Abstract
Background/Aims
Understanding leukemic stem cell (LSC) is important for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) treatment. However, association of LSC with patient prognosis and genetic information in AML patients is unclear.
Methods
Here we investigated the associations between genetic information and the various LSC phenotypes, namely multipotent progenitor (MPP)-like, lymphoid primed multipotent progenitor (LMPP)-like and granulocyte-macrophage progenitors (GMP)-like LSC in 52 AML patients.
Results
In secondary AML patients, MPP-like LSC was significantly higher than de novo AML (p = 0.0037). The proportion of MPP-like LSC was especially high in post-myeloproliferative neoplasm AML (p = 0.0485). There was no correlation between age and LSC phenotype. Mutations of KRAS and NRAS were observed in MPP-like LSC dominant patients, TP53 and ASXL1 mutations in LMPP-like LSC dominant patients, and CEBPA, DNMT3A and IDH1 mutations in GMP-like LSC dominant patients. Furthermore, KRAS mutation was significantly associated with MPP-like LSC expression (p = 0.0540), and TP53 mutation with LMPP-like LSC expression (p = 0.0276). When the patients were separated according to the combined risk including next generation sequencing data, the poorer the prognosis, the higher the LMPP-like LSC expression (p = 0.0052). This suggests that the dominant phenotype of LSC is one of the important factors in predicting the prognosis and treatment of AML.
Conclusions
LSC phenotype in AML is closely associated with the recurrent mutations which has prognostic implication. Further research to confirm the meaning of LSC phenotype in the context of genetic aberration is warranted.
Keywords: Acute myeloid leukemia, Leukemic stem cell, Next generation sequencing, Prognosis
INTRODUCTION
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a clinically heterogeneous disease characterized by multitudes of chromosomal abnormalities and gene mutations. With advances in next generation sequencing (NGS) techniques, more sophisticated risk stratification models have been adapted for better management of the disease [1-3]. Unfortunately resistance to treatment and relapse remains a big challenge, and some feel that the mutation status alone is not enough to predict the prognosis of AML.
Leukemic stem cells (LSCs) are cells with self-renewal capacity to repopulate a leukemia and often thought as the major cause of resistance and relapse despite their low frequency [4-6]. The origin of these cells, whether it be from normal hematopoietic stem cells or from more mature progenitors that gain stem-ness features, may differ among patients [7-9], but previous reports on the prognostic implications of LSCs support the importance of eliminating LSCs to improve AML clinical outcomes [4]. As such, understanding the relationship between LSC and genetically defined sub-clones can, in turn, help to understand the heterogeneity of AML [10]. However, to date, there are only a few reports specifically focusing on this topic. To this end, we conducted this study to (1) examine the phenotypic diversity of AML-LSC, (2) explore the association between AML-LSC phenotypes and gene mutations, and (3) investigate the prognostic implications of AML-LSCs.
METHODS
Study design and subjects
Newly diagnosed adult AML patients, defined as 18 years or older, were included for this study. Patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia were excluded. The patient selection and bone marrow sample acquisition was done between October 2016 and July 2018. At the end, a total of 52 patients were included for analyses. Their medical records were reviewed and analyzed for demographics, baseline disease characteristics, factors related to treatment, response to treatment, adverse events including treatment related mortality, and survival outcomes. Data available up to March 2019 were used. Their bone marrow samples collected at AML diagnosis were subjected to flow cytometry and NGS.
The diagnosis of AML was made according to the WHO classification of hematopoietic neoplasms [11], which requires identification of 20% or more leukemic blasts in the bone marrow. Secondary AML was defined as AML following myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) or myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) confirmed prior to the diagnosis of AML. Cytogenetic studies were performed onsite, whose satisfactory performance was monitored by a national external quality assurance scheme. Bone marrow cells were cultured for 24 hours then karyotype was analyzed using the standard G-banding technique. The karyotypes were constructed and chromosomal abnormalities were reported in accordance with the International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature [12]. Prognostic grouping of cytogenetics was performed according to Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) criteria [13]. Risk stratification was mainly based on cytogenetics, and NGS results for those with available data, according to 2019 National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines [14].
