisphere in md-aMCI compared with sd-aMCI is expected, as it corresponds to the progressive deterioration of several cognitive functions other than memory preceding the conversion to AD. These anatomic observations fit with functional data collected in the same cohort, revealing altered right hemispheric electrophysiologic patterns during face recognition in md-aMCI compared with sd-aMCI.80 The more pronounced damage of inferior fronto-occipital and inferior longitudinal fasciculi in md-aMCI compared with sd-fMCI is in agreement with the retrogenesis hypothesis in AD that postulates an early involvement of late-myelinating pathways in the initial phases of the degenerative process.29,31 The comparison between sd-fMCI and sd-aMCI yielded no significant group differences. There are 2 possible explanations for this result. First, md-aMCI is known to be a very heterogeneous group that covers not only the linear evolution of sd-aMCI over time but also several AD pathology-independent causes of dementia.81 Alternatively, the small number of cases included in the sd-aMCI group may be not sufficient to identify subtle MR imaging differences compared with sd-fMCI. Supporting the idea that sd-fMCI cases form an etiopathogenetically distinct group, possibly not evolving to AD, a recent study by Grambaite et al82 reported increased radial and mean diffusivities in rostral middle frontal, medial orbitofrontal, caudal anterior cingulate, posterior cingulate, and retrosplenial cortices that correlated with attention/executive deficits in these cases. Further investigations in larger cohorts, including longitudinal follow-up of the different MCI subtypes, are needed to explore the biologic substrates of cognitive deficits in sd-fMCI.
SVM Individual Classification Analysis
Neuroimaging research has been dominated for decades by group-level comparisons, typically of a patient group versus a control group, with the aim of identifying group-related changes in brain morphometry. While such group-level studies provide fascinating insights into disease-related morphometric alterations from a research perspective, these group-level results cannot be transferred into clinical neuroradiology to identify the early stages of the dementing process at an individual level. To obtain individual discrimination between MCI subgroups, we adopted a complex methodology including a processing chain of TBSS preprocessing of DTI FA data, feature selection of the most discriminative voxels, and subsequent SVM classification.30,83 The classification accuracy of approximately 97% for all MCI subtypes in our series implies that only 1 subject was incorrectly classified, regardless of MCI subgroup. Note that the inclusion of a control group is not necessary for such individual-level classification analyses, as a classifier that perfectly discriminates, for example, 1 MCI subtype versus healthy controls may not necessarily also discriminate between the different MCI subtypes. In fact, the brain regions (or features) that best discriminate between MCI subtypes are probably different from those regions that best discriminate between patients with MCI and healthy controls. The implemented individual-level classification analysis is fundamentally different from the “classic” group-level comparisons and explains why we did not include a healthy control group in this study.
At first glance, it might appear counterintuitive that the SVM individual classification was very successful in discriminating sd-fMCI versus sd-aMCI, despite the absence of threshold-free cluster enhancement–corrected suprathreshold differences for the corresponding TBSS group comparison. This can, however, be readily explained by the major conceptual differences between these techniques. For the TBSS group-level analysis, around 150,000 voxels are analyzed. This large amount of multiple comparisons requires strict multiple-comparisons correction. In contrast, the SVM analysis creates only 1 parameter per case and hence there is no need for multiple comparisons. In addition, TBSS analyzes each voxel separately, while SVM combines multiple features (or voxels), thus enhancing the signal-to-noise ratio. Both effects are complementary and readily explain the higher sensitivity of SVM compared with TBSS.
Two previous studies successfully applied a SVM classifier to discriminate patients with AD versus healthy controls based on gray matter (after voxel-based morphometry preprocessing), with accuracies of 89%42 and 94.5%.45 Three more recent gray matter contributions classified stable versus progressive MCI with accuracies of 75%,16 81.5%,44 and 85%.43 In 1 of our previous SVM studies based on WM (after DTI TBSS preprocessing), the classification of stable versus progressive MCI reached an accuracy of 98%.30 Only 1 previous study explored individual classification of aMCI versus non-MCI using a binary logistic regression model of single anatomic regions.36 DTI changes in the left posterior cingulate distinguished aMCI from non-MCI with a sensitivity of 80% and specificity of 60.3%. The multi-voxel pattern recognition approach of the current investigation combines multiple regions for the individual classification analysis and yielded substantially higher classification accuracies.
Strengths and Limitations
Strengths of the present work include the selection of community-based cases of MCI, in-depth neuropsychologic characterization, as well as combined use of TBSS and SVM analyses. Several limitations should, however, be considered when interpreting these data. From a clinical viewpoint, this cross-sectional group comparison investigates the structural substrates of MCI subgroups but did not provide information about their evolution over time. Whether the observed DTI changes alone, or in combination with molecular AD markers such as amyloid imaging or CSF amyloid/τ levels, could predict rapid cognitive decline (or conversion to AD) in each MCI subgroup remains to be elucidated. Correlations between neuropsychologic and neuroimaging data were not performed in order to avoid multiple comparison biases created by the limited sample. This latter point may also affect the results of the SVM analysis. In fact, the very high accuracy rates of individual classification exceeded our expectations. These values were obtained by a well-established 10-fold cross-validation, where 9 parts are used for training and the remaining part is used for testing the classifier. Even though this cross-validation approach is a standard method in the field of machine learning/multi-voxel pattern analysis, and is appropriate for the number of subjects involved in our study, the present results seem too optimistic, probably related to some degree of overfitting of the data. Moreover, we first performed a feature selection (rationale discussed above), which might further contribute to some degree of overfitting. Finally, the nonlinear (radial basis function kernel) SVM does not provide an easy-to-interpret weight vector to examine the biologic compromise associated with MCI subtypes. Additional validation in larger independent datasets, which should be ideally acquired on different MR scanners, is warranted to confirm the present findings.
Conclusions
The reliable definition of MCI subtypes is a sine qua non condition for developing appropriate curative or symptomatic treatments before the irreversible brain damage that characterizes severe forms of dementia. Our data show that a highly accurate classification of MCI subtypes at the individual level can be obtained by SVM analysis of DTI-derived modifications in FA. The high proportion of subjects with MCI who already undergo brain MR imaging during work-up of dementia suspicion in routine clinical settings, in combination with the short measurement time of DTI and potentially almost automatic postprocessing of the data, imply a potential benefit and clinical practicability of this objective and individual classifier.
Acknowledgments
We thank all subjects for participating in the study.
ABBREVIATIONS:
- AD
Alzheimer disease
- aMCI
amnestic MCI
- FA
fractional anisotropy
- MCI
mild cognitive impairment
- md-aMCI
multiple domains MCI
- sd-aMCI
single domain amnestic MCI
- sd-fMCI
single domain frontal MCI
- SVM
support vector machine
- TBSS
tract-based spatial statistics
Appendix
Essential Data Processing Steps
DTI data acquisition
TBSS data preprocessing (including reconstruction of FA, longitudinal diffusivity, radial diffusivity, and mean diffusivity, as well as spatial normalization into Montreal Neurological Institute; standard space)
-
Group-level analysis:
Group-level comparison of FA, longitudinal diffusivity, radial diffusivity, and mean diffusivity using Randomise Permutation Testing
- Individual-level classification feature selection using Relieff:
- 10 repetitions of 10-fold cross-validation
- SVM classification
- 10 repetitions of 10-fold cross-validation
- Radial basis function kernel
- GAMMA from 0.01 to 0.09 with increments of 0.01,
- C fixed to 1.00
Footnotes
Disclosures: Sven Haller—RELATED: Grant: This work is supported by Swiss National Foundation grant SNF 3200B0-116193 (PG) and SPUM 33CM30-124111 (Giannakopoulos, Herrmann, and Gold) as well as an unrestricted grant of the Velux Stiftung (Foundation).* Panteleimon Giannakopoulos—RELATED: Grant: Swiss National Foundation for Research, Comments: Unrestricted grant from the federal organism in charge of the research promotion in Switzerland; UNRELATED: Grants/Grants Pending: Swiss National Foundation for Research. (*Money paid to institution)
References
- 1. Nitsch RM, Hock C. Targeting beta-amyloid pathology in Alzheimer's disease with Abeta immunotherapy. Neurotherapeutics 2008;5:415–20 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Duara R, Barker W, Loewenstein D, et al. The basis for disease-modifying treatments for Alzheimer's disease: the Sixth Annual Mild Cognitive Impairment Symposium. Alzheimers Dement 2009;5:66–74 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Holmes C, Boche D, Wilkinson D, et al. Long-term effects of Abeta42 immunisation in Alzheimer's disease: follow-up of a randomised, placebo-controlled phase I trial. Lancet 2008;372:216–23 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Lannfelt L, Blennow K, Zetterberg H, et al. Safety, efficacy, and biomarker findings of PBT2 in targeting Abeta as a modifying therapy for Alzheimer's disease: a phase IIa, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 2008;7:779–86 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Petersen RC, Negash S. Mild cognitive impairment: an overview. CNS Spectr 2008;13:45–53 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Petersen RC. Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. J Intern Med 2004;256:183–94 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Mariani E, Monastero R, Mecocci P. Mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review. J Alzheimers Dis 2007;12:23–35 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Forlenza OV, Diniz BS, Nunes PV, et al. Diagnostic transitions in mild cognitive impairment subtypes. Int Psychogeriatr 2009;21:1088–95 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Ashburner J, Friston KJ. Voxel-based morphometry–the methods. Neuroimage 2000;11:805–21 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Scahill RI, Schott JM, Stevens JM, et al. Mapping the evolution of regional atrophy in Alzheimer's disease: unbiased analysis of fluid-registered serial MRI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002;99:4703–07 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Karas GB, Burton EJ, Rombouts SA, et al. A comprehensive study of gray matter loss in patients with Alzheimer's disease using optimized voxel-based morphometry. Neuroimage 2003;18:895–907 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Karas GB, Scheltens P, Rombouts SA, et al. Global and local gray matter loss in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Neuroimage 2004;23:708–16 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Karas G, Sluimer J, Goekoop R, et al. Amnestic mild cognitive impairment: structural MR imaging findings predictive of conversion to Alzheimer disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2008;29:944–49 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Chupin M, Gerardin E, Cuingnet R, et al. Fully automatic hippocampus segmentation and classification in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment applied on data from ADNI. Hippocampus 2009;19:579–87 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Holland D, Brewer JB, Hagler DJ, et al. Subregional neuroanatomical change as a biomarker for Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009;106:20954–59 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Plant C, Teipel SJ, Oswald A, et al. Automated detection of brain atrophy patterns based on MRI for the prediction of Alzheimer's disease. Neuroimage 2010;50:162–74 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Della Nave R, Ginestroni A, Tessa C, et al. Brain white matter damage in SCA1 and SCA2. An in vivo study using voxel-based morphometry, histogram analysis of mean diffusivity and tract-based spatial statistics. Neuroimage 2008;43:10–19 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Della Nave R, Ginestroni A, Tessa C, et al. Brain white matter tracts degeneration in Friedreich ataxia. An in vivo MRI study using tract-based spatial statistics and voxel-based morphometry. Neuroimage 2008;40:19–25 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Ibrahim I, Horacek J, Bartos A, et al. Combination of voxel based morphometry and diffusion tensor imaging in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 2009;30:39–45 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Haller S, Xekardaki A, Delaloye C, et al. Combined analysis of grey matter voxel-based morphometry and white matter tract-based spatial statistics in late-life bipolar disorder. J Psychiatry Neurosci 2011;36:391–401 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Agosta F, Pievani M, Sala S, et al. White matter damage in Alzheimer disease and its relationship to gray matter atrophy. Radiology 2011;258:853–63 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H, et al. Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 2006;31:1487–505 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Damoiseaux JS, Smith SM, Witter MP, et al. White matter tract integrity in aging and Alzheimer's disease. Hum Brain Mapp 2009;30:1051–59 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Liu Y, Spulber G, Lehtimaki KK, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging and tract-based spatial statistics in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Aging 2011;32:1558–71 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Teipel SJ, Meindl T, Grinberg L, et al. The cholinergic system in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: an in vivo MRI and DTI study. Hum Brain Mapp 2011;32:1349–62 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Teipel SJ, Pogarell O, Meindl T, et al. Regional networks underlying interhemispheric connectivity: an EEG and DTI study in healthy ageing and amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Hum Brain Mapp 2009;30:2098–119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Arenaza-Urquijo EM, Bosch B, Sala-Llonch R, et al. Specific anatomic associations between white matter integrity and cognitive reserve in normal and cognitively impaired elders. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 2011;19:33–42 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Bosch B, Arenaza-Urquijo EM, Rami L, et al. Multiple DTI index analysis in normal aging, amnestic MCI and AD. Relationship with neuropsychological performance. Neurobiol Aging 2012;33:61–74 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Teipel SJ, Meindl T, Wagner M, et al. Longitudinal changes in fiber tract integrity in healthy aging and mild cognitive impairment: a DTI follow-up study. J Alzheimers Dis 2010;22:507–22 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Haller S, Nguyen D, Rodriguez C, et al. Individual prediction of cognitive decline in mild cognitive impairment using support vector machine-based analysis of diffusion tensor imaging data. J Alzheimers Dis 2010;22:315–27 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. O'Dwyer L, Lamberton F, Bokde AL, et al. Using support vector machines with multiple indices of diffusion for automated classification of mild cognitive impairment. PLoS One 2012;7:e32441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Jak AJ, Bangen KJ, Wierenga CE, et al. Contributions of neuropsychology and neuroimaging to understanding clinical subtypes of mild cognitive impairment. Int Rev Neurobiol 2009;84:81–103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. He J, Farias S, Martinez O, et al. Differences in brain volume, hippocampal volume, cerebrovascular risk factors, and apolipoprotein E4 among mild cognitive impairment subtypes. Arch Neurol 2009;66:1393–99 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Whitwell JL, Petersen RC, Negash S, et al. Patterns of atrophy differ among specific subtypes of mild cognitive impairment. Arch Neurol 2007;64:1130–38 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Bell-McGinty S, Lopez OL, Meltzer CC, et al. Differential cortical atrophy in subgroups of mild cognitive impairment. Arch Neurol 2005;62:1393–97 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Chua TC, Wen W, Chen X, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of the posterior cingulate is a useful biomarker of mild cognitive impairment. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 2009;17:602–13 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Zhuang L, Wen W, Zhu W, et al. White matter integrity in mild cognitive impairment: a tract-based spatial statistics study. Neuroimage 2010;53:16–25 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Grambaite R, Stenset V, Reinvang I, et al. White matter diffusivity predicts memory in patients with subjective and mild cognitive impairment and normal CSF total tau levels. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2010;16:58–69 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Stebbins GT, Murphy CM. Diffusion tensor imaging in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. Behav Neurol 2009;21:39–49 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Noble WS. What is a support vector machine? Nat Biotechnol 2006;24:1565–67 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Haller S, Lovblad KO, Giannakopoulos P. Principles of classification analyses in mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2011;26:389–94 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Klöppel S, Stonnington CM, Chu C, et al. Automatic classification of MR scans in Alzheimer's disease. Brain 2008;131:681–89 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Fan Y, Batmanghelich N, Clark CM, et al. Spatial patterns of brain atrophy in MCI patients, identified via high-dimensional pattern classification, predict subsequent cognitive decline. Neuroimage 2008;39:1731–43 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Misra C, Fan Y, Davatzikos C. Baseline and longitudinal patterns of brain atrophy in MCI patients, and their use in prediction of short-term conversion to AD: results from ADNI. Neuroimage 2009;44:1415–22 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Magnin B, Mesrob L, Kinkingnehun S, et al. Support vector machine-based classification of Alzheimer's disease from whole-brain anatomical MRI. Neuroradiology 2009;51:73–83 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. “Mini-Mental State.” A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 1975;12:189–98 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Barberger-Gateau P, Commenges D, Gagnon M, et al. Instrumental activities of daily living as a screening tool for cognitive impairment and dementia in elderly community dwellers. J Am Geriatr Soc 1992;40:1129–34 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand 1983;67:361–70 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Wechsler D. Adult Intelligence Scale, Revised (WAIS-R), The Psychological Corp., New York, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- 50. Milner B. Interhemispheric differences in the localization of psychological processes in man. Br Med Bull 1971;27:272–77 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Buschke H, Sliwinski MJ, Kuslansky G. Diagnosis of early dementia by the Double Memory Test: encoding specificity improves diagnostic sensitivity and specificity. Neurology 1997;48:989–97 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Baddeley A, Emslie H, Nimmo-Smith I. Doors and people. A test of visual and verbal recall and recognition. Thames Valley Test Company: Bury St. Edmunds, UK, 1994 [Google Scholar]
- 53. Reitan RM. Validity of the Trail Making Test as an indicator of organic brain damage. Percept Mot Skills 1958;8:271–76 [Google Scholar]
- 54. Butters N, Granholm E, Salmon DP, et al. Episodic and semantic memory: a comparison of amnesic and demented patients. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 1987;9:479–97 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Borkowski JG, Benton AL, Spreen O. Word fluency and brain damage. Neuropsychologia 1967;5:135–40 [Google Scholar]
- 56. Heaton RK. Wisconsing Card Sorting Test Manual 1981 [Google Scholar]
- 57. Kaplan EF, Goodglass H, Weintraub S. The Boston naming test (2nd edition), 1983 [Google Scholar]