The study was conducted in compliance with all national and international ethical standards for research with humans and for research using radiopharmaceuticals. This study was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Hospital (IRB No. H-1902-140-101). Written informed consent was obtained from all patients. All authors had access to the study data and reviewed and approved this study.
Flow cytometry
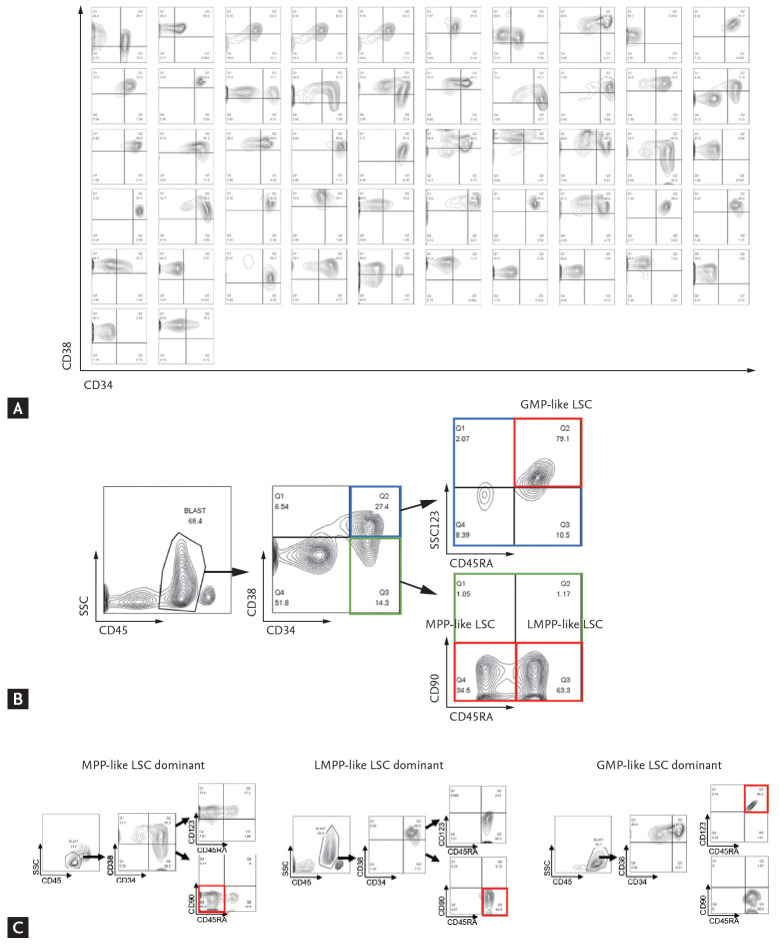
Mononuclear cells were isolated from the patient’s bone marrow aspirates by ficoll gradient centrifugation and cryopreserved in serum-free medium. Stored cells were thawed to Iscove’s Modified Dulbecco’s Medium and washed with fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) buffer (2% fetal bovine serum, Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline). Cells were stained with following anti-human monoclonal antibodies: CD45-APC/cy7 (557833), CD34-APC (555824), CD38-BV421 (562445), CD90-PE (555596), CD123-PE/Cy7 (560826), and CD45RA-PerCP/Cy5.5 (563429) (BD Bioscience). Analyses were performed on a FACSCanto II (High Throughput Sampler, BD Bioscience, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) and FlowJo version 10.0 program (BD Bioscience). First, the expression profiles of CD34 and CD38 markers were analyzed (Fig. 1A). Then, the phenotypes of LSCs were further analyzed per methods proposed by Goardon et al. [15]; multipotent progenitor (MPP)-like LSC (CD34+CD38–CD90–CD45RA–), lymphoid primed multipotent progenitor (LMPP)-like LSC (CD34+CD38+CD90–CD45RA+) and granulocyte-macrophage progenitors (GMP)-like LSC (CD34+CD38+CD123+CD45RA+). The CD45 and side scatter properties were used for gating bulk leukemic blast cells and sub-gated from the cells [16], as shown in Fig. 1B. End results showed that there was a dominantly expressed LSC phenotype in each patient (Fig. 1C). In some cases, two or more LSC phenotypes co-existed. The percentage of cell fractions satisfying each LSC phenotype markers in CD34+ cells was calculated.
Figure 1.
Phenotypic diversity of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) leukemic stem cells (LSCs). (A) CD34 and CD38 surface marker profiles of all 52 patients. (B) Gating strategy for AML-LSCs. (C) Three distinct populations were analyzed as LSC phenotypes: left, multipotent progenitor (MPP)-like LSC; middle, lymphoid primed multipotent progenitor (LMPP)-like LSC; right, granulocyte-macrophage progenitors (GMP)-like LSC.
Targeted capture and massive parallel sequencing
The DNA capture probes for 76 target genes were designed using the Agilent SureDesign web-based application (https://earray.chem.agilent.com/suredesign/, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The target regions included protein coding exons with 10 bp intron flanking regions and hot spot regions of the 20 genes involved in recurrent translocations. DNA was extracted on a Chemagic 360 instrument (Perkin Elmer, Baesweiler, Germany). The genomic DNA was sheared using Covaris S220 focused-ultrasonicator (Covaris, Woburn, MA, USA). We used 50 ng of total input genomic DNA. A library preparation was performed according to Agilent’s SureSelectQXT Target Enrichment protocol (Agilent Technologies). Paired-end 150-bp sequencing was using NextSeq 550 Dx platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). Targeted sequencing raw data was obtained in FASTQ format.
Secondary analysis using in-house bioinformatics pipeline
The produced sequencing data was analyzed using the Seoul National University Hospital First Hemic Panel Analysis Pipeline (FHPAP). First, we performed the quality control of the FASTQ file and analyzed only the data that passed the criteria. Pair-end alignment to HG19 reference genome was performed using BWA-men and the GATK Best Practice [17,18]. After finishing the alignment step, an “analysis-ready BAM” was produced and a second quality control is performed to determine if further variant calling is appropriate. In the pipeline, SNV, InDel, CNV, translocation, FLT3 ITD, and KMT2A PTD were analyzed using at least more than two analysis tools including in-house and open-source software. Along with in-house software, GATK UnifiedGenotyper, SNVer, LoFreq were used for SNV/InDel detection [18-20], Delly and Manta for Translocation discovery [21,22], and THetA2 and CNVKit for purity estimation and CNV calling [23,24], respectively. FLT3 ITD and KMT2A PTD were analyzed by only the in-house software. Detected variants was annotated by SnpEff with various database such as RefSeq, COSMIC, dbSNP, ClinVar, and gnomAD. Then germline variant was filtered using the population frequency of these databases (> 1% population frequency) [25-30]. Finally, the variants were confirmed throughout a comprehensive review of a multidisciplinary molecular tumor board.
Statistical analysis
The relapse free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) curves were estimated using the Kaplan–Meier method. The RFS was derived from the date AML diagnosis to that of relapse or death from any cause, while the OS was defined as the time from AML diagnosis to death from any cause. If patients survived, RFS and OS was censored on the last date of follow-up when no death or relapse was confirmed. Complete remission rate, based on the revised recommendations of the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) group, with induction was compared. Induction TRM was also analyzed, and defined as mortality during induction chemotherapy. The differences between groups were assessed using a Mann–Whitney test or one-way analysis of variance for continuous variables, and Pearson chi-square test for categorical variables, as indicated. All data were analyzed using the SAS Enterprise Guide version 6.1 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA) and the statistical software R (www.r-project.org). A p value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Patient characteristics, AML subtypes and LSC phenotypes
The baseline characteristics of the enrolled patients are presented in Table 1. There were 40 de novo AML and 12 secondary AML patients. Among secondary AML patients, there were four post-MPN AML patients and eight post-MDS AML patients. The median age of the whole group was 62 years.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics
| Characteristic | Total | De novo AML | Secondary AML | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 52 | 40 | 12 | NA |
| Age, yr | 62 (23–88) | 63 (23–88) | 60 (40–81) | 0.656 |
| ≤ 65 | 33 (63.5) | 26 (65.0) | 7 (58.3) | |
| > 65 | 19 (36.5) | 14 (35.0) | 5 (41.7) | |
| Sex, male | 33 (63.5) | 26 (65.0) | 7 (58.3) | 0.674 |
| Cytogenetic risk | ||||
| Low | 6 (11.5) | 6 (15.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.001 |
| Intermediate | 38 (73.1) | 32 (80.0) | 6 (50.0) | |
| High | 8 (15.4) | 2 (5.0) | 6 (50.0) | |
| Combined riska | ||||
| Low | 7 (13.5) | 7 (17.5) | 0 | 0.037 |
| Intermediate | 19 (36.5) | 15 (37.5) | 4 (33.3) | |
| High | 12 (23.1) | 6 (15.0) | 6 (50.0) | |
| Unknown | 14 (26.9) | 12 (30.0) | 2 (16.7) | |
| Extramedullary involve | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA |
| Laboratory findings | ||||
| Bone marrow blast, % | 63.7 ± 22.4 | 66.5 ± 20.2 | 54.5 ± 27.6 | 0.281 |
| WBC count, /L | 29,169 ± 54,648 | 31,740 ± 61,259 | 20,599 ± 20,903 | 0.334 |
| Platelet count, × 109/L | 86.1 ± 72.0 | 81.3 ± 52.5 | 102.1 ± 117.9 | 0.564 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 9.2 ± 2.0 | 9.0 ± 2.0 | 9.8 ± 2.2 | 0.292 |
Values are presented as median (range), number (%), or mean ± standard deviation.