- 58. Ghent L. Perception of overlapping and embedded figures by children of different ages. Am J Psychol 1956;69:575–87 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Schnider A, Hanlon RE, Alexander DN, et al. Ideomotor apraxia: behavioral dimensions and neuroanatomical basis. Brain Lang 1997;58:125–36 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Poeck K. Clues to the nature of disruption to limb praxis. Neuropsychological Studies of Apraxia and Related Disorders; 1985:99–109 [Google Scholar]
- 61. Welsh KA, Butters N, Mohs RC, et al. The Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease (CERAD). Part V. A normative study of the neuropsychological battery. Neurology 1994;44:609–14 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Hughes CP, Berg L, Danziger WL, et al. A new clinical scale for the staging of dementia. Br J Psychiatry 1982;140:566–72 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Petersen RC, Doody R, Kurz A, et al. Current concepts in mild cognitive impairment. Arch Neurol 2001;58:1985–92 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Libon DJ, Xie SX, Eppig J, et al. The heterogeneity of mild cognitive impairment: a neuropsychological analysis. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2010;16:84–93 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Petersen RC, Morris JC. Mild cognitive impairment as a clinical entity and treatment target. Arch Neurol 2005;62:1160–63; discussion 1167 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Petersen RC, Roberts RO, Knopman DS, et al. Mild cognitive impairment: ten years later. Arch Neurol 2009;66:1447–55 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Fazekas F, Chawluk JB, Alavi A, et al. MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer's dementia and normal aging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1987;149:351–56 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Smith SM, Johansen-Berg H, Jenkinson M, et al. Acquisition and voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data with tract-based spatial statistics. Nat Protoc 2007;2:499–503 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Woolrich MW, et al. Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage 2004;23:S208–19 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Smith SM, Nichols TE. Threshold-free cluster enhancement: addressing problems of smoothing, threshold dependence and localisation in cluster inference. Neuroimage 2009;44:83–98 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Kononenko I, Šimec E, Robnik-Šikonja M. Overcoming the myopia of inductive learning algorithms with RELIEFF. Appl Intell 1997;7:39–55 [Google Scholar]
- 72. Platt J. Sequential minimal optimization: a fast algorithm for training support vector machines. Advances in Kernel Methods-Support Vector Learning 1999;208. Available at: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi-10.1.1.55.560&rep=rep1&type=pdf
- 73. Scholkopf B, Sung KK, Burges CJC, et al. Comparing support vector machines with Gaussian kernels to radial basis function classifiers. IEEE Trans Signal Process 1997;45:2758–65 [Google Scholar]
- 74. Acosta-Cabronero J, Williams GB, Pengas G, et al. Absolute diffusivities define the landscape of white matter degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Brain 2010;133:529–39 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Zhang Y, Du AT, Hayasaka S, et al. Patterns of age-related water diffusion changes in human brain by concordance and discordance analysis. Neurobiol Aging 2010;31:1991–2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Pievani M, Agosta F, Pagani E, et al. Assessment of white matter tract damage in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Hum Brain Mapp 2010;31:1862–75 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Salat DH, Tuch DS, van der Kouwe AJ, et al. White matter pathology isolates the hippocampal formation in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 2010;31:244–56 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Adler CM, Holland SK, Schmithorst V, et al. Abnormal frontal white matter tracts in bipolar disorder: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Bipolar Disord 2004;6:197–203 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Nguyen D, Vargas MI, Khaw N, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging analysis with tract-based spatial statistics of the white matter abnormalities after epilepsy surgery. Epilepsy Res 2011. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Deiber MP, Ibanez V, Herrmann F, et al. Face short-term memory-related electroencephalographic patterns can differentiate multi- versus single-domain amnestic mild cognitive impairment. J Alzheimers Dis 2011;26:157–69 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Stephan BC, Matthews FE, Hunter S, et al. Neuropathological profile of mild cognitive impairment from a population perspective. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 2012;26:205–12 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Grambaite R, Selnes P, Reinvang I, et al. Executive dysfunction in mild cognitive impairment is associated with changes in frontal and cingulate white matter tracts. J Alzheimers Dis 2011;27:453–62 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Haller S, Bartsch A, Nguyen D, et al. Cerebral microhemorrhage and iron deposition in mild cognitive impairment: susceptibility-weighted MR imaging assessment. Radiology 2010;257:764–73 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]