AML, acute myeloid leukemia; NA, not applicable; WBC, white blood cell.
Combined risk refers to risk stratification based on available next generation sequencing data including TP53, ASXL1, RUNX1 mutation status.
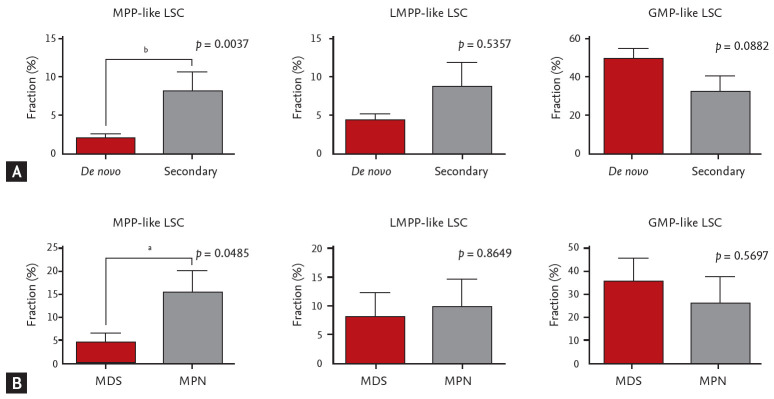
When different LSC phenotypes were considered, secondary AML group showed higher fraction of CD34+CD38– cells (p = 0.0245) and MPP-like LSCs (p = 0.0037) compared to de novo AML group (Fig. 2A). When secondary AML was further classified into post-MPN versus post-MDS, there was a statistically significant increase in percentage of MPP-like LSCs in post-MPN AML compared to post-MDS AML (p = 0.0485) (Fig. 2B). Collectively, secondary AML, particularly post-MPN AML, was associated with higher fraction of the MPP-like LSC phenotype compared to its de novo counterpart.
Figure 2.
Leukemic stem cells (LSCs) phenotypes and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) subtypes. (A) The multipotent progenitor (MPP)-like LSCs are present in higher fraction in secondary AML patients compared to de novo AML patients. (B) Post-myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) AML is associated with higher fraction of MPP-like LSCs compared to post-myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) AML. The graphs were drawn using a percentage that meets cell surface markers, which means each cell. Error bars indicate mean ± standard deviation. LMPP, lymphoid primed multipotent progenitor; GMP, granulocyte-macrophage progenitor. ap < 0.05, bp < 0.01.
To determine the association between the age and LSC phenotype compositions, patients were divided into two group according to age at AML diagnosis at cutoff of 65 years (Supplementary Fig. 1). The CD34+CD38– cell fraction was higher for younger patients (i.e., ≤ 65 years), but there were no differences in LSC phenotypes between the two age groups.
Risk stratification, survival and LSC phenotypes
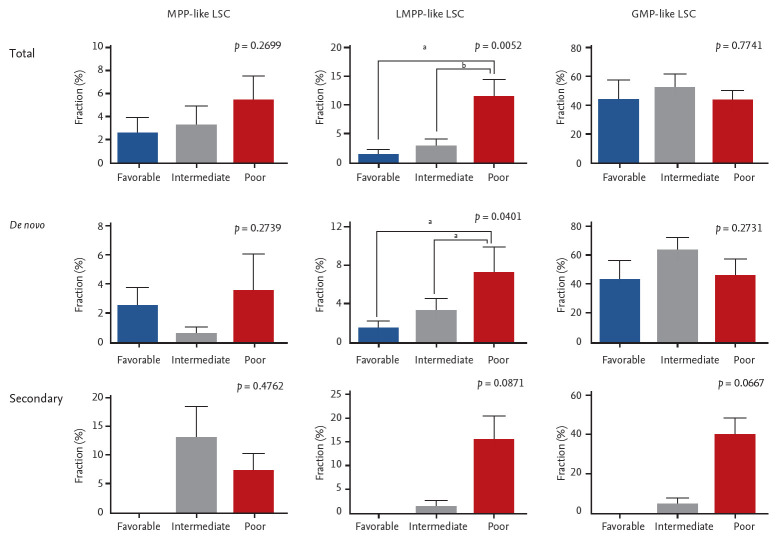
While data on conventional cytogenetics was available in all patients, the NGS data was not available in 14 patients due to lack of quality-assured samples. The majority of the patients were classified as intermediate risk by both cytogenetics risk stratification and combined risk stratification based on NGS data (Table 1). No correlation was seen between cytogenetics risk and LSC phenotypes (Supplementary Table 1). On the other hand, LMPP-like LSC was predominant in the poor risk group by combined risk stratification (p = 0.0052) (Fig. 3). This was true for both de novo AML (n = 28, p = 0.0401) and secondary AML (n = 10, p = 0.0871) patients (Supplementary Table 2).
Figure 3.
The association between acute myeloid leukemia risk stratification based on next generation sequencing data and leukemic stem cells (LSCs) phenotypes. Error bars indicate mean ± standard deviations. MPP, multipotent progenitor; LMPP, lymphoid primed multipotent progenitor; GMP, granulocyte-macrophage progenitor. ap < 0.05, bp< 0.01.
For survival analyses, the patients were grouped according to their dominant LSC phenotypes (Fig. 4). There were ten patients in MPP-like LSC group, 11 in LMPP-like LSC group, and 31 in GMP-like LSC group. For the entire cohort, the mean RFS was 10.8 months and mean OS 12.3 months (Supplementary Table 3). Supplementary Fig. 2 represents the survival curves of the patients undergoing treatment per dominant LSC phenotype. In light of small number of patients with heterogeneous treatment schema, only those who underwent treatment regardless of intensity were included for survival analyses. Furthermore, to compensate the innate differences in survival among different AMLs, de novo AML and secondary AML were analyzed separately. There was no correlation between RFS or OS and LSC phenotype in either group.
Figure 4.
The dominant leukemic stem cell (LSC) phenotype and heatmap of mutations. MPP, multipotent progenitor; LMPP, lymphoid primed multipotent progenitor; GMP, granulocyte-macrophage progenitor; AML, acute myeloid leukemia.
Individual mutations and LSC phenotypes
The mutational landscape of enrolled patients is shown in Fig. 4. We looked for specific mutations that were enriched in each LSC phenotype group. Mutations in CEPBA (6 out of 7), DNMT3A (4 out of 7), and IDH1 (3 out of 5) were predominantly clustered in GMP-like LSC group. On the other hand, mutations in NRAS (4 out of 6) and KRAS (3 out of 4) were dominantly found in MPP-like LSC group, while mutations in TP53 (4 out of 5) and ASXL1 (5 out of 6) were often found in LMPP-like LSC group.
This observation was verified by comparing the LSC phenotype composition of specific mutation carriers versus non-carriers (i.e., wild-type). The differences in LSC expression per CEBPA, DNMT3A, and IDH1 mutations were not statistically significant. Interestingly, KRAS mutants showed higher fraction of MPP-like LSC compared to KRAS wild-types (Fig. 5). Also, the fraction of GMP-like LSC was significantly lower in KRAS mutants. NRAS mutants also showed similar tendencies, but the difference did not reach statistical significance. For TP53 and ASXL1 mutants, LMPP-like LSC was present in higher fraction. For TP53 mutants, the expression of LMPP-like LSC was significantly higher by 3.4-folds (p = 0.0276) compared to wild-type. ASXL1 mutants also showed trends towards higher expression of LMPP-like LSC (p = 0.0654).
Figure 5.
The relationship between individual gene mutation and leukemic stem cells (LSCs) phenotypes. Error bars indicate mean ± standard deviations. MPP, multipotent progenitor; LMPP, lymphoid primed multipotent progenitor; GMP, granulocyte-macrophage progenitor; WT, wild type. ap < 0.05.
DISCUSSION
The importance of our study lies in that we showed for a given AML patients there is a dominant LSC phenotype and LSCs are associated with clinical outcomes, supporting the significance of cancer stem cell model for human AML. First of all, based on detailed characterization of the surface immunophenotype of AML-LSCs we found that AML show evidence of a hierarchical cellular organization (Fig. 1). We also recognized that the composition of LSC phenotypes is associated with AML phenotypes. For example, secondary AML patients showed higher fraction of MPP-like LSCs compared to de novo AML patients (Fig. 2). Given that MPP-like LSCs are at the apex of LSC hierarchy, these cells are thought capable of initiating AML [4] and able to protect themselves from chemotherapy via ATP-binding cassette transporters [31-33]. In this regard, the higher expression of MPP-like LSCs could explain the poor response to standard treatments traditionally associated with secondary AML. Furthermore, the higher expression of MPP-like LSCs in post-MPN AML compared to post-MDS AML could explain the dismal prognosis associated with post-MPN AML, despite the relative indolent clinical course in their chronic phase and the presence of druggable target.
Interestingly, age did not seem to affect the composition of LSCs (Supplementary Fig. 1). The expression of CD34+CD38– cell fraction was higher in younger patients, but this was probably due to the higher total number of cells in younger patients. When each LSC phenotype was considered, there was no difference between age groups. From clinical point of view, this finding implies two things: (1) this could explain the unsatisfactory RFS with hypomethylating agents (HMA) alone, and (2) this supports the role of allogeneic stem cell transplantation in elderly AML patients and at the same time highlights the unmet medical needs for better transplant techniques in such population. Whilst it is true that HMA has broadened the therapeutic options for elderly AML, since LSCs are reported to be more hypomethylated compared to leukemic blasts to begin with, these agents cannot eradicate LSCs hence the short RFS [34]. Thus, allogeneic stem cell transplantation remains the only currently available option of eradicating LSCs [6].
Moving onto the association between LSCs, gene mutations and prognostic implications, we found that LSC phenotypes by themselves do not predict survival outcomes but when taken in together with gene mutations they carry certain predictive values. It is true that AML risk stratification has been refined considerably with the advent of NGS. However, even within the same risk group some patients do much worse than others. KRAS/NRAS mutations deserve special attention in this regard. It has been found that there is a sequential order for the acquisition of AML defining gene mutations during leukemogenesis. Somatic mutations in signaling pathways that drive proliferation, such as KRAS/NRAS, are considered later events in AML transformation [35,36]. In our samples the variant allele frequencies of KRAS/NRAS mutations were less than 10% in most patients, confirming these mutations are acquired later during clinical course. Whether RAS mutations confer prognostic values or not is yet to be settled [37-39], thus they are not incorporated in the current risk stratification schema [14]. Although the relationship is somewhat tenuous, we showed that RAS mutants might actually be associated with worse prognosis because they tend to carry higher fraction of MPP-like LSCs (Fig. 5).
The obvious limitation of our study includes the small number of patients included. Another pitfall of our study is that the NGS was carried out with DNA extracted from bone marrow samples at diagnosis, rather than with the gated LSCs. However, we believe the value of our study lies in that it contains adequate scientific clues to inspire future studies regarding the genetics of LSC and their prognostic values. Given that merging of data on genomic and epigenomic landscape of AML with biology of LSCs is still in its infancy, our data might provide certain clues for further investigations.
In conclusion, our findings provide better insights into the characteristics and clinical implications of LSC. Although in a small scale, we provide evidence that specific LSC phenotypes are associated with certain mutations thus should be in the AML risk stratification process.
KEY MESSAGE
1. Leukemic stem cells (LSCs) are associated with clinical outcomes in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients, supporting the significance of cancer stem cell model for human AML.
2. The composition of LSC phenotypes is associated with AML phenotypes. For example, secondary AML patients showed higher fraction of multipotent progenitor-like LSCs compared to de novo AML patients.
3. LSC phenotypes, when taken in together with gene mutations, carry certain predictive values. This can explain why even within the same risk group some patients do much worse than others.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant (No. NRF-2016R1A5A1011974).
The abstract of this manuscript has been presented as a poster at the 61st American Society of Hematology Annual Meeting, 2019, Orlando, FL, USA.
Footnotes
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Supplementary Material
LSC phenotype according to AML risk stratification by cytogenetics only
LSC phenotype according to AML risk stratification based on NGS data
Treatment schema and outcomes
The age at acute myeloid leukemia diagnosis and leukemic stem cell (LSC) phenotypes. MPP, multipotent progenitor; LMPP, lymphoid primed multipotent progenitor; GMP, granulocyte-monocyte progenitor.
Survival analyses. (A) Relapse free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) of 39 de novo acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients undergoing treatment. (B) RFS and OS of 10 secondary AML patients undergoing treatment. MPP, multipotent progenitor; LSC, leukemic stem cell; LMPP, lymphoid primed multipotent progenitor; GMP, granulocyte-monocyte progenitor.
REFERENCES
- 1.Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Ley TJ, Miller C, et al. Genomic and epigenomic landscapes of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:2059–2074. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1301689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Papaemmanuil E, Gerstung M, Bullinger L, et al. Genomic classification and prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:2209–2221. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1516192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Estey EH. Acute myeloid leukemia: 2019 update on risk-stratification and management. Am J Hematol. 2018;93:1267–1291. doi: 10.1002/ajh.25214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Thomas D, Majeti R. Biology and relevance of human acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Blood. 2017;129:1577–1585. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-10-696054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pollyea DA, Gutman JA, Gore L, Smith CA, Jordan CT. Targeting acute myeloid leukemia stem cells: a review and principles for the development of clinical trials. Haematologica. 2014;99:1277–1284. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2013.085209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pollyea DA, Jordan CT. Therapeutic targeting of acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Blood. 2017;129:1627–1635. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-10-696039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Riether C, Schurch CM, Ochsenbein AF. Regulation of hematopoietic and leukemic stem cells by the immune system. Cell Death Differ. 2015;22:187–198. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Taussig DC, Miraki-Moud F, Anjos-Afonso F, et al. Anti-CD38 antibody-mediated clearance of human repopulating cells masks the heterogeneity of leukemia-initiating cells. Blood. 2008;112:568–575. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-10-118331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Plesa A, Dumontet C, Mattei E, et al. High frequency of CD34+CD38-/low immature leukemia cells is correlated with unfavorable prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. World J Stem Cells. 2017;9:227–234. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v9.i12.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kreso A, Dick JE. Evolution of the cancer stem cell model. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;14:275–291. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2014.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood. 2009;114:937–951. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-03-209262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Brothman AR, Persons DL, Shaffer LG. Nomenclature evolution: changes in the ISCN from the 2005 to the 2009 edition. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2009;127:1–4. doi: 10.1159/000279442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Slovak ML, Kopecky KJ, Cassileth PA, et al. Karyotypic analysis predicts outcome of preremission and postremission therapy in adult acute myeloid leukemia: a Southwest Oncology Group/Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study. Blood. 2000;96:4075–4083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dohner H, Estey E, Grimwade D, et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2017 ELN recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood. 2017;129:424–447. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-08-733196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Goardon N, Marchi E, Atzberger A, et al. Coexistence of LMPP-like and GMP-like leukemia stem cells in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2011;19:138–152. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.12.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Vergez F, Green AS, Tamburini J, et al. High levels of CD34+CD38low/-CD123+ blasts are predictive of an adverse outcome in acute myeloid leukemia: a Groupe Ouest-Est des Leucemies Aigues et Maladies du Sang (GOELAMS) study. Haematologica. 2011;96:1792–1798. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2011.047894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Li H. Exploring single-sample SNP and INDEL calling with whole-genome de novo assembly. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:1838–1844. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Van der Auwera GA, Carneiro MO, Hartl C, et al. From FastQ data to high confidence variant calls: the Genome Analysis Toolkit best practices pipeline. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2013;43:11.10.1–11.10.33. doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi1110s43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wei Z, Wang W, Hu P, Lyon GJ, Hakonarson H. SNVer: a statistical tool for variant calling in analysis of pooled or individual next-generation sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:e132. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wilm A, Aw PP, Bertrand D, et al. LoFreq: a sequence-quality aware, ultra-sensitive variant caller for uncovering cell-population heterogeneity from high-throughput sequencing datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:11189–201. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chen X, Schulz-Trieglaff O, Shaw R, et al. Manta: rapid detection of structural variants and indels for germline and cancer sequencing applications. Bioinformatics. 2016;32:1220–1222. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rausch T, Zichner T, Schlattl A, Stutz AM, Benes V, Korbel JO. DELLY: structural variant discovery by integrated paired-end and split-read analysis. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:i333–i339. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Oesper L, Satas G, Raphael BJ. Quantifying tumor heterogeneity in whole-genome and whole-exome sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 2014;30:3532–3540. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Talevich E, Shain AH, Botton T, Bastian BC. CNVkit: genome-wide copy number detection and visualization from targeted DNA sequencing. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016;12:e1004873. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cingolani P, Platts A, Wang le L, et al. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. Fly (Austin) 2012;6:80–92. doi: 10.4161/fly.19695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.O’Leary NA, Wright MW, Brister JR, et al. Reference sequence (RefSeq) database at NCBI: current status, taxonomic expansion, and functional annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(D1):D733–D745. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tate JG, Bamford S, Jubb HC, et al. COSMIC: the Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D941–D947. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sherry ST, Ward MH, Kholodov M, et al. dbSNP: the NCBI database of genetic variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29:308–311. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.1.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Landrum MJ, Lee JM, Riley GR, et al. ClinVar: public archive of relationships among sequence variation and human phenotype. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(Database issue):D980–D985. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lek M, Karczewski KJ, Minikel EV, et al. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature. 2016;536:285–291. doi: 10.1038/nature19057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Dean M, Fojo T, Bates S. Tumour stem cells and drug resistance. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:275–284. doi: 10.1038/nrc1590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Raaijmakers MH. ATP-binding-cassette transporters in hematopoietic stem cells and their utility as therapeutical targets in acute and chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2007;21:2094–2102. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2404859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wang X, Huang S, Chen JL. Understanding of leukemic stem cells and their clinical implications. Mol Cancer. 2017;16:2. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0574-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Craddock C, Quek L, Goardon N, et al. Azacitidine fails to eradicate leukemic stem/progenitor cell populations in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplasia. Leukemia. 2013;27:1028–1036. doi: 10.1038/leu.2012.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Corces-Zimmerman MR, Hong WJ, Weissman IL, Medeiros BC, Majeti R. Preleukemic mutations in human acute myeloid leukemia affect epigenetic regulators and persist in remission. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:2548–2553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1324297111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Corces-Zimmerman MR, Majeti R. Pre-leukemic evolution of hematopoietic stem cells: the importance of early mutations in leukemogenesis. Leukemia. 2014;28:2276–2282. doi: 10.1038/leu.2014.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zhou JD, Yao DM, Li XX, et al. KRAS overexpression independent of RAS mutations confers an adverse prognosis in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget. 2017;8:66087–66097. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.DiNardo CD, Cortes JE. Mutations in AML: prognostic and therapeutic implications. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2016;2016:348–355. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2016.1.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Liu X, Ye Q, Zhao XP, et al. RAS mutations in acute myeloid leukaemia patients: a review and meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 2019;489:254–260. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2018.08.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
LSC phenotype according to AML risk stratification by cytogenetics only
LSC phenotype according to AML risk stratification based on NGS data
Treatment schema and outcomes
The age at acute myeloid leukemia diagnosis and leukemic stem cell (LSC) phenotypes. MPP, multipotent progenitor; LMPP, lymphoid primed multipotent progenitor; GMP, granulocyte-monocyte progenitor.
Survival analyses. (A) Relapse free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) of 39 de novo acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients undergoing treatment. (B) RFS and OS of 10 secondary AML patients undergoing treatment. MPP, multipotent progenitor; LSC, leukemic stem cell; LMPP, lymphoid primed multipotent progenitor; GMP, granulocyte-monocyte progenitor.